PSY 339.01 Learning and Behavior Exam 2, April 17, 2025 SBU Spring 25'
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 6-9, PowerPoints
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Novel Behavior
“can’t reforge a behavior that doesn’t exist”
can and does emerge through the application of operant principles
shaping
novel behavior can emerge as a consequences of the reinforcement of successive approximation of a target behavior
skinner demonstrated that you could get a pigeon to engage in a completely new behavior by reinforcing any behavior, that was remotely close the target behavior
simple procedure that we have lots of practice with
pairing two stimulus together
Behavior Chaining
We have learned to put all of the different behavior engaged in these activities together into a sequences that result in some reinforcer or another
behavior that we engage in are complex and can be broken down into multiple different behaviors
Chaining
procedure of establishing a behavior chain
Task analysis
the procedure of identifying the component elements of behavior chain
forward chaining
starts with the first behavior in the chain and works forward towards the bfindal behavior: hard and not ideal
backward chaining
starts with the last behavior and works backwards towards the first behavior
problem solving
Involves trail and error (Thorndike’s cats)
Insightful problem solving
Does not involve learning: it ermine from a sudden “insight” that results from complex cognitive processes
Wolfgang Kohler:insight learning
Published a series of studies that claimed that animals were capable of “insight”: The Mentality of Apes
Demonstrated that chimp, Sultan, had the insight to stack empty crates and climb on top of them to reach a bunch of bananas suspended form ceiling
Insight
From a Behavioral Perspective
emerges as a consequence of history
harlow (1949)
demonstrated that insight “evolves” over time
his food under the lid of 1 of 2 boxes of different shapes and color
on the 2nd trail, he always hid the food under the lid of box either the same shape as the first trip but the box was to the same
at first, the monkeys did not reliably select the right box
as training progressed however, their ability to select the right box on the 2nd trail increased to nearly 90%
learned helplessness
Martin Seligman
Restrained dog in a harness and administered several shocks
Dogs then placed, unrestrained in a “shuttle-box” where one side of the box would deliver shock following the onset of the light but the other side of the box would not (AKA: Escape Procedure)
the absence of reinforcement (escaping the shock. Behavior failed to operate on the environment the dog learned to do nothing
Superstitious behavior
operant learning, in classic experiment, Skinner demonstrated that non-contingent deliver of food to pigeons reliably produced very specific behavior in 6 out of 8 of his pigeons
delivered food grain every 15 second regardless of behavior
whatever the pigeon happened to be doing at the time was repeated over and over again
- these behavior were maintained even though they were to responsible
Coincidental reinforcement
mislead an organism to believe inaccurately that their behavior has operated onto environment
schedule reinforcement
variation in the arrangement of reinforcement contingencies
schedule effects
the distinctive effects on behavior produced by the different schedules of reinforcement
schedule effects the learning process via thier effects on the
acquisition of new behavior
rate of behavior
pattern of behavior
progressive schedules of reinforcement
each reinforcer is delivered the next reinforcer requires more of something (ratio- more response, interval- more Tim
multiple schedule
involves the simultaneous availability of 2 or more simple schedules of reinforcement in which each schedule is associated with a particular stimulus (each stimulus is called Discriminative stimulus or SD)
mixed schedule
is the same as multiple schedules except the 2 or more schedules are associated with a particular discriminative stimulus (SD)
stimulus control
multiple schedules are effective for demonstrating that the discriminative stimulus is controlling behavior
chain schedule
reinforcement occurs only upon completion of entire series of schedules that are signaled in some way I.e:
stimulus control class experiences
cleaning out your closet
making thanksgivings dinner
tandem schedule
chain schedule but there is nothing to signal the end of one schedule and the beginning of the next, figure it out
concurrent schedules of reinforcement
choice
involve 2 or more simple schedules that are active at the same time (was opposed to sequenced)
organisms get to choose and the choice really depends on the characteristics of the individual schedules
matching law
given the opportunity to respond on two or more reinforcement schedules the role of responding on each schedule will match the reinforcement available on schedule
