Lesson 41/42: Basic organs and structures in the abdominal and pelvic cavity. Lower urogenital system
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
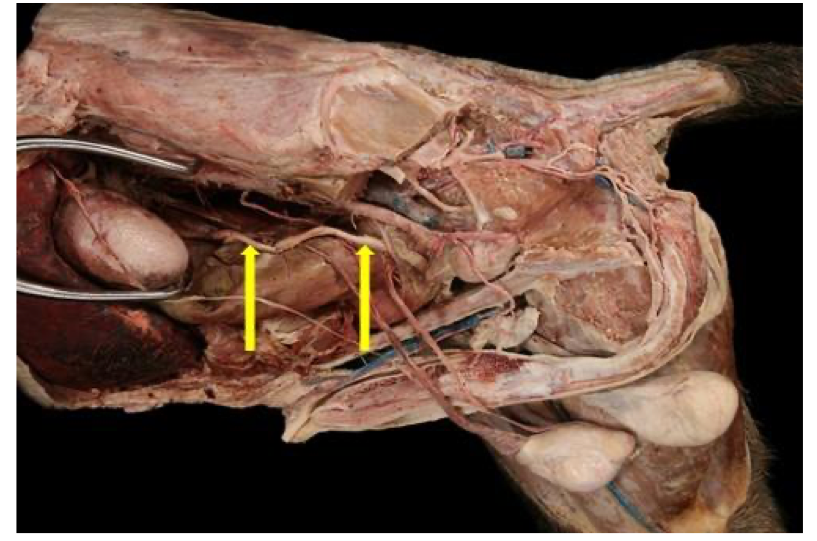
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow.
Ureter
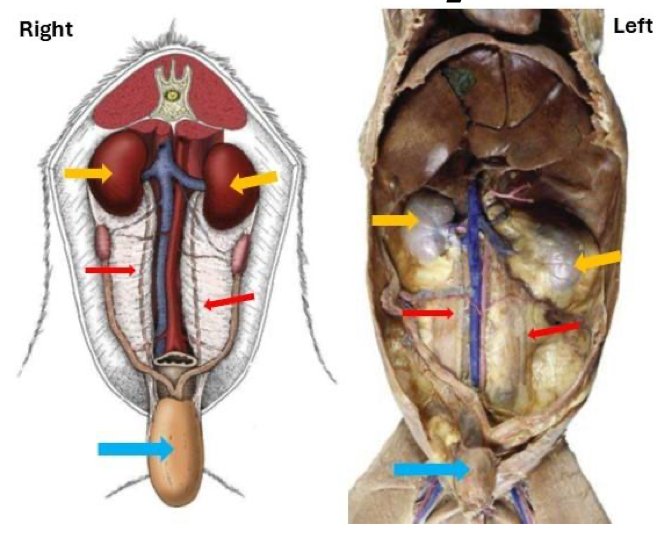
Identify the structure indicated by the blue arrows.
Bladder
What is a muscular tube that transports urine from the renal pelvis in most species to the urinary bladder?
Ureter
What muscular tube in the lower urogenital tract is divided into an abdominal part and a pelvic part?
Ureter
The ureter opens obliquley on the dorsal surface of the neck of what organ?
Bladder
Why is it important that the ureter penetrates the bladder wall very obliquely?
It guards against reflux in the ureter when the bladder fills up.
In males the ureter crosses above what towards the end of its course?
deferent duct
The inclusion of the ureter within what ligament places it at the some risk in the common spay procedure in females?
Borad ligament
Due to the nature of the bladder how does it change the topography?
The distensible nature creates variability in size, position, and relationships.
Where is the bladder located in the body?
Dorsal side to the bladder is the uterus/vagina/deferent ductus
Ventral side to the bladder is the pelvic and abdominal floor
What are the three parts of the bladder?
Cranial vertex (apex)
Intermediate body
Caudal neck
The neck of the bladder narrows to continue onto the what at the junction with the urethra?
