Art History 21 Terms - Horvat (Midterm)
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Catacomb
An underground network of tombs. Were used for religious practice, particularly Christianity. Created during Roman Empire.

Loculus/-i
Burial Niches, the spaces that would dig into the walls of Catacombs to insert remains of deceased.
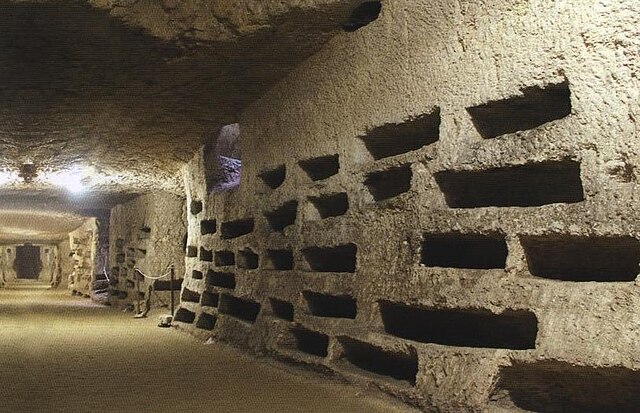

Cubiculum
Large rooms carved out of the walls in catacombs. Used as a room to store deceased bodies.
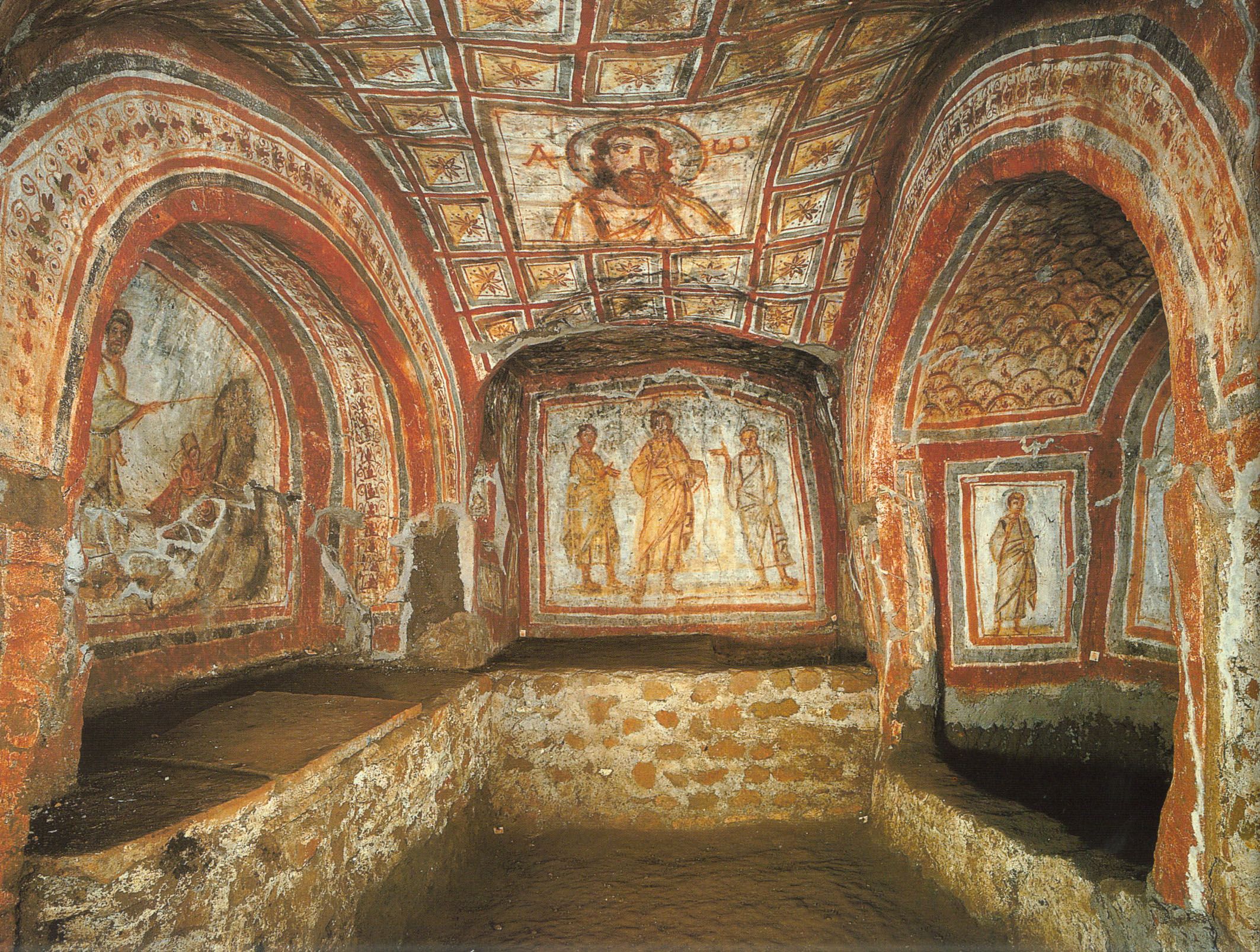

