Medical coding terms cha. 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Thel
Nipple
Epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue is a type of body tissue that covers the inside and outside of the body, and lines hollow organs and body cavities. It's made up of sheets of tightly packed cells that perform a variety of functions,
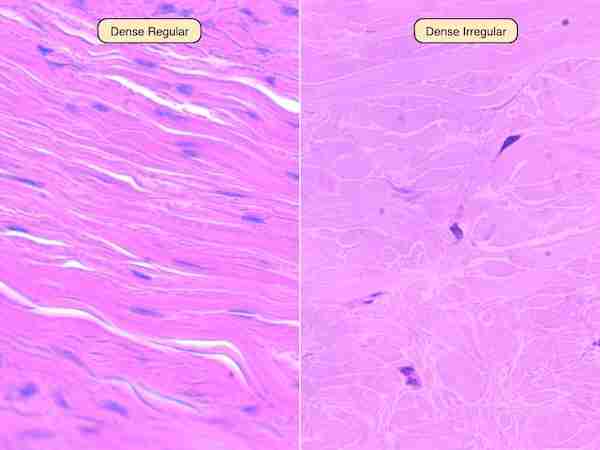
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is a type of tissue in the body that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs. It's made up of cells, fibers, and a gel-like substance called ground substance.
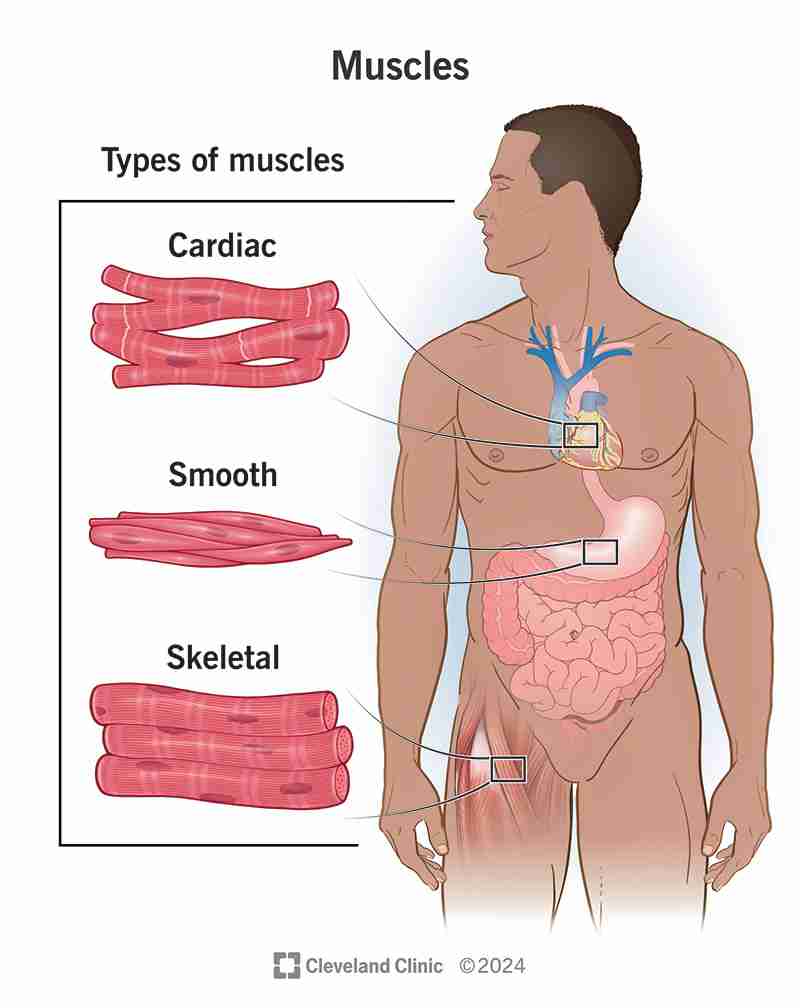
Muscle tissue
includes three types: heart muscle, skeletal muscle, and visceral muscle, all of which share the unique property of being able to contract and relax.
Chym/o
Juice
Stromal tissue
Stromal tissue is a type of tissue that supports and structures organs, glands, and other tissues in the body
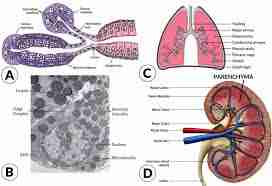
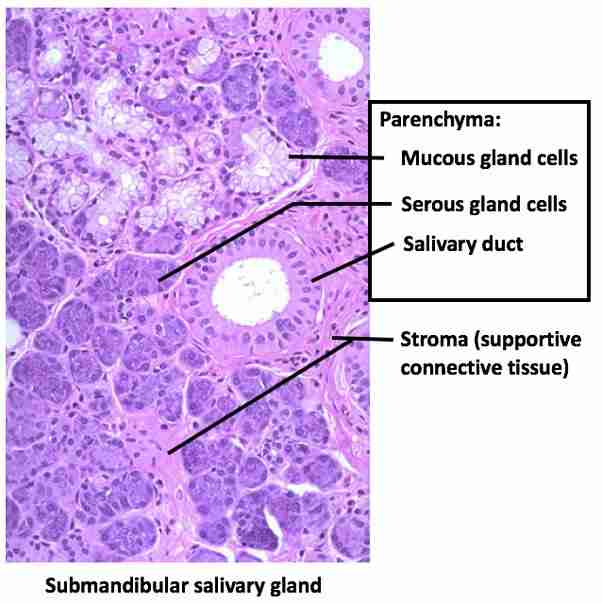
Parenchymal tissue
Parenchymal tissue" refers to the functional tissue within an organ, essentially the "working" part of the organ
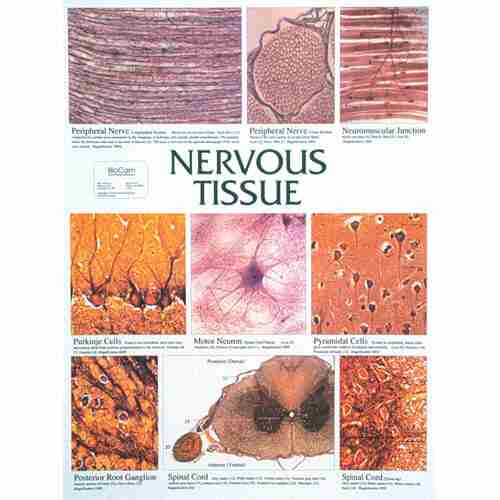
Nervous tissue
includes cells that provide transmission of information to regulate a variety of functions, for example, neurons (nerve cells). When tissue is destroyed by disease or trauma, the possibility of tissue replacement may be an option.
Autologous tissue
tissue is that which is taken from one part of an individual’s body and is transplanted to another location. Auto- means “self.” An example would be a vein that is used to bypass a blocked coronary
Allogeneic
allogeneic, this time referring to being produced by a different human being. All/o means “different.”
Zooplastic tissue
Zooplastic tissue is that which is derived from an animal, for example, a cow or pig heart valve that is used to temporarily replace a structure until human donor tissue is available. Zo/o means “animal.
Syngeneic tissue
f tissue is syngeneic, as in the case of identical twins, it refers to a genetically identical individual. Syn- means “together or joined,” as in the sharing of the same DNA. Synonyms for the term syngeneic are isoplastic, isogeneic, and isologous. The combining form is/o means “equal.
Viscera/viscus/organo
Organs
Intraluminal
existing, happening, or placed inside the esophagus
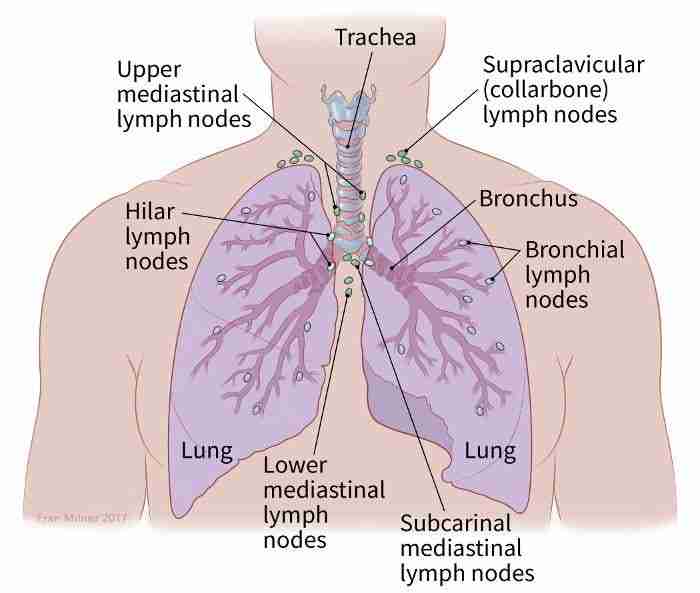
Hilar
the area where nerves and blood vessels attach to an organ
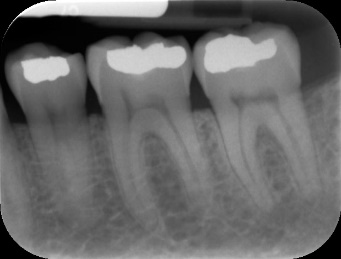
Periapical
Periapical periodontitis or apical periodontitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root
Antral
relating to or situated in a cavity or chamber, esp within a bone or the body.
