Lecture 3 - What is Family Nursing?
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What are the goals of theory utilization in nursing?
To describe, explain, and predict, thereby increasing knowledge, enhancing understanding, and improving nursing care.
What is theoretical pluralism in family nursing?
The selection and use of multiple theories for practice in accordance with the demands of the situation.
What are the three major categories of the CFAM?
Structural, developmental, and functional.
What are the 6 theoretical foundations of CFAM?
Postmodernism, systems theory, cybernetics, communication theory, change theory, and biology of cognition.
What is the theory of postmodernism about?
Valuing pluralism and questioning ideas/assumptions that we take for granted.
What are the main concepts of systems theory?
- Family is a part of a larger system
- Family as a whole is greater than the sum of its parts
- A change in one family member affects all members
- The family can create balance between change and stability
- Family behaviours are best understood from a circular view and not linear
What are the three subsystems of family?
Structure, function, and processes.
What is cybernetics in the context of family systems?
The science of communication and control theory, focusing on self-regulation and feedback processes within family systems.
What are the key concepts of communication theory in family nursing?
- All nonverbal communication is meaningful
- All communication has two major channels
- A dyadic relationship has varying degrees of symmetry and complementarity
- All communication has two levels
What are the 2 major channels for communication?
Digital and analog.
What is digital communication?
Verbal communication.
What is analog communication?
Nonverbal communication.
What does symmetry mean in the context of family nursing?
Two individuals have equal status.
What does complementarity mean in the context of family nursing?
One person is giving, while the other is receiving.
What are the 2 levels of communication?
Content and relationship.
What is change theory?
A comprehensive description or illustration of how or why a desired change is expected to happen in a desired context.
What are the 2 levels of change?
First-order and second-order.
What is first-order change in families?
Change that occurs within a system without altering its structure, typically involving repeated problem-solving strategies.
What is second-order change in families?
Change that alters the system itself, including changes in the rules governing the system.
How does change theory apply to family dynamics?
It describes how change is continuous and reciprocal, affecting cognitive, affective, or behavioral domains.
What are the key concepts of change theory?
- Change is dependent on the perception of the problem
- Change is determined by structure
- Change is dependent on context
- Change is dependent on co-evolving goals for treatment
- Understanding alone does not equal change
- Change doesn't always occur equally in family members
- Facilitating change is the nurse's responsibility
- Change occurs through the interventions offered by the nurse
- Change can have multiple causes
What is the role of a nurse in maintaining family stability?
To help maintain or restore the stability of the family and assist them in achieving the highest level of functioning.
What are the two avenues to explain the world in the biology of cognition?
Objectivity and objectivity-in-parentheses.
What does 'objectivity' imply?
Only one domain of reference explains the world, and we exist independently of observers.
What does 'objectivity-in-parentheses' imply?
Truths are created by observers; nothing is certain, and everyone's view is a version of interpretation.
What are the three major assessment categories in CFAM?
Structural Assessment, Developmental Assessment, and Functional Assessment.
What does Structural Assessment in CFAM focus on?
It examines who is in the family, the connections among members, and the family's context.
What are the 3 subcategories of the structural assessment?
Internal, external, and context.
What is included in the Internal Structure of a family?
Family composition, gender and gender identity, sexual orientation, rank order, subsystems, and boundaries.
What does External Structure in CFAM refer to?
Connections to extended family and larger systems such as work and social media.
What factors are considered in the Family Context of CFAM?
Ethnicity, race, social class, spirituality/religion, and environment.
What is a genogram?
A diagram of the family constellation used for family assessment.
What is an ecomap?
A diagram that shows connections to the outside world and community resources.
What is the index person in a genogram?
The person with the health concern.
What should genograms include?
- At least 3 generations
- Members placed on a horizontal line based on generation
- Children denoted by vertical lines
- Ranked from left to right starting with oldest
What does Developmental Assessment in CFAM explore?
The family developmental life cycle that is unique to each family.
