General Principles of Exercise Prescription: Muscular Fitness
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Skeletal Muscles
600+ muscles varying in shape and size.
Sarcomere
Smallest contractile unit made of proteins.
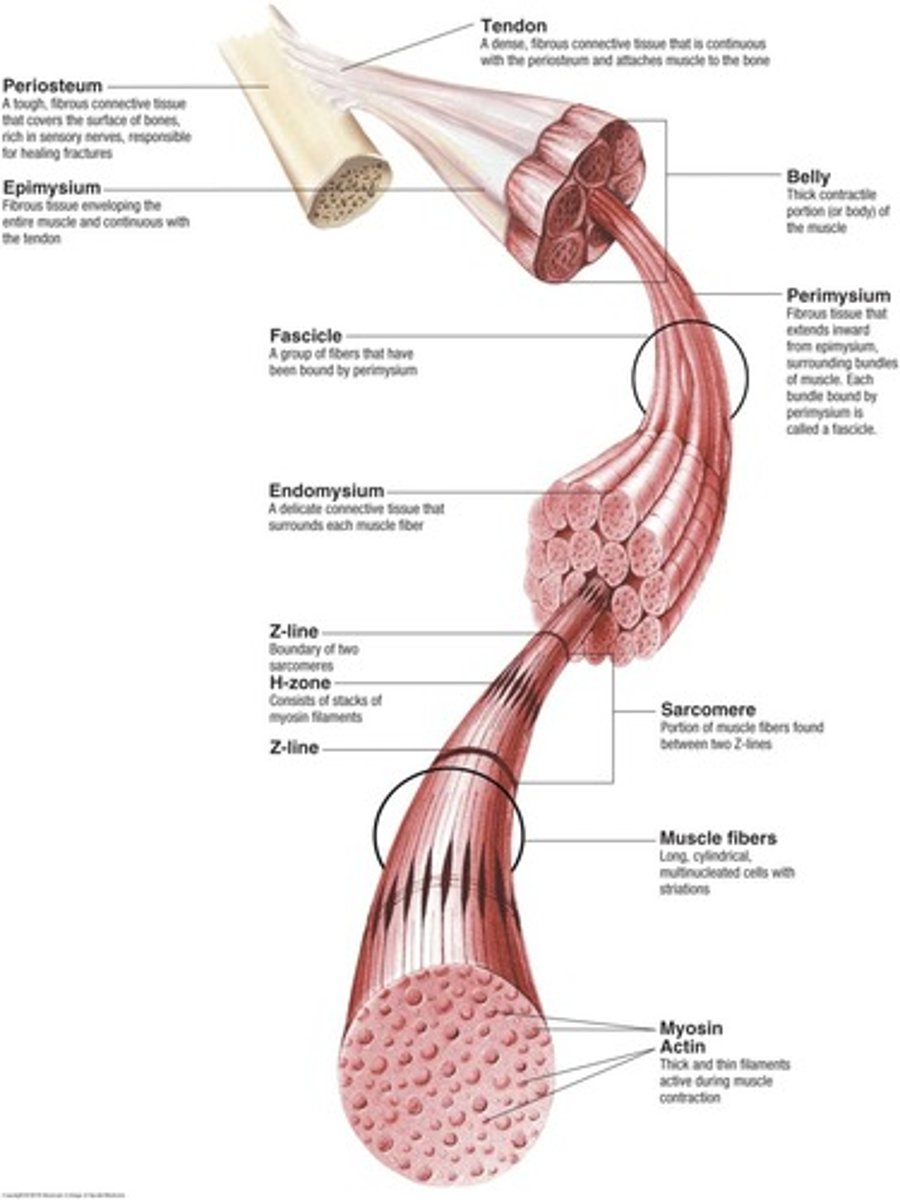
Myofibril
Structure composed of many sarcomeres.
Fascia
Connective tissue providing muscle stability and flexibility.
Muscle Types
Three types: skeletal, smooth, cardiac.
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary muscle, striated in appearance.
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle forming internal organs.
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary muscle found in the heart.