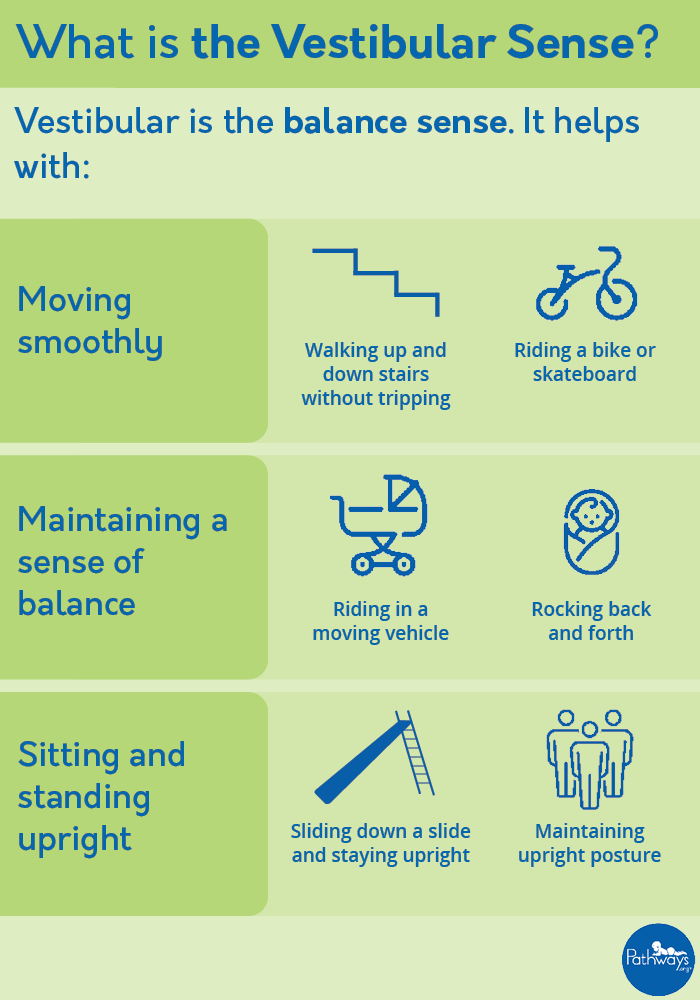
Vestibular
relating to a vestibule, particularly that of the inner ear, or more generally to the sense of balance.
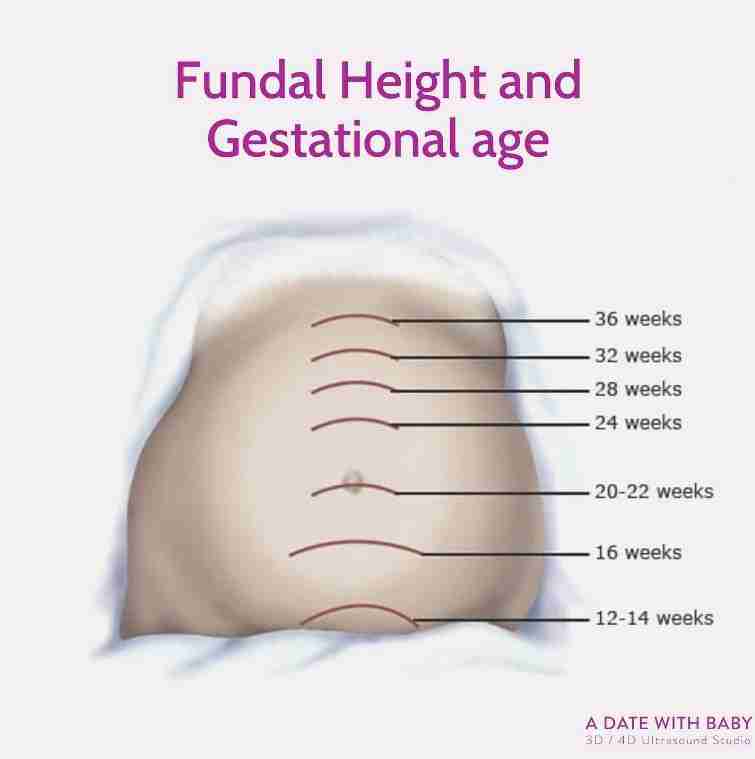
Fundal
Fundal height is the distance from the pubic bone to the top of the uterus measured in centimeters.
Cortical
relating to the outer layer of the cerebrum.
"the imaging of the brain showed cortical atrophy"
Myel/o
Spinal cord or bone marrow
Meta
Beyond, change
ia/ism
Condition/state of
On
Structure
Plasm
Formation
-some
Body
Stasis
Controlling, stopping
Um
Structure, thing, membrane
-us
Structure
Necropsy
A necropsy is a surgical examination of a dead body, most commonly a dead animal, in order to learn why the animal died
Histology
