Microbiology Lab: Fungi and Protozoan Pathogens
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms, unicellular or multicellular.
Hyphae
Filamentous structures forming the body of fungi.
Mycelium
Network of hyphae, serves as the fungal body.
Septate Hyphae
Hyphae divided by septa, allowing compartmentalization.
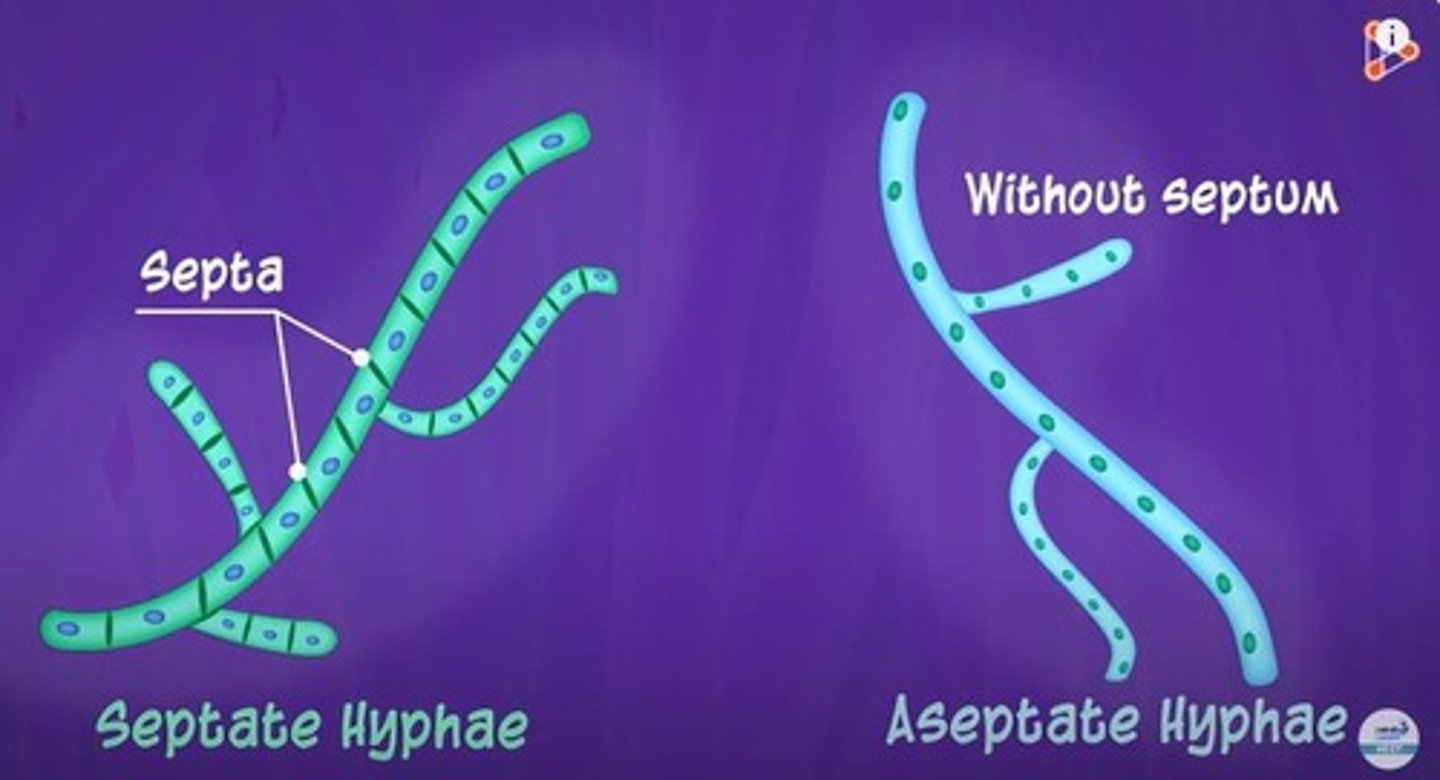
Aseptate Hyphae
Coenocytic hyphae without septa, continuous cytoplasm.