given two behavior, B1 and B2 each on its own reinforcement schedule (r1 and r2 respectively) the relative frequency of each behavior equals the relative frequency of reinforcement available
distribution of behavior matches the availability of reinforcers
concurrent interval schedules
i.e., you have choice between an F1-2’ and F1-4’ schedules you are going to choose to engage in more of the behavior on the FI-2’ schedule because that is the best option in terms of the work-to-reinforcement relationship
partial reinforcement effect (PRE)
Unreinforced response that occurs during an intermittent schedule should weaken the tendency to respond, not make it stronger
The Discrimination Hypothesis
suggests that the PRE occurs because it is more difficult to discriminate between intermittent reinforcement and extinction than between continuous reinforcement and extinction
The frustration hypothesis
Suggest that the PRE occurs because on intermittent schedules of reinforcement, the organism becomes frustrated
intermittent schedules of reinforcement, every non reinforced act leads to “frustration”
frustration → behavior→reinforcer
when the behavior is then placed on extinction schedule fraction p[ersits na they have learned that frustration should be followed by the behavior
the sequential hypothesis
PRE to differences in the sequences of cues during training
on a CRF schedule all target behavior receive reinforcement so the deliver of reinforcer becomes a cue to emit the target behavior again i.e, the sequences looks like this and they learn the highlighted association
R→SR→R→SR→R
On a intermittent schedule, sometimes the target behavior results in reinforcement and sometimes it doesn’t so the sequences of reinforcement (SR) and nonreinforcement (NR) becomes a signal for the behavior i.e the sequences looks like this and they learn the highlighted association
R→NR→R→NR→R→NR→R→NR→R→SR
The response unit hypothesis
PRE is an illusion that results from the incorrect way in which we are defining the target behavior
on CRF schedule the target behavior is measured an individual instance
Intermittent schedule(FR-4 schedule), an individual instance should be measured as 4 successive target responses
behavior on intermittent fasting reinforcement only seems more resistant to extinction because we have failed to consider the Response Unit required for reinforcement
Learned Helplessness in Human
can’t change the course of negative events and that failure is inevitable and insurmountable
Learned Industriousness
People are reinforced for effort and persistence despite difficulties and this increases their tendency to work hard at difficult task a prolonged period
Eisenberg (1992)
Gave students a short choice to copy 10 nonsense words in a very short period of time for large monetary reward
students attempted to complete the task with the same level of effort (baseline)
divided the group
low group- traded on tasks on object counting, picture memory and shape matching with a low criterion for reinforcement
high group: trained on the same tasks but required a higher criterion for reinforcement
Found- after the training, both groups repeated the baseline
The high group exhibited higher level of effort on the same copying task as baseline even though they had learned that it was nearly impossible to earn the large reward
Schedule
follows a certain rule that describes that contingency between a response and reinforcer
schedule of reinforcement
variation in the arrangement of reinforcement contingencies
Schedule Effects
The distinctive effects on behavior produced by the different schedules of reinforcement
Acquisition of new behavior
rate of behavior
pattern of behavior
Continuous Reinforcement (CRF) Schedule
Method in which reinforcement follow behavior every time in occur
rapid increases in the rate of behavior especially of shaping and chaining
common in the real world for pretty basic behavior
Intermittent Schedules
Method in which reinforcement occurs on some occasion but no on other
produce very distinctive effect on behavior
common in the real world for complex behavior
Law of effect
If a behavior results in a(n)
“satisfying star of affairs” it will become more likely (Reinforcement)
“annoying state of affairs” it will become less likely (Punishment)
negative conditioning
Skinner defined punishment as (blank) and generally used the term to refer to withdrawal of reinforcement
argued that punishment was essentially “symmetrical” to reinforcement
found that punishment had little effect on learning
Why didn’t when Thorndike when he tested for punishment via the law of effect it didn’t work ?
He found that although punishment suppresses behavior, it does not result in long term learning effects
He later argued that punishment was asymmetric to reinforcement
What did skinner find that has similar effects to Thornidke?
