Microanatomy
1/988
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
989 Terms
Plasma membrane
The membrane that the cell is bound by, separating the cell from the external environment
Substance of the nuecleus
Nucleoplasm
What is the nucleus bound by
Nuclear envelope
Cytoskeleton
Cytosolic network of minute tubules and filaments
Phospholipid polar head composition
Glycerol conjugated to nitrogenous compound such as choline, ethanolamine, or serine via phosphate bridge
What is ratio of cholesterol to phospholipid in a cell
1:1
Role of cholesterol in cell membrane
Prevent overly dense packing of FA tails
How are extrinsic proteins connected to cellular membrane
Weak electrostatic forces
Glycoproteins + Glycolipid
Many membrane proteins and some lipids are conjugated with short chains of polysacharides. They form the glycocalyxR
Role of glycocalyx
Cell recognition, intercellular adhesion formation, adsorption of molecules to cell surface, mechanical + chemical protection
3 mechanisms of external information transport to cell interior
Lipid soluble messengers pass through cell to bind to intracellular receptor
Messenger binds to cell surface, activating cytoplasmic second messengers to pass on information
Nerve cells release neurotransmitters that bind to nerve cell or muscle cell opening an ion channel for membrane depolarization
Contents of the nucleus
DNA, nucleoprotein, RNA
Types of nucleoprotein
Histone protein: bind to DNA and control DNA coiling
Non-histone protein: include enzymes for DNA and RNA synth, regulatory proteins
Types of chromatin inside the nucleus
Heterochromatin: Tightly coiled inactive chromatin in irregular clumps around periphery
Euchromatin - DNA active in RNA synthesis
Role of nucleoli
Sites of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly - seen in cells with highly active protein synthesis
Nuclear envelope
2 layers of membrane with intramembranous space
Outerlayer continuous with RER
Inner aspect is nuclear lamina, consiting of polypeptides called lamins - link membrane proteins and heterochromatinR
Role of nuclear pores
Allow inner and outer membranes to be continuous - allow exchange of metabolites, macromolecules, ribosomal subunits between nucleus and cytoplasm
Composition of ER
Interconnecting network of membranous tubules, vesicles, and flattened sacs (cisternae)
rER function
Exported protein + lysosomal protein production
What is synthesized on free ribosomes
Proteins destined for the cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondria
Function of sER
Lipid biosynthesis and membrane synthesis and repair
Golgi function
Processing and packaging of macromolecules for export out of cell or storage for use inside cell
Role of transition vesicles
Shuttle rER molecules to Golgi
Lysosomes
Membrane bound organelles with around 50 digestive enzymes to breakdown macromolecules
Classes of lysosomes
Primary - only digestive enzymes
Secondary - enzymes and molecules that the cell must break down
what happens to products of lysosomal digestion
Released otuside the cell or absorbed and used again by the cell
Peroxisomes
Membrane bound organelles with different enzymes than lysosomes: they have oxidases
Unique feature of mitochondria
Contains one or more stands ot circular DNA and ribosomes, allowing for synthesis of 37 of its own proteins. It also allows the mitochondria to undergo self-replication
Cytoskeleton structural elements
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
Microfilaments
Fine strands of actin
Intermediate filaments
Immediate size - proteins have purely structural function
Microtubules
Largest cytoskeleton component, originate from centriole found in th centrosome
Centrosome components
2 centrioles - each centriole consists of nine triplets of microtubules in a cylindrical manner
4 functions of the cytoskeleton
Provides structural support to plasma membrane, cellular organelles, and some cytosolic enzyme systems
