FPC4: Pathology Week 2
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
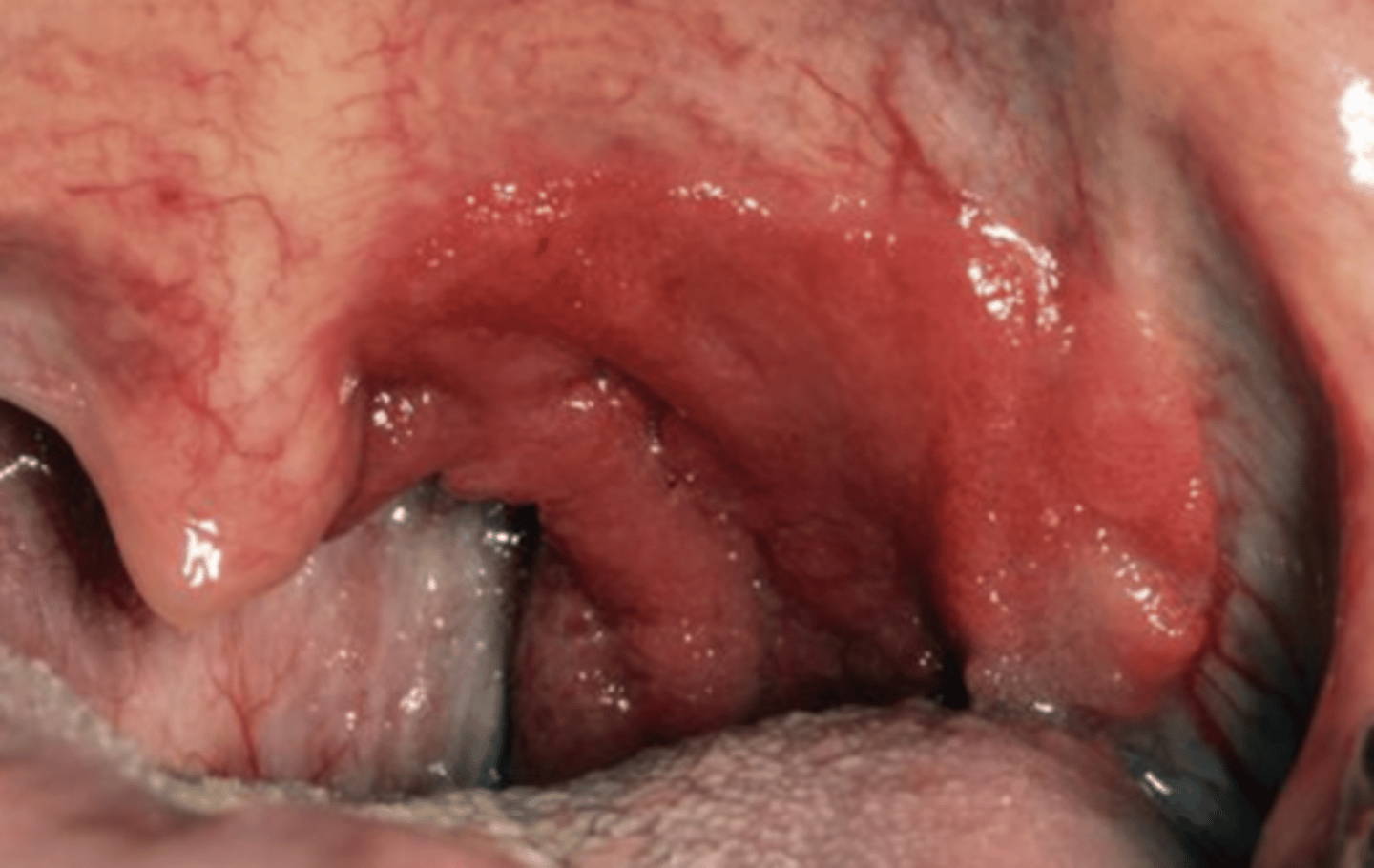
Leukoplakia
A white patch or plaque that CANNOT be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease
Leukoplakia requires a _______ diagnosis
clinical
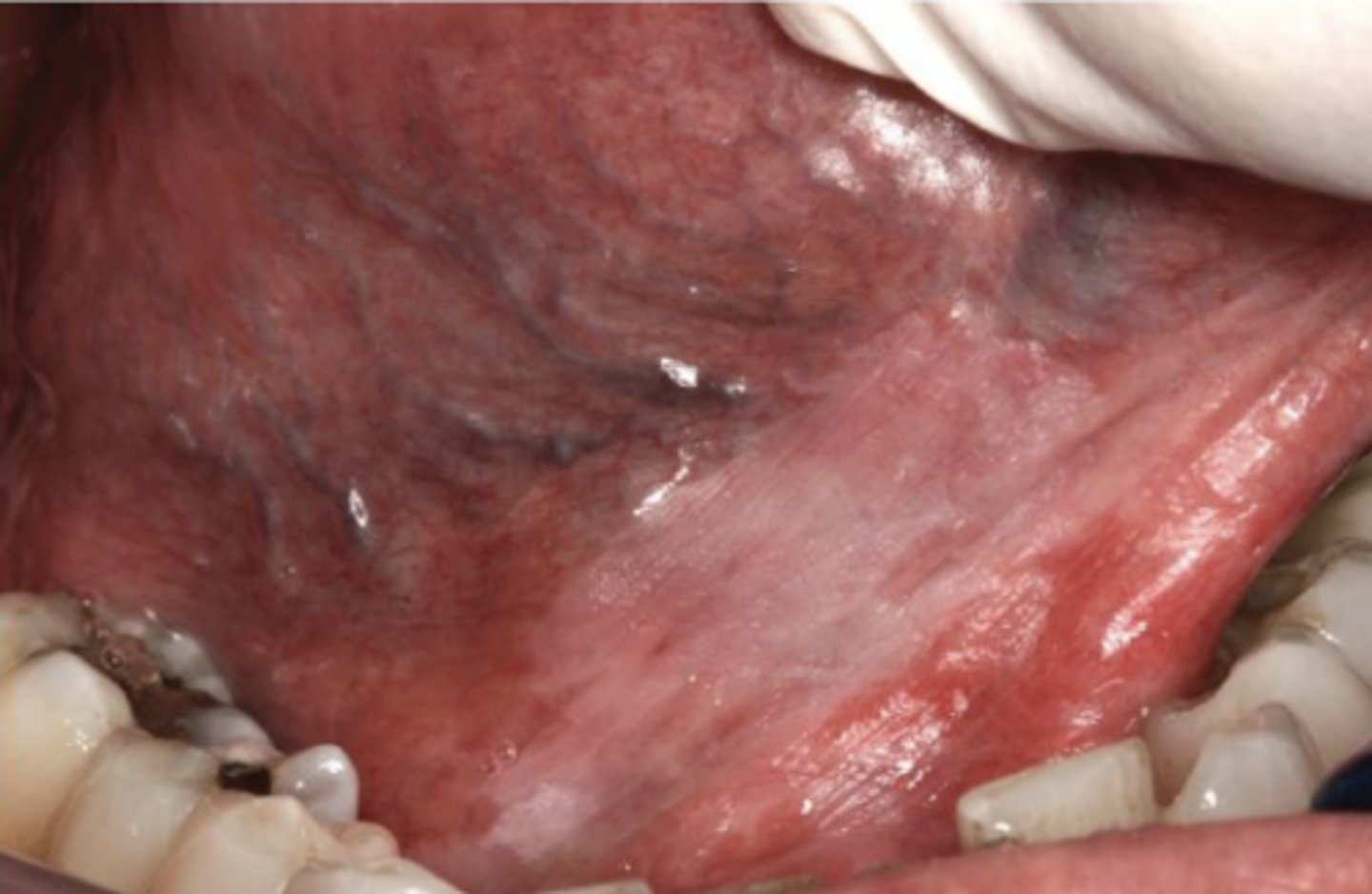
What is the most common precancer feature?
Leukoplakia
The cause of leukoplakia is ________
multifactorial
_____% of oral cancers have leukoplakia nearby
33
What are the contributing factors for leukoplakia?
Tobacco
Alcohol
UV radiation
Trauma*
Sanguinaria*
Microorganisms*
T/F: Leukoplakia has been found 5 years earlier in those who developed squamous cell carcinoma
True
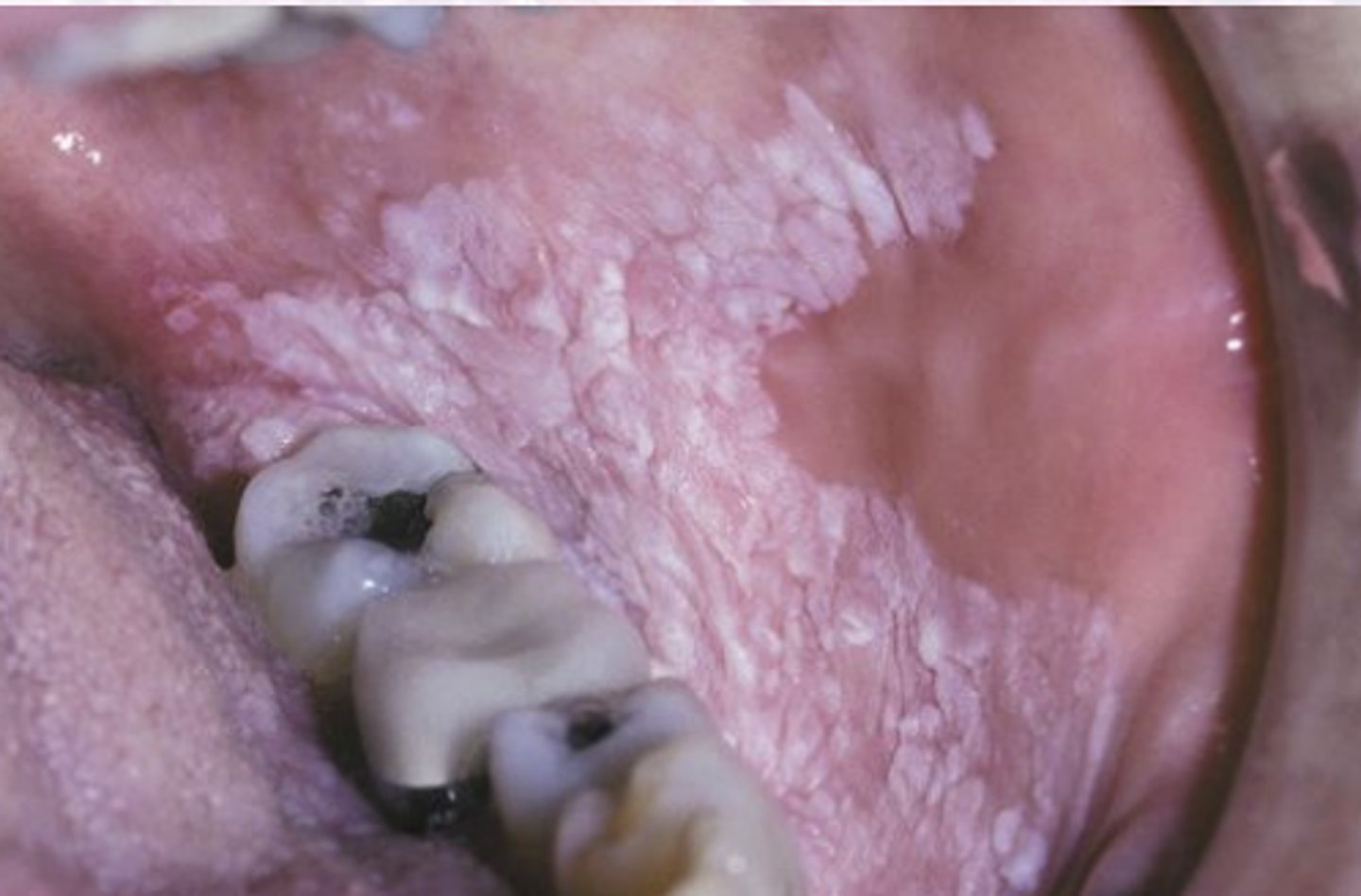
Thin leukoplakia appearance (homogenous)
Flat, slightly elevated, white, or gray plaque
Thick leukoplakia appearance (non-homogenous)
thickened, leathery, distinctly white plaques
Granular/Nodular Leukoplakia
Increased surface irregularities
Verrucous/Verruciform Leukoplakia
Blunt, sharp, wart like projections
What is the best identification method for leukoplakia?
Thorough head and neck exam
Biopsy
What features of histology slides under a microscope would indicate dysplasia has occured?