Internal urethral orifice
What are the two ligaments that support the bladder?
Lateral ligaments
Median ligaments
How do the lateral ligaments support the bladder?
Bilateral which attach the lateral surface of the bladder to the lateral walls of the pelvic cavity
How does the Median ligament support the bladder?
Extends from the ventral surface of the bladder to the abdominal pelvic floor
Which ligament contains the urachus, the stalk of the embryonic allantois?
Median ligament
Which ligament conveys the umbilical arteries to the umbilicus?
Lateral ligaments
The remant of th eurachus forms a scar at the vertex, while the umbilical arteries are transformed into what ligaments?
Round ligaments
When the bladder is empty the mucosa is folded to form mucosal elevations called what?
rugae
When the bladder is distended there are two folds that do not disappear what are they called?
The ureteric columns
The ureteic columns unite to form what that continues to the urethra?
Urethral crest
The triangular area bound by the ureteric columns and the opening of the urethra is called what?
Trigone of the bladder
Where is the trigone located in the bladder?
Dorsal triangular area located within lines connecting the ureteral openings in the bladder and the urethral exit
What is the artery that is the main supply to the bladder?
Caudal vesical artery
Describe the blood supply to the bladder starting with the internal iliac artery?q
Internal iliac artery → Internal Pudendal artery → Vaginal/Prostatic artery → Caudal vescical artery
What is another artery that supplies blood to the bladder but not the main blood supply?
Umbilical artery
List the structures closely realted to the dorsal surface/wall of the urinary bladder in the males?
Ductus Deferens
Genital folds
ureters
Accessory sex glands
What nerve supplies sympathetic innervation to the bladder?
Hypogastric nerves
Where do the hypogastric nerves arise from?
Caudal mesenteric ganglion
Where does the hypogastric nerve radiate to in the bladder?
Pelvic plexus
Which nerves provide parasympathetic innervation to the bladder?
Pelvic nerve
Where does the pelvic nerve radiate to in the bladder?
Pelvic plexus
Which nerve provides sensory information as well as somatic innervation to the urethralis muscle?
Pudendal nerve
The female urethra extends in what direction on the pelvic floor ventral to the reproductive tract?
Caudally
What are the two parts of the male urethra?
Pelvic part
Penile part
What are the two parts of the pelvic part of the male urethra?
Pre-prostatic portion
Prostatic portion
Which part of the urethra begins at the ischial arch, at the root of the penis?
Penile urethra
What type of of tissue of the urethra surrounded by?
Corpus spongiosum tissue
Where does the urethra terminate at in the horse and ruminants?
Urethral process
What is the bony structure in the dog, at the distal end of the glans penis?
Os penis
What does the os penis form to fit the penile urethra?
Urethral groove
What is the muscosal projection (hillock) in the pre-prostatic part of the pelvic urethra called?
Colliculus seminalis
What is the enlargement of the urethral crest that protrudes into the limen of the urethra?
Colliculus seminalis
Where do the ducts of the vas deferens and the prostate open and secrete into the pelvic urethra?
Colliculus seminalis
What is the striated muscle that surrounds the thickened walls of the urethra for most of its length?
Urethralis/urethral muscle
The contraction of the urethralis muscle closes what in the urethra?
The external opening and the lumen of the urethra
Which nerve causes volumtary contral of the urethralis muscles?
Somatic fibers of the pudendal nerve
T/F Normal ureters are seen on plain radiographs or an ultrasonography?
False
What type of imaging is used to outline the ureter for diagnostics?
Intravenous urography
In an ultrasound what are readily identidied in the trigone region of the urinary bladder dorsally?
