FOR 232 lecture exam 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
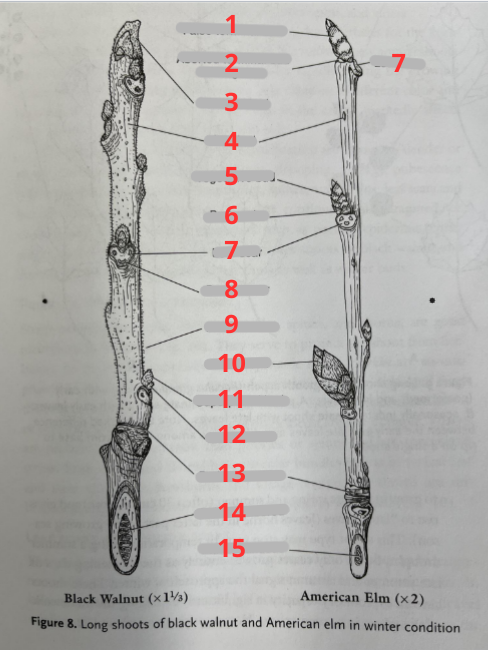
false terminal bud
aborted terminal bud/twig scar
terminal bud
lenticel
vegetative bud
bud scale
leaf scar
bundle scar
pubescence
flower bud
superposed bud
lateral bud
bud scale scars
pith chambered
pith continuous