Provides means for movement of intracellular organelles, PM, and other cytosol constituents necessary for routine functions of all cells
Provides locomotor mechanism for ameboid movements and specialized motile structures such as cilia and flagella
Responsible for contractility in specialized tissues such as muscle
Result of mitosis
2 identical daughter cells
Cell cycle phases
G1 - cell differentiation and specialized functions performed as part of whole tissue
S phase - synthesis phase, DNA replication occurs
G2 - Period which cells prepare for mitotic division
M phase - Mitosis
G0 - Phase of continuous differentiated function
4 phases of mitosis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase
Chromosome condensation, nucleoli disappear, dissolution of nuclear envelope. Centrioles migrate to opposite poles of cell
Metaphase
Each duplicated chromosome becomes attached to mitotic spindle and are arranged in the plane of the spindle equator known as the metaphase plateA
Anaphase
Centrioles pulled apart and the chromatids of each duplicated chromosome are drawn to opposite ends of the spindle. By the end, two groups of identical chromosomes are clustered at opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reassembles, nucleoli becomes apparent, cytoplasmic division occurs
Location of meiosis
Only in germ cells of the gonads during formation of gametes
How many cel division processes of meiosis are there
2
First meiotic division
Results in 2 non-identical daughter cells. No chromatid separation, but there is exchange of genetic information between chromatids of homologous pairs of duplicated chromosomes
Second meiotic division
Spitting or rearranged duplicated chromosomes to liberate chromatids which migrate to opposite poles of the spindle
Product of meiosis
4 non-identical daughter cells
2 mechanisms of cell death
Apoptosis, necrosis
Apoptosis
Method of cell death is an active process, requiring the expenditure of energy. Has various triggers and does not incite an inflammatory reaction
Necrosis
Cell death in pathological conditions. Characterized by the inability of cells to produce energy to maintain homeostasis and incites an inflammatory reaction
Apoptosis mechanism
Cell receives signal to initiate apoptosis
Condensation of nuclear chromatin (pyknosis)
Cell shrinks away from neighbors with loss of cell-cell contacts
Nuclear material breaks into fragments (karyorrhexis) which is accompanied by dissolution of nuclear membrane
Cytoplasmic blebs break away from cell surface and eventually the entire cell breaks up (karyolysis)
Macrophages phagocytose cellular debris
What is epithelia
Group of tissues which cover exposed body surfaced and line body cavities, tubes, and organs
Roles of epithelial
1. Selective diffusion
2. Absorption
3. Secretion
4. Physical protection
5. Containment
One function of epithelia is containment - what does this mean?
Epithelia forms a barrier on the body, preventing loss of fluid or pathogens from entering our body
General anatomy of epithelia
- Form continues sheets comprising of one or more layers.
- Closely bound to each other by cell junctions
- Supported by basement membrane (separates epithelia from underlying supportive surfaces)
How do the epithelia receive oxygen and metabolites
Via diffusion from supporting tissues. Basement membrane is never penetrated by blood vessel
How is epithelia classified
1. Number of cell layers
2. Shape of component cells
3. Presence of surface specializations
Simple epithelium
Single layer of epithelial cells on basement membrane
Role of simple epithelium
Found at interfaces of selective diffusion, absorption, or secretion (but no protection against mechanical force)
Stratified epithelium
Several layers of cells sit on basement membrane
Squamous epithelium
Flattened cells
Simple squamous epithelium
Flattened, irregularly shaped cells, forming continuous surface
Role of simple squamous epithelium
Allows for passive transport (diffusion) of gases or fluids
Where can simple squamous epithelium be found?