Study of tissues
Coxal
Hip
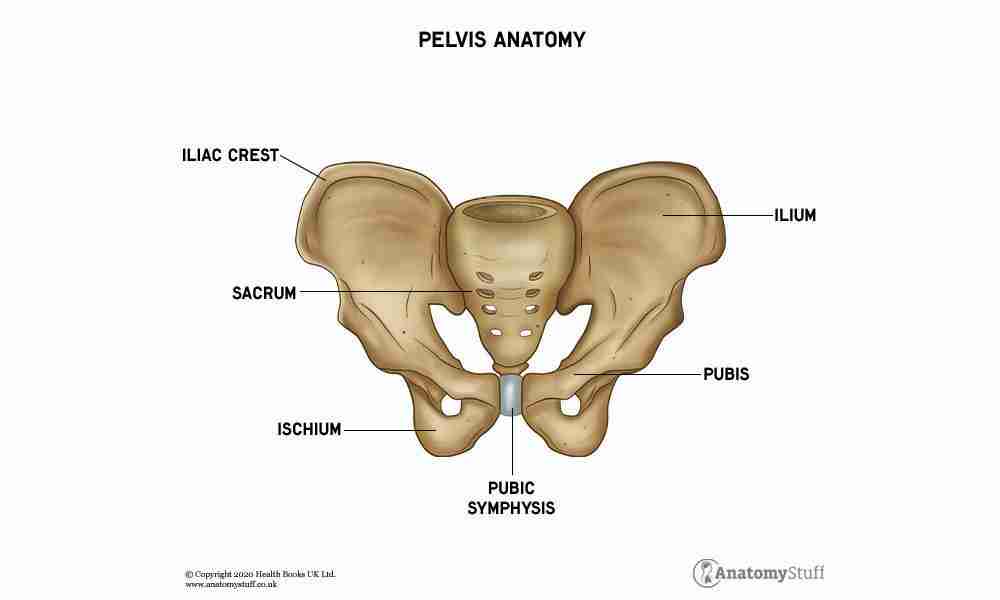
Pelvis
Middle part of body
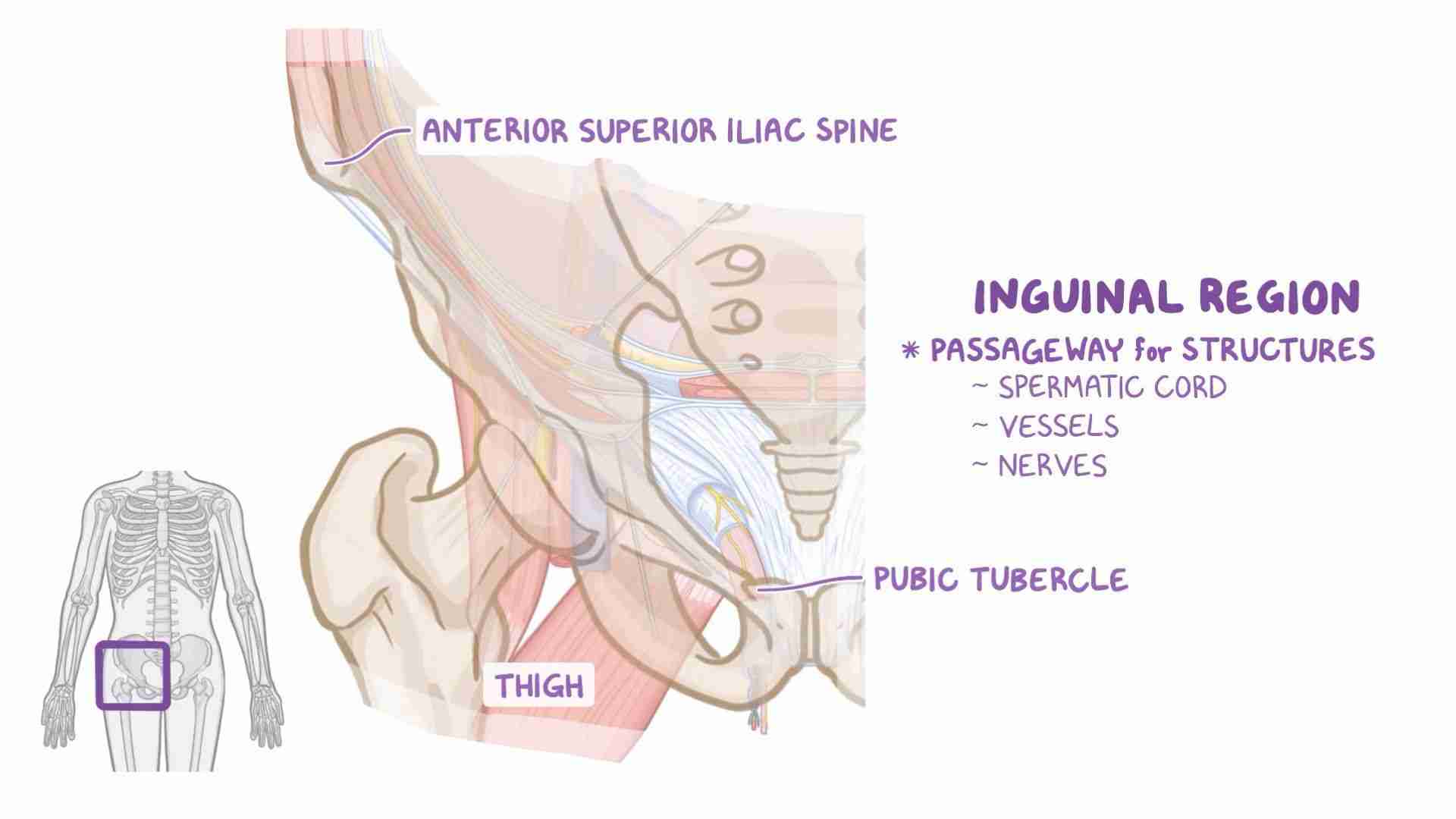
Inguinal
The inguinal region, also known as the groin, is a part of the lower anterior abdominal wall that's located between the thigh and the pubic tubercle:
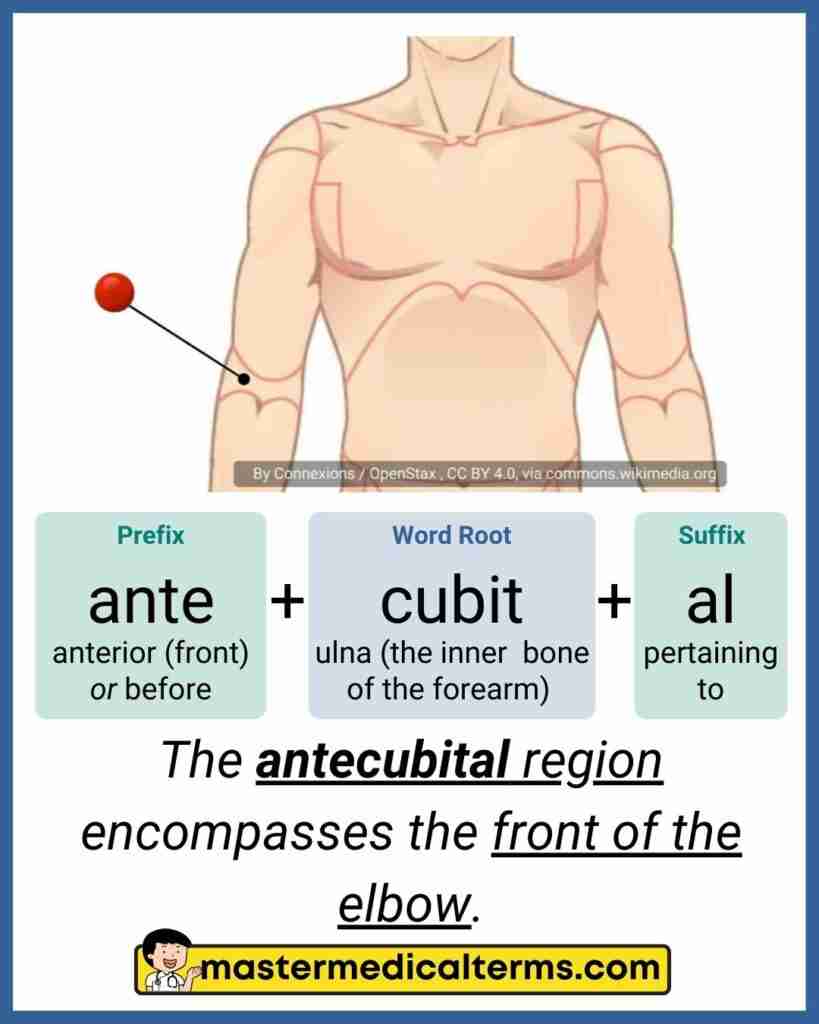
Antecubital
Front of forearm
Crural
Leg
Patellar
Kneecap
Man/o
Pressure
Man/u, man/i
Hand
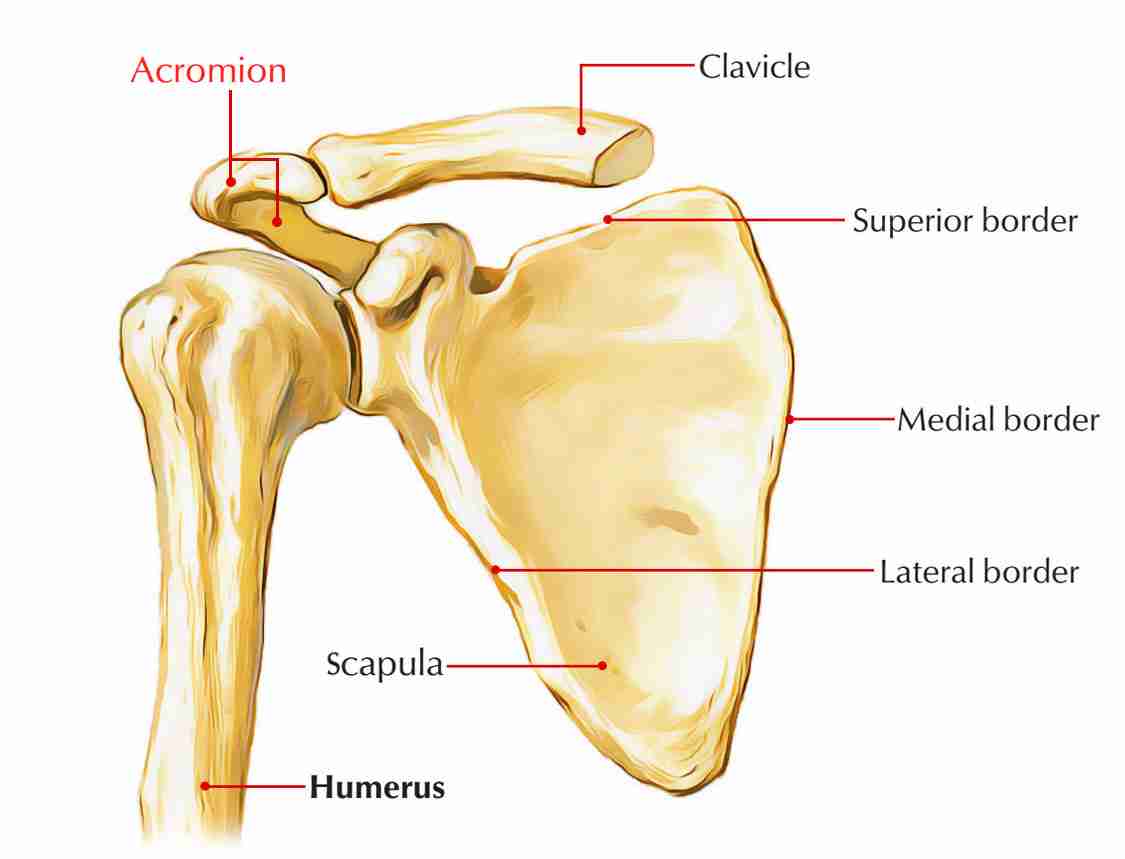
Acromion
High point on shoulder
Nuchal
Back of neck
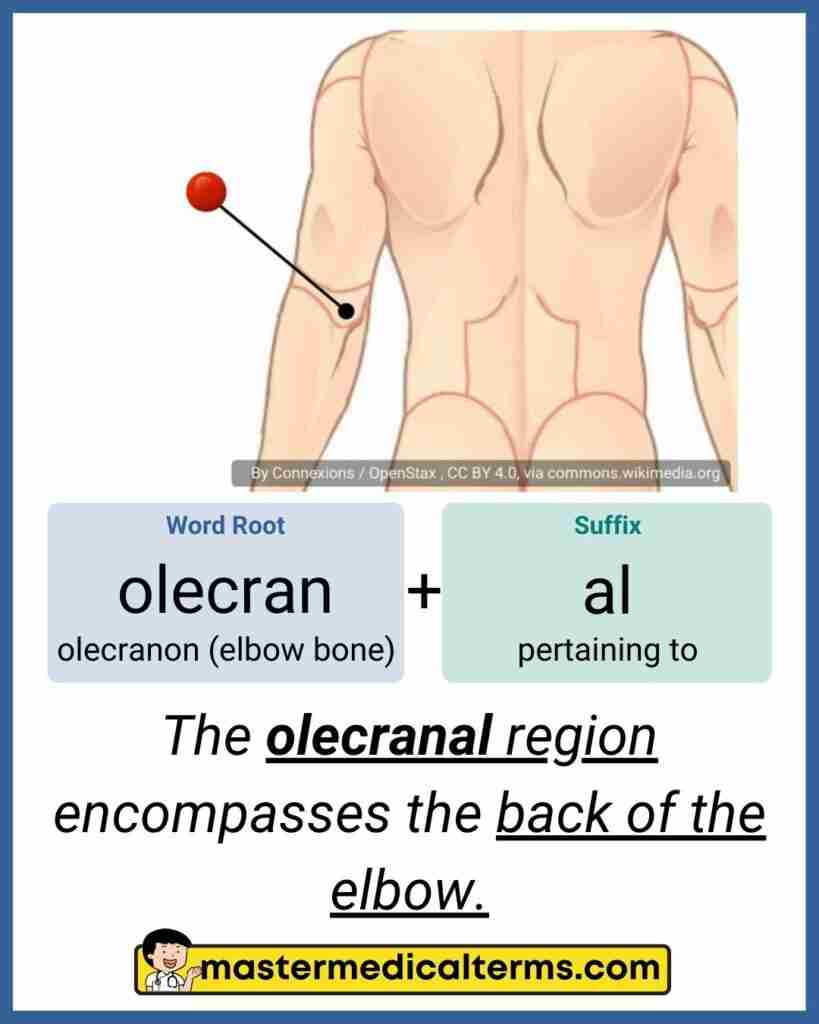
Olecranal
Back of elbow
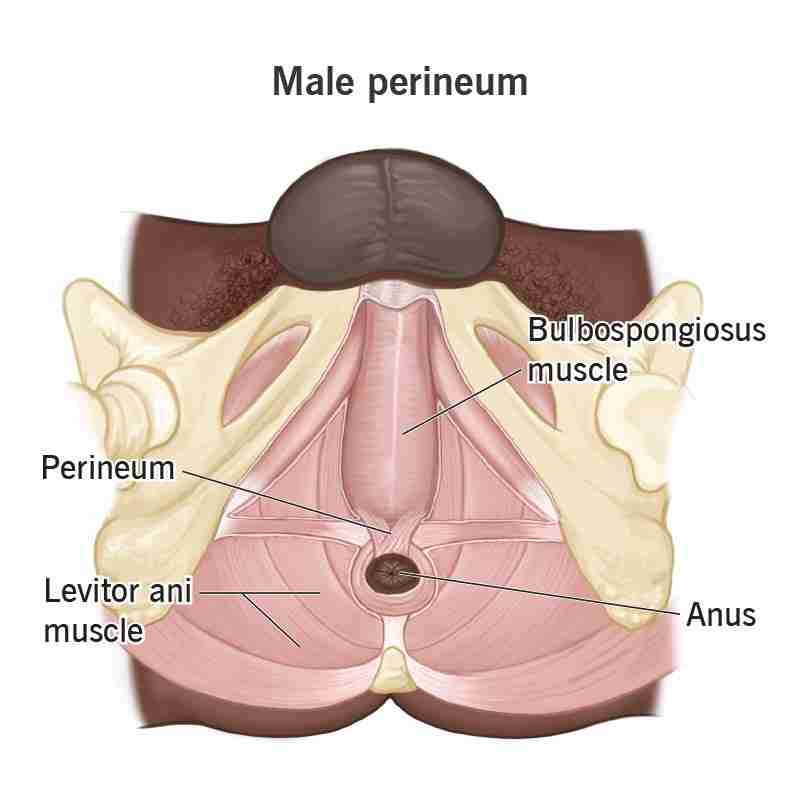
Perineal
The perineum is the space between the external genitalia and the anus
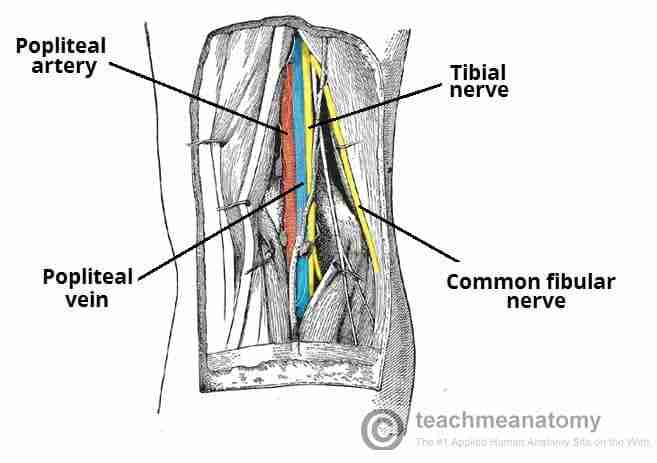