what leaf arrangement?
alternate

what leaf arrangement?
opposite

what leaf arrangement?
whorled

what leaf type?
simple

what leaf type?
compound
4 functions of tree roots
anchorage
storage
absorption
conduction
pith
small and pulpy core running up the center of the trunk
heartwood
sapwood that has been clogged with resins, gums and other extractives; supports tree
bark
insulates tree against temperature extremes; keeps sapwood and phloem from drying out
phloem
thin, spongy layer of tubes that carry dissolved sugars and growth hormones from the leaves to other parts of the tree
travels nutrients from top to bottom
“phlo low”
cambium
thin reproductive layer that forms new tissue, adding to the phloem and sapwood to increase tree’s girth
xylem/sapwood
active part of the tree’s wood through which water and mineral are conducted from the roots to the leaves; also stores nutrients and helps to support the tree
water movement
“xy high”
ray
carries nutrients laterally through the wood; also stores nutrients
growth ring
concentric ring divided into earlywood and latewood indicating the amount of wood added to a tree’s diameter in one growing season
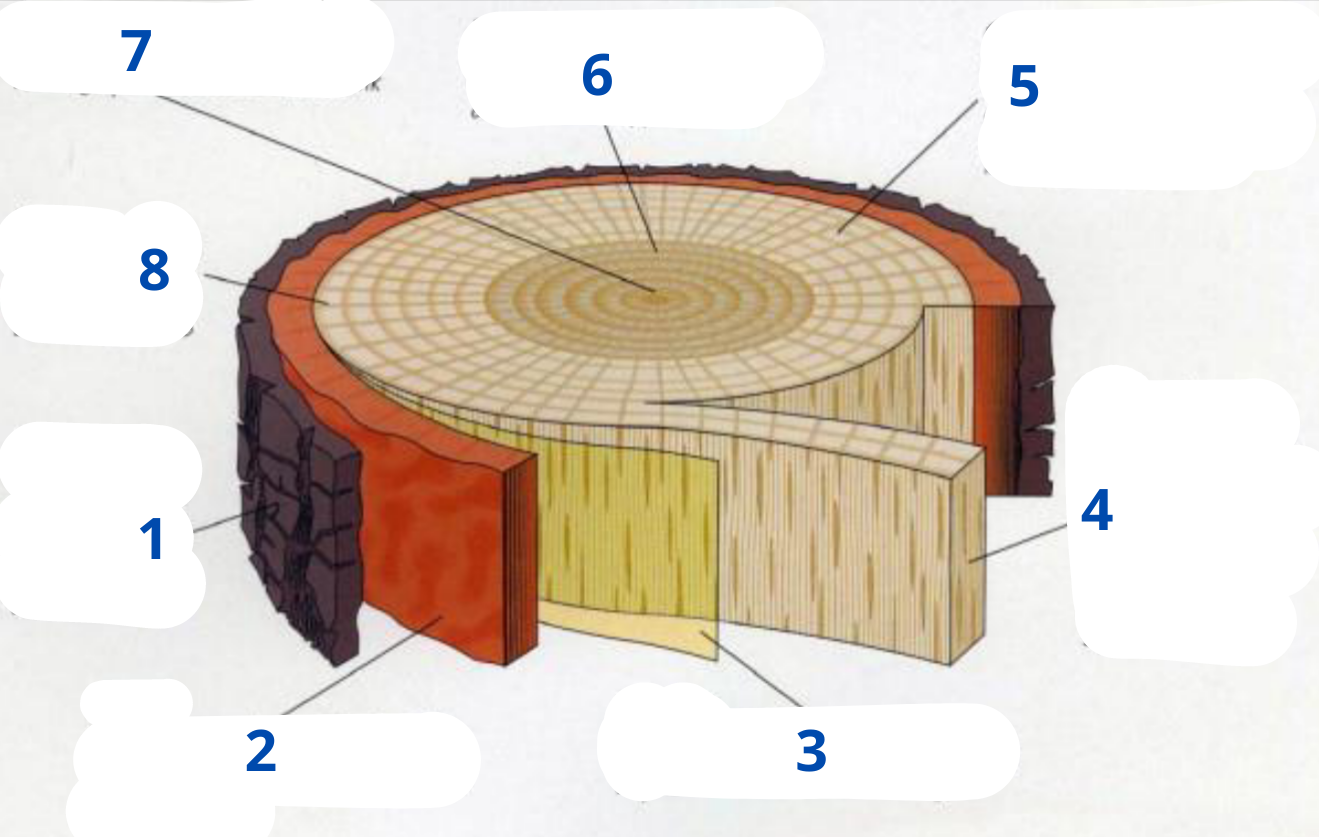
tree diagram
bark
phloem
cambium
xylem/sapwood
growth ring
heartwood
pith
ray
cavitation
occurs if the water potential becomes too negative
water potential is
greater during the day than at night
indeterminate growth
= free growth
roots and stems
increase in length/girth
determinate growth
= fixed growth
leaves and flowers
reach a fixed size and stop growing
what is auxin?
hormone used for growth
better site = higher ___ production
what is abscisic acid?
hormone used in stomate closure and senescence
apical dominance
height first then diameter growth
gymnosperms: strong
angiosperms: weak
root production is always first and important
plant tropisms
geotropism
thigmotropism
phototropism
geotropism
negative: stem grows away from gravity
positive: root grows towards gravity
phototropism
negative: roots grow away from light
positive: plant bending towards light
thigmotropism
vines or things that respond to touch
response to grow or protect
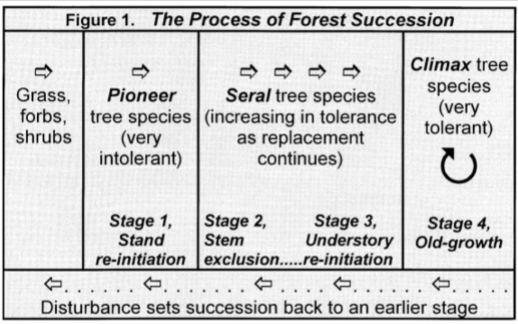
forest succession based on shade tolerance
shade tolerance ratings and examples
very tolerant - 10 - ex: sugar maple, eastern hemlock
tolerant - 8 & 9 - ex: eastern hophornbeam/ironwood
moderately tolerant - 6 & 7 - ex: american elm
moderately intolerant - 4 & 5 - ex: white oak, northern red oak
intolerant - 2 & 3 - ex: red pine, northern pin oak
very intolerant - 1 - ex: paper birch, jack pine
leaf characteristics related to shade and sun exposure
sun adapted plants:
smaller, more divided
thicker leaf
thicker cuticle
fewer stomates
stomates on lower surface
stomates close quickly
shade tolerant plants:
broader
thinner leaf
thinner cuticle
more stomates
stomates on both surfaces
stomates less responsive
pioneer species
apical dominance less important
short-lived, intolerant
opportunistic regeneration strategies
aggressive resprouting
small, numerous, widely disseminated seeds
ex: aspen, sumac, paper birch, jack pine
gap-phase species
apical dominance very important
mid-tolerant species regeneration
moderate competition, sufficient moisture
persist, wait for breaks in the canopy (gaps), then fast growth
ex: basswood, american elm, white ash, yellow birch
tolerant species
apical dominance moderately important
persist in very little light
moisture
very slow growth
ex: sugar maple, eastern hemlock, american beech, balsam fir
light compensation point
where photosynthesis = respiration