Types of Microscopes + Cells or Debris?
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH2 Section2. Answer w/definition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
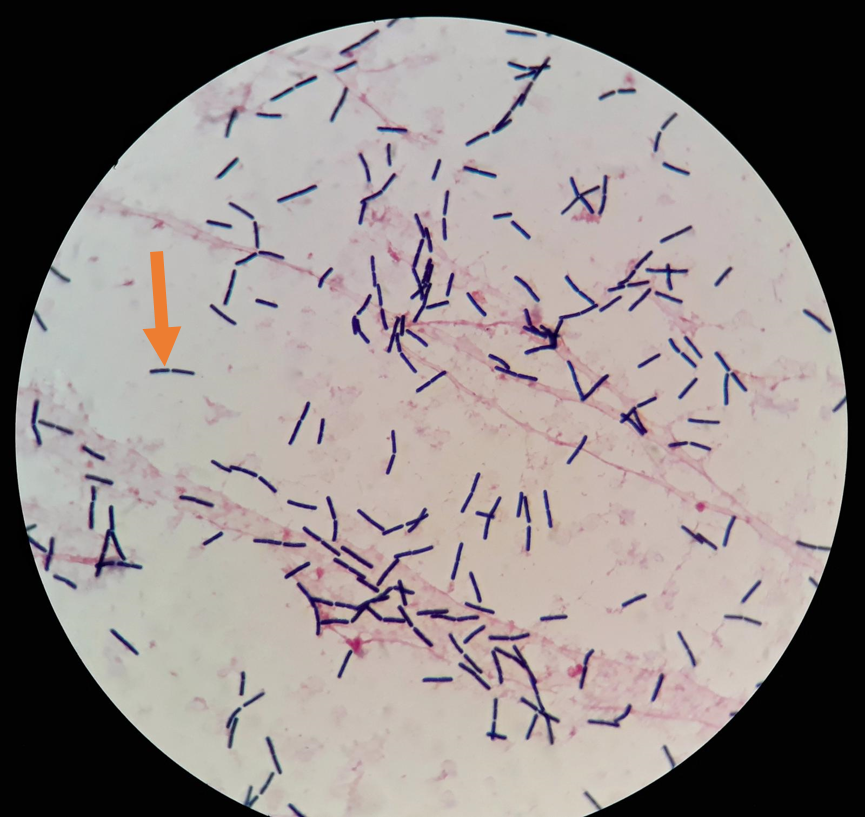
Is this a cell or debris
cell
For (D) aka Limit of Resolution, you want a ____ numerator (lambda) and ____ denominator (obj lens + condesor)
small, large
Ways to Improve Limit of Resolution
Increase magnification
Shorten working distance (focal length)
Adding oil
If D is less than distance…..
2 cells seen as seperate
If D is more than distance…
2 cells blur into one
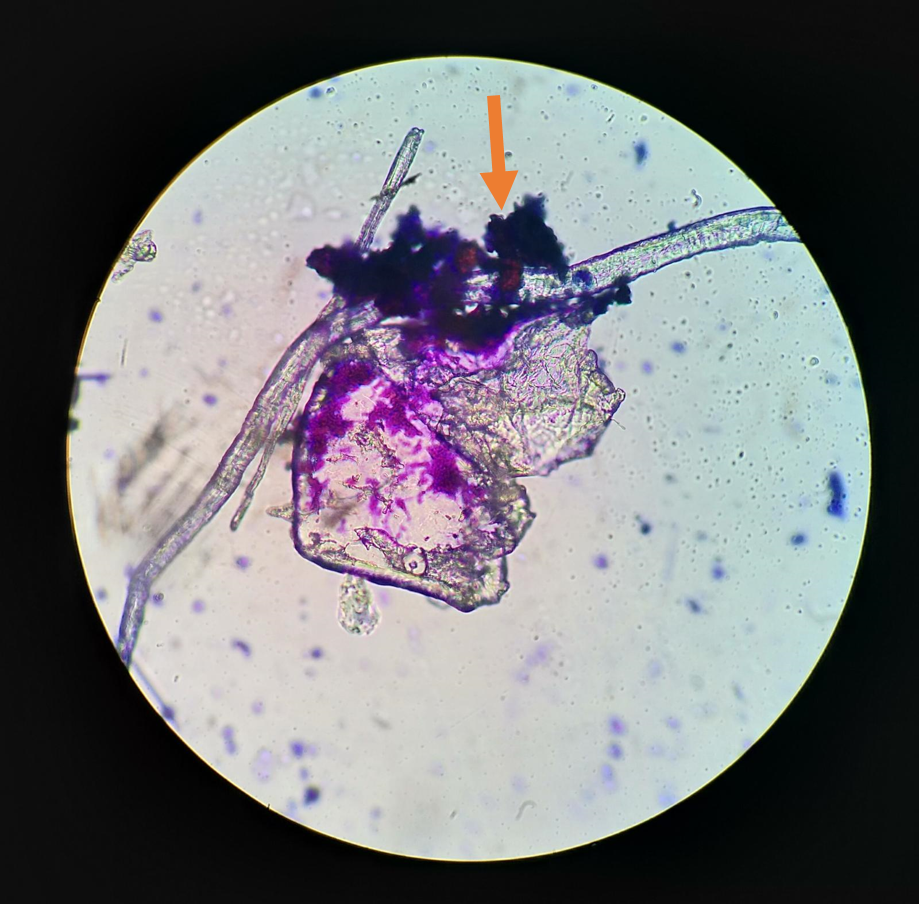
Is this a cell or debris
debris
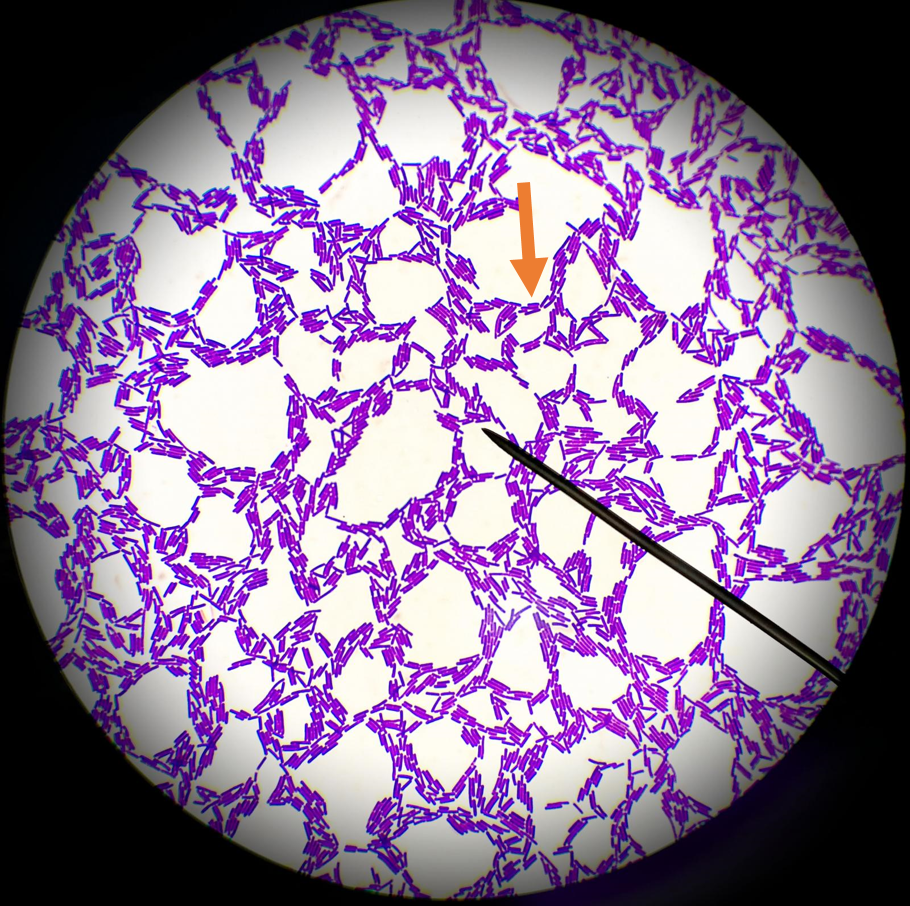
Is this a cell or debris
cell
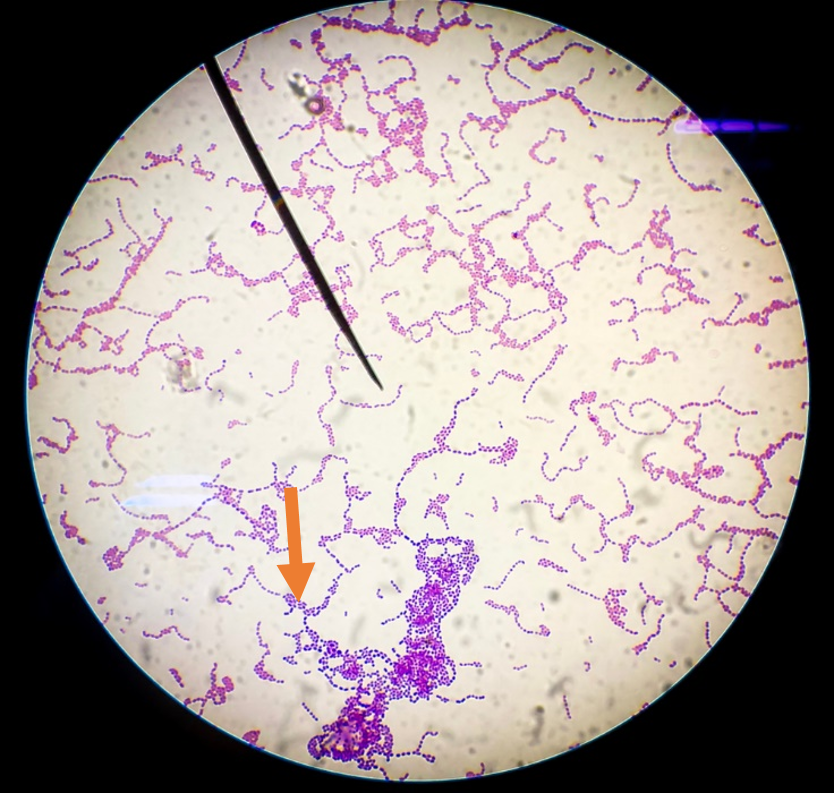
Is this a cell or debris
cell
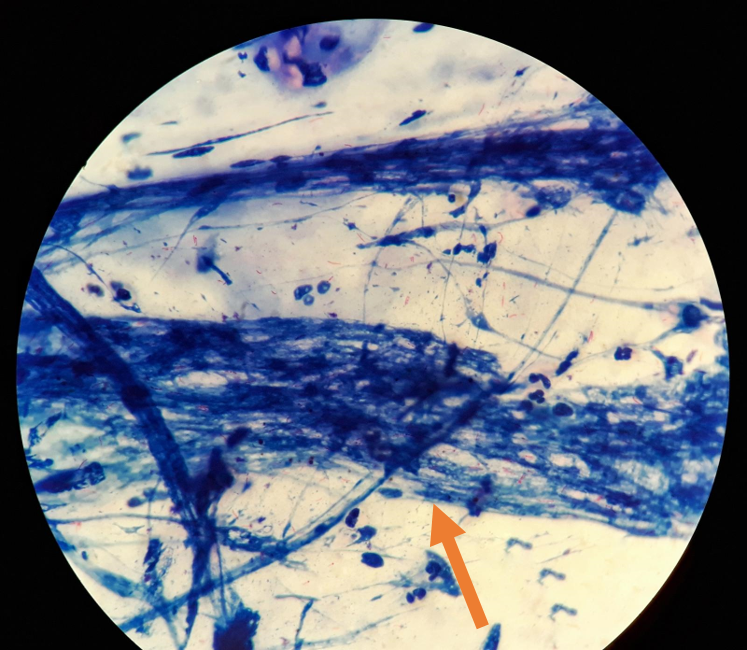
Is this a cell or debris
debris
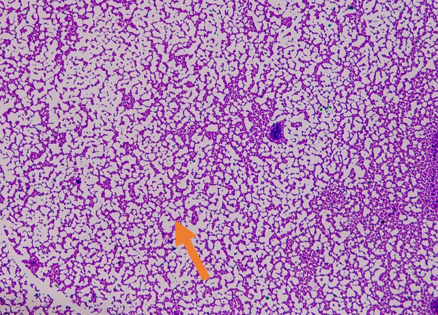
