3 stages of translation ( elongation and termination)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
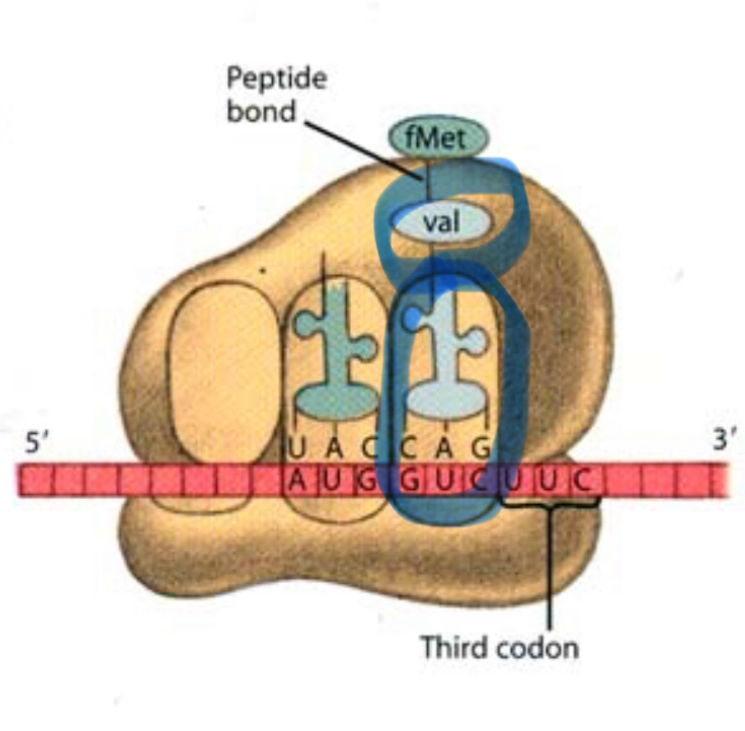
What enters the A site during elongation?
A tRNA carrying the next amino acid.
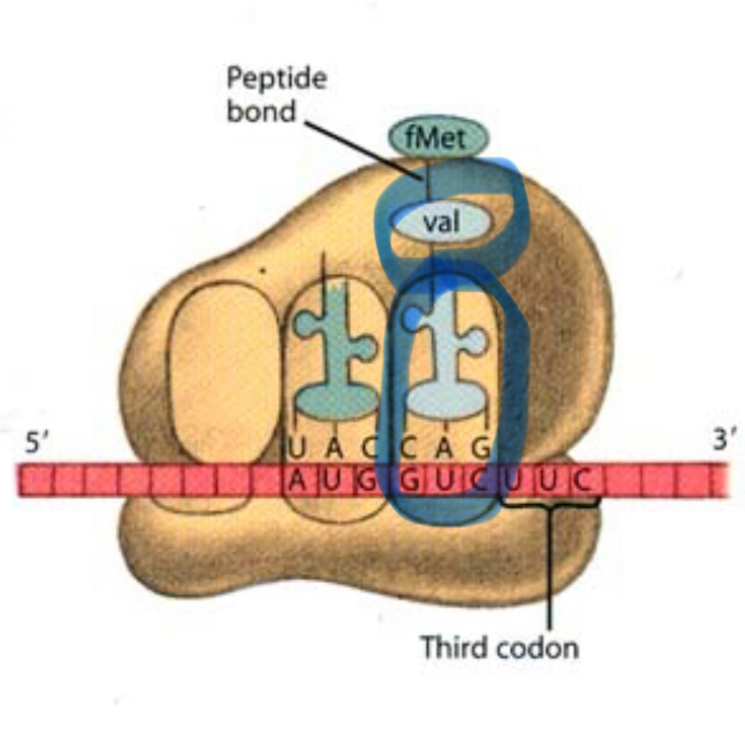
What allows the tRNA to bind correctly in the A site?
Its anticodon pairing with the mRNA codon.