Arcosolium
Arched cell in a Roman catacomb.
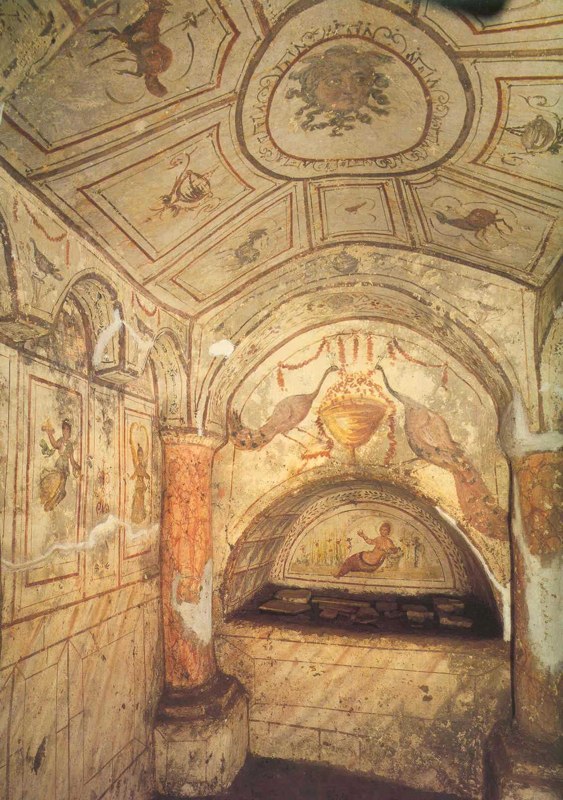

Domus ecclesiae
The earliest Christian places of worship, churches that existed in private homes.
Epitaph
A phrase that was written in memory of someone who had died; scripture. Usually on tombs of those in the catacombs and on tombstones.
Ichthys (eucharistic fish)
“Jesus Fish”, a symbol consisting of two intersecting arcs, the ends of the right side extending beyond the meeting point so as to resemble the profile of a fish. Used to recognize churches and other believers during a time when they faced persecution in the Roman Empire.

Orant
A standing figure with both arms raised. This was a gesture of p-rayer in the Early Christian period.