Ureteral papillae
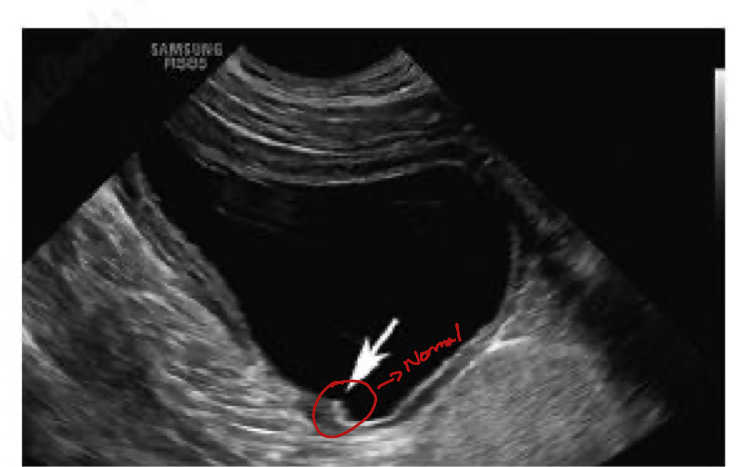
In an ultrasound what is represented focally thickened regions within the urinary bladder wall which slightly protrudes onto the luminal surface of the bladder wall?
Ureteral papillae
What are three common clinal considerations that can be seen on imaging of the ureters?
Ectopic ureters
Ureteral calculi
Hydroureter
What is a dilation of the ureter, my be congenital or it may be result of blockage from the presence of the calculus or other obstruction?
Hydroureter
How does the bladder present under normal conditions in a radiograph?
Homogenously soft tissue
Opacity with a round to oval shape
Which species is the bladder more cranial than dogs?
Cats
T/F Females bladders are more cranial than males.
True
What type of diagnostic gives the most information about the mucosal surface and the thickness of the bladder wall?
Double-constrast cystography
How does a bladder look in an ultrasound?
Homogeneously anechoic
What are the 4 layers of the urinary bladder wall?
Hypoechoic mucosa → Hyperechoic submucosa → Hypoechoic Muscularis → Hyperechoic serosa
Why is it important to look at the bladder from multiple angles during an ultrasound?
The lumen of the urinary bladder is prone creating artifacts that should not be misinterpret as abnormal urinary bladder content
How do you tell a mass vs a stone in an ultrasound?
Bladder stomes tend to cast a shadow where the tumor does not
What is the most common tumor found in the bladder?
Transitional cell carcinoma
Where are transitional cell carcinomas found in the bladder?
In the trigone
What is urethrography?
Introduction of a positive contrast medium through a catherter
T/F the prostatic/pelvic urethra is narrower than the extra-pelvic portion.
False
In dogs the distal penile urethra is obscured by what?
Os penis
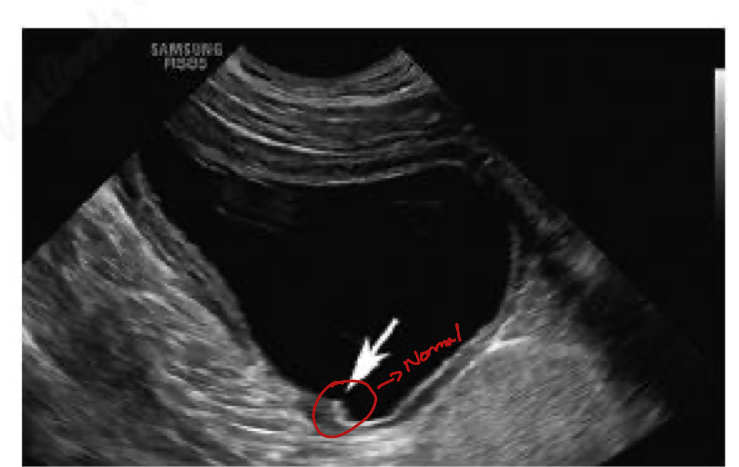
What is this animal suffuring from?
Urethral calculi
How thick is the urethral wall?
2mm
How are the walls of the urethral wall described on an ultrasound?
eccentric, hypoechoic tubular structure
What can be visualized as a tubular hypoechoic structure continuing caudal to the trigon region of the urinary bladder?
Proximal urethra
What statement best describes the location of the urinary bladder?
