Final Primatology Exam
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
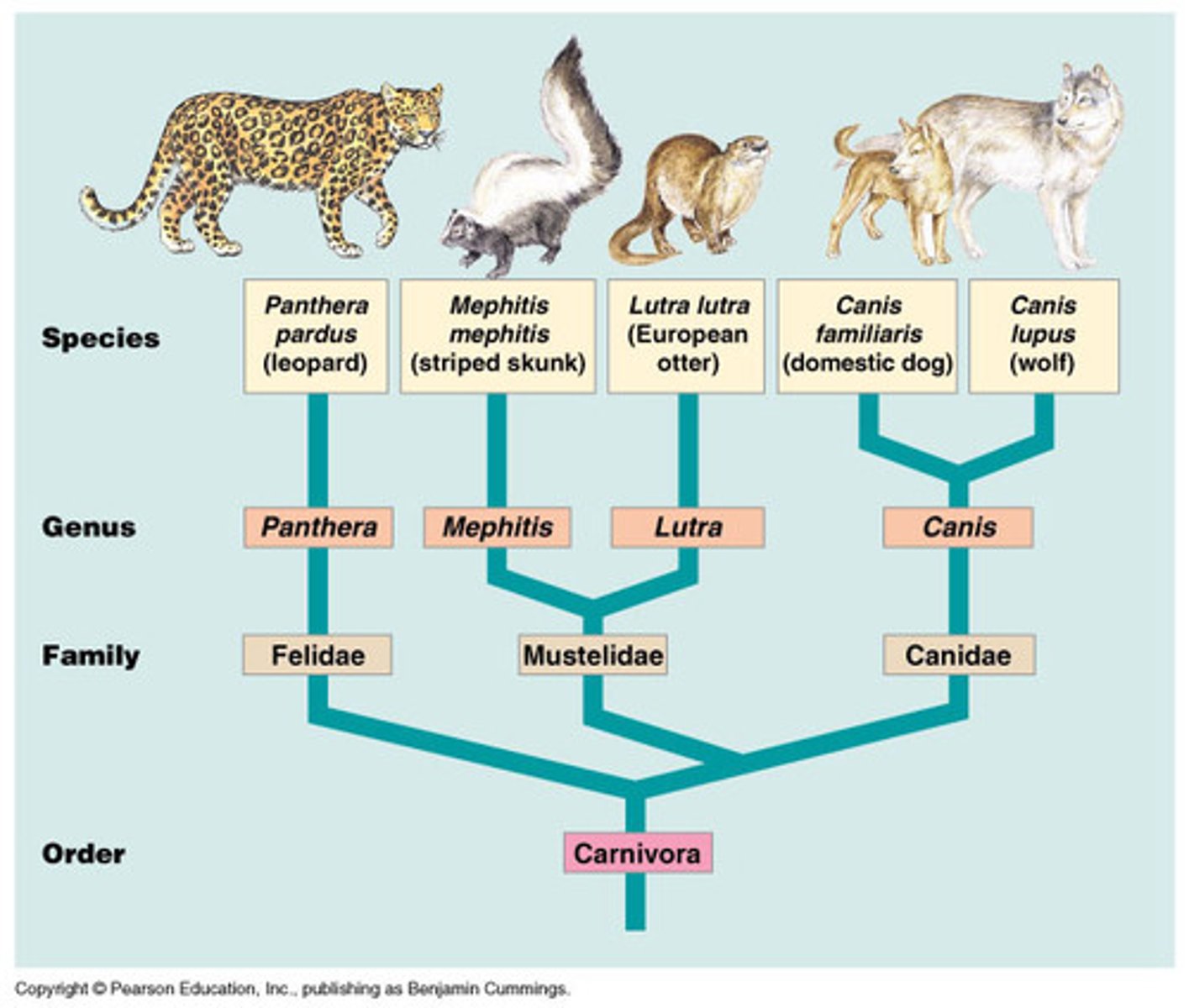
What is the common name for Family Hominidae?
Great Apes
What is solitary noyau?
Solitary animals do not live in a group. Instead, males live alone and females live either alone or with their dependent offspring.
What is polygyny?
One male, several females.

What is Fission-fusion?
A fission-fusion social structure describes a social system where large groups of individuals frequently divide into smaller subgroups (fission) or merge back together (fusion) based on factors like resource availability and social needs.
Who are the Leakey's Angels
"Leakey's Angels," also known as "The Trimates," refers to three pioneering female primatologists: Jane Goodall, Dian Fossey, and Birutė Galdikas.
Who is Jane Goodall, and what Taxonomy of Primate did she study?