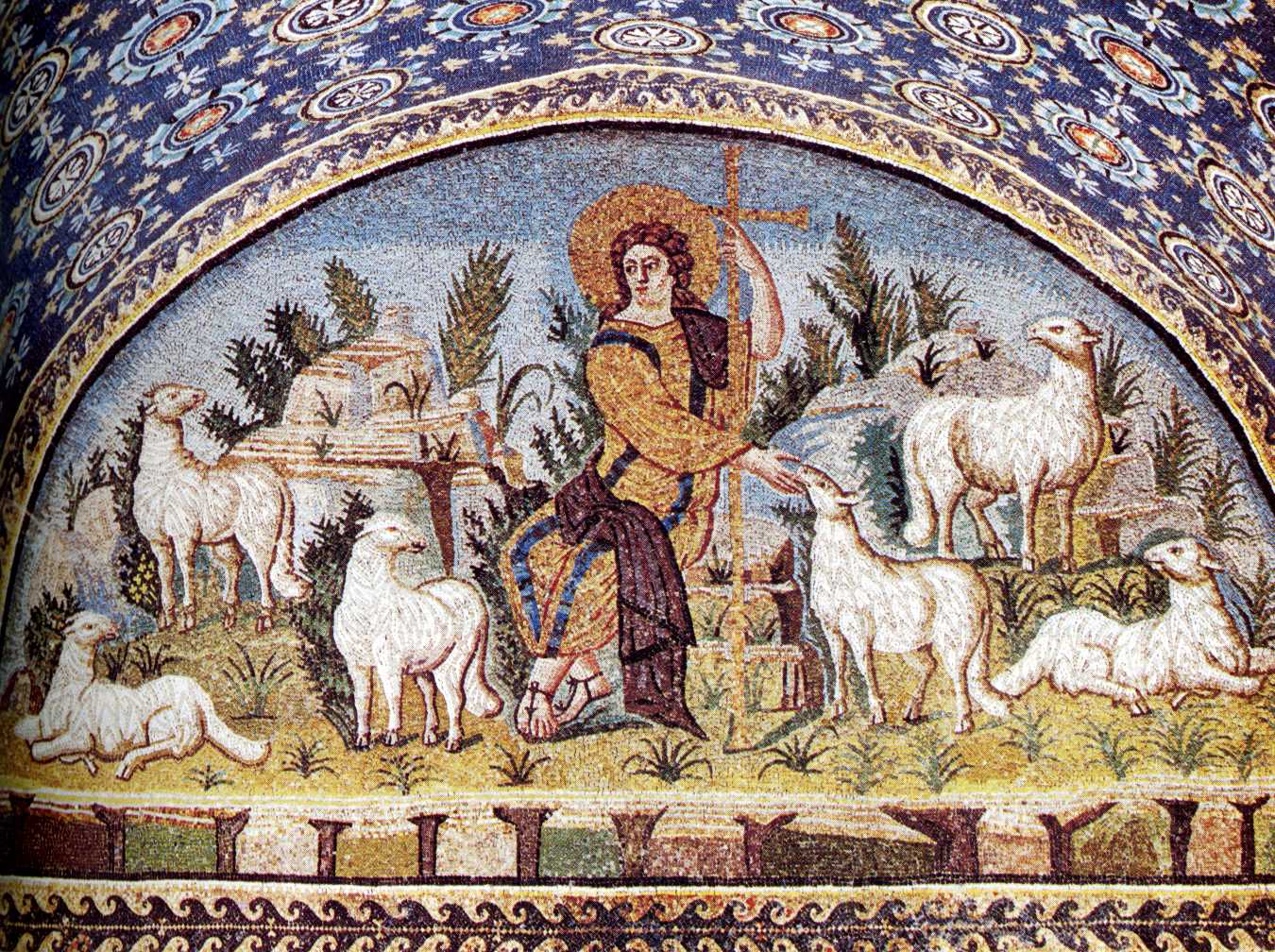
the Good Shephard
The Good Shepherd is a common motif from the Catacombs of Rome and in sarcophagus reliefs, where Christian and pagan symbolism are often combined, making secure identifications difficult.

Horror vacui
A phenomenon in which the entire surface of a space or an artwork is filled with detail and content, leaving as little perceived emptiness as possible.