Popliteal
Back of knee
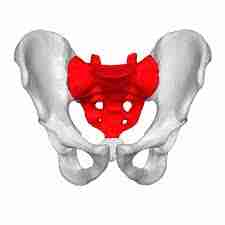
Sacrum
Sural
Calf
Lateral
To the right or left
Bilateral
Both the left and right sides
Antr/o
Cavity
Afferent
Towards
Efferent
Away
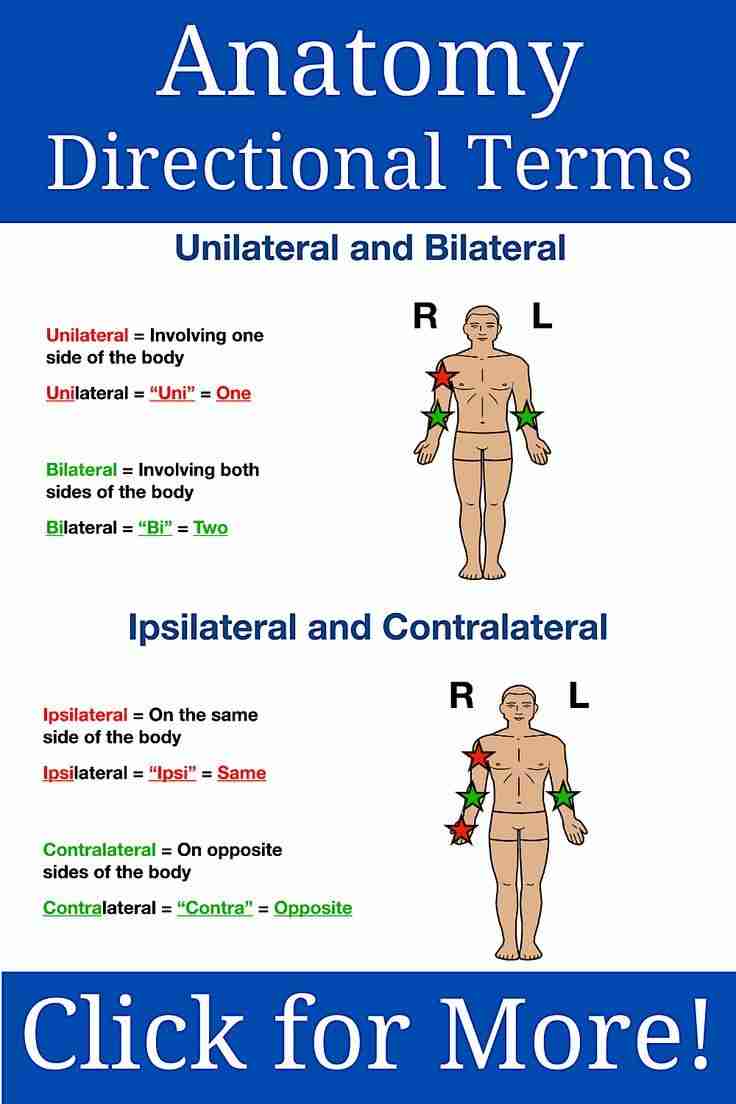
Contralateral
On the opposite side of another structure
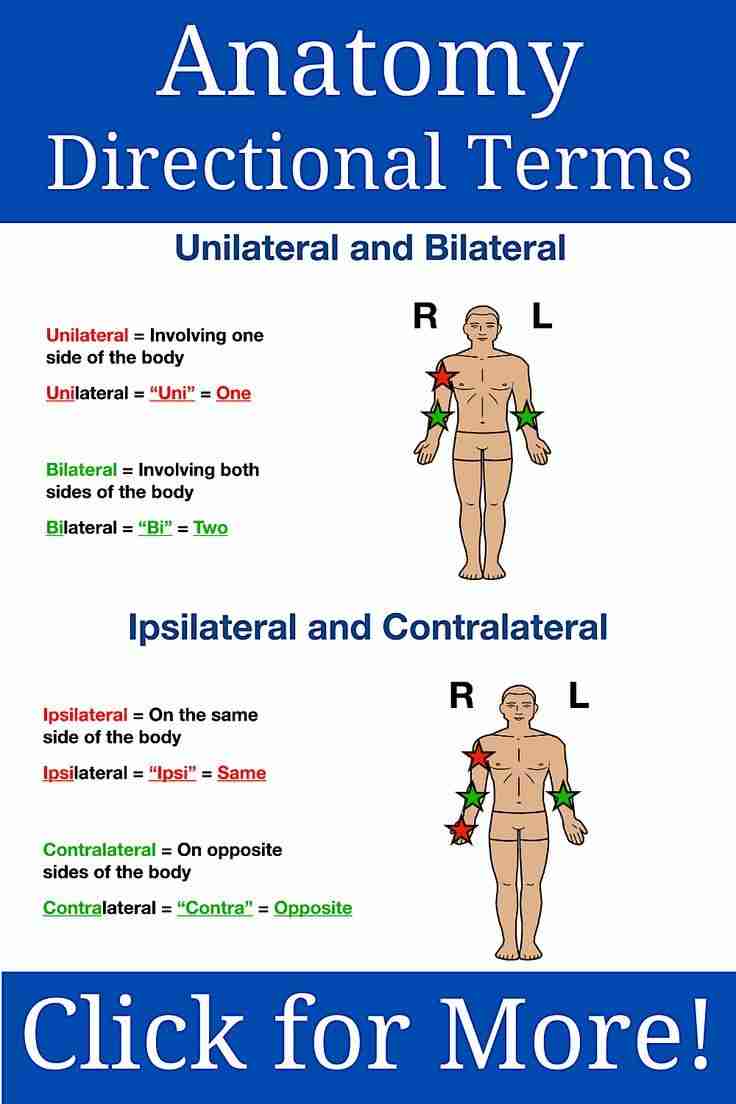
Ipsilateral
On the same side
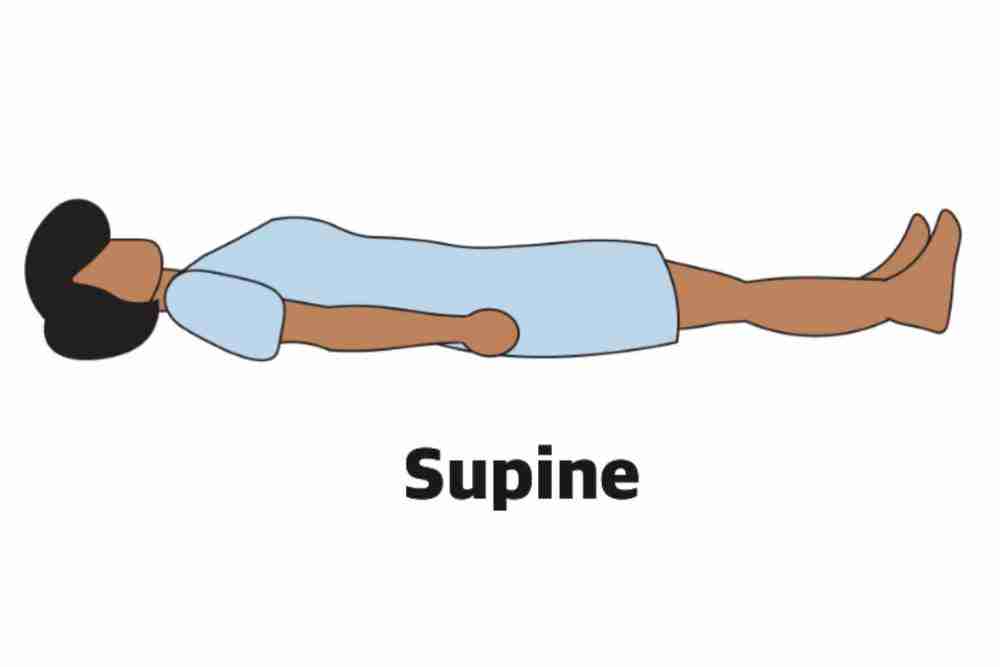
Supine
Lying on back
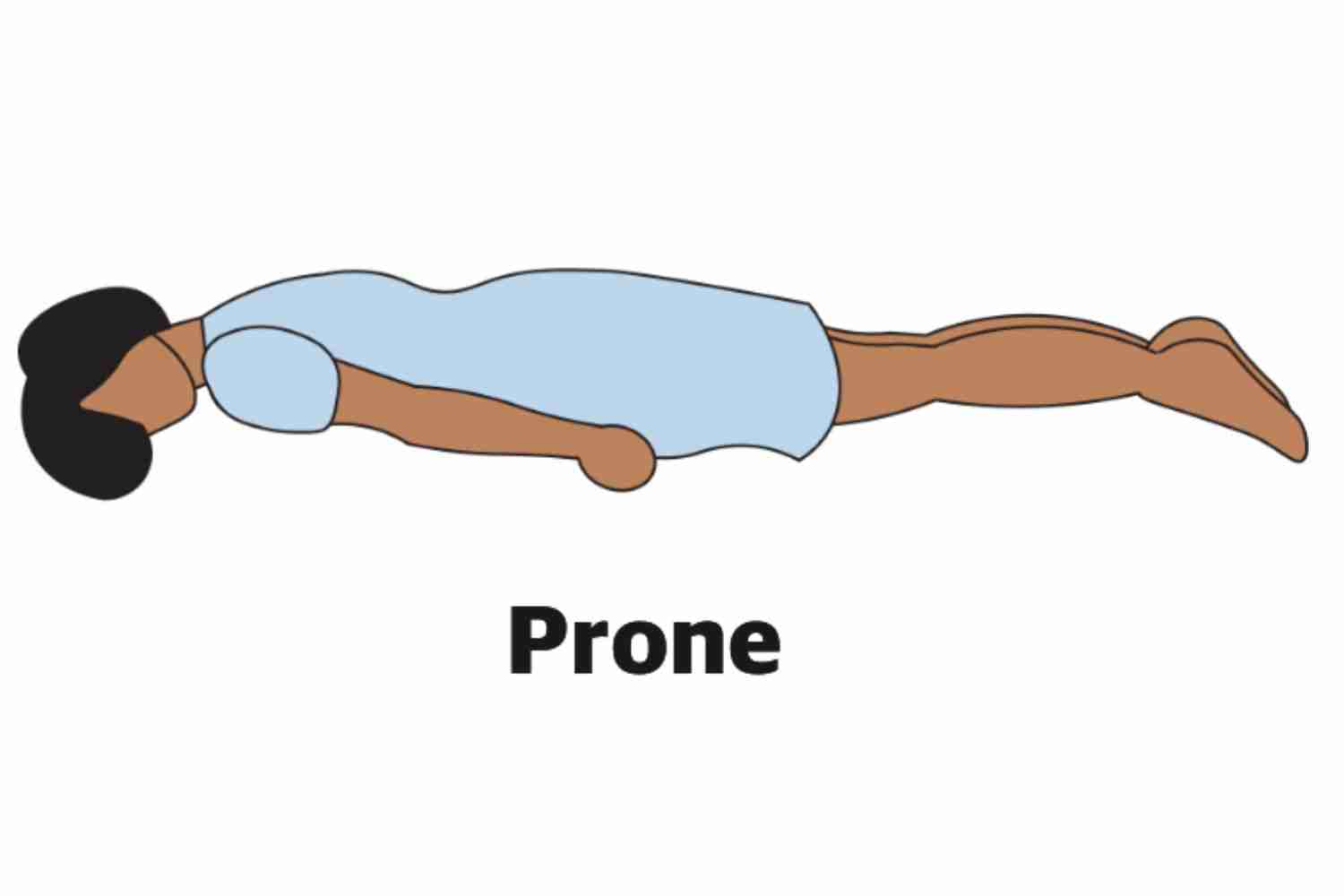
Prone
Lying on stomach
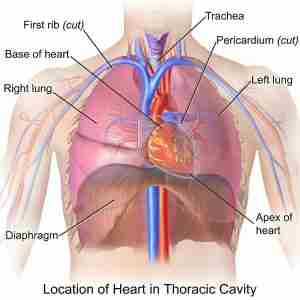
Thoracic cavity
Your thoracic cavity is a space in your chest that contains organs, blood vessels, nerves and other important body structures. It's divided into three main parts: right pleural