Bulbous rete ridges
loss of maturation
Dyskeratosis
Hyperchromasia
Pleomorphism
Mild grade dysplasia
lower 1/3 of epithelium
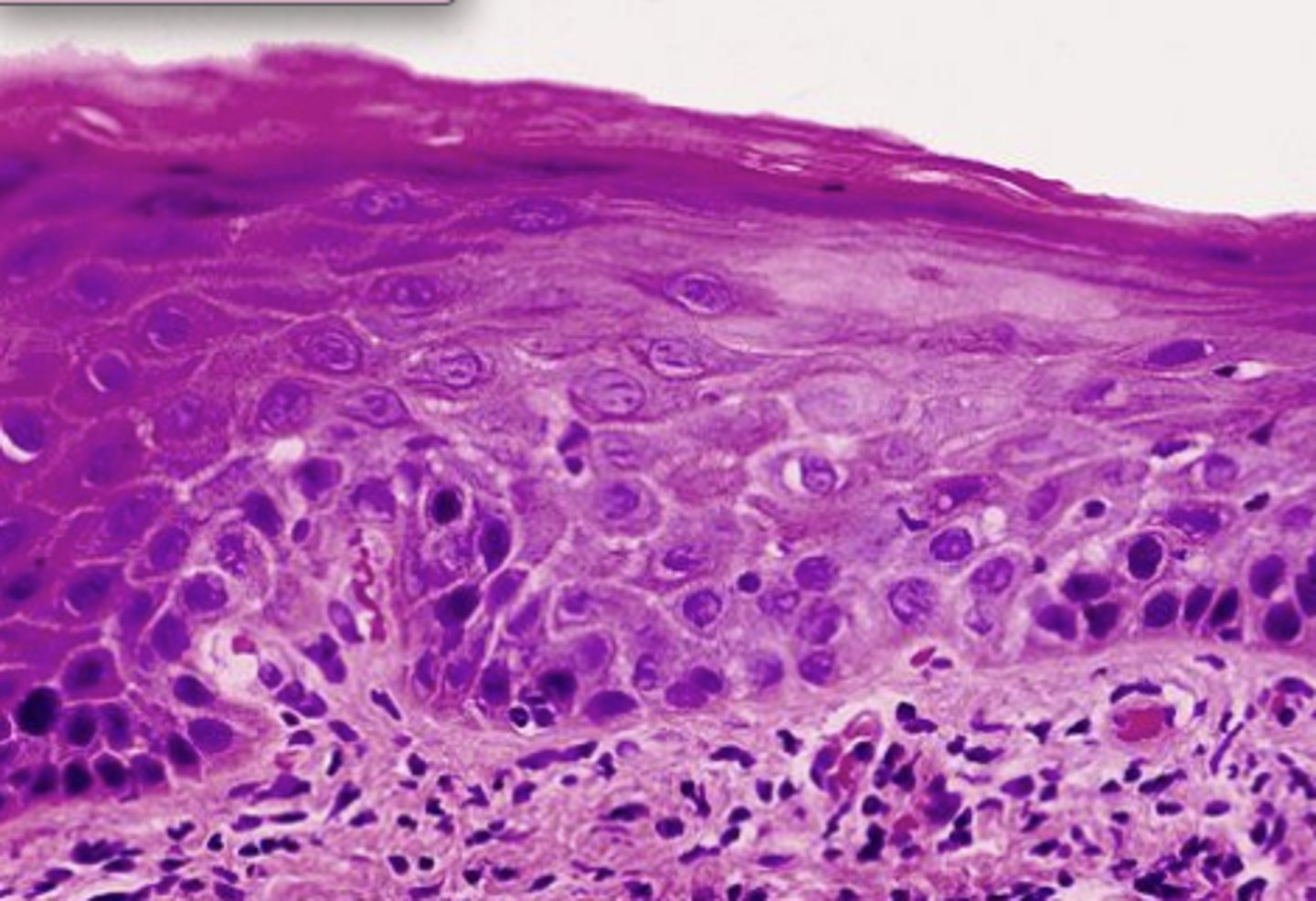
Moderate grade dysplasia
Lower 1/2 of the epithelium
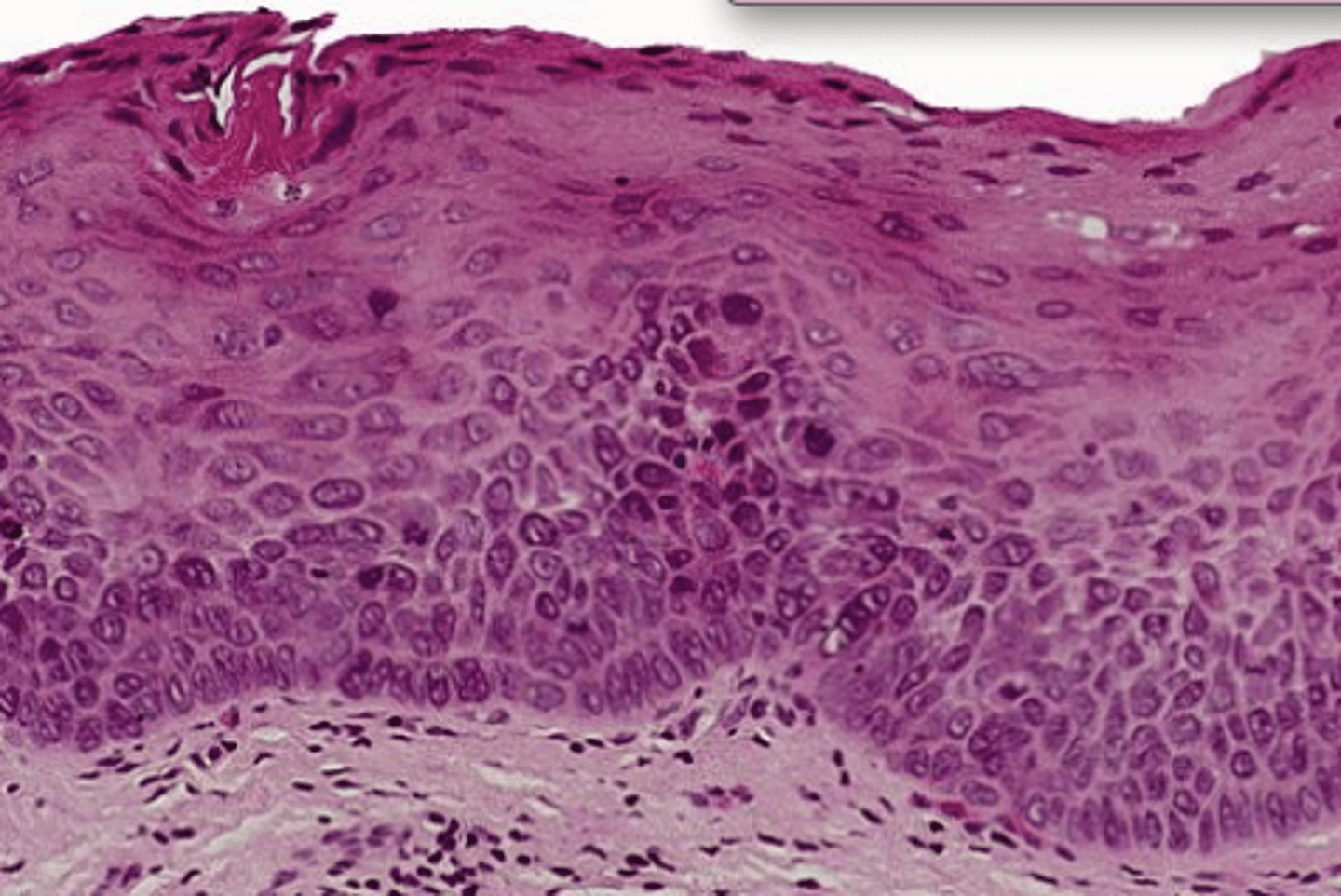
Severe grade of dysplasia
above the midpoint
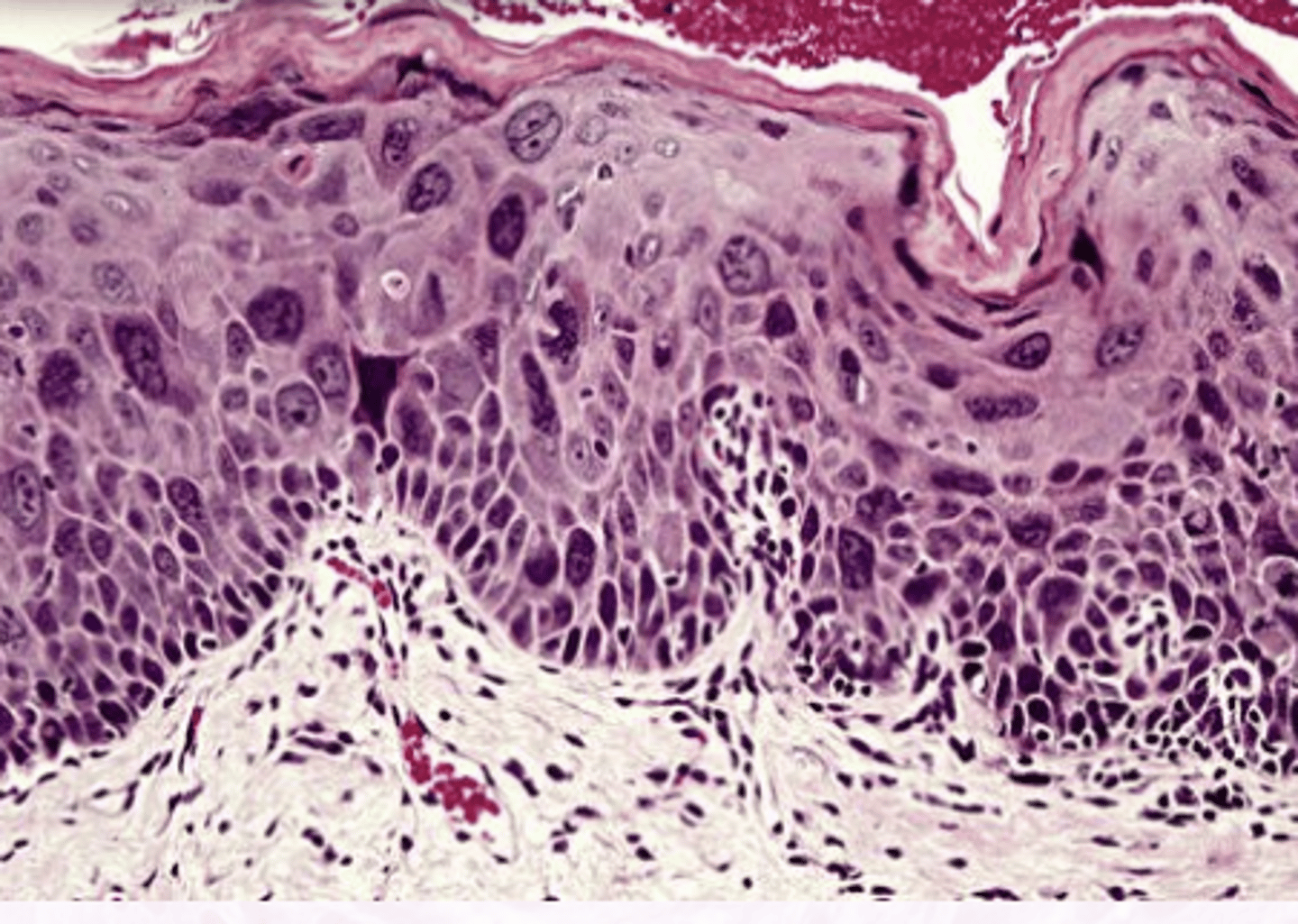
Carcinoma in situ (CIS)
Full thickness dysplasia, NO invasion
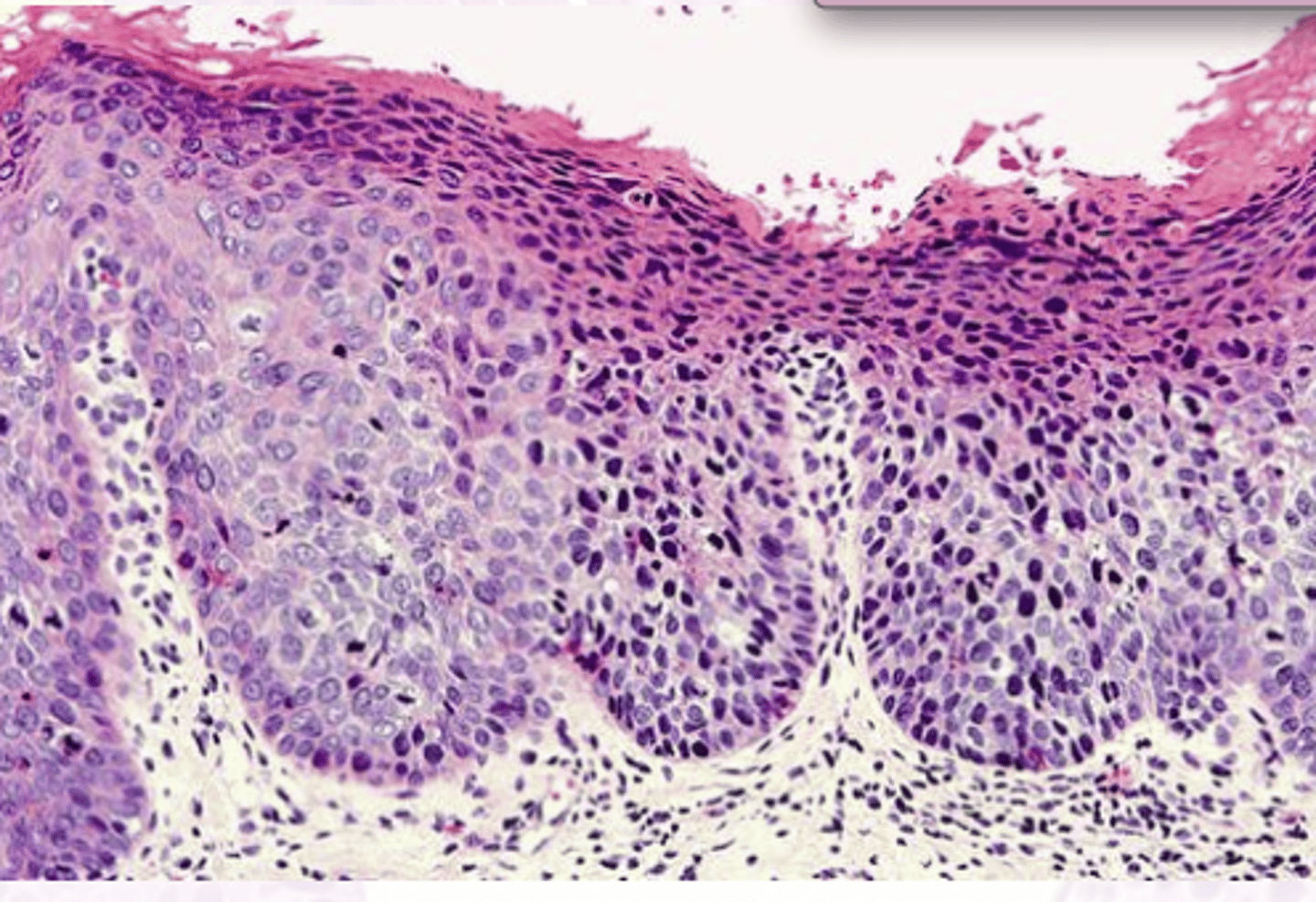
You should biopsy the _____ areas of leukoplakia
worst
If you biopsied leukoplakia and the histology results showed no dysplasia, what is the next step?
Follow up every 6 months
If you biopsied leukoplakia and the histology results showed mild dysplasia,, what is the next step?
Excise or conservative measures
If you biopsied leukoplakia and the histology results showed moderate to severe dysplasia, what is the next step?
Complete removal, LONG TERM follow up is essential!
What is the ratio of F:M for Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia?
4:1
F>>M
What are the characteristics of Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia?
MULTIPLE, slowly spreading, keratotic plaques
*This will eventually transform into SCC
No association with tobacco use is one of the findings for which premalignant epithelial pathology?
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia
What is the clinical presentation of Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia?