Studied chimpanzees in Gombe Stream National Park, Tanzania, revolutionizing our understanding of their behavior and social structures. (Pan)
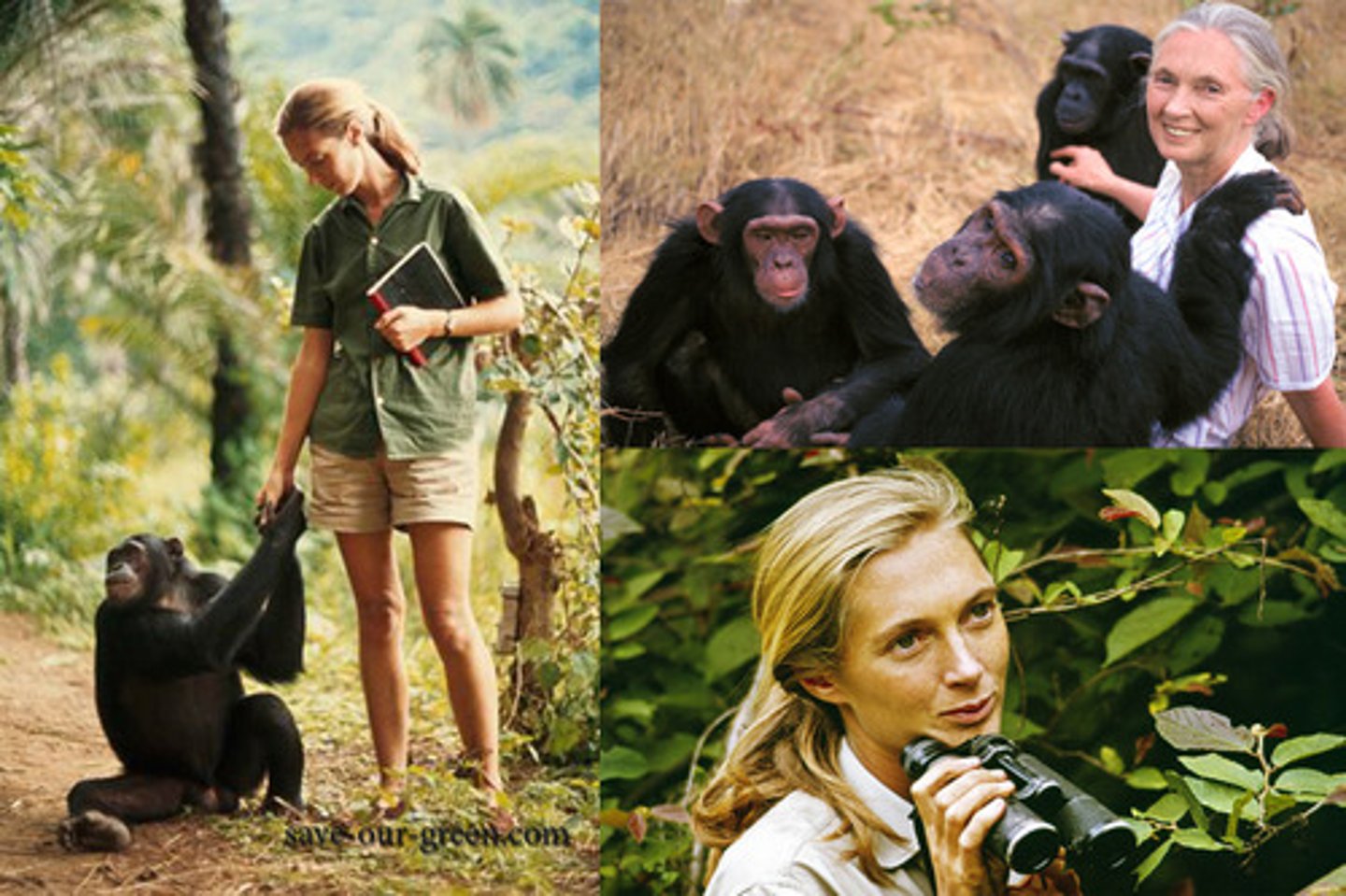

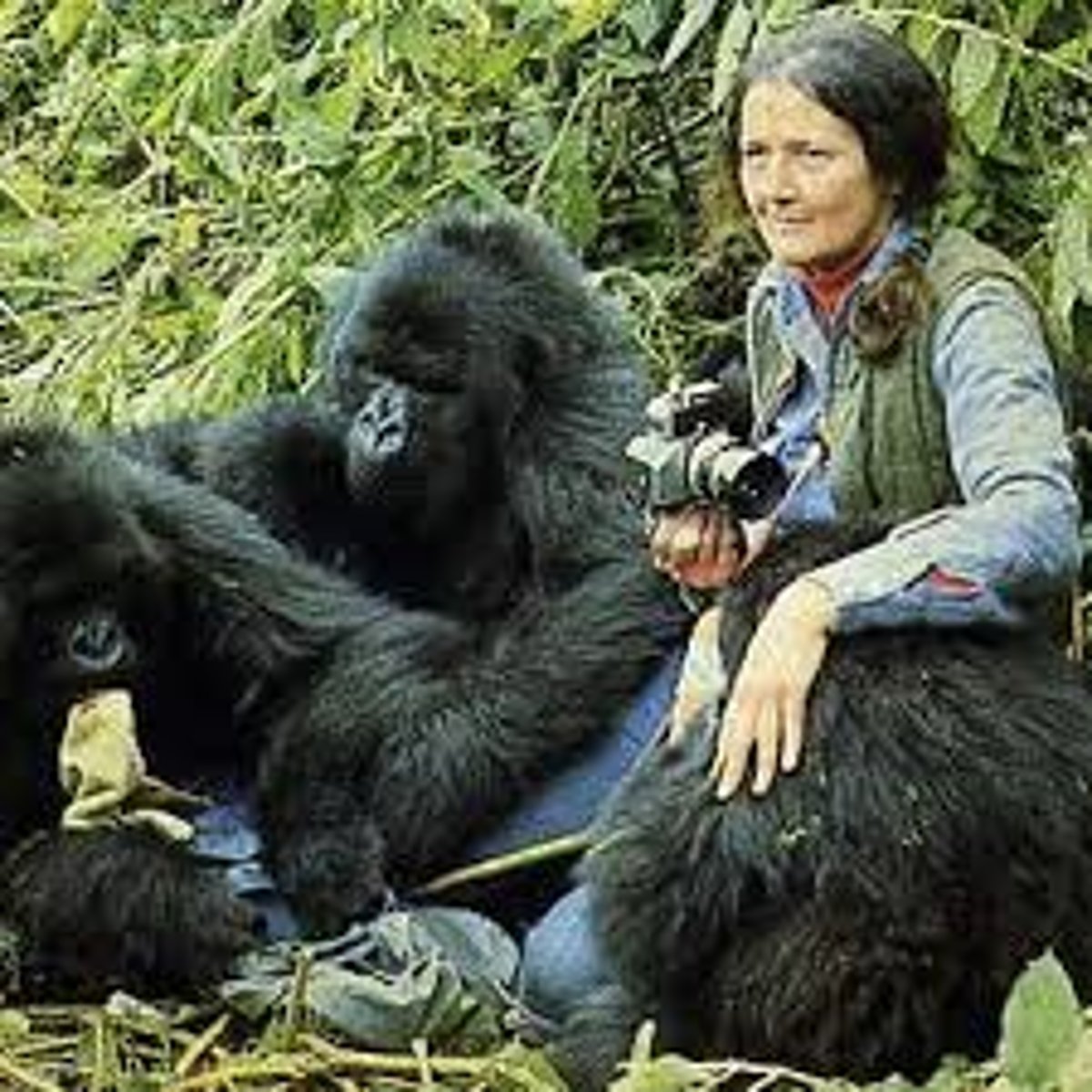
Who is Dian Fossey, and what Taxonomy of Primate did she study?
