Psychology 2521 Midterm 1 - Structure of the Nervous System (Neuroanatomy)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Nerves
The central nervous system communicates to rest of body via __________________
Neuraxis
goes from the bottom of the spinal cord to the front of the forebrain. In humans, the neuraxis rotates 90 degrees at the head
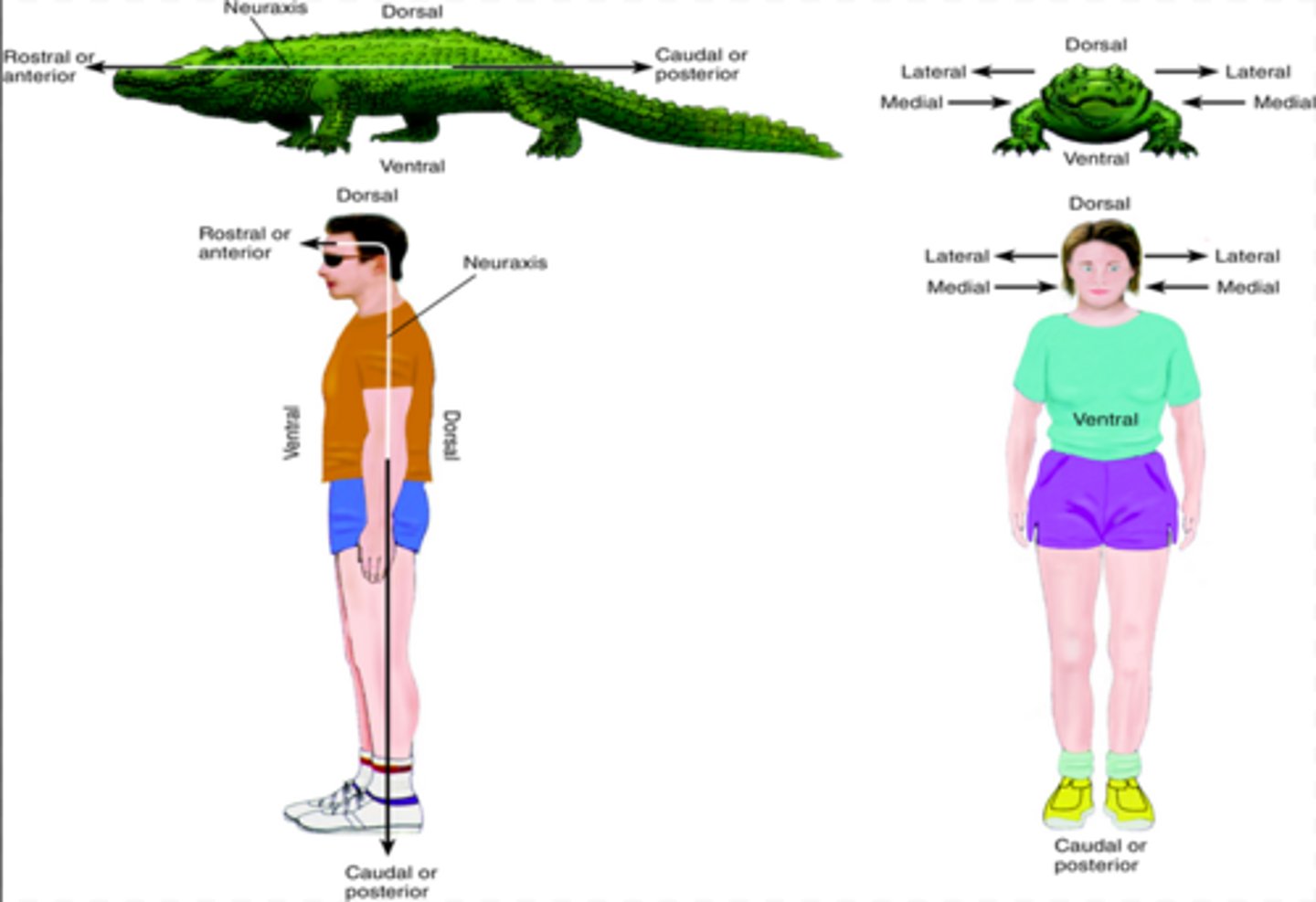
Medial
toward midline
Lateral
toward side
Ipsilateral
same side
Contralateral
opposite side
Dorsal
Top (think dorsal fin)
Superior
Dorsal is also known as ______________________
Ventral
Bottom (think ventre)
Inferior
Ventral is also known as ______________________
Anterior
Front
Rostral
Anterior is also known as ____________________
Posterior
Back
Caudal
Posterior is also known as _____________________
Planes of View
1. Coronal/Cross Section
2. Sagittal Section
3. Horizontal Section
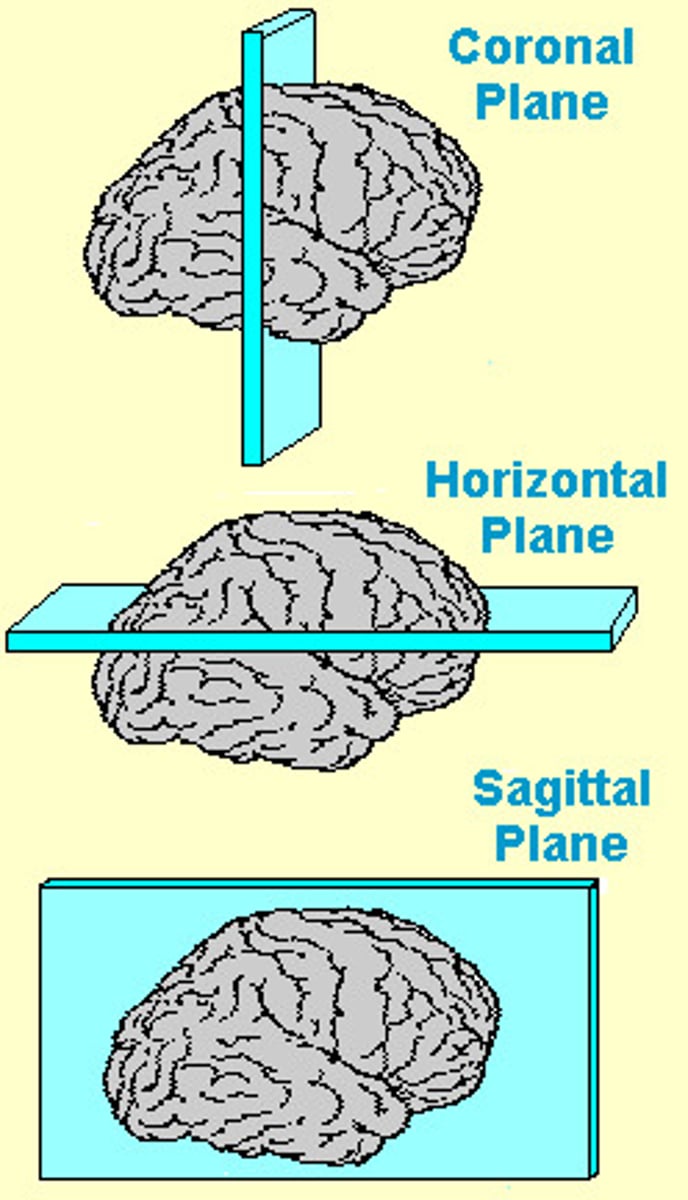
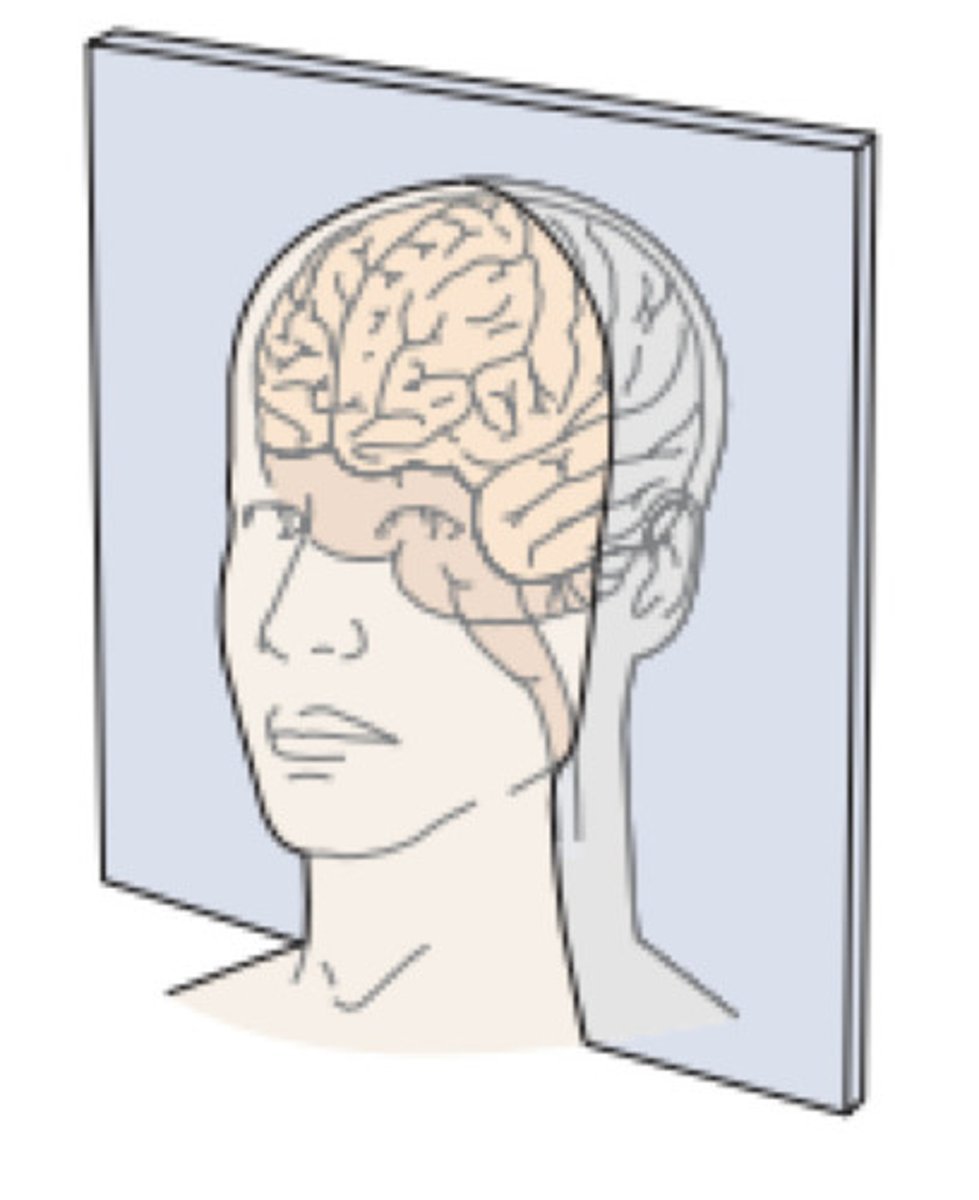
Coronal (cross) Section
View from front
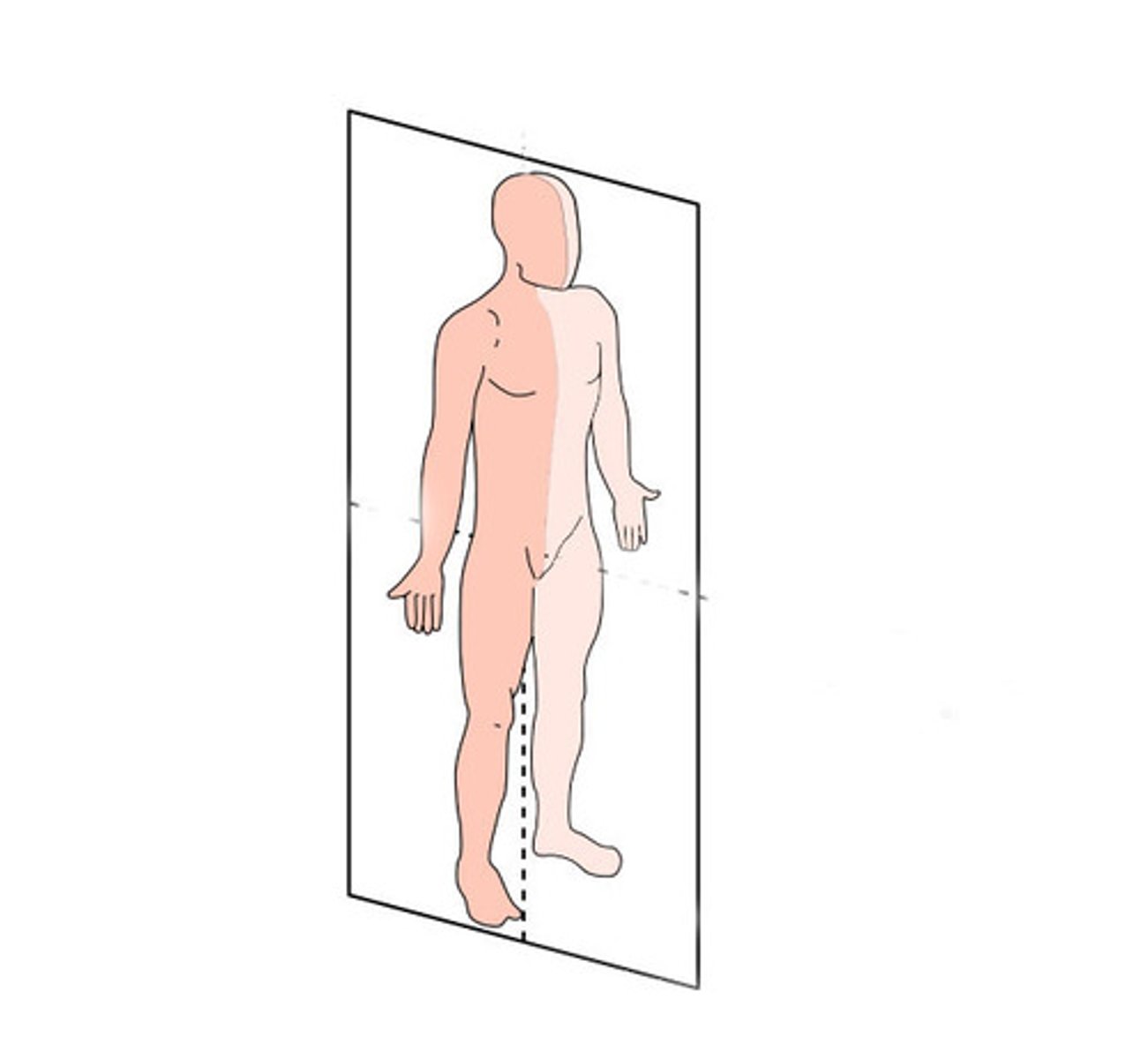
Sagittal Section
View from side
Horizontal Section
View from top
Meninges
Protective layers of tissues surrounding the brain and spinal cord
Layers of the meninges
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid mater
3. Pia mater
