Peripheral Vascular Diseases
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Aortic aneurysm
A full-thickness dilation of an artery to 1.5+ times its normal diameter commonly involves the abdominal aorta
male, white, smoking, family hx, HTN, atherosclerosis, older age
Risk factors for aortic aneurysm
Loss of elastin and collagen in the media due to inflammatory processes and oxidative stress (more commonly at branch points)
What is the pathophys as to what happens with aortic aneurysms?
abdominal U/S (100% sensitivity)
What is the initial test for AAA?
CT angio (size, anatomy assessment)
What are the pre-operative test for AAA?
MRI, MRA, X rays
What are some other tests for AAA?
Stop smoking, blood pressure control (beta blockers, ACEI), Statins, daily exercise
Managing Aortic aneurysm
open surgical repair (large/complex), EVAR (smaller, accessible)
For AAA larger than 5.5 cm, those with rapid expansion (0.5cm/year), or symptomatic aneurysms - what is the game plan
one time U/S for men 65-75 with hx of smoking, 1st degree relative
What are the screening recommendation for AAA?
U/S, CT
What imaging modalities can be used to monitor small aneurysms (less than 4 cm (biannual), 4.0-5.0 cm (every 6-12 months))
Aortic Dissection
A tear in the intimal lumen that allows blood to enter the media creating a false lumen that can move towards the distal aorta (anterograde) or towards the heart (retrograde)
ascending aorta (emergency)
Standford type A classification involves the
descending aorta (medically managed)
Standford type B classification involves the
Male, older age, HTN, connective tissue disorders, preexisting aortic aneurysm, bicuspid aortic valve, atherosclerosis, smoking, winter months, trauma, iatrogenic injury, coke, meth
Risk factors for Aortic Dissection

aortic rupture, cardiac tamponade, end-organ ischemia (stroke, renal)
Complications of aortic dissection
CT Angio
Patient presents to the ER with severe chest pain which he describes as tearing. On a physical exam you note a diastolic blowing murmur at the RUSB as well as a pulse deficit on the legs. Patient is currently stable. What is the gold standard diagnostic test?
TEE (transesophageal echo)
Patient presents to the ER with severe chest pain which he describes as tearing. On a physical exam you note a diastolic blowing murmur at the RUSB as well as a pulse deficit on the legs. Patient is currently unstable. What diagnostic test do you want to run?
d-dimer (high NPV for rule out), EKG, CXR
Additional tests for aortic disection
emergent surgical repair using open surgical techniques
For Type A dissection, what is the game plan
Beta blocker to target SBP 100-120, morphine for pain, Endovascular repair (TEVAR - if there’s any malperfusion syndrome, rupture, or uncontrolled HTN)
For Type B dissection, what is the game plan
Peripheral artery disease (PAD, peripheral vascular disease (PVD), arteriosclerosis obliterans, critical limb ischemia (CLI), intermittent claudication)
What is a group of chronic atherosclerotic, inflammatory, occlusive, and aneurysmal diseases that cause chronic obstruction of noncoronary and noncerebral arteries - primarily affecting the lower extremities?
smoking, DM, HTN, hypercholesterolemia, CKD, elevated CRP, female, black patients, increasing age
Risk factors for PAD
Asymptomatic, intermittent claudication, rest pain, ulcers, gangrene, leg discomfort not relieved by rest, acute limb ischemia
What are some ways that PAD presents itself
pulses on a doppler
Viable acute limb ischemia
no pulses on a doppler
Threatened acute limb ischemia
no pulses on a doppler, amputation is a must
Irreversible acute limb ischemia
diminished pulses, cool skin, dependent rubor, trophic changes (hair loss), bruits over femoral arteries
What are some physical exam findings that are red flags for PAD
Ankle-brachial index (ABI - abnormal is under 0.90, severe is under 0.5)
What is the 1st line diagnostic test for PAD
duplex u/s, CTA, MRA, digital subtraction angiography
What are some imaging studies we can do for PAD
lipid profile, HbA1c, CRP (only designed to identify comorbid conditions)
What are some laboratory studies we can do for PAD
Stop smoking, exercise, healthy diet, antiplatelet agents, statins, ACEI/ARB, cilostazol (intermittent claudication), revascularization (endovascular, surgical bypass), amputation (last resort)
Treatment plan for PAD to reduce cardiovascular risk, improve limb-related symptoms, and prevent critical limb ischemia
Giant cell arteritis (GCA)
Chronic vasculitis affecting large and medium sized arteries - commonly branches of the external carotid such as the temporal artery that can lead to vision loss, stroke, aortic aneurysm formation and dissection
ESR, CRP, ALP, U/S (halo sign)
70 y/o female presents to the ER for a severe temporal HA. She also reports pain while chewing, tongue pain, vision loss, stiffness in shoulders, and difficulty swallowing. On a physical exam you node scalp tenderness and nodular temporal arteries. Vitals are stable with the exception of a fever. What labs or imaging do you want?
temporal artery biopsy
What is the gold standard diagnostic for GCA?