Muscle Bundles
Fasciculi covered by perimysium.
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding individual muscle fibers.
Sarcolemma
Membrane enclosing muscle cell contents.
Actin
Thin filament involved in muscle contraction.
Myosin
Thick filament forming cross bridges in contraction.
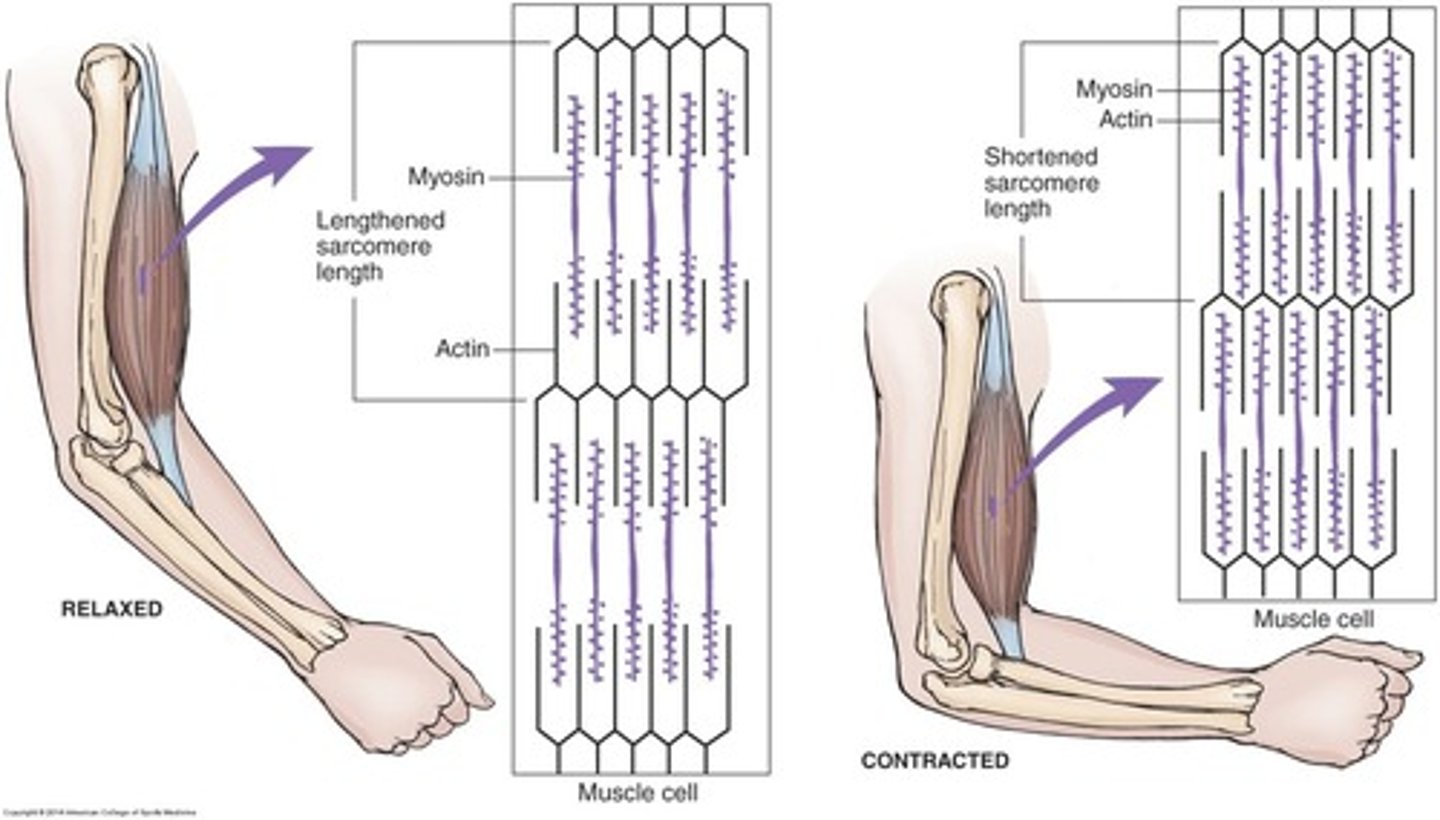
Sliding Filament Theory
Actin slides over myosin during muscle contraction.