What is family development?
The unique path is constructed by a family that is shaped by predictable and unpredictable events and societal trends.
What is a family cycle?
The typical path most families follow that is generally predictable.
What are the 3 parts of the developmental assessment?
Stages, tasks, and attachments.
What are the stages of family development?
Emerging young adults, couple formation/joining of families, families with young children, families with adolescents, launching children and moving on at midlife, families in late middle age, and families nearing the end of life
What is the primary task for emerging young adults?
Accepting emotional and financial responsibility for self.
What are the second-order tasks of emerging adults?
- Differentiation of self in relation to family origin
- Development of intimate peer relationships
- Establishment of self with respect to work and financial independence
- Establishment of self in community and larger society
- Establishment of one's worldview, spirituality, religion, and relationship to nature
- Parents shifting to a consultative role in young adult relationships
What is the primary task of couple formation/joining of families?
Commitment to a new, expanded system.
What are the second-order tasks of couple formation/joining of families?
- Formation of a couple system
- Expansion of family to include new partner and extended family
- Realignment of relationships among couple, parents and siblings, extended family, friends, and larger community
What is the primary task of families with young children?
Accepting new members into the system.
What are the second-order tasks of families with young children?
- Adjustment of couple system to make space for children
- Collaboration in child-rearing and financial and housekeeping tasks
- Realignment of relationships with extended family to include parenting and grandparenting roles
- Realignment of relationships with community and larger social system to include new family structure and relationships
What is the primary task of families with adolescents?
Flexible family boundaries that are needed to support child independence and grandparent aging.
What the second-order tasks of families with adolescents?
- Shift of parent-child relationships to permit adolescent to have more independent activities and relationships and to move more flexibly into and out of the system.
- Families helping emerging adolescents negotiate relationships with community
- Refocus on midlife couple and career issues
- Begin shift toward caring for older generation
What is the primary task of launching children and moving on at midlife?
Accepting multiple exits and entries in the system.
What are the second-order tasks of launching children and moving on at midlife?
- Renegotiation of couple system as a dyad
- Development of adult-to-adult relationships between parents and grown children
- Realignment of relationships to include in-laws and grandchildren
- Realignment of relationships with community to include new constellation of family relationships
- Exploration of new interests/career, given the freedom from childcare responsibilities
- Dealing with care needs, disabilities, and death of parents (grandparents)
What is the primary task of families in late middle age?
Managing shifting generational roles.
What are the second-order tasks of families in late middle age?
- Maintaining or modifying own and/or couple and social functioning and interests in the face of physiological decline: exploration of new familial and social role options
- Supporting more central role of middle generations
- Making room in the system for the wisdom and experience of the elders
- Supporting older generation without over-functioning them
What is the primary task for families nearing the end of life?
Accepting the limitations of family members, death, and completing of one family cycle.
What are the second-order tasks of families nearing the end of life?
- Dealing with loss of spouse, siblings, and other peers
- Making preparations for death and legacy
- Managing reversed roles in caretaking between middle and older generations
- Realignment of relationships with larger community and
social system to acknowledge changing life cycle relationships
What is the focus of functional assessment in family nursing?
How individuals behave in relation to one another.
What are 2 aspects of the functional assessment?
Instrumental functioning and expressive functioning.
What does instrumental functioning refer to?
Roles and activities of daily living, especially important for families with chronically ill members.
What are the 9 categories of expressive functioning?
Emotional communication, verbal communication, nonverbal communication, circular communication, problem solving, roles, influence and power, beliefs, and alliances and coalitions.
Which 5 categories of expressive functioning are considered patterns of communication?
Emotional communication, verbal communication, nonverbal communication, circular communication, and problem-solving.
What is emotional communication?
The range and types of emotions or feelings that families
express or the practitioner observes.
What is verbal communication?
The meaning of an oral (or written) message between those involved in the interaction.
What is nonverbal communication?
