L28 Motor Control and Disease I (Imported from Quizlet)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Spinal motor, spinal sensory
Simple reflexes involve local circuit control of _________ ________ neurones by __________ _______ neurones
Lower motor neurons
All movements produced by the skeletal musculature are initiated by ...?
Central pattern generators
The spinal cord contains _________ ________ ____________ that generate complex behaviours without input from the brain
Muscle movement
What does stimulation of motor cortex elicit?
That electrical stimulation of part of the cortex elicits contraction of contralateral body muscles
When did Fritsch and Hitzig demonstrate (using dogs) in 1870s?
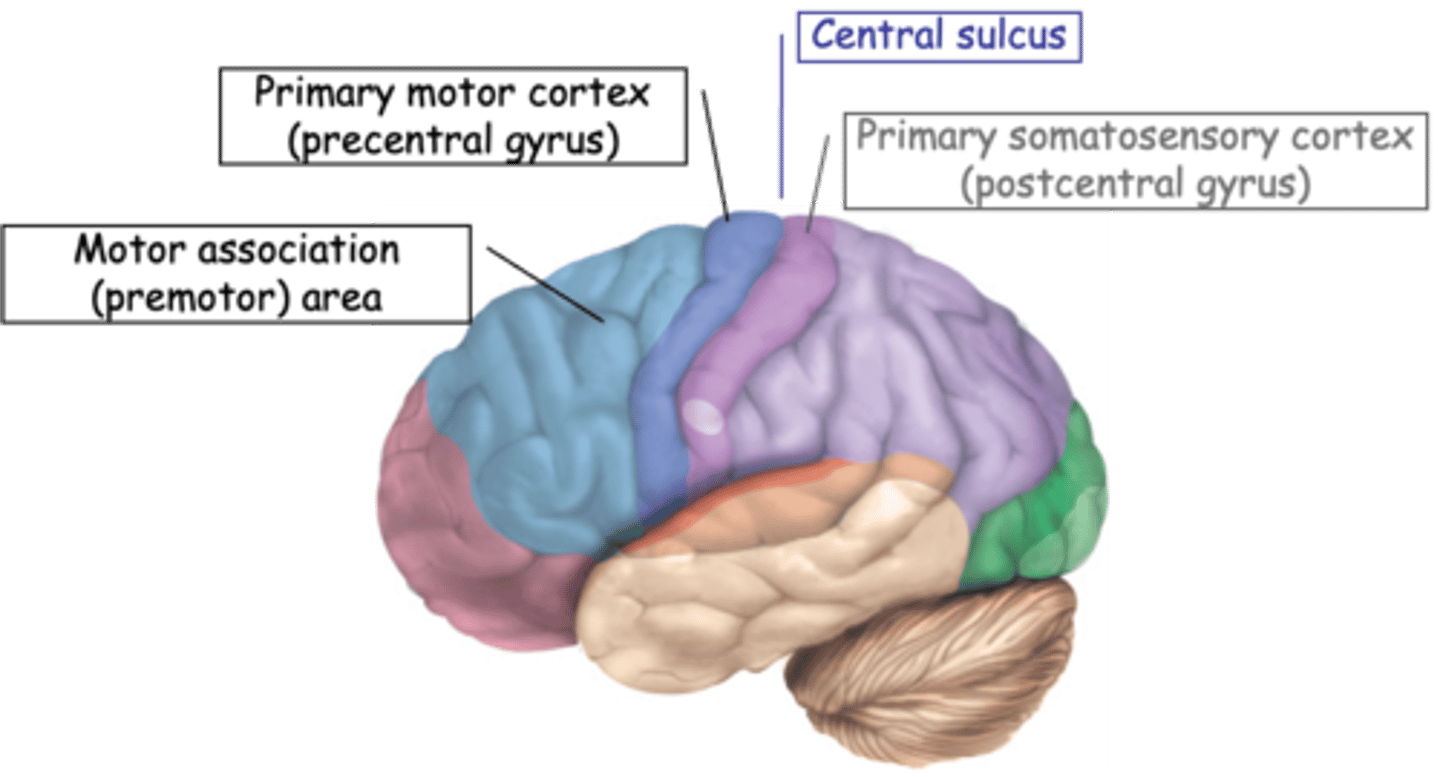
The motor cortex, or more specifically the primary motor cortex
What did the contralateral body muscle region become known as?
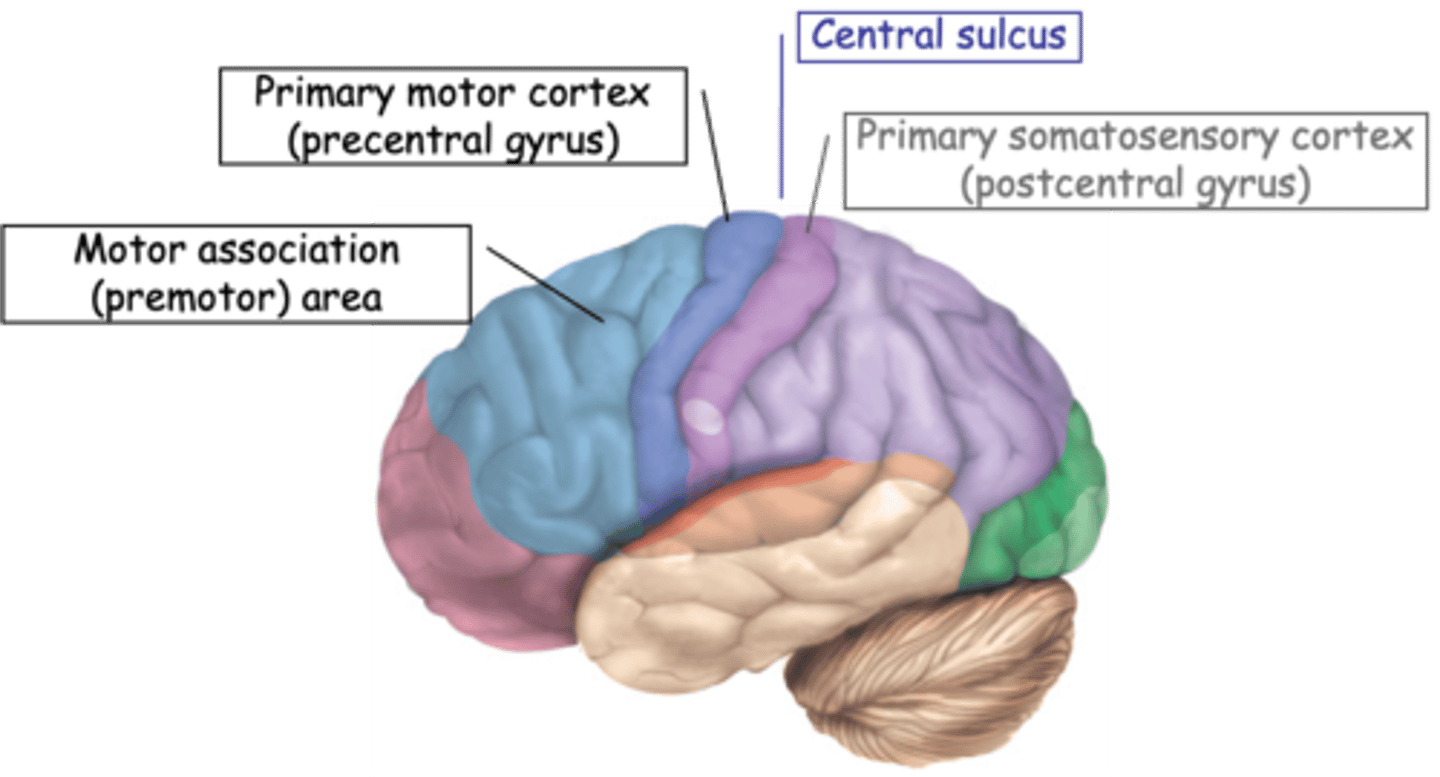
Upper motor neurons
What are the neurons found in the brain that control motor function called?
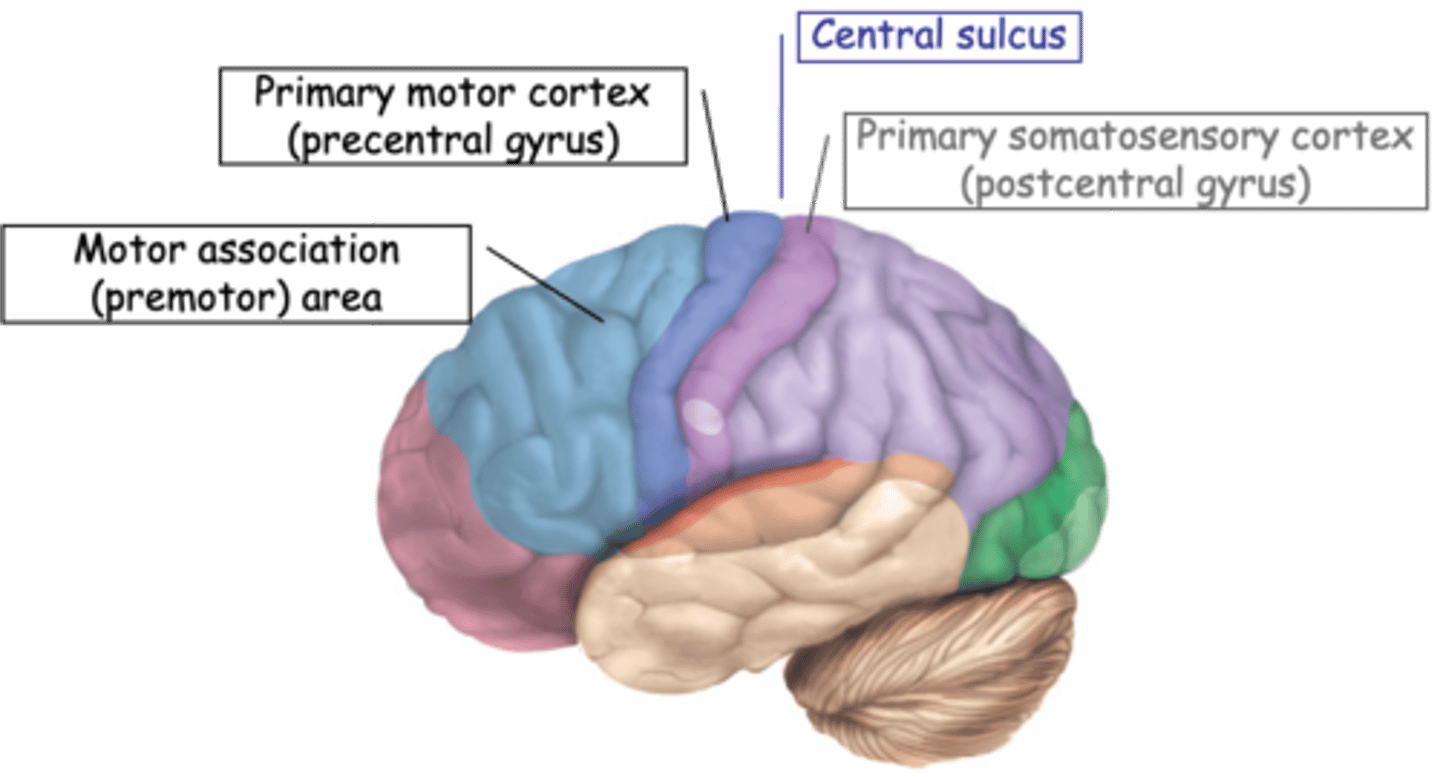
Somatotopically
Motor cortex is also ________________ mapped
Correlated the site of stimulation with the location of muscle contraction and demonstrated a topographic map similar to that of the somatosensory system
What did Sherrington and Penfield (early 1900s) do?
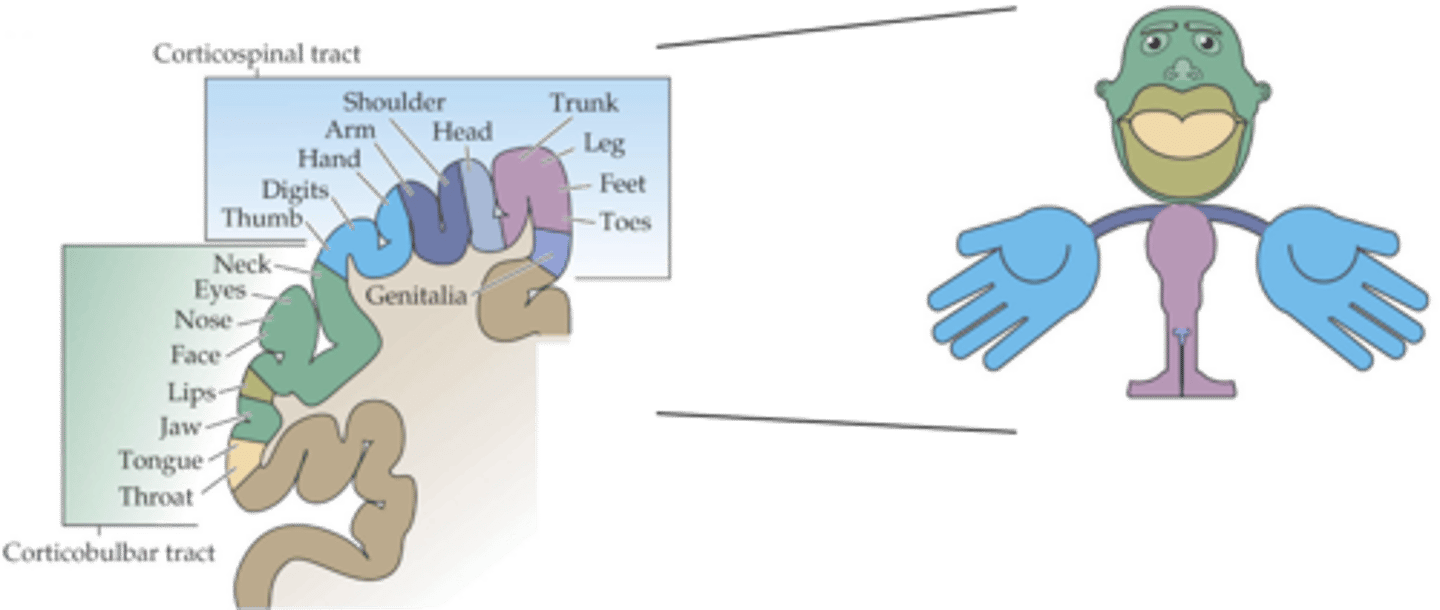
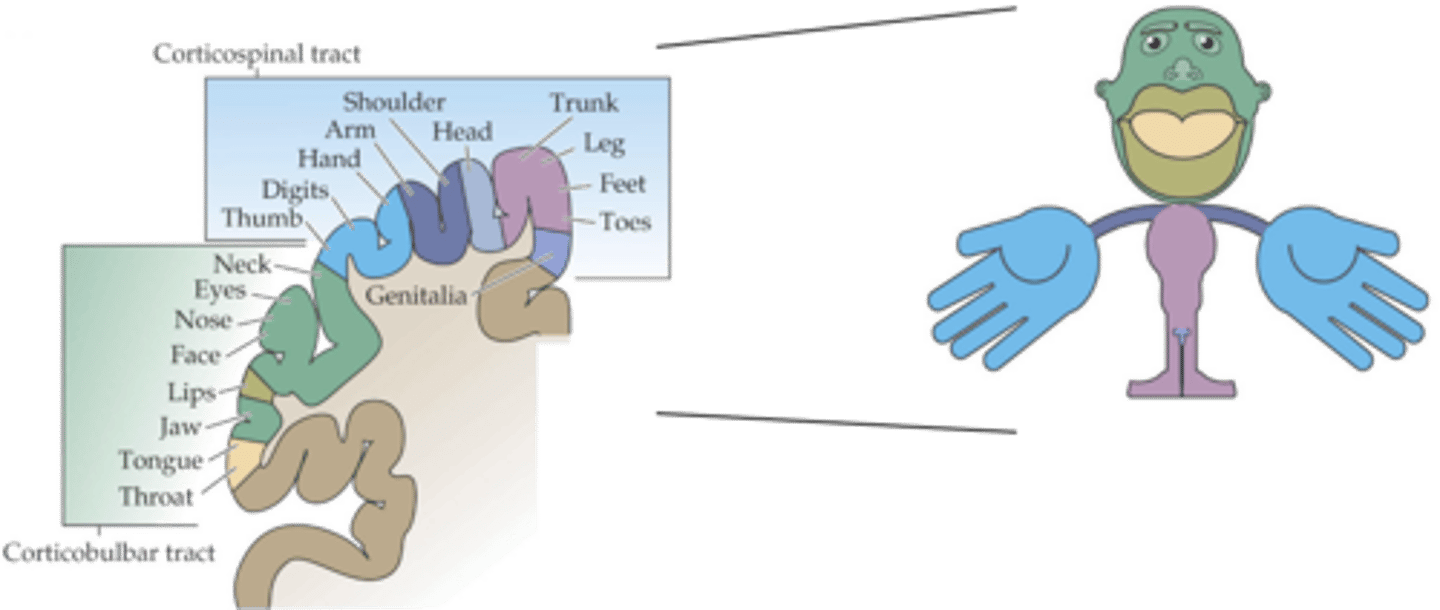
Medially, laterally
Lower body is represented __________, upper body __________
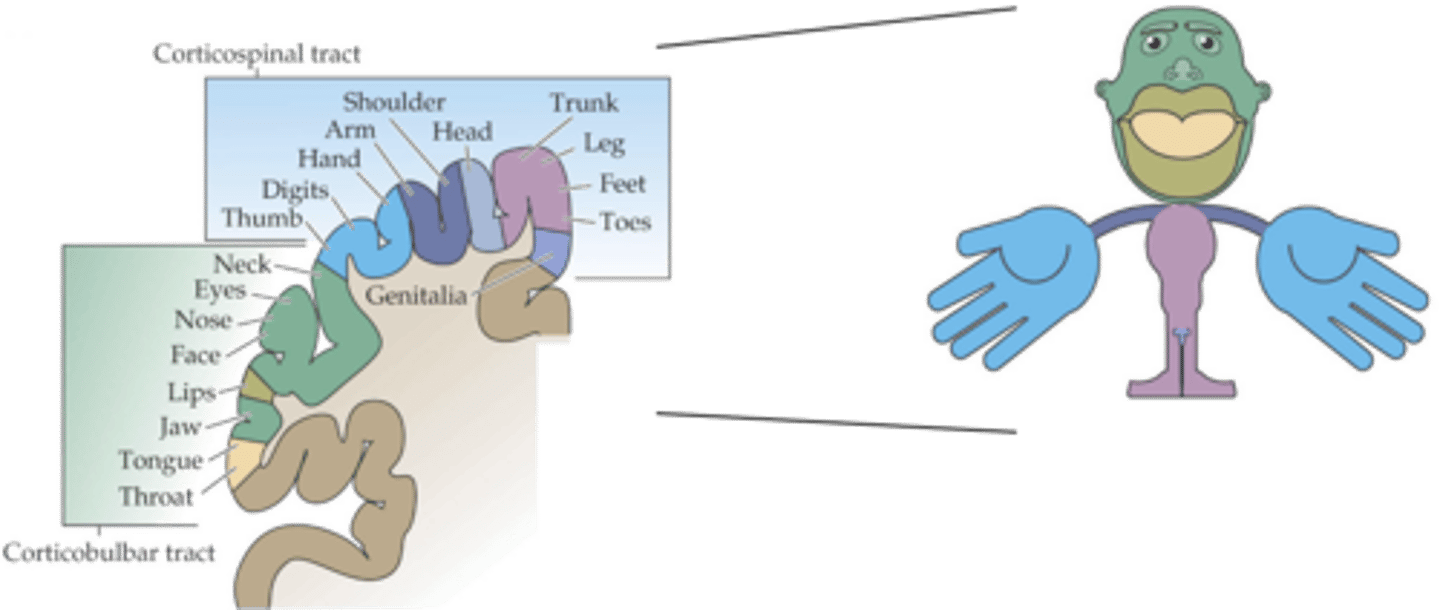
Density of innervation (and behavioural significance)
What do the proportions reflect?
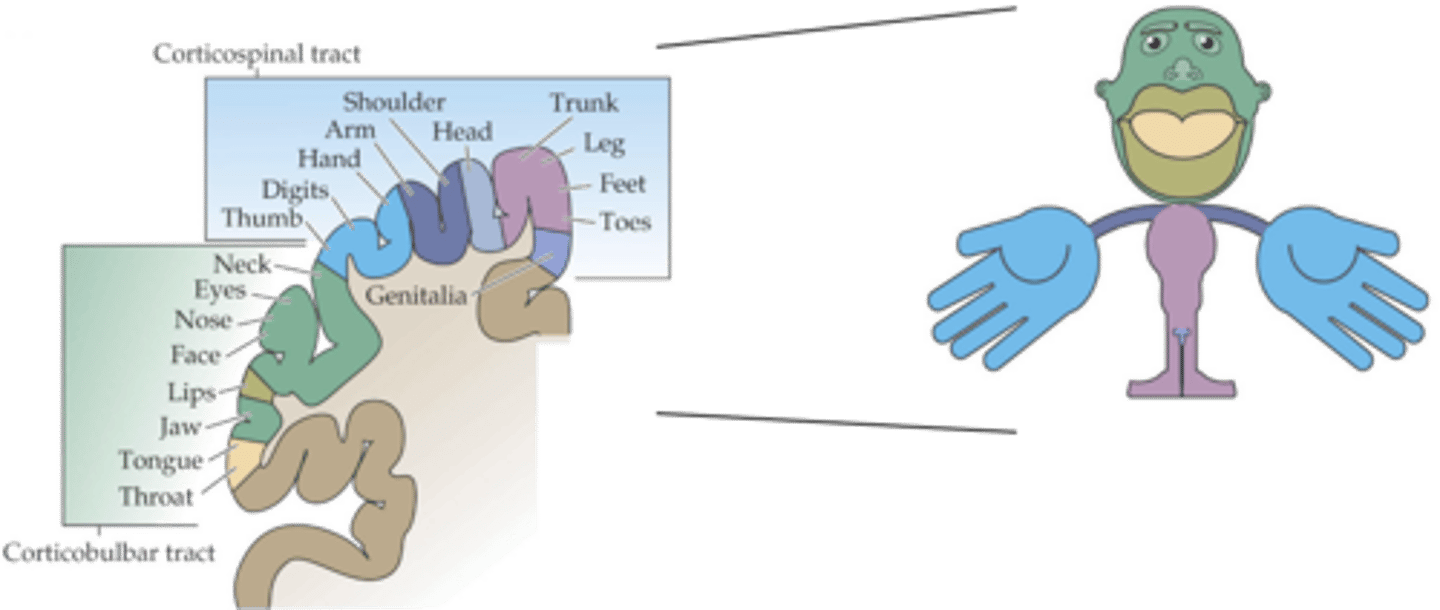
Trunk movement
What do axial muscles control?
