Bio 20A Final Study Guide
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What fraction of the offspring of BbDdgg and BbDdGg parents will have the same phenotype as the first parent?
- 3/4
- 9/16
- 3/16
- 9/64
- 1/2
- 9/32
9/32
This question concerns three linked genes. Bubba's genotype is Bb Dd Ee . His parents' genotypes were bbDDEE and BBddee. In the absence of recombination, Bubba is capable of producing which of the following gametes?
- bDE and Bde
- BDe and bdE
- bDe and BdE
- BDE, BdE, bDE, BDe, bdE, Bde, bDe, bde
- BB, bb, DD, dd, EE and ee
- Bb, Dd and Ee
bDE and Bde
Independent assortment occurs during (check all that apply):
-anaphase of meiosis II
-anaphase of meiosis I
-anaphase of mitosis
-metaphase of mitosis
-metaphase of meiosis II
-metaphase of meiosis I
metaphase of meiosis I
DNA wrapped around an octamer of histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 is a _____________
nucleosome
Match the terms with their definitions.
Terms:
-Centromere
-Chromatin
-Chromatid
-Sister chromatids
Def:
-a generic term that is used to refer to DNA plus associated proteins
-a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
-the region of a chromosome at which the kinetochore assembles
-a highly condensed pair of replicated chromosomes
Centromere-the region of a chromosome at which the kinetochore assembles
Chromatin-a generic term that is used to refer to DNA plus associated proteins
Chromatid-a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
Sister chromatids-a highly condensed pair of replicated chromosomes
DNA replication occurs during:
-S phase
-G0
-M phase
-prophase
-G1
-G2
S phase
Match the terms with the most accurate definitions
-Chromosome
-Kinetochore
-Homologous chromosomes
-a pair of chromosomes in diploid cells that contain the same genes, but the alleles may be different
-an entire DNA double helix plus associated proteins
-A complex of proteins assembled at the centromere to which spindle microtubules attach
Chromosome-an entire DNA double helix plus associated proteins
Kinetochore-A complex of proteins assembled at the centromere to which spindle microtubules attach
Homologous chromosomes-a pair of chromosomes in diploid cells that contain the same genes, but the alleles may be different
When a plant with light blue flowers is self-crossed, it has 16 progeny with light blue flowers and 5 progeny with white flowers. This is probably an example of:
-polygenic inheritance
-environmental effects
-complete dominance
-crossing over
-incomplete dominance
complete dominance
Different, unlinked autosomal genes control fur color and eye color in bears. The brown allele of the fur color gene is dominant to the blonde allele. The black allele of the eye color gene is dominant to the hazel allele. Two bears - Bruno and Ursula - are heterozygous for both the fur and eye color genes. What fraction of Bruno and Hazel's cubs will have brown fur and hazel eyes?
-9/16
-all of them will have brown fur and hazel eyes
-1/2
-1/4
-1/16
-3/4
-3/16
3/16
What fraction of the offspring of AaBbCc and AaBbCc parents will have the genotype AaBBCc?
- 3/4
- 3/16
- 9/16
- 1/8
- 1/2
- 1/4
- 1/16
1/16
Homologous chromosomes are separated during ___________ (check all that apply)
-anaphase of meiosis I
-telophase of meiosis II
-anaphase of meiosis II
-anaphase of mitosis
-prophase of meiosis I
anaphase of meiosis I
Meiosis II produces:
-diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
-haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
-somatic cells
haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
Match the genetic disease with the corresponding mutation:
-Hemophilia A
-Tay Sachs Disease
-Sickle Cell Disease
-Cystic Fibrosis
-mutation in gene encoding ß globin protein
-mutation in a gene encoding a lysosomal hydrolase
-mutation in gene encoding Factor VIII
-mutation in a gene encoding a chloride transport protein
Hemophilia A-mutation in gene encoding Factor VIII
Tay Sachs Disease-mutation in a gene encoding a lysosomal hydrolase
Sickle Cell Disease-mutation in gene encoding ß globin protein
Cystic Fibrosis-mutation in a gene encoding a chloride transport protein
During mitosis, chromosomes begin to condense during
prometaphase:
-telophase
-prophase
-anaphase
-cytokinesis
-metaphase
prophase
Mendel's dihybrid crosses led him to propose:
-that genes encode proteins
-the principle of independent assortment
-the principle of incomplete dominance
-the principle of segregation
-that DNA replication is semi-conservative
the principle of independent assortment
Which of the following are possible interpretations of a genetic test for BRCA1 and 2 mutations? Check all that apply
-The patient will definitely develop breast or ovarian cancer
-The patient will not develop breast or ovarian cancer
-The patient may not have an increased risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer
-The patient has an increased risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer
-The patient may not have an increased risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer
-The patient has an increased risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer
Down syndrome can result from which of the following? (check all that apply)
-nondisjunction during meiosis II
-a mutation in a chloride transport protein
-nondisjunction during meiosis I
-a mutation in a DNA repair enzyme
-a mutation in a lysosomal hydrolase
-nondisjunction during meiosis II
-nondisjunction during meiosis I
Place the following events of meiosis in the order in which they occur.
