Reservoir Mid-Term
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Modules 1-8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Give 3 examples of unconventional hydrocarbon deposits
Oil sands
Shale oil/gas
Coal Bed Methane
Name the 3 classifications of petroleum recovery methods
Primary
Reservoir is producing under its natural energy
Secondary
Pressure Maintenance Methods are needed
Injection of water, gas, or both to maintain reservoir pressure
Tertiary (EOR Methods)
Chemical Flooding, Thermal Recovery Methods (ie. SAGD) etc.
Name 3 natural drive mechanisms for an oil reservoir and 1 natural drive mechanism for a gas reservoir.
Oil Reservoir:
Solution Gas Drive
Water Drive
Gas Cap Drive
Gas Reservoir:
Gas Expansion Drive
What is petroleum?
A complex mixture of naturally occurring hydrocarbons
What is the latin root of “petroleum” ?
“petro” → rock
“oleum” → oil
ie. “Rock Oil”
What are the 2 theories of petroleum origin?
Organic Theory
Solid “kerogen” is formed from buried organic materials and cooked and broken down under high P&T into liquids and gases.
Inorganic Theory
Not produced from living organisms but from carbon and hydrogen within the earth combining under the right P&T to create hydrocarbons.
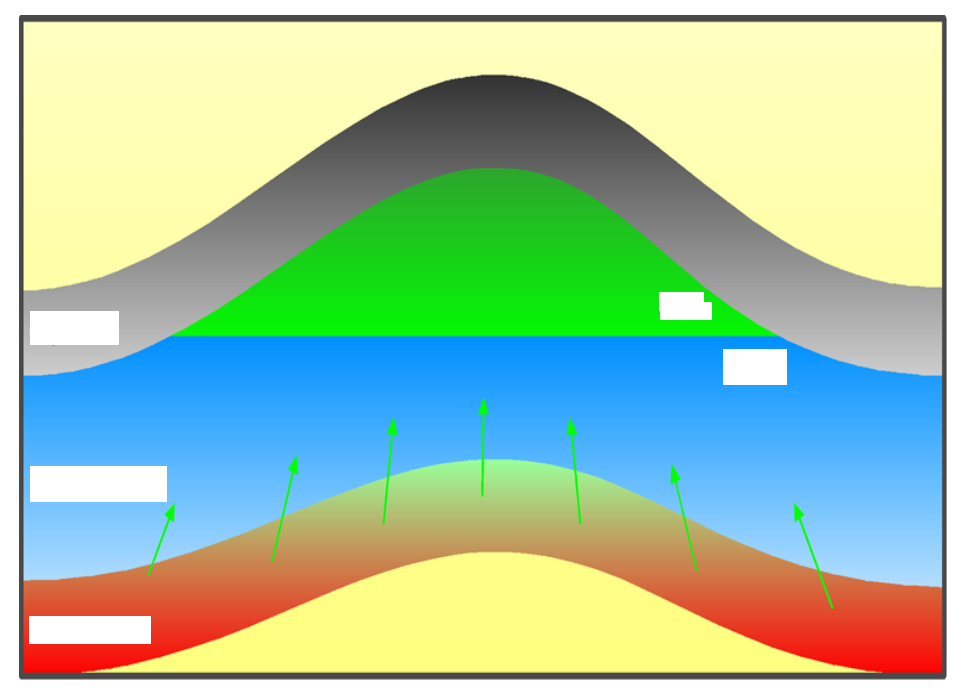
Label the diagram of a hydrocarbon cap and seal
What is the simplest hydrocarbon combound?
Methane (CH4)
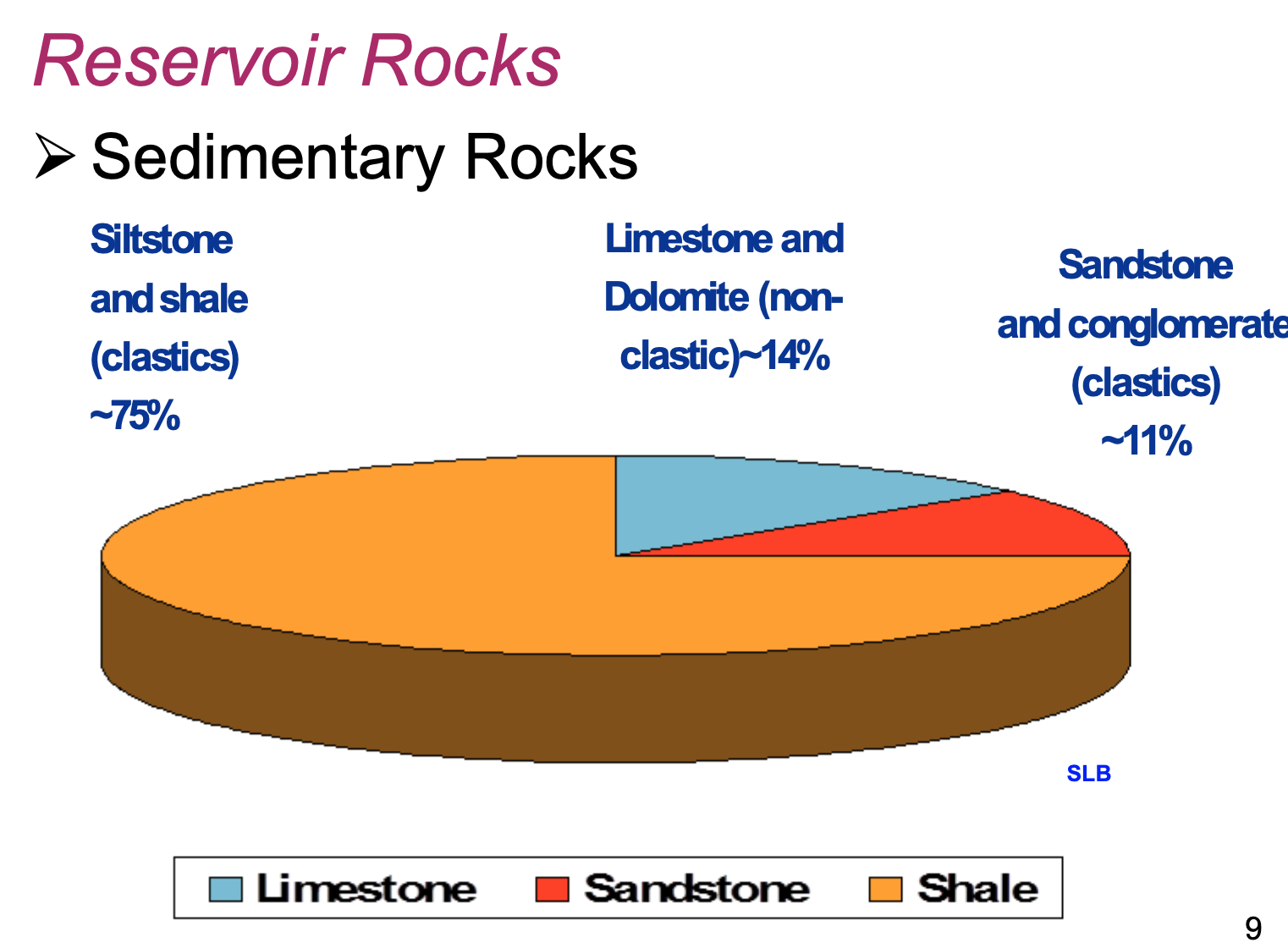
What types of rocks are reservoir rocks?
Sedimentary
Which types of sedimentary rocks make up roughly 75% of all reservoir rocks?
Siltstone and shale
Name the 2 ways that reservoirs can be classified
Based on:
Reservoir Trap
Reservoir Fluids
Name the 3 types of Reservoir Traps
Structural
Stratigraphic
Combination
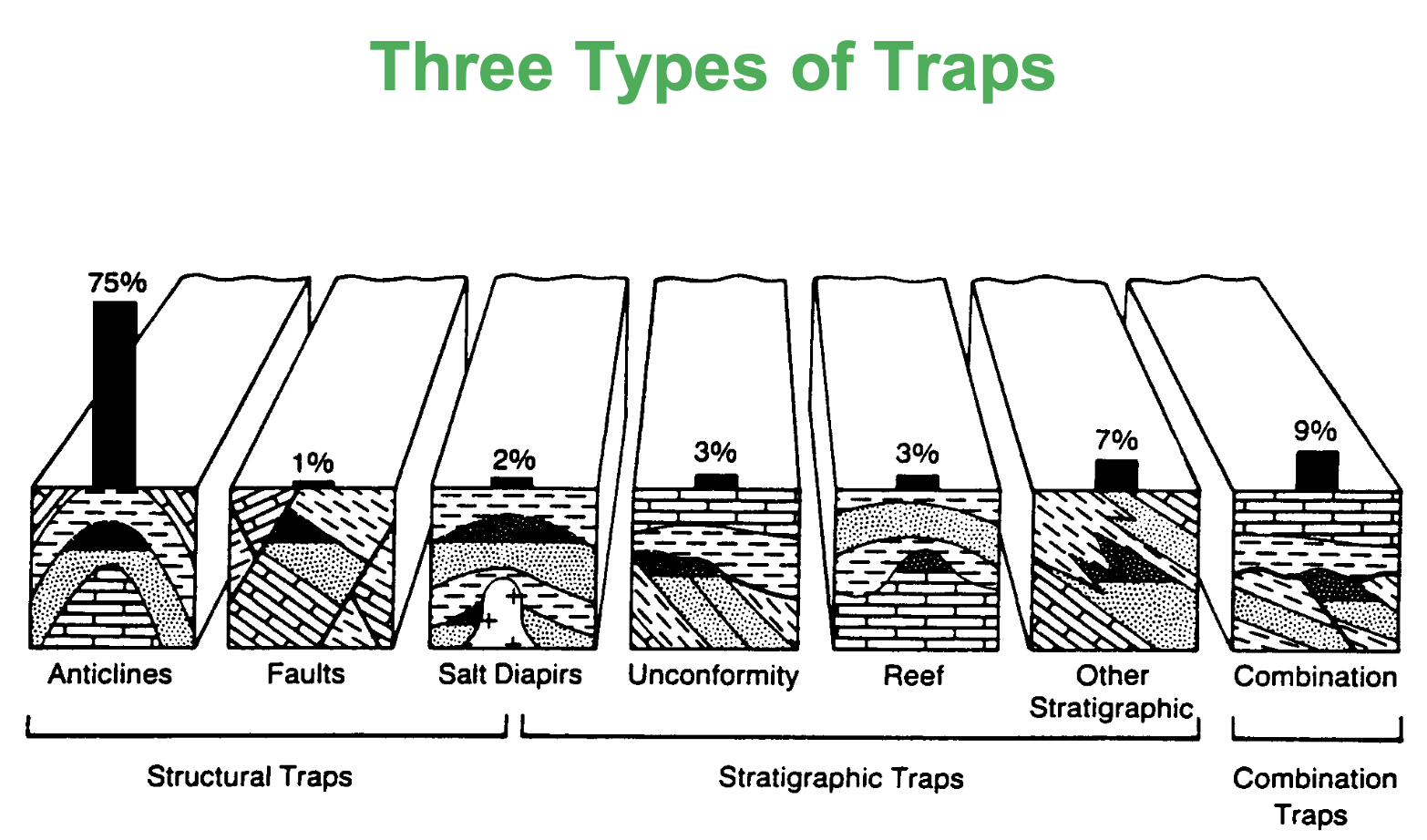
Traps formed when tectonic movement exerts forces on the subsurface strata structure. Strata is deformed and generate folds and faults.