Shoulder, elbow, pelvis, knee movement
What do proximal muscles control?
Hands, feet, digits (fingers and toes) movement
What do distal muscles control?
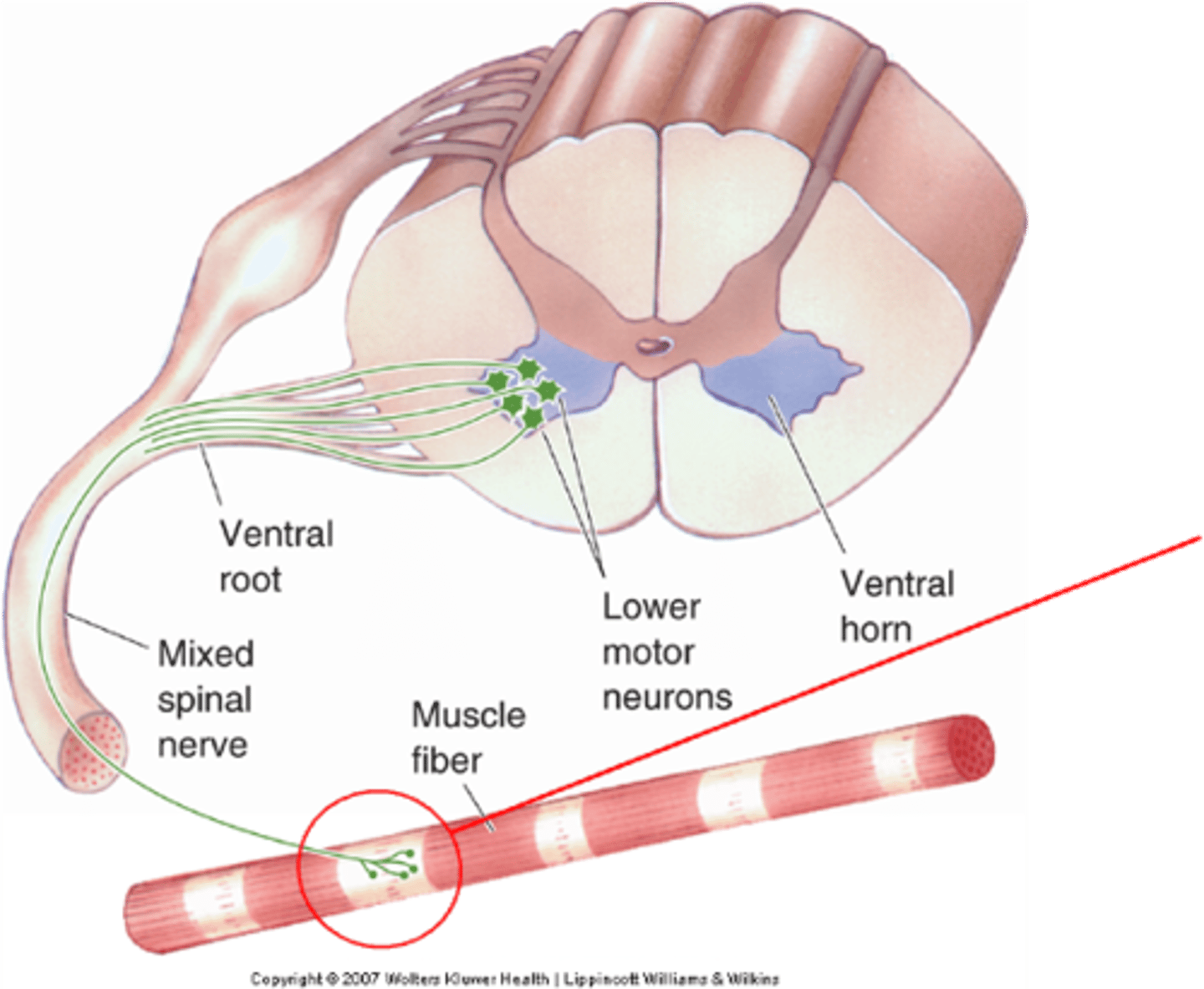
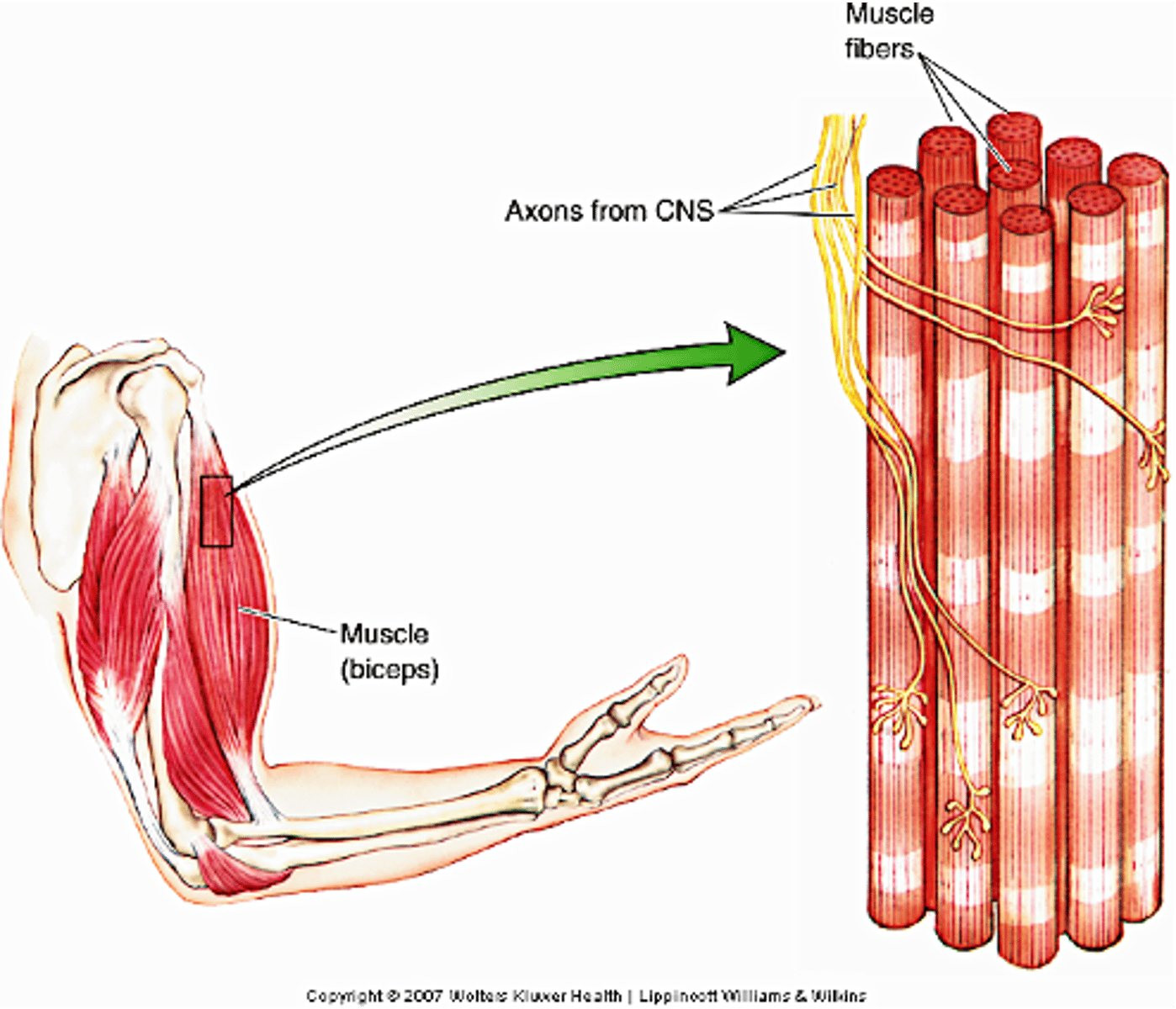
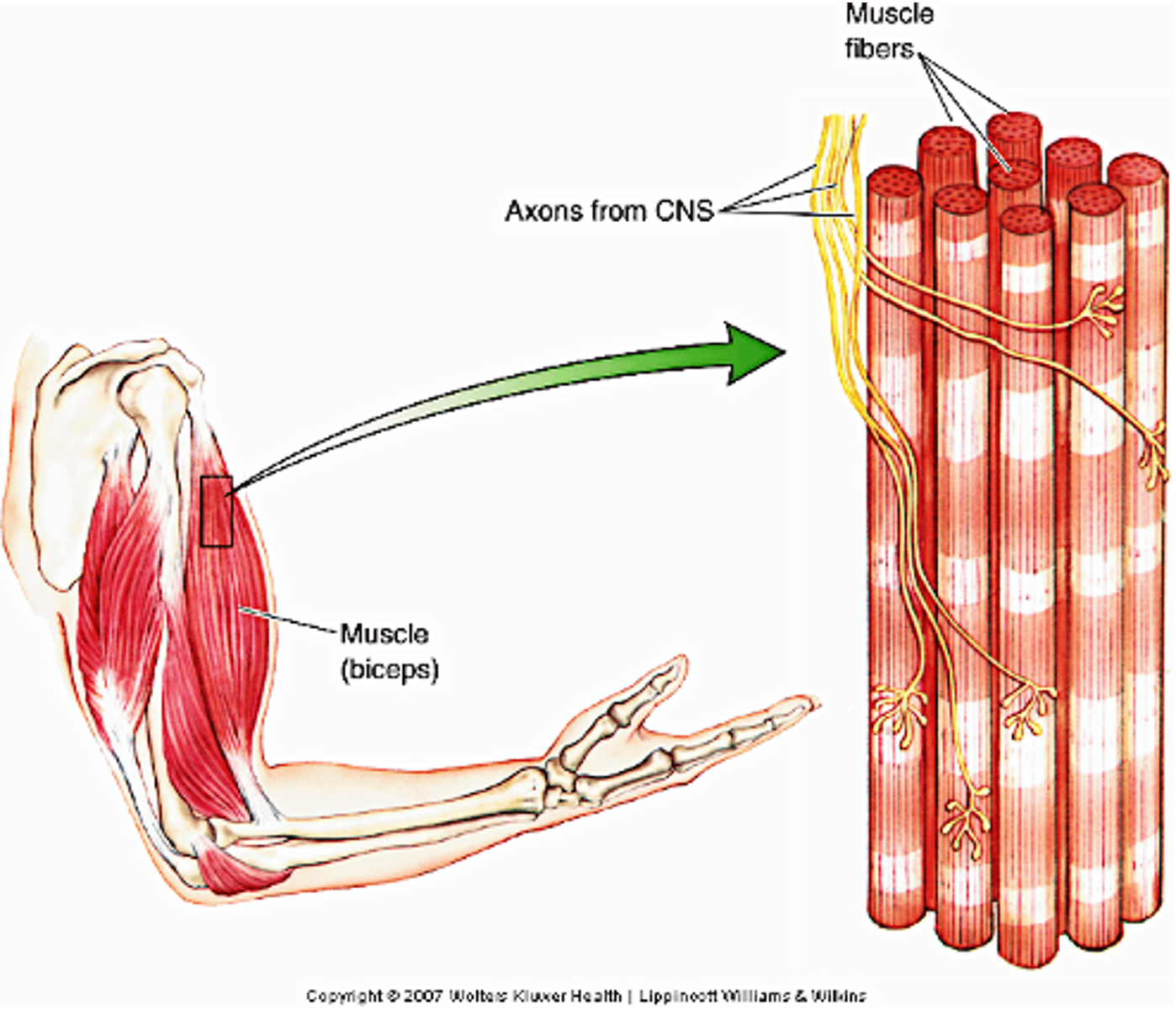
Neuro Muscular Junction (NMJ)
Innervation is via a specialised synapse called the ...?
Alpha
Each muscle fibre receives input from a single lower motor neuron, which kind is it - alpha MNs or gamma MNs?
Alpha MNs
Muscles also contain muscle spindles that receive input from gamma motor neurons, so a single muscle will receive inputs from both alpha and gamma MNs - when we talk about lower motor neurons (LMNs) we are talking about ...?
Motor neuron and all the muscle fibres it innervates
What is a motor unit?
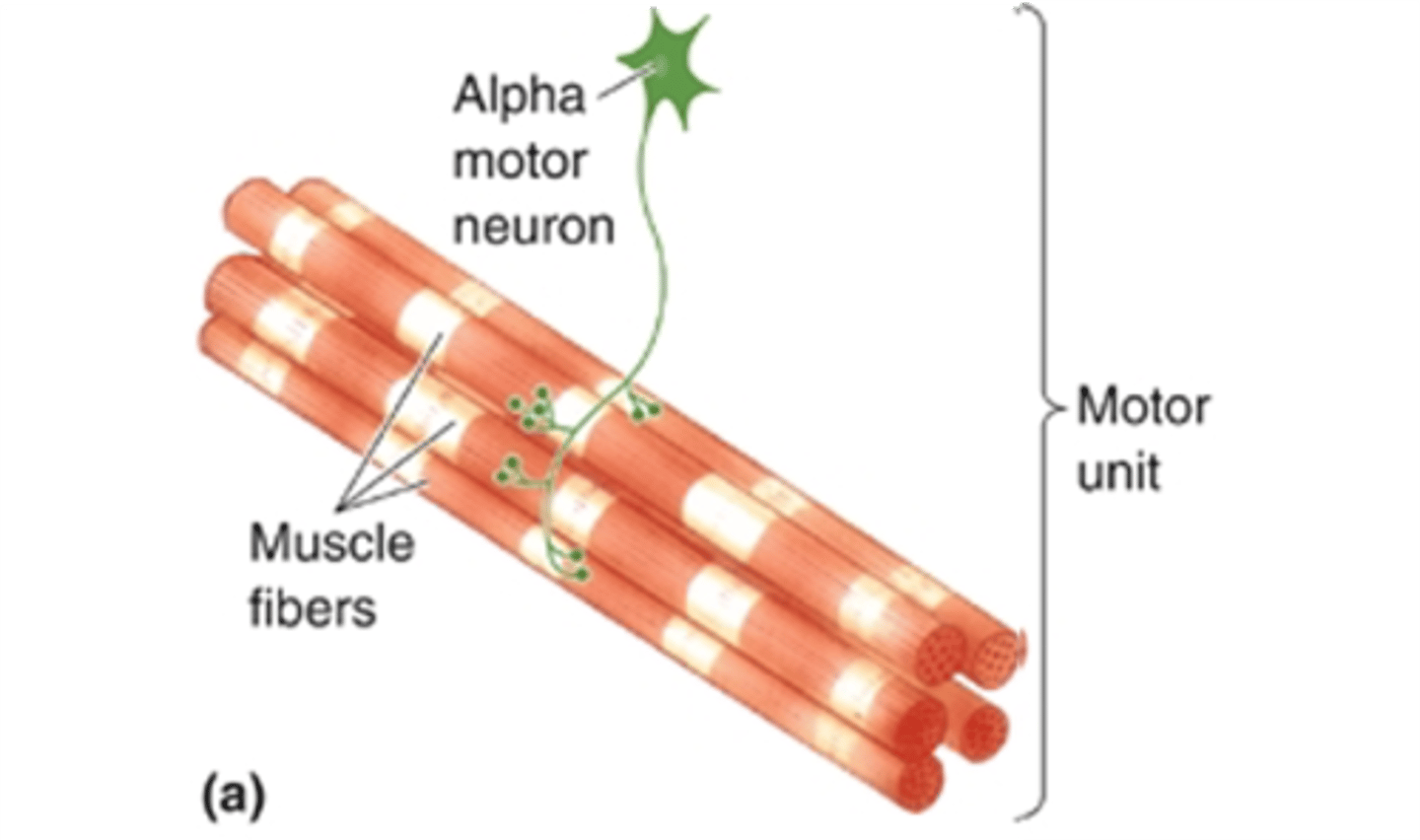
All the motor neurons that innervate a single muscle
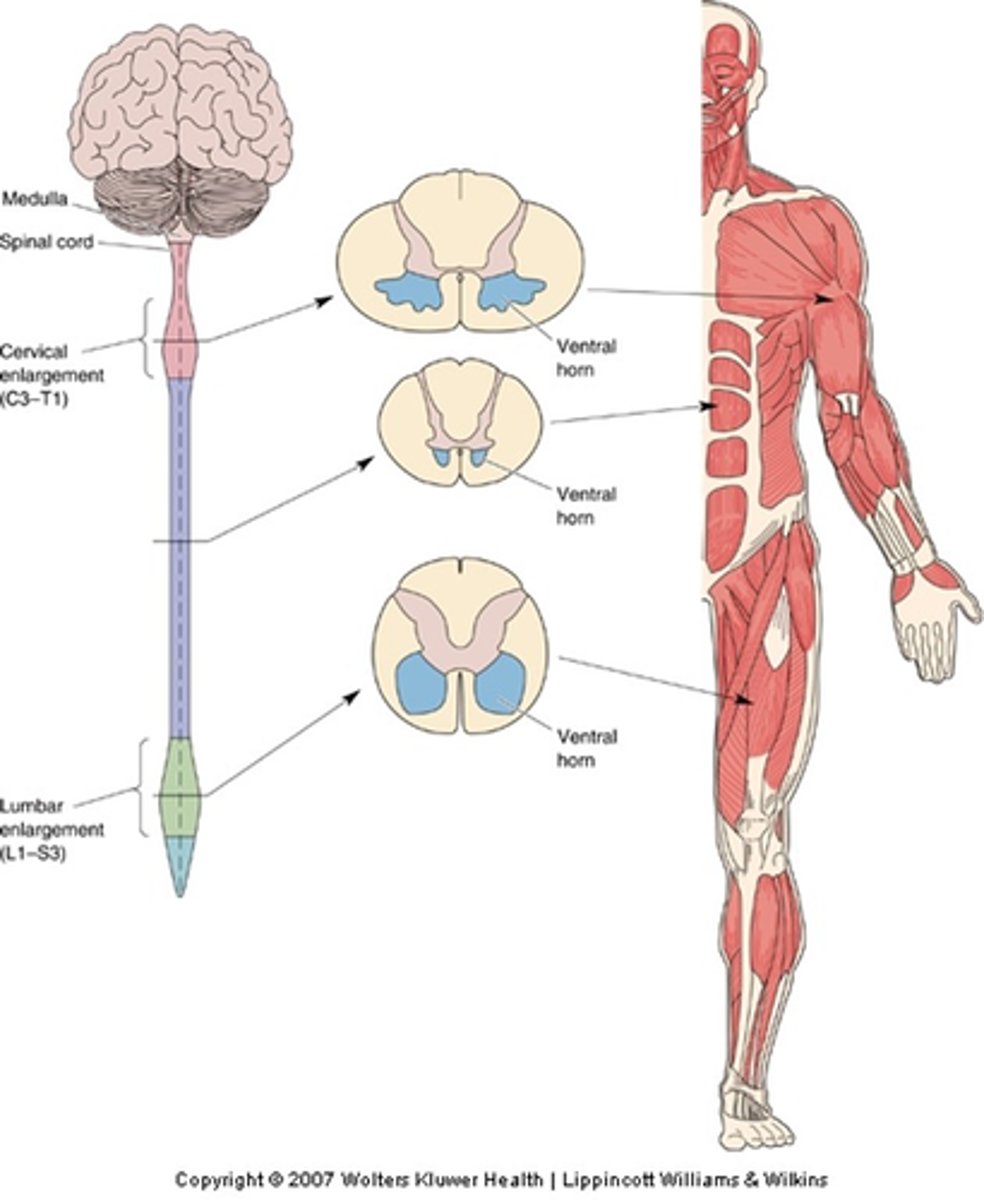
What is a motor neuron pool?
