Unit 5A.11: Chest & Lungs Assessment
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Kyphosis
Increased curve of the thoracic spine that results from a loss of lung resiliency and loss of skeletal muscle
Normal
Barrel Chest
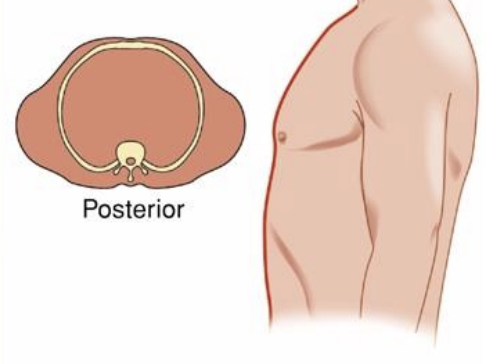
Pectus Excavatum (Funnel Chest)
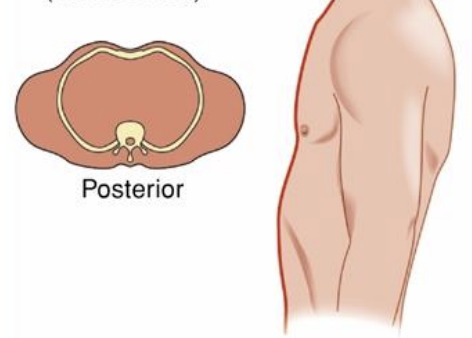
Pectus Carinatum (Pigeon Breast)
1:2
What is the normal ratio of anteroposterior to transverese diameter?
45 degrees
The ribs should slope downward at approximately ___ in relation to the spine.
Trapezius
What muscle should a normal client not use to assist breathing?
12-20 breaths/minute
What is the normal breathing pattern?
Normal
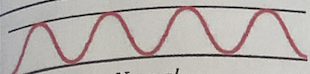
Tachypnea
More than 24 breaths/minute and shallow
May be caused by:
Fever
Anxiety
Exercise
Respiratory Insufficiency
Alkalosis
Pneumonia
Pleurisy

Bradypnea
Less than 10 breaths/min and regular
May be normal in well-conditioned athletes
Can occur with
Medication-induce depression of the respiratory center
Diabetic Coma
Neurologic Damage
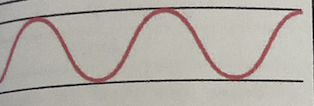
Hyperventilation
Increased rate and depth
Usually occurs with
Extreme exercise
Fear
Anxiety
Disorders of CNS
Salicylate Overdose
Severe Anxiety
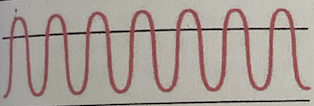
Kussmaul
Rapid, deep, labored
Type of hyperventilation associated with diabetic ketoacidosis

Hypoventilation
Decreased rate and depth, irregular
Usually associated with narcotic or anesthetic overdose
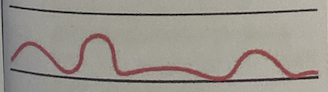
Cheyne-Stokes Respiration
Regular pattern characterized by alternating periods of deep, rapid breathing, followed by periods of apnea
May result from
Severe congestive heart failure
Drug overdose
Increased intracranial pressure
Renal Failure
May be noted in elderly patients during sleep
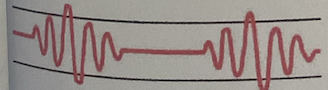
Biot’s
Irregular pattern characterized by varying depth and rate of respirations followed by periods of apnea
May be seen with
Meningitis
Severe brain damage
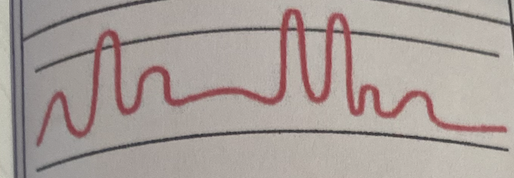
Ataxic
Significant disorganization with irregular and varying depths of respiration
More extreme expression of Biot’s respirations indicating respiratory compromise

Air Trapping
Increasing difficulty in getting breath out
In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease

Apnea
temporary cessation of breathing, especially during sleep

Apneustic
involves a prolonged inhalation, followed by a pause, and then a very short, inadequate exhalation
linked to injuries or damage in the upper pons region of the brain, which controls breathing

Subcutaneous Emphysema
What is another name for crepitus?
Crepitus
Crackling sensation that occurs when air passes through fluid or exudate
Fremitus
Vibrations of air in the bronchial tubes transmitted to the chest wall
T9 & T10
Where on the posterior chest wall should the hands be placed to assess chest expansion?
5-10 cm
What is the normal measurement for chest expansion?
Hyperresonance
What is the sound elicited in cases of trapped air such as in emphysema or pneumothorax?
T7
Where should percussion for diaphragmatic excursion begin?
3-5 cm
What is the measurement for normal diaphragmatic excursion?
Up to 7-8 cm
What is the measurement for diaphragmatic excursion in well- conditioned clients?
C7
Where should auscultation for breath sounds be started in the posterior chest wall?
Stridor
Harsh, honking wheeze with severe broncholaryngospasm
Pleural Friction Rub
Low-pitched, dry grating sound