Punishment
Effect on behavior if behavior doesn’t decrease, whatever consequences are delivering is not really a punisher
(Azrin & Holz, 1966)
it is a consequences for a specific behavior
the behavior must decrease in strength
the consequences must cause the decrease in strength
How is punishment defined by and by who?
positive and negative
two types of punishment
Positive punishment
The behavior causes the appearance of an unwanted stimulus or an increase int he intensity of unwanted stimulus
Negative punishment
The behavior causes the removal of a desired stimulus or reduction in the intensity of desired stimulus (placing a child in Time-Out)
Contingency
The degree to which punishment weakens a behavior varies with the degree to which a punishing event depend on that behavior
delay in the delivery of the punisher it becomes less effective
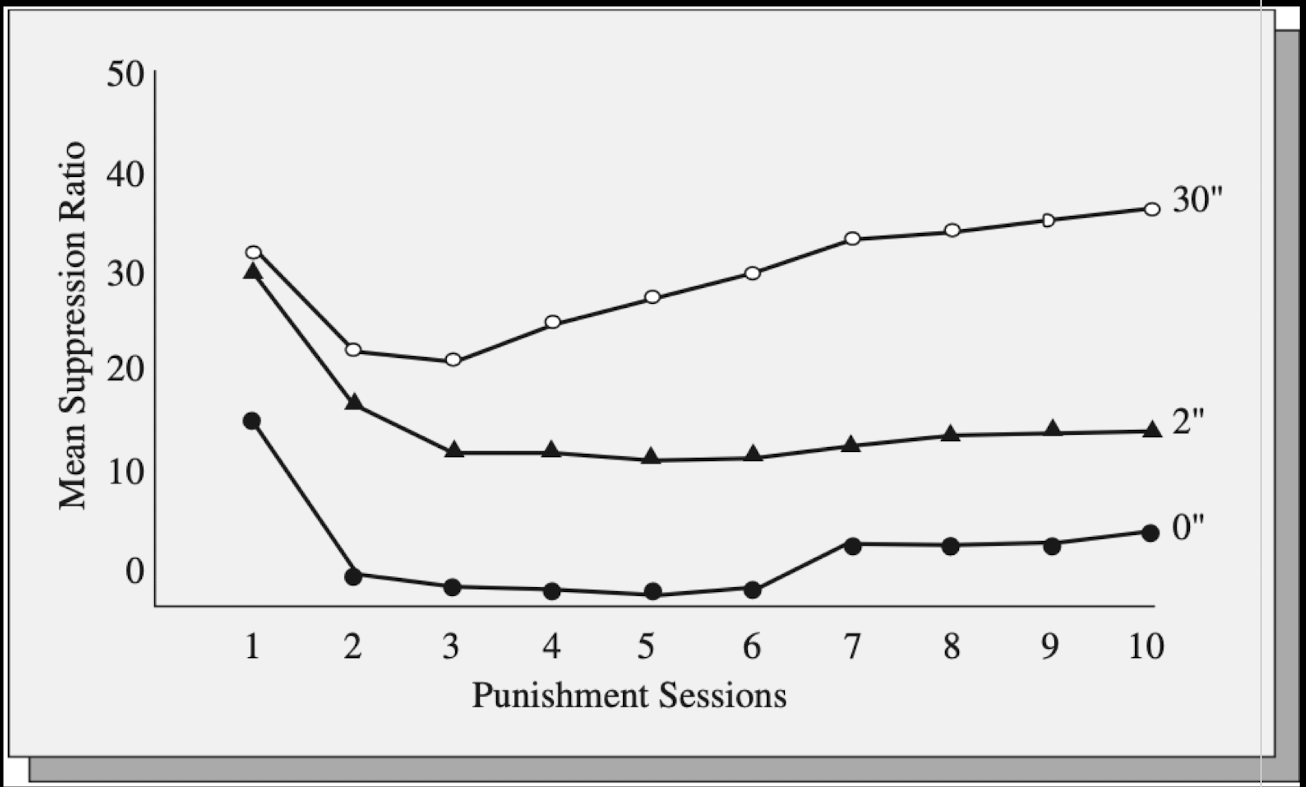
Intensity and Introductory level of Punisher
being with effective level of punishment that will cypress behavior that the outset-Goldilocks
(blank): more intense level of shock result int he better response suppression
beginning with a weak punisher and increasing intensity and increasing intensity leads organism to persist through increase- they become “tolerant”
the problem is that it can be really difficult to know from the outset what intensity of a punisher will prove effective
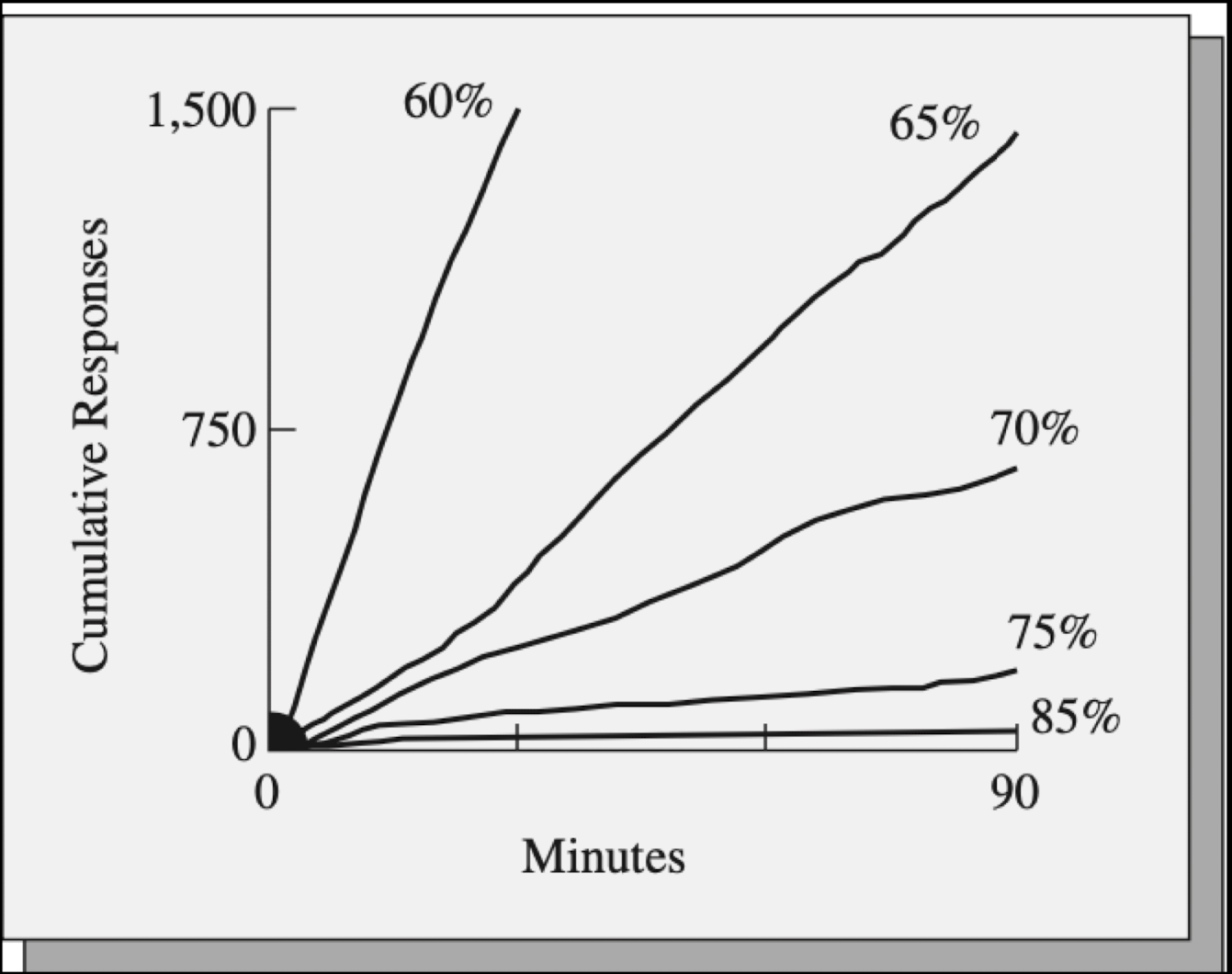
Heman & Azrin, 1964
Classic study in humans
male psychiatric patients counted to perform a behavior that was punished with very loud sound if it periodically produced reinforces
if you gave them another way to earn the reinforcer they did that instead