Earlier
Segregation of alleles
Independent Assortment
DNA replication
Separation of sister chromatids
Recombination
Later
-DNA replication
-Recombination
-Independent Assortment
-Segregation of alleles
-Separation of sister chromatids
Sister chromatids are separated during ___________ (check all that apply)
-anaphase of meiosis II
-binary fission
-anaphase of meiosis I
-anaphase of mitosis
-anaphase of meiosis II
-anaphase of mitosis
Meiosis I produces:
-Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-Diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
-Diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-Gametes
-Haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
Match each of the following genetic disorders with the appropriate category
-Sickle Cell Disease
-Huntington Disease
-Down Syndrome
-Hemophilia A
-Chromosome disorder
-Autosomal dominant disorder
-Autosomal recessive disorder
-X-linked recessive disorder
Sickle Cell Disease-Autosomal recessive disorder
Huntington Disease-Autosomal dominant disorder
Down Syndrome-Chromosome disorder
Hemophilia A-X-linked recessive disorder
A diploid cell in G1 of the cell cycle has 32 DNA double helices. How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present in the organism from which this cell was obtained?
IMPORTANT NOTE: your answer must be in the form of only a number, not a word, phrase or explanation. For example, 10 would be an appropriate answer, but ten, 10 chromosomes, 10 homologous chromosomes, 10 pairs, or ten pairs would not. No credit will be given for any answers that are not in the proper format.
16
This question deals with a human genetic disease caused by an X-linked recessive mutation. Jack and Jill are both healthy. Both Jill's father and Jack's father had the disease but their mothers were healthy. What is the probability that one of Jack and Jill's daughters will have the disease?
0
1
1/4
1/2
1/16
3/4
0
E. coli and other prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually via:
-meiosis
-either mitosis or meiosis
-binary fission
-mitosis
binary fission
During mitosis, spindle microtubules attach to the ________ of chromosomes.
-nucleosomes
-axonemes
-centrosomes
-telomeres
-kinetochores
kinetochores
Cell cycle checkpoints ensure that:
-sister chromatids are properly aligned on the metaphase plate prior to anaphase
-all of the above
-DNA has been replicated prior to division
-DNA damage is repaired prior to DNA replication
-a cell has grown sufficiently prior to division
all of the above
Which of the following kinds of cells divide by binary fission?
-plant cells
-human cells
-bacteria
bacteria
What would happen when a cell undergoing mitosis is fused with a cell in G1?
-Both cells would enter interphase
-The G1 cell would immediately enter mitosis
-The M cell would enter G1, the G1 cell would enter mitosis
-The M cell would immediately enter G1
-Both cells would enter S phase
-The G1 cell would immediately enter mitosis
Match each of the following to the corresponding stage of the cell cycle:
Stages:
-S phase
-Prophase
-anaphase
-telophase
-metaphase
-prometaphase
-Cytokinesis
-Chromosomes begin to condense
-nuclear envelope reforms
-DNA replication
-interphase microtubules break down
-S phase
-the cell splits in two
-sister chromatids have been lined up at the metaphase plate
-Chromatids pulled toward opposite poles of the cell
-mitotic spindle breaks down
-microtubules attach to the kinetochore
S phase-DNA replication
Prophase-Chromosomes begin to condense; interphase microtubules break down
anaphase- S phase; Chromatids pulled toward opposite poles of the cell
telophase-mitotic spindle breaks down; nuclear envelope reforms
metaphase-sister chromatids have been lined up at the metaphase plate
prometaphase-microtubules attach to the kinetochore
Cytokinesis-the cell splits in two
Interphase includes which of the following stages of the cell cycle? Check all that apply
-S
-M
-G1
-G2
-S
-G1
-G2
The term "chromatid" refers to:
-DNA wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins
-DNA and associated proteins
-the ends of a chromosome
-the complex of proteins that assembles at the centromere during mitosis
-a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
a highly condensed chromosome that is visible during mitosis or meiosis
A eukaryotic cell in G1 has 10 DNA double helices. If this cell underwent mitosis, how many DNA molecules (i.e. DNA double helices) would be present in the cell during prophase?