Diffuse
Rough
Corrugated
thickened
Leukoplakia lesions of hard palate, lingual gingiva, alveolar ridge, BM
Erythroplakia
Red plaque or patch that cannot be clinically identified or pathologically diagnosed as any other condition
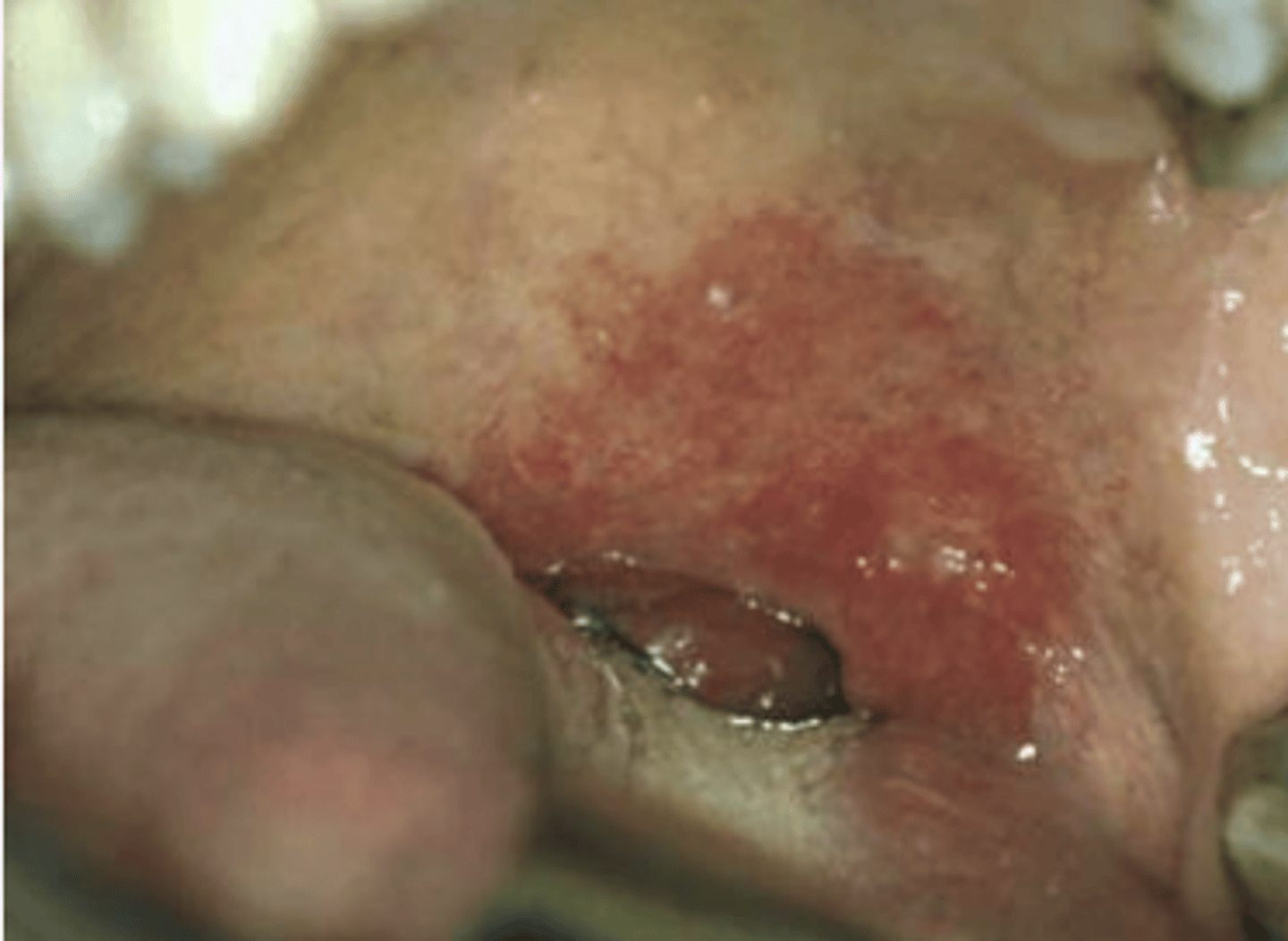
Which premalignant epithelial pathology shows severe epithelial dysplasia, CIS, or invasive SCCa at the time of biopsy?
Erythroplakia
Where are the most common sites for erythroplakia?
Floor of mouth
tongue
Soft palate
What are the features of Erythroplakia?
Well-delineated
Velvety red
Flat lesion
T/F: Biopsy is not required for erythroplakia
False
What is the treatment for erythroplakia?
BIOPSY!
Recurrence is common
If the erythroplakia histology results come back with moderate dysplasia a or worse, what is the next step?
Remove all lesions!
Long term follow up is recommended
Erythroleukoplakia
Erythroplakia + Leukoplakia
Speckled/intermixed red and white lesions
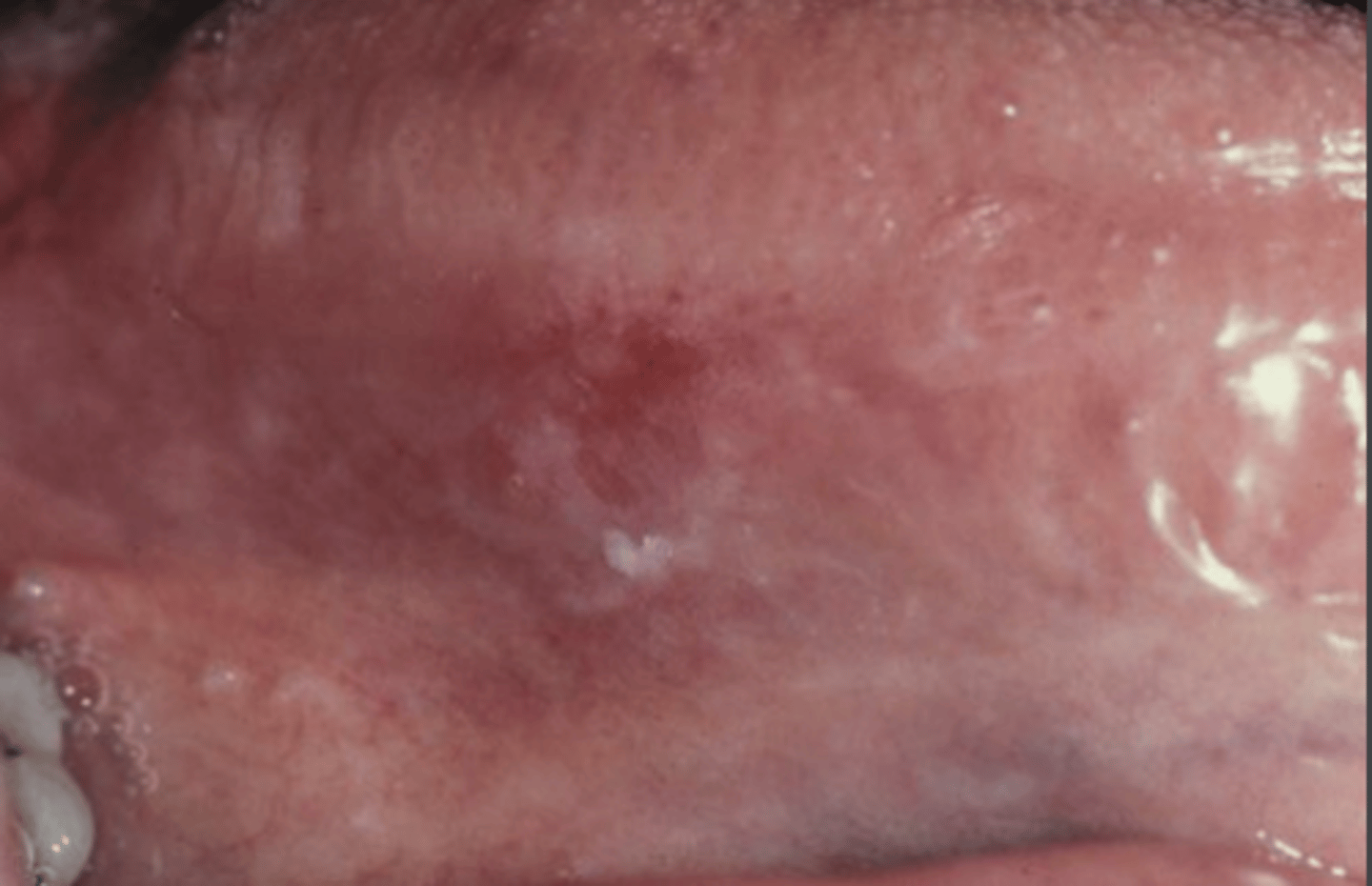
What is erythroleukoplakia frequently diagnosed as in a biopsy?
Dysplasia
What is Nicotine Stomatitis?
White change of hard palate
Associated with smoking
Response to heat (chronic drinkers of hot drinks)
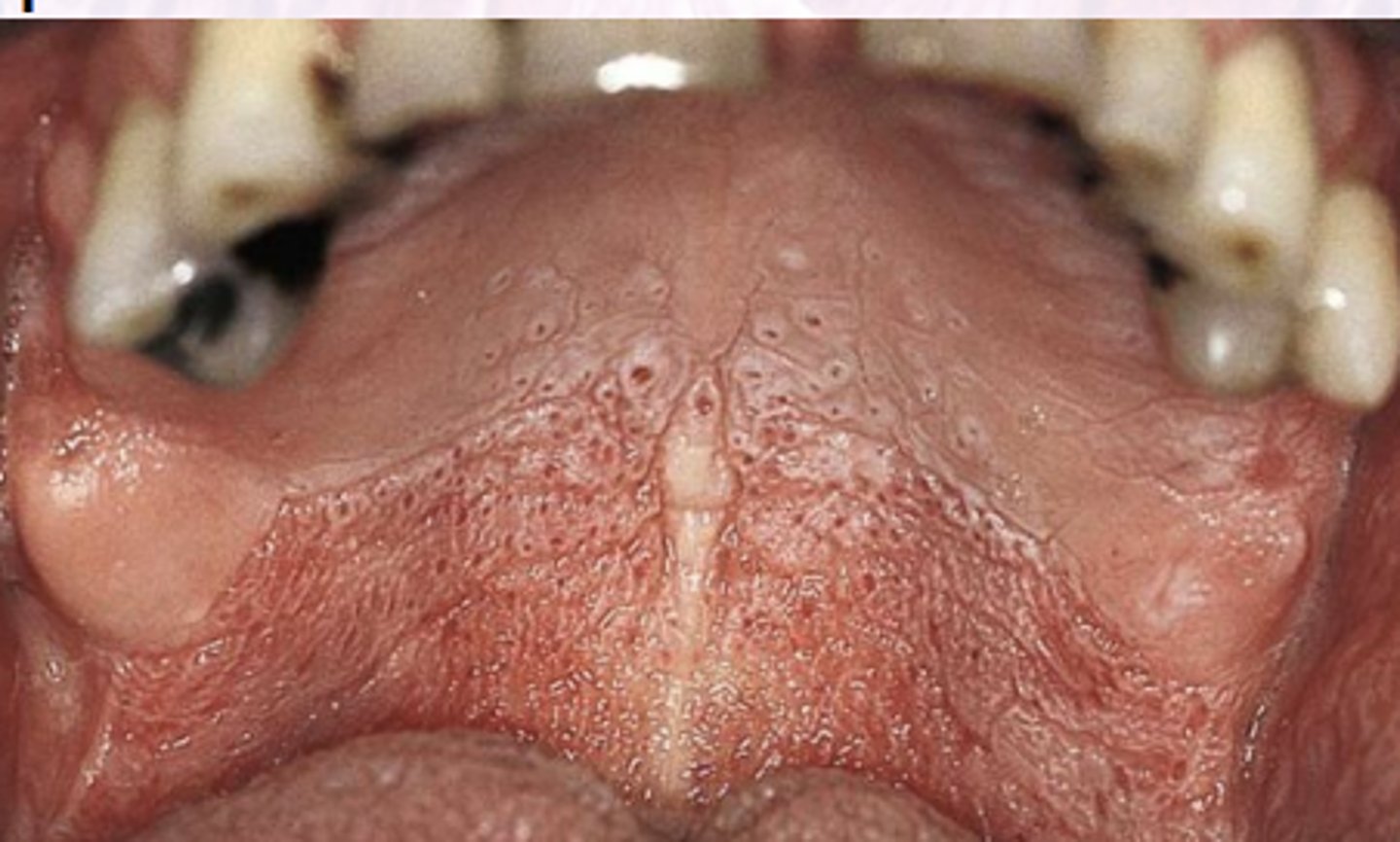
What is the clinical presentation of Nicotine Stomatitis?
"Dried Mud Appearance"
Diffuse gray/white mucosa
Elevates papules with punctate red centers
inflamed minor salivary glands
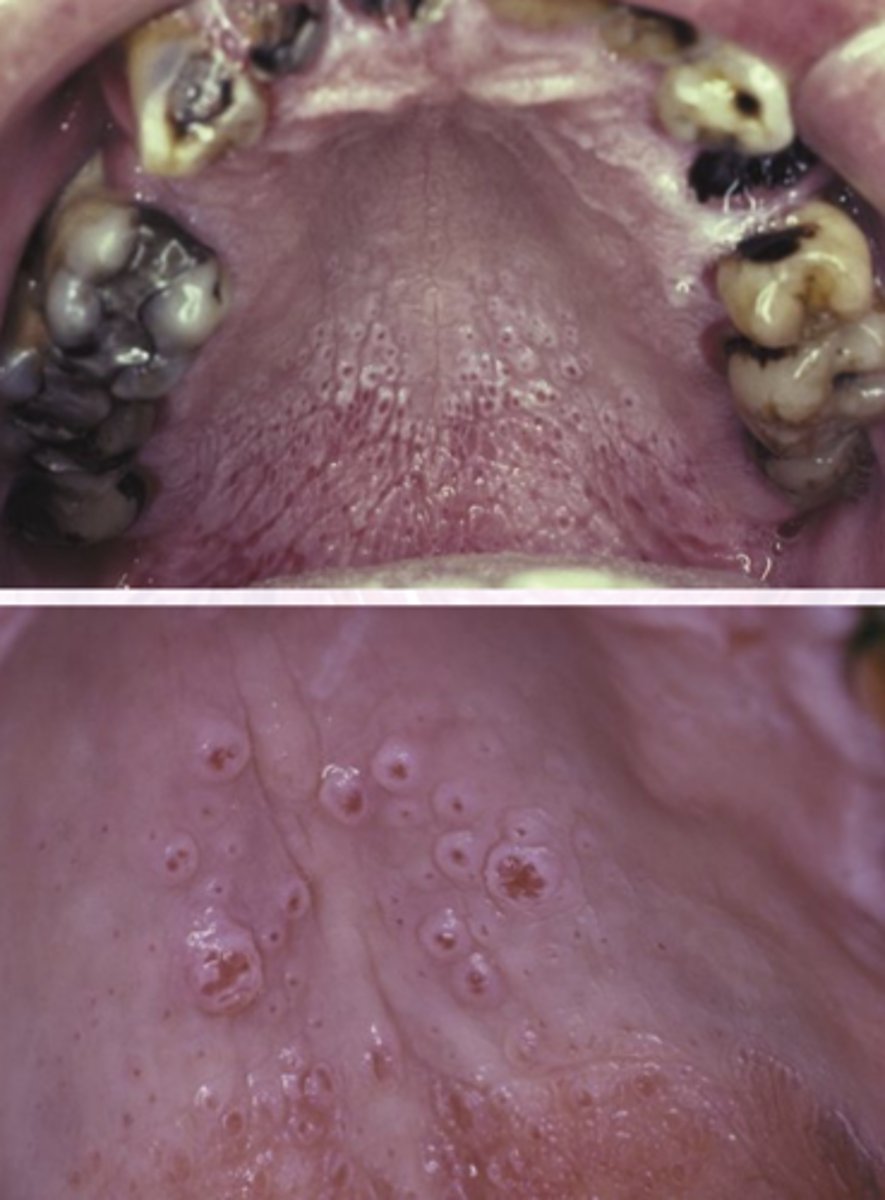
What is the treatment for nicotine stomatitis?
