chol
1/348
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
349 Terms
Endocrine system
The body system that secretes hormones into the bloodstream to regulate metabolism, growth, development, and other long-distance processes.
Hormone
A chemical messenger produced by endocrine cells that is secreted in the blood to distant target cells with specific receptors.
Autocrine
Signaling where the secreted molecule acts on the same cell that produced it. (same hormone bind to the same cell)
Paracrine
Signaling where the secreted molecule affects nearby cells within the same tissue. (ex: pancreas - insulin release)
Autocrine vs Paracrine
Autocrine acts on the secreting cell; paracrine acts on neighboring cells.
Endocrine gland
A ductless gland that releases hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Exocrine gland
A gland that secretes products onto surfaces or into cavities via ducts. (smelly and sebaceous)
Neuroendocrine organ
An organ containing nervous tissue that produces hormones (e.g., hypothalamus).
Hypothalamus
The brain region that links nervous and endocrine systems and regulates pituitary function.
Boss (nickname for hypothalamus)
Informal term describing the hypothalamus because it controls many cellular processes via pituitary signaling.
Pituitary gland
The master endocrine gland; releasing hormones that regulate other glands, controlled by hypothalamic signals.
Anterior pituitary
The glandular part of the pituitary that synthesizes and releases tropic and other hormones.
Posterior pituitary
The neural part of the pituitary that stores and releases hormones made in the hypothalamus (ADH, oxytocin).
Adrenal cortex
Outer region of the adrenal gland; produces corticosteroids.
Adrenal medulla
Inner region of the adrenal gland; secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine).
Thyroid gland
Gland that produces thyroid hormones (T3/T4) regulating metabolic rate.
Parathyroid glands
Small glands posterior to the thyroid that secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulating calcium.
Pineal gland
Small gland producing melatonin and regulating circadian rhythms.
Pancreas (islets)
Endocrine tissue producing insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose.
Hormone receptor
A protein that binds its specific hormone to elicit a cellular response.
Water-soluble hormone
Hydrophilic hormones that cannot cross the plasma membrane and act on surface receptors and second messengers. Coupled via g-proteins to second messengers
Lipid-soluble hormone
Hydrophobic hormones that diffuse through the plasma membrane and bind intracellular receptors to regulate gene expression.
Amino acid-based hormone
Hormones derived from amino acids; typically water-soluble (with exceptions like thyroid hormones).
Lipid-soluble hormones derived from cholesterol; diffuse into cells and regulate gene transcription.
Lipid-soluble hormones derived from cholesterol; diffuse into cells and regulate gene transcription.
Biogenic amines
Hormones derived from tyrosine or tryptophan; often catecholamines; typically water-soluble.
Prostaglandins (autocrine)
Autocrine lipid mediators derived from arachidonic acid that act on the secreting cell or nearby cells.
Histamine (paracrine example)
Paracrine mediator affecting nearby cells such as parietal cells to regulate acid secretion.
Intracellular receptor
Receptor located inside the cell that binds lipid-soluble hormones and modulates gene expression.
Plasma membrane receptor
Receptor on the cell surface that binds water-soluble hormones to activate second messenger pathways.
Second messenger
A small intracellular molecule that relays and amplifies signals from receptors.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
A second messenger produced by adenylyl cyclase that activates protein kinases.
G protein
A heterotrimeric GTP-binding protein that couples receptors to effector enzymes.
Gs protein
Stimulatory G protein that increases adenylyl cyclase activity and cAMP production.
Gi protein
Inhibitory G protein that decreases adenylyl cyclase activity and cAMP production.
Gq protein
G protein that activates phospholipase C, elevating DAG and IP3.
Adenylyl cyclase
Enzyme converting ATP to cyclic AMP in the cAMP signaling pathway.
Phospholipase C
Enzyme cleaving PIP2 into DAG and IP3 to trigger PKC activation and Ca2+ release.
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Lipid second messenger that activates protein kinase C.
Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
Second messenger that triggers Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum.
Protein kinase C (PKC)
Kinases activated by DAG that phosphorylate target proteins to propagate signals.
Calcium (Ca2+) as second messenger
Calcium ions act as intracellular second messengers affecting various cellular processes.
Tyrosine kinase receptor
Receptor with intrinsic kinase activity that autophosphorylates and activates signaling (e.g., insulin receptor).