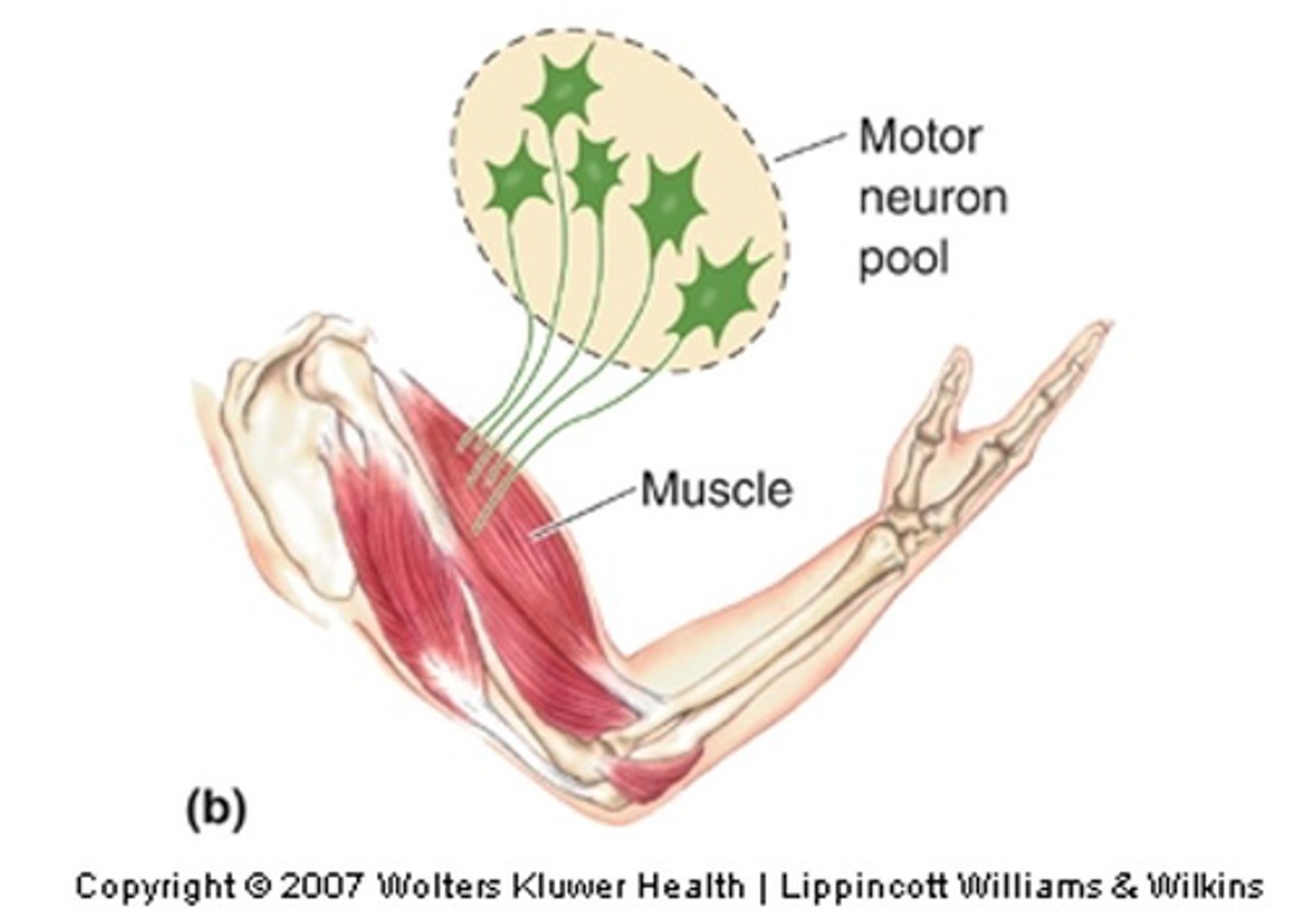
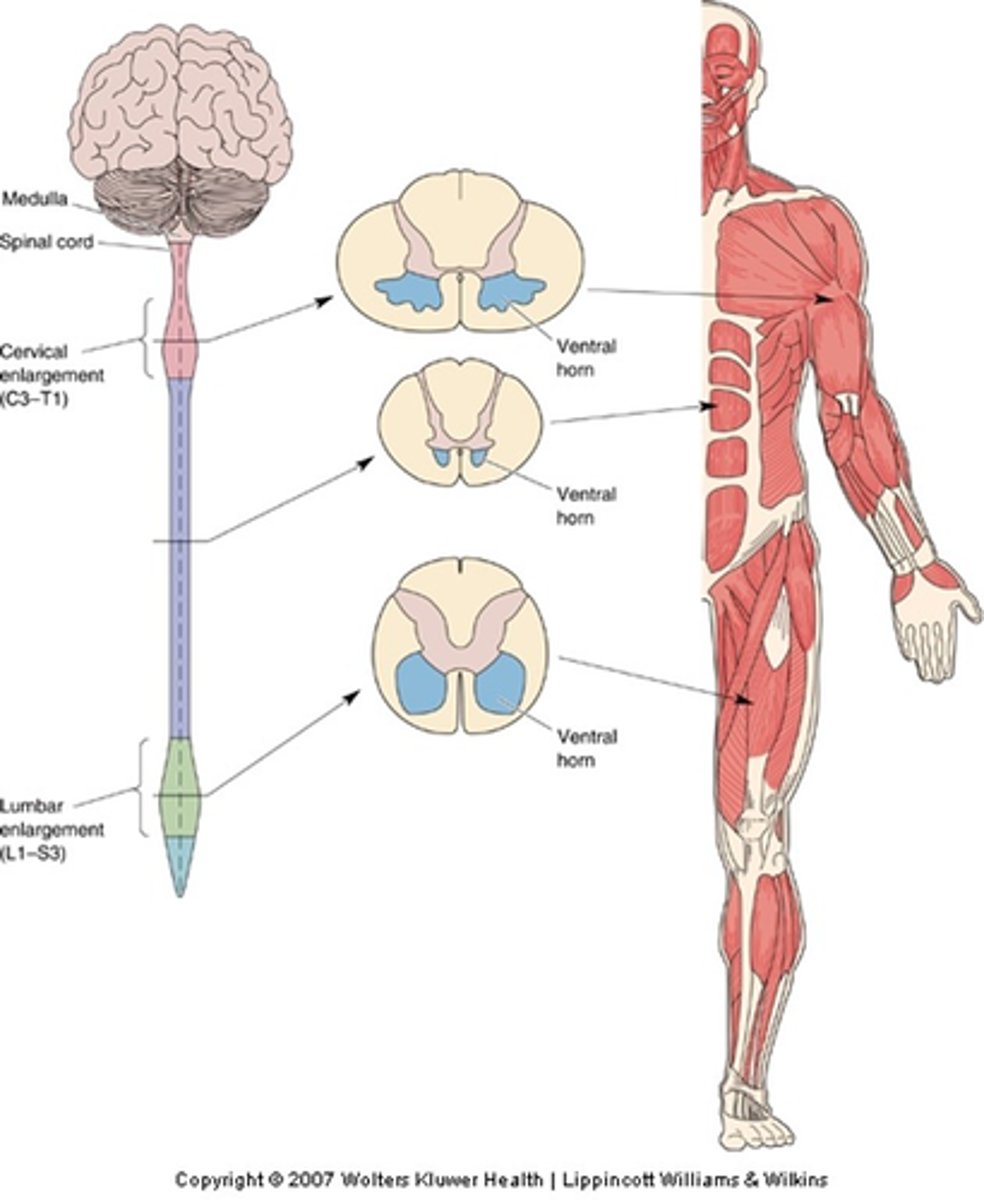
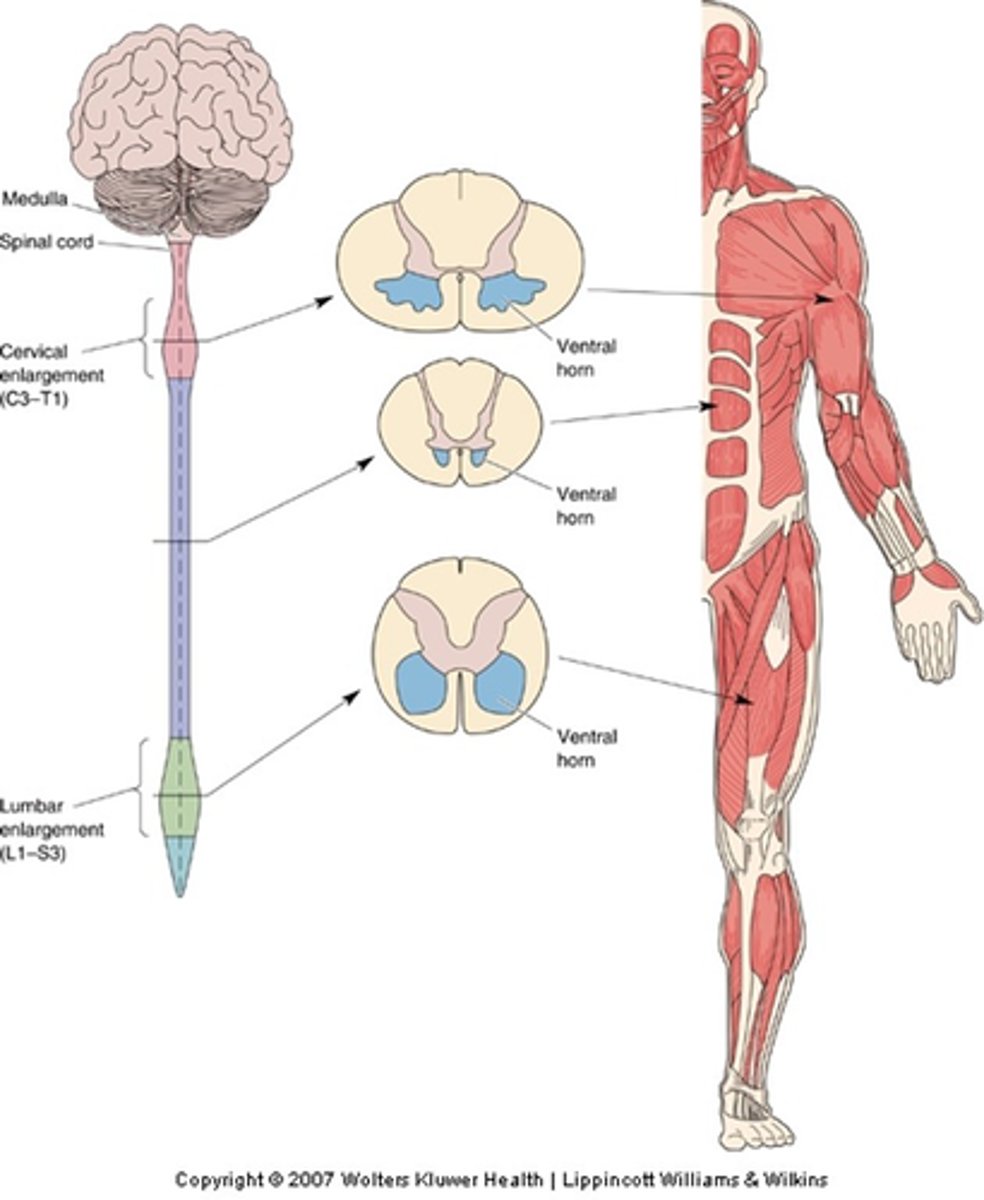
Spinal cord
Motor pools are spatially organised in the __________ ______
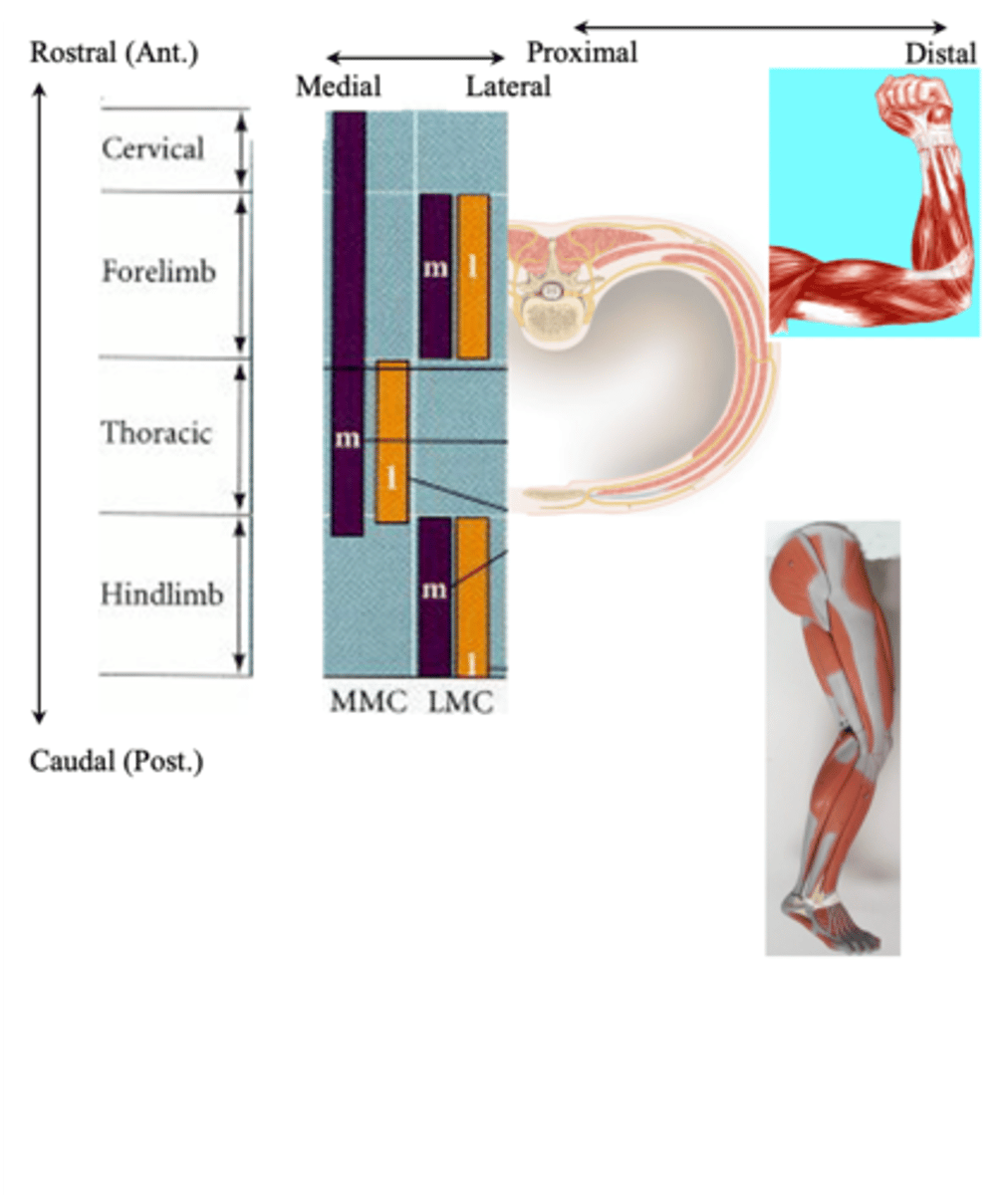
Rod-shaped clusters, spinal cord, vertebral
All the motor neurons innervating a particular muscle - the motor pool for that muscle - are grouped in ____-___________ __________ within the _________ ______ extending over several ___________ segments
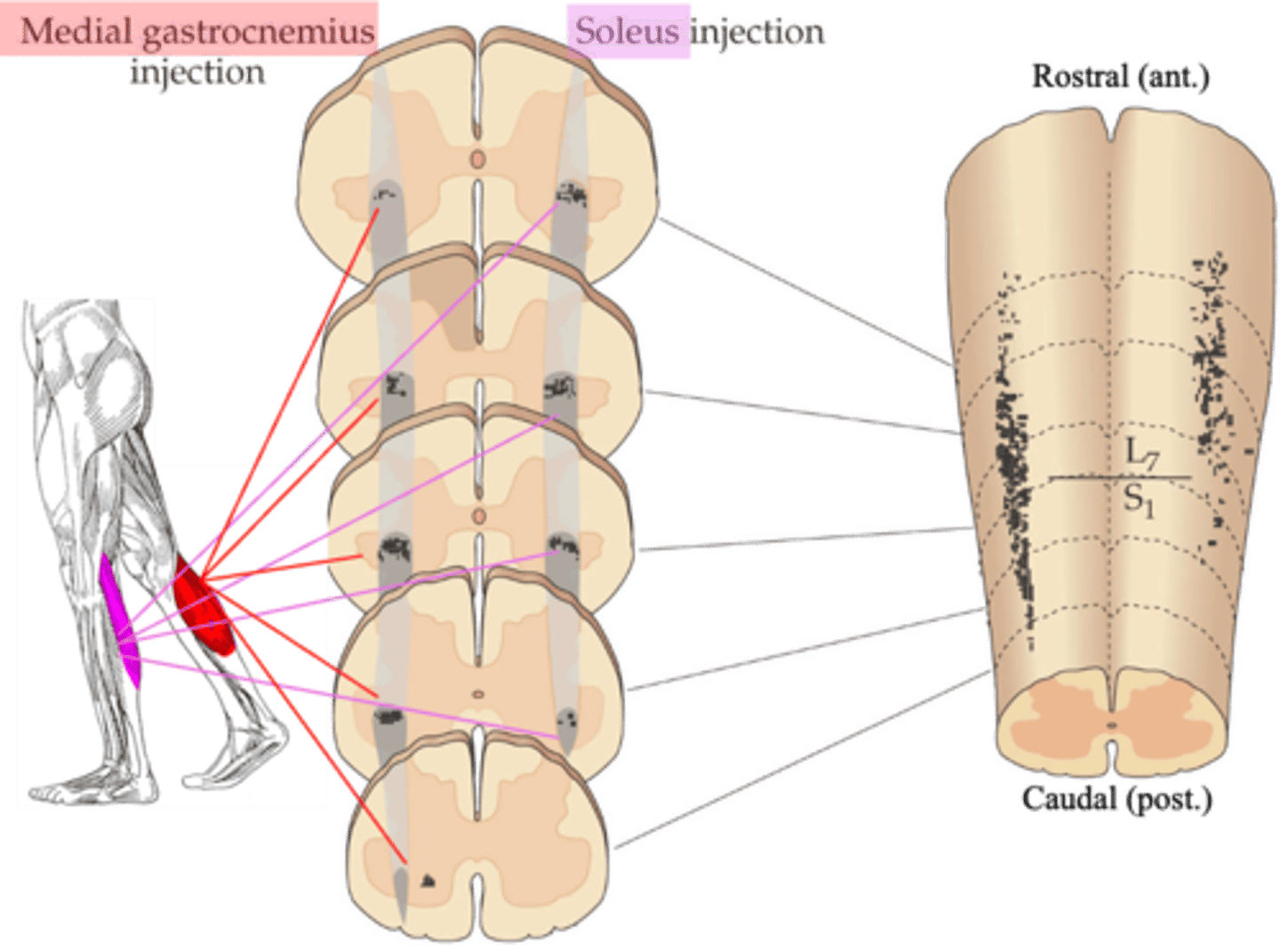
Tracers were injected into specific muscles, which then were transported back along the motor axons to the cell bodies in the spinal cord
- Injection into the gastroceneumius
- Labels a different set of motor neuron cell bodies to injection of the soleus
What were the experiments done in animals to help us understand motor pools?