- Lines blood vessels (endothelium)
- Lines body cavities (mesothelium): pleural (lung), pericardial (heart), peritoneal (abdominal)
- Alveoli of lungs
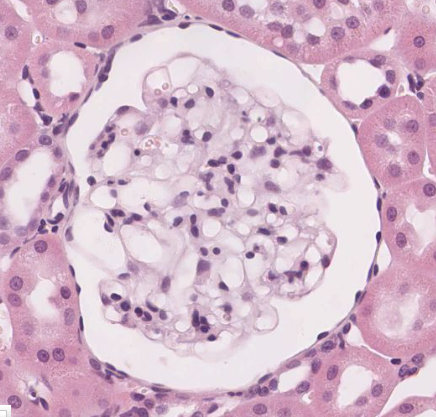
- Bowman's capsule in kidney (allowing for nutrients from glomerulus)
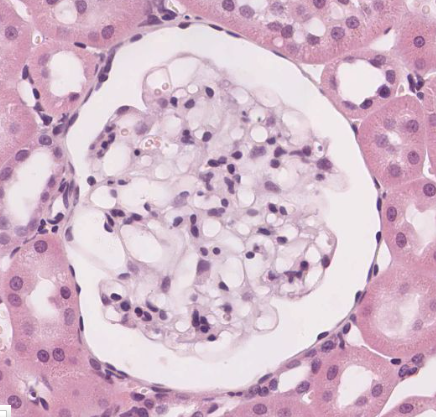
What epithelium is this? What is the strucure?
Simple squamous epithelium. Structure is Bowman's capsule from the kidney
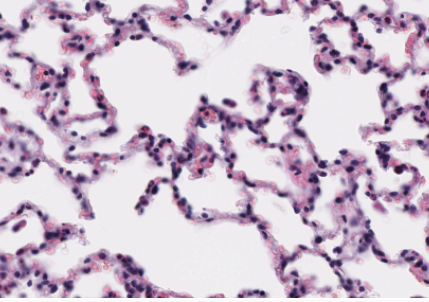
What epithelium is this? What is the structure?
Simple squamous epithelium. Structure is alveoli from the lung
simple cuboidal epithelium
Intermediate between simple squamous and simple columnar epithelium. Epithelial cells appear square, with a round nucleus
Role of simple cuboidal epithelium
Lines small ducts and tubules - used for excretory, secretory, or absorptive functions
Where can simple cuboidal epithelium be found?
- Kidney tubules;
- ducts and secretory portions of small glands
- ovary surface
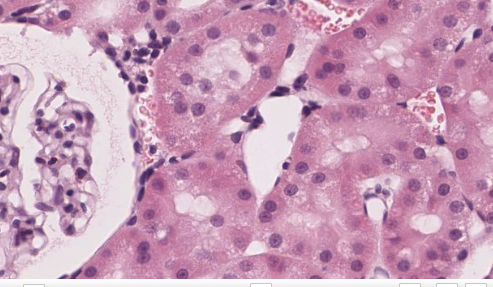
What type of epithelium is shown on the right side? What is the structure
Simple cuboidal. Structure is kidney tubules (see glomerulus + bowman's capsule to the left)
simple columnar epithelium
Similar to cuboidal, but cells are taller and appear like columns, perpendicular to basement membrane. Nucleus is often elongated, and location is variable in the cytoplasm
Function of simple columnar epithelium
absorption and secretion
Where is simple columnar epithelium found?
Digestive tract (colon, small intestine, stomach)
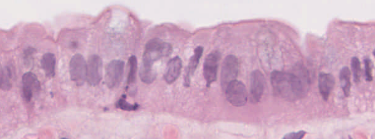
What type of epithelium is this?
Simple columnar
Simple columnar ciliated
Simple columnar epithelia with cilia on apical surface
Role of cilia
Beat in wave like manner - generating a current to propel fluid into one direction along epithelial surface
What is often seen among ciliated cells?
Non-ciliated cells, usually with a secretory function (like goblet cells)
Are cilia seen on stratified cells?
Never
Where is simple columnar ciliated epithelium found?
Fallopian tubes
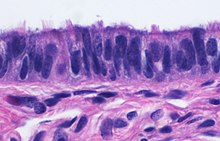
What type of epithelium is this?
Simple columnar ciliated. This is the fallopian tubes
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Psuedostratified = has the apperance of stratified epithelia, but is one cell layer to basement membrane. Nucleus location is variable. Nuclei is mainly found on basal side of cells. Have cilia
Where is Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium found?