Structural Traps
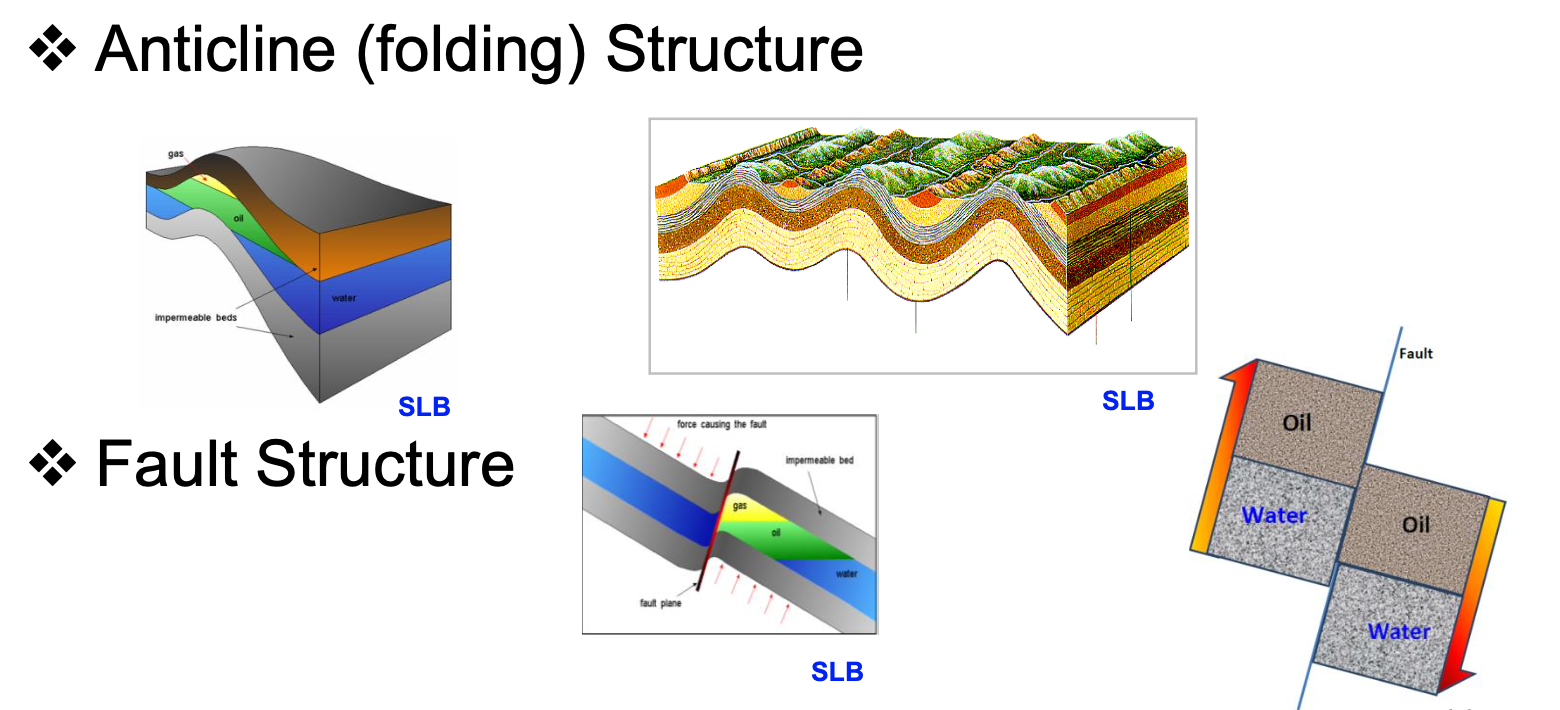
Traps formed as a result of depositional conditions in the sedimentary process.
Stratigraphical Traps
Reef traps
Unconformity traps
Lens traps
Based on the phase diagram of reservoir fluids, petroleum reservoirs can be classified in what 3 ways?
Single Liquid Phase
Single Gas Phase
Two Phase (liquid and gas)
What is Reservoir Engineering?
Reservoir Engineering is the study of hydrocarbon reservoirs and their rock and fluid properties, in order to:
calculate reserves
forecast production
design recovery schemes that maximize recovery and minimize cost
Maximum possible reservoir porosity is estimated at what percentage?
38%
Cubic packing (theoretical) → 48%
What type of recovery method can often produce up to 85% of the gas in a gas reservoir?
Primary
ie. Gas expansion drive
Name the 3 main Core Analysis tests
Porosity
Permeability
Fluid Saturations
Define:
Bulk Volume
Grain Volume
Pore Volume
Bulk Volume (BV): Total volume of a portion of a reservoir
BV = GV + PV
Grain Volume (GV): Volume of the solid parts (ie. rock) in the bulk volume
measured experimentally
Pore Volume (PV): Volume of the empty space in the bulk volume
PV = BV - GV
PV = (mwet core - mdry core)/ρf
Refers to the affinity of fluids to adsorb on the rock surface
Wettability
Volume of hydrocarbon within pore volume
Hydrocarbon Volume
Ratio of Fluid Volume to Pore Volume
Fluid Saturation
ie. So or Sg
Ratio of Pore Volume to Bulk Volume
Porosity (Φ)
What type of logging method can be used to measure Total Porosity? Explain how it works.