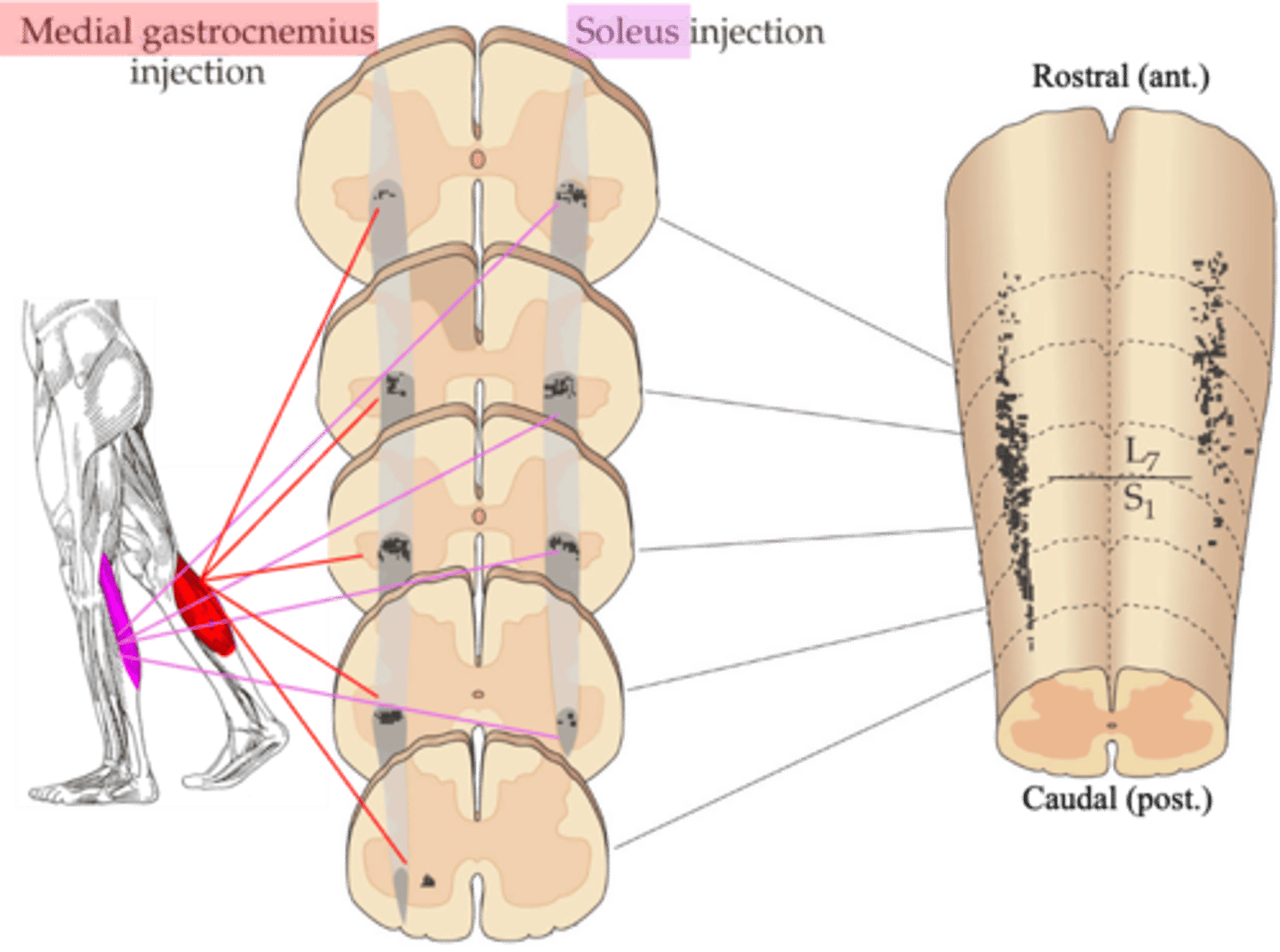
Mediolateral, rostrocaudal, ventral horn
Even though the experiment labelled muscles in different legs, careful comparison makes it obvious the motor pools for each muscle occupy a distinct ______________ (and ______________) position within the __________ _______ of the spinal cord
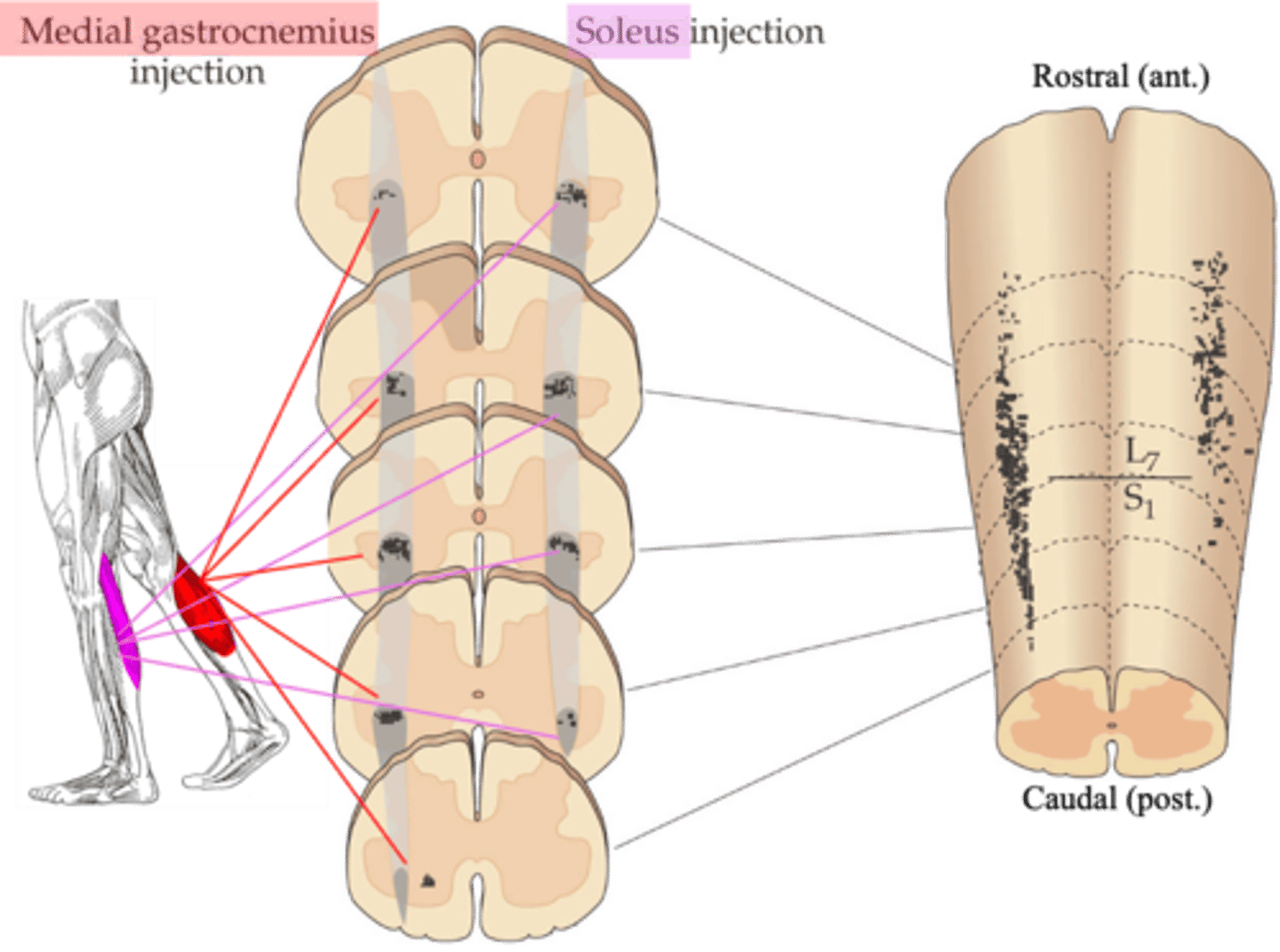
Sections of spinal cord in which these tracers have been visualised
What does the middle diagram represent?

3D reconstruction of where the tracers went
What does the right hand diagram represent?
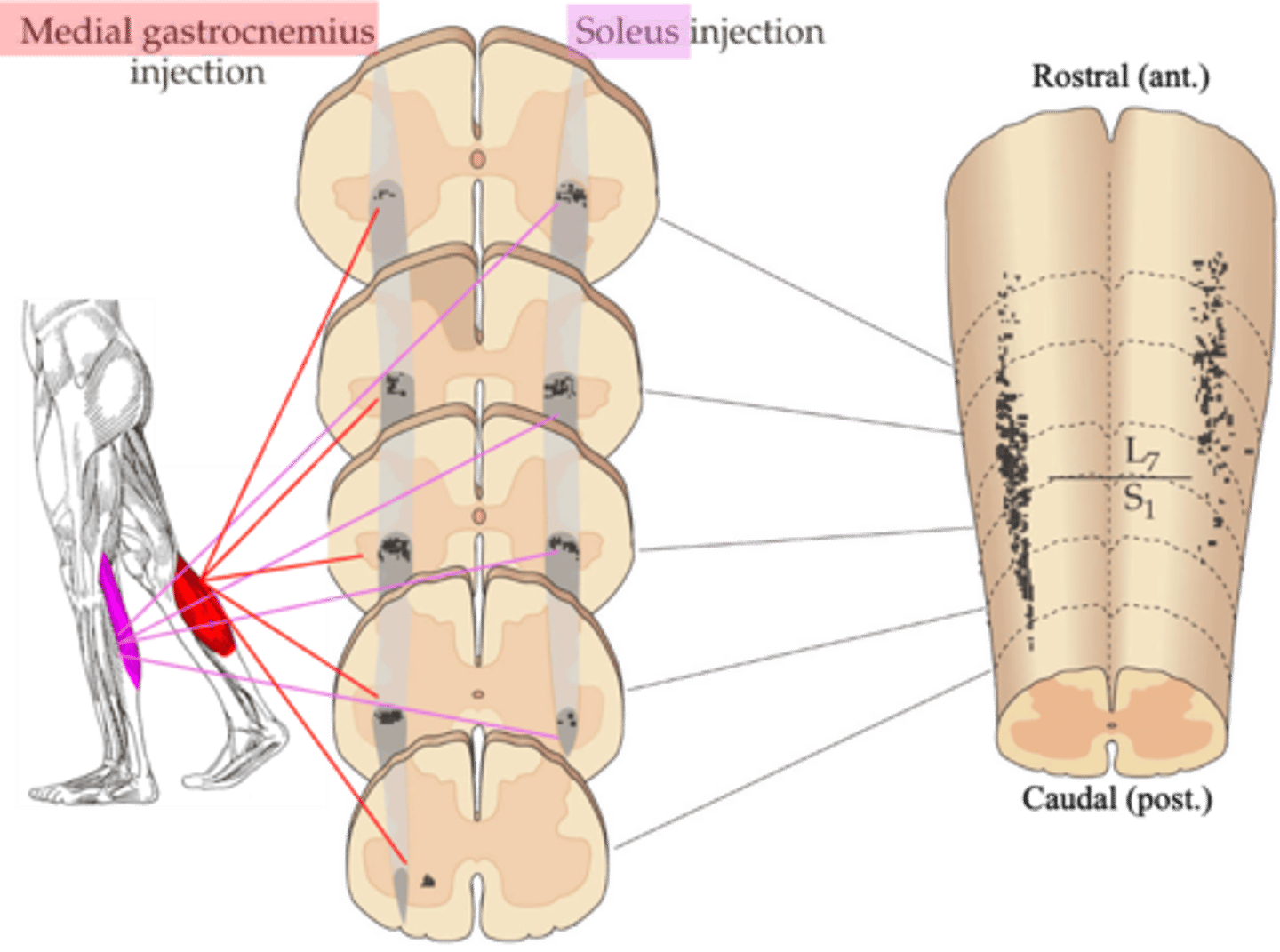
Somatotopically, medio-laterally, rostro-caudally
Motor pools are organised __________________ both _______-___________ and _______-__________ (A-P)
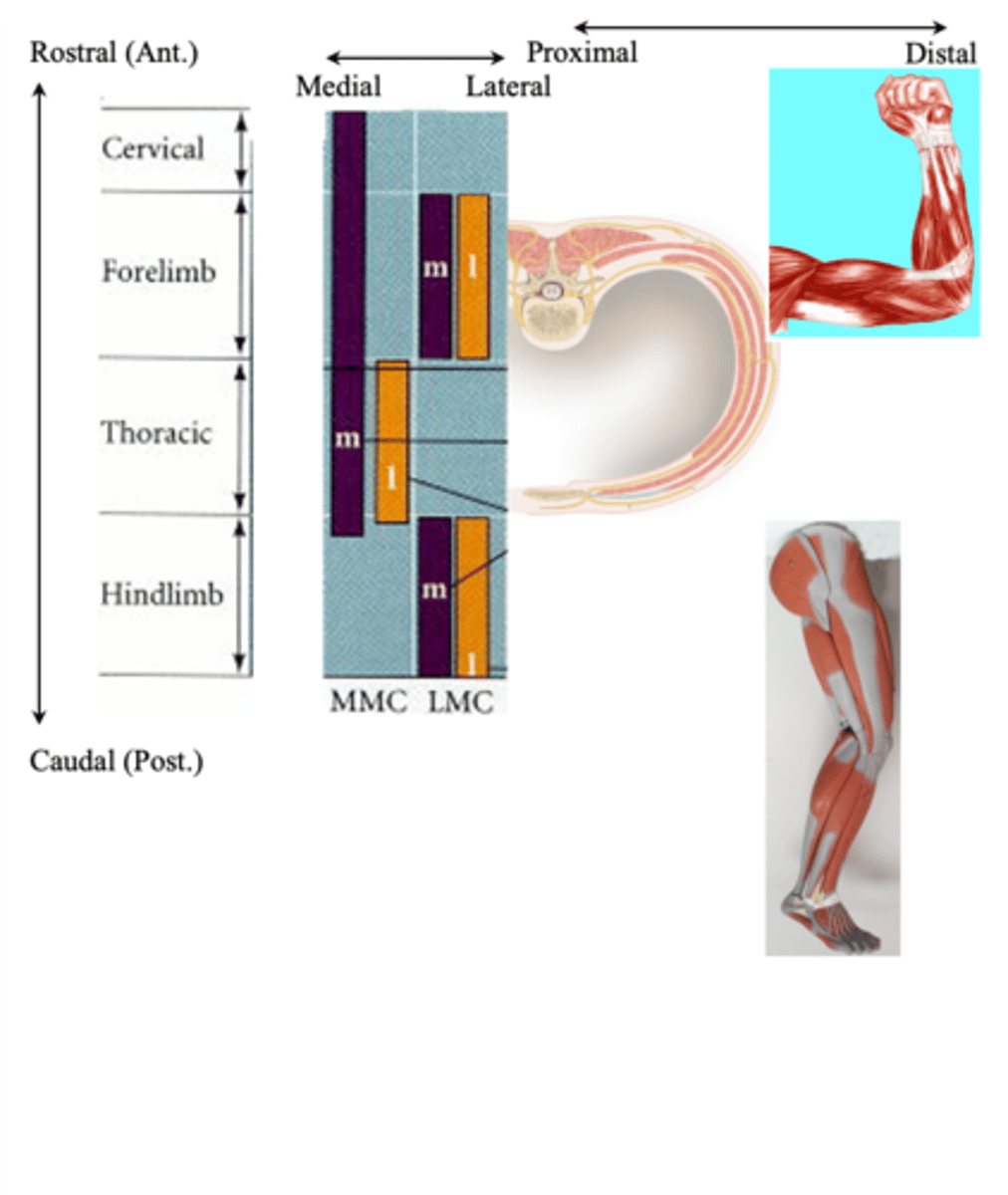
Whether its MNs innervate a proximal or distal muscle
What does the medic-lateral position of a motor pool reflect?
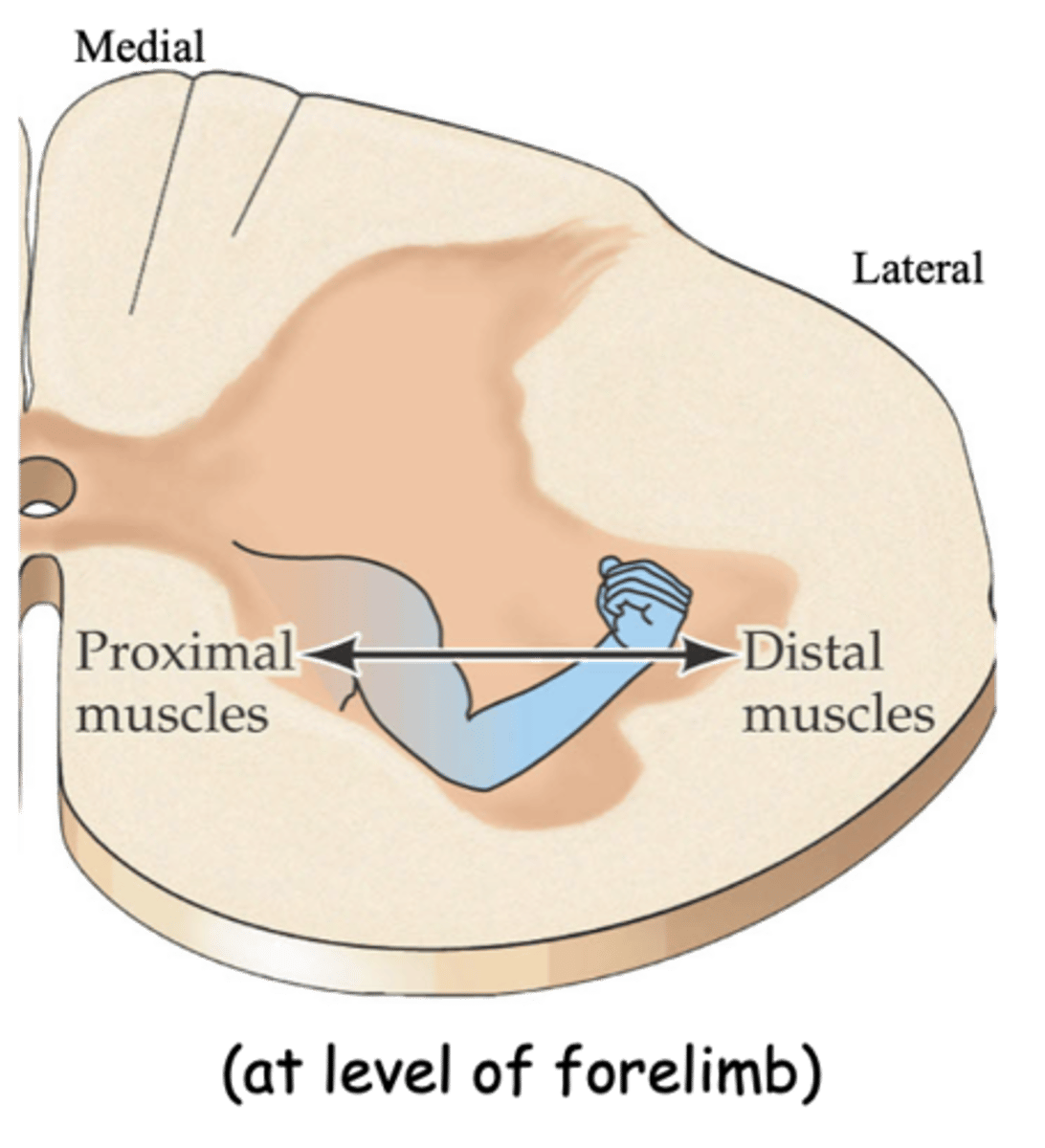
Its organisation reflects the organisation of the body (i.e. there is a 3D representation (map) of the body's musculature within the spinal cord)
What does somatotopic mean?
The location of the upper motor neurons that innervate lower motor neurons in the spinal cord
What does somatotopy in the motor cortex reflect?