Researched mountain gorillas in the Virunga National Park, Rwanda, documenting their behavior and culture. (Gorilla)

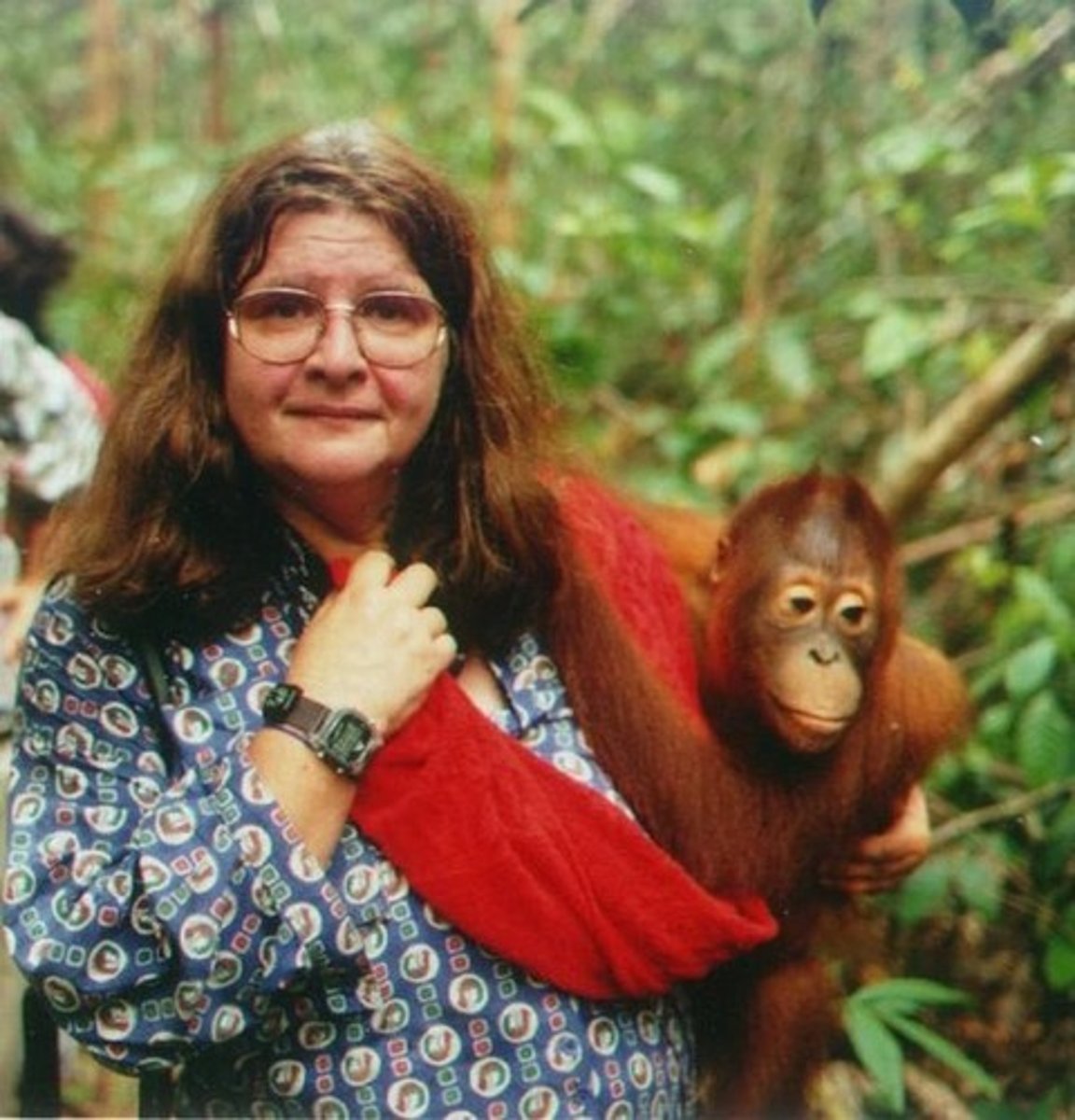
Who is Birutė Galdikas, and what Taxonomy of Primates did she study?
Studied orangutans in Borneo, contributing