Acoustic Well Log
Acoustic tool generates sound waves and sends them through the formation from source to receiver.
Tool measures Sonic Transit Time → translates it into Formation Density and subsequently Formation Porosity.
Sound waves travel faster through solid rock than fluid in pore spaces.
The denser (less porous) the formation, the faster the sound wave travels.
The more porous the formation, the slower the sound wave travels.
What type of logging method can be used to measure Effective Porosity? How does it work?
Neutron Density Log
Tool bombards the formation with neutrons.
Measures dispersion and reflection back to tool.
The more porous the formation, the slower the neutrons rebound back to the tool.
The less porous, the faster the neutrons rebound back to the tool.
Porosity ________ as depth increases.
decreases
due to higher overburden pressure from the weight of overlying rocks
Name some factors that affect the porosity of reservoir rock
Sorting
Cementation
Packing
Grain shape
Existence of fractures
Depth
Porosity formed when Reservoir Rock was originally created or consolidated (i.e. space between deposited grains).
Primary Porosity
Porosity formed after rock was created or consolidated.
Secondary Porosity
Includes: effects of fractures, faults, dissolution, dolomitization, etc.
Give the grain densities of:
Sandstone
Limestone
Dolomite
Sandstone = 2.65 g/cm3
Limestone = 2.7 g/cm3
Dolomite = 2.8 g/cm3
The minimum water saturation (Sw) in pore space
Irreducible Water Saturation (Swirr)
The minimum oil saturation (So) in pore space
Residual Oil Saturation (Sor)
The minimum gas saturation (Sg) in pore space with connected paths filled with gas that flows by itself as a separate phase
Critical Gas Saturation (Scg)
What 4 data points would you need in order to calculate the initial hydrocarbon volume in a reservoir?
Reservoir average thickness
Reservoir average area
Average porosity
Average fluid saturation
Which method used to calculate reservoir volume make use of contour maps of the reservoir?
Planimetric
Original hydrocarbon volume in place before any production
Resource
Volume of hydrocarbons that are economically recoverable using existing technology
Reserves
Total vertical reservoir rock thickness measured from top to bottom of the formation
Gross Thickness
In a reservoir, this is the total sum thickness of the layers that meet a porosity cut-off requirement
Net Thickness
The sum thickness of the productive layers of the reservoir
Net Pay Thickness
ie. layers of the reservoir with:
Φ ≥ Φ cut-off
SHC ≥ SHC cut-off
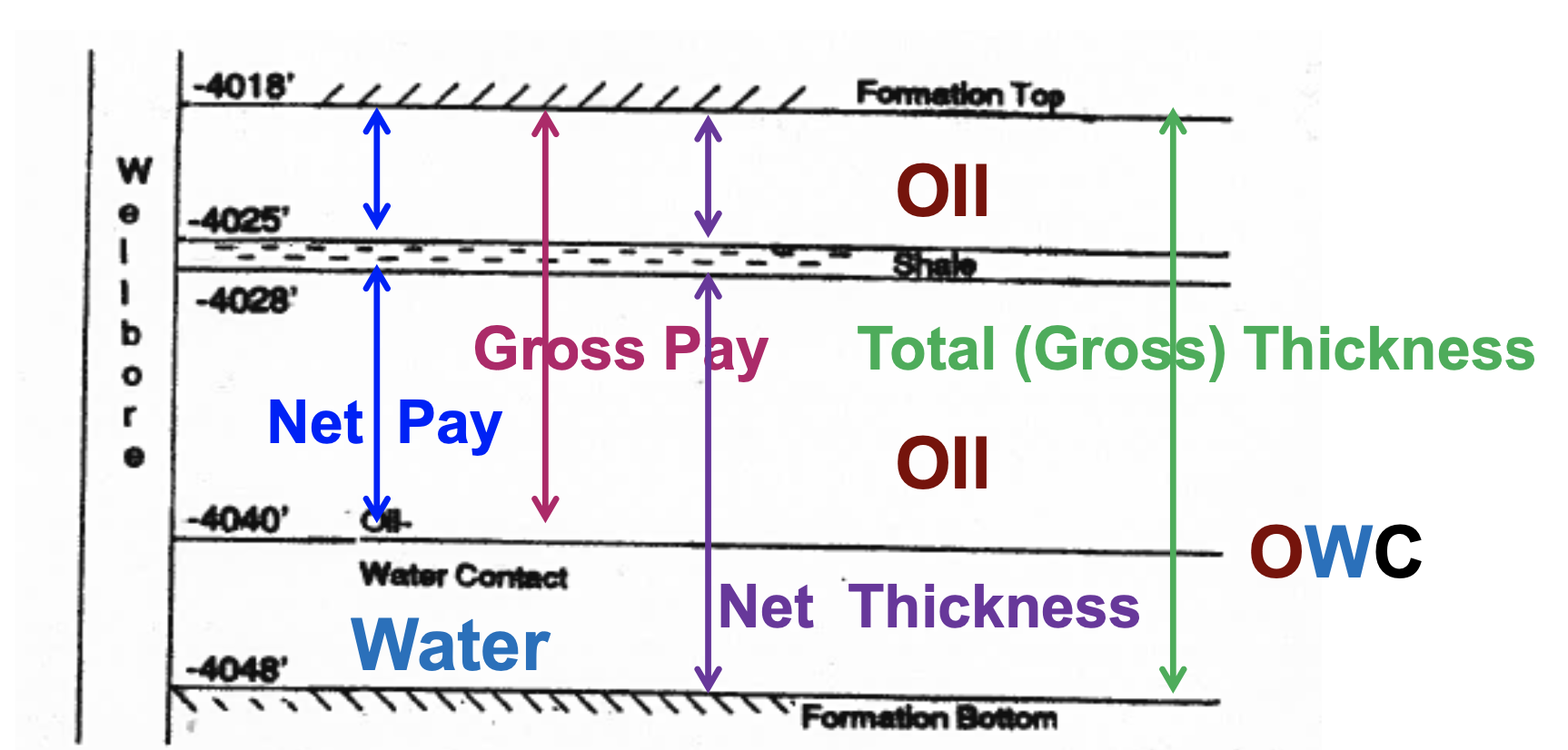
Represents the reservoir storage capacity of hydrocarbons (O or G)
Saturation-Porosity-Thickness (SΦh)
Represents the reservoir pore space capacity of the rock
Porosity Thickness (Φh)
A special closed system with no energy crossing the boundary
Isolated system
A system with a fixed amount of mass. No mass enters or exits the system boundary.