All-or-None Principle
Muscle fibers contract fully or not at all.
Agonists
Primary movers in joint actions.
Synergists
Accessory muscles assisting in joint movement.
Antagonists
Muscles opposing movement of agonists.
Type I Fibers
Slow twitch, high endurance, low force.
Type II Fibers
Fast twitch, high force, low endurance.
Size Principle
Recruitment from smallest to largest motor units.
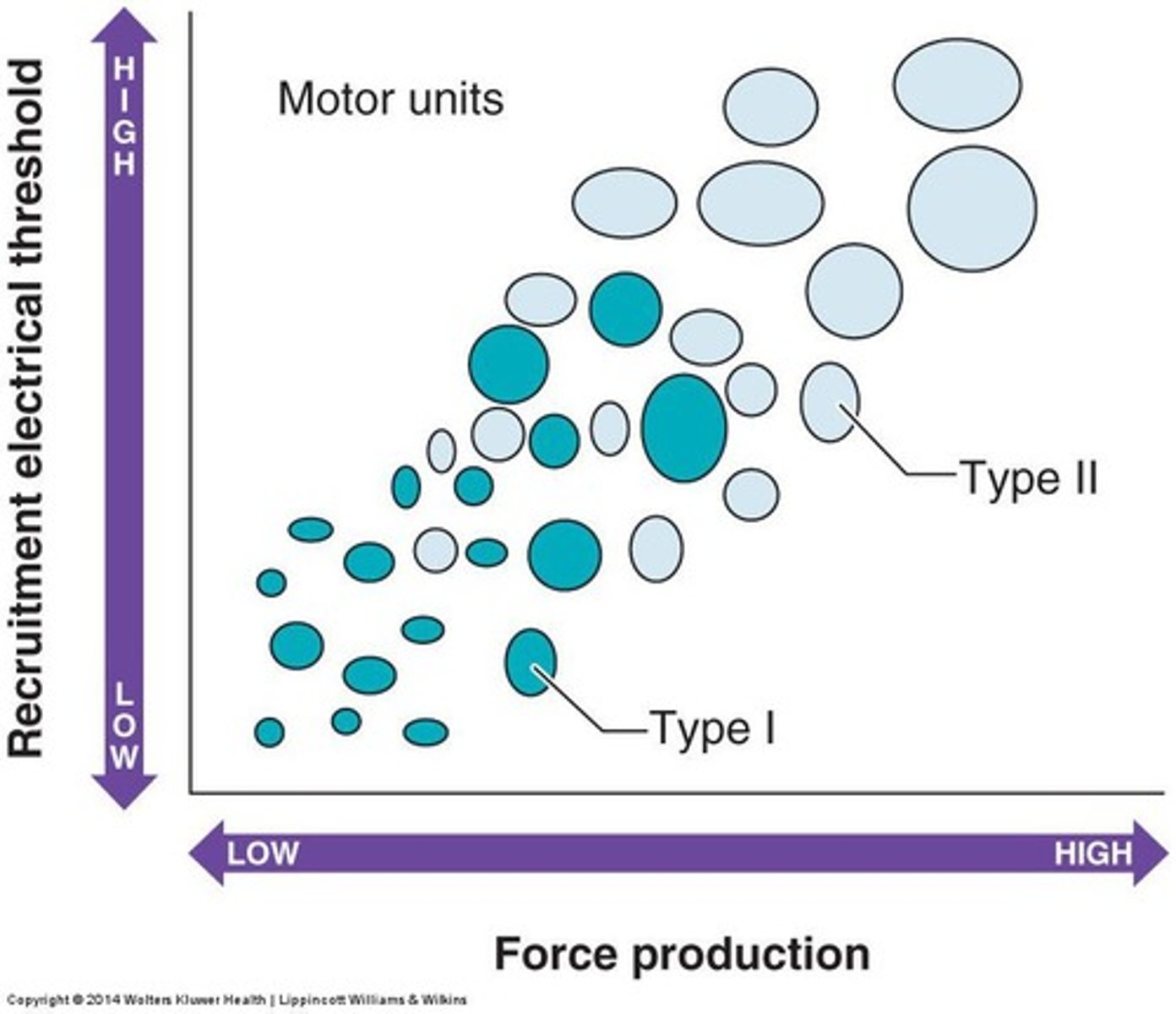
Motor Unit
Motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates.