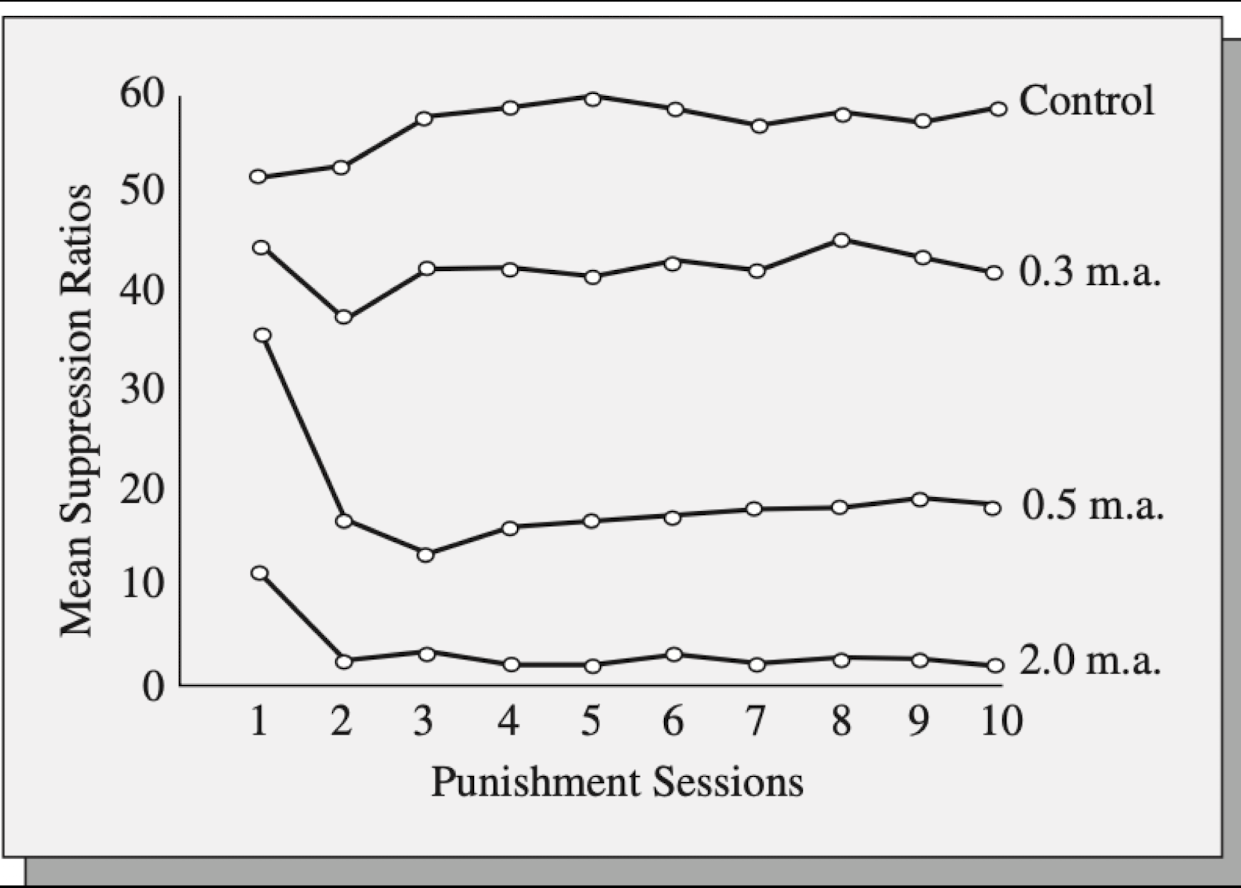
Motivating Operation
High level of motivation will reduce the effectiveness of a punisher
rate the key pecking for a bird at different levels of food deprivation (based on % of free-feeding body weight) when responses periodically produce food delivery and every 100th response produced a shock
at the lowest level of food deprivation (85% free feeding weight), punishment proved very effective: at higher levels of deprivation, it proved less effective
Addiction is punishing but the motivation for drug administration is just too high for a punisher to compete with
disruptive effect
Skinner proposed that response suppression only occurred because punishment had “(blank)“
greater suppressive effect
Punishment has a greater suppressive effect on behavior than does aversive stimulation independent of behavior.