The various nonverbal and paraverbal messages that family members communicate (Ex. Body posture, gestures, eye contact).
What is circular communication?
Reciprocal communication where each person influences the other's behaviour.
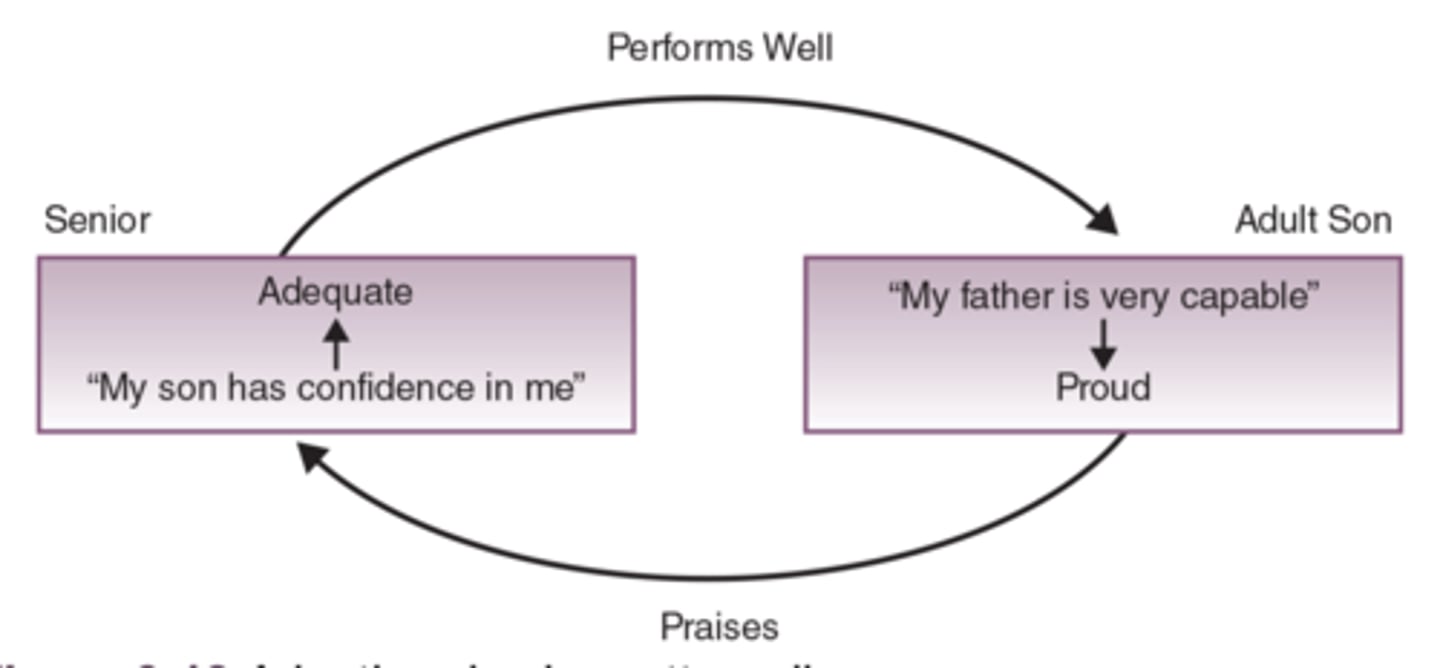
What is a positive circular pattern?
A circular pattern that forms a cycle of support.

What is a negative circular pattern?
A circular pattern that forms a cycle of hate.