significantly to our knowledge of these great apes' lives in the wild. (Pongo)

What is phylogenetics?
Phylogenetics is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships between organisms, species, or groups of organisms
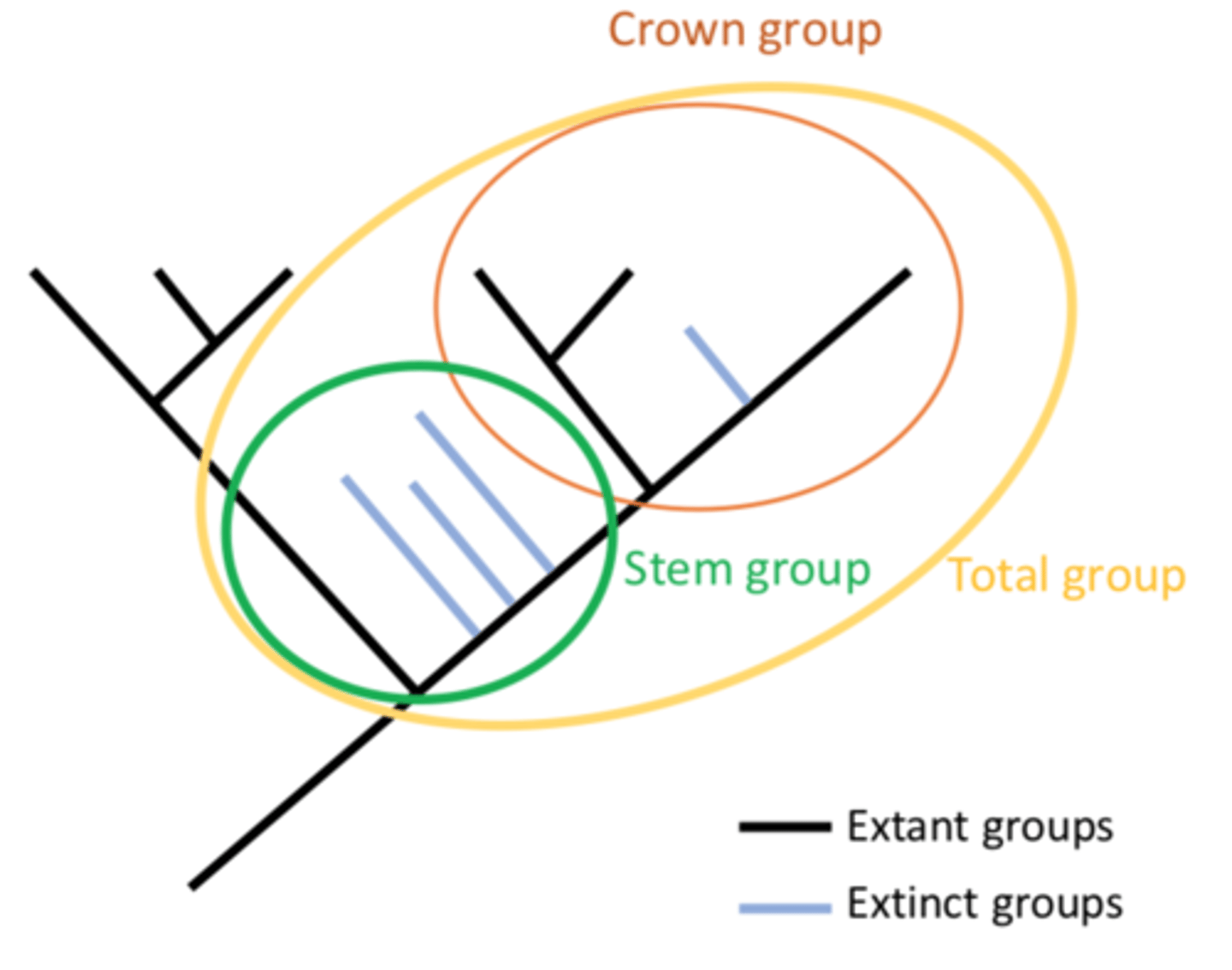
What is Stem Group?