Concentric Contraction
Muscle shortening during contraction.
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle lengthening during contraction.
Isometric Action
Muscle loaded with no joint movement.
Muscular Fitness
Collective term for strength, endurance, and power.
Muscular Strength
Maximum force exerted by muscles during contraction.
Muscular Endurance
Ability to sustain repeated muscle contractions over time.
Muscular Power
Rate of performing work; strength applied quickly.
Older Adults
Individuals aged 65 years and above.
Power Training
Training to enhance muscle power, especially in older adults.
Resistance Exercise Frequency
Train major muscle groups 2-3 times per week.
48 Hours Rest
Minimum recovery time between sessions for same muscle group.
Whole Body Training
Training all muscle groups in a single session.
Split Training Routine
Training selected muscle groups across multiple sessions.
Multijoint Exercises
Exercises targeting multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Single Joint Exercises
Exercises focusing on one specific muscle group.
Agonist Muscle
Muscle primarily responsible for movement during exercise.
Antagonist Muscle
Muscle that opposes the action of the agonist.
Resistance Training Equipment
Tools like weights, bands, and machines for strength training.
Compound Exercises
Exercises involving multiple joints and muscle groups.
Core Muscle Exercises
Exercises targeting abdominal and back muscles for stability.
Muscle Imbalances
Unequal strength between opposing muscle groups, risking injury.