cavity, left pleural cavity and mediastinum. The five organs in your thoracic cavity are your heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea and thymus.
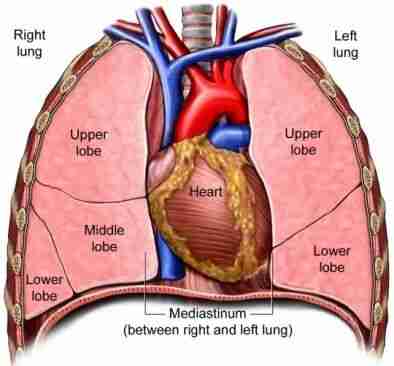
Mediastinum
Your mediastinum is a space in your chest that holds your heart and other important structures. It's the middle compartment within your thoracic cavity, nestled between your lungs.
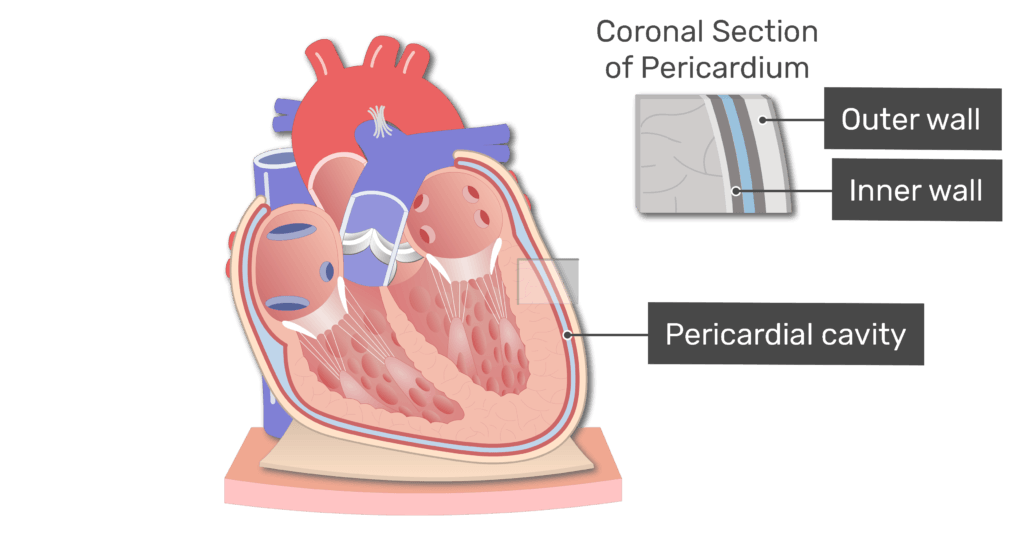
Pericardial cavity
The pericardial cavity is a fluid-filled space that surrounds the heart
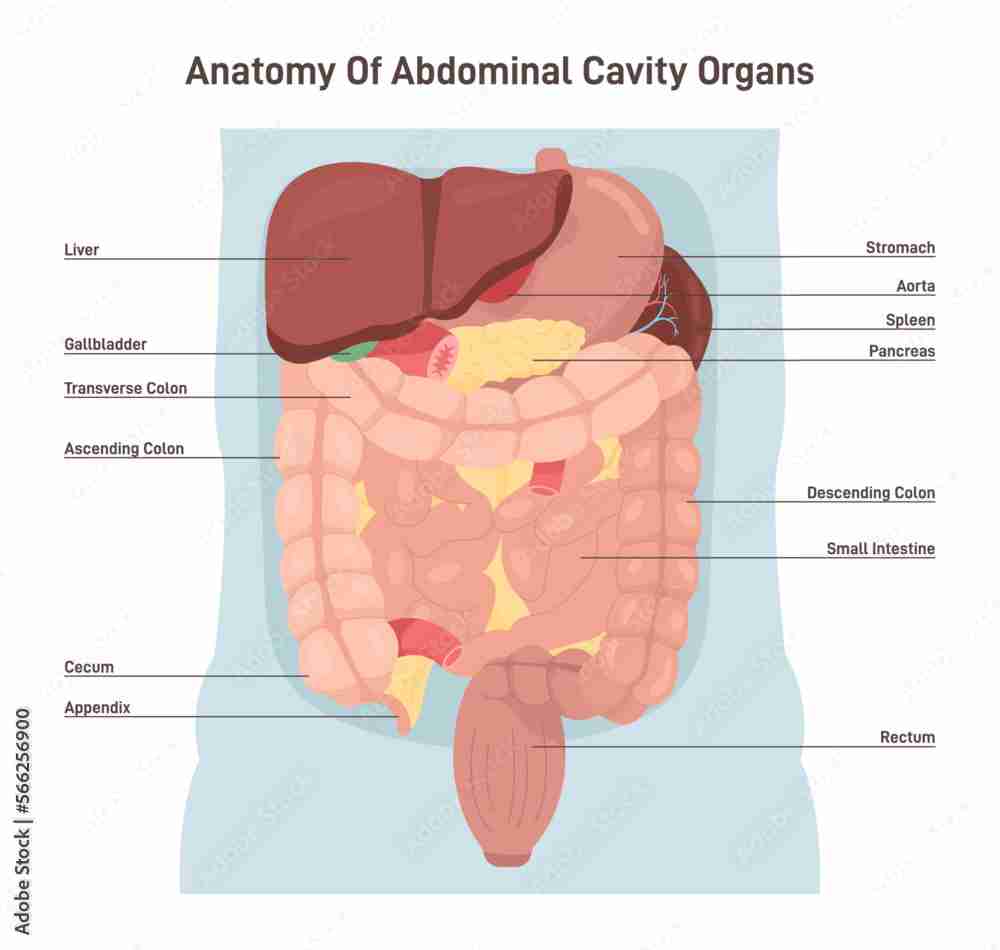
Abdominal cavity
a large, hollow space in the body that contains many organs, including the digestive tract, liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands.