Other disruptive event do not lead to the same effect as punishment
at least in the short run
Punishment works (blank)
immediate behavior change
punishment can produce (blank)
side effects
punishment can have (blank)
avoid
escape from punishment can prove problematic in that the punished subject will often (blank) the source of punishment, which can damage relationship and lead to cheating and lying
attack
aggression can arise form punishment the punished subject may (blank) the person inflicting the punishment, others nearby, or even inanimate objects
malaise, apathy
suppression of behavior on the whole can arise form punishment- leading to (blank) or (blank)
Intergenerational transmission of domestic violence
Imitation of punishment can prove a problem: Those who have been punished may go on to punishment those around them
response prevention
alter the environment so that the unknown reinforcer for behavior is simply not available
extinction
identify the reinforcer and ensure that it is no longer available
often don’t known or can’t control for all of the source of reinforcement
Issues with the approaches, response, prevention and extinction?
Differential Reinforcement
Most effect strategies, involve coming non-reinforcement of unwanted behavior and reinforcement of some other behavior
Differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA)
Differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI)
Differential reinforcement of low rate (DRL) behavior
Three basic type of Differential Reinforcement
Differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA)
reinforcement becomes available for a specfied alternative to the unwanted behavior
Differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI)
reinforcing a behavior that is incompatible with the unwanted behavior
Differential reinforcement of low rate (DRL) behavior
the behavior earns reinforcement only if it occurs at a low rate
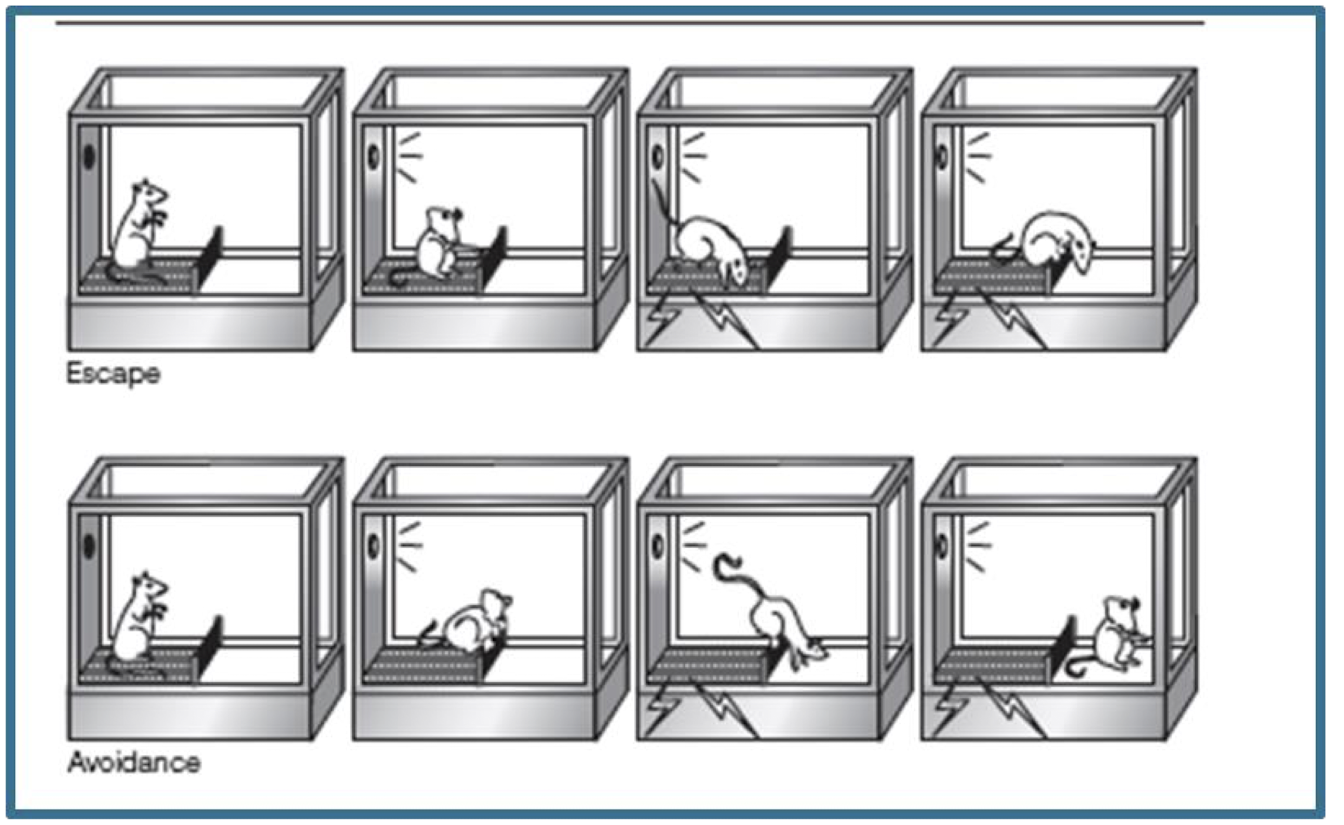
escape behavior
performance of behavior terminates an aversive stimulus
avoidance behavior
performance of a behavior prevents the occurrence of an aversive stimulus
shuttle avoidance procedure
escape
shock (SD) Cross Barrier (R) →Removal of shock (SR)
Avoidance
Light (SD): Cross barrier (R) →Avoidance of shock (SR)
Rat first learns to escape shock and then to avoid shock
Two process theory of avoidance
avoidance behavior is the result of both classical and operant conditioning
classical conditioning: an emotional response comes to be elicited by a CS