Extinct organism outside the group, on the lineage to that of the most common ancestor
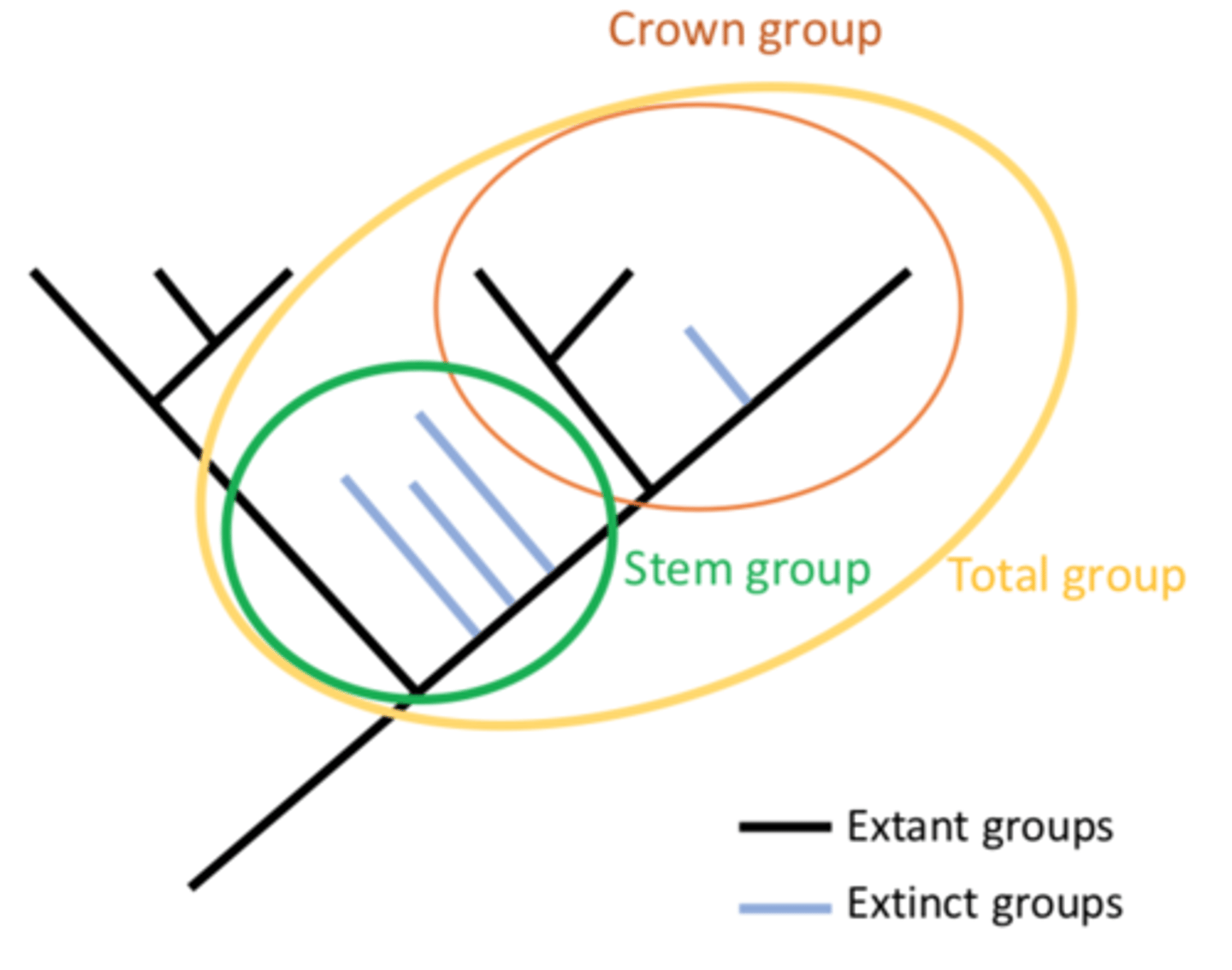
What is a crown group?
a group comprising all the extant clades of a group of interest and the most recent extinct clade
What is a sister group?
groups that share most recent common ancestry

Who are the euarchontoglires?