The bladder is variably situated in the abdominal or pelvic floor depending on its degree of fullness
What statement correctly describes the innervation of the urethralis muscle?
Pudendal nerve, voluntary control, somatic
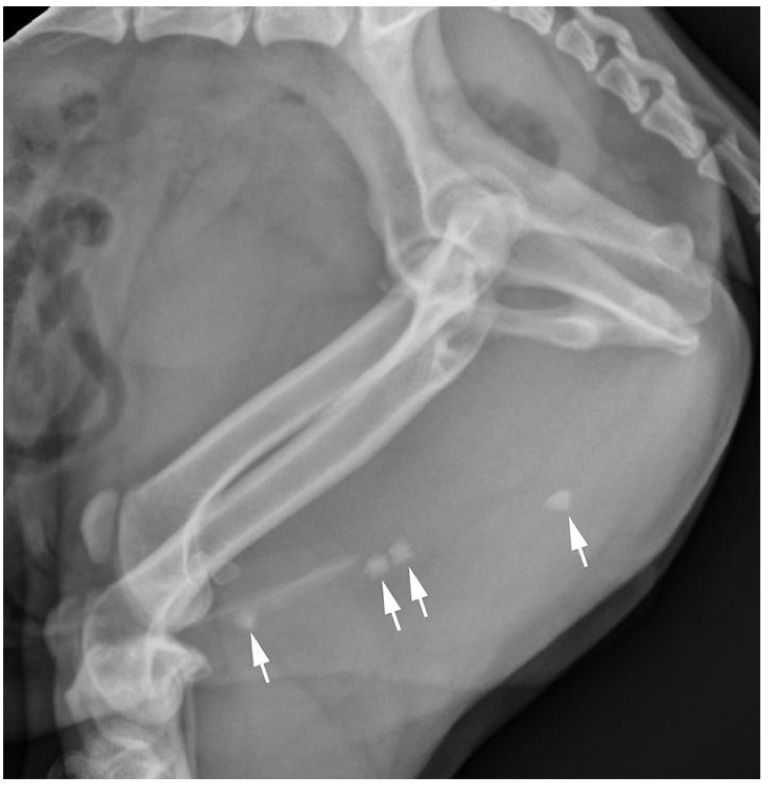
What organ is obstructed by the calculi?
Penile urethra
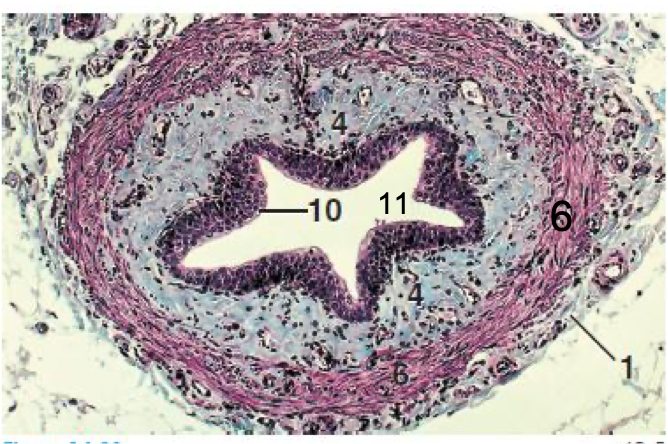
What is this a cross-section of?
Ureter
The ureter consists of what epithelium?
Transitional epithelium
What is the sub-epithelial layer of the ureter?
Lamina propria
Where do the tubulo-alveolar mucus glands occur in the horses ureter?