Martyr
Someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external party. Used to inspire prayer.
Patron
The person or group of people paying for the image—who was considered the primary force behind a work's creation.
Sarcophagus
A coffin for inhumation burials, widely used throughout the Roman empire starting in the second century A.D. Most luxurious were of marble, but they were also made of other stones, lead and wood.
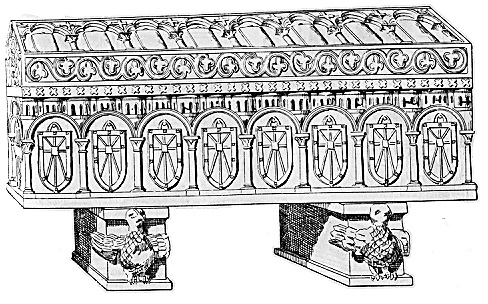
Chi-Rho/Christogram
Early symbol of Christ. Mimics a monogram/cross. The first two letters of Christ's name in Greek. Constantine put this on his war flag to unify Rome.
Tetrarchy
“Rule of Four”, refers to the division of an organization or government into four parts, with a different person ruling each part.
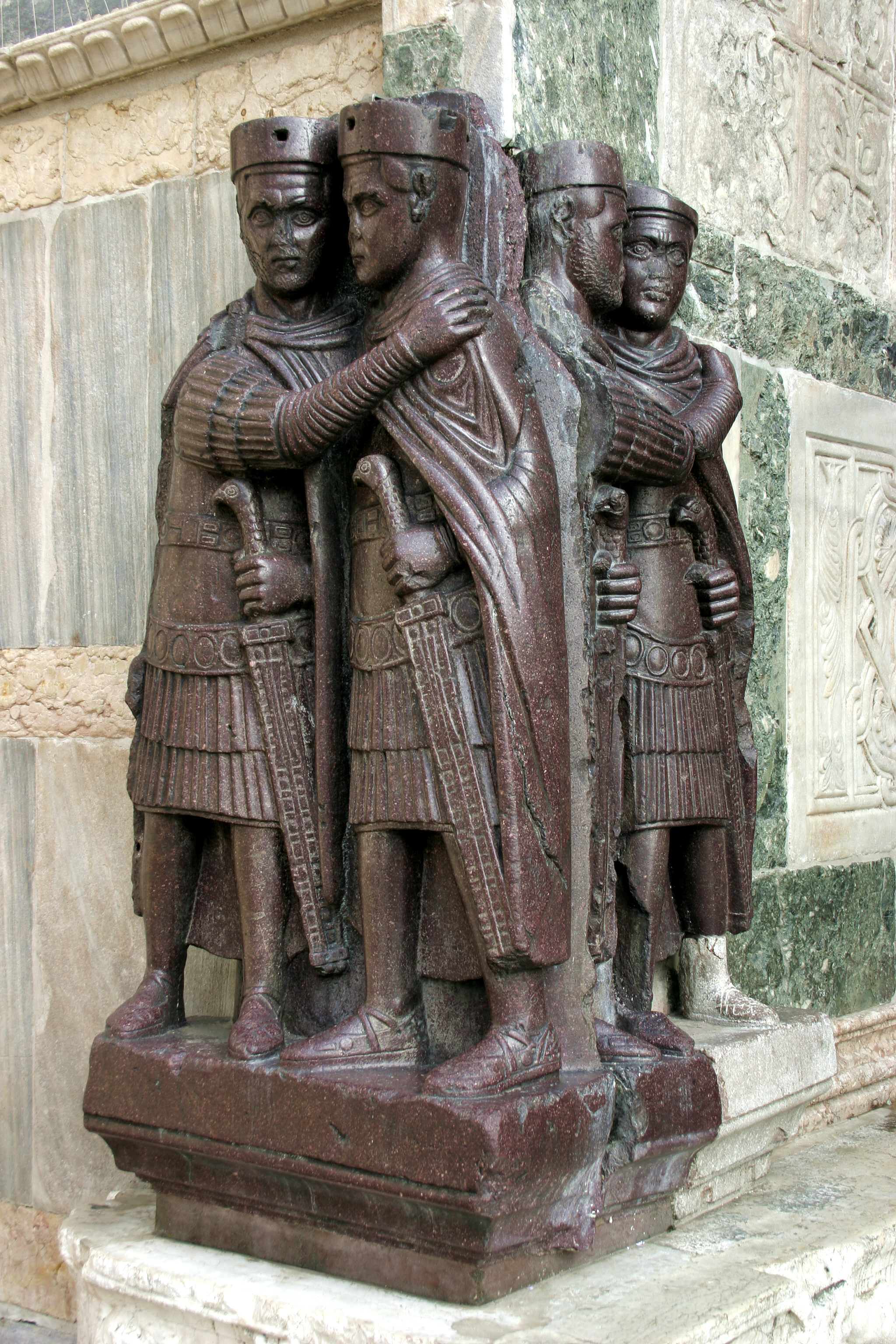