Mycorrhizae
Symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots.
Aspergillus niger
Mold known for producing black spores.
Rhizopus stolonifer
Common black bread mold, a zygomycete.
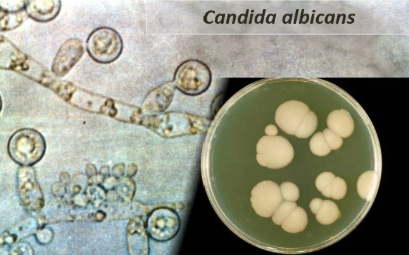
Candida albicans
Yeast, opportunistic pathogen causing infections.
Pseudohyphae
formed when yeast cells undergo a process of incomplete cell separation during budding
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Baker's yeast, used in fermentation processes.
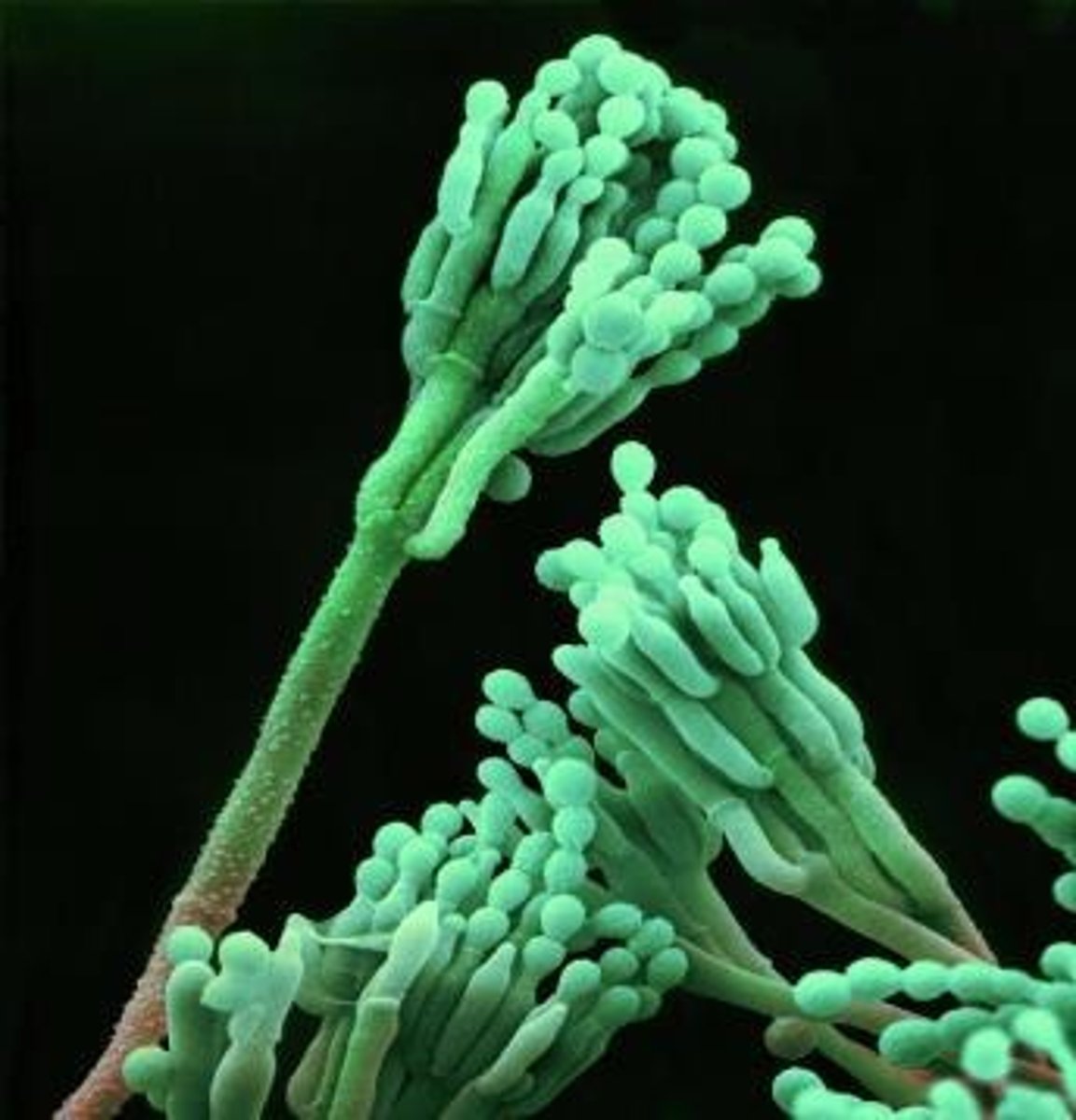
Penicillium chrysogenum
Mold that produces the antibiotic penicillin.