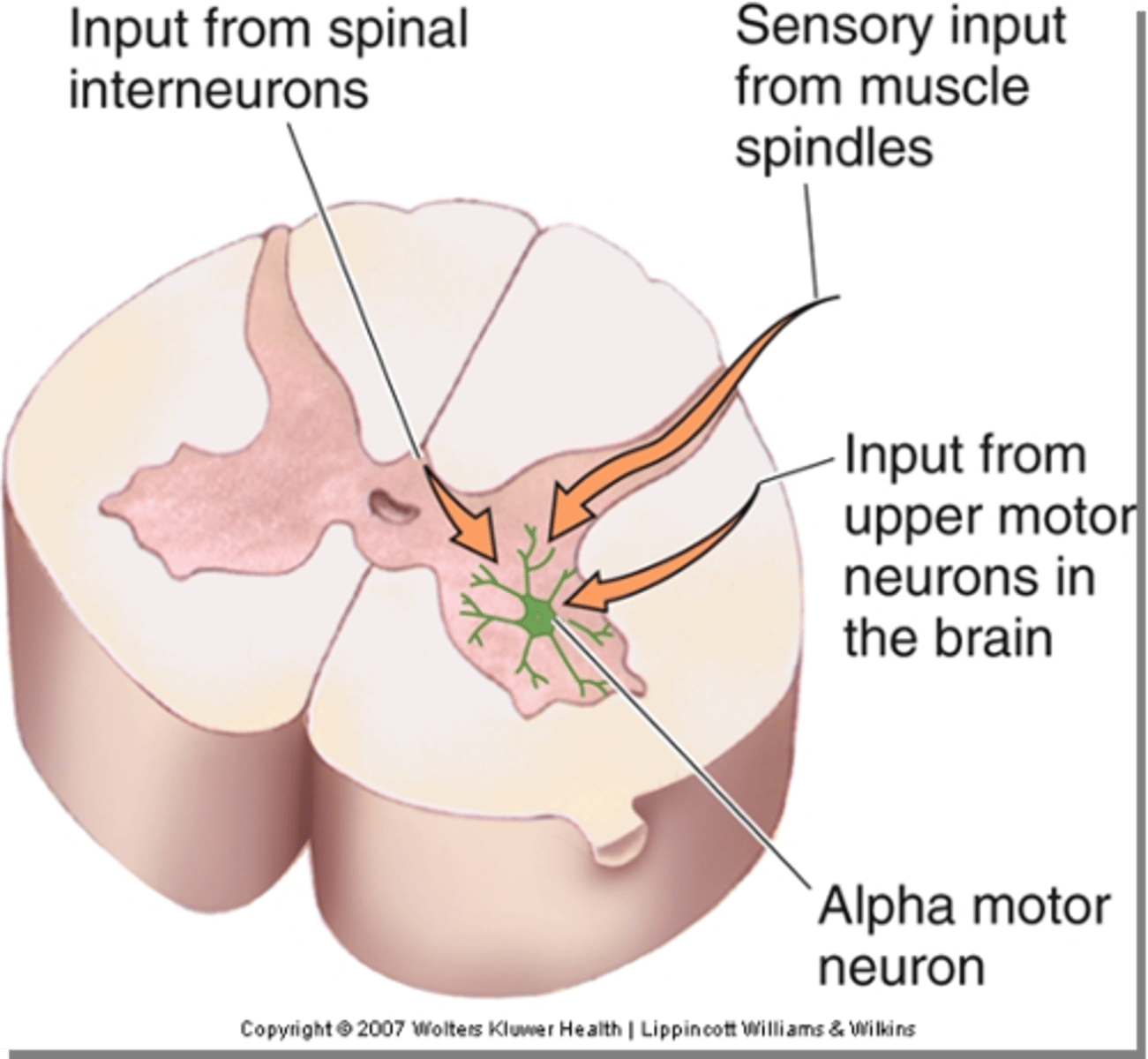
Local sources, upper motor neurons
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) receive inputs from _________ ___________ in the spinal cord, but also directly from ________ ________ _________ (UMNs)
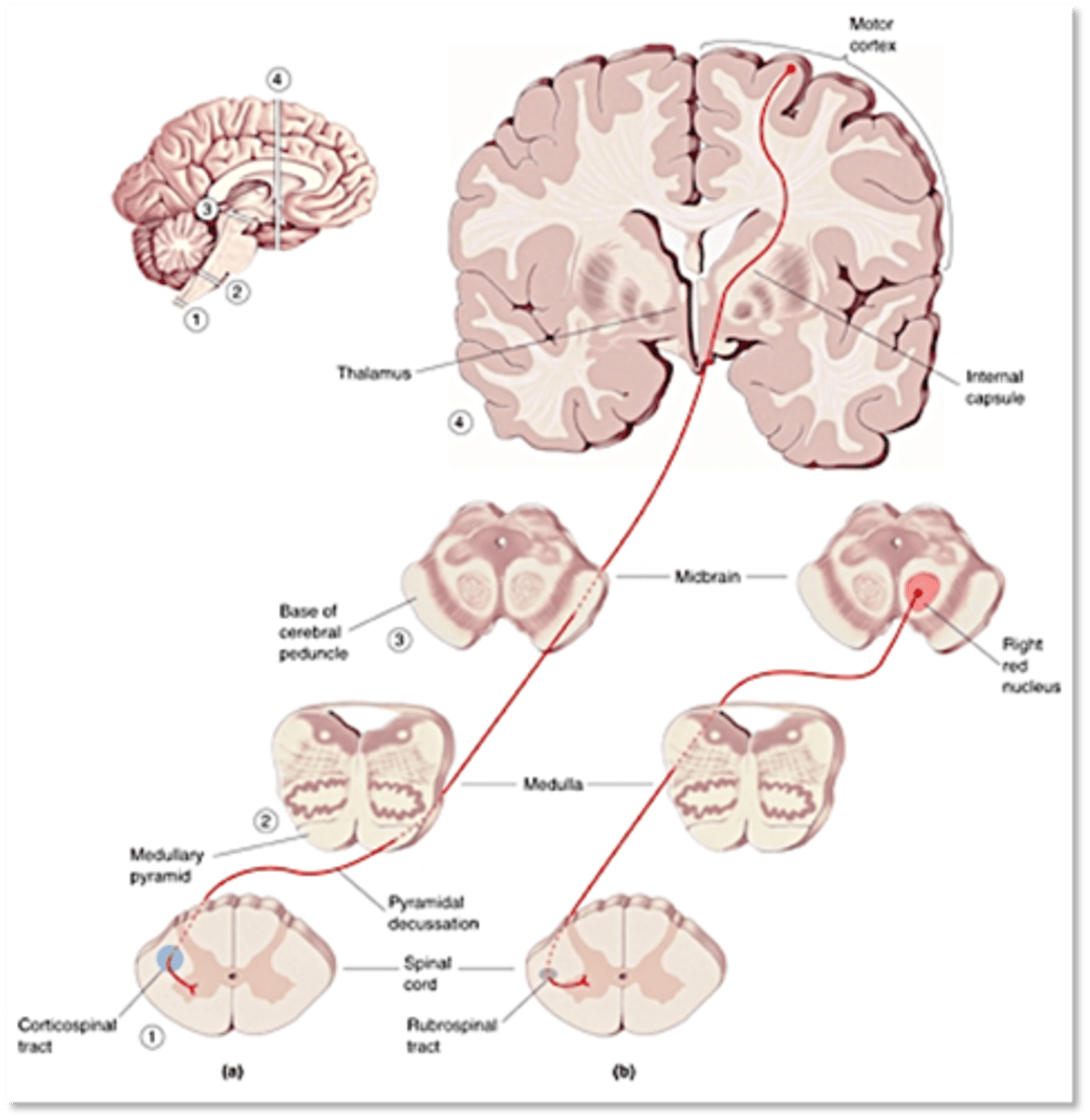
Descending tracts
Upper motor neurons project axons to lower motor neurons via the ______________ _________ of the spinal cord
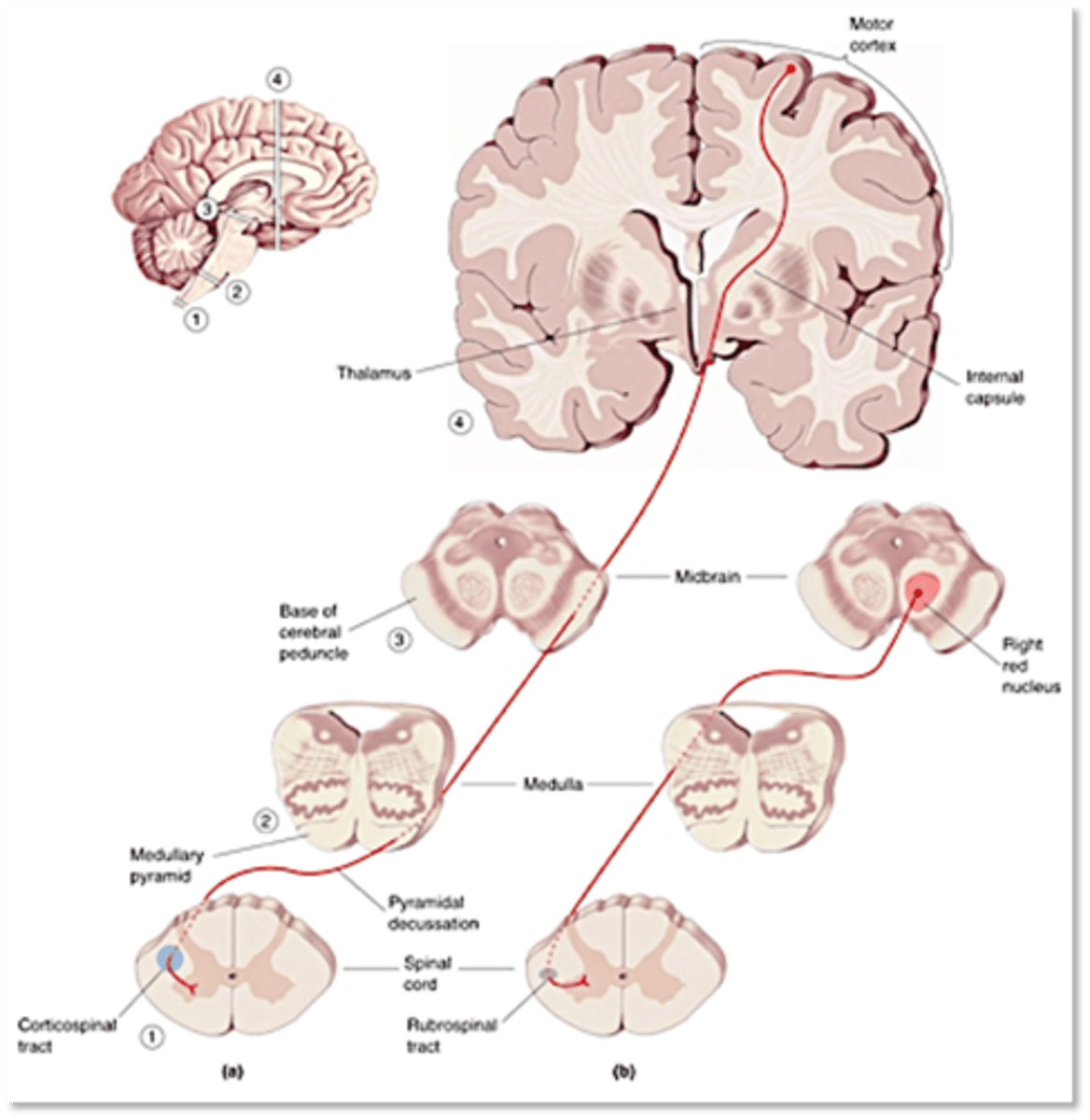
Coritcospinal tract, lateral
Key among these for the control of voluntary movement is the __________________ _________ (CST) one of the __________ pathways of the spinal cord
Five (V)
The axons of the CST originate in which layer of the motor cortex?
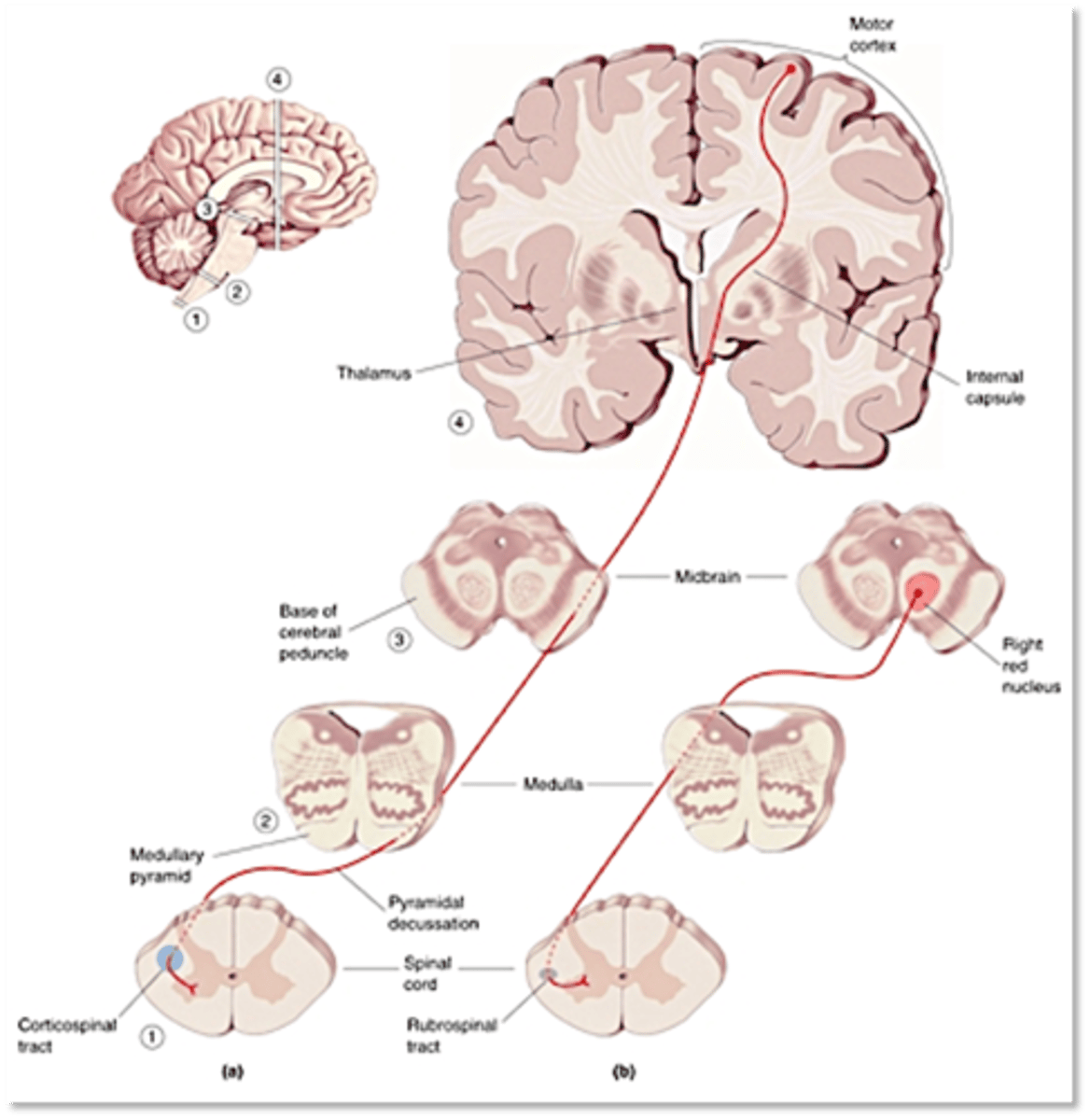
Corticospinal tract
Pyramidal cells of the motor cortex project axons in the ...?
Six
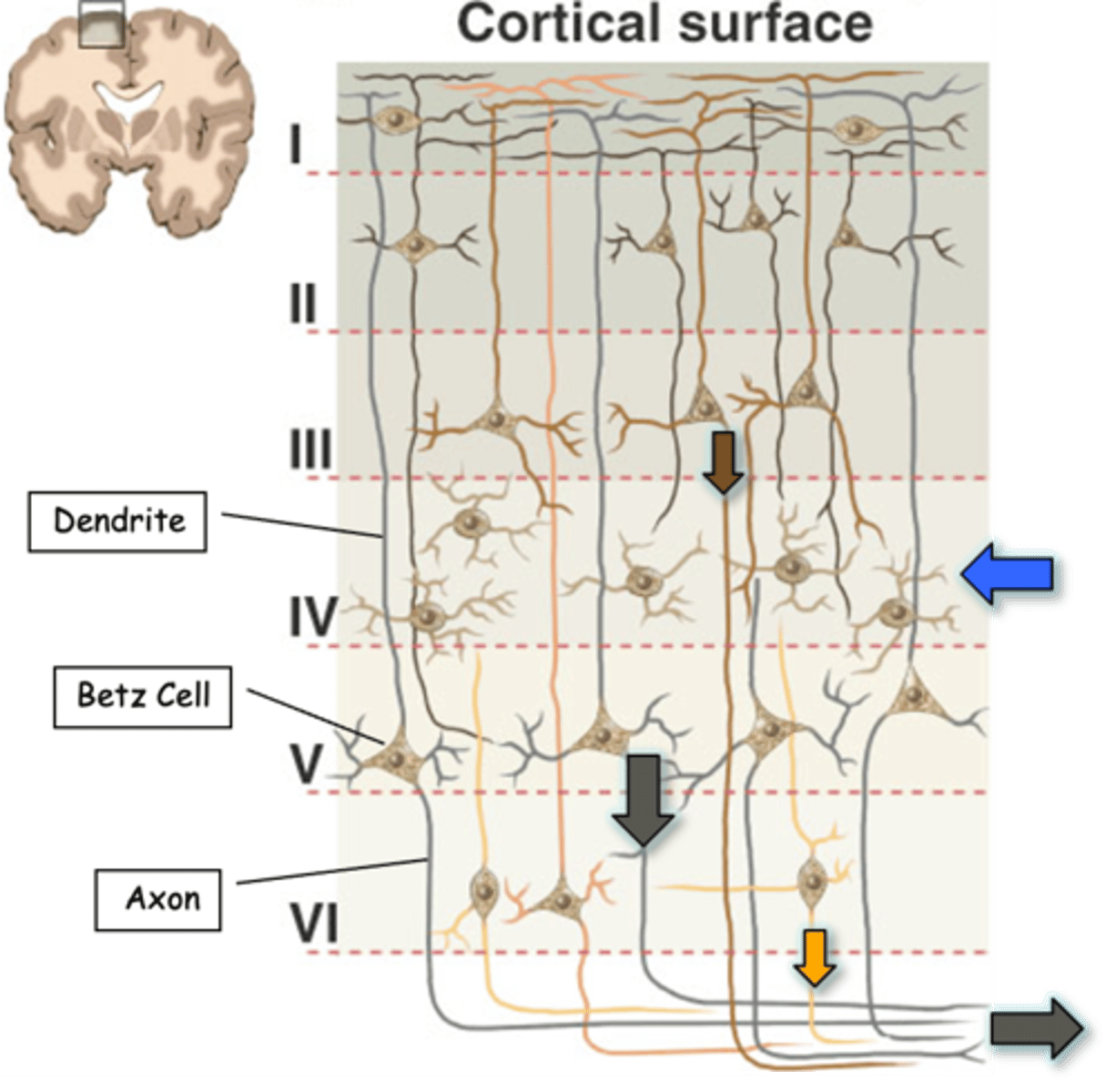
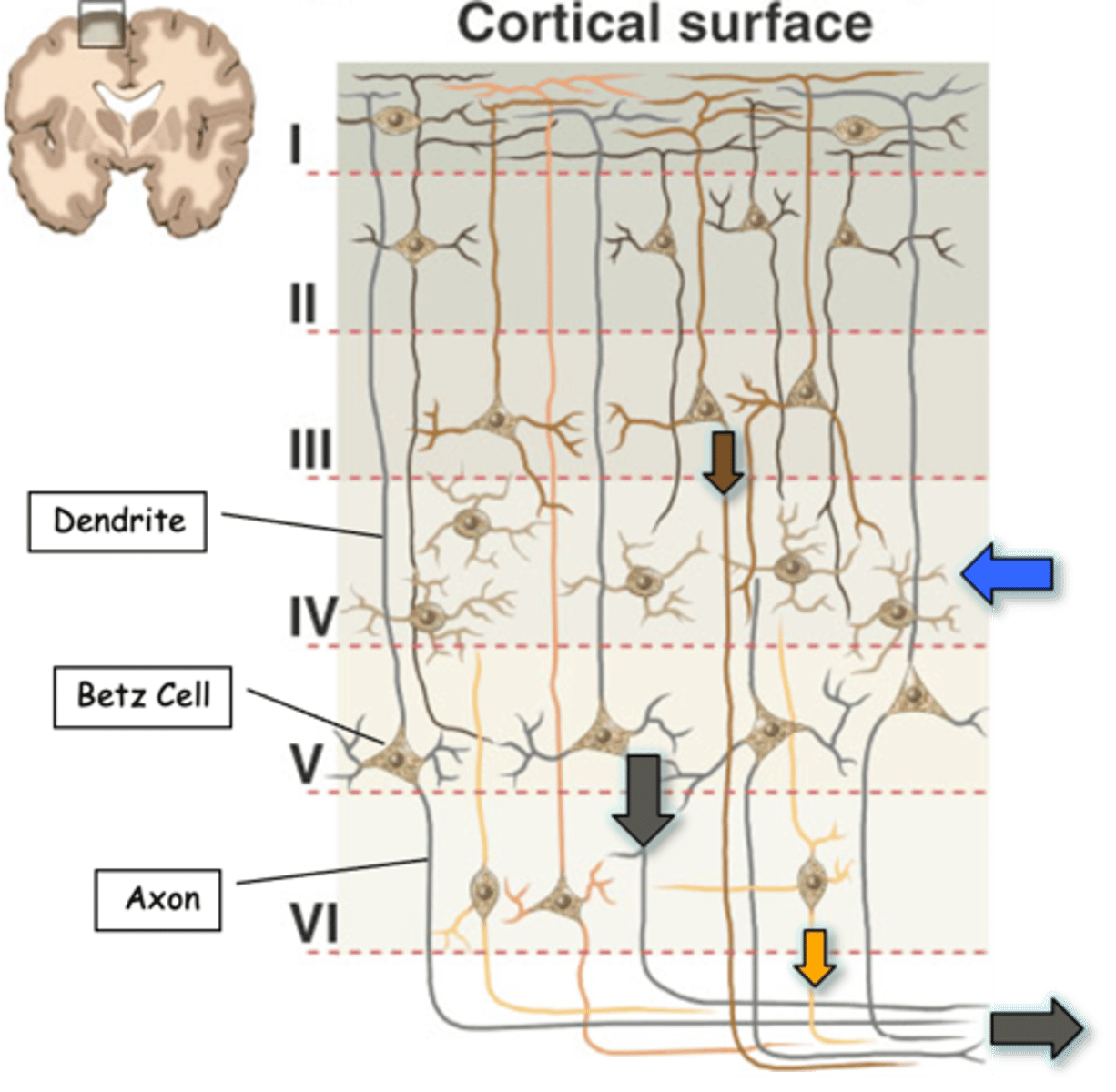
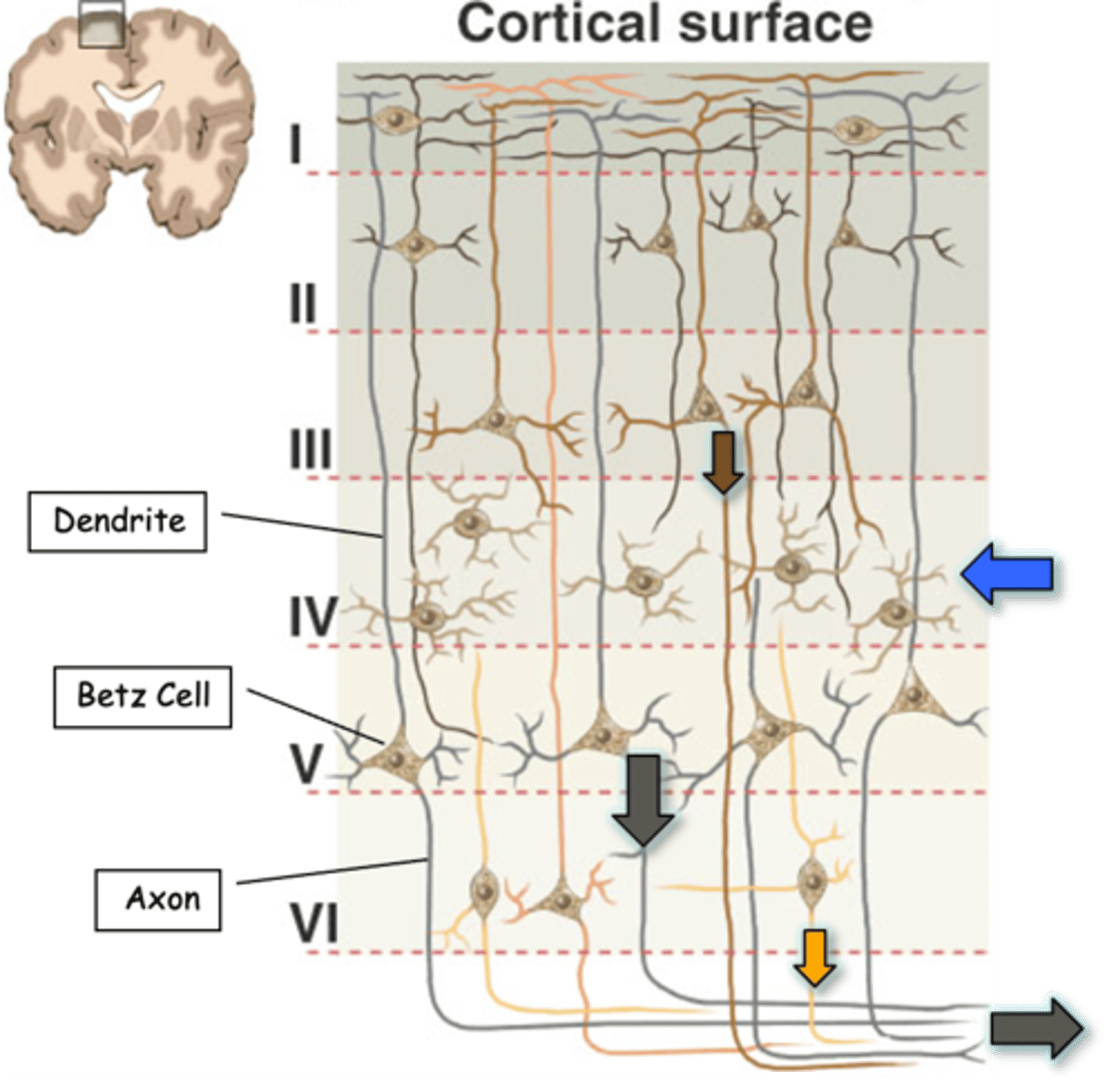
90% of cortex, including the motor cortex, is a _____ layered structure
Stellate
Main inputs to the cortex are to __________ cells in layer IV (blue arrow)
III, V, VI