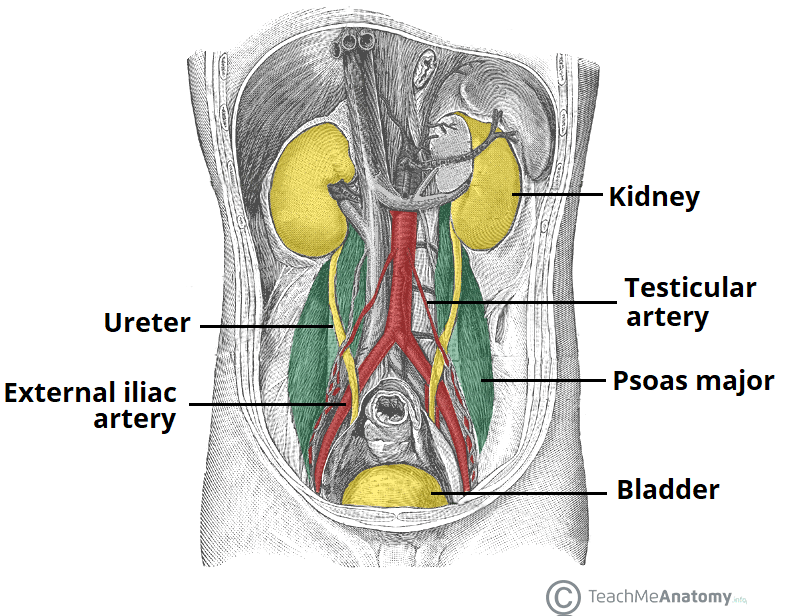
Pelvic cavity
The pelvic cavity is a bowl-shaped space in the body that contains the bladder, rectum, and part of the colon, as well as the internal reproductive organs:
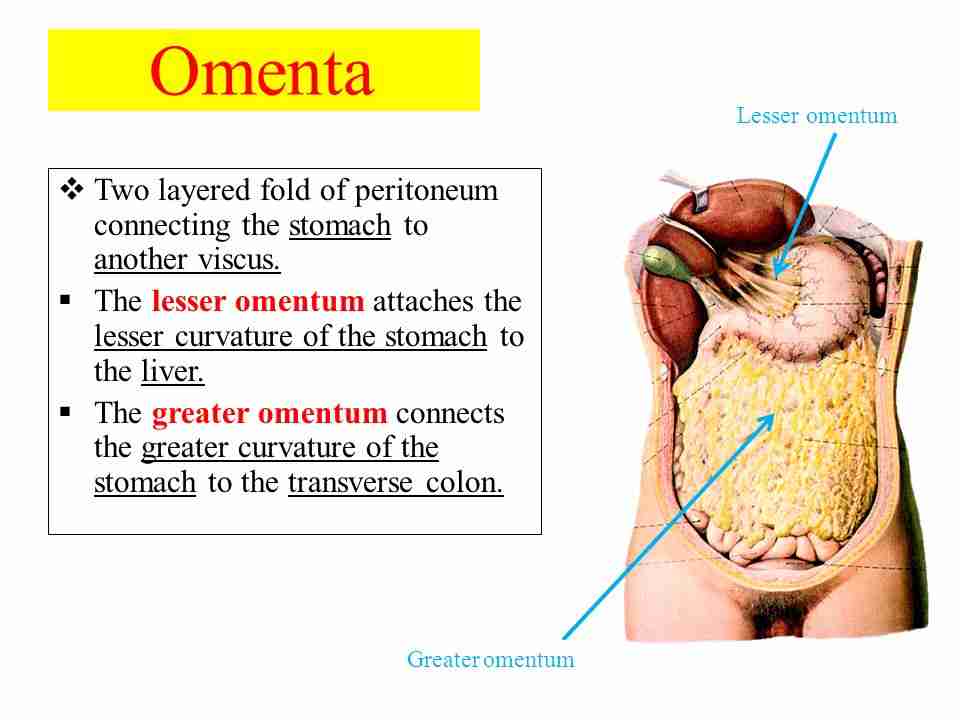
Omentum
the fatty tissue that starts in your stomach and drapes over your intestines.
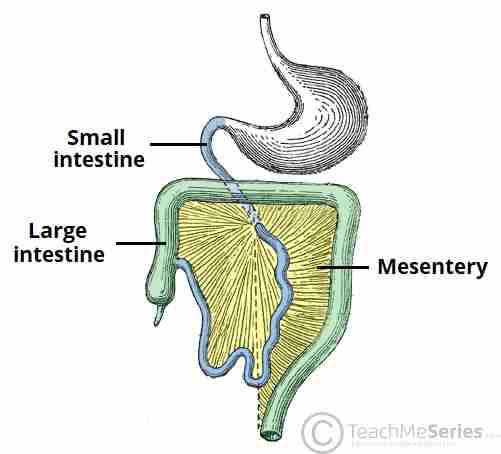
Mesentery
fold of membrane that attaches the intestine to the wall around the stomach area and holds it in place.
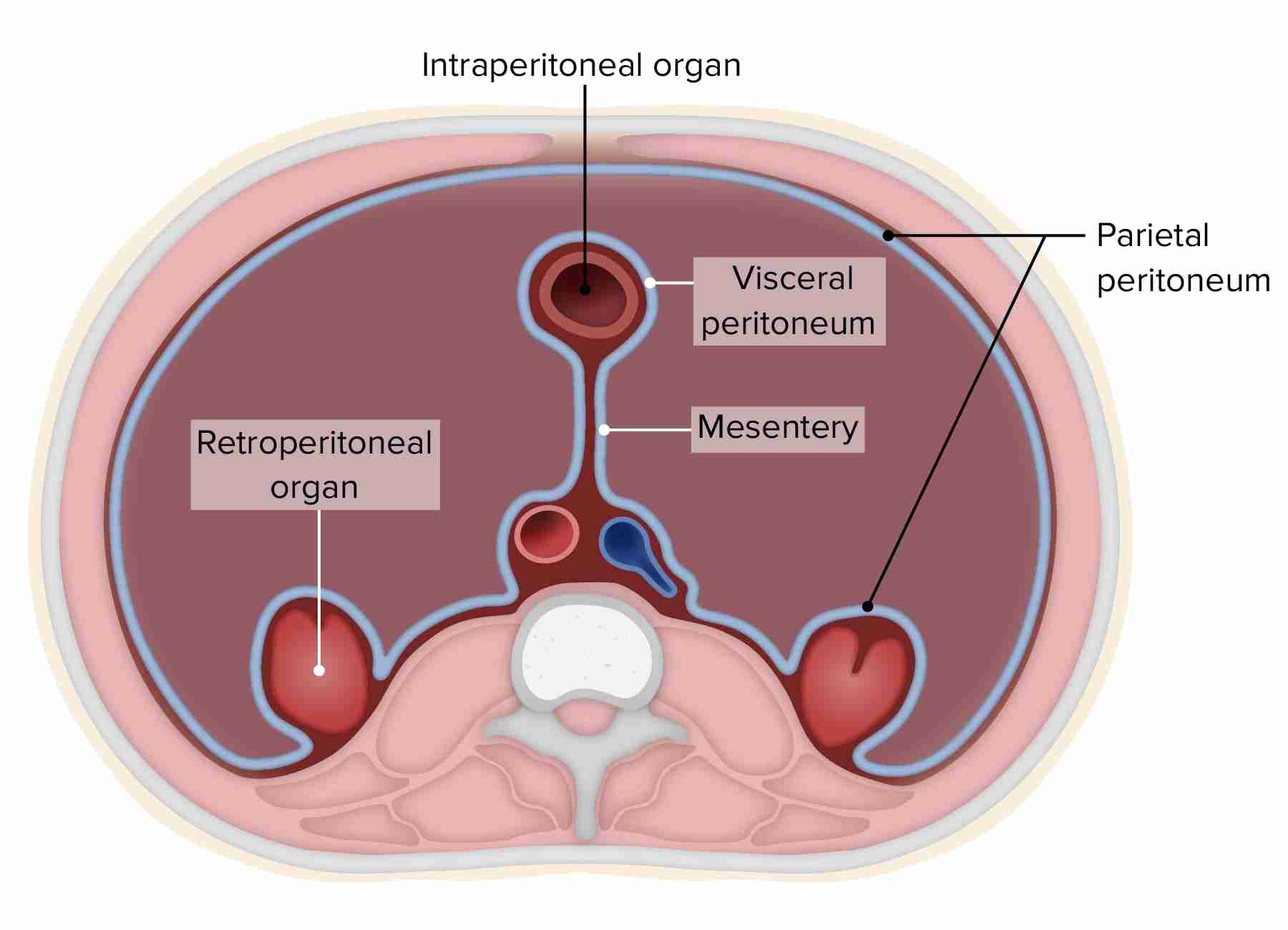
Retroperitoneum
the space behind the peritoneum that contains the kidneys, aorta, ureters, duodenum, and pancreas.