The Euarchontoglires is a major group (clade/superorder) of placental mammals, also known as Supraprimates. It includes five main groups: rodents (like mice and squirrels), lagomorphs (rabbits and hares), treeshrews, primates (monkeys, apes, and humans), and colugos (flying lemurs).
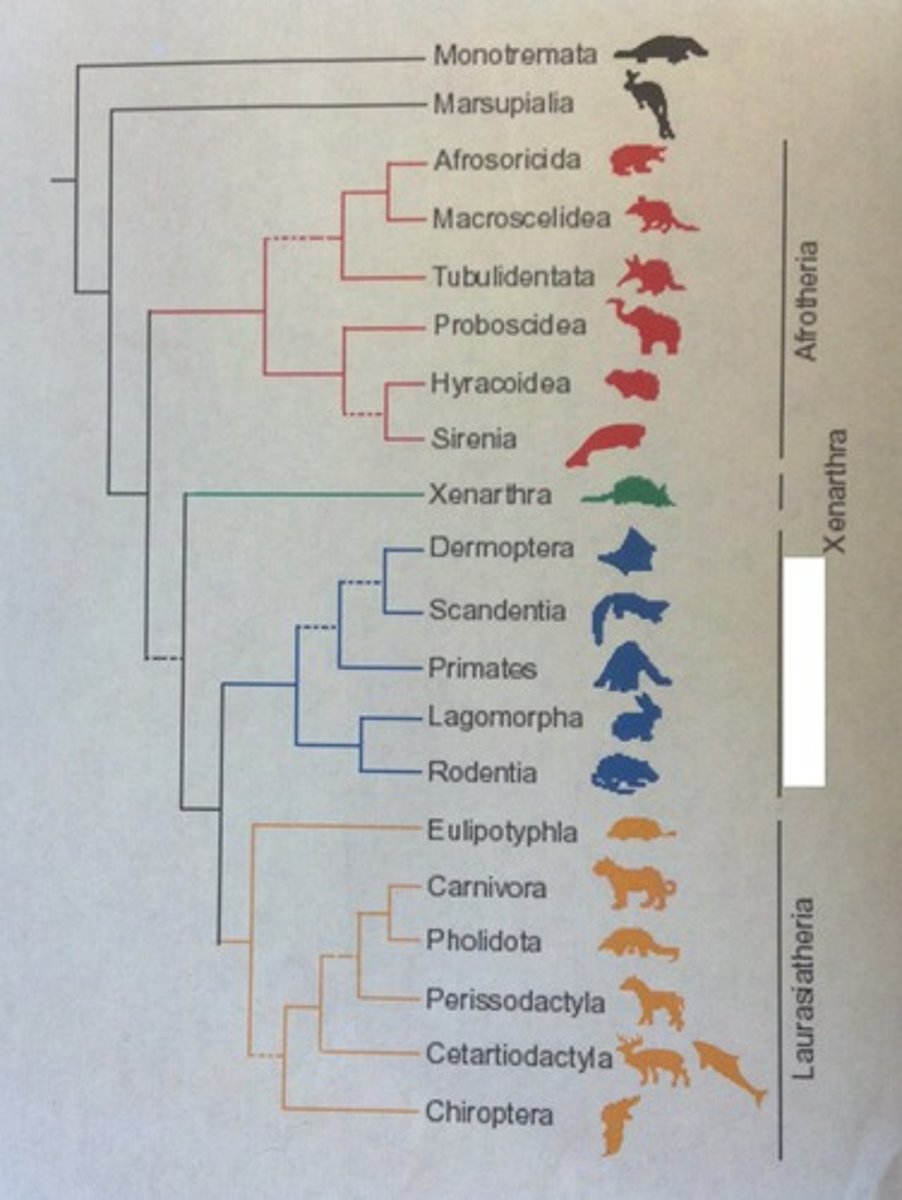
Example of Lagomorpha
rabbit, hares

Example of Rodentia
rats, hamsters, beavers

Example of Scandentia
Treeshrews

Example of dermoptera
Flying Lemurs

Are plesiadapiformes true primates?
No, While plesiadapiformes share a common ancestry with true primates and exhibit some primate-like traits, they are not classified as true primates themselves. Instead, they represent an important evolutionary step towards the development of modern primates.

Provide traits distinguishing plesiadapiformes and prosimians
Plesiadapiforms lack the postorbital bar, a bony structure around the eye socket, which is a characteristic feature of true primates. They also lack the fused mandible and unfused lower leg bones common in primates, and their big toe is not fully opposable like in primates.