Lamina propria
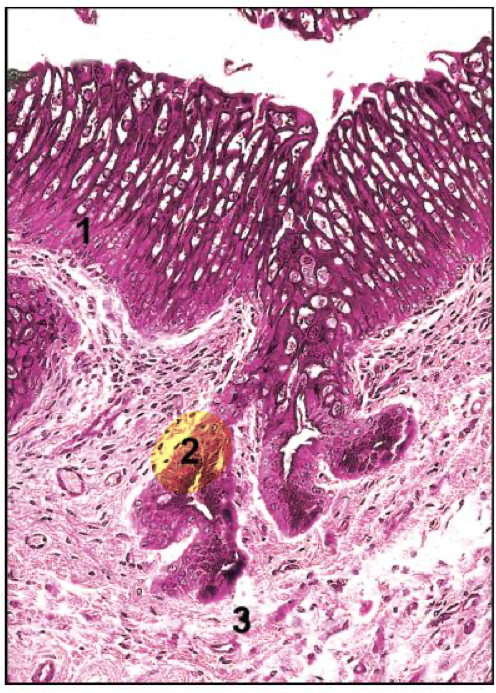
What is number 2 showing?
The tubulo-alveolar mucus glands in the horses ureter
What layer of the ureter is lacking in comparison to other organs of the urinary tract?
Submucosa
What is the thickest layer providing the major contractile forces in the ureter?
Tunica muscularis
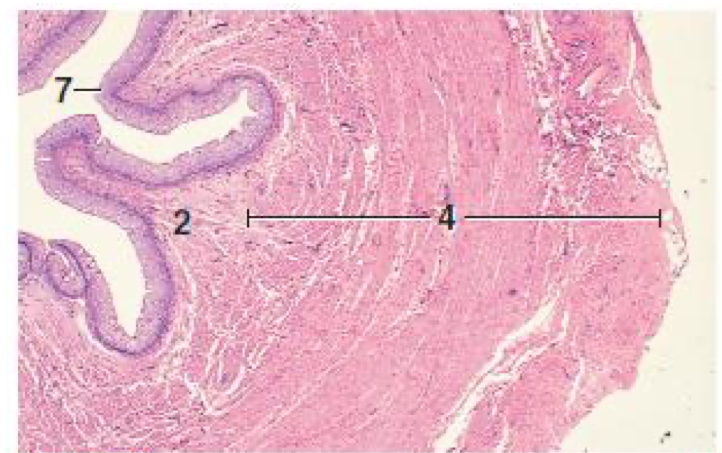
What does number 4 represent in this histology picture?
Tunica muscularis
What are the three ill-defined layers of the smooth muscles of the tunica muscularis?
Longitudinal → Circular →Longitudinal
What is the outermost layer that contains loose connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels and surround the muscularis layer?
Tumica adventitia or serosa
What layer of the urinary bladder contains elastic fibers and a layer of small bundles of discontinuous smooth muscle?
submucosal layer
What layer of the urinary bladder consists of three layers and is referred to as the detrusor muscle of the bladder?
Tunica muscularis
What muscle consists of the smooth muscle fibers under control of the automonic nervous system?
Detrusor muscle
What layer of the urinary bladder has parasympahtetic ganglia and nerve receptors that are present o the bladder wall surface?
Tunica serosa
What are the layers of the urinary bladder from lumen to outermost layer?
Tunica mucosa → Tunica/Propria submucose → Tunica Muscularis → Tunica Adventitia serosa
In what species is the small bundles of smooth muscle which form a discontinuous lamina musclularis of the submucosa absent?
Cats
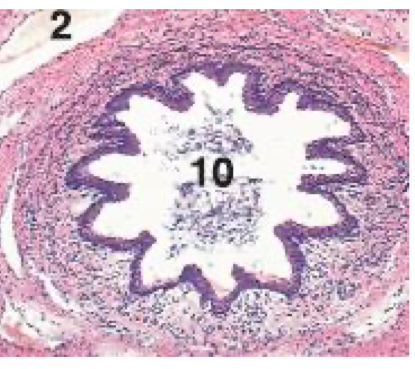
What is the organ is shown in this cross-section?
Urethra
How are male and female urethra differ from eachother?
The male urethra is long and also serves a genital function
The female urethra is short and only used for urinary purposes
What is the epithelium of the tunica mucosa of the urinary bladder?
Transitional urothelium
What is the epithelium of the tunica mucosa of the urethra?