Main outputs are from layers ___ (brown arrow), _ (black arrow) and __ (yellow arrow)
Pyramidal, V
Axons of corticospinal tract derive from large _______________ cells (also known as Betz cells) in layer _
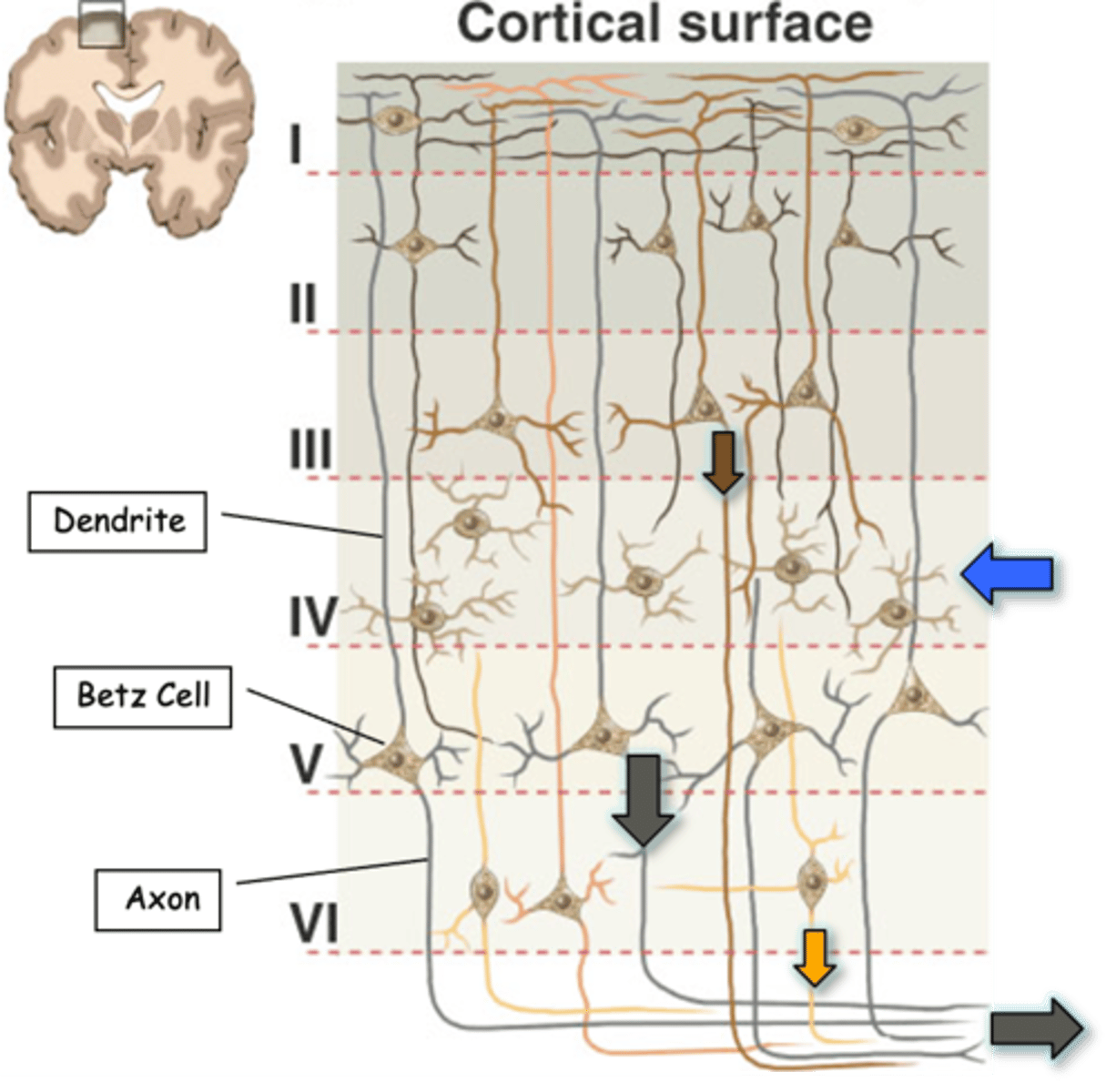
Lateral, medial
Similar to the somatosensory system, CST outputs to the upper body originate from ________ motor cortex, outputs to lower body from _________ motor cortex
Different sets of upper motor neurons control different functions
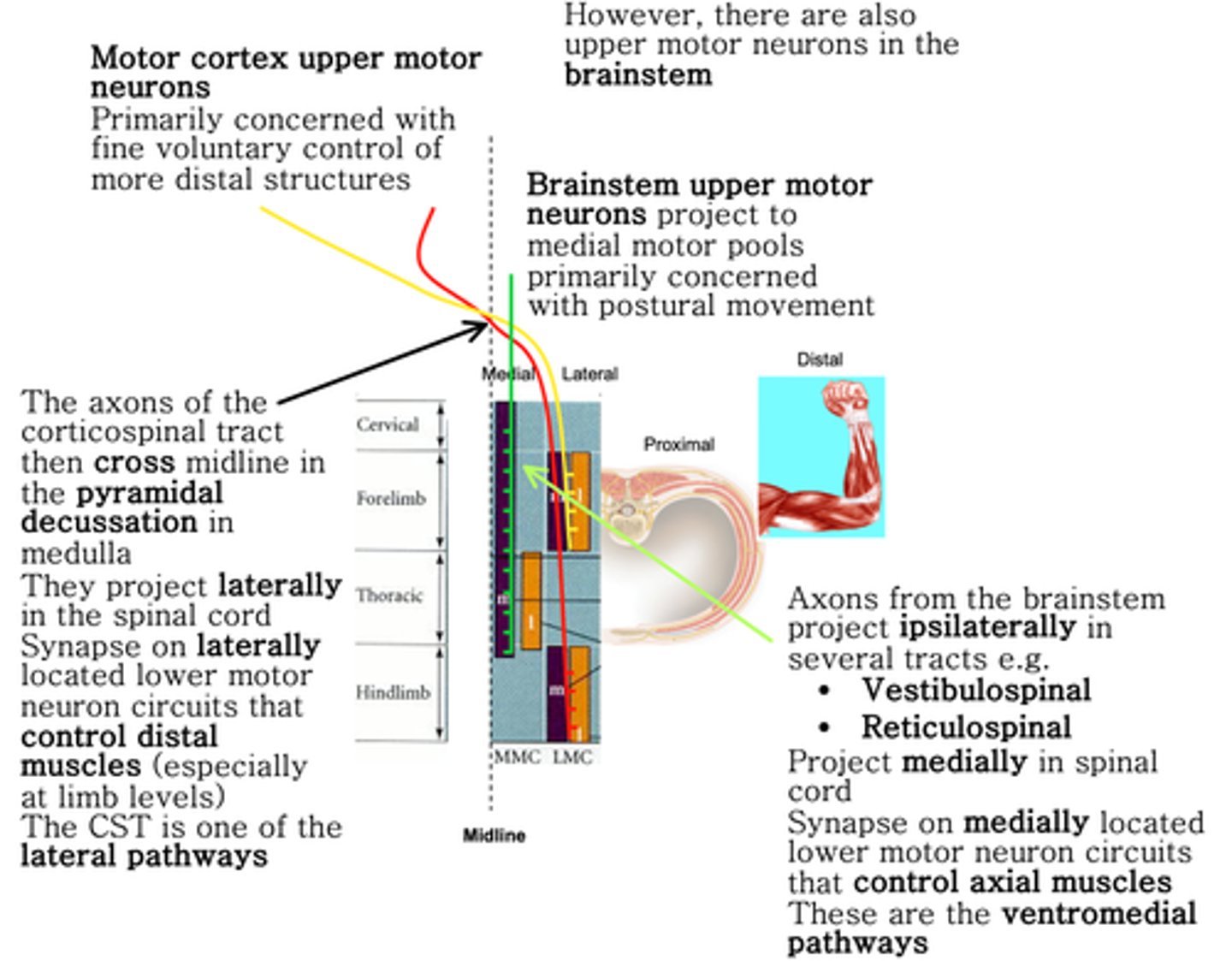
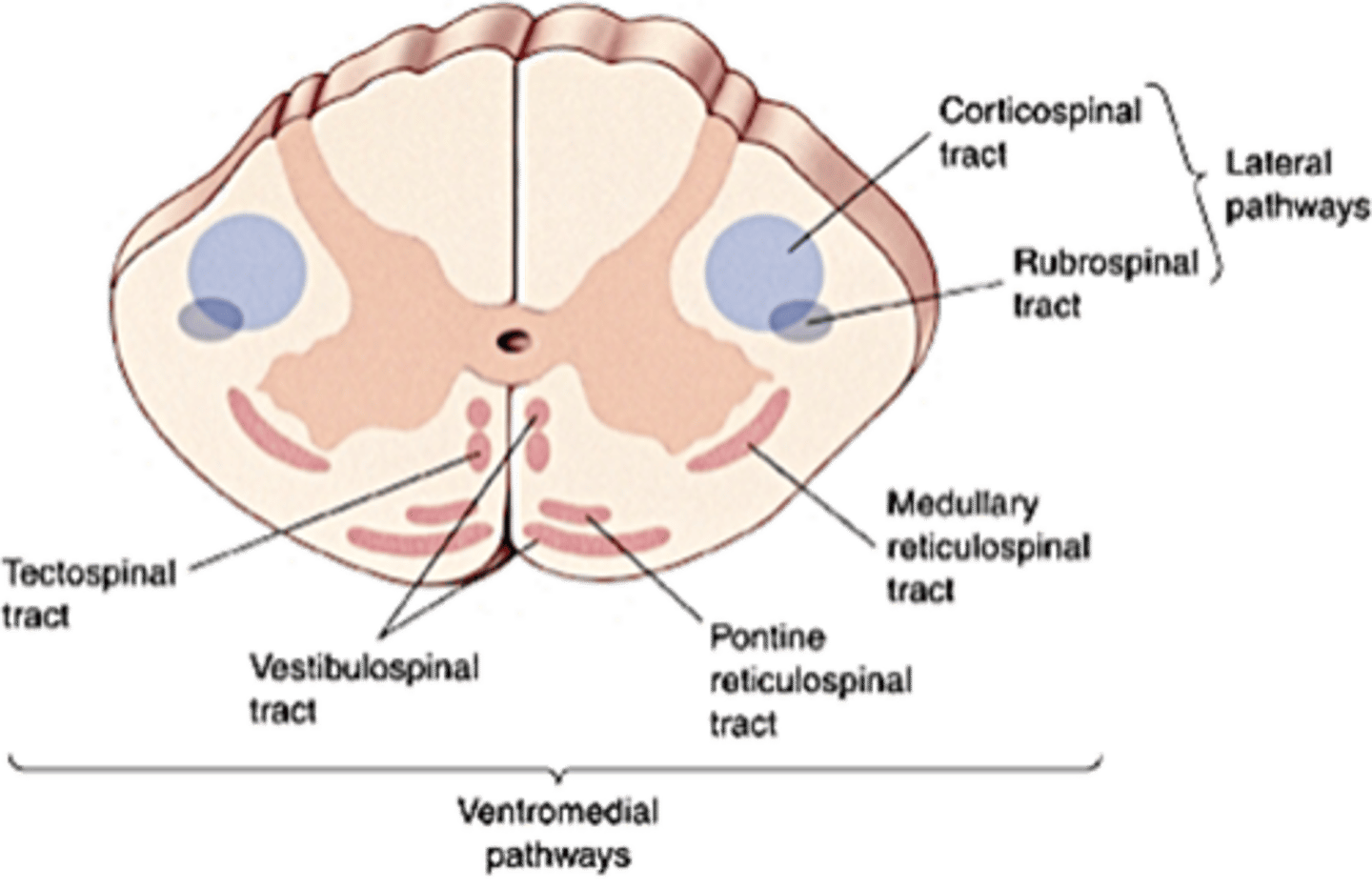
Posture
What do the ventromedial pathways control?
Ipsilaterally, medially
The ventromedial pathways project mainly ______________ and _________
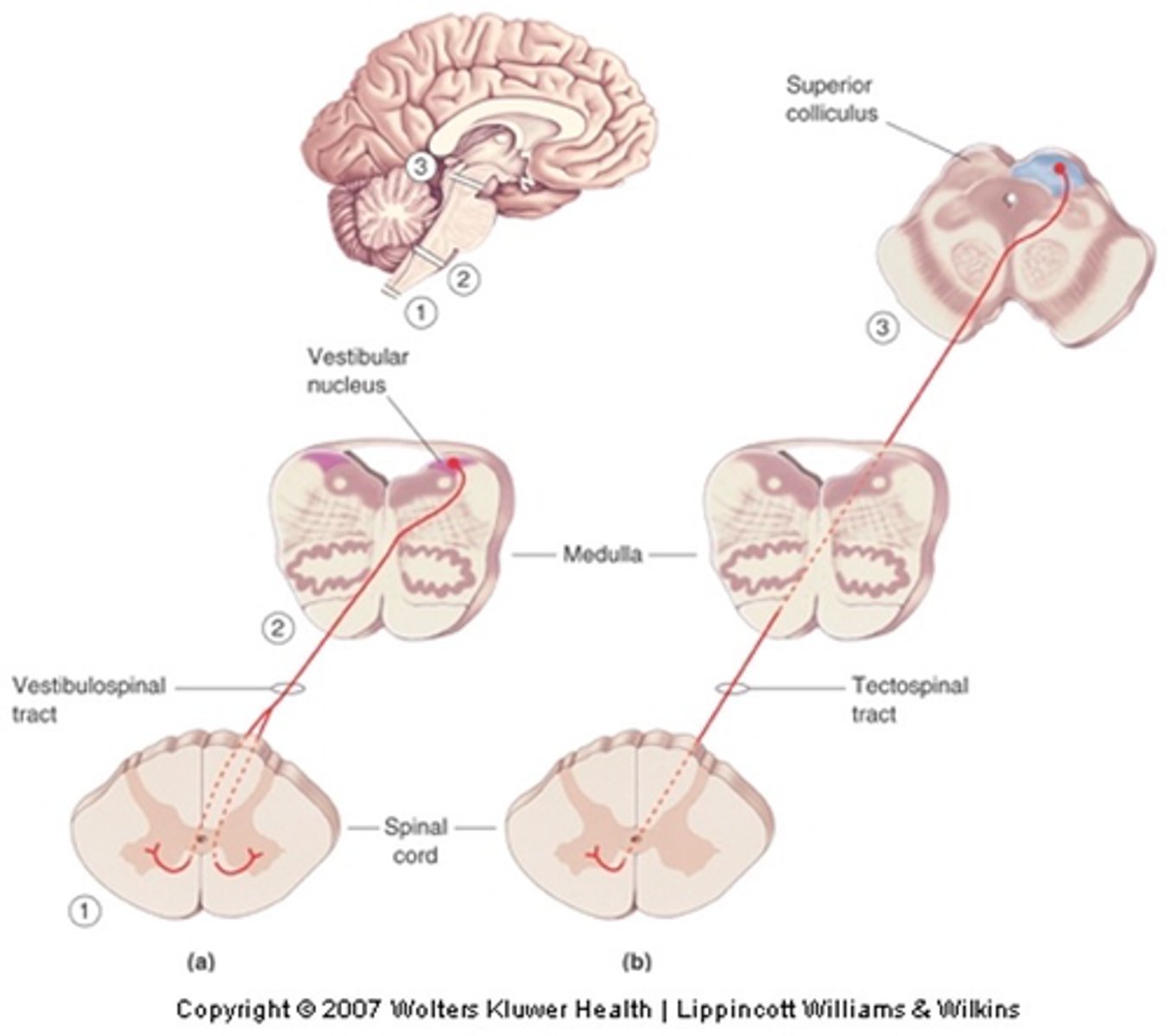
Head balance and turning (inputs from vestibular system)
What is the vestobulospinal tract involved in?
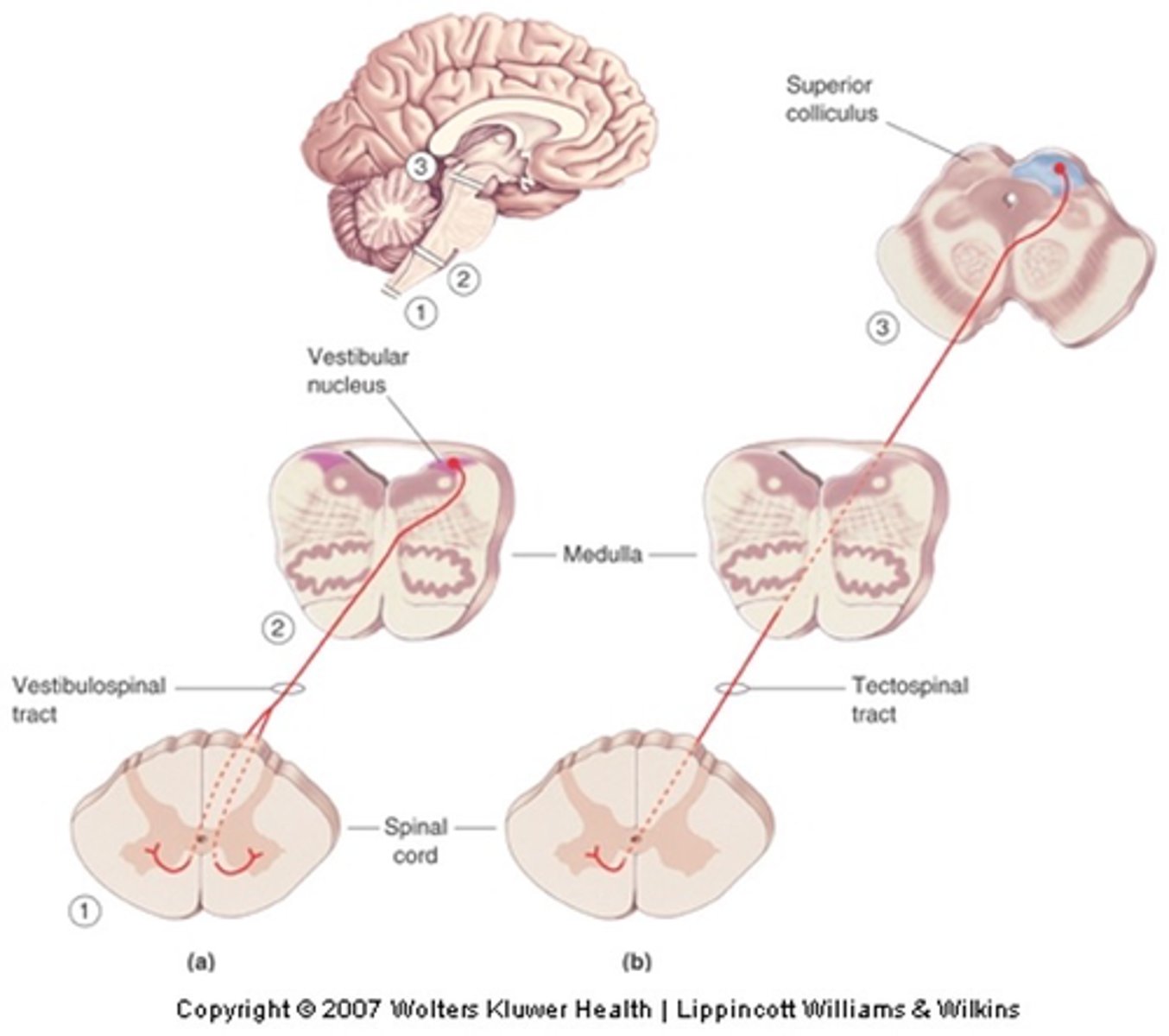
Orienting response (inputs from visual system via superior colliculus)
What is the tectospinal tract involved in?
Antigravity reflexes
What do reticulospinal tracts control?
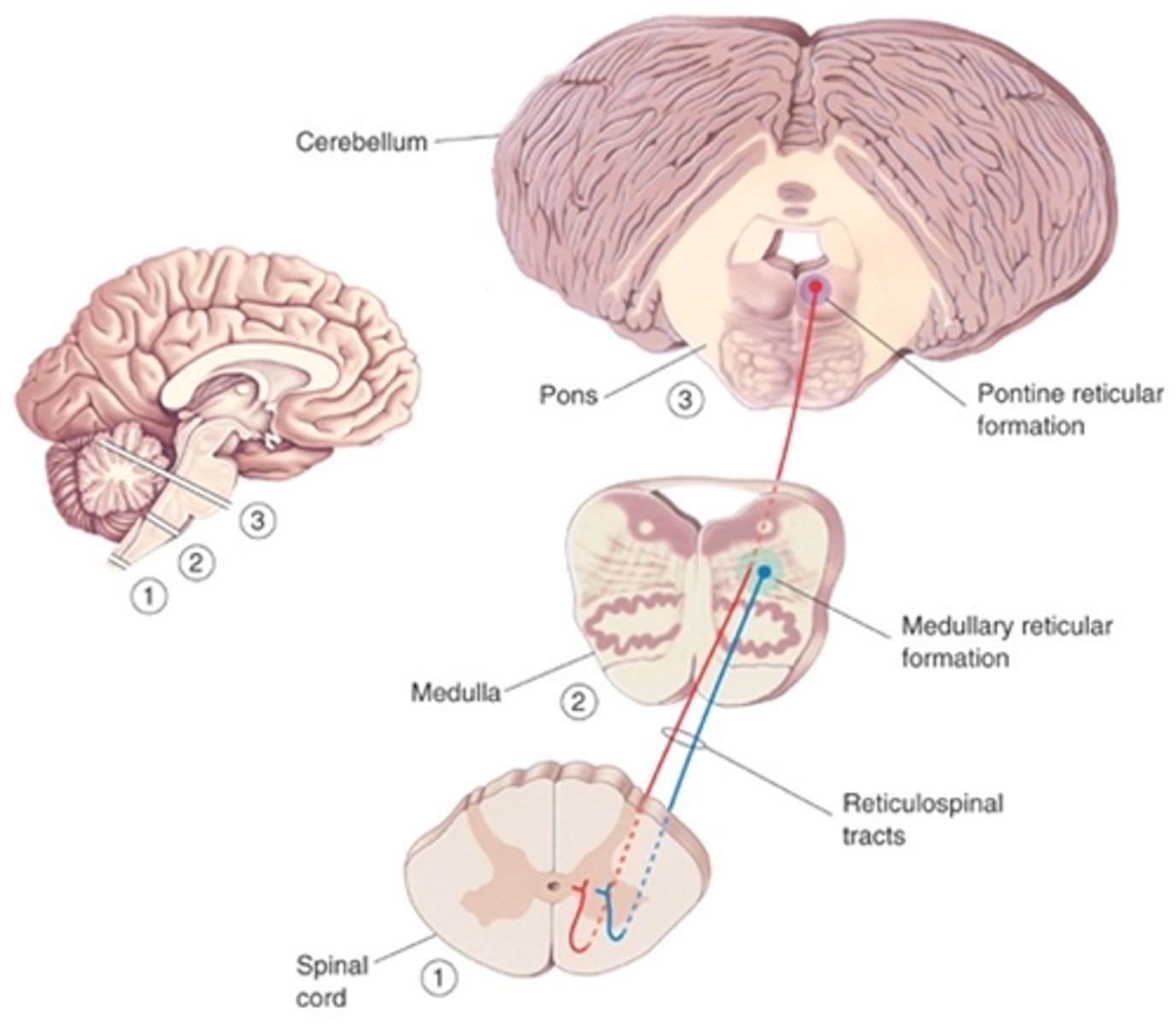
Complex voluntary movements
What do upper motor neurones of the motor cortex initiate?