Arboreal Hypothesis
hypothesis for the origin of primate adaptation that focuses on the value of grasping hands and stereoscopic vision for life in the trees
Visual Predation Hypothesis
the proposition that unique primate traits arose as adaptations to preying on insects and on small animals
Angiosperm Radiation Hypothesis
The proposition that certain primate traits, such as visual acuity, occurred in response to the availability of fruit and flowers following the spread of angiosperms.
What is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM)?
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) was a period of rapid and significant global warming that occurred around 56 million years ago.
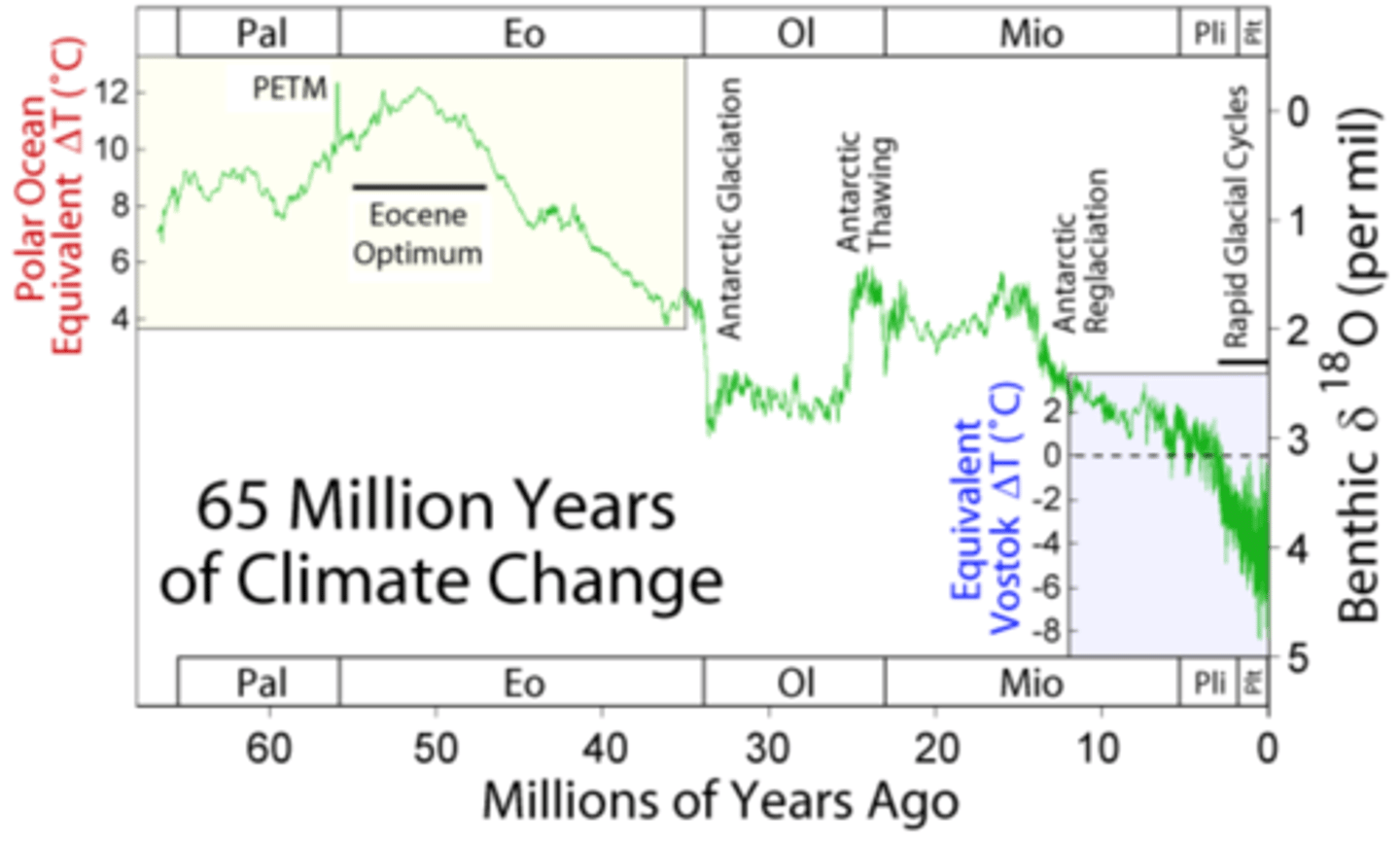
What effect did the PETM have on mammalian fossil records?
Fossils from this period provide insights into the adaptations of mammals to warmer climates, such as getting smaller, including changes in dental morphology and limb structure that reflect dietary shifts and habitat use.
How is genus Cantius represented in the fossil record?