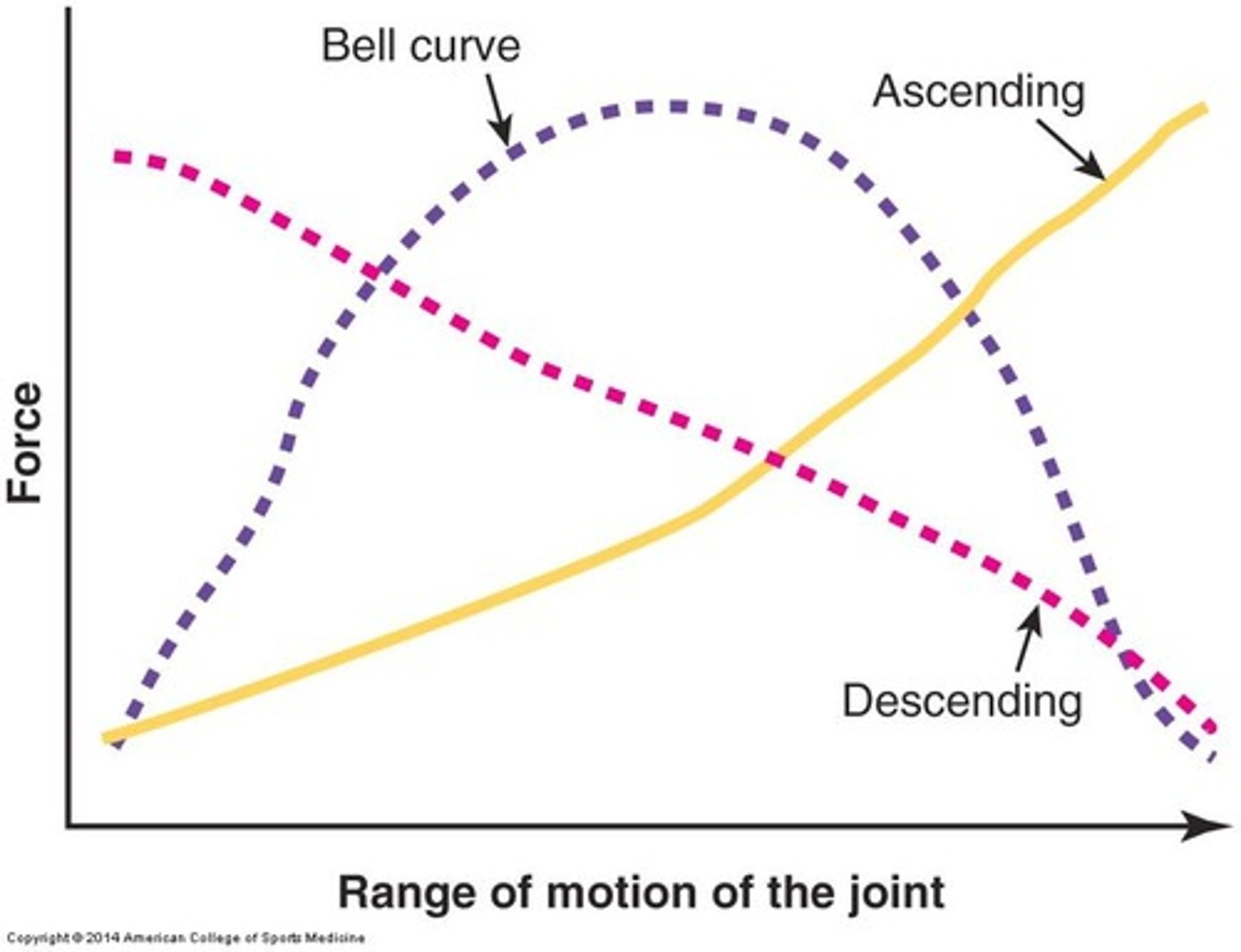
Variable-Resistance Devices
Equipment adjusting resistance throughout the range of motion.
Strength Curve Types
Ascending, descending, and bell-shaped strength curves exist.
Resistance Training Modalities
Various methods and equipment used for resistance training.
Resistance Bands
Elastic bands used for strength training and rehabilitation.
Volume of resistance exercise
Total sets and repetitions for muscle training.
Sets
Number of times an exercise is performed.
Repetitions
Number of times a specific exercise is completed.
Rest interval
Time taken to recover between sets.
Muscle fatigue
Point at which muscles can no longer perform.
One repetition maximum (1-RM)
Maximum weight lifted for one complete repetition.
Resistance training intensity
Amount of weight used relative to 1-RM.
Muscular endurance
Ability to sustain repeated muscle contractions.
Proper form
Correct technique during exercise execution.
Controlled movements
Deliberate and steady execution of exercises.
Full range of motion (ROM)
Complete movement through a joint's full capability.
Concentric phase
Muscle shortening during lifting phase of exercise.
Eccentric phase
Muscle lengthening during lowering phase of exercise.
Valsalva maneuver
Forced exhalation against a closed airway.
Training for novices
Single set significantly improves strength for beginners.
Older adults training
Begin with 10-15 reps at 40%-50% 1-RM.
Muscle group training
Focus on specific muscles with targeted exercises.
Resistance exercise recommendations
Guidelines for sets, reps, and intensity.