Conidia
Asexual spores where spores are produced and freely released
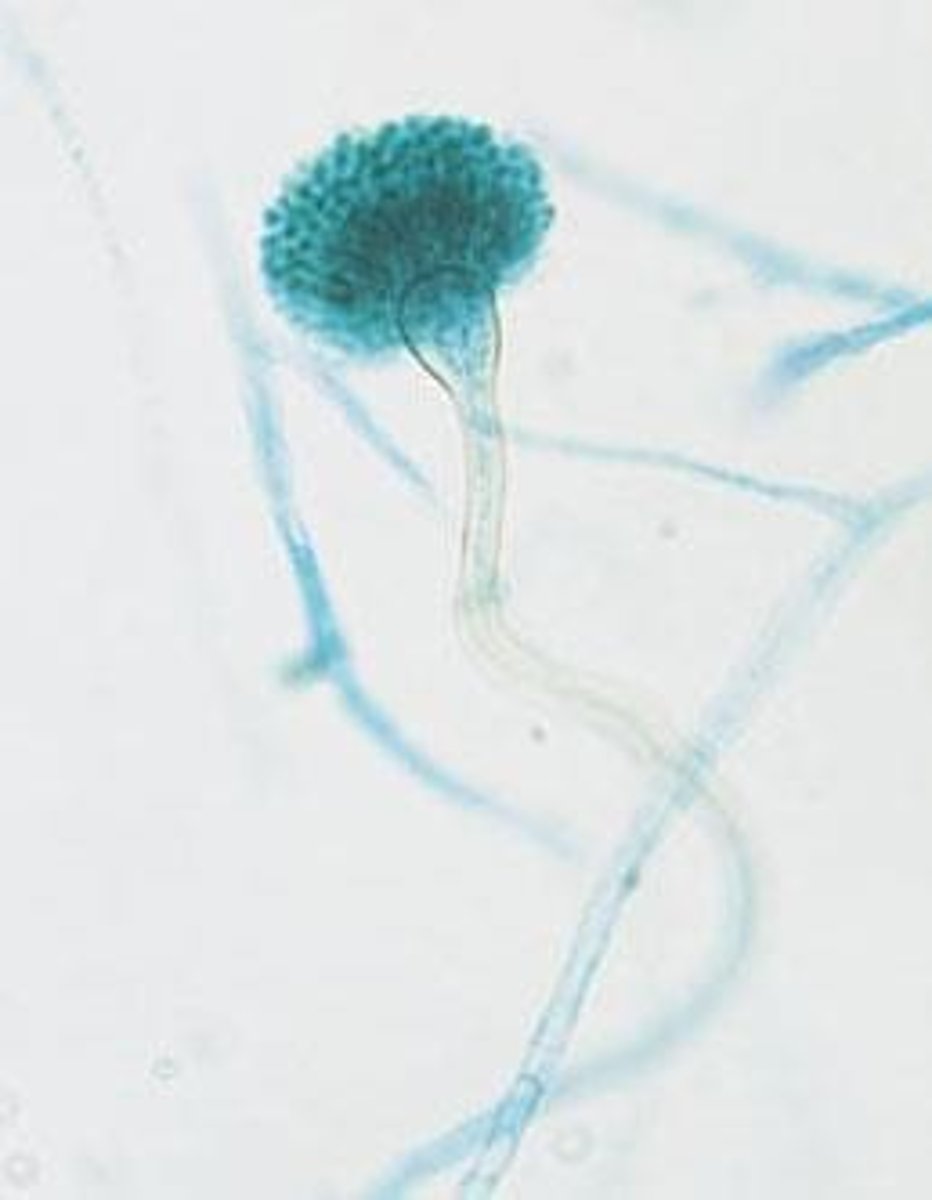
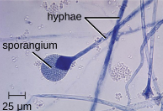
Sporangia
asexual spores where spores are contained in a sac-like head
Ascospores
Sexual spores formed in an ascus.