Retro
Behind, back
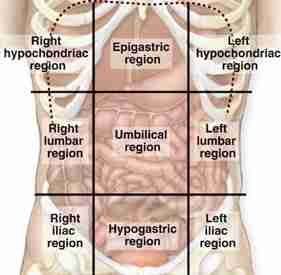
Hypochondriac regions
The hypochondriac regions are two areas in the upper abdomen, located on either side of the epigastric region:
Right hypochondriac region: Contains the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, and part of the small intestine
Left hypochondriac region: Contains the spleen, colon, left kidney, and part of the stomach
Epigastric regions
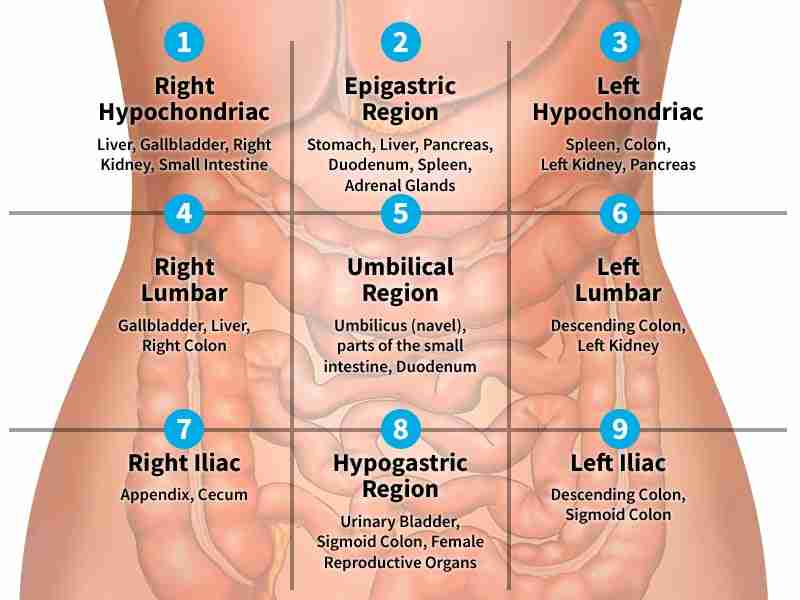
Hypogastric region
hypogastric region, also known as the pubic region, is the part of the abdomen below the stomach and between the two iliac regions:
The hypogastric region contains many organs, including:
Bladder
Part of the sigmoid colon
Anus
Uterus and ovaries in females
Prostate in males
Ductus deferens and seminal vesicles in males
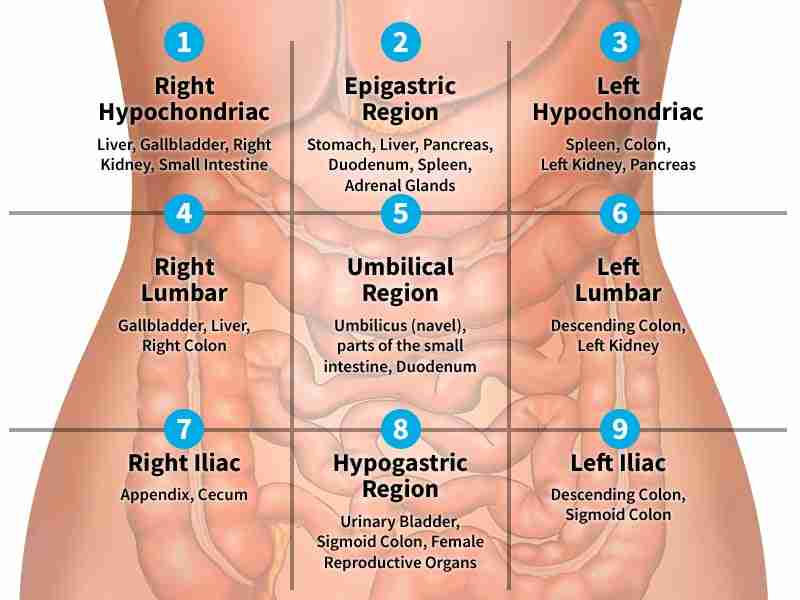
Iliac/ inguinal regions
the lower lateral abdominal region, also known as the groin or inguinal region:
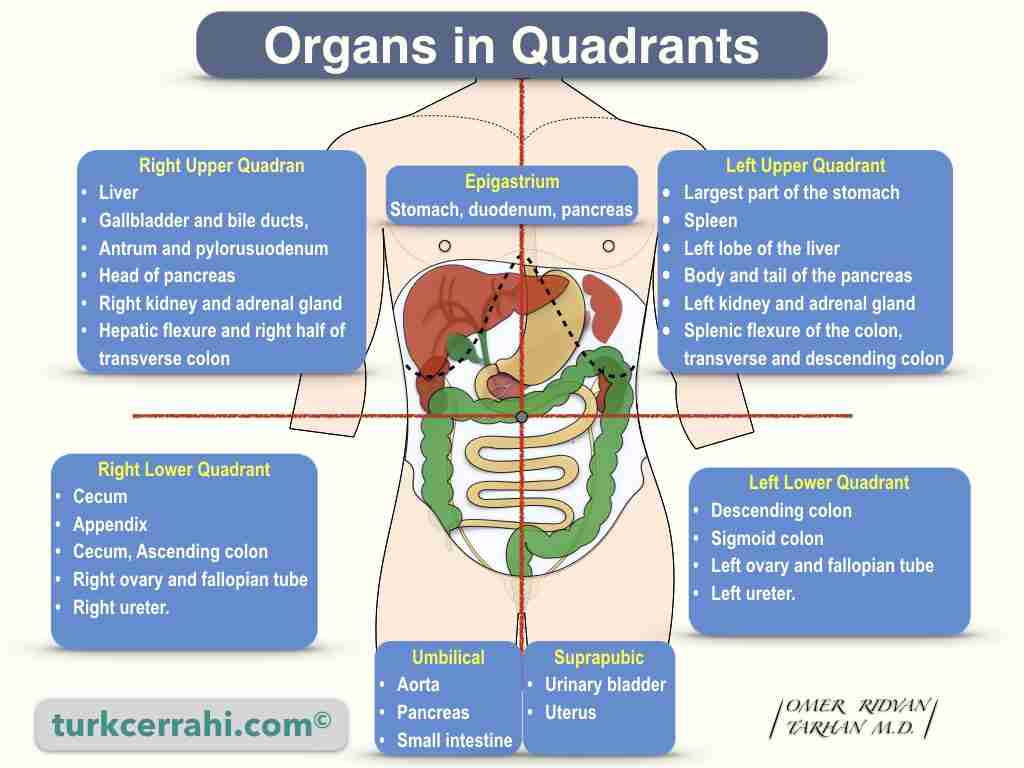
Abdominopelvic quadrants
See image
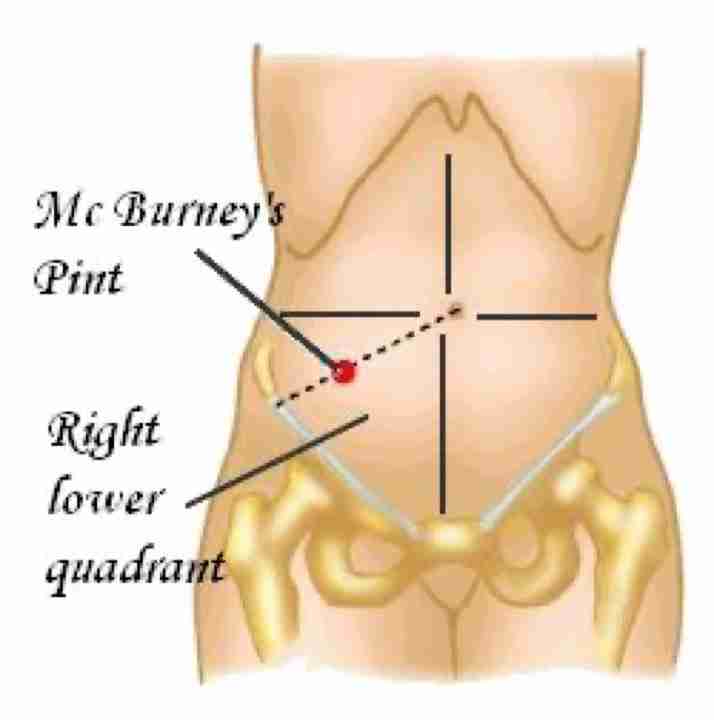
McBurneys point
Image
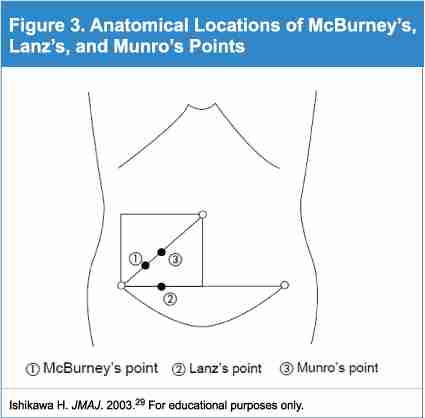
Munros point
This is a standard site of entrance for surgeons who perform laparoscopic surgery
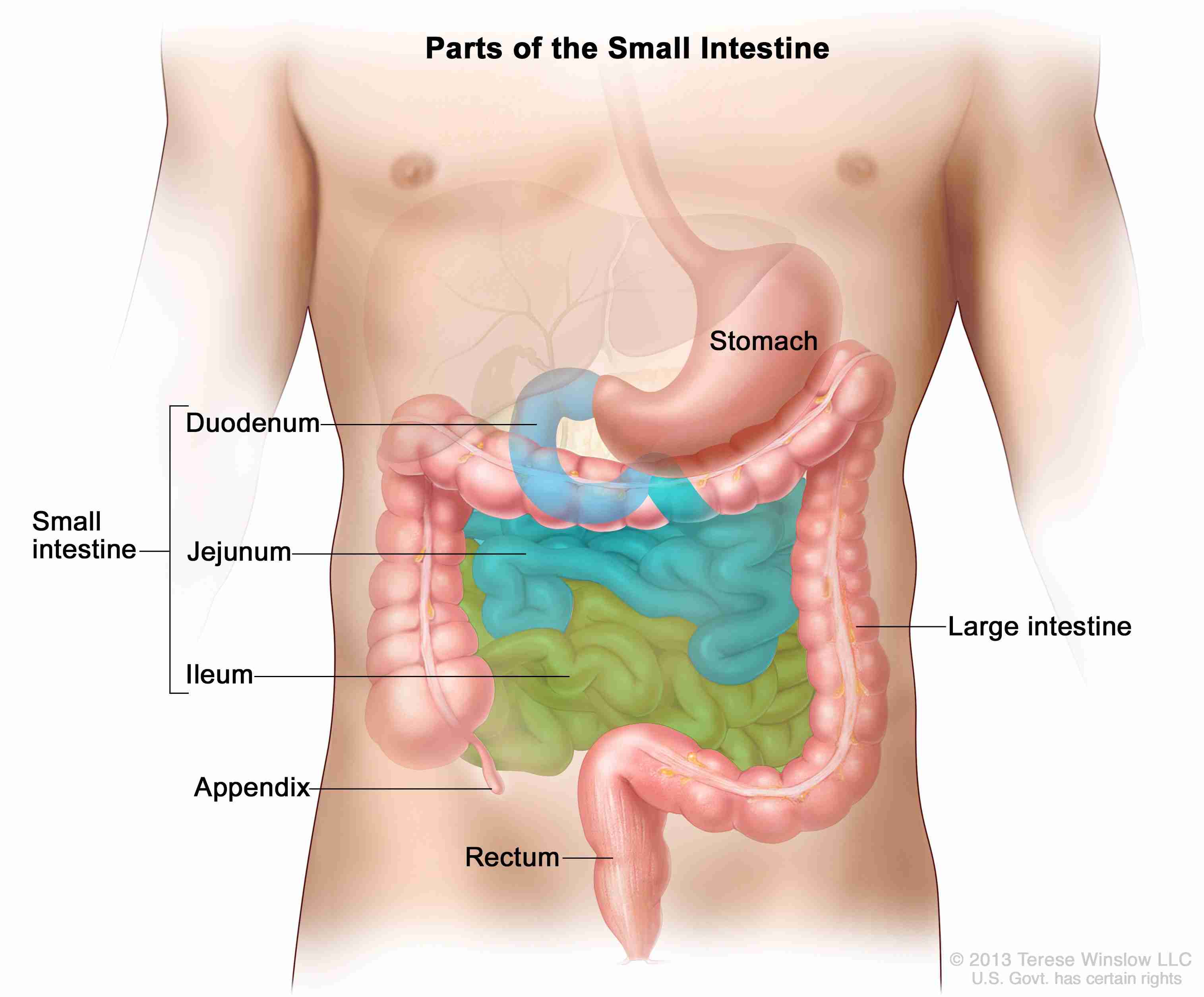
Ileum
The last part of the small intestine.