Closed System (or Control Mass)
Energy (heat or work) may cross the system boundary
What type of system is assumed for a reservoir?
Closed system
vapour + liquid within closed boundary
The dividing surface between Liquid and Vapour Phases.
Interface
What would be the effect of increasing the temperature in the reservoir while keeping the pressure constant?
Vaporization of some molecules from liquid to vapour phase
What would be the effect of increasing the pressure in the reservoir while keeping the temperature constant?
Condensation of some molecules from vapour to liquid phase
What is the phase affinity for light hydrocarbons? For heavy hydrocarbons?
Light hydrocarbons → affinity for vapour phase
Heavy hydrocarbons → affinity for liquid phase
When there is no longer a driving force to push molecules from one phase to another, what state is the system said to be in?
Equilibrium
Name 4 types of equilibrium
Thermal Equilibrium
Entire system has constant T
Mechanical Equilibrium
Entire system has constant P
Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical composition (mole fraction) of phases within the system remains constant
Phase Equilibrium
Mass of phases within the system remains constant
When is a system said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium?
When it is simultaneously in:
Thermal Equilibrium
Mechanical Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibrium
The general term used for any mathematical equation that relates the pressure and temperature to the volume of a system
Equation of State
ie: Ideal Gas Law, Van der Waals, etc.
What type of diagram represents equations of state in plot form?
Phase Diagram
What are the 3 assumptions used for the Ideal Gas Law?
High T, Low P
No interactions b/w gas molecules
No volume occupied by gas molecules
What two parameters does Van der Waals Equation introduce to the Ideal Gas Law?
Volume occupied by gas (b)
Attractive forces b/w gas molecules (a/V2)
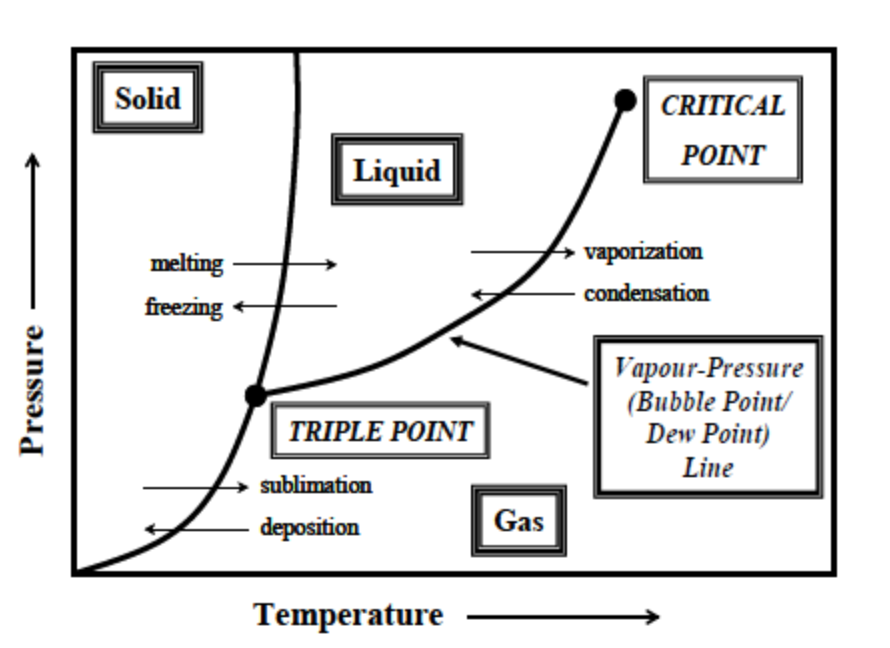
Label this single component phase diagram with the following labels:
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Triple Point
Critical Point
Bubble Point/Dew Point Line
The region of a two phase diagram where both liquid and vapour are present
Phase Envelope
In a two phase diagram, is the bubble point and dew point line the same?
Negative
In a two-phase diagram, what single phase will exist at a high T and low P ?
What about at a high P and low T ?