Light (NS): shock (US)→fear (UR)
light (CS)→Fear (CR)
Operant conditioning: moving away from the CS is negatively reinforced by a reduction in emotional response
light (SD): Cross barrier (R)→ Reduction in fear (SR)
Two issues with two process model
Problem with Two-Process Model
First problem- if you are always able to avoid the aversive outcome (dog bite ) why would it still cause fear? it should extinguish and if its no longer causing fear, how can fear reduction serve as a reinforcer
second problem: we are behaviorist why are we walking about an emotional response
Stampfl procedure: Laboratory Developed Phobia
An avoidance conditioning procedure used in animals
rats are put in 5’ long “alley” box that has a dark compartment at its end
they are allowed to explore freely and typically settle in the dark compartment
once they aer settled in the dark component a painful foot shock is given and they run to other end of the alley
on the first trail, rats waited until they were close to dark component before running to the other end of the alley
when they passed a motion-detector , the conveyor belt shut off for 3 minutes
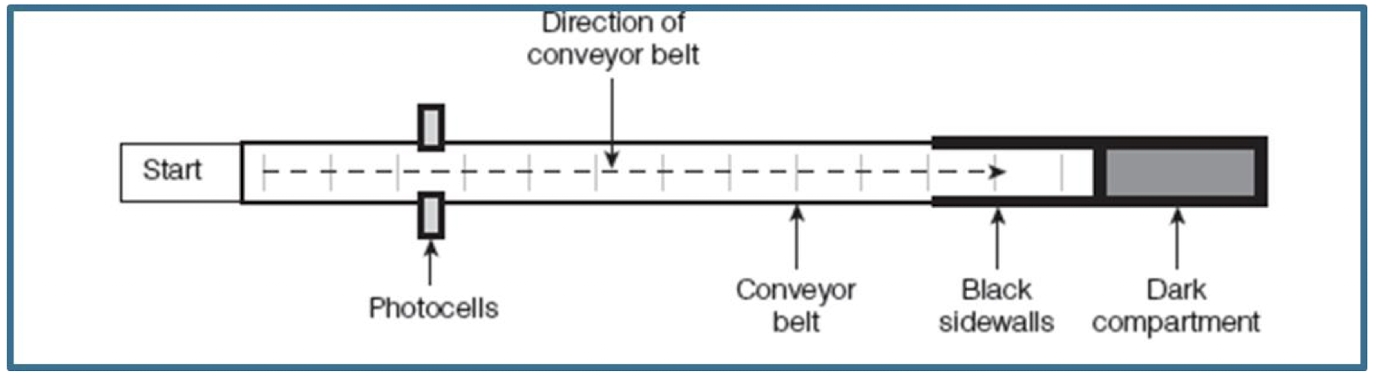
Phobia
One trail conditioning: the 2nd time the conveyor belt starts up. the animals runs past the motion detector immediately and will continue to do so for more than 1000 trails
One-process theory of avoidance
Does not invoke emotions, avoidance behavior is reinforced by avoiding the aversive stimulus
avoid averse stimulus (R)→ less exposure to aversive stimulus (SR)
asserts that a punishing stimulus directly weakens the punished repose (operant Learning)
Two- process theory
Assert that punishing stimulus becomes associated with fear or anxiety through classical conditioning, and the avoidance of this negative emotional state then reinforces the suppression of the punished behavior through operant conditioning (Pavlovian and Operant Learning)
Intrinsic punishment
inherent aspect of the behavior being punished: activity itself is punishing (e.g., smoking makes you feel nauseated)
extrinsic punishment
not an inherent aspect of behavior being punished simply follows the behavior (e.g being told you smoke? is that ever disgusting)
primary (unconditioned) punisher
event that is innately punishing (e.g being jabbed with a needle)s
secondary (conditioned punisher
event that is pushing because of past association with other punisher (e.g going to a doctor who often gives you a needle)
generalized (generalized secondary) punisher