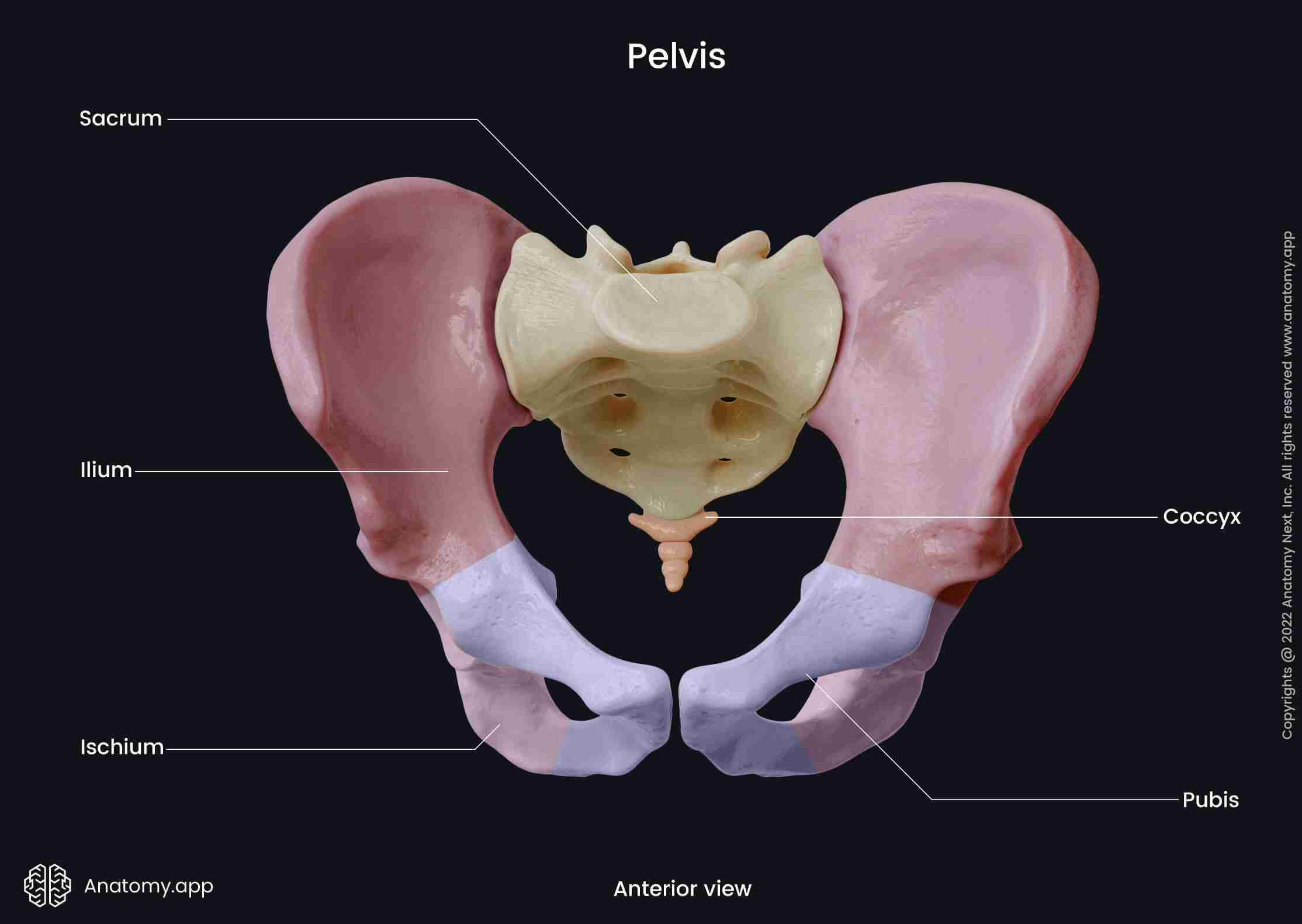
Ilium
makes up the upper portion of the hip bone and pelvis.
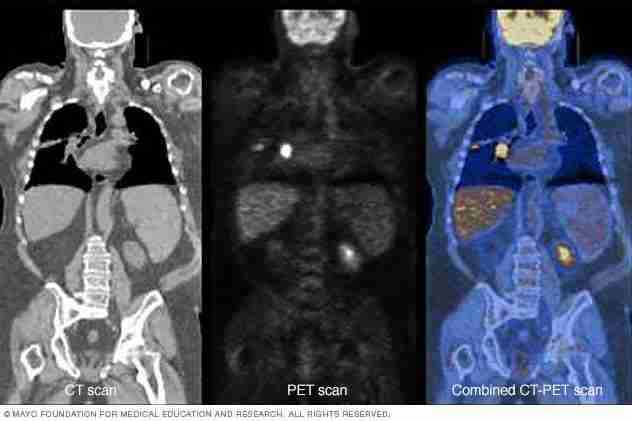
PET scan
PET scans are often used to diagnose or monitor conditions such as cancer, coronary artery disease, heart attack, brain disorders, and more.
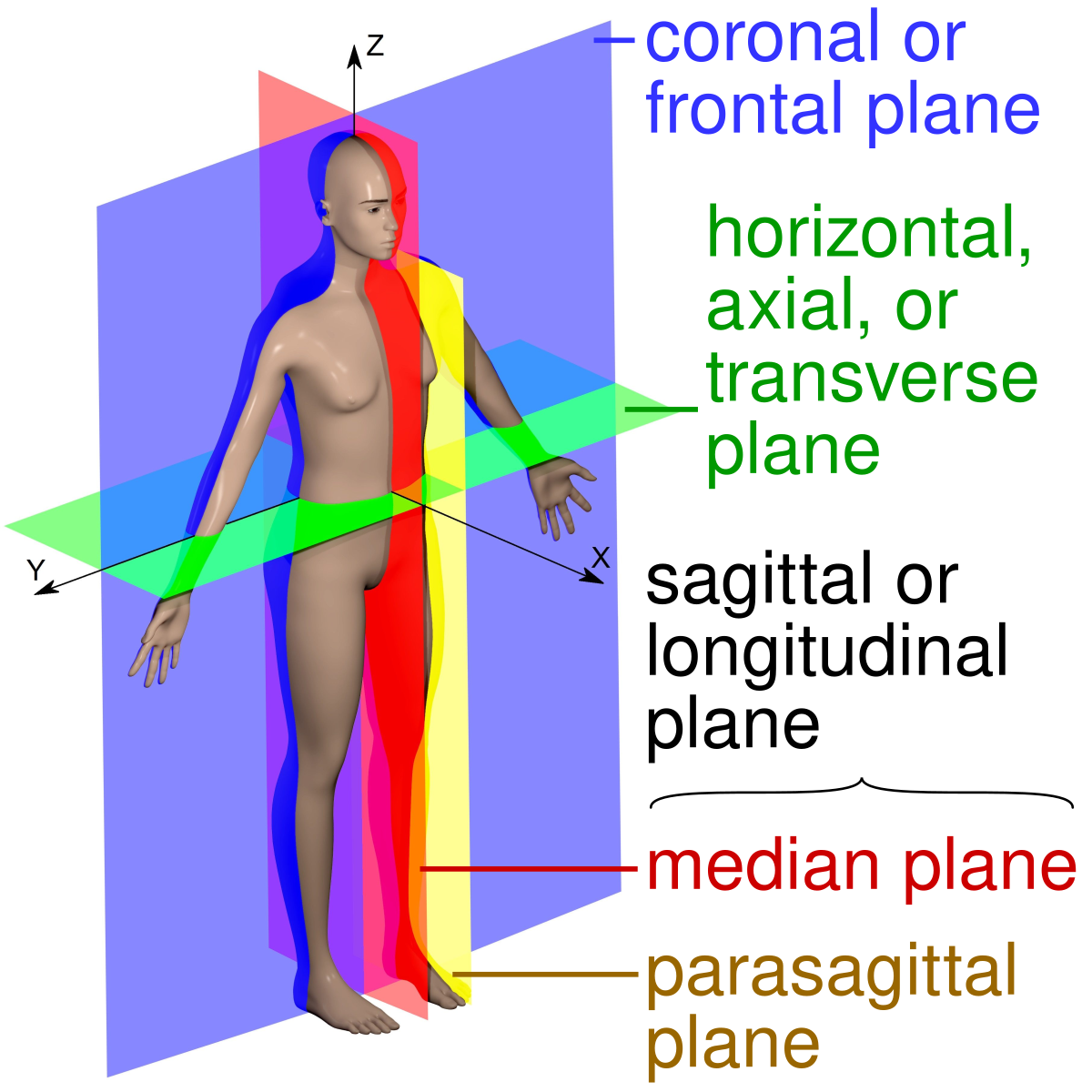
Anatomical planes
Transverse axial plane: separates into superior and inferior
Coronal frontal plane: separates anterior and posterior
Sagittal longitudal: separates left and right sides
Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition ant anterior AP anteroposterior CT computed tomography inf inferior lat lateral LLQ left lower quadrant LUQ left upper quadrant MRI magnetic resonance imaging PA posteroanterior
Abbreviations
PET positron emission tomography pos posterior RLQ right lower quadrant RUQ right upper quadrant sup superior
Dextro
On the right
Levo
To the left
Ipsi
Same, self