Encourage pt to stop smoking
Should return normal after 1-2 weeks
What is the prognosis for nicotine stomatitis?
Reversible
Which condition in itself is NOT considered premalignant?
Nicotine Stomatitis
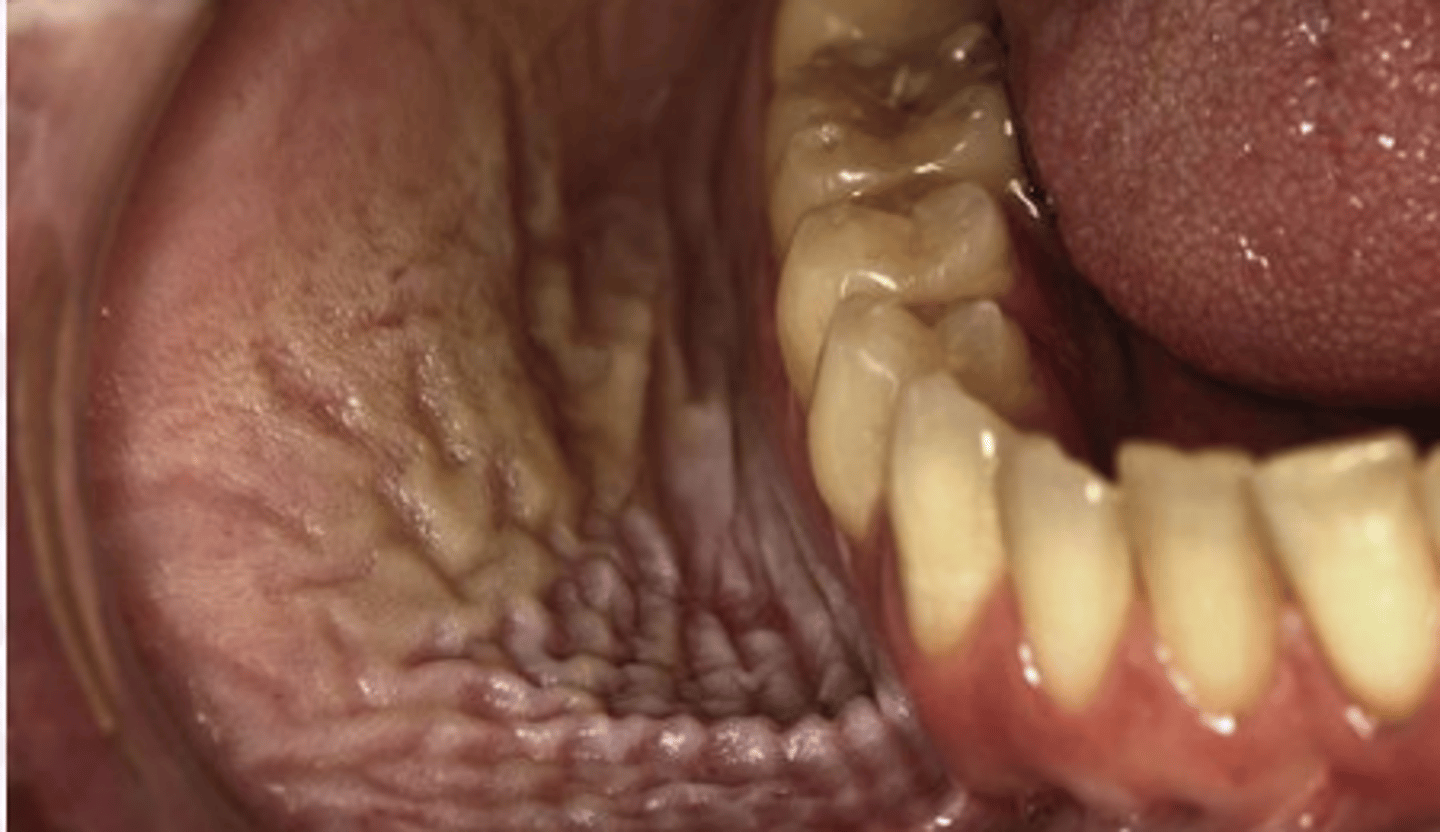
What populations are more likely to develop Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis?
Tobacco chewers (15%)
Snuff users (60%)
Very Common in Young individuals**
What is the clinical presentation of Smokeless tobacco keratosis?
Velvety, wrinkled gray white appearance
Stretching reveals a pouch ~Rippled sand
thin distinct borders
If a smokeless tobacco keratosis lesion becomes thickened, leathery ulcerated, or nodular, what should you do?
Biopsy
Smokeless Tobacco keratosis
These histology characteristics are indicative of what oral pathology?
Intracellular Edema & glycogen rich cells
CHEVRONS
Amorphous Eosinophilic material
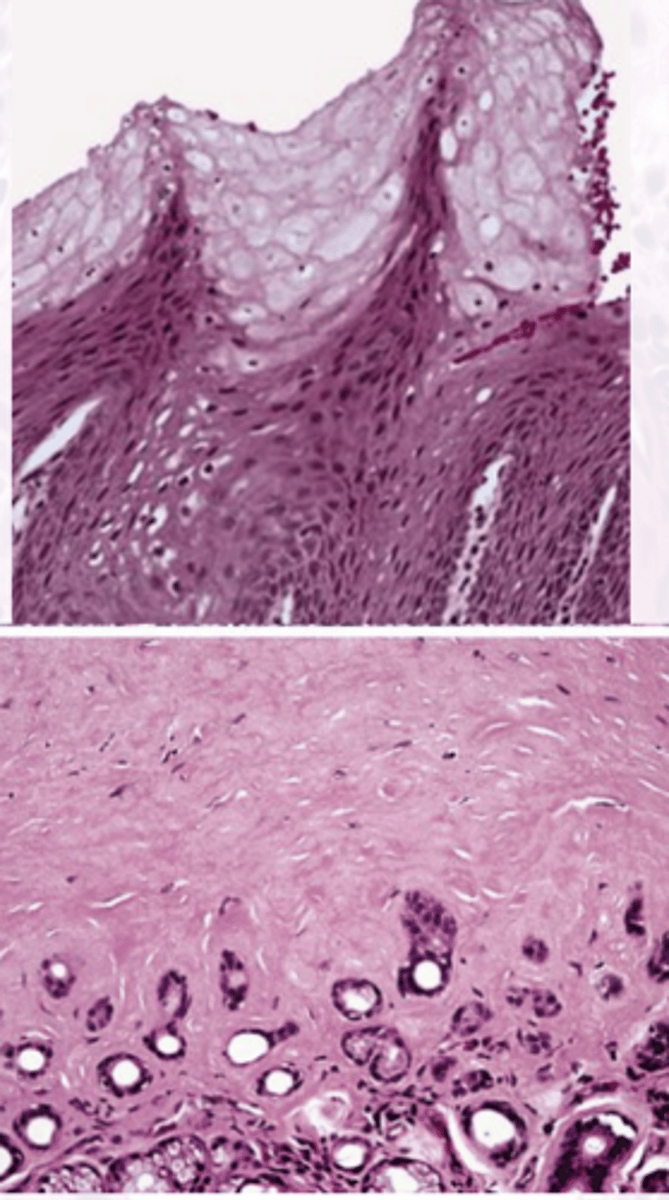
What is the prognosis for smokeless tobacco keratosis?
Low malignant transformation risk
Biopsy atypical appearances
Patients with Smokeless tobacco keratosis can develop squamous cell carcinoma after a few ________
decades
What premalignant epithelial lesion is considered to be a "high risk lesion"?
Oral Submucous fibriosis
What causes Oral submucous fibrosis?
Chronic progressive connective tissue scarring.
This leads to mucosal rigidity
What is the etiology of oral submucous fibrosis?
Betel Quid (paan)
What is the main symptom of oral submucous fibrosis?
Trismus (difficulty opening mouth all the way)
What is the clinical presentation of oral submucous fibrosis?
Petechiae
Vesicles
Xerostomia
Melanosis
Blotchy, Marble-like appearance
might be able to feel fibrous bands
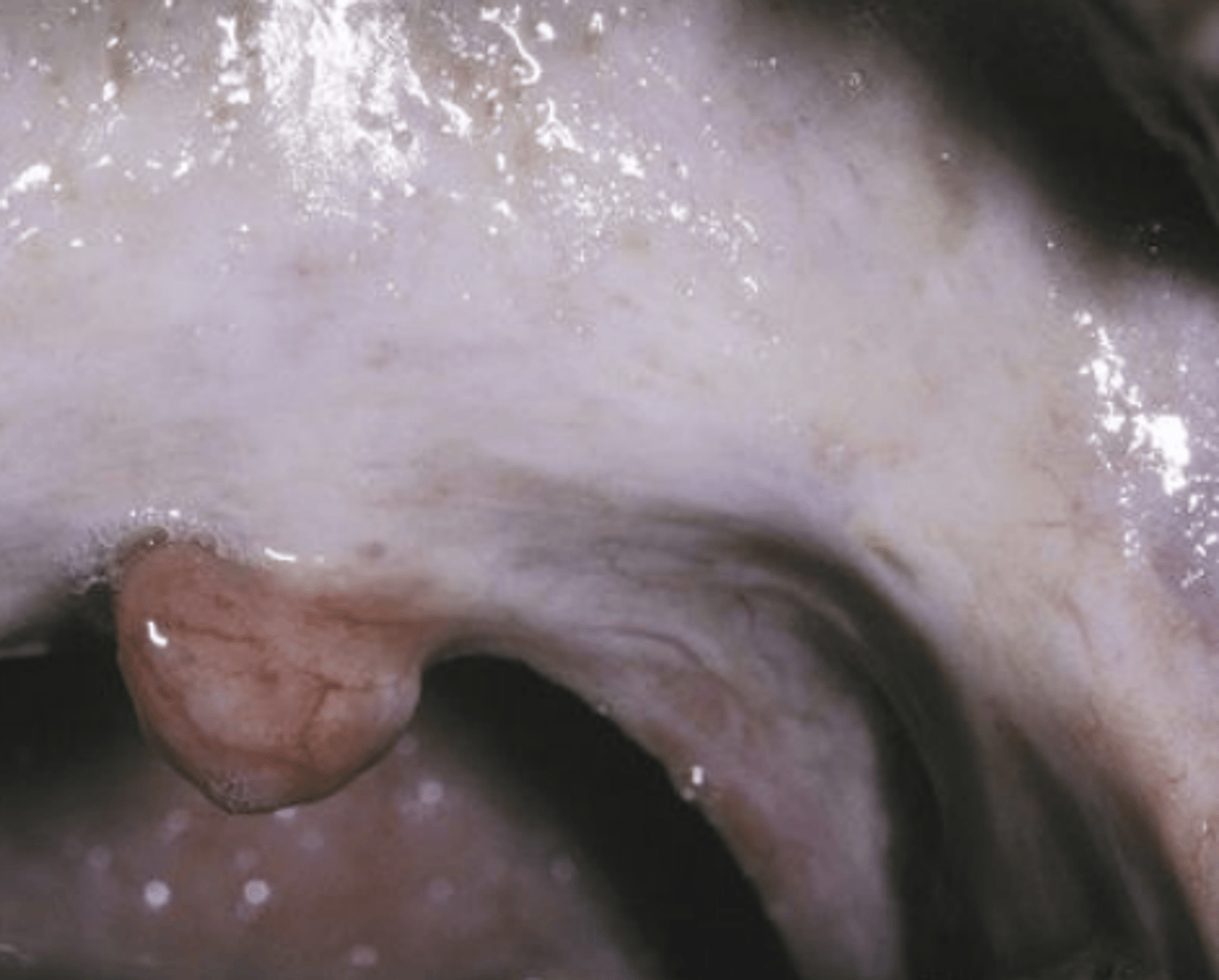
Which premalignant epithelial pathology does not regress?
Oral Submucous fibrosis
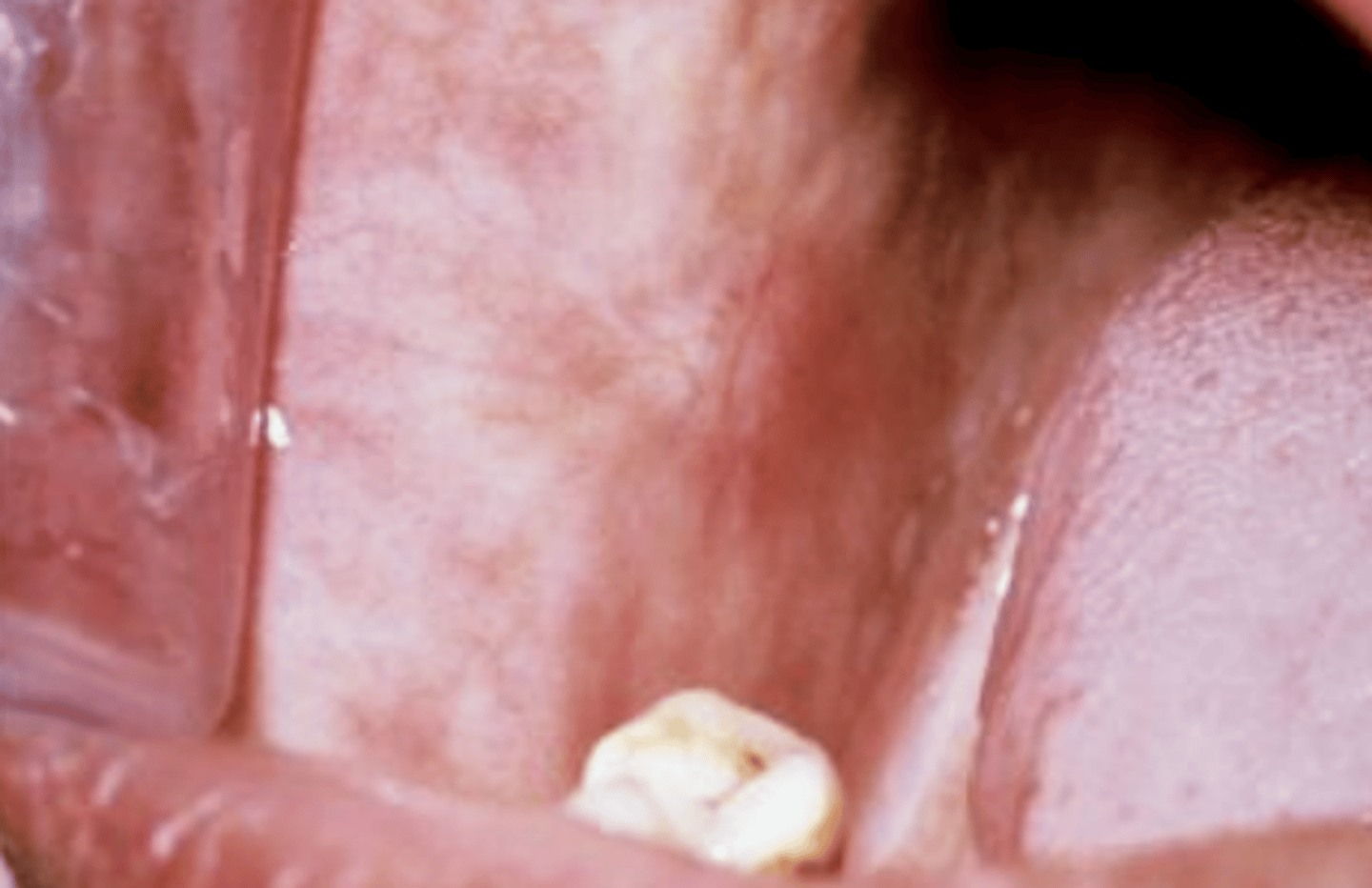
Which premalignant epithelial pathology puts you at the highest risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma?