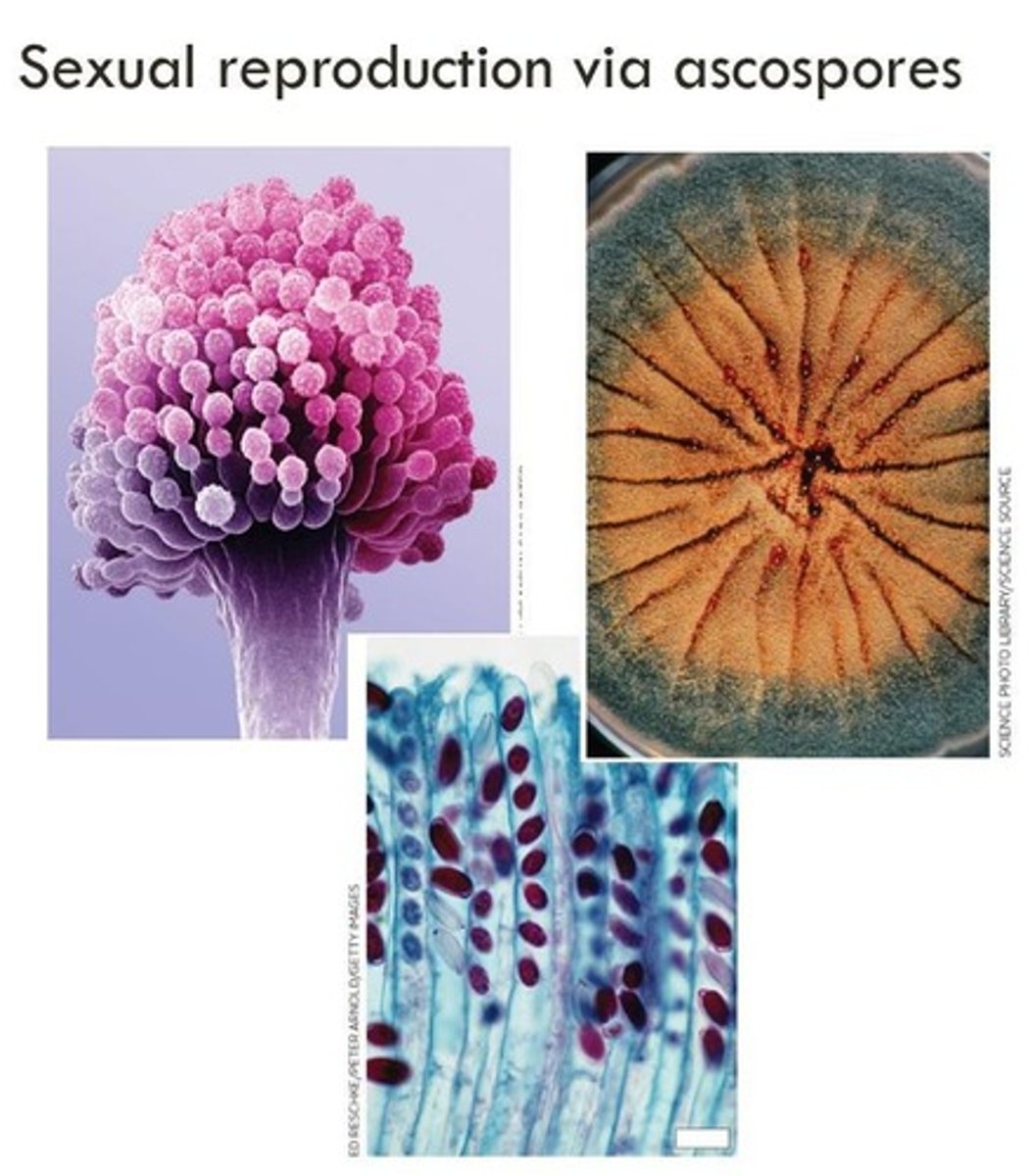
Saprophytic
Feeding on dead or decaying matter
Zygospore
Thick-walled resting spore of zygomycetes.