High T, Low P → single phase vapour
Low T, High P → single phase liquid
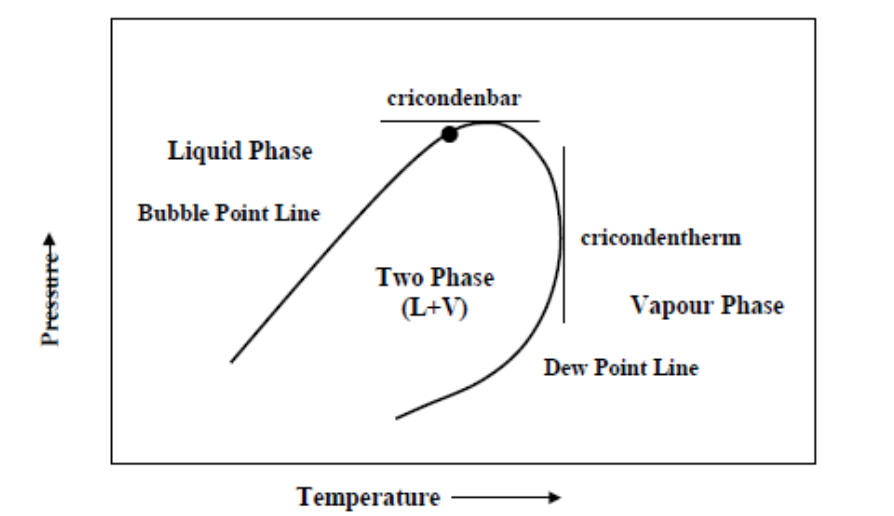
The point at which the bubble point line meets the dew point line on a two-phase diagram
Critical Point
The maximum pressure at which 2 phases coexist on a two-phase diagram
Cricondenbar
The maximum temperature at which 2 phases coexist on a two-phase diagram
Cricondentherm
A fluid that exists above the phase envelop on a two-phase diagram
Supercritical Fluid
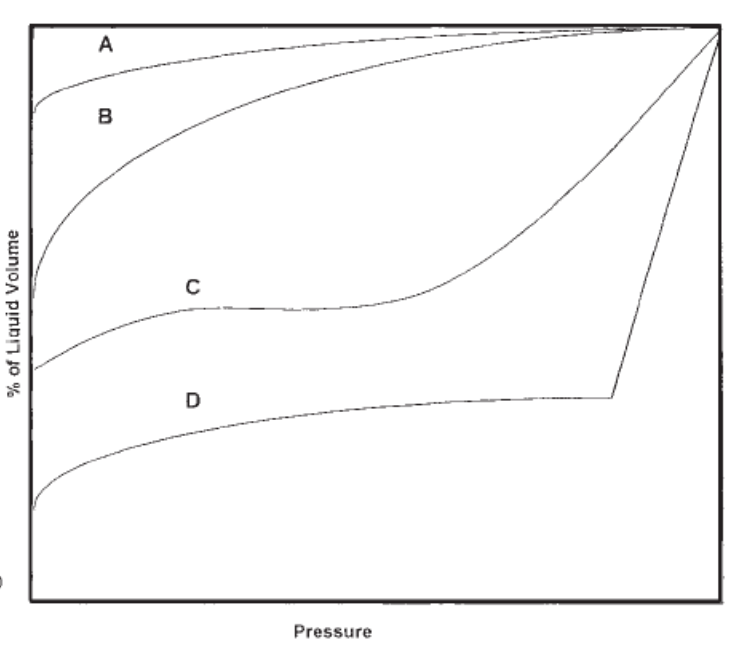
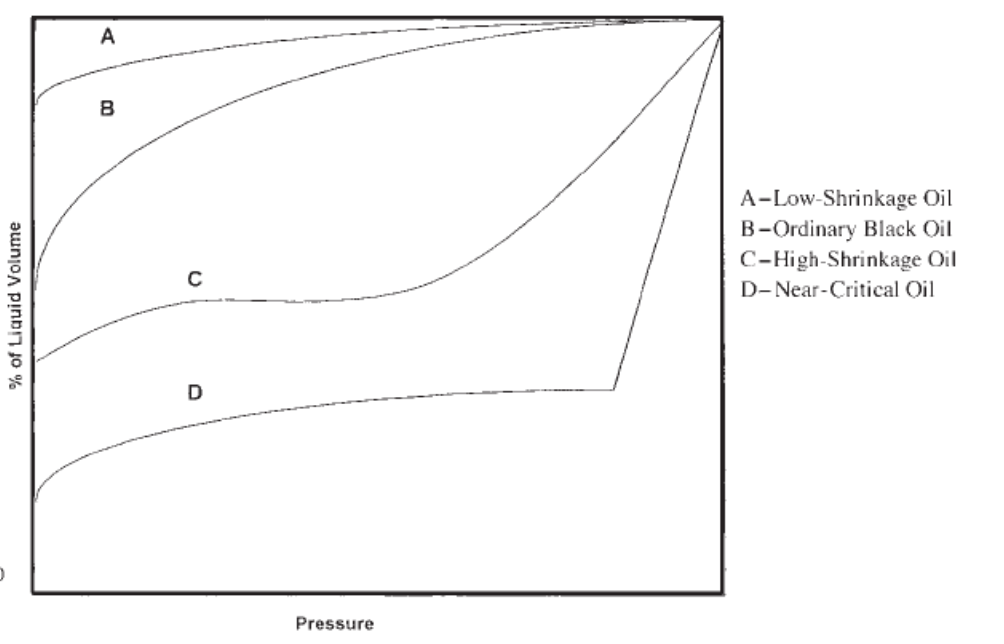
Name the type of oil represented by each liquid-shrinkage curve on the graph
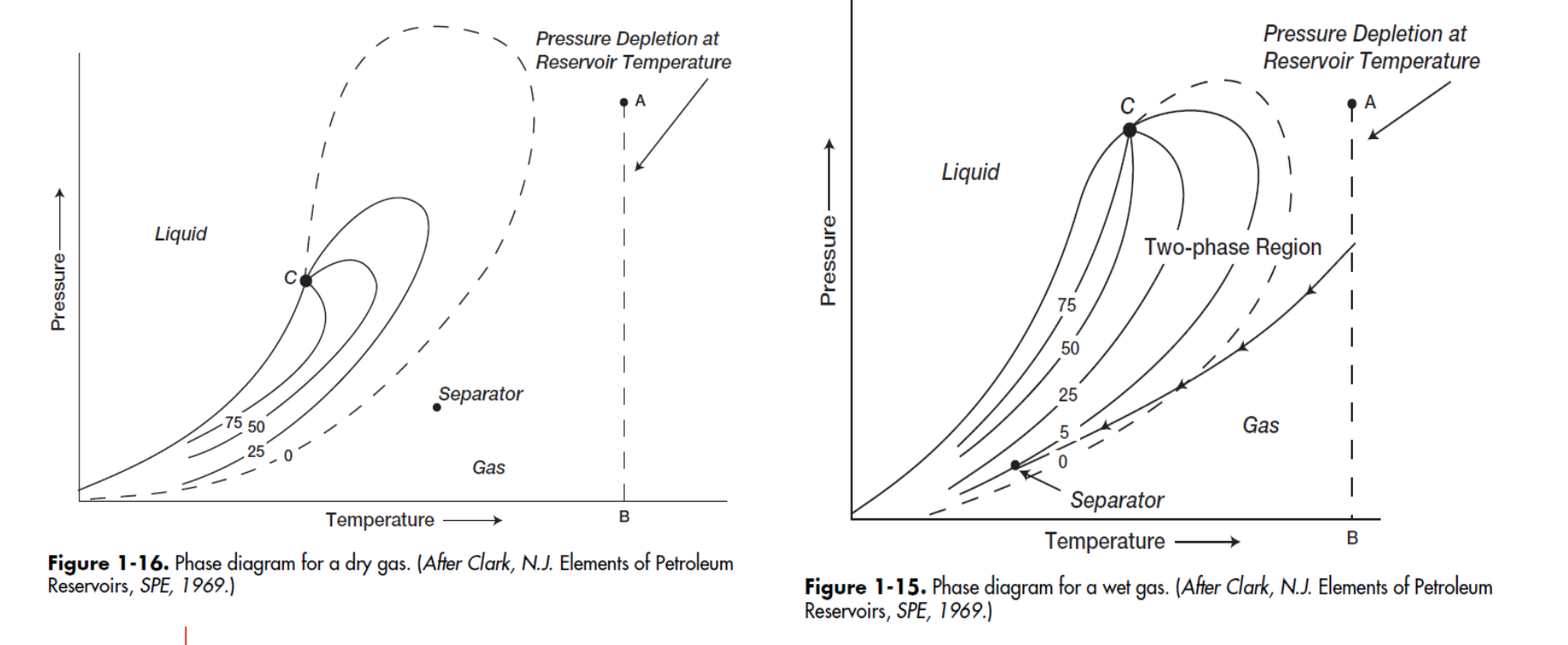
In this type of reservoir, when the pressure falls below the dew point pressure, some of the gas in the reservoir condenses into liquid hydrocarbons.
Retrograde Gas Condensate
In phase diagrams for the various types of gas reservoirs, which type has separator conditions (ie. P&T) that lie outside the phase envelope?
Dry Gas
because there is only one phase (gas) present at surface conditions
On a P-T phase diagram for a pure substance, what is the name of the point at which the boundaries between the three phases - solid, liquid, and gas - intersect?
Triple Point
A test designed to simulate a pressure depletion process for black oil, which enables the Rso and Bo to be measured
Differential Liberation Test
An experimental procedure used to estimate the bubble point of a reservoir fluid
Flash Expansion Test
Refers to crude oil that contains dissolved gas in solution under high pressure, as it exists naturally in the reservoir
Live Oil
live oil mass varies with the amount of gas dissolved in the oil
Crude oil that has no dissolved gas in it
Dead Oil
the mass of dead oil is fixed because there is no dissolved gas in the oil
Refers to the reduction in the volume of crude oil when it is brought from reservoir conditions to surface conditions during production
Oil shrinkage
The point at which oil is fully saturated with gas
The Bubble Point
When the reservoir pressure is greater than the bubble point pressure, what type of oil is present?
Undersaturated Oil
all the gas is dissolved in the oil
no free gas in the reservoir
When the reservoir pressure is less than or equal to the bubble point pressure, what type of oil is present?