Oral Submucous Fibrosis
What is actinic keratosis?
A premalignant cutaneous lesion caused by UV damage
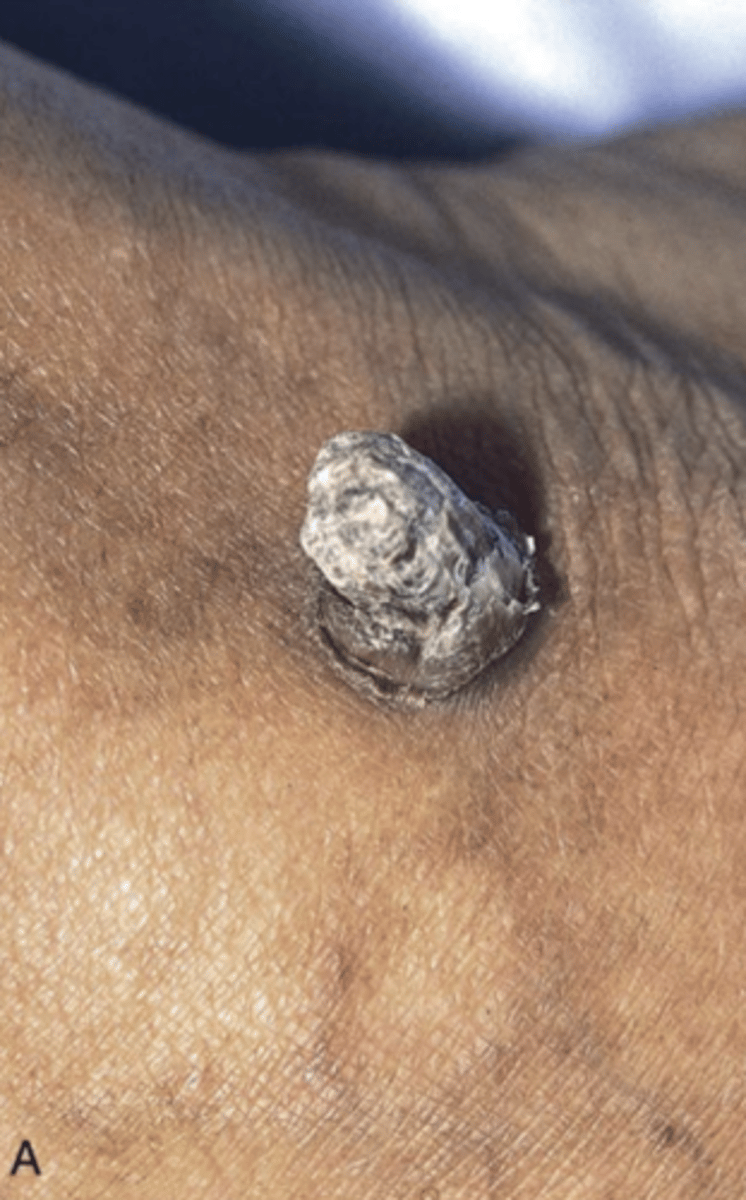
Which premalignant epithelial lesion is a common medical complaint to physicians?
Actinic Keratosis
What is the clinical presentation of actinic keratosis?
Irregular, scaly plaques
Erythematous background area
"Sandpaper texture"
can have a central horn
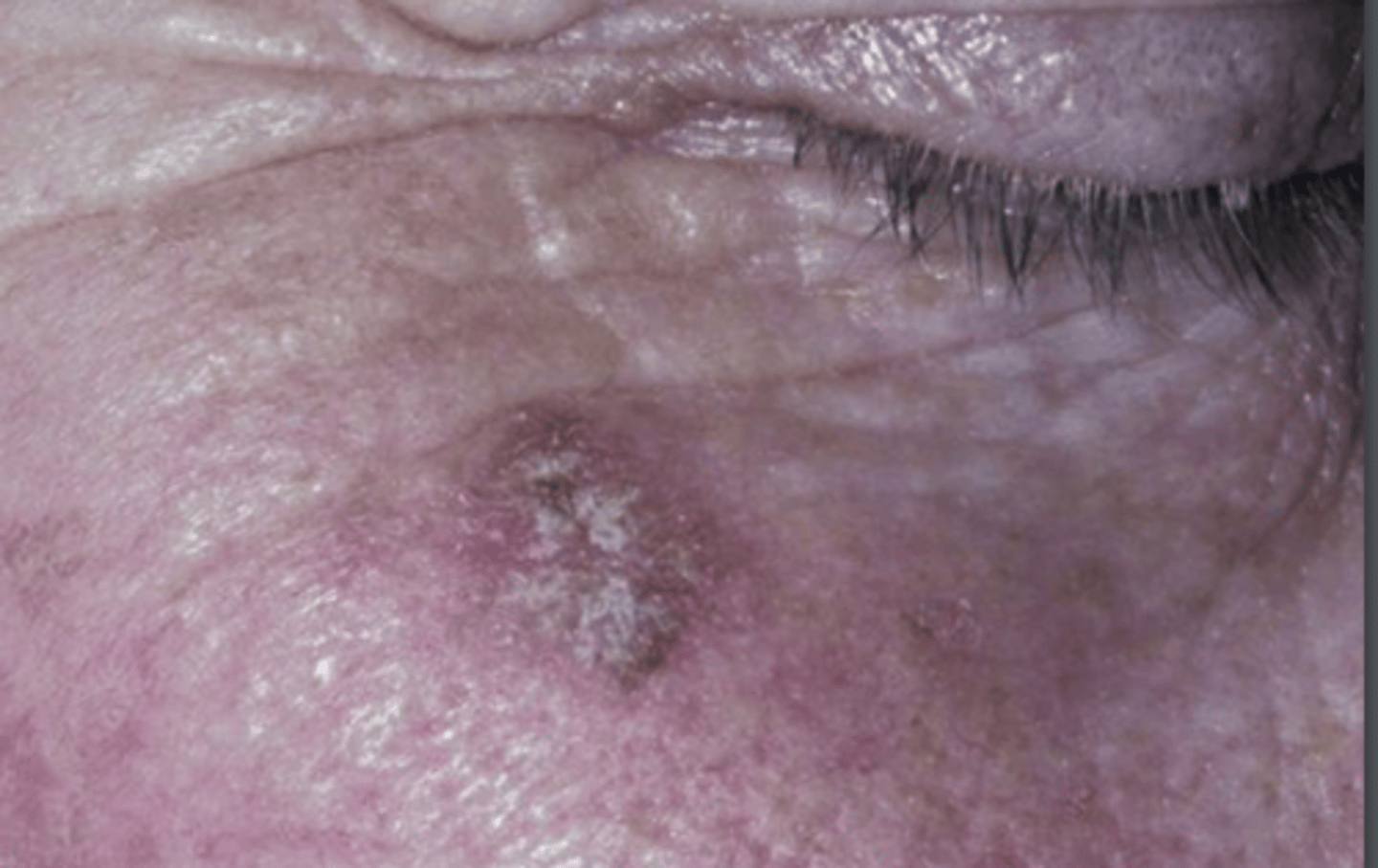
Actinic Keratosis
These histology characteristics are indicative of what epithelial pathology?
Hyperkeratosis
Dysplasia
Solar Elastosis
Chronic inflammation
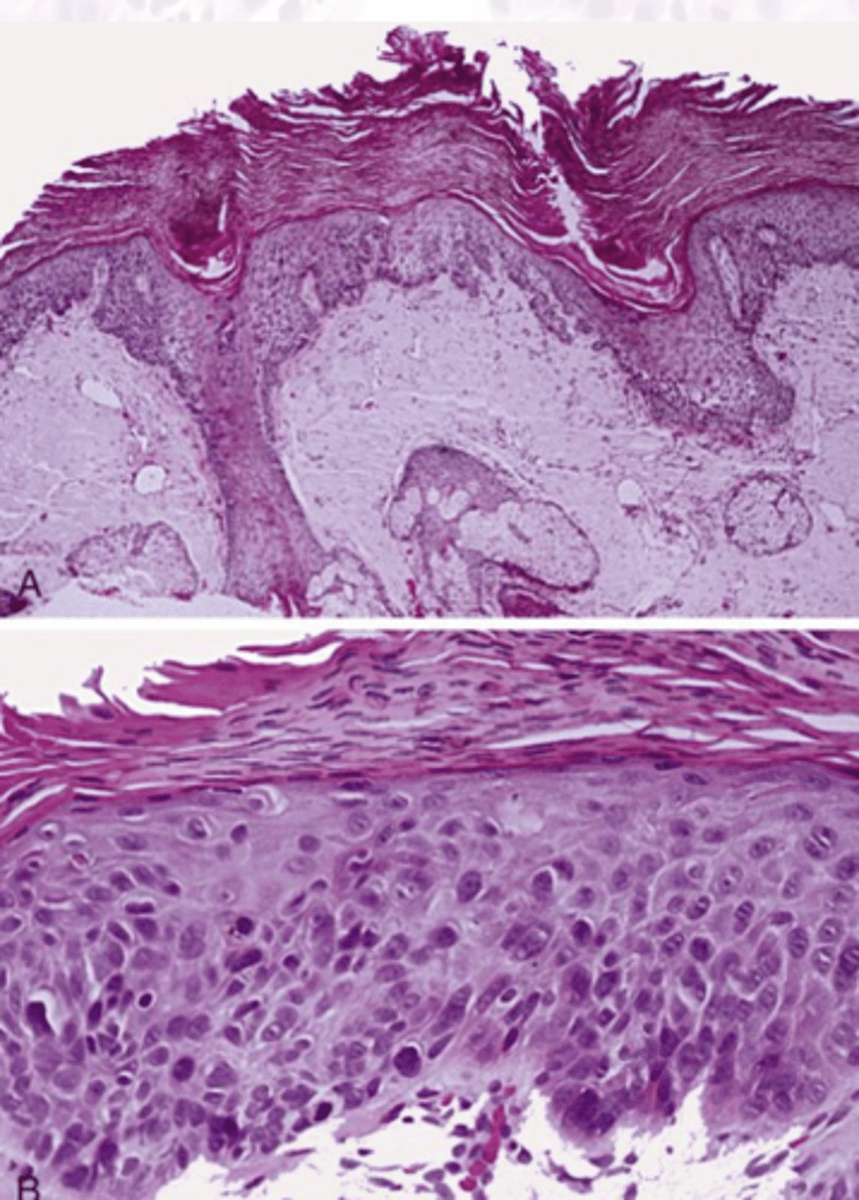
What is the treatment for actinic keratosis?
Premalignant!
Should be excised
Long term follow up
Protective measures (30 SPF)
What is actinic cheilitis?
Actinic Keratosis of the lip & vermillion border
Due to chronic UV exposure
What premalignant epithelial pathology has a strong male predilection?
Actinic cheilitis
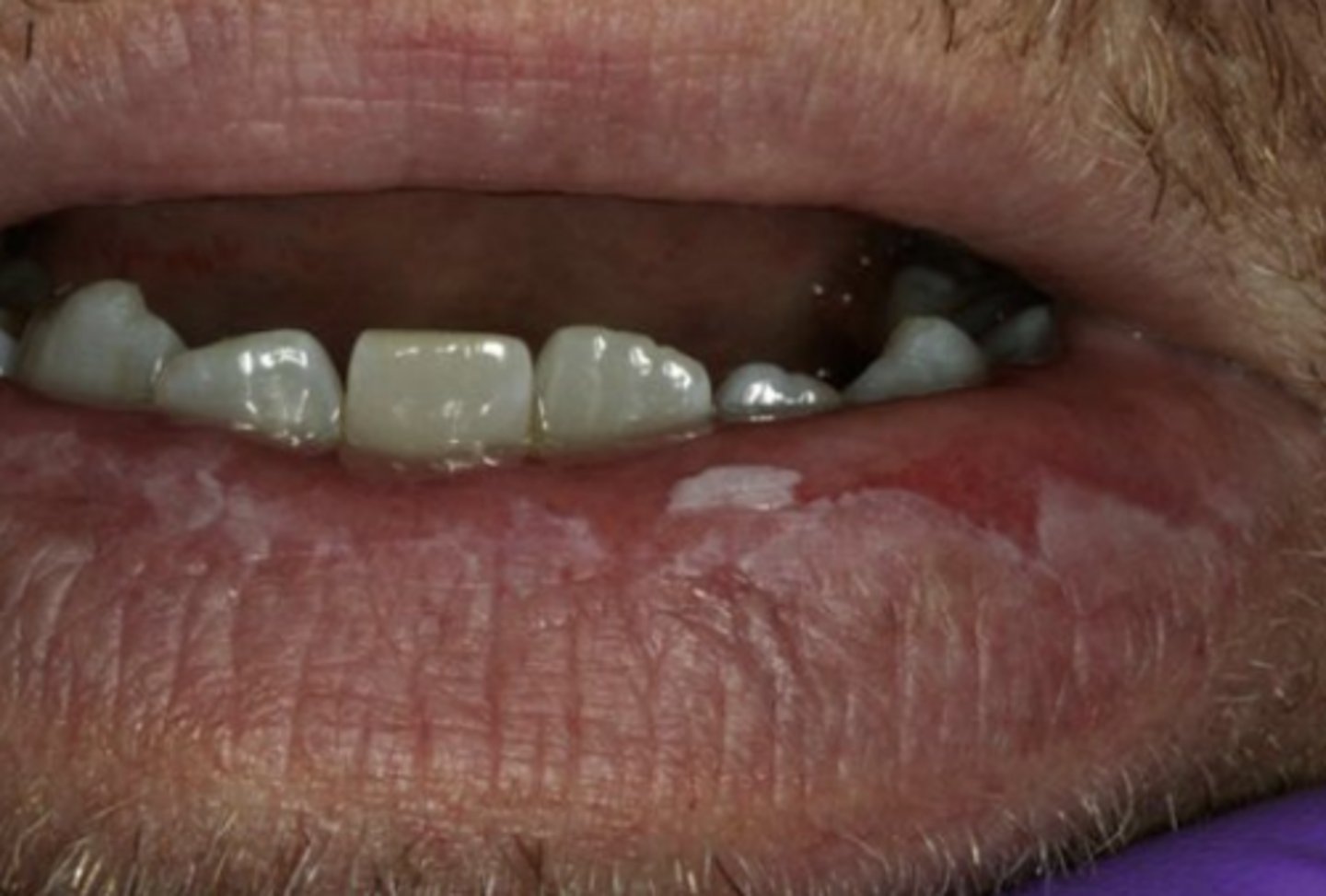
What is the clinical presentation of actinic cheilitis?