Is this a cell or debris
debris
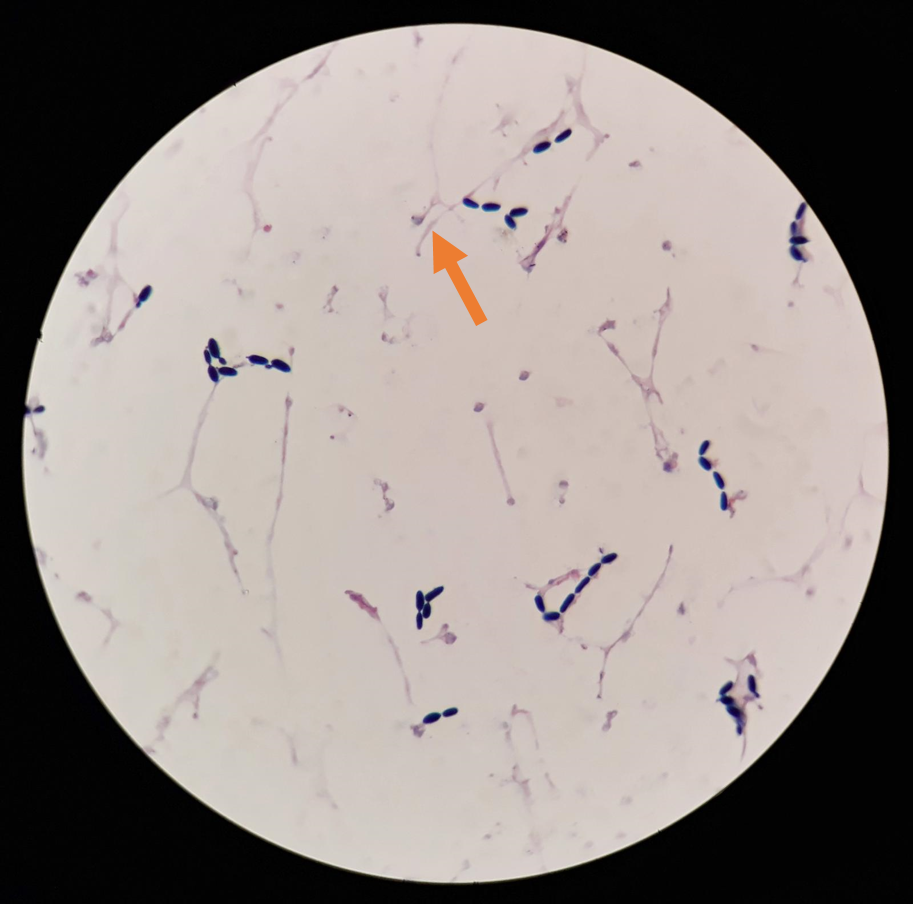
Is this a cell or debris
debris
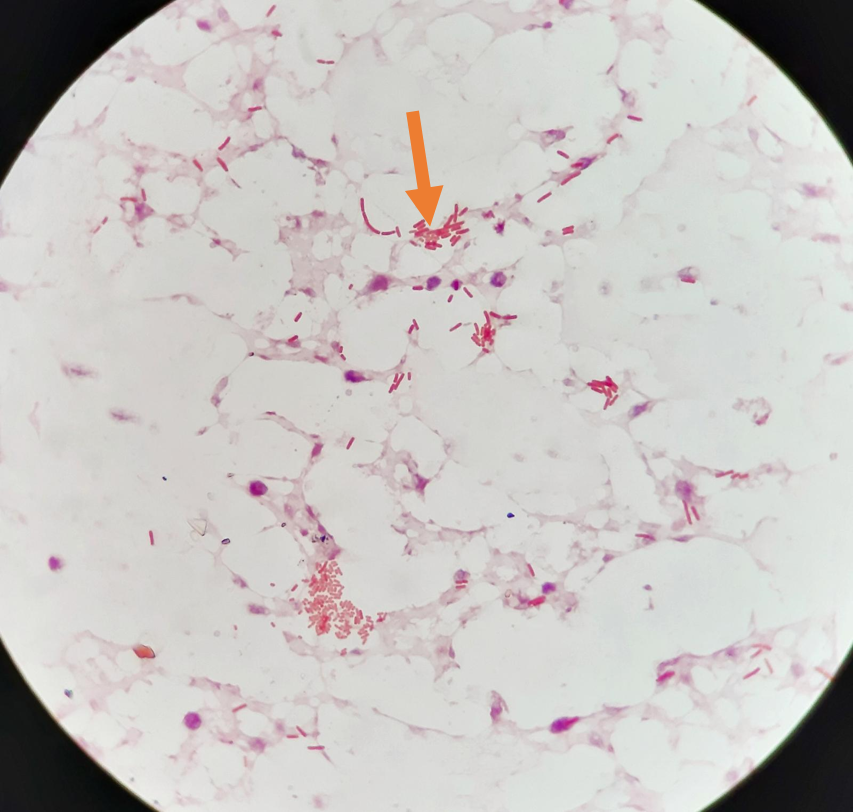
Is this a cell or debris
cell

Coccus/cocci
circular
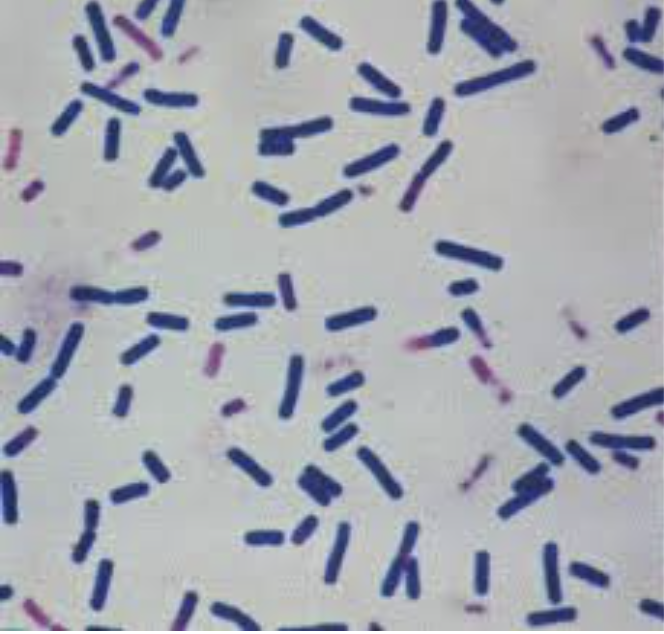
bacillus/bacilli
rod
ovoid coccus
oval
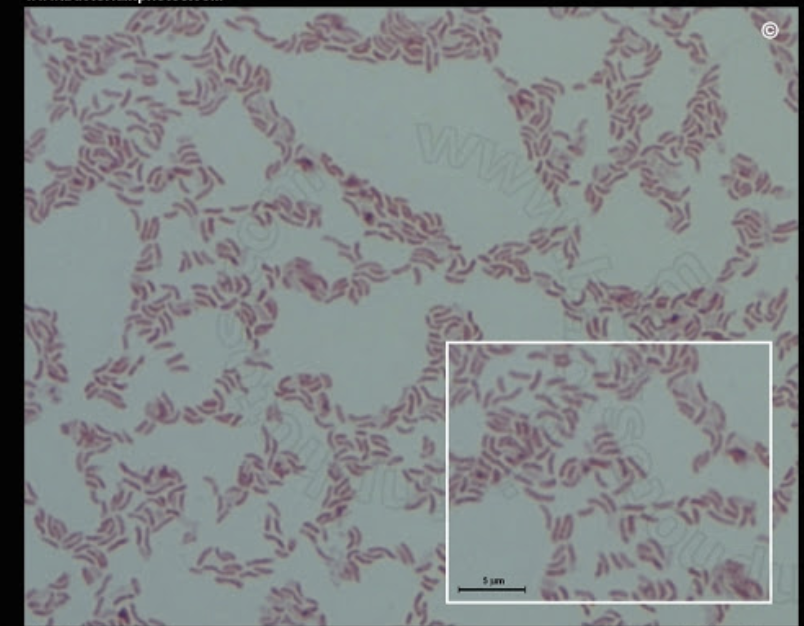
vibrio/vibrios
curved rod
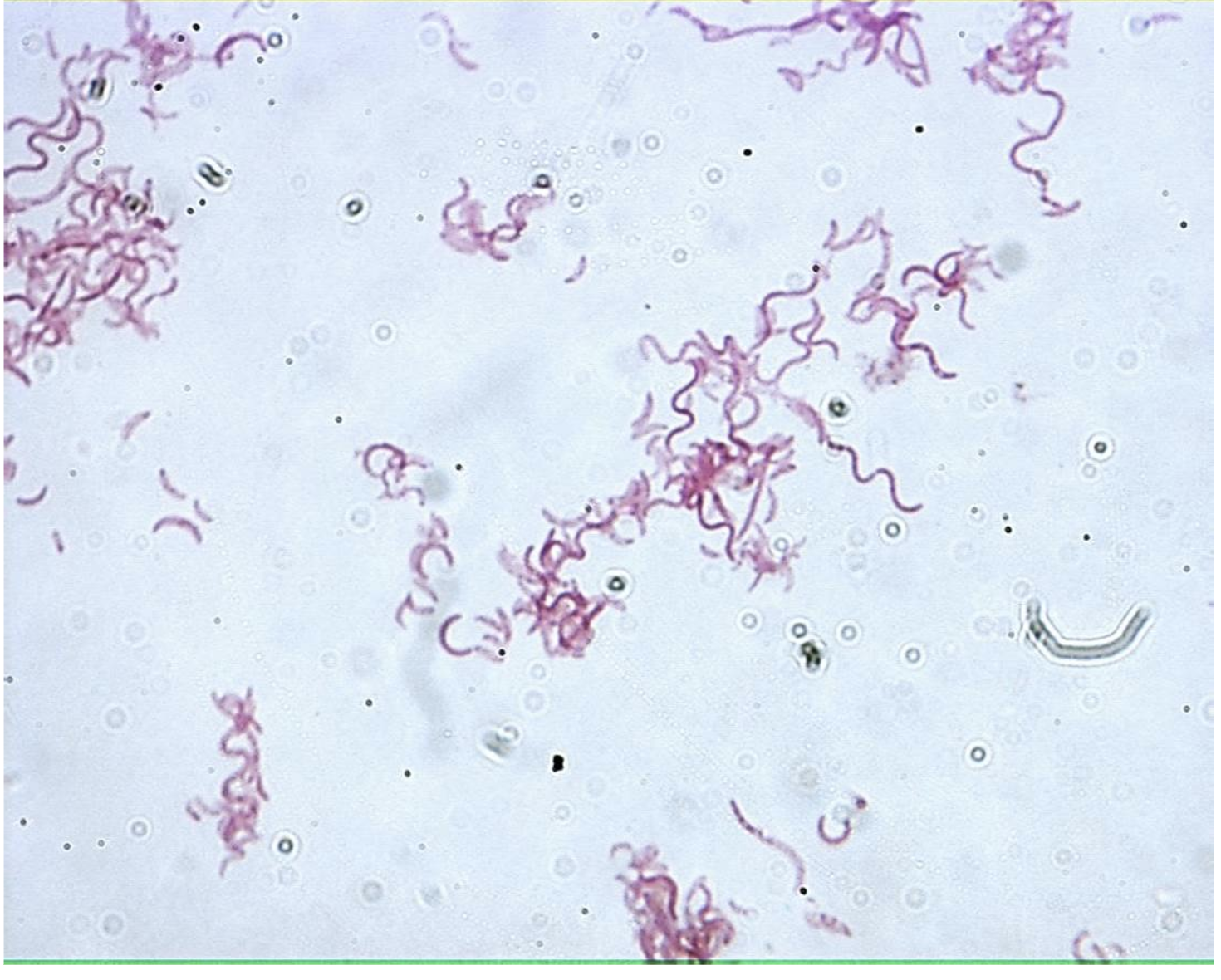
sprillium/spirilla
spiral
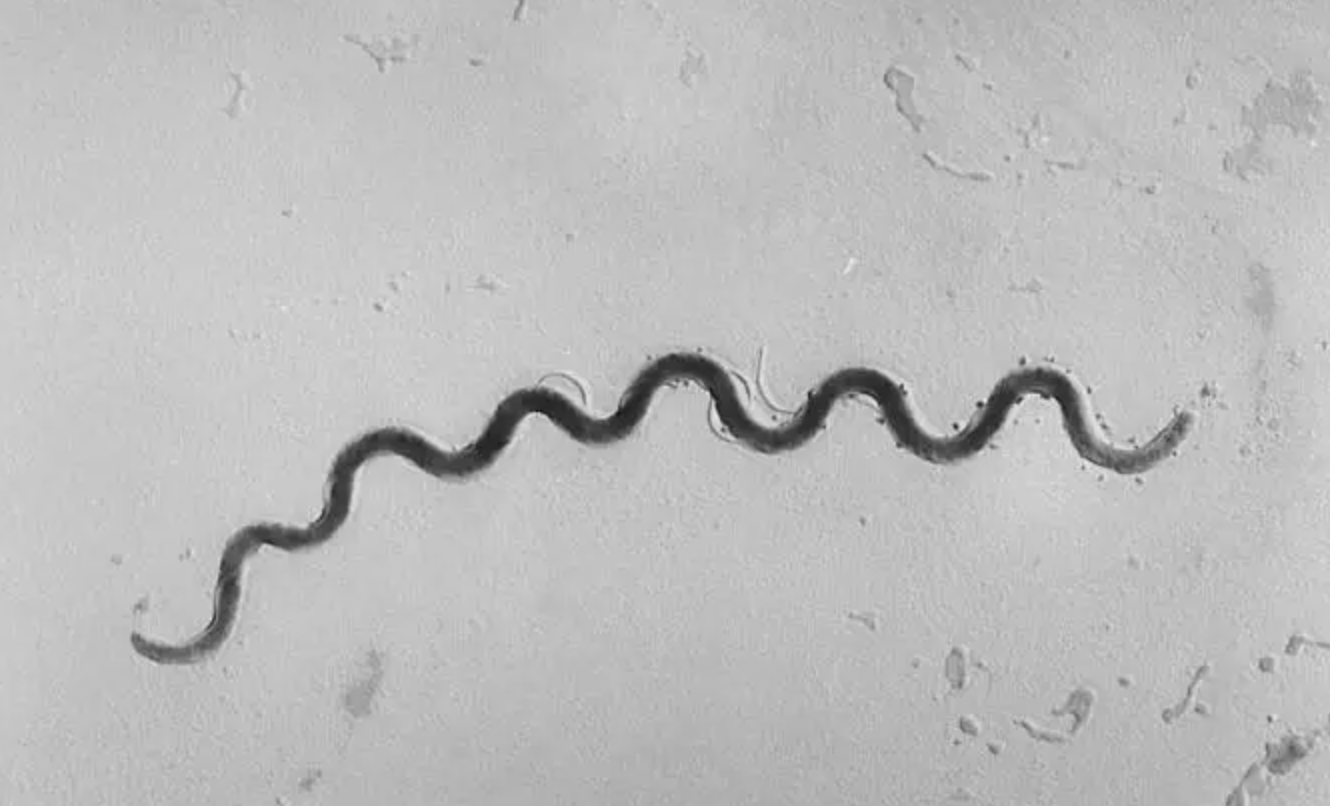
spirochete/spirochetes
flexible spiral
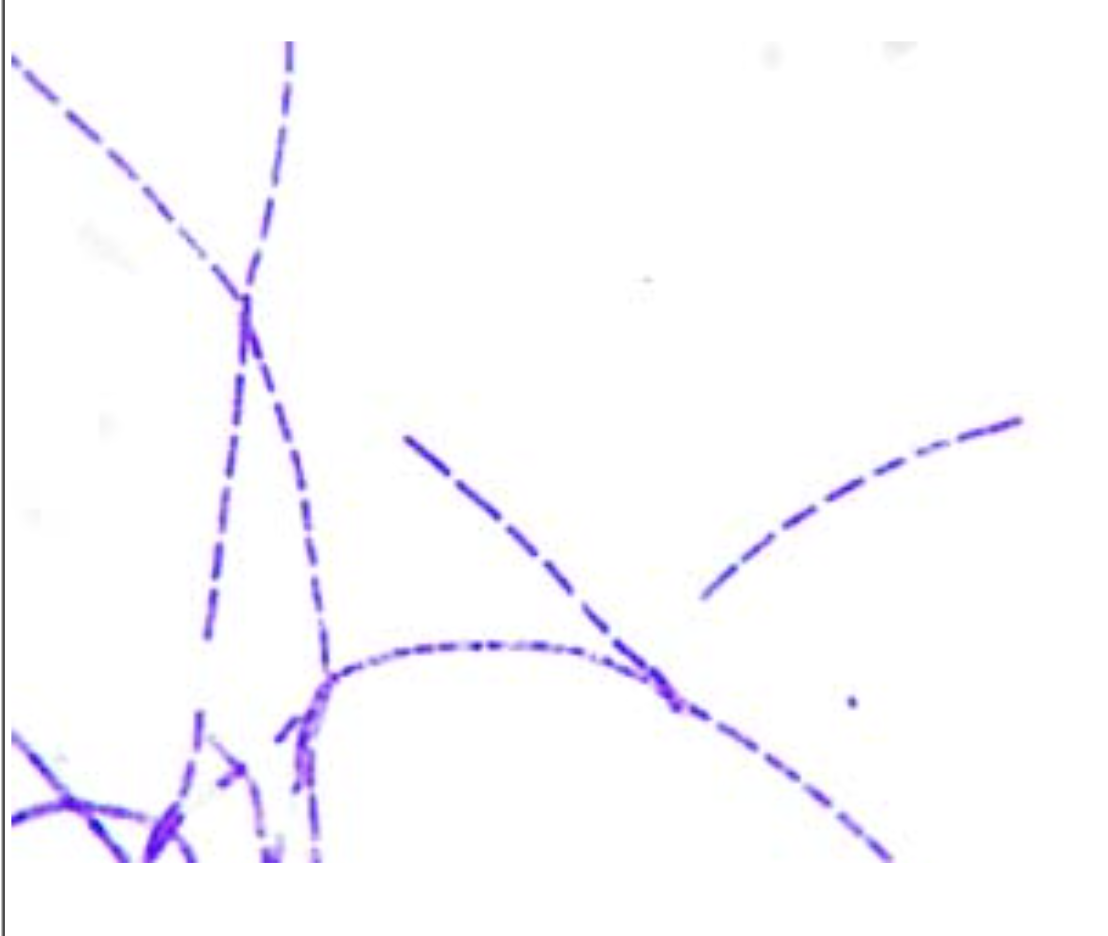

Strepto
chains
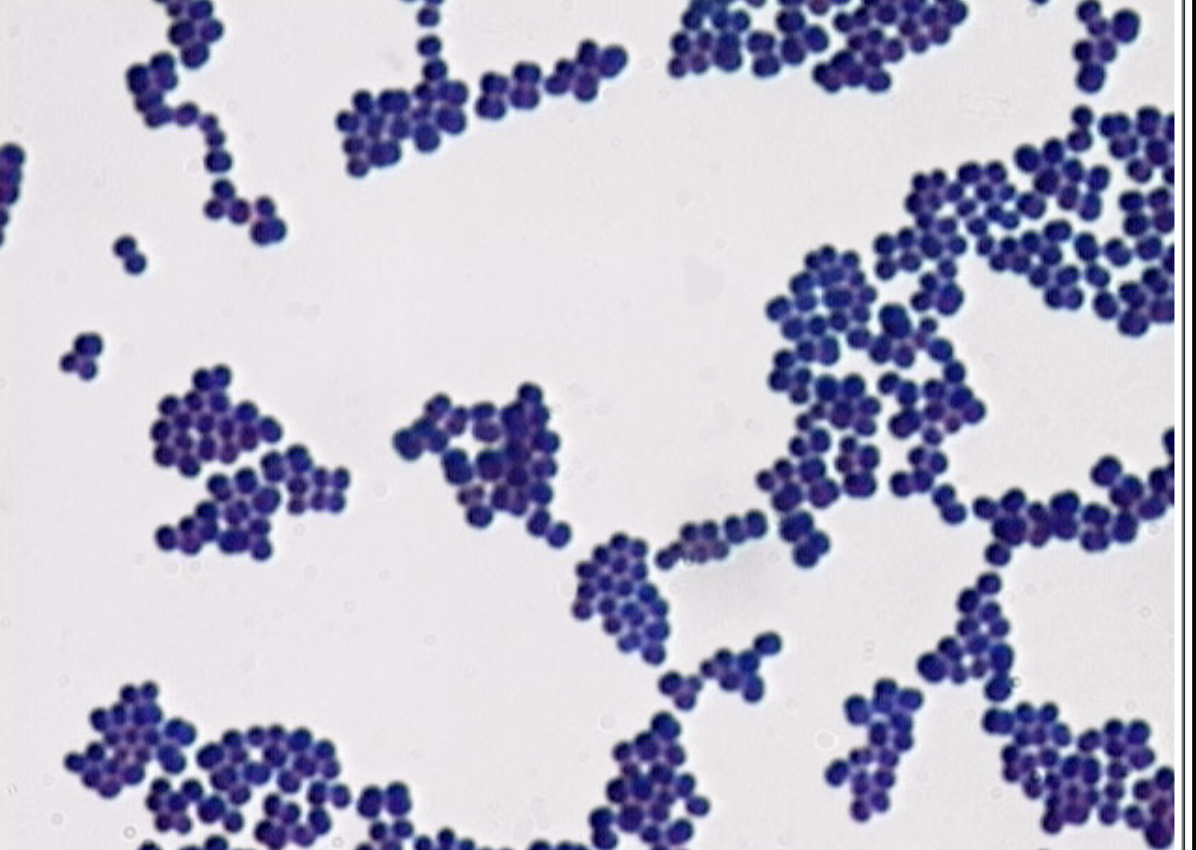
Staphylo
clusters
Diplo
2 cells connected together
Tetrad
4 cells connected together
Sarcina
8 cells in a cube
Single
no obv arrangement. Dependent on shape
If all the possible cells seem to be very small then its likely….
bacteria
If all the possible cells seem to be take up a large amount of the field of view then its likely….