Contralaterally, corticospinal, lateral
Upper motor neurons of the motor cortex project mainly ______________ via the _________________ tract primarily to muscles involved in precise limb movements, particularly those of the hands in humans - one of the _________ pathways of the spinal cord
Coritcobulbar
Upper motor neurons of the motor cortex also project via the __________________ tract to the hypoglossal nucleus in the brainstem, which controls the movements of the tongue - important for speech in humans
Maintenance of posture and balance
What are upper motor neurons of the brainstem more concerned with?
Reicular formation, vestibular nucleus (vestibular co-ordination) and superior colliculus (visual co-ordination)
Upper motor neurons of the brainstem are located in several nuclei including ...?
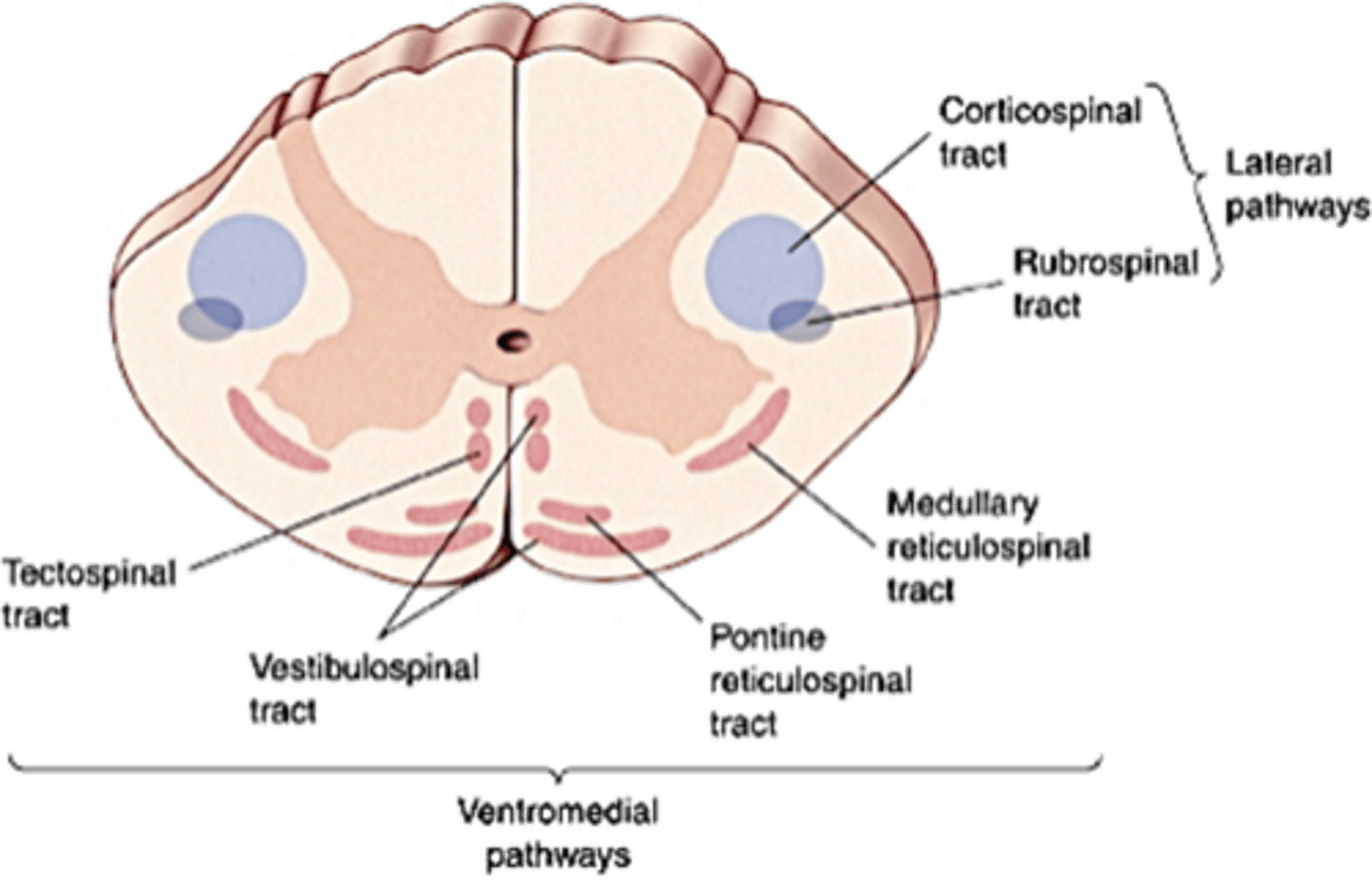
Ipsilaterally, axial, ventromedial
Upper motor neurons of the brainstem project mainly _____________ to lower motor neurons controlling ______ muscles concerned with maintaining posture - the ______________ pathways of the spinal cord
Lower motor neurons, muscle fibres
Upper motor neurons always synapse on __________ _________ __________ (or their interneuron circuitry) whereas lower motor neurons always synapse directly on _________ __________
Volunteer will lift lever in response to auditory stimulus (tone)
Recording from different muscles reveal that the first to contract are those in the leg
This anticipatory 'feedforward' mechanism pre-adjusts body posture to compensate for the forces that will be generated when the lever is lifted
Describe the experiment involving integration of postural control with voluntary movement
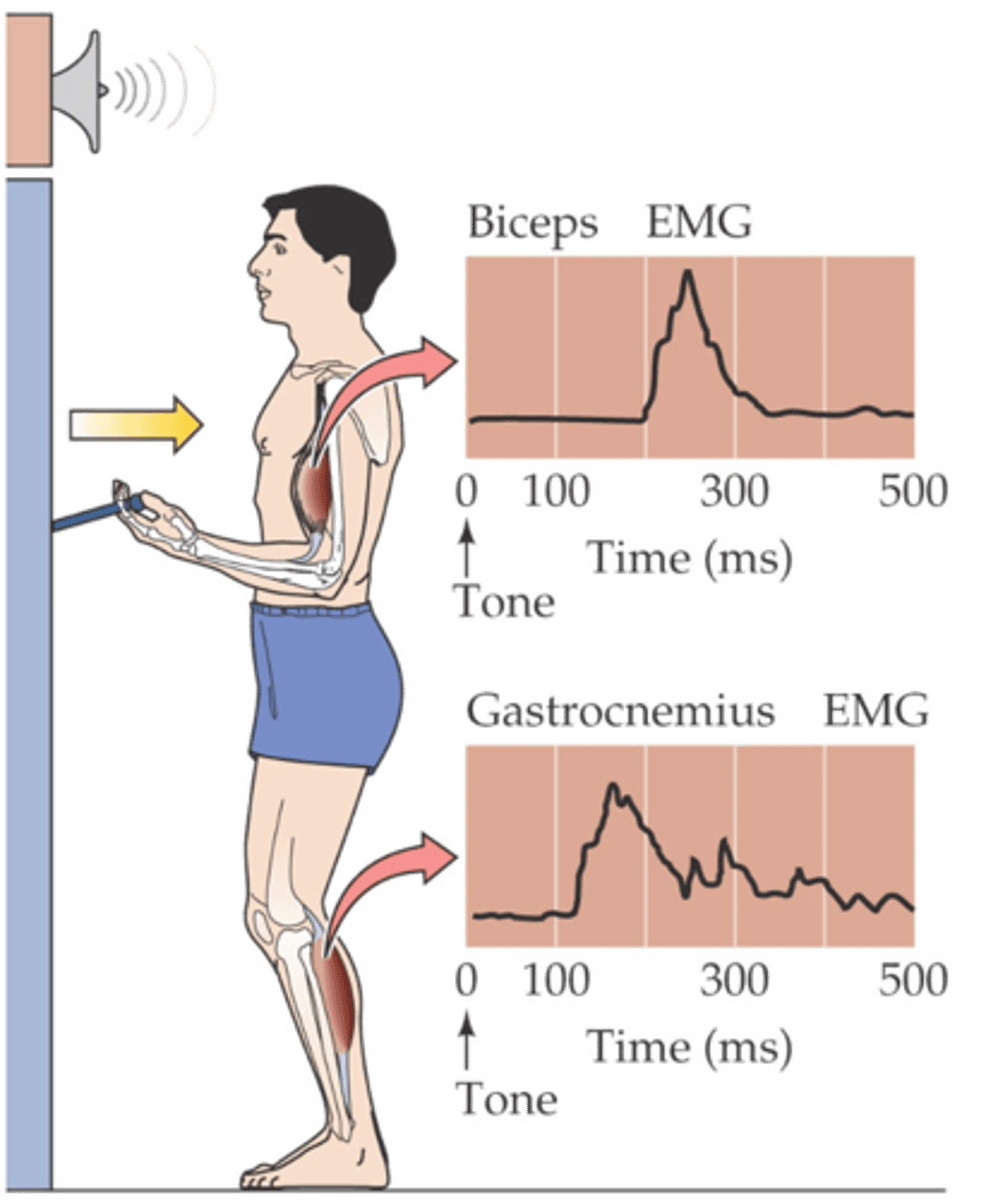
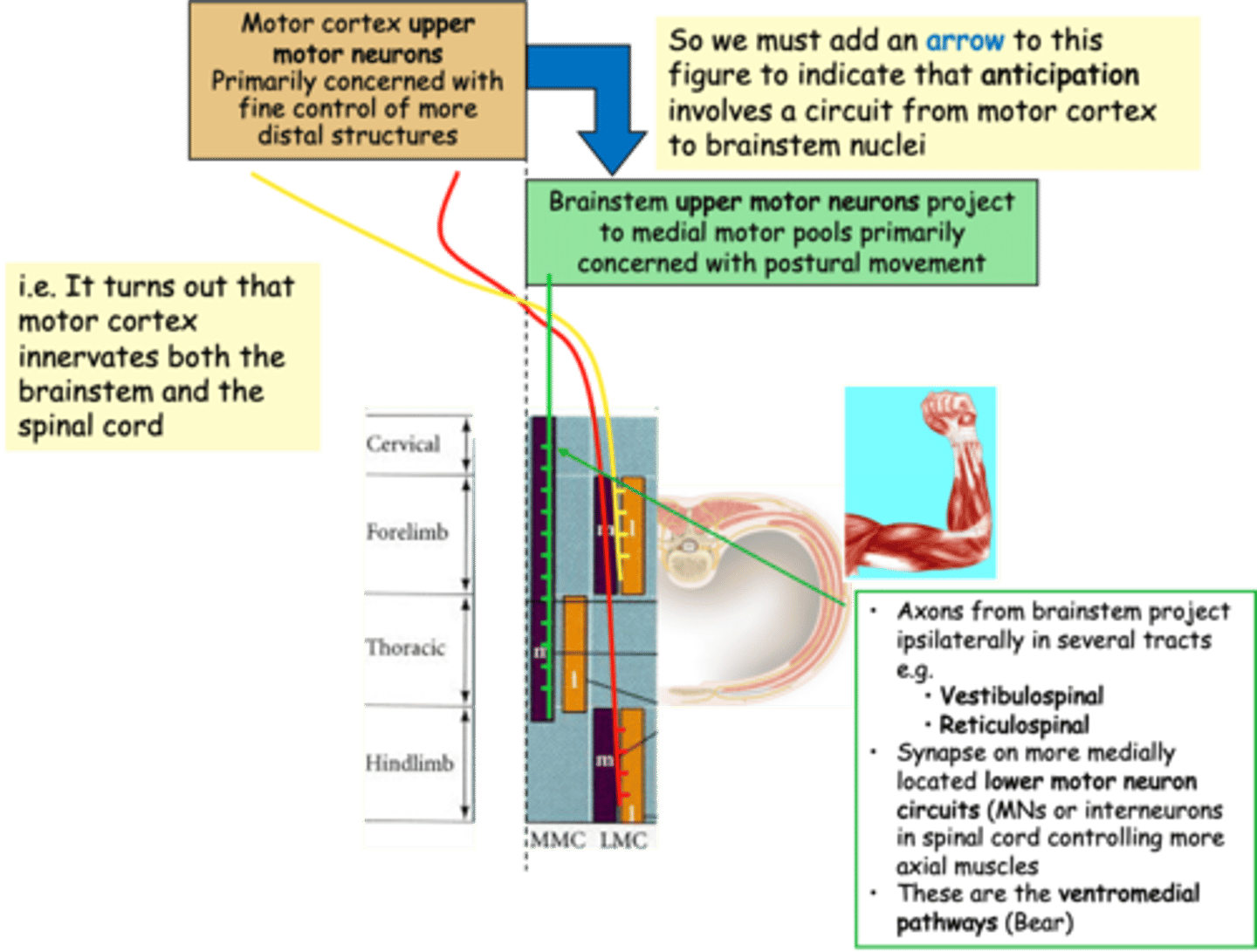
That upper MNs in the cortex influence spinal cord circuits by two routes
Feedforward mechanism makes sense when you realise what?
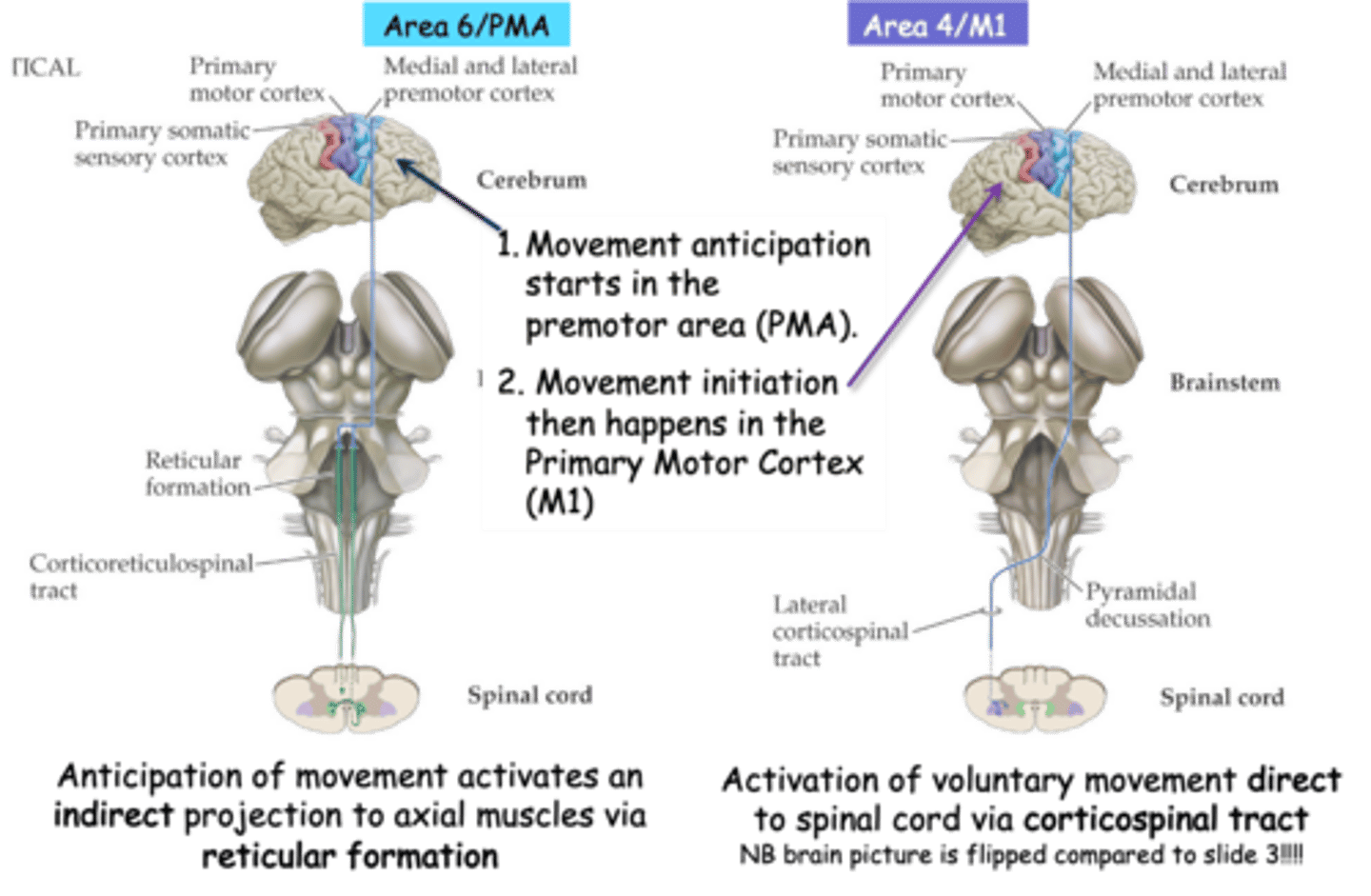
Precedes
Activity in the PMA ___________ activity in M1 and coincides with movement planning/anticipation
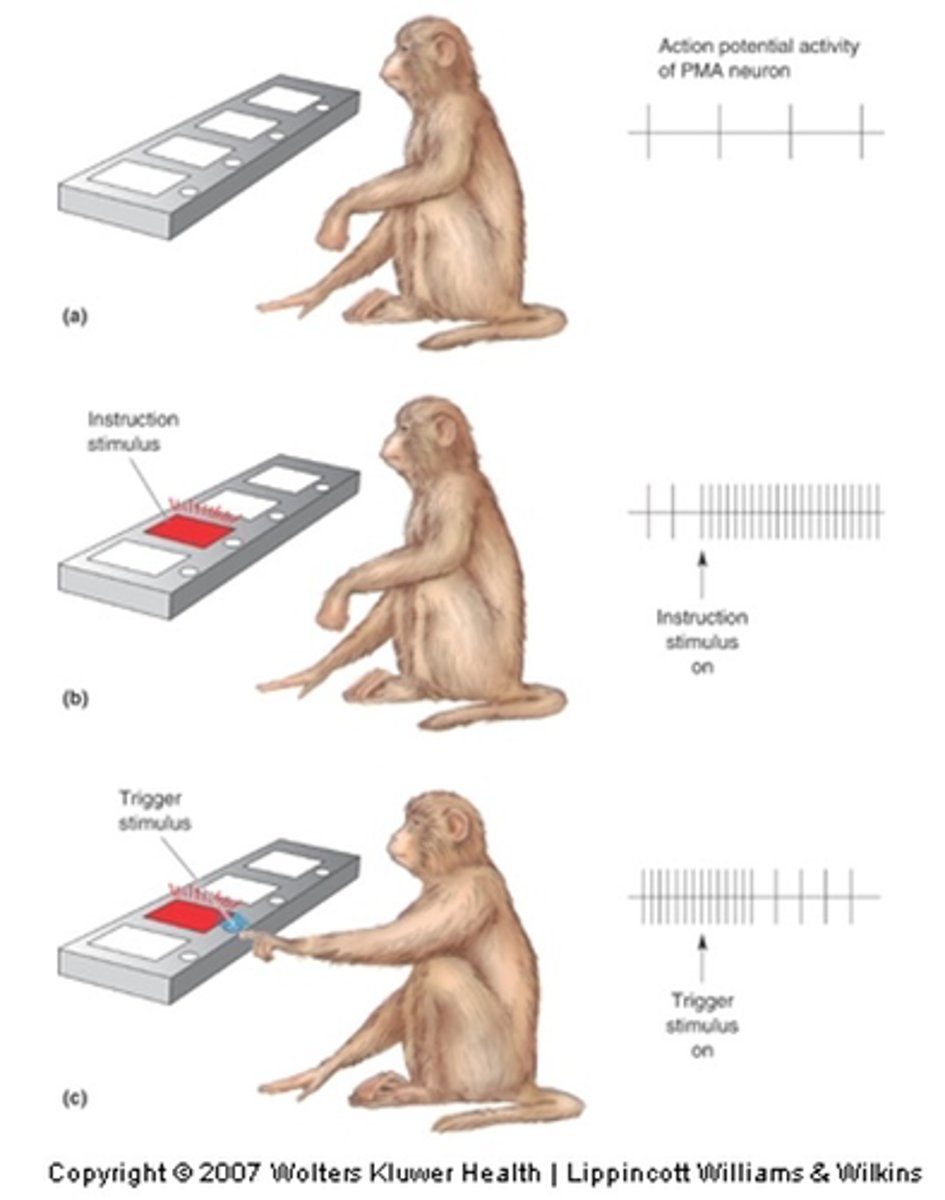
Move
Clearly motor neurons, both lower and upper are vital to our ability to ______ and hence to our behaviour and survival in complex environments
When they are dysfunctional the consequences are significant
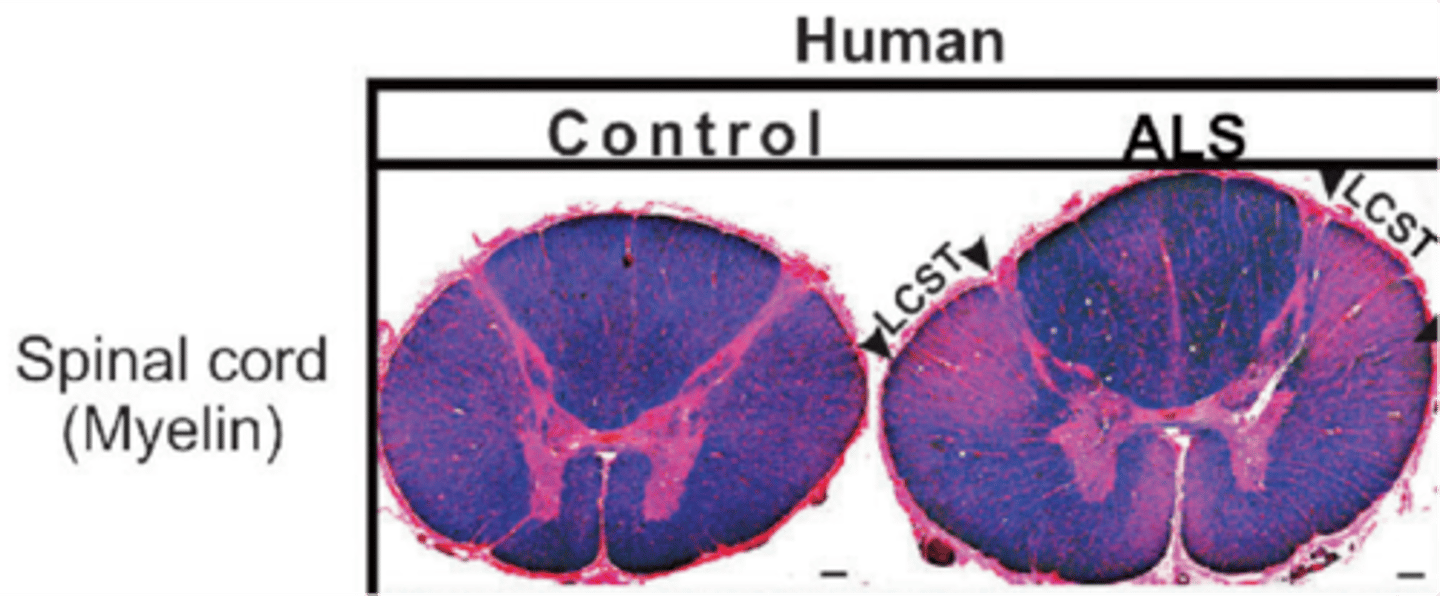
A degenerative disease of motor neurons
What is MND/Amyotropic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
Jean-Martin Charcot in 1869
When was MND/ALS first described and by whom?