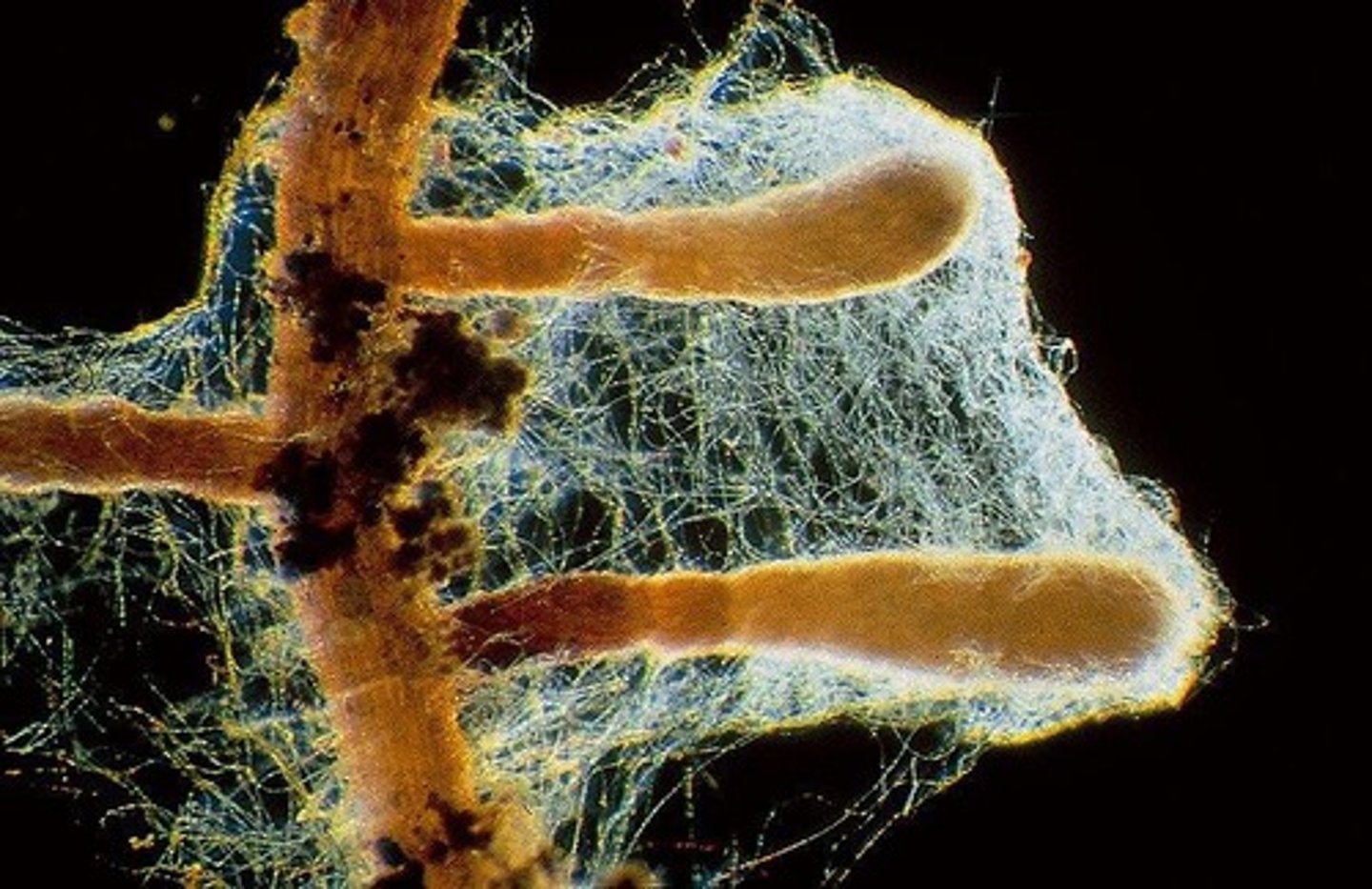
Sporangium
Specialized structures the produce and release asexual spores called sporangiospores. (present in Zygomycota)
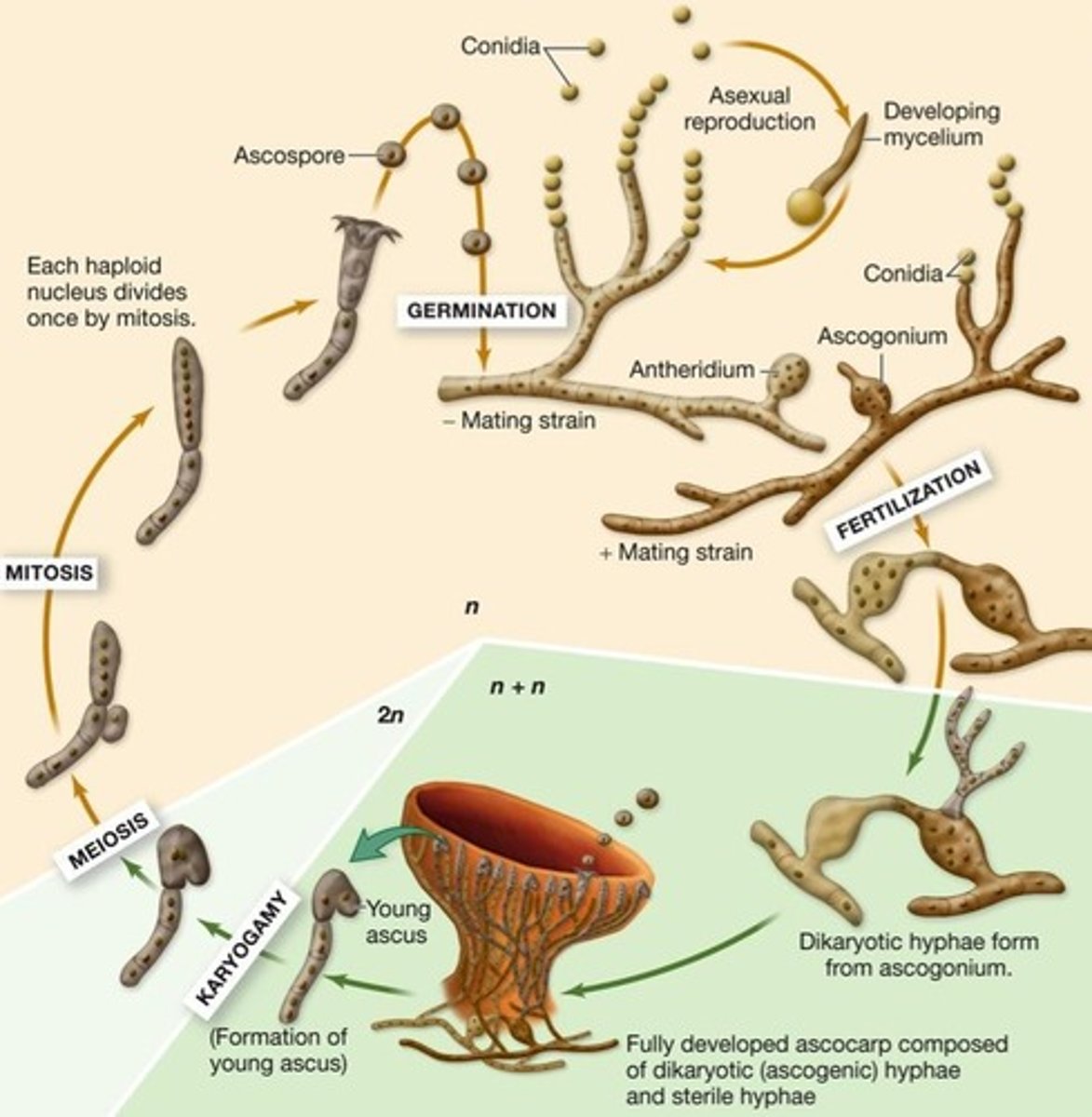
Dimorphic Fungi
have both yeast and filamentous-like appearance depending on the environment
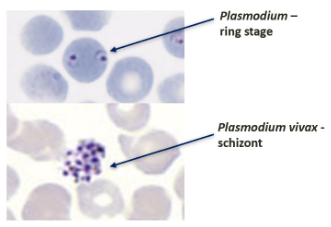
Plasmodium
Genus of parasites causing malaria in humans.