Diffuse, irregular border of lower lip
Blotchy, smooth pale areas
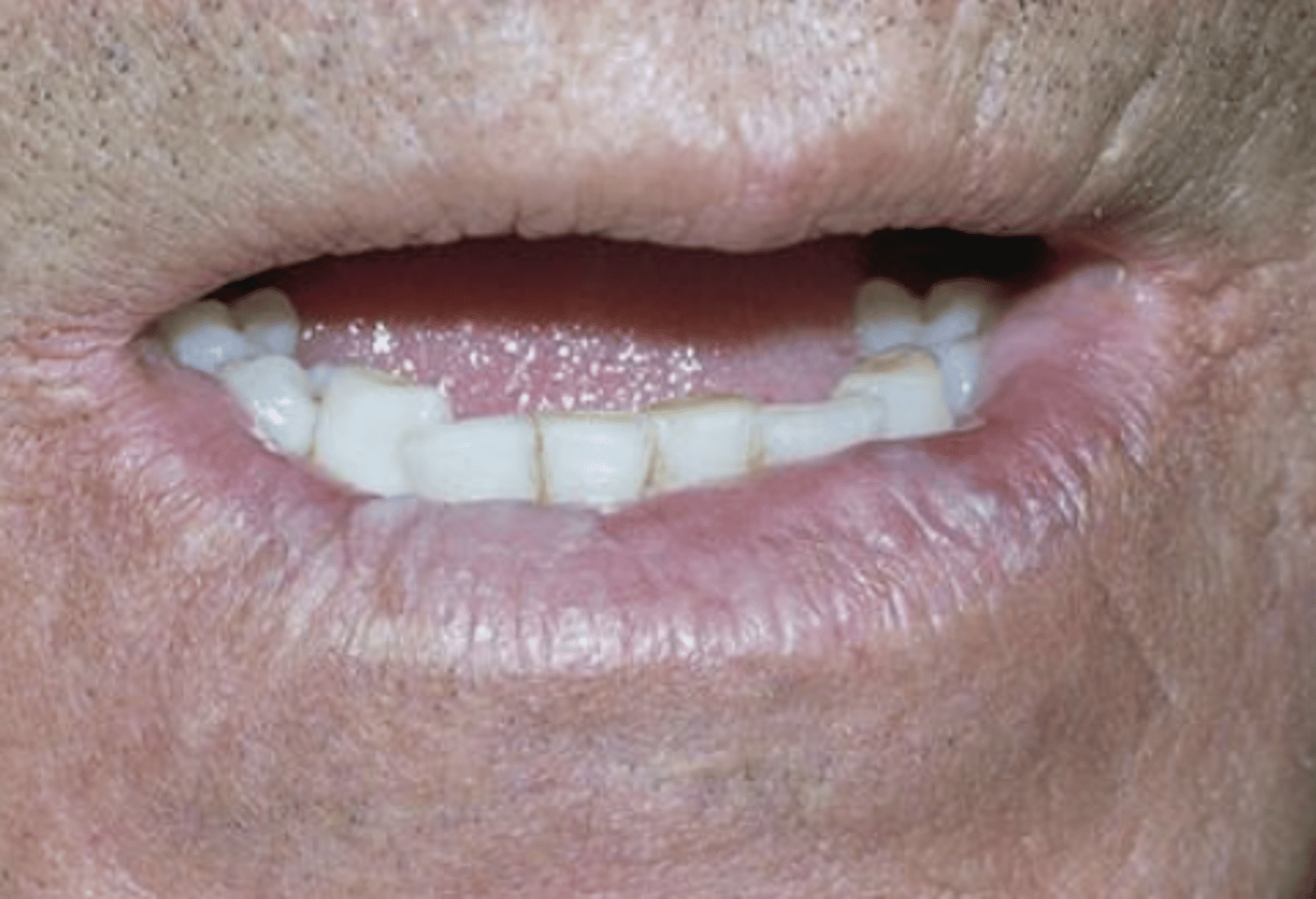
What are the early signs of actinic cheilitis?
Atrophy of lips, dryness/fissures
blurring of the margins with the skin
What are progression signs of actinic cheilitis?
Roughened, scaly areas on the drier portions
For actinic cheilitis, _____ ulcerations SHOULD BE BIOPSIED
chronic
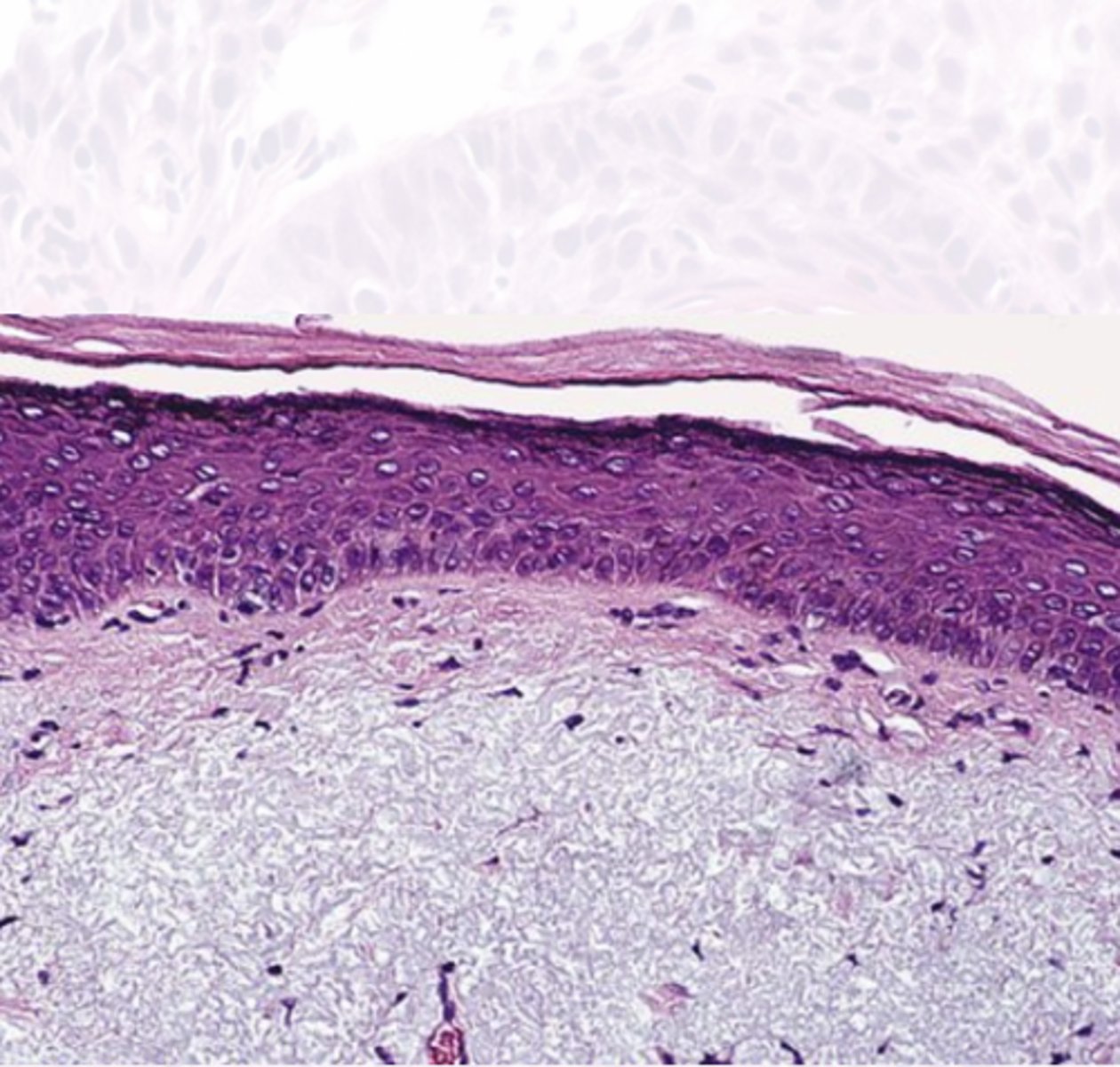
Actinic cheilitis
These histology characteristics are indicative of what premalignant epithelial pathology?
*Solar Elastosis*
Inflammation
Dysplasia
Hyperkeratosis
What is the treatment for actinic cheilitis?
Its irreversible
biopsy this
Protect yourself from sun
What epithelial pathology doubles the risk for developing SCCa of the lip?
Actinic cheilitis
What are the characteristics of Keratocanthoma?
NOT seen intra-orally
95% are solitary lesions
Enlarges rapidly
Can mimic SCCa
cause: UNKNOWN
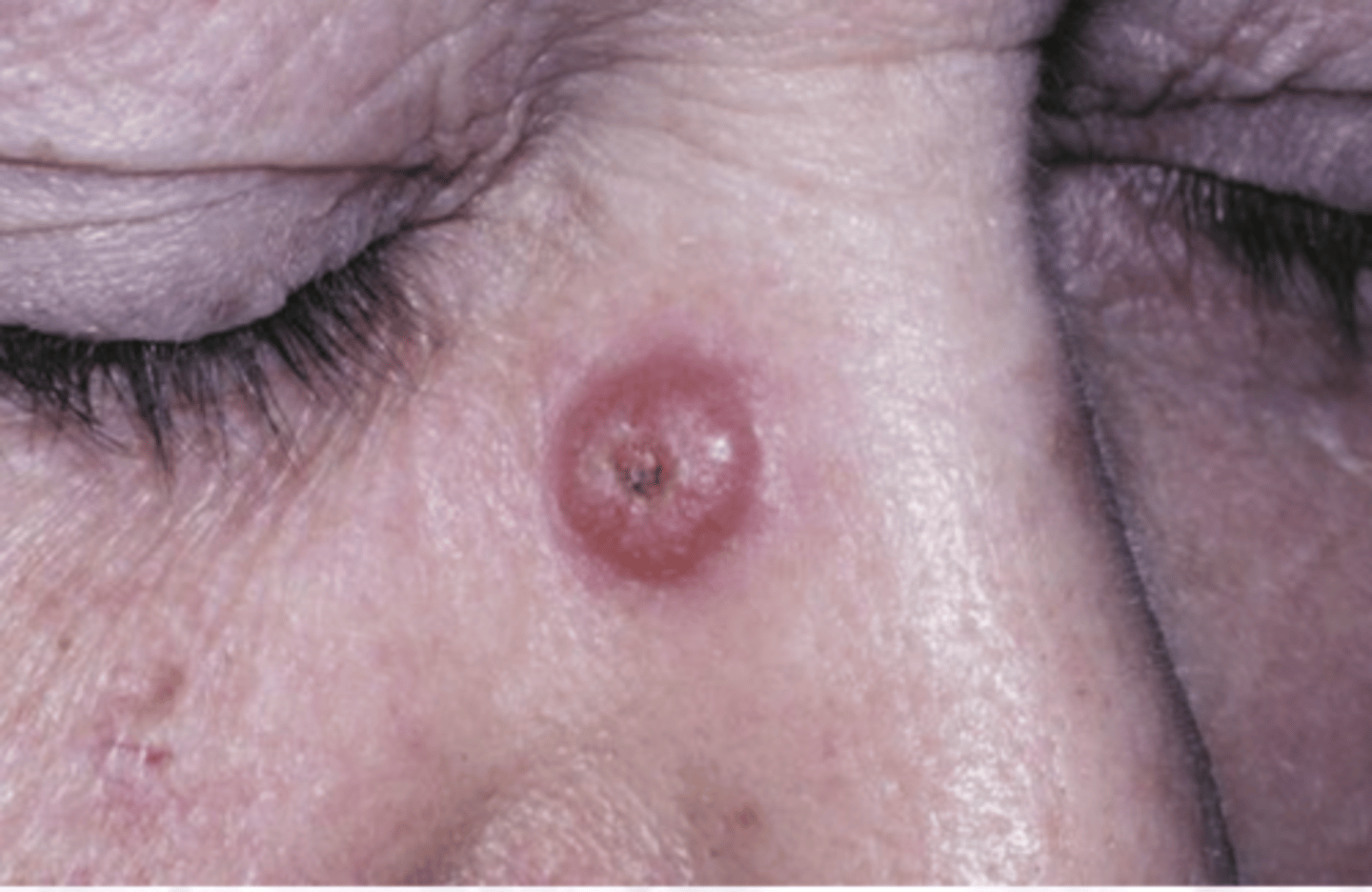
What is the clinical presentation of keratocanthoma?