event that is punishing because of its past association with many other punishers (e.g., a mean look from someone )
extinction punishment
behavior no longer leads to a thing It used to lead to
negative punishment
behavior leads to the removal of something that you already have
positive punishment
dependent on behavior: Punishment specifically aims to decrease a behavior
Aversive stimuli q
describe something unpleasant or unwanted, without implying a change in behavior
punisher
theoretically, all positive punters are aversive but if an aversive event occurs and it doesn't lead to a reduction in behavior it (blank)
noncontingent punishment
aversive event was essentially uncontrollable (even unpredictable) such that whatever you do, you are unable to influence your exposure to that event
Applied Behavior Analysis
animal training
child rearing
Parent use reinforcement and punishment to shape their children’s behavior
language development, self control, diligence or effort, problematic behavior
Child Neglect
When a child is neglected, their efforts to operate on the environment are largely ignored, there are no consequences
Makes et al 2020
Child brain is significantly smaller than average (3rd percentile and has enlarged ventricles and cortical atrophy
Marshmallow test
Put a 5 year old in a room with one marshmallow and tell them they can eat it if they want but If they wait a few minutes you’ll give them 2 marshmallows to eat
Self control
Children wait for the marshmallow, those children are more successful on academic and social level and are generally more happy as adult than those that didn’t wait
Larson and colleagues (1998)
You can teach children self control to address problematic behaviors,
Found that they could teach aggressive adolescent boys to use self control technique to reduce their disruptive behavior
Work suggest that people who do not have good self control do not lack willpower or character
they lack instruction and instruction is all about reinforcement
Skinner’s Teaching Machine
instructional program including short presentation of information followed by question. Each time student completed one question correctly, they would more on to the next, the opportunity to move on offered the only reinforcer, most student found the task of each question easy enough to make few mistakes, allowing them to succeed at more and more difficult material
The Headsprout Program
A program that ensure that every student experiences a high rate of reinforcement, little failure and little frustration during the learning process