Dura mater
The outer layer (hard mother)
Arachnoid
The middle layer (spider-web)
Pia mater
Closest to brain (delicate mother)
Subarachnoid space
area between arachnoid and pia mater, filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- brain "floats" in CSF
Ventricular System
A series of fluid-filled interconnected chambers within the brain
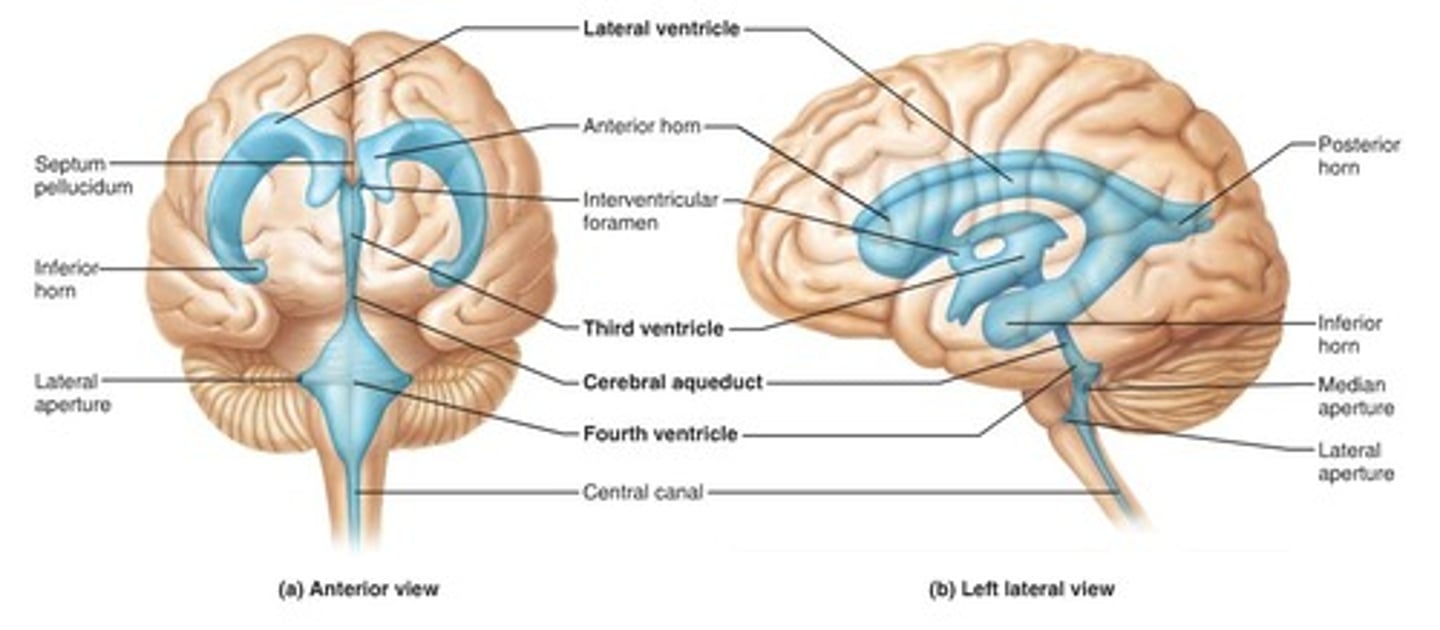
Functions of the ventricular system
CSF flows between ventricles via aqueducts and down into spinal canal. Also flows out into subarachnoid space surrounding brain. As pressure increases, CSF reabsorbed into veins and general blood circulation. Carries waste by-products from brain such as neurotransmitter metabolites
Lateral ventricles
Fluid-filled chambers, one on each side of brain (numbered I and II)
Third ventricle
Fluid-filled chamber in middle of brain near hypothalamus. Separates the right and left sides of the hypothalamus
Fourth Ventricles
Fluid-filled chamber in hindbrain (between cerebellum and pons
Choroid plexus
CSF is produced continuously by cells ____________________ in ventricles
Divisions of the brain/central nervous system
1. Forebrain
2. Midbrain
3. Hindbrain
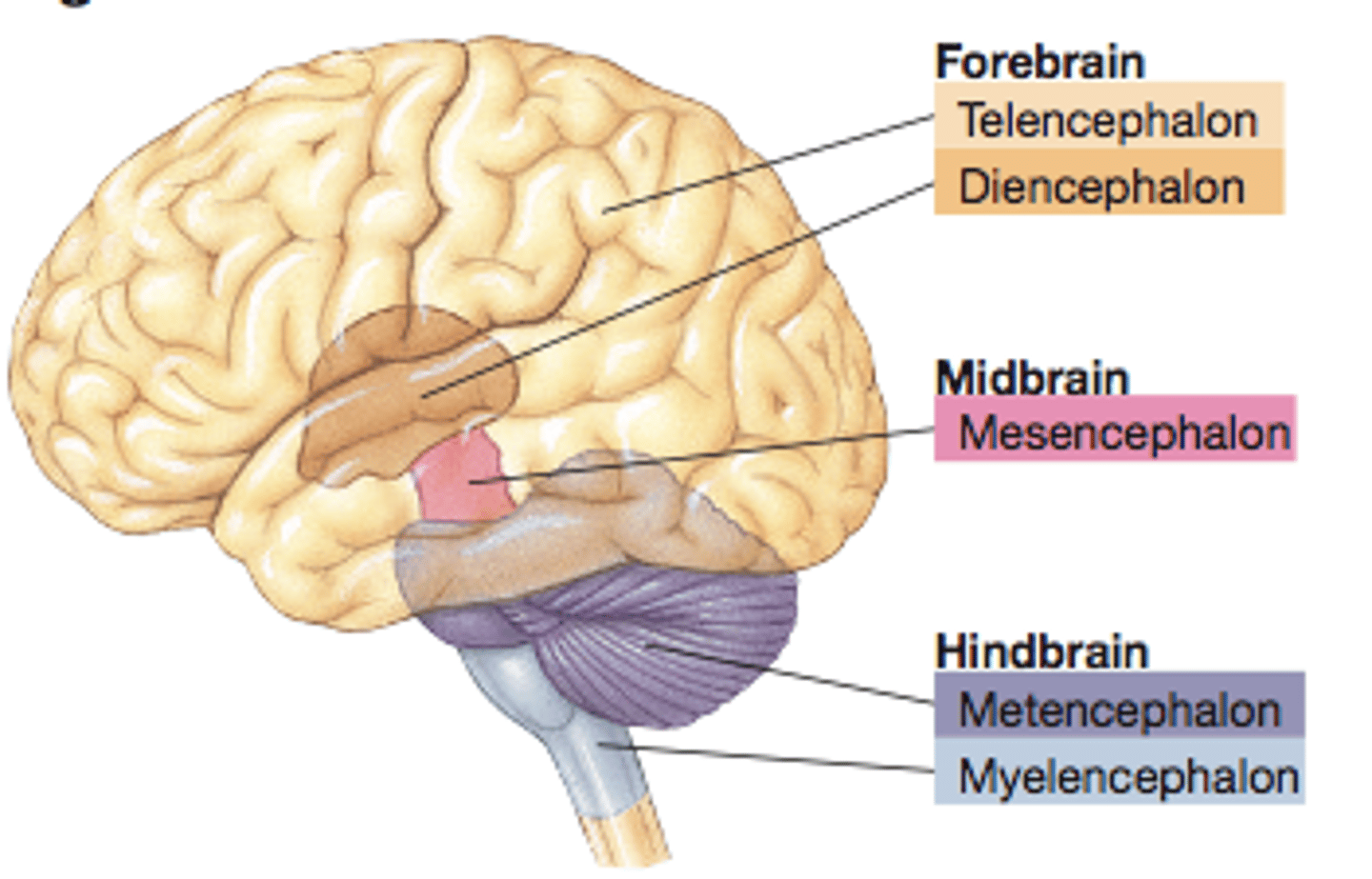
Divisions of the Forebrain
1. Telencephalon
2. Diencephalon