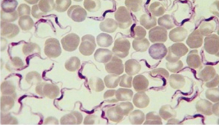
Trypanosomes
Flagellated protozoans causing diseases like sleeping sickness.
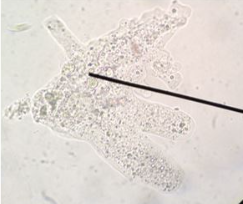
Amoeba proteus
Free-living amoeba, moves via pseudopods.
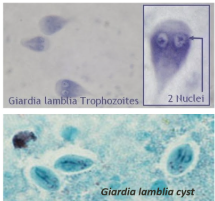
Giardia lamblia
Protozoan causing giardiasis, transmitted fecal-orally.
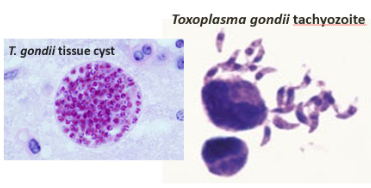
Toxoplasma gondii
Parasite associated with cats, causes toxoplasmosis.
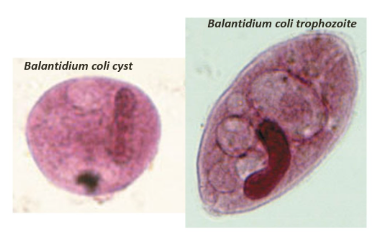
Balantidium coli
Ciliate causing balantidiasis, transmitted fecal-orally.
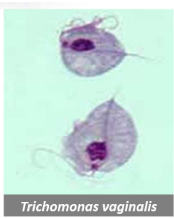
Trichomonas vaginalis
Protozoan causing trichomoniasis, a common STD.
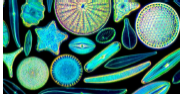
Diatoms
Photosynthetic protists with silica frustules.
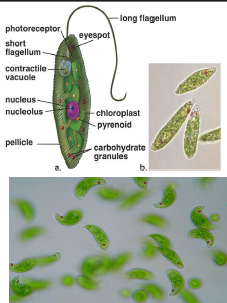
Euglena
Unicellular organism with both plant and animal features.
Helminths
Multicellular parasites, including flatworms and roundworms. Multicellular, heterotrophic, invertebrate animals
Cestodes
Flatworms known as tapeworms, segmented body structure. Adult tapeworms are elongated (2mm to 10m), segments called proglottids, hermaphroditic (each proglottid has male and female reproductive organs), scolex at the head end with hooks for attachment, inhabit the intestinal lumen of animals. Examples include Taenia species and Dipylidium.
Trematodes
Flatworms known as flukes, have suckers for attachment. Adult flukes are leaf-shaped, unsegmented, with prominent oral and ventral suckers, monoecious or dioecious.
Nematodes
Roundworms with cylindrical bodies, true body cavity. Adult and larval forms are cylindrical and they have a true body cavity or pseudocoelom. Phylum Nematoda includes organisms like Ascaris lumbricoides and Enterobius vermicularis (pinworms). Most have separate sexes (dioecious) and also reproduce by laying eggs. Eggs are often infective to mammals through ingestion, but some worms can directly burrow through skin. Some can be completely microscopic as adults, while others can become very large. Roundworm infections typically involve many worms per host, whereas flatworm infections usually involve only one.