The fossil genus Cantius is well-represented in the North American early Eocene fossil record, particularly in the Bighorn Basin of Wyoming. It is considered an early adapiform primate, a lineage that includes both modern-day lemurs and other extinct primates. Cantius is particularly notable for providing a good example of gradual evolution in the fossil record, with a lineage from Cantius to the genus Notharctus documented through sequential fossil discoveries.
When did genus Cantius go extinct?
The genus Cantius went extinct during the middle Eocene Epoch, which occurred between 55 and 34 million years ago.
Where have fossils of Genus Cantius been found?
Fossils of the genus Cantius have been found in North America, particularly in the Great Divide Basin of Southwest Wyoming, and in Europe.
How is genus Teilhardina represented in the fossil record?
The fossil genus Teilhardina is represented in the fossil record as one of the oldest known omomyiform primates, appearing in the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) around 56 million years ago. It is found in Asia, Europe, and North America, making it the only primate genus known to have inhabited all three Holarctic continents prior to Homo.

When did Genus Teilhardina go extinct?
The genus Teilhardina, a group of extinct omomyid primates, went extinct during the Early Eocene epoch, roughly 47 million years ago.
Where have fossils of genus Teilhardina been found?
Fossils of the primate genus Teilhardina have been found in several regions, including Asia, Europe, and North America. Specifically, they have been discovered in China, Belgium, France, and the USA (including states like Wyoming and Mississippi).
In which superfamily is Cantius assigned?
The genus Cantius is assigned to the superfamily Adapoidea
In which superfamily is Teilhardina assigned?
The genus Teilhardina is assigned to the superfamily Omomyoidea.
What is the relationship between early anthropoids?
Unresolved
What is the Qatari Formation in the Fayum Oasis
Currently a desert landscape was one a jungle and is home to many anthropoids fossils from the Eocene and Olicene
Adipum (Parapithicdae)
Old world anthropoid with 3 Premolars
Small Brain
Arboreal Leaping
Aegyptothicus (Prophiltropcidea)
Old world anthropid with 2 premolars
Very small brain
Large frugivore
Superfamily: Proconsuloidea
Has BOTH monkey and ape features
Generalized Arboreal Quadruped w/ monkey like limbs
Y-5 molars
Y-5 Molars
A primitive anthropoid trait
Hylobatidae
gibbons and siamangs
Yuanmopithicus Xiaoyaun
Yunnan China
Consist of teeth and partial jaw
What is the biggest taxon of primates?
Gigantapithicus Blacki
Dryopithicids
-Early Miocene apes found in various locations in Europe.
-France and Spain.
-Unique locomotion
-Flexinle spine
Sivapithecus
A genus of Miocene sivapithecids, proposed as ancestral to orangutan
-Cranillaru similar
-Long narrow midface
Concave facial profile
Gigantapithecus
G Gigantus
G Blacki
Extant the late Miocene and Pleistocene era
Fossil record is teeth and jaws
Choropithecus (Abysarrus)
- gorilla‐like (teeth and diet)
- Probably ancestor to modern gorillas, putting the gorilla vs chimp/human line split about 8‐9
MYA, consistent with molecular data
- Interestingly, in 2016 the sole fossil (teeth) was re‐dated to 8 MYA from previous dating of 10
MYA, which conflicted with the molecular estimate of this split and with the idea that Ouranopithecus was the first ape back from Europe.
Tribes: Danini
Extant 500,000 found in Kapthurin Formation, Kenya
Femur from Uganda
When did old world monkeys first appear?
The Early Miocene
When did the first major radiation for old world monkeys happen
The late Miocene to the pliestocene
Do old wild monkeys have more extinct or extant taxa?
Extant
How are extant taxa of old world monkeys similar to extinct taxa?
Similar but larger
Family Victoriapithecus
Provide a idea of variant between Old world monkeys
Family Cercopithecidae
Family of old world monkeys
fossil macaques
Widespread in Europe Africa and Asia
Similar to living Macqus
Fossil: Non Macques
Primarily from the Pliestcene
Pretty similar to extant genera
Fossil Colobus
Many are not like extant genera
Broader distribution
Genetic diversity in adaptations
How did plathrynni get to South America
Vegetation rafts
How did the vegetation rafts move?
Sea currents
Are African anthropoids and fossils playrhine are similar?
Yes
Fossil Platyrrhines
-Branisella from Late Oligocene (26 Ma) of Bolivia, oldest new world monkey
Monkey beds in La Venta
The salla beds in Bolivia
Ex. Cebupithd (Pithecidae)
Fossil lemurs are split into which groups?
Megaladapines (Koala Lemurs)
Palaeopropithecines (Sloth Lemurs)
Archaeolemurines (Monkey Lemurs)
Megaladapines
Koala Lemurs
Vertical Clinger, Climber
Foliovores
Palaeopropithecines
Sloth Lemurs
Suspensory Behavior
Foliovore Indriids
Archaeolemurines
Monkey Lemurs
Mixed Locomotion
Mixed Diet