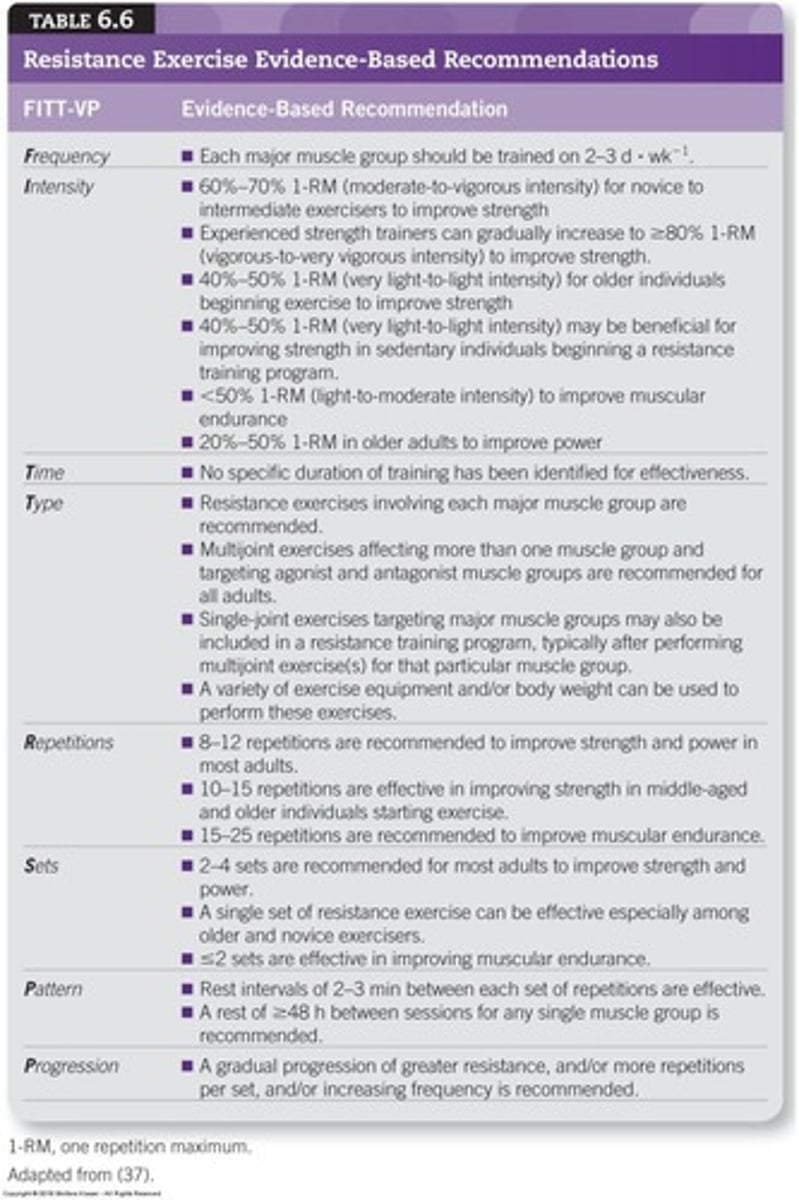
Deconditioned individuals
Those with low fitness levels needing gradual training.
Exercise variety
Using different exercises to prevent mental staleness.
Higher repetitions
15-25 reps for endurance-focused training.
Adaptation to resistance training
Adjustment period before increasing intensity or volume.
Progressive Overload
Increasing resistance or training frequency for muscle growth.
Maintenance Training
Training once a week maintains strength if intensity is constant.
FITT Principle
Framework for designing exercise programs: Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type.
Periodization
Systematic variation in training volume and intensity.
Hypertrophy Phase
Focus on muscle size increase through resistance training.