Stratified columnar or cuboidal
What is the epithelium of the tunica mucosa of the urethral orifice/in the tip of the penis?
Stratified squamous
In which layer of the urethra are there endothelium-lined caverns/vascular spaced that form an erectile plexus?
lamina propria-submucosa
What layer of the urethra is composed of smooth muscle in the vicinity of the urinary bladder and skeletal muscle in the remainder of the urethra>
Tunica muscularis
What layer of the urethra is composed of loose connective tissue furnished blood vessels and nerves/nerve endings?
Tunica adventita
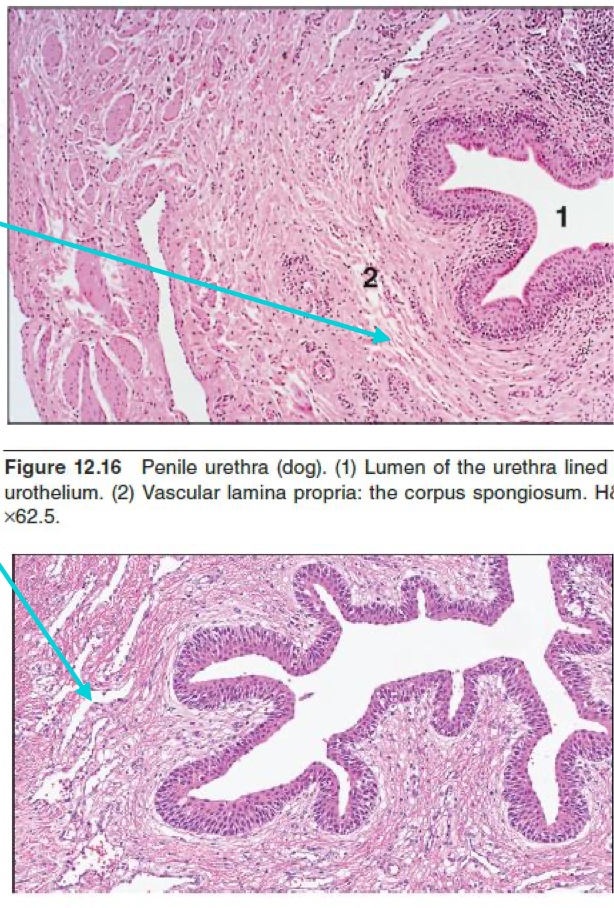
What is the blue arrows pointing to?
Endothelium-lined caverns/vascular spaces in the lamina propria-submucosa
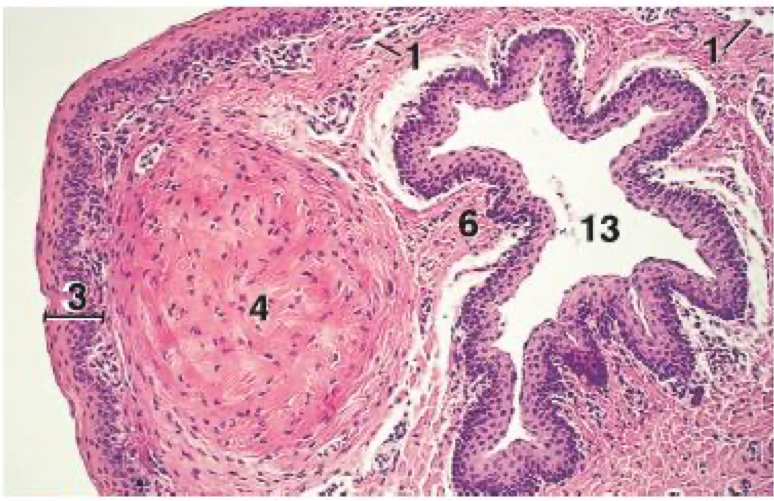
What organ is this a cross-section?
Urethral process of a small ruminant
Where are the urinary and reproductive tracts located in the body?
Central midline of the abdominal and pelvic cavities