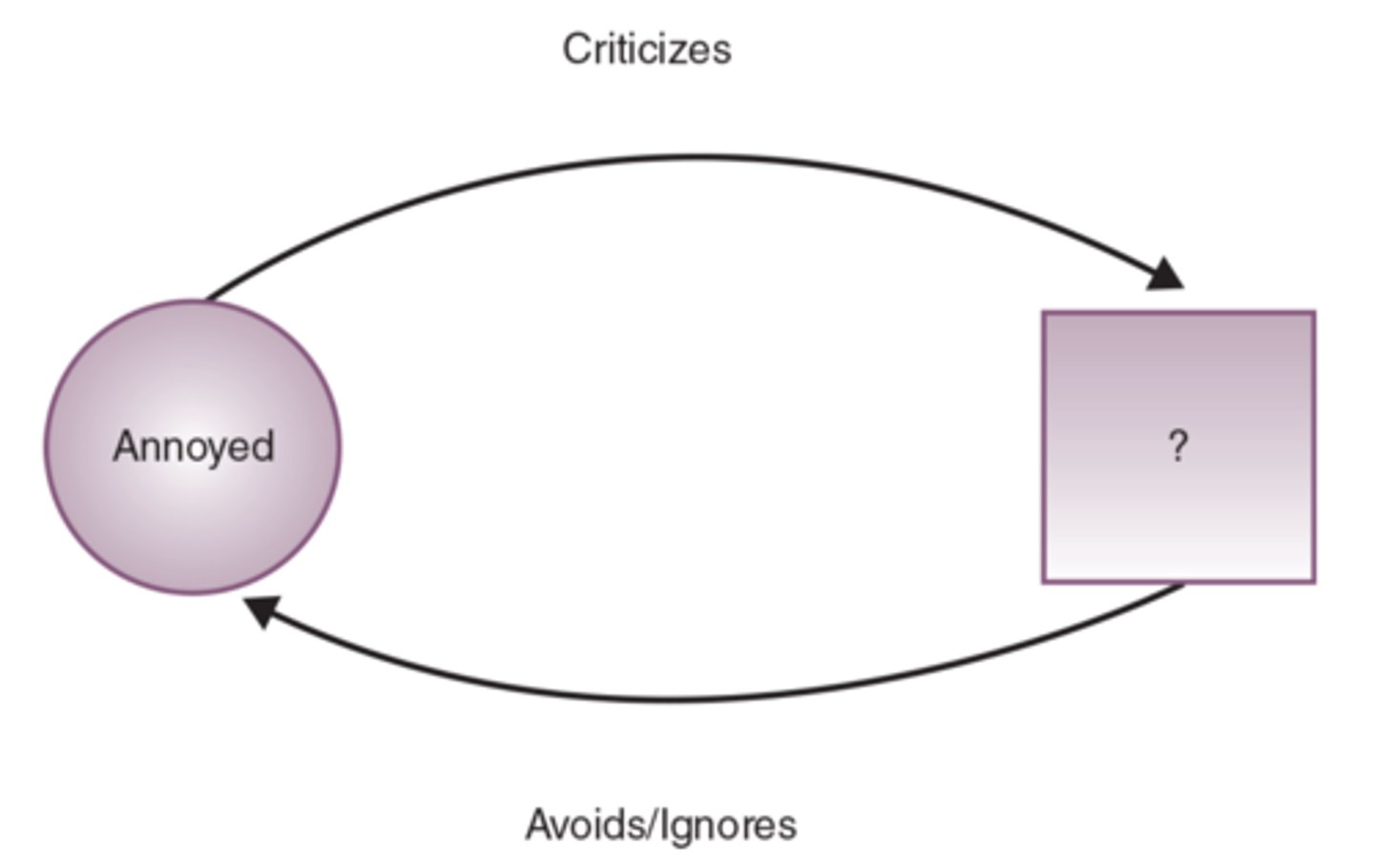
What are the limitations of Circular Pattern Diagrams?
Can make us look at families for the collaborative cause of the problem, can encourage nurses to believe they are outside the family system, they ignore power differentials
What does problem-solving in family communication refer to?
The effectiveness of families in solving their own problems, influenced by their beliefs and past successes.
What do roles refer to as part of expressive functioning?
The established patterns of behaviour for family members that are influenced by culture, race, and others' sanctions and norms.
What does influence and power refer to as part of expressive functioning?