Basilica (Roman vs. Christian)
Roman: Used for governmental and adminstrative purposes, courts of law, business matters, and large group meetings.
Christian: Used for large churches and cathedrals.
Nave
The central longitudinal space of a basilica church. It is usually flanked on its long sides by aisles which are separated from the nave by columns or piers. Represents the Church on earth, the state of redeemed humanity
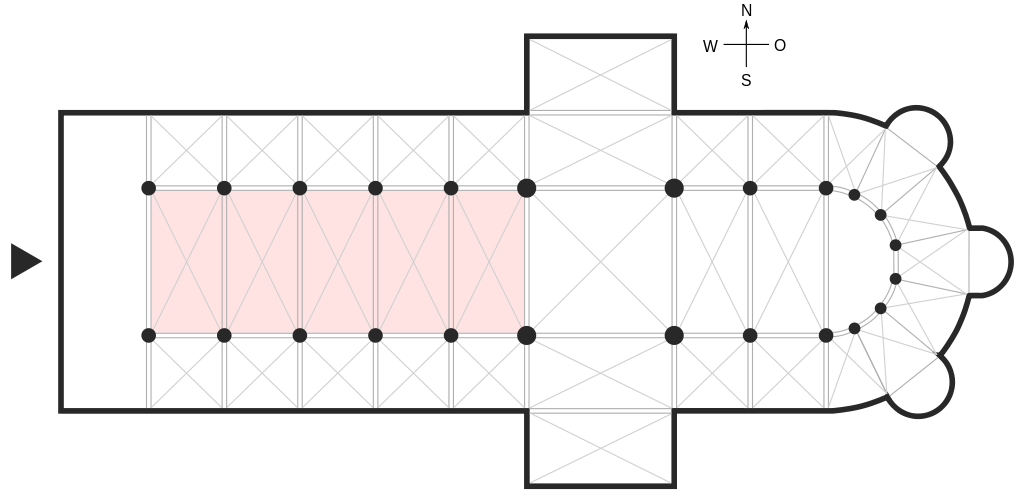
Apse
Semi-circular, domed, or vaulted recess part of the structure that indicates the end of the Church (East side). Considered to be the most holy location in Basilica.
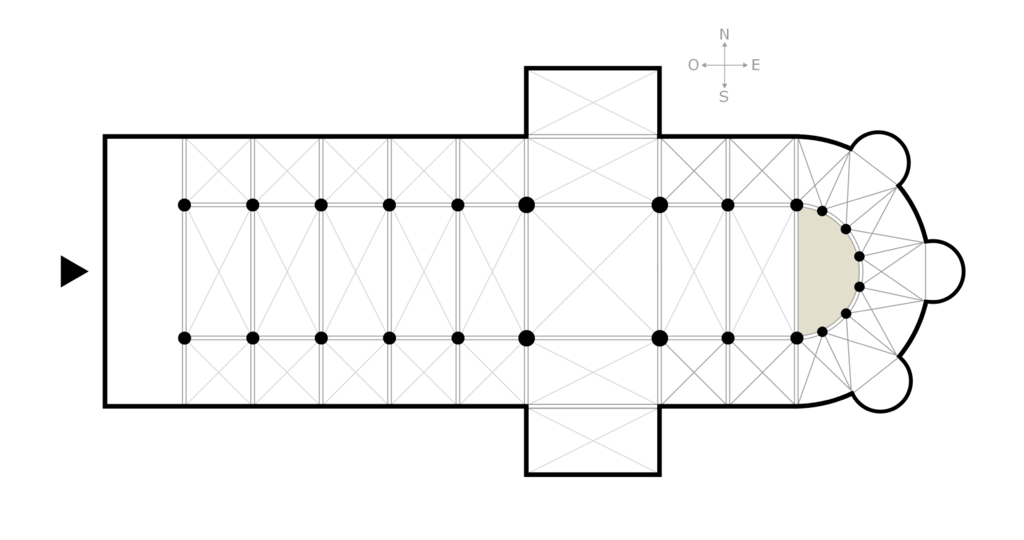
Aisle
Open area of a church parallel to the nave and separated from it by columns or piers.
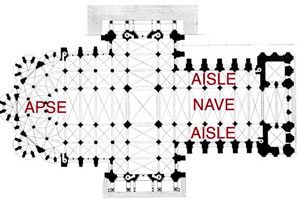
Narthex
A low projection at the western end of a church, like a porch.
Relic
A body part or object associated with a religious figure, such as Christ, the Christian saints, or the Buddha.
Reliquary
A container for relics.
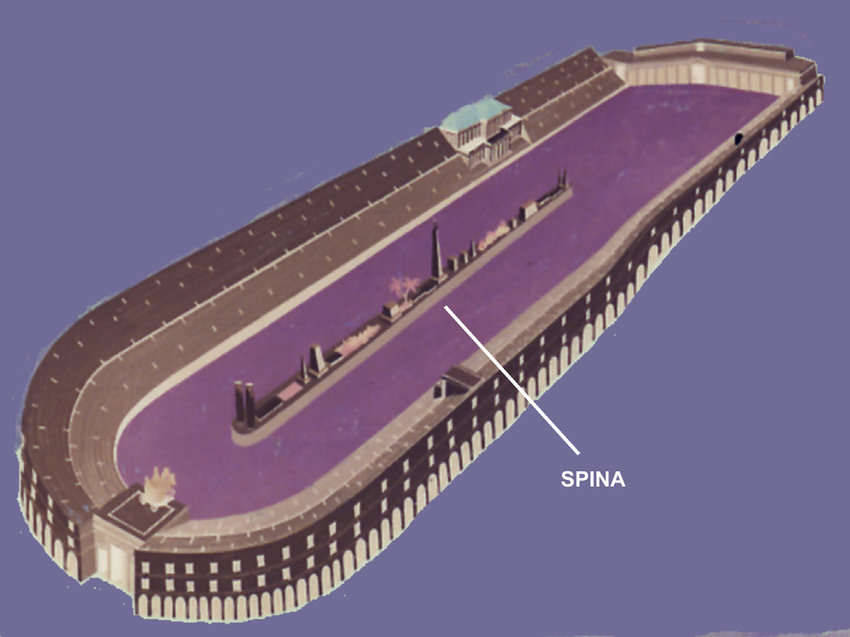
Hippodrome
Greek stadium designed for horse racing and especially chariot racing.

