7-Tumor Markers
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is cancer
disease that starts with uncontrolled cell proliferation from 1 cell
What is ‘screening’? List examples.
Testing for cancer when no symptoms to allow for early diagnosis
Examples:
breast exams
mammograms
fecal occult
rectal exam
Why are tumor markers not useful for screening?
most tumor markers are found in normal cells (PSA comes closest to being specific)
What is a tumor marker?
produced by tumor and used to determine size and therapy response
What would make the best tumor marker?
Tumor specific
Absent in healthy ppl
readily detectable
free (unbound)
What uses do we tumor markers for?
high risk pop screen
staging/prognosis
choosing treatments
monitor therapy
detect reoccuance
What characteristics does a blood tumor marker have?
not specific for malignant tissues
measurable in blood
origin related to malignancy
detect/monitor
progression
Types of Tumor Markers
Glyco- or Muco- proteins from Adenocarcinoma
Tissue-specific proteins
Oncofetal proteins/antigens
Tumor-produced hormones
Enzymes
Propriety gene expression
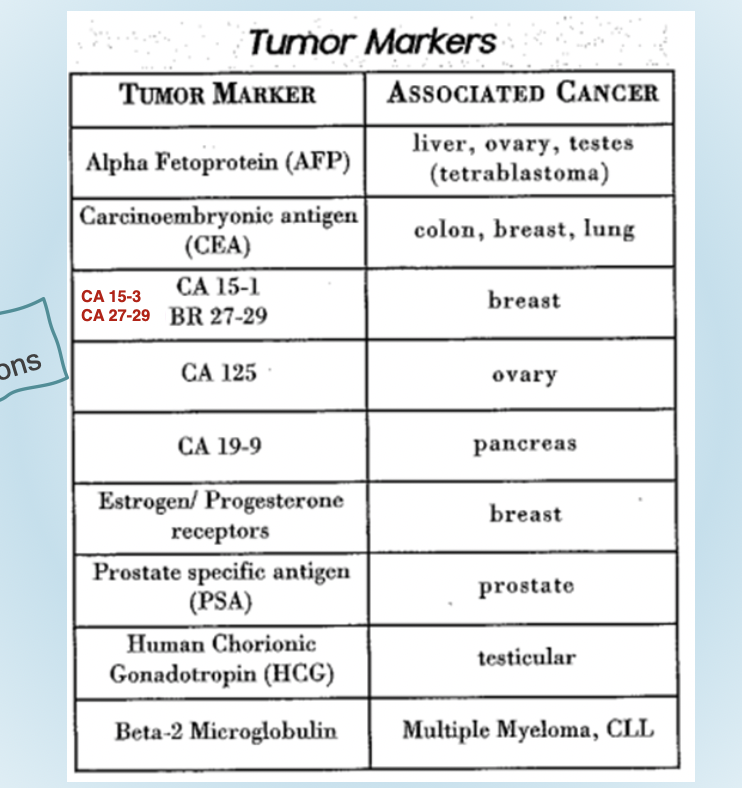
Glyco or Muco proteins from Adenocarcinomas
Ex:
CA 125
CA 15-3 (CA 27.29)/CA 19-9
Tissue specific proteins
Ex:
Immunoglobulins
PSA; Thyroglobulin
Receptors (estrogen/progesterone, non serologic)
Oncofetal proteins/antigens
Ex
AFP
CEA
What are Oncofetal proteins/antigens
produced during fetal life and disappear but reappear in cancer
Tumor produced hormones
Ex

Enzymes
Ex
PSA
ALP
PSA is a serine____enzyme, what are the 2 major forms
protease
2 forms:
free
complexed
PSA is _____specific for prostate and related glands
nearly
Men with prostate cancer have_____circulating Free PSA
less
PSA is useful as a TM in pts with
prostate cancer
Free PSA and screening

CA-125 is a marker for
monitoring ovarian cancer therapy
CA-125 is useful in determining
prognosis of pts with endometrial carcinoma
What are monoclonal gammopathies
uncontrolled division of plasma cell leading to abnormal incr in monoclonal proteins (antibodies)
What diagnosis does it help make
multiple myeloma
The ____protein may be useful as a TM for monitoring disease
Bence-Jones
What is the Bence-Jones protein
immunoglobulin light chain (kappa or lambda) in urine
What is Bence-Jones protein famously known for
Multiple Myeloma
ß2-Microglobulin is a component of the _____molecule
class I
ß2-Microglobulin is on all ______cells
nucleated
ß2-Microglobulin has elevated ____ and used in the diagnosis of____
serum levels; Multiple Myeloma
High ß2-Microglobulin levels indicate a ______prognosis
poor
Thyroglobulin only produced in the ____gland
thyroid gland (follicles)
Thyroglobulin is elevated in ____or _____cancer
papillary or follicular thyroid
thyroglobulin main use is to
monitor pts being treated for thyroid cancer
If thyroglobulin is used for a tumor marker what should also be tested? why
anti-Tg since they can interfere with assay
CA 19-9 is used in monitoring what?
pancreatic cancer
hepatobiliary cancer
CA 19-9 can also be elevated with what issue
any bile duct obstruction
CA 19-9 is not used for staging but high levels do indicate what?
poor prognosis
CA 15-3 and CA 27-29; What type of patient uses these TMs?
women with metastatic breast cancer
CA 15-3 and CA 27-29: What are these TMs useful in monitoring?
course of disease
What are the main 3 things AFP is used for?
open neural defects in fetus
Hepatocellular carcinoma
testicular cancer
How is AFP used in the cancers?
diagnosing, staging, prognosis, monitoring
screen high risk populations (ethanol, hepatitis)
What type of protein is CEA?
Glycoprotein “Oncofetal protein”
CEA is the most widely used TM for what?
colorectal cancer
CEA can also be elevated in what?
non-malignant conditions: smokers, COPD, alcohol, hepatitis
lung, breast, GI cancer
How is CEA used?
prognosis, post surgery, response to chemo
What are the 3 cancers/diseases that HCG is used for?
ovarian
testicular
gestational trophoblastic
What are 65% of elevated ACTH patients seen with?
small cell carcinoma of lung “oat lung”
How does small cell carcinoma of the lung present on the patient?
Cushing syndrome: excess cortisol
What is the biomarker for prolactinoma?
Prolactin
What is the most common pituitary tumor?
Prolactinoma
Know TM with its cancer