Only in the respiratory tract (lung, trachea). AKA respiratory epithelium
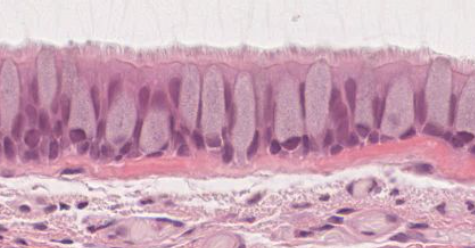
What type of epithelium is this? Where is it found?
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium. This is in respiratory tract (image is from trachea). Notice how nuclei are in the basal part of cell.
Role of stratified epithelium
Mainly protective function. Ill-suited for absorption.
How is stratified epithelium classified?
Based on cell type on apical surface. Most cells on basal surface are always cuboidal
Stratified cell sloughing
Apical cells have less access to nutrients, and will slough off. They are quickly replaced. Because of this, cancer drugs (targeting rapidly dividing cells) often harm stratified epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium
Variable number of cells, with squamous cell on apical surface. Basal cells divide continiusly
Where is stratified squamous epithelium found?
- Oral cavity
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Anal canal
- Uterine, cervix, vagina
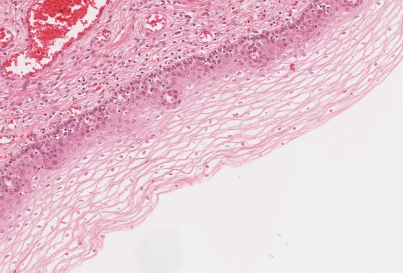
What type of epithelium is this?
Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
Specialized form of stratified squamous epithelium with layer of keratin (protein)
How is keratin formed?
Keratinization - During maturation, epithelial cells accumulate cross-linked cytoskeletal proteins
Role of keratin
Withstands constant abrasion and desiccation
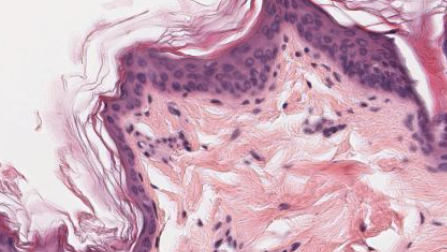
What type of epithelium is this? Where is it found?
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. This is found on skin
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Thin, stratified epithlium which usually consists of 2-3 layers of cuboidal/low columnar cells
Where is stratified cuboidal epithelium found?
Larger ducts of exocrine glands (esp. salivary glands)
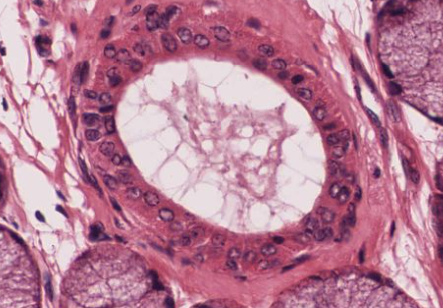
What type of epithelium is this? Where is it found?
Stratified cuboidal epithelium. This is from a salivary gland
Transitional epithelium
Form of stratified epithelium - has both features of stratified squamous and cuboidal epithelium. Top layer of cells are called "umbrella cells" - often multinucleated
Function of urothelium
Bladder needs to stretch when filling with urine. When stretched, cells look squamous, After urination, cells look more cuboidal
Where is transitional epithelium found?
Found only in the urinary tract. AKA urothelium
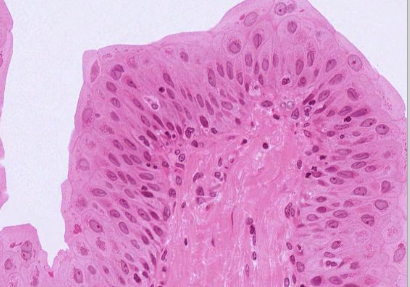
What type of epithelium is this? Where is it found?
Transitional epithelium. Found in urinary tract
Metaplasia
change from one type of epithelium to another