Spina
Wall or barrier along the middle of a Roman circus around the ends of which the contestants turned. It was decorated with obelisks and other monuments.
Kathisma
“Seat of Mary” A seat, a division of the psalter used in Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine catholic churches.

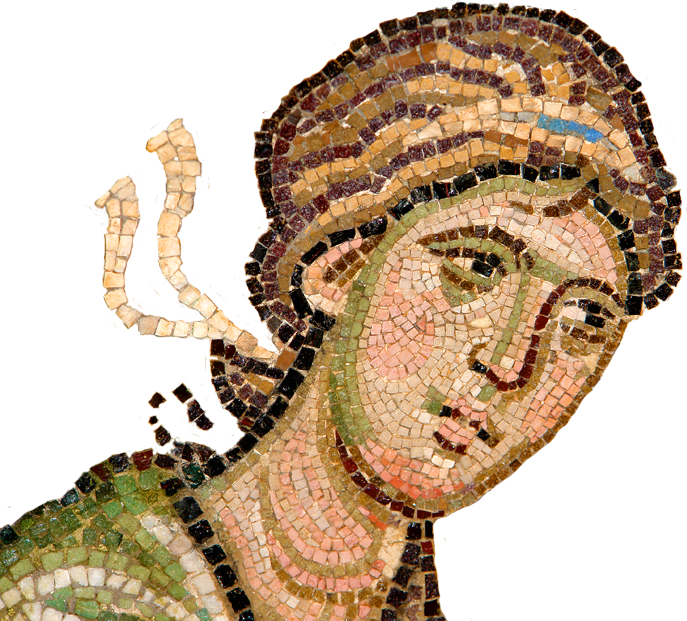
Mosaic
A decoration created by setting small pieces of glass, stone, or marble in a matrix- often concrete.