Division of the Midbrain
1. Mesencephalon
Divisions of the Hindbrain
1. Metencephalon
2. Myelencephalon
Structures of the Forebrain
1. Cerebral cortex
2. Basal ganglia
3. Limbic system
4. Thalamus
5. Hypothalamus
Structures of the Midbrain
1. Tectum
2. Tegmentum
Structures of the Hindbrain
1. Cerebellum
2. Pons
3. Medulla oblongata
Structures in the Telencephalon
1. Cerebral cortex
2. Basal ganglia
3. Limbic system
Structures in the Diencephalon
1. Thalamus
2. Hypothalamus
Structures in the Mesencephalon
1. Tectum
2. Tegmentum
Structures of the Metencephalon
1. Cerebellum
2. Pons
Structures of the Myelencephalon
1. Medulla oblongata
Forebrain
Most anterior division of the brain
Telencephalon
- Cerebral Cortex
- two cerebral hemispheres (corpus callosum); four lobes
- subcortical structures: cingulate gyrus, limbic system, basal ganglia
Four Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex
Frontal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Frontal Lobe
primary motor cortex
premotor cortex
prefrontal cortex
Functions:
-language production
- regulates emotion
- olfaction
Movement and cognition
Primary Motor Cortex
controls voluntary movement
Premotor Cortex
planning of movement (motor association cortex)
Prefrontal Cortex