Steroids (prednisone, methylprednisolone - taper), low dose ASA, methotrexate/tocilizumab (refractory), prophylactic osteoporosis treatment, monitor for steroid induced effects
Treatment for GCA
ESR, CRP, Watch for HA, visual disturbances, fever; regular glucose and bone health assessments
Game plan for monitoring GCA
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Partial or total thrombotic occlusion of the deep venous system - most often in the legs
endothelial injury, venous stasis, hypercoagulable state
Virchow’s triad - AKA key contributors to DVT
CBC (rule out cellulitis), D Dimer, Compression U/S (1st line), venography (gold standard but invasive), MRI/CT venography
Patient presents to the ER for swelling in her right leg. She recently had a hip replacement and is currently on bed rest. On a physical exam you note warmth, tenderness, and redness in the affected area, pitting edema of the right leg, and a positive Homan’s sign. What fdo you want to order
NOACs (1st line), LMWH, warfarin bridged with heparin; serial imaging
Treatment plan for DVT
LMWH, UFH, DOACs, compression stockings, intermittent pneumatic compression
Primary prevention of DVTs during hospitalizations
long term anticoags in high risk peeps, compression stockings, patient education
Secondary prevention of DVTs
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI)
Dysfunction in the venous system of lower extremities leading to venous HTN that can be caused by valvular incompetence, DVT, failure of calf muscle pump, varicose veins
distention of veins, capillary leakage, formation of fibrin cuffs
What are the effects of venous HTN in CVI
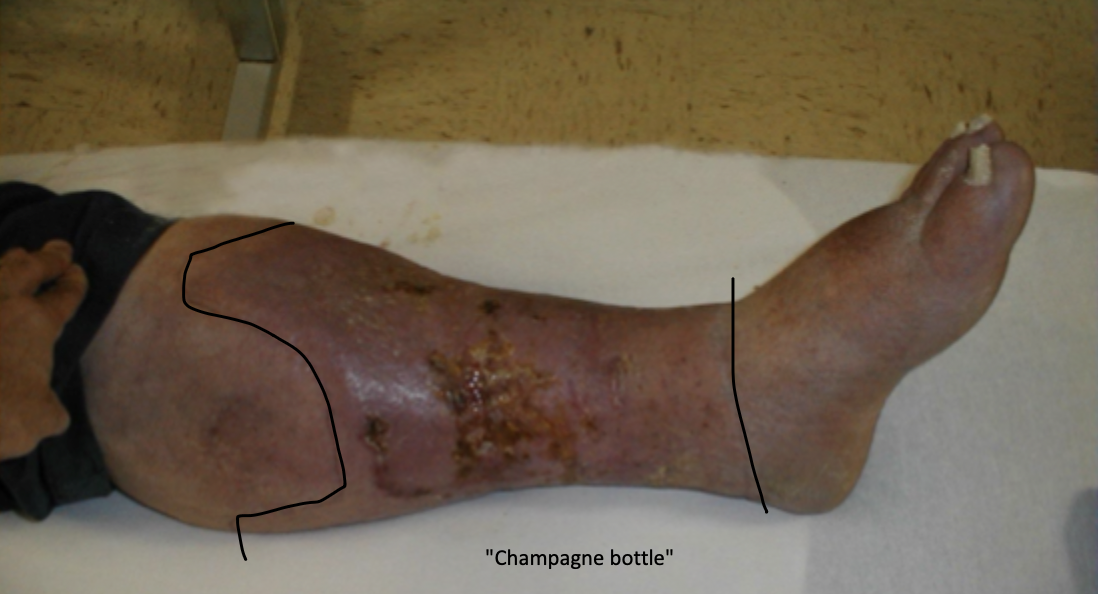
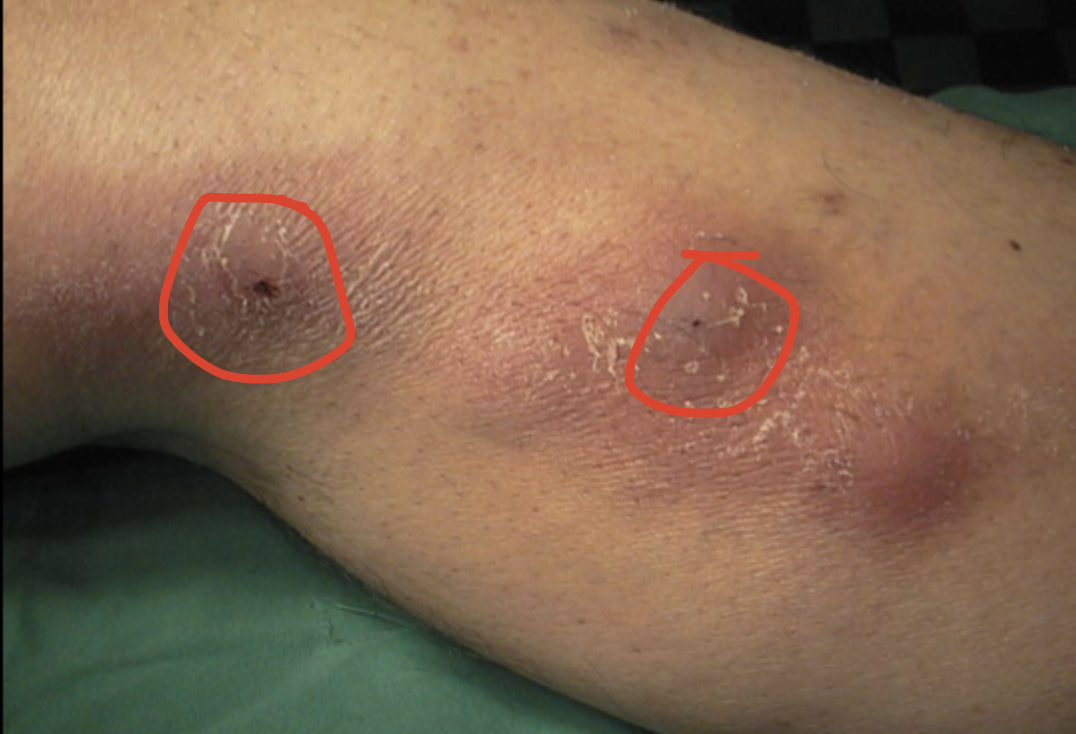
varicose veins, telangiectases, reticular veins, edema, brown discoloration, eczema, lipodermatoscelerosis, venous ulcer