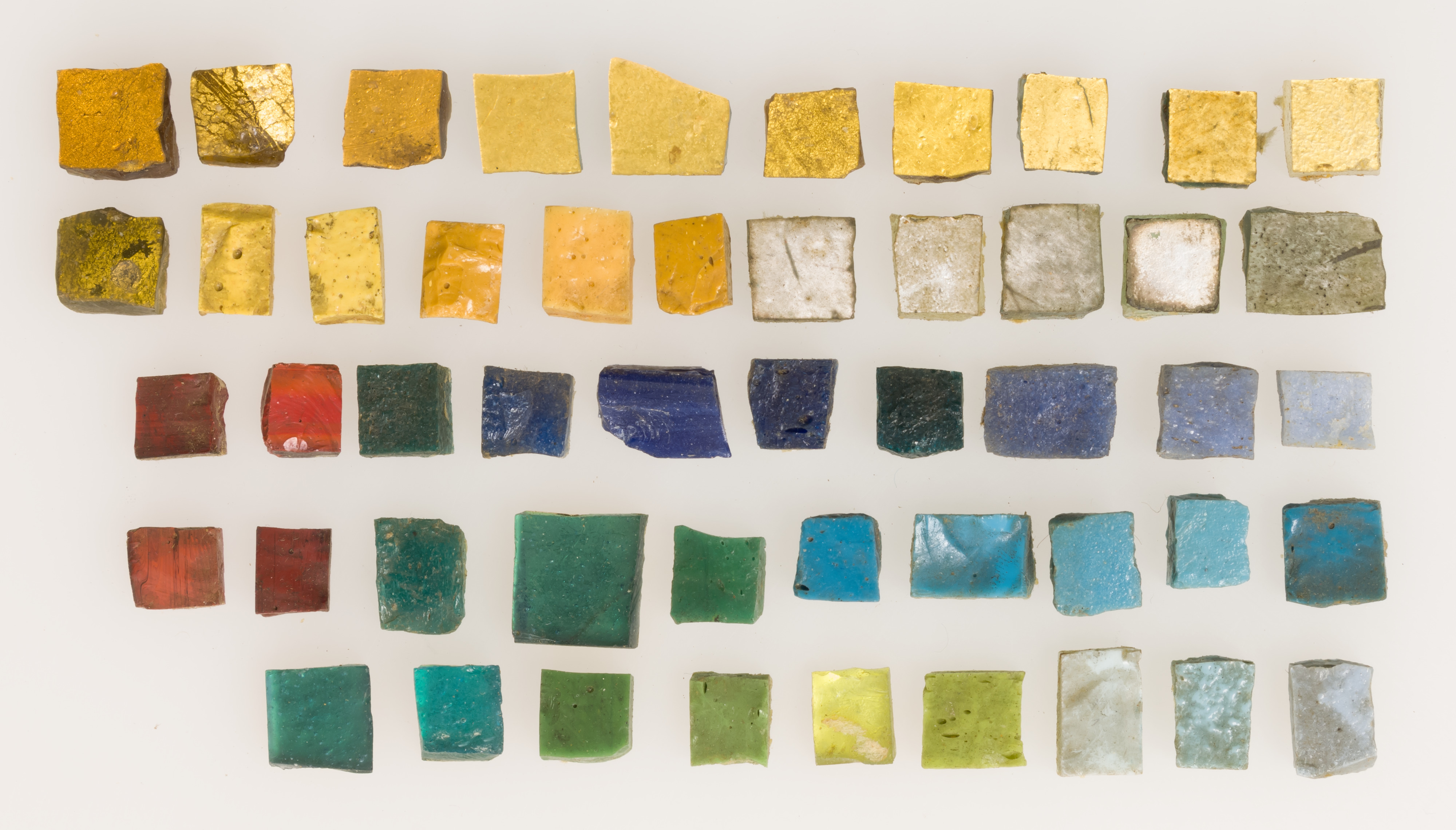
Tessera/tesserae
Small piece of stone, glass,etc. used in making a mosaic.

Icon
Referred to a person, symbol, image or picture that is widely admired for its conspicuous feature or allegiance. In art, icon mostly refers to a religious painting (usually Jesus Christ or another holy/ religious figure).

Iconoclasm
“Image breaking” and refers to a recurring historical impulse to break or destroy images for religious or political reasons.

Opus sectile
Form of pietra dura popularized in the ancient and medieval Roman world where materials were cut and inlaid into walls and floors to make a picture or pattern

Stucco
A plaster-like material consisting of lime, sand, water, and other ingredients. Stucco can be used for covering walls, or, when molded or carved, for architectural decoration.

Cloisonne
Technique of creating designs on metal vessels with colored-glass paste placed within enclosures made of copper or bronze wires, which have been bent or hammered into the desired pattern.

Monogram
Originally a cipher consisting of a single letter, later a design or mark consisting of two or more letters intertwined.
Colophon
An inscription placed at the end of a book or manuscript and giving details of its publication—e.g., the name of the printer and the date of printing.