The behaviour used by one person to influence or affect another's behaviour and is influenced by gender, race, culture, and values.
What do beliefs refer to as part of expressive functioning?
The fundamental attitudes, premises, values, and assumptions held by individuals and families that influence behaviours.
What do alliances and coalitions refer to as part of expressive functioning?
The directionality, balance, and intensity of relationships
between family members or between families and nurses.
What are the four stages of family interviewing?
Engagement, assessment, intervention, and termination.
What is the engagement stage of family nursing interviews?
The stage in which the family is greeted and made comfortable and the relationship continues, based on compassion, collaboration, and consultation.
What is the assessment stage of family nursing interviews?
The stage when problem identification and exploration occurs, including delineation of strengths; it is an ongoing process.
What is the intervention stage of family nursing interviews?
The stage when the nurse and the family collaborate on areas for desired change.
What is the termination stage of family nursing interviews?
The stage when the therapeutic relationship between the nurse and the family is ended.
What skills are important for family interviewing?
Perceptual skills, conceptual skills, executive skills.
What are perceptual skills?
The ability to make relevant observations.
What are conceptual skills?
The ability to give meaning to observations.
What are executive skills?
Observable interventions that elicit responses.
What is the purpose of the engagement stage in family interviewing?
- To promote a positive nurse-family relationship
- Recognize each family member's strengths
- Prevent future misunderstandings.
What are some skills and ideas for the engagement stage in family interviewing?
- Invite all involved family members
- Explain the interview
- Start with introductions and structural assessment
What are the A's of the ABC's of engaging families?
- Assume a confident approach
- Ask purposeful questions
- Address every member
- Adjust conversation to each member
What are the B's of the ABC's of enganing families?
- Begin by providing structure
- Behave in a curious way
- Build strengths
- Bring resources
What are the C'S of the ABC's of engaging families?
- Create mutual trust
- Clarify expectations
- Collaborate and command
- Cultivate racial/ethnic sensitivity
What are the 4 parts of the assessment stage?
- Problem identification
- Relationship between family interaction and health problem
- Attempted solutions to solving problems
- Goal exploration
What are some skills and ideas for the assessment stage in family interviewing?
- Explore assessment components of CFAM
- Ask each family member for information
- Obtain verification of your understanding
- Use CFAM to help plan your interview and analyze information
- Know your limits
What is the purpose of interventions with families?
To validate emotional responses, offer commendations, and plan interventions addressing the 3 domains of family nursing.
What are some skills and ideas for the intervention stage of family interviewing?
- Encourage family to explore solutions to problems
- Plan interventions in the 3 domains
- Provide information to enhance knowledge and facilitate problem-solving skills
- Assign tasks aimed at improving family function
What are key considerations when planning family interventions?
The level of family functioning and the level of competence of the nurse.
What is the purpose of therapeutic termination in family nursing?
To refer when necessary, provide information, obtain feedback, identify supports, summarize efforts, and conclude the interview.
Why is a 15-minute family interview important?
Due to time constraints in healthcare, it allows for purposeful and healing interactions.
What are the key ingredients of a 15-minute family interview?
Therapeutic conversation, manners, genograms and ecomaps, therapeutic questions, and commendations.
What is a therapeutic conversation?
A purposeful, time-limited interaction that aims to acknowledge and affirm family members.
What is the art of listening?
Listening to families' illness stories while showing compassion and offering commendations.
What are genograms important for?
To identify individuals, ages, occupations/school grade, religion, ethnic background, and the current health status of all members.
What are ecomaps important for?
To assess all the community resources and connections for each family member.
What are therapeutic questions?
Questions that focus on the key, defining element in a therapeutic conversation and include linear, circular, and interventive questions.
What are commendations?
Positive statements about family strengths, resources, or competencies.
What is the difference between commendations and a compliment?
Commendations are observations of behaviour that occur across time, while compliments are observations of a one-time occurrence.