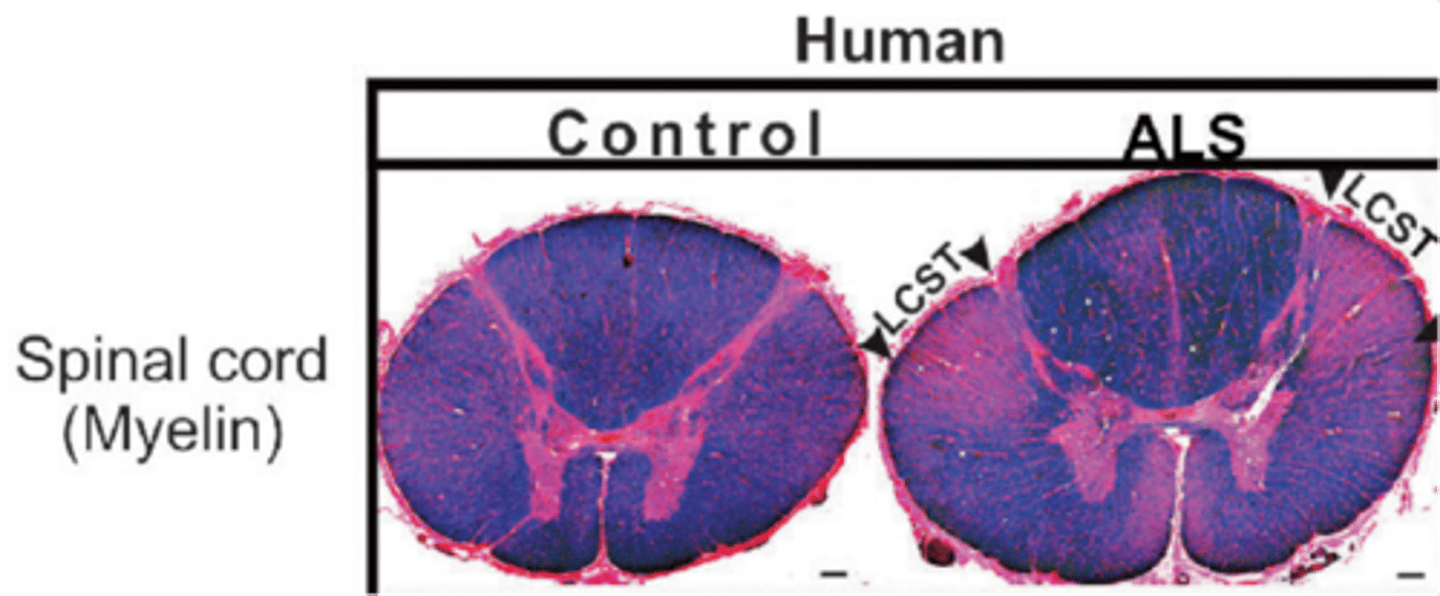
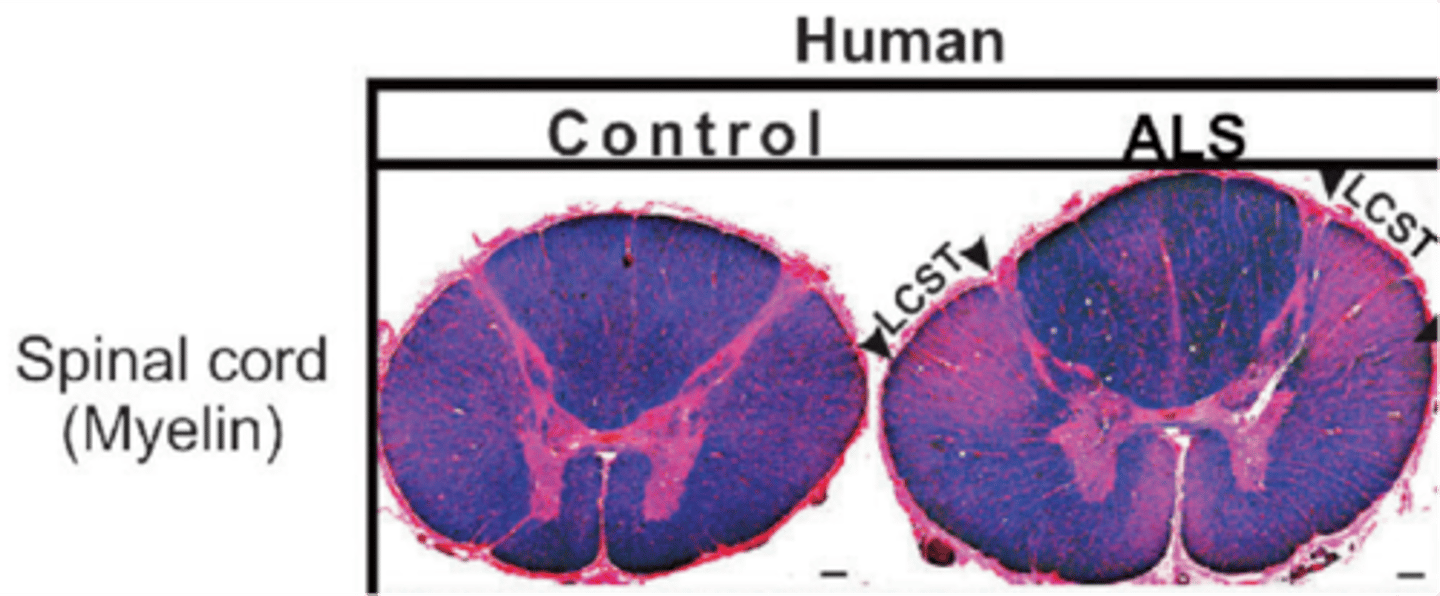
Muscle atrophy (amyotrophic means 'loss of muscle nourishment') and sclerosis ('hardening' or 'scarring') of the lateral spinal cord, which is the mark of degeneration of axons in the CST (pink)
MND/ALS is characterised by what?
New York Yankees baseball star Lou Gehrig when he contracted it in 1938
Who made MND/ALS famous and when?
Muscle paresis (weakness) or paralysis
Loss of muscle tone due to loss of stretch reflexes
Ultimately, leads to severe muscle atrophy
Patients usually die from lung dysfunction (due to atrophy of intercostal muscles)
What is lower motor neuron disease characterised by?
Muscle weakness
Spasticity due to increased muscle tone (due to failure of modulation of stretch reflex)
Hyperactive reflexes
Loss of fine voluntary movement
Patients usually die from loss of input to the bulbar muscles (tongue and pharynx) via the corticobulbar tract
What is upper motor neuron disease characterised by?
Intellect
What is not compromised in neither version of motor neuron disease?
5
Most MNS patients die within _ years of diagnosis
Neurodegenerative
ALS is one of several ______________________ diseases
Where overstimulation, typically by glutamate, leads to neuronal cell death
Excitoxicity is a possibility of ALS, what is it?
Hypoxic
A 'vicious cycle' of glutamate release can occur particularly in _________ conditions e.g. after cardiac arrest, stroke or brain trauma
-> Lou Gehrig's ALS has been suggested to have been triggered by the blow of a baseball to his head
Blocker, glutamate
The only drug to have any effect on ALS is a __________ of ___________ release (Riluzole) but this only delays the disease by a couple of months
10
About __% of cases of ALS have a clear genetic (inherited) basis
Superoxide dismutase
One of these results from mutations in the gene encoding ____________ ___________ (SOD1), a key enzyme that 'maps up' the free radicals that accumulate in metabolically active cells
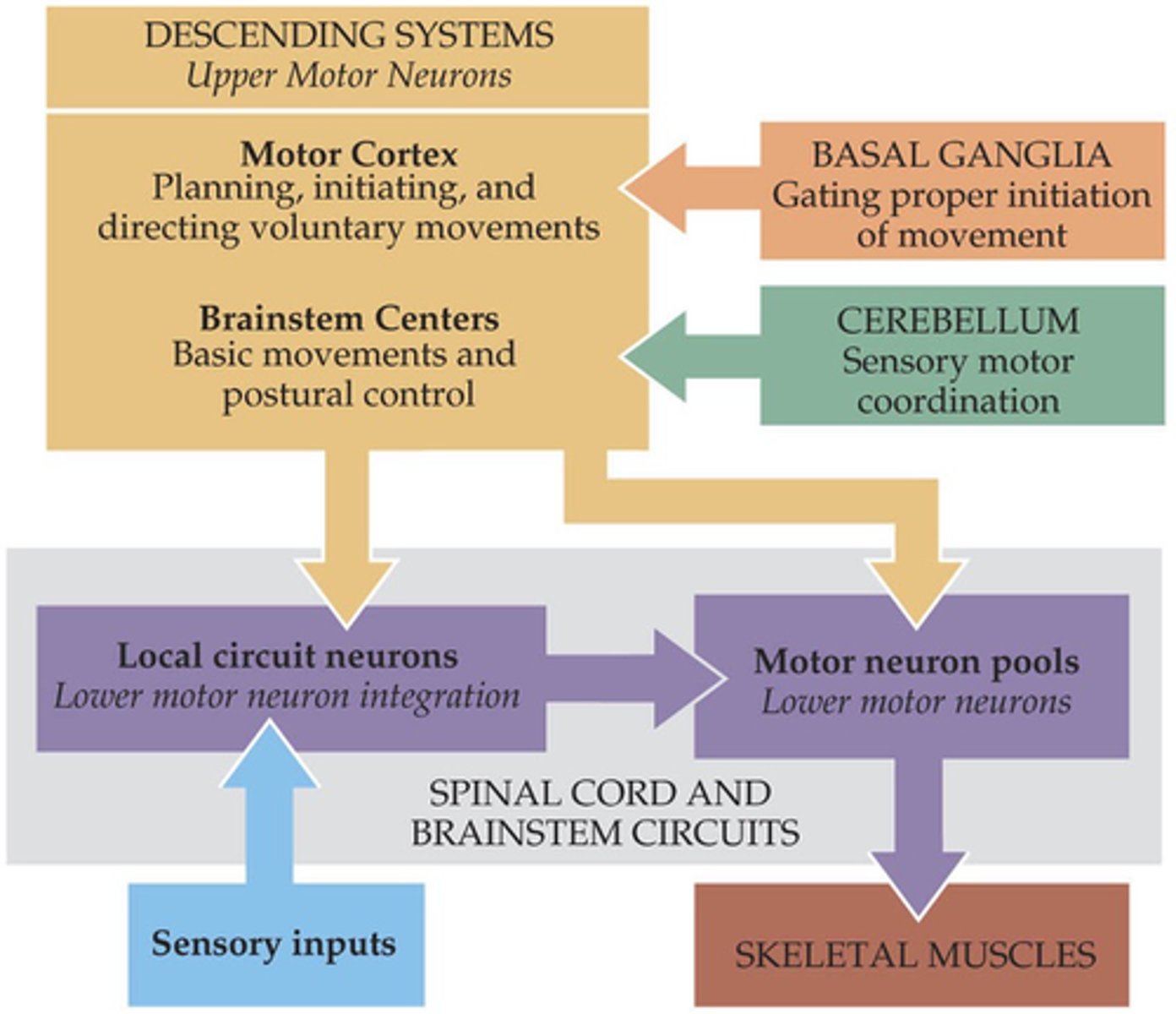
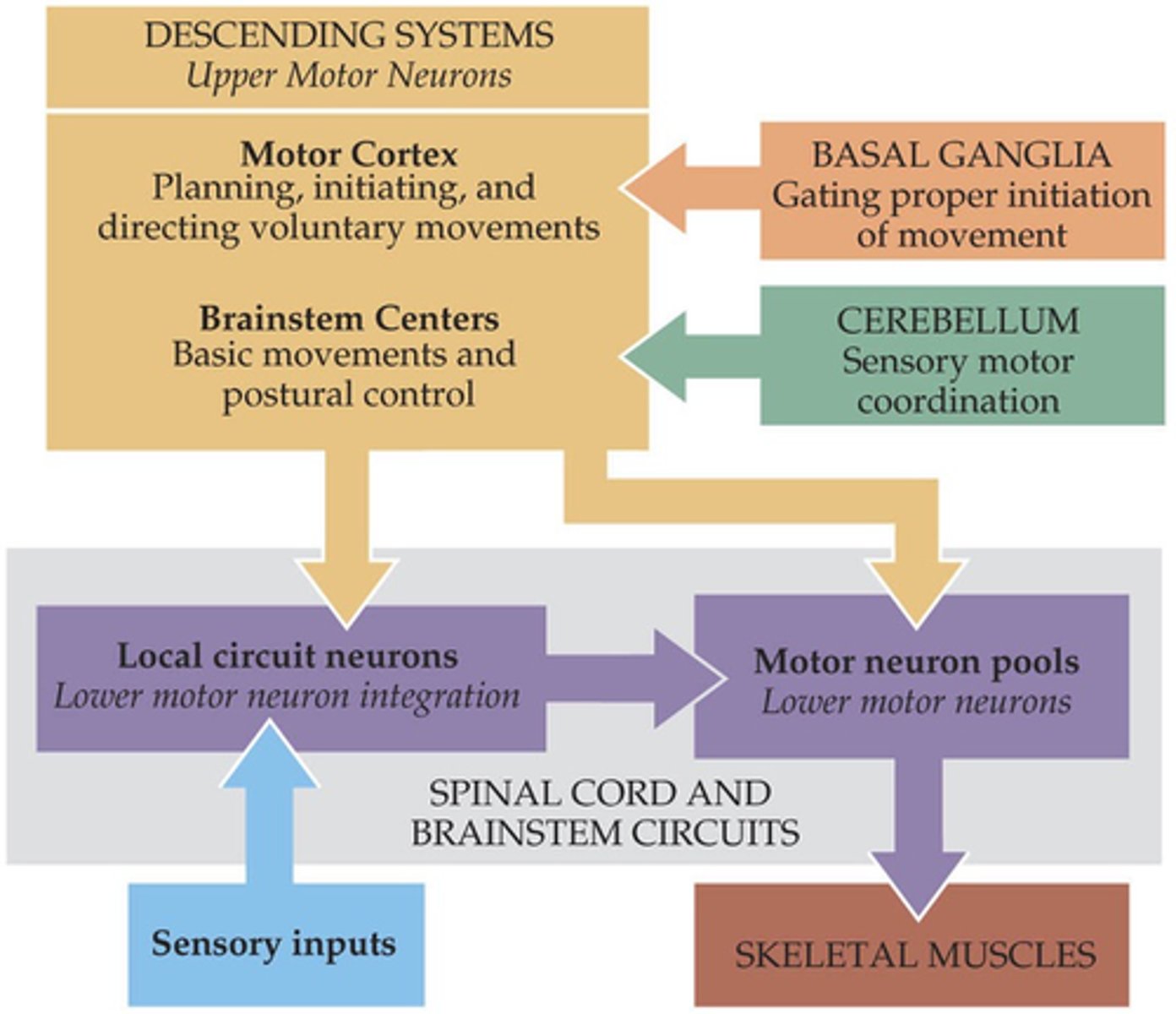
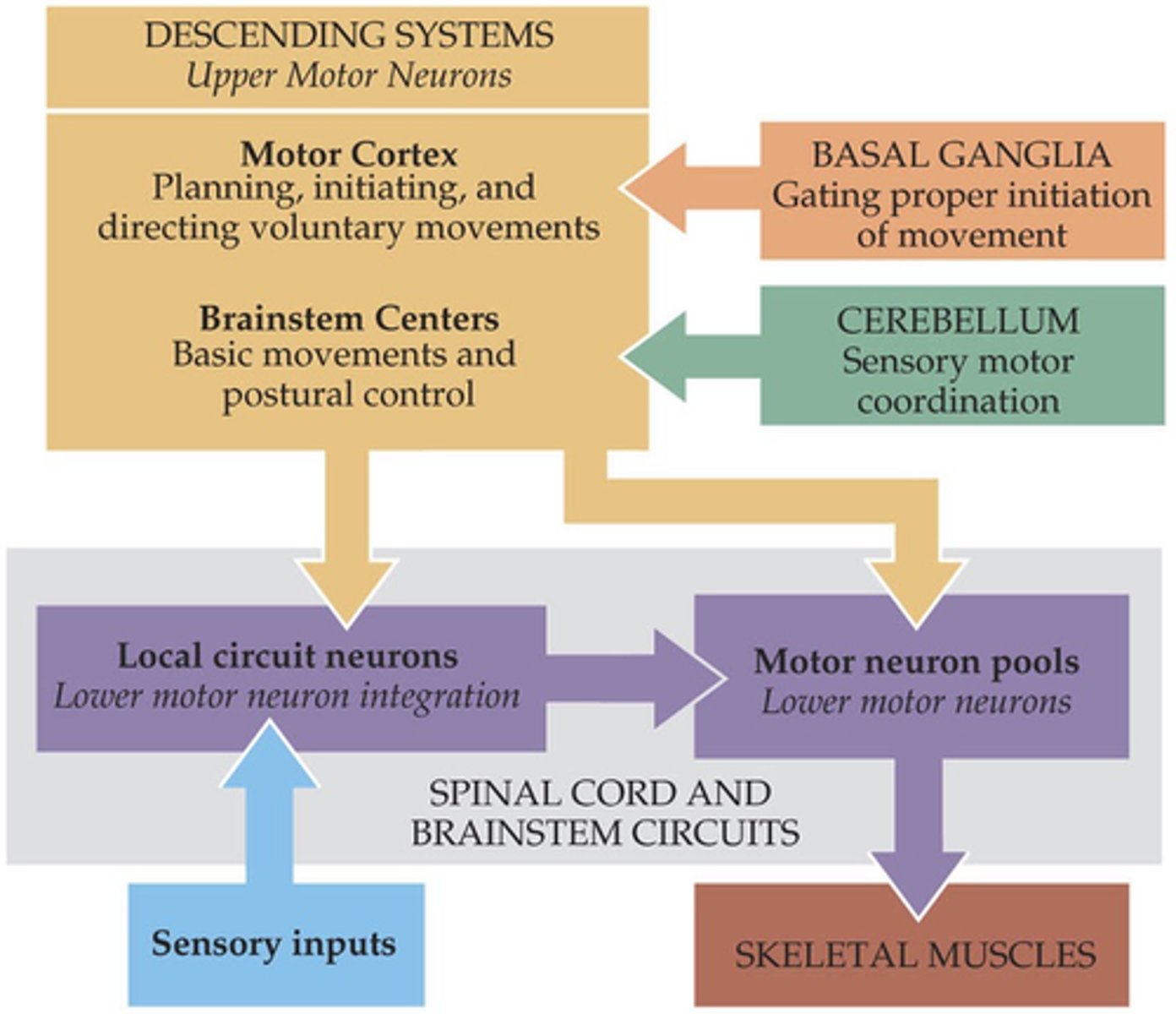
Descending pathways
The brain exerts control over spinal motor units via specific ______________ __________
Lower
Spinal motor neurons = ________ motor neurons
Upper
_________ motor neurons reside in brainstem and cortex, controlling postural and voluntary movements respectively
Voluntary
Postural control is integrated with ___________ movement and is part of movement planning/anticipation
Upper, lower
Motor neuron degeneration can affect either ________ or ________ motor neurons and is almost always fatal