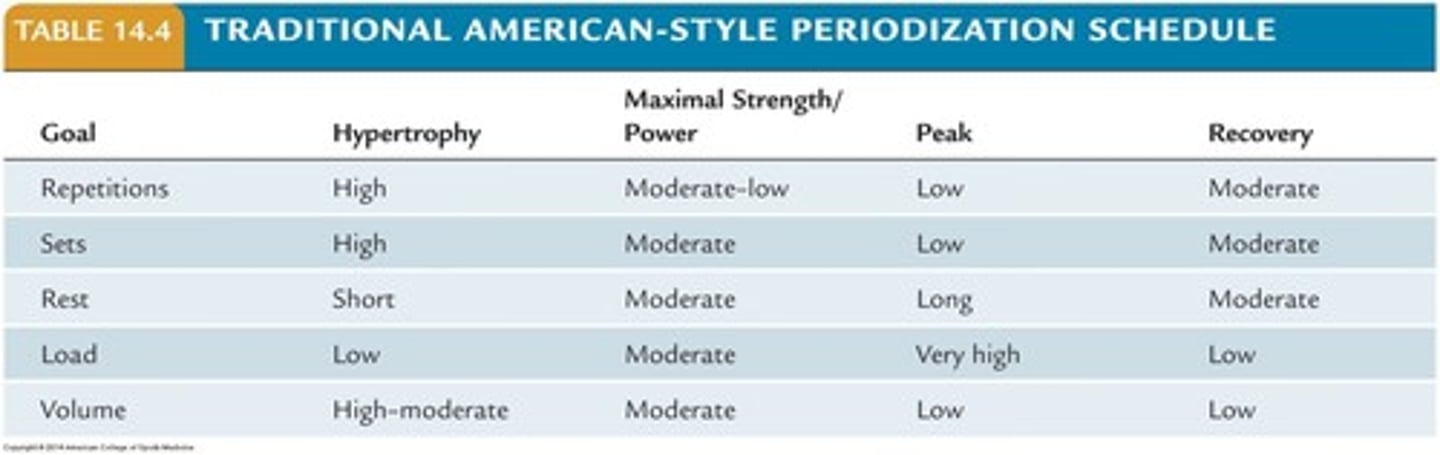
Strength/Power Phase
Emphasizes maximal strength and explosive power development.
Peaking Phase
Preparation for competition with optimal performance focus.
Recovery Phase
Allows muscles to recuperate and adapt post-training.
Macrocycle
Long-term training plan, typically one year.
Mesocycle
Medium-term training phase, usually 4-6 months.
Microcycle
Short-term training phase, lasting 1-4 weeks.
Linear Periodization
Gradual increase in intensity with decreasing volume.
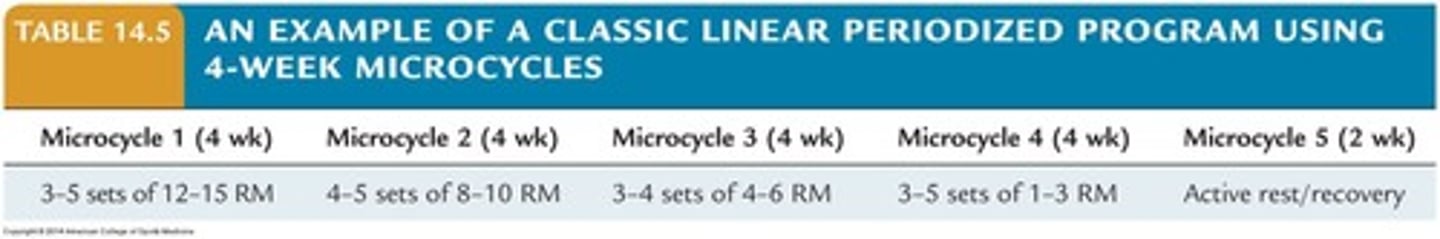
Reverse Linear Program
Decreases intensity while increasing volume for endurance.
Nonlinear Periodization
Varies intensity and volume within the same week.

Daily Undulating Periodization (DUP)
Flexible training approach with varying daily stimuli.
Unplanned Nonlinear Periodization
Workout schedule based on daily readiness to train.
Spotting Procedures
Safety measures for assisting during resistance exercises.
Flexibility Exercises
Improve joint range of motion through regular stretching.