ASYMPTOMATIC
CENTAL KERATIN PLUG
Verruciform, irregular surface
Can be black, brown, yellow, red
Firm, well demarcated
Sessile, dome shaped
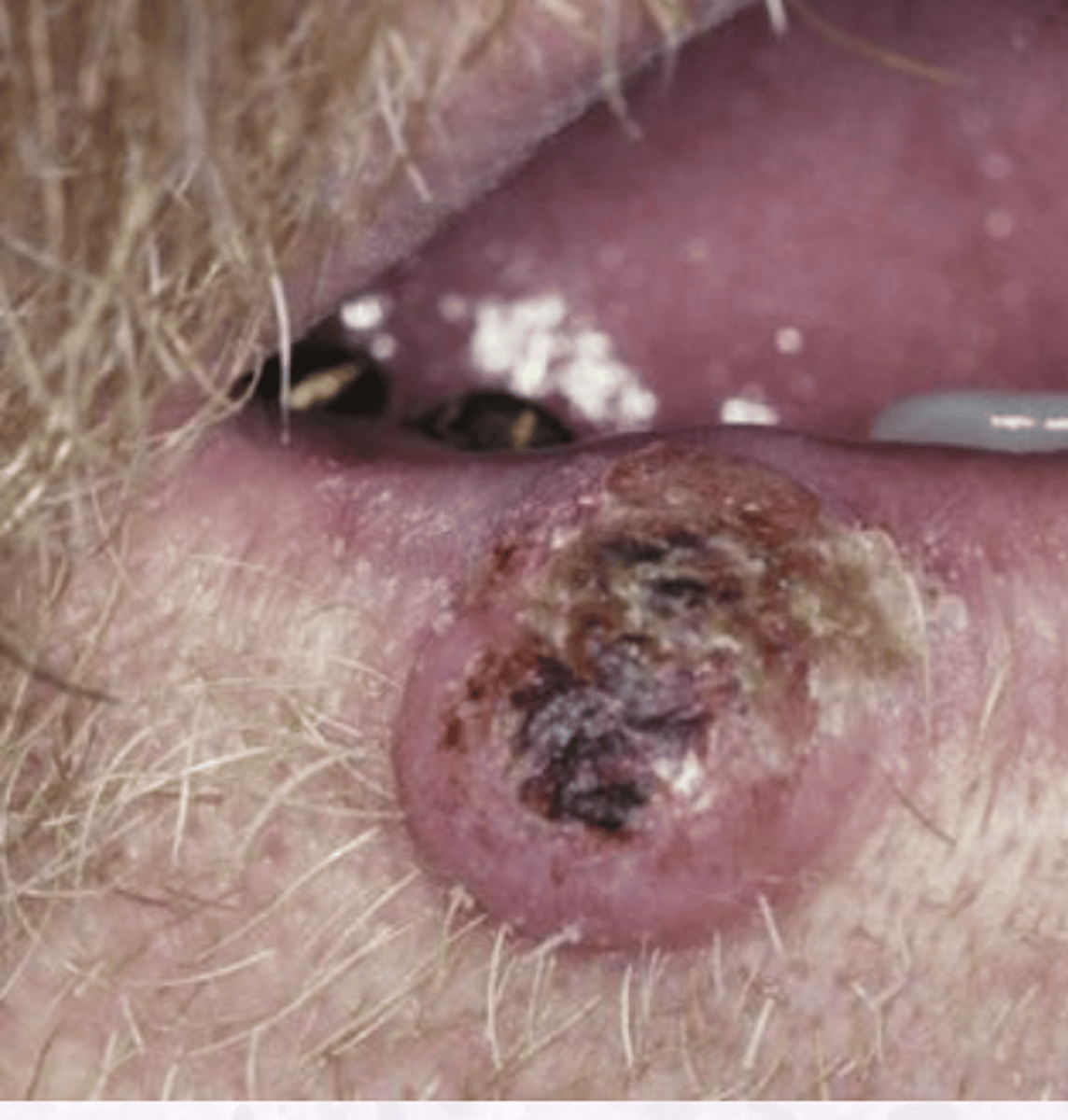
What occurs in the "growth" stage of a Keratocanthoma?
Lesion grows 1-2 cm within 6 weeks
What occurs in the "stationary" phase of keratocanthoma?
The lesion stabilizes in size
What ocurs in the "involution" stage of Keratocanthoma?
Spontaneous regression of lesion
6-12 mo
Usually scars
What are the histology characteristics of Keratocanthoma?
Dyskeratosis
Keratin pearls
Central crater buttress
Pronounced chronic inflammation
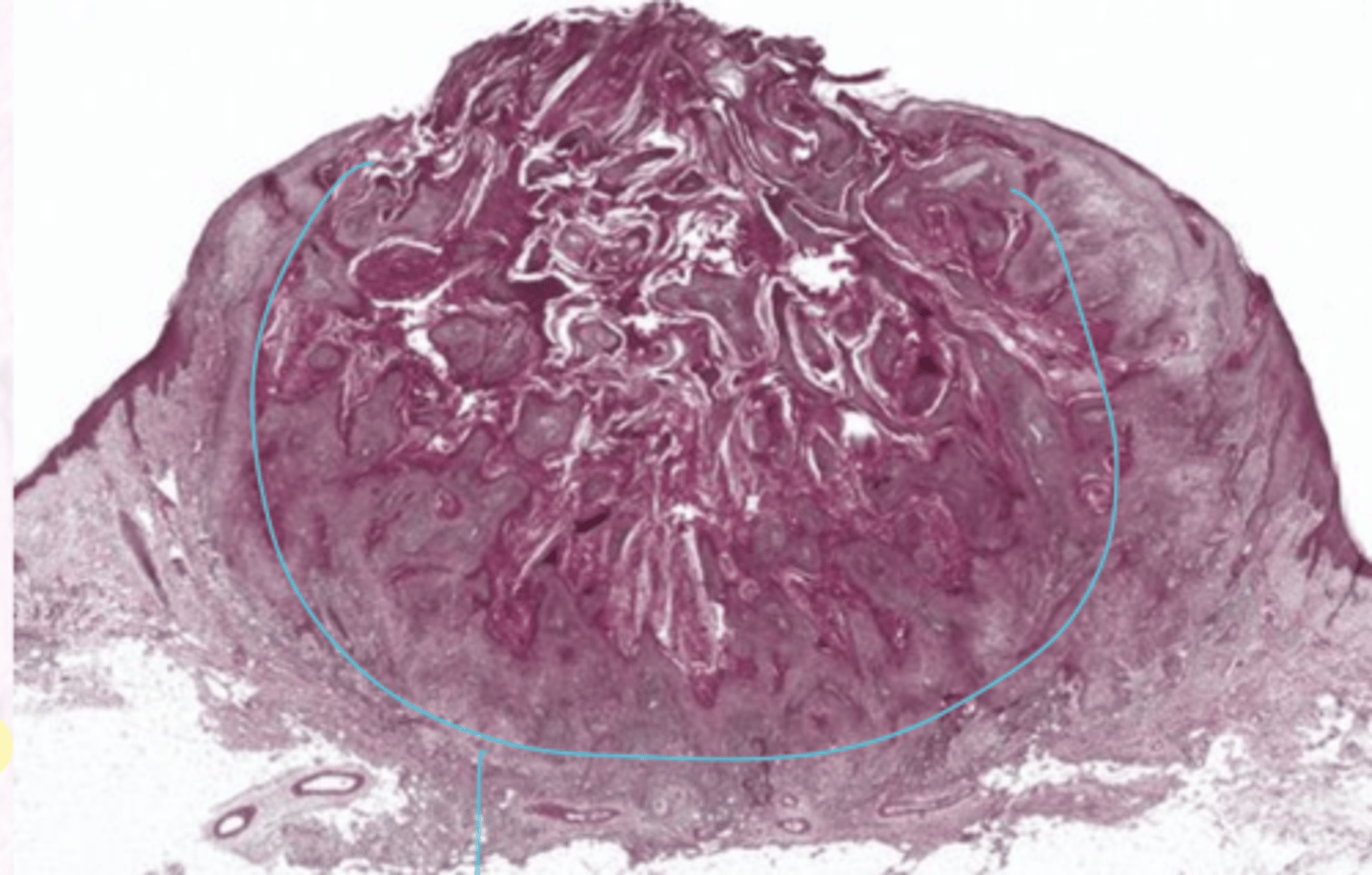
What is the treatment for keratocanthoma?
Excision without waiting for regression
*this is difficult to distinguish from SCCa clinically
4-8% recur
Carcinoma refers to _________ cancer
Epithelial
Squamous cell carcinoma refers to cancer on the _____ and _______
Skin, Mucosa
Adenocarcinoma refers to cancer on the _______ and _________
glands, glandular epithelium
Sarcoma is _________ _______ cancer
connective tissue
Why/how is tobacco a risk factor for epithelial cancers?
DOSE DEPENDENT + CUMULATIVE
80% of those with oral cancer were smokers
Contains >70 carcinogens
Smokeless tobacco risk factors
Chronic use increases risk
50% of all cancers in occurs occur at the placement site
Betel Quid (paan) risk factors
Combination of betel lieaf, slaked lime, areca palm nuts, and tobacco leaf
Associated with pre-cancerous lesions
Alcohol risk factors
DOSE DEPENDENT + TIME DEPENDENT
2-14x increase risk in heavy drinkers only
Alcohol in combination with tobacco increases the risk of developing cancer by ______x
15
What is the "risk profile" for HPV?
Caucasian males
Associated with sexual behavior
NOT associated with tobacco/alcohol use
What are the high risk types of HPV?
HPV-16 and HPV-18
What are the characteristics of HPV?
Persistent infection
70% of oropharyngeal cancers in N. America
High risk EPV E6 and E7 oncogene expression
What does HPV E6 ad E7 oncogene expression do?
E6--Degrades p53 (tumor suppressor gene)
E7-- Inactives Rb (tumor suppressor gene)
What are the characteristics of Squamous Cell carcinoma?
Multifactorial
>90% of oral cavity cancers*
Tobacco and alcohol are most common causes **
Risk increases with age
increased HPV associated oropharyngeal tumors
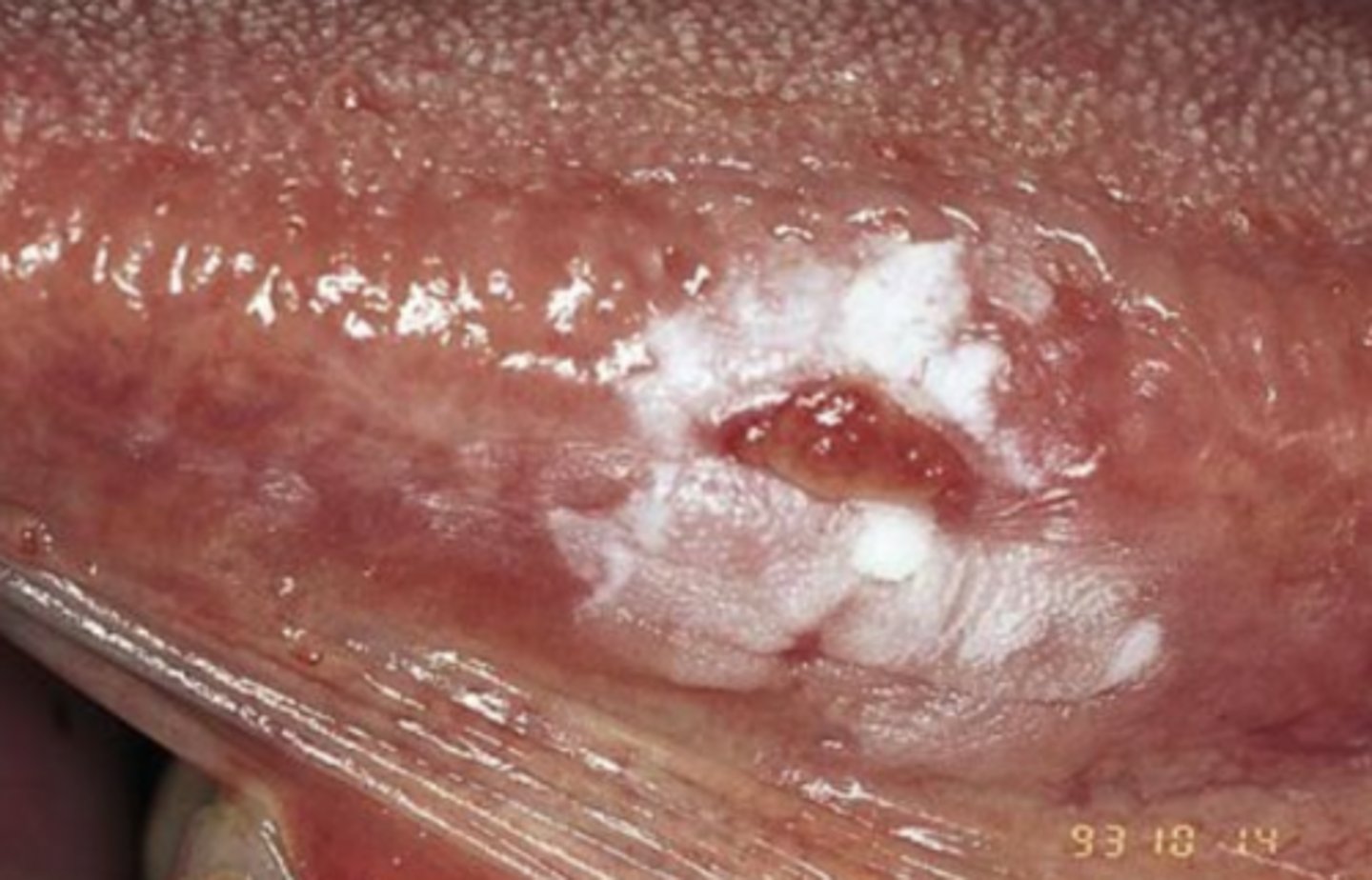
Pt's with squamous cell carcinoma are usually aware of changes ____-____ months before seeking help
4-8
What are the HIGH RISK locations for squamous cell carcinoma?