debris
Bright-field Microscope
produces image w/bright background & dark or pigmented cells. Gives 2D image & stains the cell or background
Dark-field Microscope
Produces dark background with illuminated specimen. Gives 2D image
Phase-contrast Microscope
produces image in shades of grey, has the cells have a ring of light surrounding them. Gives 2D image
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscope
Produces specimen looking as shade of grey & its natural color. Gives 3D image
uses 2 beams of light→travel through speciment @diff times, then rejoin in obj lens
Provides interior view of eukaryotic cells
Fluroescent Microscope
Produces image appearing brightly colored w/black background. Has ambiguous imaging
relies on adding fluorescent dye to chemically bond to certain molecules.
Illuminated via UV + requires computer
GFP
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Produces detailed image that gets darker the position of image the longer it takes electron to return. Gives 3D image & interior of cell isn’t seen
Electron beam hits specimen →computer interprets & displays
Transmission electron Microscope (TEM)
involves cutting specimen into very thin slices, then directing electron at slice. Gives 2D image & interior of cell is seen
What are the 2 types of electron microscopes (uses electrons to create very detailed image thats interpreted by computer)?
Scanning electron microscope and Transmission electron microscope
Limit of Resolution
For a hypothetical microscope, you have some options listed below:
Objective lens of 40X with a NA of 0.85
Objective lens of 100X with a NA of 1.25
Condenser lens with an NA of 1.25
Wavelength of light around 350nm
Wavelength of light around 550nm
Q1: Using this information, which components would you include in your microscope to have the best resolution? Include calculations to support your choice.
350nm/1.25 + 1.25 = 140nm
Limit of Resolution Formula
D = lambda / condensor + objective lens (want numerator smaller than denominator)
Limit of Resolution
For a hypothetical microscope, you have some options listed below:
Objective lens of 40X with a NA of 0.85
Objective lens of 100X with a NA of 1.25
Condenser lens with an NA of 1.25
Wavelength of light around 350nm
Wavelength of light around 550nm
Q2: If there were two cells that are 245nm apart, using your microscope, would these cells be seen as separate or will they blur into one? Explain your answer choice.
These cells would be seen as 2 seperate since distance is smaller than D, giving seperation. Any larger would blur into one
D = 140nm
To improve numerical aperature you’d have to
shorten focal length
When naming cell morphology + arrangement, what goes first?