executive function attention, short term memory
Temporal Lobe
primary auditory cortex
auditory association cortex
visual association cortex (forms)
Hearing
Primary Auditory Cortex
the first relay station for auditory information in the cortex
Parietal Lobe
primary somatosensory cortex
somatosensory association cortex
vision (movement)
Sensation
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
receives touch related information from the body
Occipital Lobe
primary visual cortex
Vision
Primary Visual Cortex
receive, segment, and integrate visual information
Left hemisphere
analyzes information (serial)
Right hemisphere
synthesizes information (holistic)
Corpus callosum
a large fiber bundle that crosses the midline and carries information between the left and right cerebral hemispheres
Limbic System
Ring of structures including the hippocampus and the amygdala. Involved in learning, memory, and emotions
Basal Ganglia
Group of subcortical nuclei in the forebrain. Involved in the control of movement
Diencephalon
Second major division of the forebrain
- Pineal gland (epithalamus)
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
Thalamus
Projects sensory information to specific regions of cerebral cortex and receives information from it
Hypothalamus
Controls autonomic nervous system and endocrine system. Regulates behaviors related to basic survival (eating, drinking, sex/bonding, thermoregulation). Controls pituitary gland (regulation of hormones). Important for homeostasis
Pituitary Gland
regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the hormones that it produces
Mesencephalon
division of the midbrain. Includes the tectum and tegmentum
Tectum
“roof”
– Superior colliculus (vision)
– Inferior colliculus (hearing)
Superior colliculus
processing optical stimuli, orienting attention, and coordinating eye and head movements (vision)
Inferior colliculus
signal integration, frequency recognition, and pitch discrimination (hearing)
Tegmentum
“Floor”
– Substantia nigra
– Ventral Tegmental Area
– Red nucleus
– Periaqueductal gray matter
– Some reticular formation
Substantia nigra
Neurons in this region produce the neurotransmitter dopamine (DA). Involved in movement. Neurons selectively die off in Parkinson’s disease
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
Neurons in this region produce the neurotransmitter dopamine (DA). Regulates motivated behaviour and is studied extensively in addiction research
Red nucleus
a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination
Periaqueductal gray matter