1. Tongue (50%) 2/3 are painless
--Posterolateral
--Ventral
2. Floor of mouth
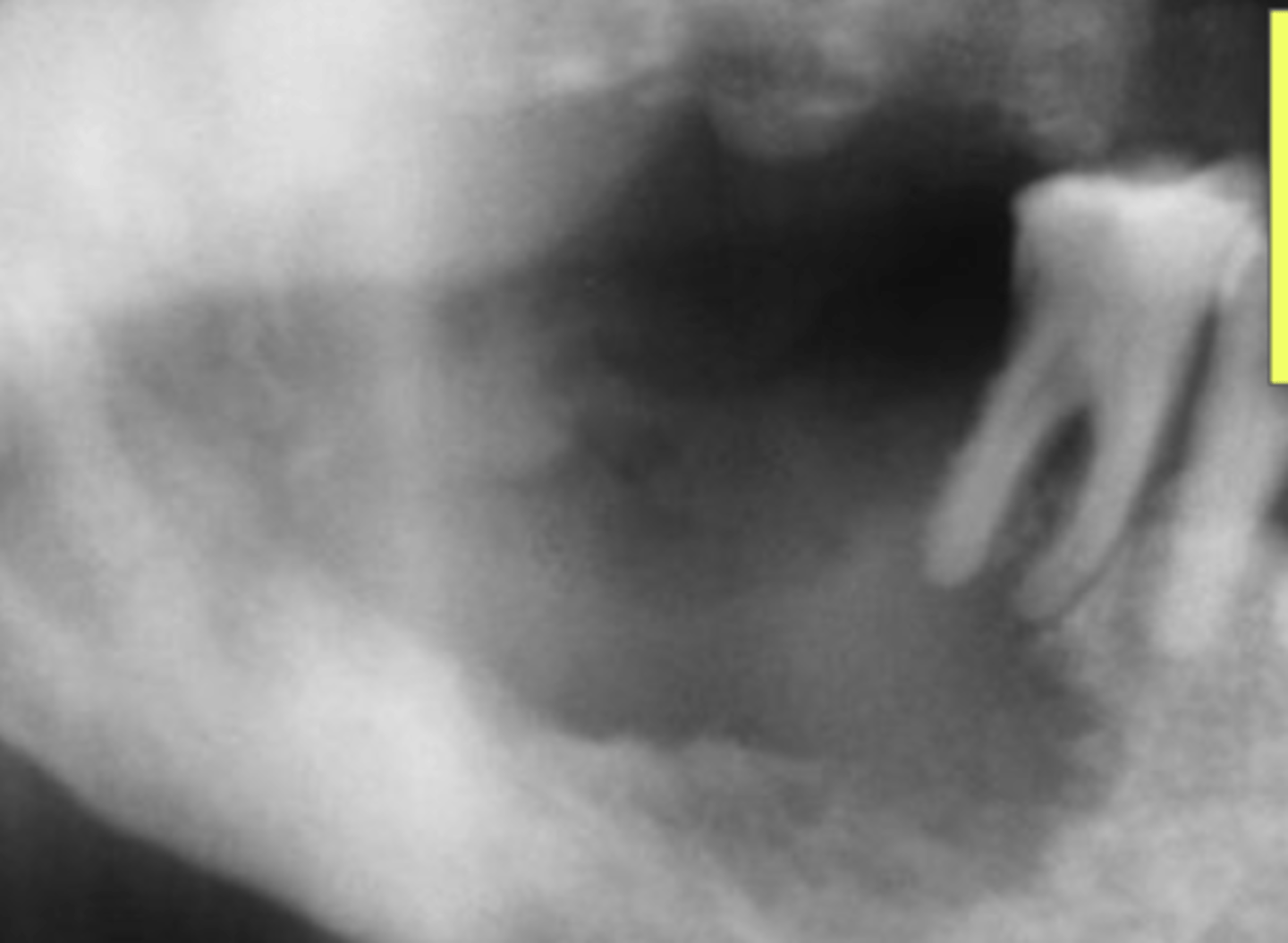
What are the radiographic features of squamous cell carcinoma?
Bone destruction
Irregular borders
Moth Eaten
What are the Characteristics of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of the Vermillion Border?
Chronic UV radiation
70% have outdoor jobs
**Usually associated with Actinic Cheilosis
90% on the lower lip
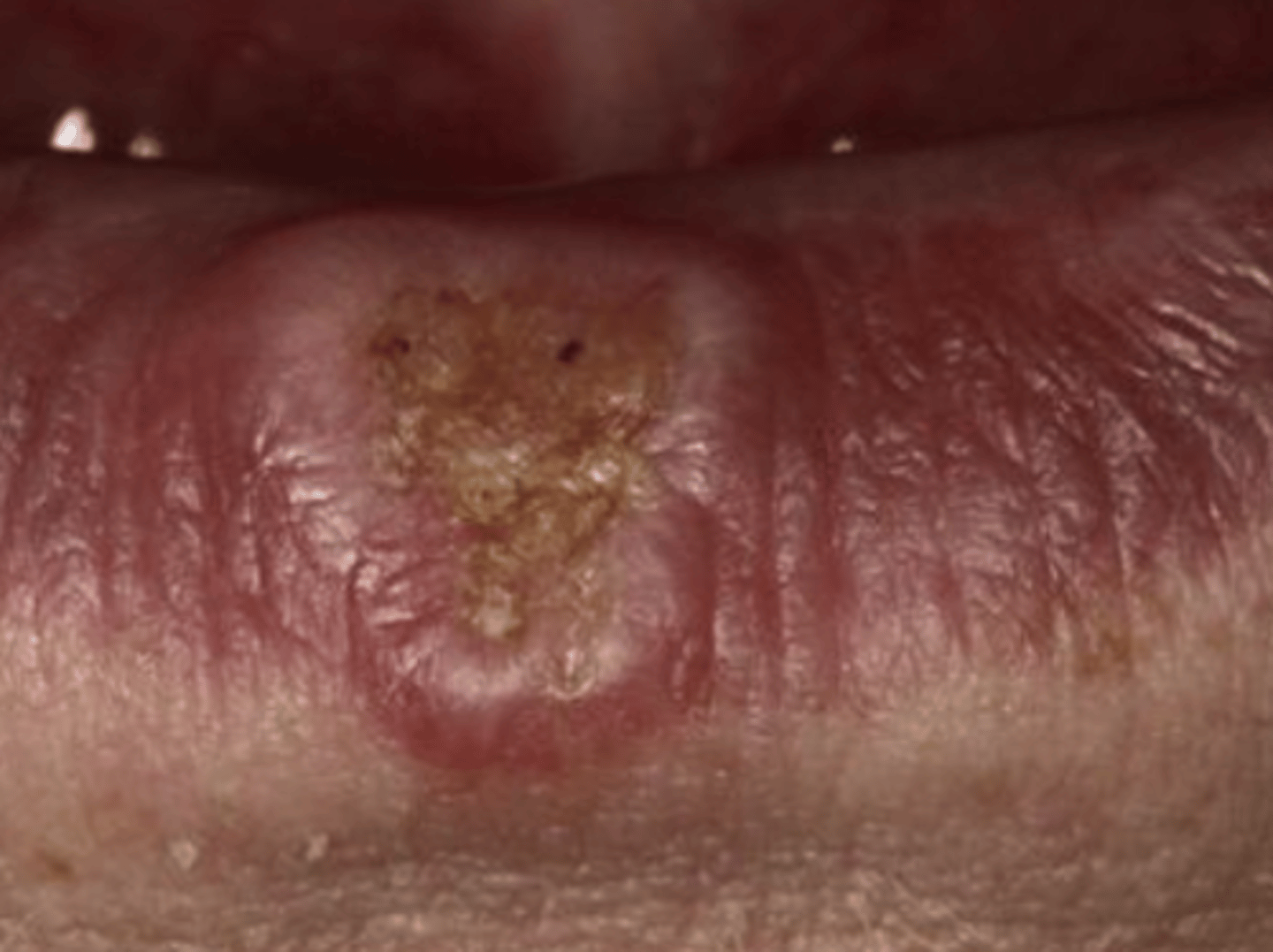
What is the clinical presentation of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of the Vermillion Border?
Asymptomatic
Crusted
Oozing
Indurated
Slow growing "problem" for 12-16 months
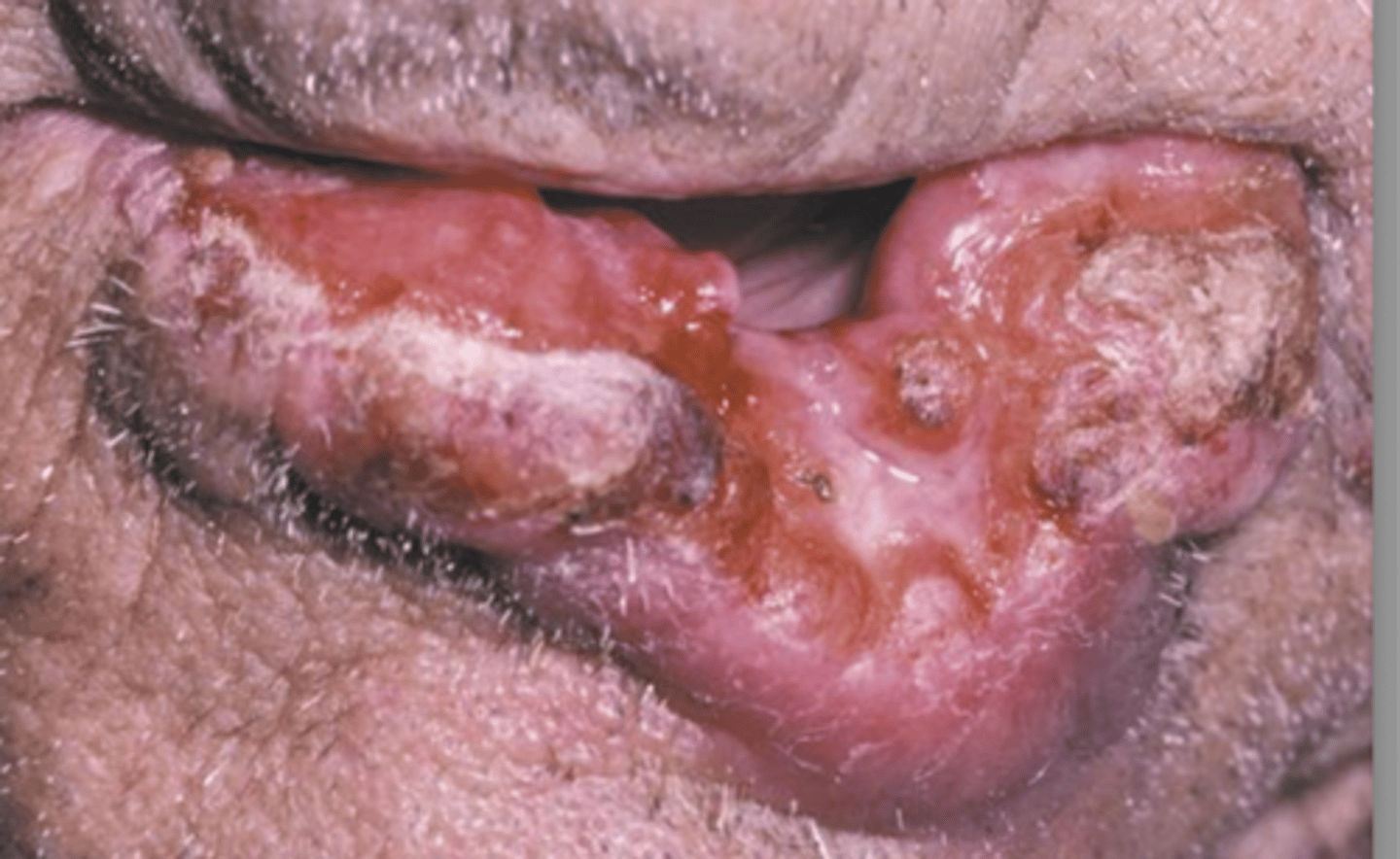
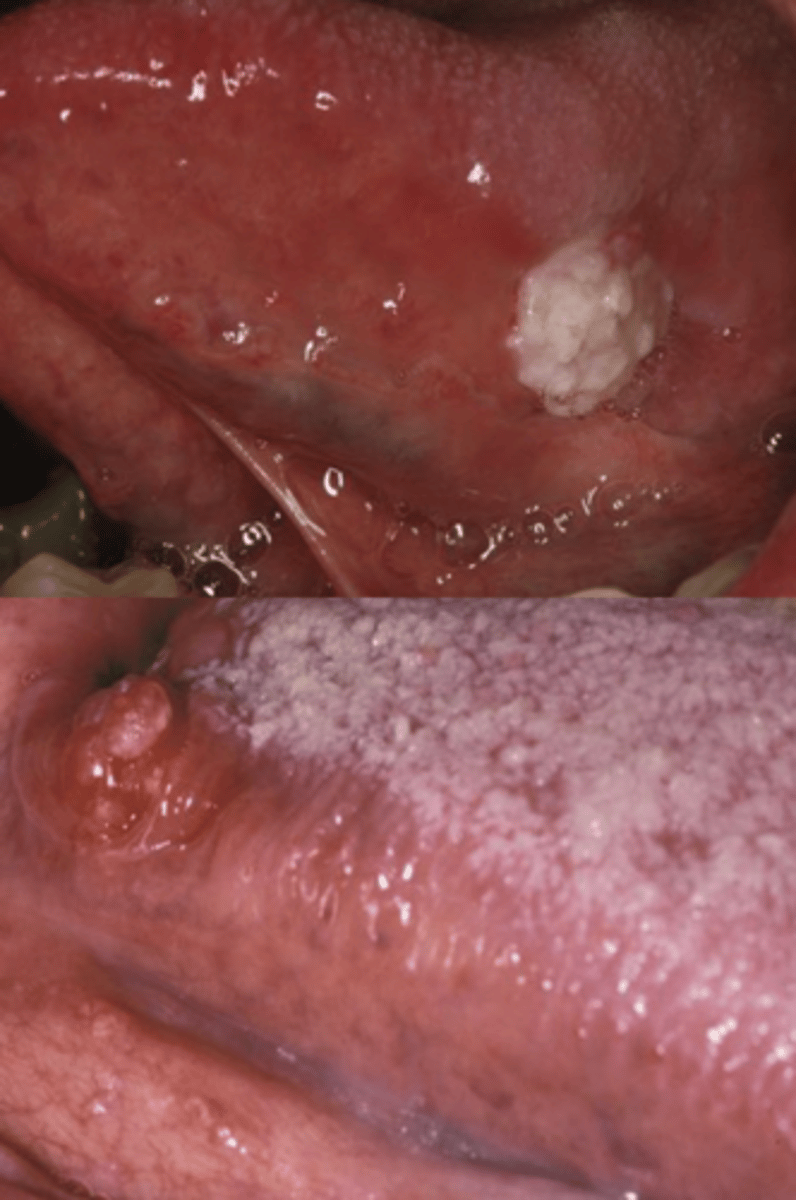
Pts with _______ ______ ______ commonly present with lesions like leukoplakia or erythroplakia first
squamous cell carcinoma
Intra-oral SCC locations: Tongue Characteristics
50% of intra-oral cancers
2/3 are asymptomatic, indurated masses or ulcers
Intra-oral SCC locations: Floor of mouth characteristics
The lesion is usually in the midline
Intra-oral SCC locations: Gingiva Characteristics
Asymptomatic
Usually posterior mandible
OFTEN MIMIC BENIGN LESIONS (4 P'S, etc)
Intra-oral SCC locations: Buccal Mucosa characteristics
Common site with betel quid users
Intra-oral SCC locations: Retromolar trigone characteristics
This is WORRISOME*
It can spread to many other areas if it starts in the RM trigone
Which types of high risk HPV are associated with Oropharyngeal Carcinomas?
HPV-16
HPV-18
HPV-33
What are the characteristics of Oropharyngeal Carcinoma?
Location: tonsillar region, base of tongue, soft palate, posterior pharyngeal wall (hard to see)
Often unrecognized for long periods of time
80% are late stage diagnoses