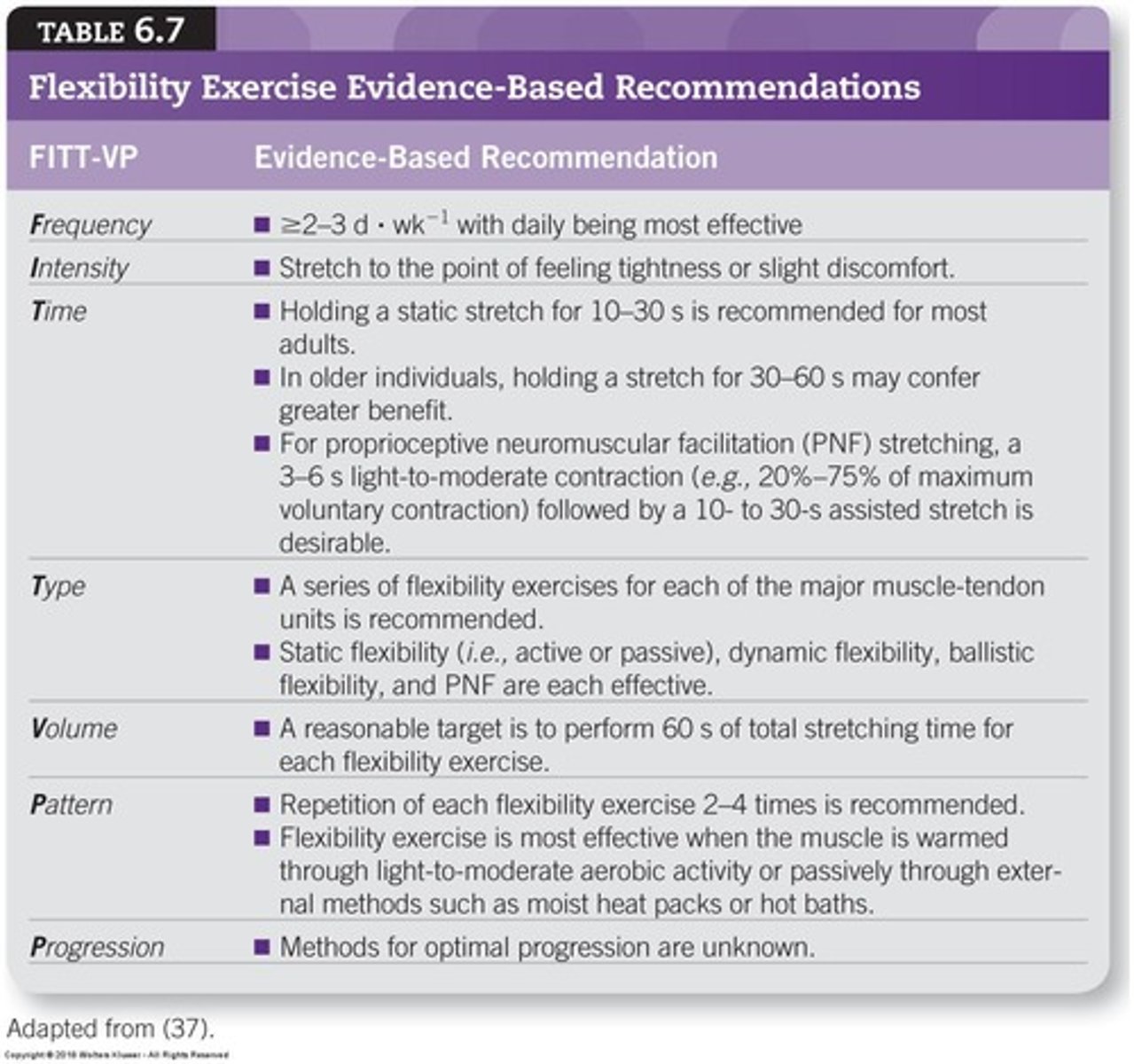
Chronic Improvement
Long-term benefits from consistent flexibility training.
Postural Stability
Balance and posture enhanced by flexibility and resistance.
Stretching Frequency
At least 2-3 times per week for effectiveness.
Static Stretching
May decrease muscle strength and power short-term.
Range of Motion (ROM)
Improved through flexibility exercises acutely and chronically.
Warm Muscles
Flexibility exercises are most effective when muscles are warm.
Flexibility Exercise Volume
60 seconds per joint recommended for flexibility exercises.
Stretch Duration
Hold stretches for 10-30 seconds to tightness.
Older Adults Stretching
Hold stretches for 30-60 seconds for effectiveness.
PNF Techniques
Involves isometric contraction followed by static stretching.
Ballistic Stretching
Uses momentum to produce muscle stretches.
Dynamic Stretching
Gradual transition between body positions with repeated movements.
Active Static Stretching
Uses agonist muscle strength to hold stretched position.