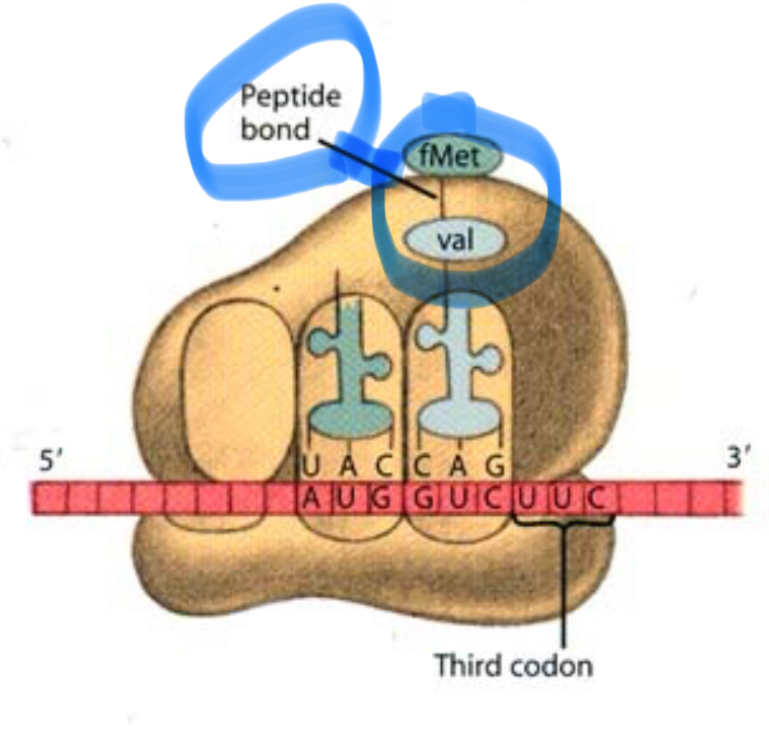
What bond forms between amino acids during elongation?
A peptide bond.
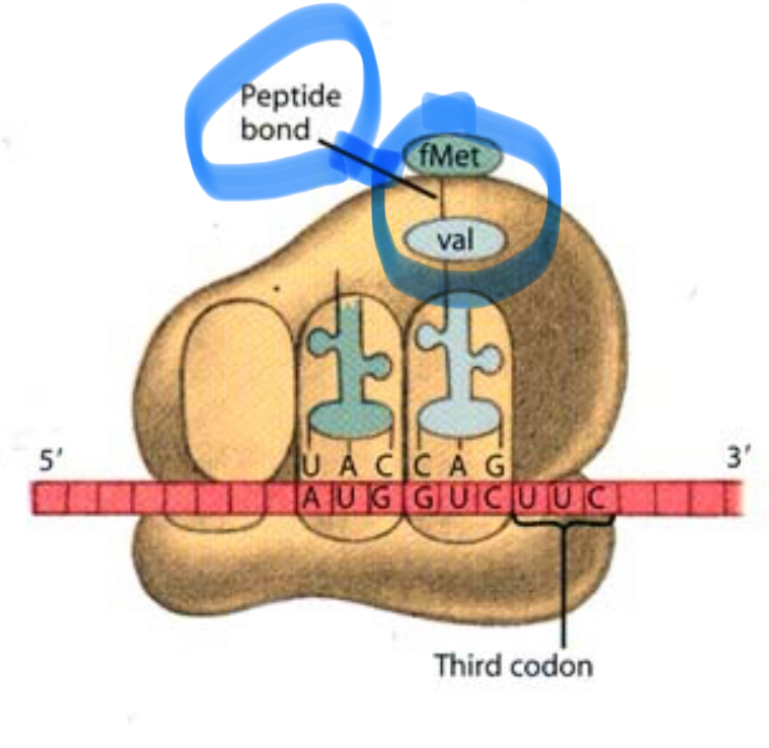
What happens to the amino acid in the P site tRNA after the peptide bond forms?
It detaches from its tRNA and joins the growing chain.
How does the ribosome move along the mRNA?
It shifts one codon forward (5’ → 3’) using GTP energy.
What happens to the tRNA in the P site after ribosome movement?
It moves to the E site and exits the ribosome.
What triggers termination?
A stop codon (e.g., UGA) entering the A site
What binds to the stop codon?
A release factor protein.
What does the release factor do?
Breaks the bond between the last amino acid and its tRNA.
What happens after the polypeptide is released?
The ribosome subunits separate and the mRNA detaches.