Canon table
A table of concordance for two or more parallel texts of the Gospels.

Gospel
Any of four biblical narratives covering the life and death of Jesus Christ.
Parchment
An animal skin which has been prepared for writing or printing. Parchment has been made for centuries, and is usually calf, goat, or sheep skin.
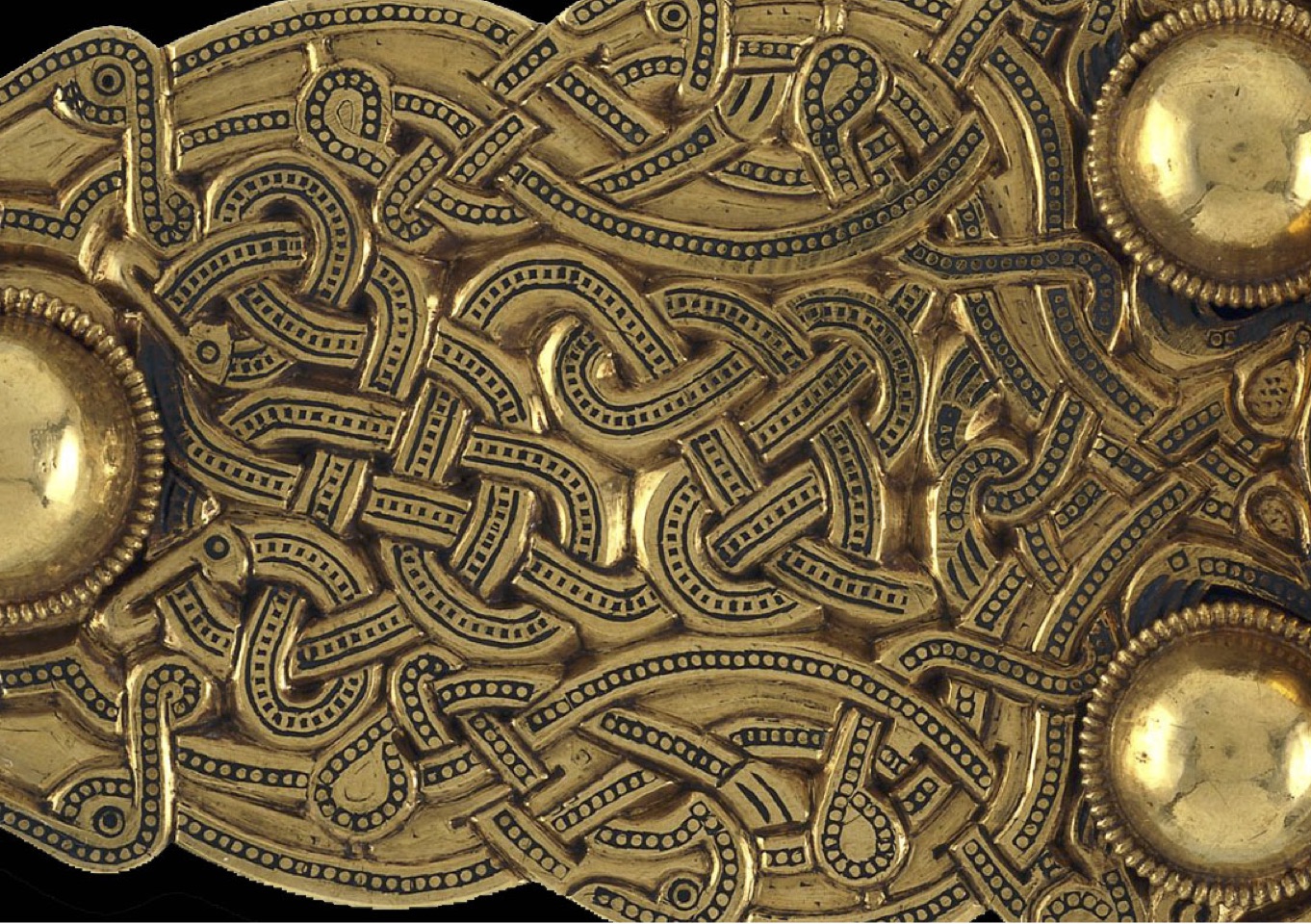
Interlace
A decorative motif consisting of threads passing aver and under each other like threads in lace.