Saturated Oil
at Pres=Pb the first bubble of gas comes out of the oil
at Pres<Pb more solution gas comes out of oil as free gas, and oil and free gas coexist
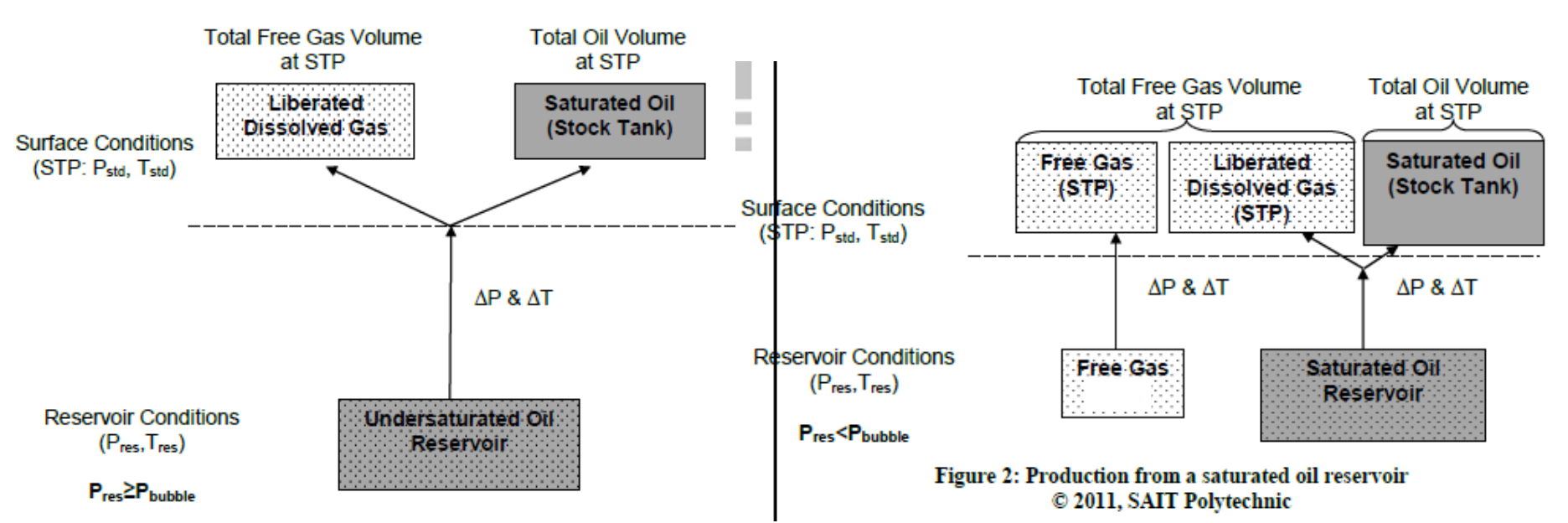
Describe the volume and phase change during production
As the °API increases, the specific gravity of the oil __________.
decreases
As the °API increases, the density of the oil __________.
decreases
When pressure increases, Rso ___________.
increases
When temperature increases, Rso ____________.
decreases
because gas tends to vaporize out of the oil at higher temperatures
At STP, the Rso will be _________.
zero (virtually)
When Rso increases, the dead oil °API ____________.
increases
When Rso decreases, the S.G. of the dead oil ____________.
increases
When Rso increases, the S.G. of the gas ____________.
increases
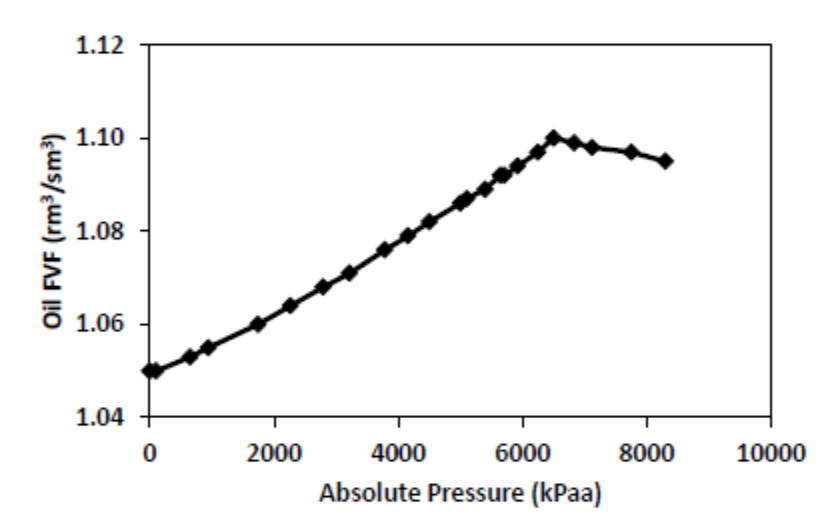
Explain the rising Bo with rising pressure until the Pb, and then the slight drop off in Bo with increasing pressure beyond the Pb
Below Pb (Saturated Oil): Bo increases as pressure increases because more gas is absorbed into the oil with increasing pressure, expanding the volume of live oil.
At Pb (Bubble Point): Bo is at its maximum, as the oil is fully saturated.
Above Pb (Undersaturated Oil): Bo decreases slightly as pressure increases due to oil compressibility, while there is no longer any gas available to dissolve in the oil.
What is the pressure requirement in an oil reservoir in order for a gas cap to exist?
A gas cap only forms when the reservoir pressure is below the bubble point pressure because gas comes out of solution and accumulates.
If the reservoir pressure is above the bubble point, the oil holds all the gas in solution, and a gas cap cannot exist.
At STP, Bo is ___________.
1
because at surface, only dead oil is present and so (dead oil)/(dead oil) = 1
When the dead oil °API increases, the Bo ____________.
increases
When the dead oil S.G increases, the Bo ____________.
decreases
When the gas S.G increases, the Bo ____________.
increases
The presence of dissolved gas ________ oil viscosity.
reduces
How does the viscosity of dead oil relate to the viscosity of live oil?
μdead oil > μlive oil
@ P ≤ Pb, μlive oil ________ when P increases.
decreases
because there is still gas remaining to be dissolved, which will decrease the viscosity of the live oil
@ P > Pb, μlive oil ________ when P increases.
increases
because there is no more gas to be dissolved, and the oil compresses, leading to a higher viscosity
Will a high shrinkage oil have a high or low Bo ?
High
If an oil shrinks a lot as it is produced to surface, does the oil have a high or low shrinkage factor?
Low
ie. shrinkage factor of .10 means that the oil will occupy 10% of the volume that it occupied in the reservoir
shrinkage factor of .75 means that the oil will occupy 75% of the volume that it occupied in the reservoir
Therefore, low shrinkage factor = relatively large amount of shrinkage
What is the liberated gas volume at bubble point pressure?
0
What is the free gas volume in the reservoir at a pressure above the bubble point pressure?
0