Insulin receptor
Is a tyrosine kinase enzyme that binds insulin and initiates signaling for glucose uptake.
Insulin
Pancreatic hormone that lowers blood glucose by promoting cellular uptake and storage of glucose.
Diabetes mellitus
Chronic disease with high blood glucose due to insulin deficiency or insulin resistance.
Hyposecretion
Reduced or insufficient secretion of a hormone.
Hyperactivity
Excessive or heightened hormone production or action.
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Cardiac hormone that reduces blood volume and pressure by promoting salt and water excretion.
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Kidney-produced hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
Leptin
Adipose-derived hormone that regulates appetite and energy balance.
Why should you understand the endocrine system?
enables you to monitor & advise patients with diseases such as diabetes mellitus.
the nervous system
Endocrine system acts with "____________” to regulate major processes
growth & development, reproduction, maintenance of electrolyte, water & nutrient balance of blood, regulation of cellular metabolism, mobilization of body defenses
Examples of metabolic activities via hormones (controls and integrates)
Target cells
Include most body cells and have receptors for a specific hormone
produce a response
Cells that do not have a receptor or hormone, is not a target cell will NOT _____
Nervous System
System that has a direct connection, effect is local and specific
Endocrine System
System has a long duration of responses, the effect is general and widespread
Gland
A specialized cell, groups of cells, or an organ of “epithelial origin” that secretes a product = a secretion
yes
can a gland be an organ?
no (hypothamalus - made up of nervous tissue)
are all organs gland?
saliva, sweat
“Extracellular effects” (nonhormonal)
Pancreas, gonads (ovaries & testes) & placenta
Organs that contain “endocrine tissue”
stomach, heart, kidneys, small intestine
Other tissues and organs that produce hormones are adipose cells, thymus and cells in the “walls” of the ______
possible 3rd class. not classified as hormones because they ahve short distance signals
Autocrine examples
Prostaglandins and smooth muscle
Gonadal & adrenocortical hormones
Steroids (lipid-soluble hormones) synthesized from cholesterol and the main places where you find them is the
.
Summary of Hormones by Chemical class
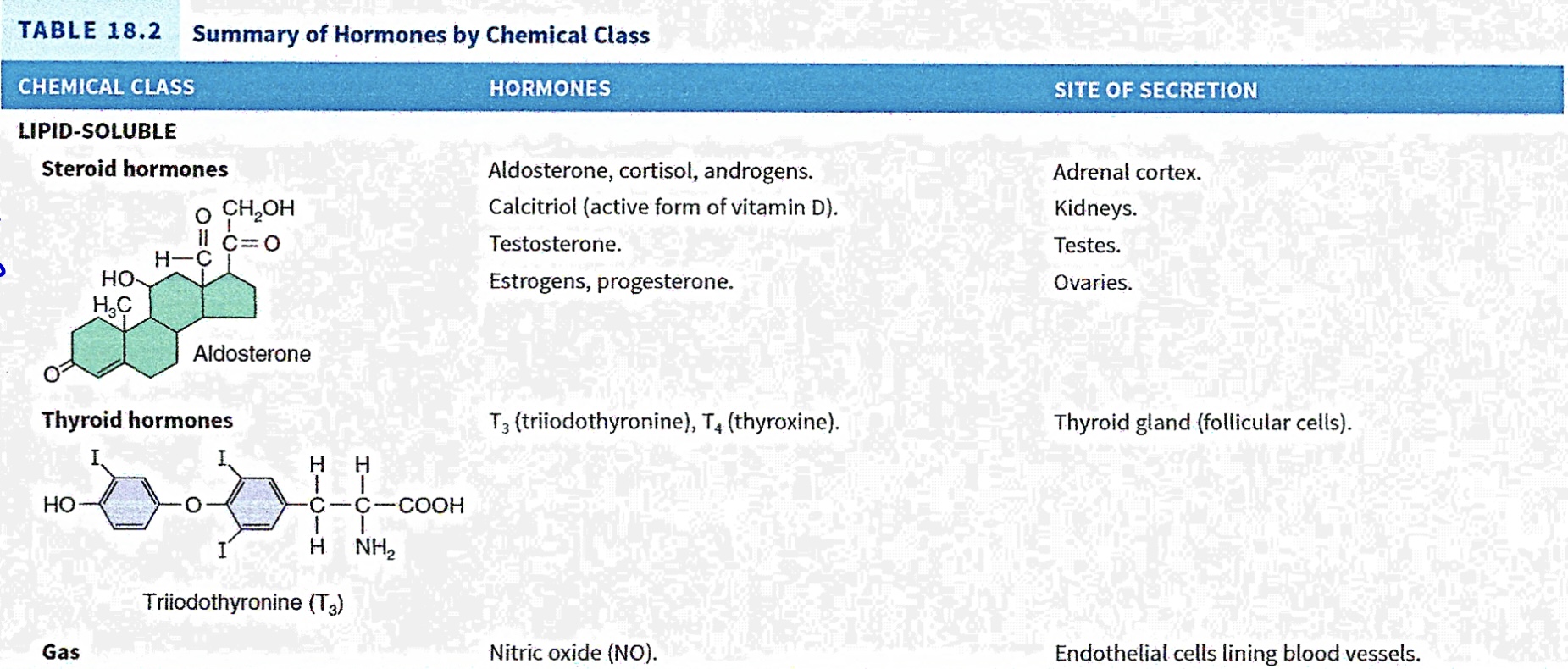
Calcitriol (active form of vitamin D)
Name lipid soluble hormone (Secreted in Kidney)
Testosterone
Name lipid soluble hormone (Secreted in Testes)
Estrogens, Progesterone
Name lipid soluble hormone ( Secreted in ovaries)
Aldosterone, cortisol, androgens
Name lipid soluble hormones (Secreted in adrenal cortex)
T3 (triiodothyronine), T4 (thyroxine)
Name lipid soluble hormones (secreted in thyroid gland) (follicular cells)
target cell type
Hormone action increases or decreases “normal cellular processes” of the target cell. response depends on ____