the gray matter located around the cerebral aqueduct within the tegmentum of the midbrain
Reticular formation
Located in the pons. made up of a net-like structure of various brainstem nuclei and neurons and covers an expansive portion of the brainstem. Main functions are modulatory and premotor, involving somatic motor control, cardiovascular control, pain modulation, sleep and consciousness, and habituation
Metencephalon
division of the hindbrain that includes the cerebellum and the pons
Cerebellum
Receives visual, auditory, vestibular, and somatosensory information and information about individual muscle movements. Modifies motor outflow, exerting a coordinating and
smoothing effect on movements
Pons
large bulge in the brain stem, relays information from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum. Contains reticular formation
Myelencephalon
division of the hindbrain that includes the medulla
Medulla Oblongata
Contains nuclei of cranial nerves (e.g. vagus nerve) which regulate vital functions (breathing and heart rate)
Spinal cord
Long, tubelike structure runs through spinal column
- subdivided (e.g., cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx)
- spinal canal in centre (CSF) and surrounded by meninges (CSF)
White matter
Descending motor tracts to muscles and ascending somatosensory tracts to brain
Gray matter
somas and interneurons
Spinal Nerves
One pair (left-right) for each vertebrae
- Dorsal root (sensory information)
- Ventral Root (motor)
Dorsal root
sensory information
Ventral root
motor information
Cranial Nerves
– twelve pairs
– attached to the ventral surface of the brain
– Most serve sensory and motor functions of the head and neck region
Vagus nerve
regulates the functions of organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities
Autonomic Nervous System
Functional branch of PNS - concerned with regulation of organs of body
Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
responsible for your body activate its “fight-or-flight” response (think speed)
Functions of Sympathetic
dilates pupils
inhibits salivation
accelerates heart
facilitates breathing
inhibits digestion
stimulates release of glucose
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
relaxes bladder
inhibits sex organs
Parasympathetic
responsible for relaxing or reducing your body's activities (think parachute)
Functions of Parasympathetic
constricts pupils
stimulates salivation
slows heart
constricts breathing
stimulates digestion
stimulates gallbladder
contracts bladder
stimulates sex organs