Clinical manifestations of CVI
duplex U/S
What is the gold standard for diagnosing CVI?
venous photoplethysmography (PPG), air plethysmography (APG)
Additional diagnostic tests for CVI
compression therapy, horse chestnut seed oil, topical steroids (short term), endoscopic perforator vein ligation, venous valvuloplasty, external vein ligation
Treatment plan for CVI
Varicose veins
Dilated, tortuous subcutaneous veins in the superficial venous system of the lower extremities, commonly the greater and long saphenous vein
venous insufficiency, vein wall distention, deep-to-superficial retrograde flow
What causes varicose veins?
family hx, female, pregnancy, standing occupations, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, increased age
Risk factors for varicose veins
worsen with standing, improve with elevation, visible tortuous veins, erythema, hyperpigmentation, scaling ulceration
Quirks of varicose veins
Handheld doppler, duplex U/S (gold standard)
How can we support our clinical diagnosis of varicose veins?
compression stockings, leg elevation, physical activity, sclerotherapy, ligation/stripping of saphenous vein, radiofrequency ablation, endovenous laser ablation
Management of varicose veins
CVI, venous stasis ulcer, increased risk of DVT
Complications of varicose veins
thrombophlebitis
Inflammation of the vein wall along with a thrombosis that often affects superficial veins
trauma/damage to veins, reduced venous flow, increased clotting tendency, buerger’s disease, Behcet’s disease, vasculitis
Risk factors of thrombophlebitis
U/S (proximal veins, during pregnancy)
How do you confirm diagnosis of thrombophlebitis?
Anticoags for 5+ cm (LMWH (pregnant), fondaparinux, rivaroxaban), NSAIDs, compression stockings, leg elevation, early ambulation, refer if recurrent or extensive
Game plan for thrombophlebitis