Lipid-soluble hormones (lipophilic)
Act on intracellular receptors that directly activate genes - induce protein synthesis (can enter cells)
whether the hormonal molecule is hydrophobic or hydrophilic
A major determinant of a hormones mechanism of action is
DAG (Diacylgycerol) & IP3 (Inositol triphosphate)
PIP2 involves G-protein (Gq) and Phospholipase C (PLC) PLC is a membrane-bound effector enzyme that splits PIP2 (phosphatidyl inositol biphosphate) into two messengers: ______ and _____
Insulin receptor
is a tyrosine kinase enzyme (receptor-enzyme) (ex: growth factors, insulin)
Chemical signaling
A chemical messenger (hormone, neurotransmitter, or drug) that binds to a receptor to initiate a cellular response.
Receptor
A binding site—often a protein—that recognizes and binds a specific ligand to trigger signal transduction.
Ligand-receptor complex
The bound form of ligand and receptor that activates downstream cellular responses.
Second messenger
Intracellular chemical that relays signals from membrane receptors to intracellular targets (e.g., cAMP, DAG, IP3, Ca2+).
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; a common second messenger produced by many receptor pathways.
DAG
Diacylglycerol; second messenger produced from PIP2 that activates protein kinase C.
IP3
Inositol triphosphate; second messenger that triggers Ca2+ release from intracellular stores.
Ca2+
Calcium ion; versatile second messenger in many signaling pathways.
PIP2
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; plasma membrane lipid cleaved to yield DAG and IP3.
Lipid-soluble hormone
Hormone that can diffuse through the plasma membrane and binds intracellular receptors.
Intracellular receptor
Receptor located inside the cell; binds lipid-soluble hormones to regulate gene activity.
Receptor enzyme
An enzyme-linked receptor; hormone binding activates the receptor’s enzymatic activity (e.g., tyrosine kinase).
Tyrosine kinase pathway
Signaling cascade activated by receptor tyrosine kinases that phosphorylate substrates to propagate the signal.
Phosphorylation
Addition of a phosphate group to a protein, often activating signaling proteins.
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
Membrane receptor that activates G proteins to modulate second messenger systems.
Promoter region
DNA region upstream of a gene where transcription factors bind to regulate transcription.
Hormone response element (HRE)
DNA sequence in a gene promoter recognized by hormone-receptor complexes to control transcription.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing messenger RNA from DNA.
Translation
Process of protein synthesis from mRNA at ribosomes.
Upregulation
Increase in receptor density on a cell in response to low hormone levels, increasing sensitivity.
Downregulation
Decrease in receptor density in response to high hormone levels, reducing sensitivity.
Affinity
Strength of binding between receptor and its ligand; high affinity means greater receptor occupancy.