(a) arrangement + shape
(b) shape + arrangement
a
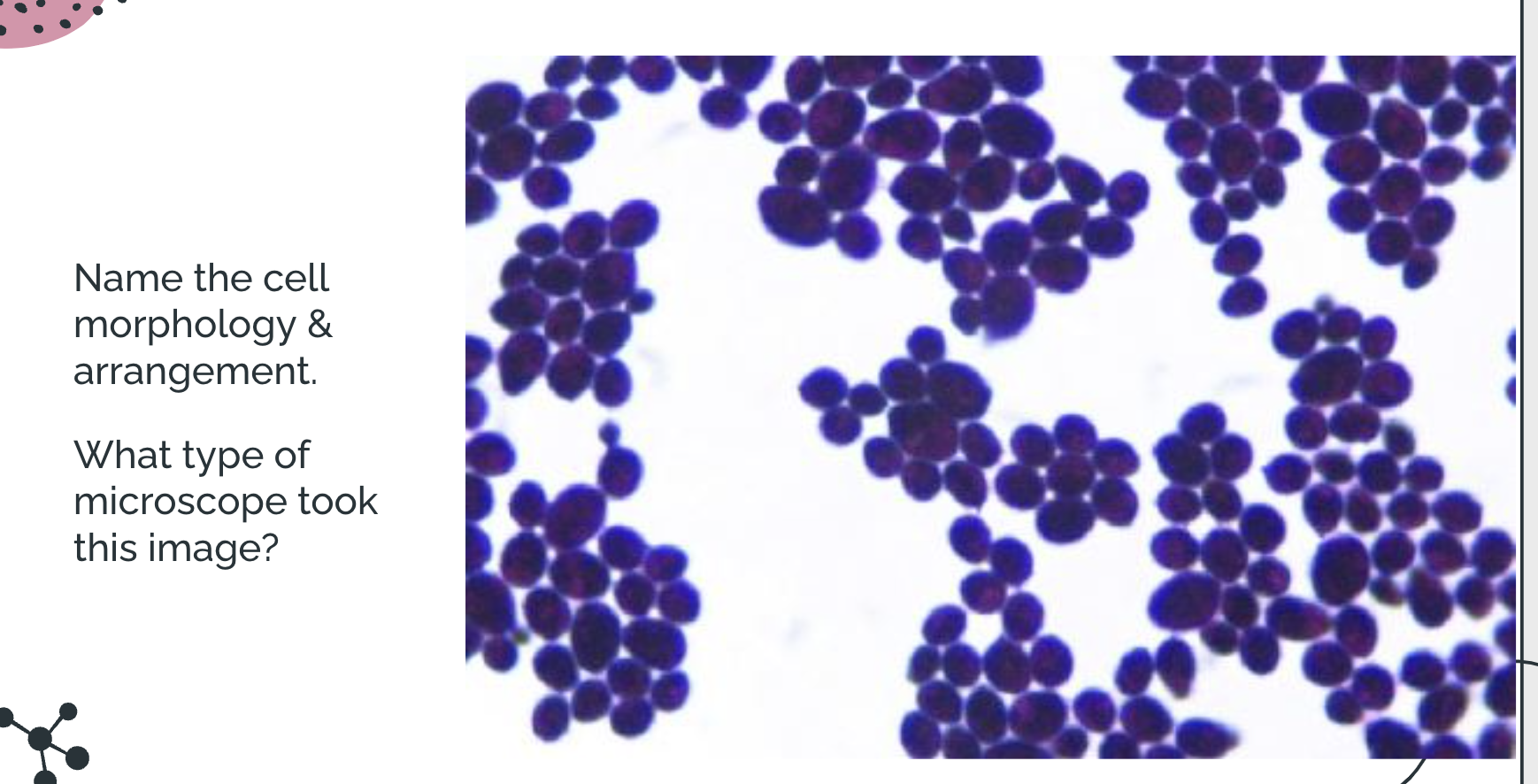
Staphylo cocci; brightfield
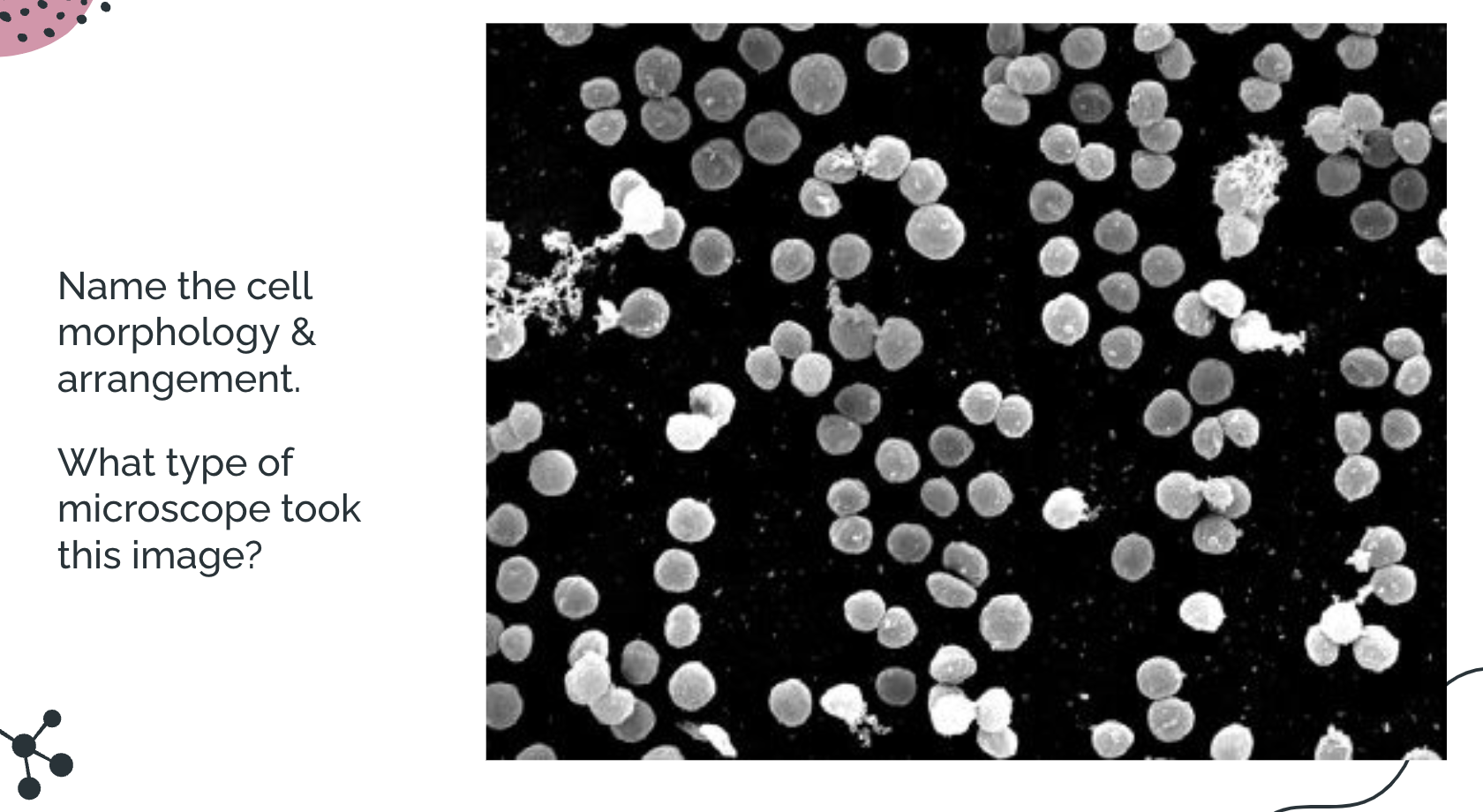
hint: thinking of layering (3D or 2D)
Single cocci; SEM
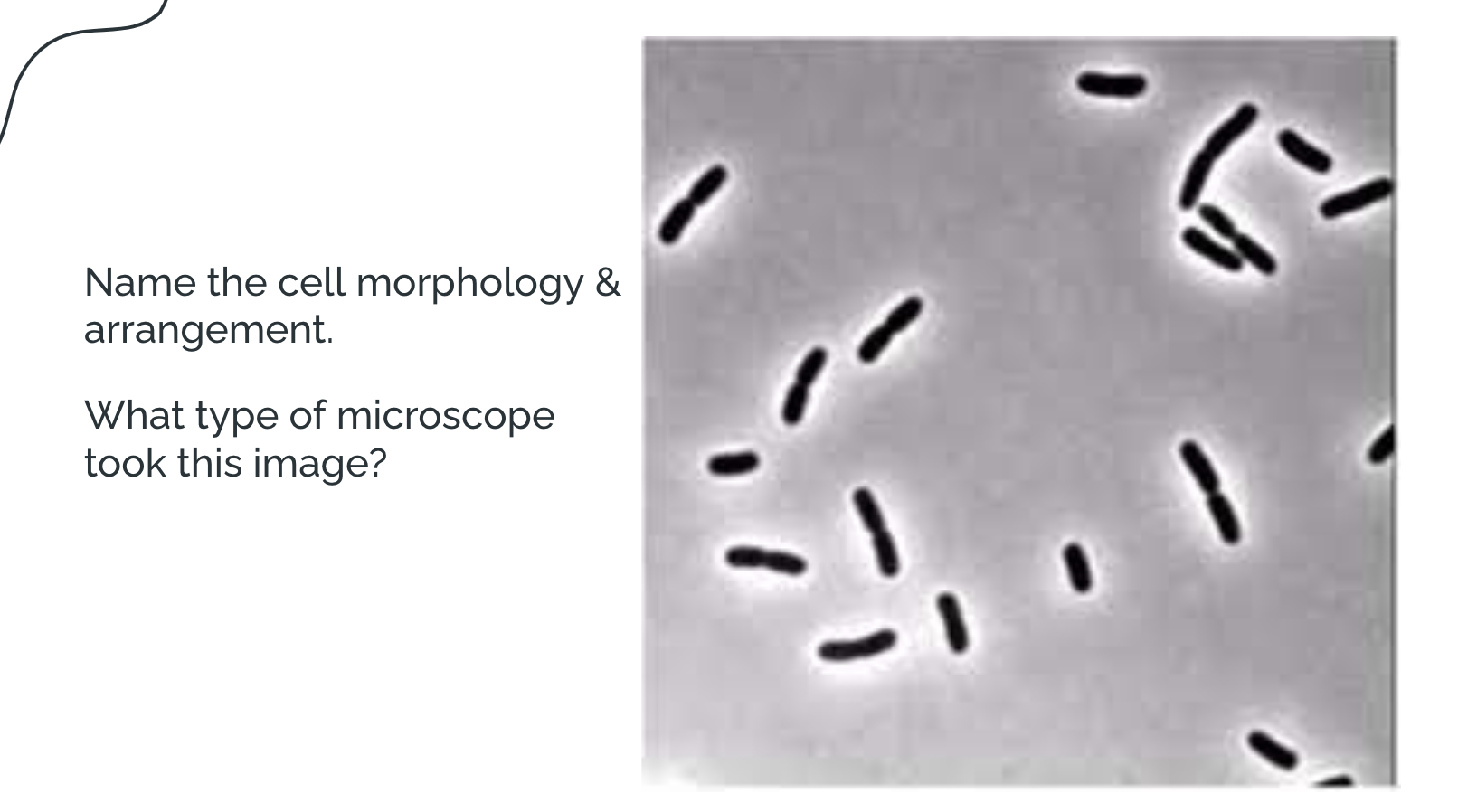
Diplo bacilli; Phase Contrast
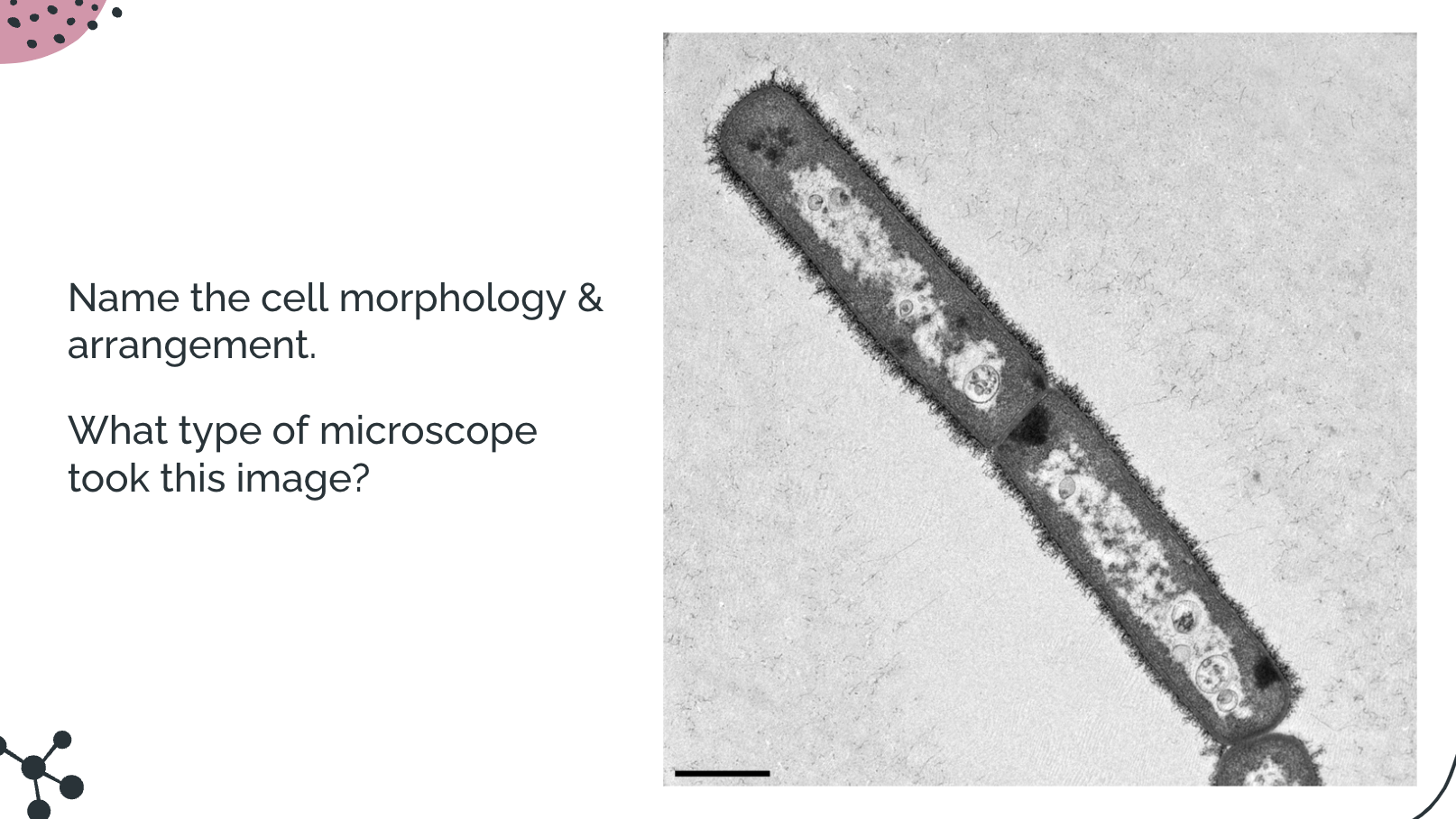
Diplo bacilli; TEM
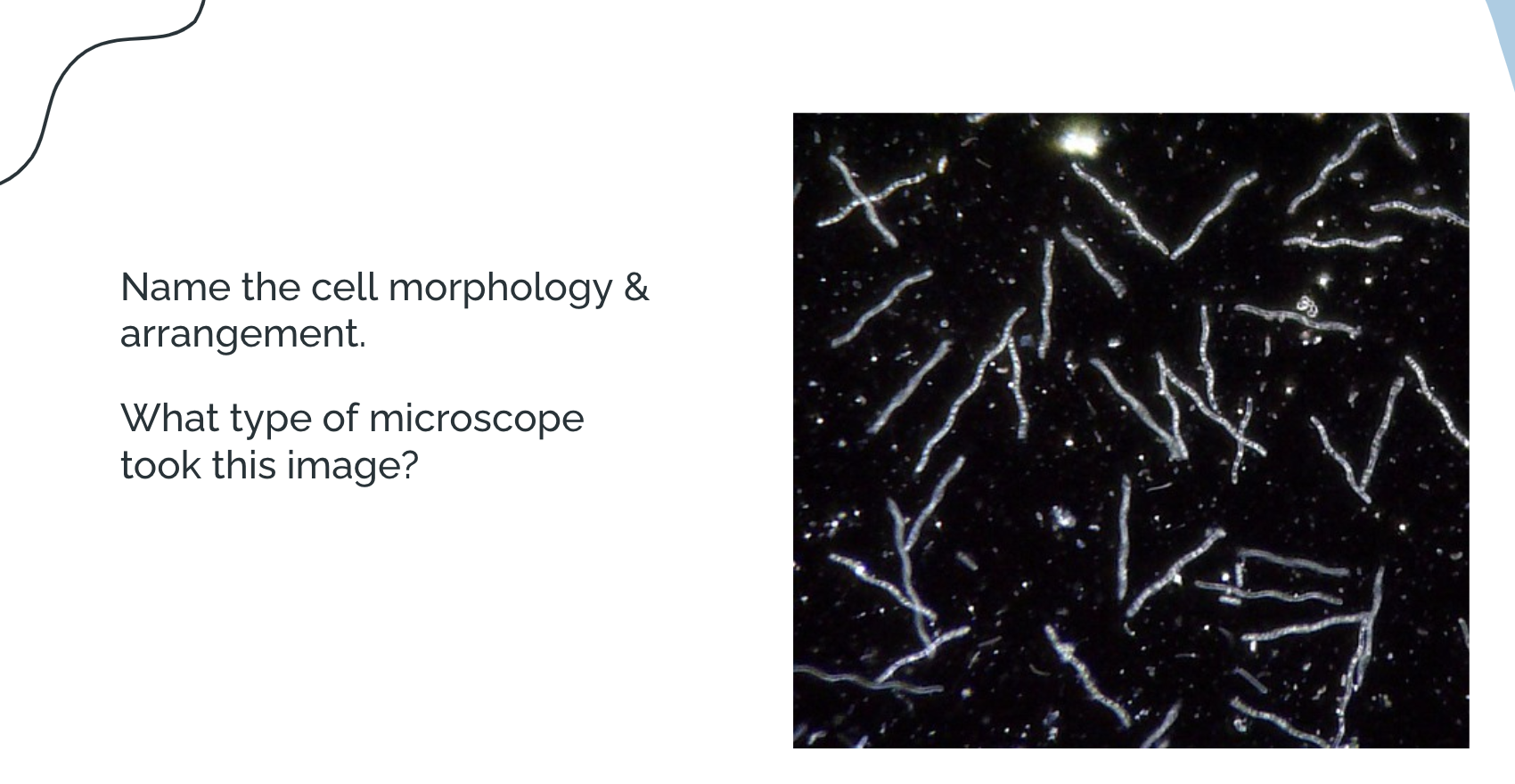
single spirillium; darkfield
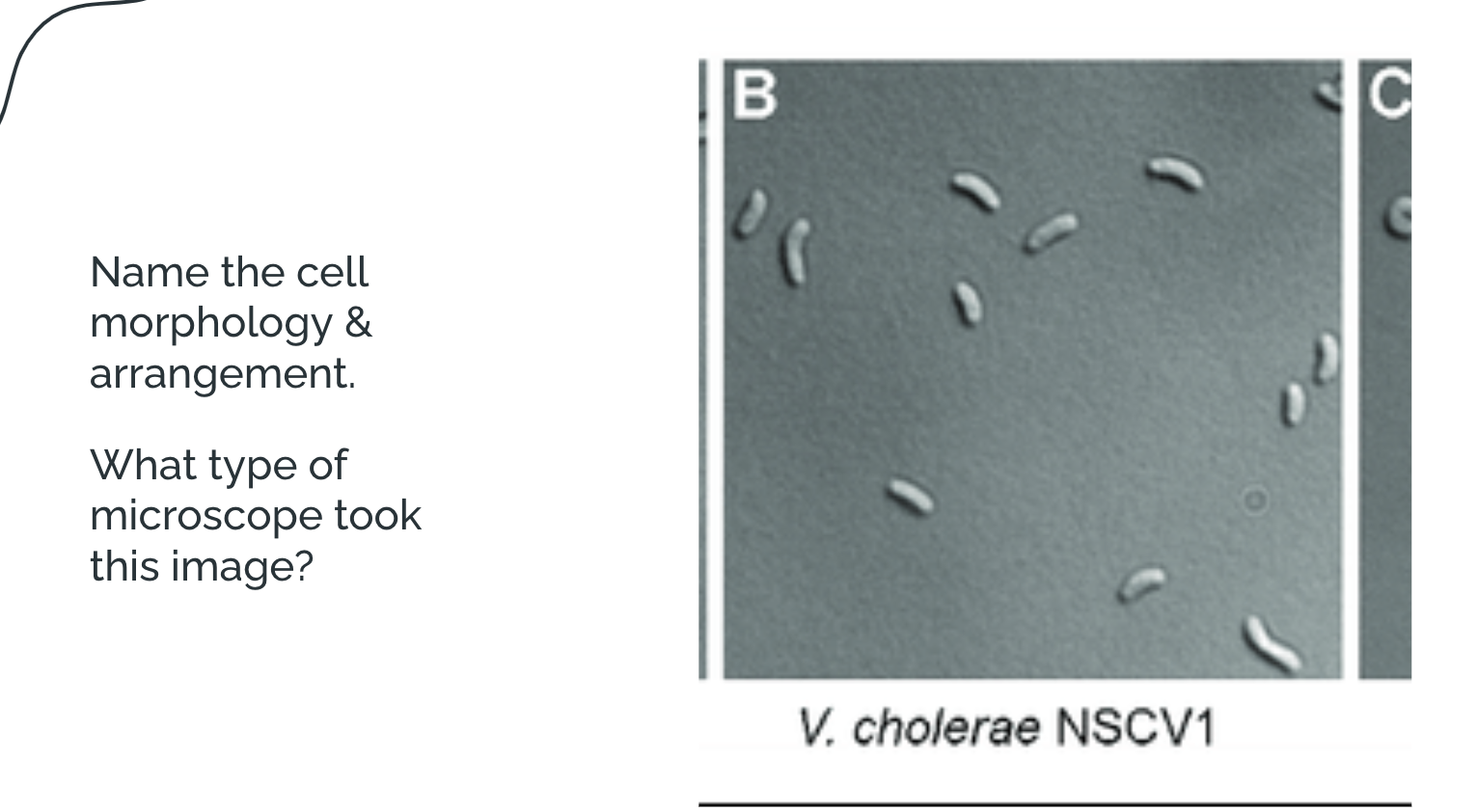
Hint: they’re smaller cells
single vibrio; DIC
Limit of Resolution
You have two microscopes available to use:
Has a wavelength of 450nm, a condenser lens of 1.25 and two objective lenses: 40x/0.25 or 60x/0.65
Has two wavelength options either 655 or 555nm, a condenser of 1.25 and a 100x/1.25 objective lens
Q1: Using this information, which microscope and set up would have the best resolution? Include calculations to support your choice.
555nm/1.25 + 1.25 = 222nm. Microscope B
Limit of Resolution
You have two microscopes available to use:
Has a wavelength of 450nm, a condenser lens of 1.25 and two objective lenses: 40x/0.25 or 60x/0.65
Has two wavelength options either 655 or 555nm, a condenser of 1.25 and a 100x/1.25 objective lens
Q2: If there were two cells that are 375nm apart, using the best set up microscope, would these cells be seen as separate or will they blur into one? Explain your answer choice.
Based off of the Resolution (222nm), the two cells will seen as separate because the distance from the 2 cells (375nm), meets the at least 222nm (aka the limit/minimum)