-40
-none of the above
-20
-10
-5
20
A cell that does not divide for an extended period is in _______
-G0
-S
-G2
-big trouble
-G1
G0
The nucleosome:
-is the fundamental unit of chromatin structure
-is the ribosome factory of eukaryotic cells
-is the interior of the nucleus
-none of the above
-is a microtubule organizing center
is the fundamental unit of chromatin structure
A mutation prevents the destruction of cyclin during the cell cycle. The most likely effect of this mutation would be:
-none of the above
-the cell would not exit mitosis
-rapid, unregulated cell division
-cancer
-all of the above
the cell would not exit mitosis
Homologous chromosomes are separated during ___________ (check all that apply)
anaphase of meiosis II
anaphase of meiosis I
anaphase of mitosis
telophase of meiosis II
prophase of meiosis I
anaphase of meiosis I
Which of the statements about homologous chromosomes are true? Check all that apply
They carry the same genes in the same order
The versions (alleles) of the genes they carry may be different
Homologous chromosomes are separated during anaphase of mitosis
Sister chromatids are homologous
They have identical DNA sequences
-They carry the same genes in the same order
-The versions (alleles) of the genes they carry may be different
Meiosis I produces:
Diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
Diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
Haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
gametes
Haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
Sources of genetic variation for organisms that reproduce sexually include:
independent assortment of chromosomes
random fusion of gametes
recombination
mutation
all of the above
all of the above
Which of the following statements are false?
-Multicellular organisms are always composed of diploid cells
-Meiosis leads to the production of haploid gametes
-The fusion of haploid gametes results in the formation of a diploid cell
-Some haploid cells can reproduce via mitosis.
-none of the above
Multicellular organisms are always composed of diploid cells
Meiosis II produces:
-haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
-haploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-diploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
-diploid cells with replicated chromosomes
-somatic cells
haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
Sister chromatids are separated during ___________ (check all that apply)
-anaphase of mitosis
-anaphase of meiosis II
-anaphase of meiosis I
-binary fission
-anaphase of mitosis
-anaphase of meiosis II
Independent assortment occurs during (check all that apply):
-metaphase of meiosis I
-metaphase of meiosis II
-metaphase of mitosis
-anaphase of meiosis I
-anaphase of meiosis II
-anaphase of mitosis
metaphase of meiosis I
A diploid cell in G1 has 5 pairs of homologous chromosomes. If this cell underwent meiosis, how many DNA molecules (i.e.DNA double helices) would be present in each gamete after the completion of meiosis?
- 5
- 10
- 20
- 40
- none of the above
5
You flip a coin three times and it comes up heads each time. A friend flips a coin 3 times and it comes up tails each time. What is the probability that both you and your friend will both come up tails on the next toss?
- 1
- 1/2
- 3/4
- 1/4
- 0
1/4
Consider the following cross:
P: AABBCC x aabbcc
F1: AaBbCc
Genes A, B and C are linked. In the absence of recombination, what gametes can be produced by the F1 progeny? Hint: draw out the chromosomes of the parents and their progeny before answering this question.
-ABC, abc, ABc, abC, AbC, aBc, aBC and Abc
-not enough information to tell
-ABC and abc
-AABBCC and aabbcc
-AAA, BBB, CCC, aaa, bbb and ccc
ABC and abc
The segregation of alleles occurs during which of the following? Check all that apply
- anaphase of mitosis
- anaphase of meiosis I
- anaphase of meiosis II
- telophase of meiosis II
- metaphase of meiosis I
anaphase of meiosis I
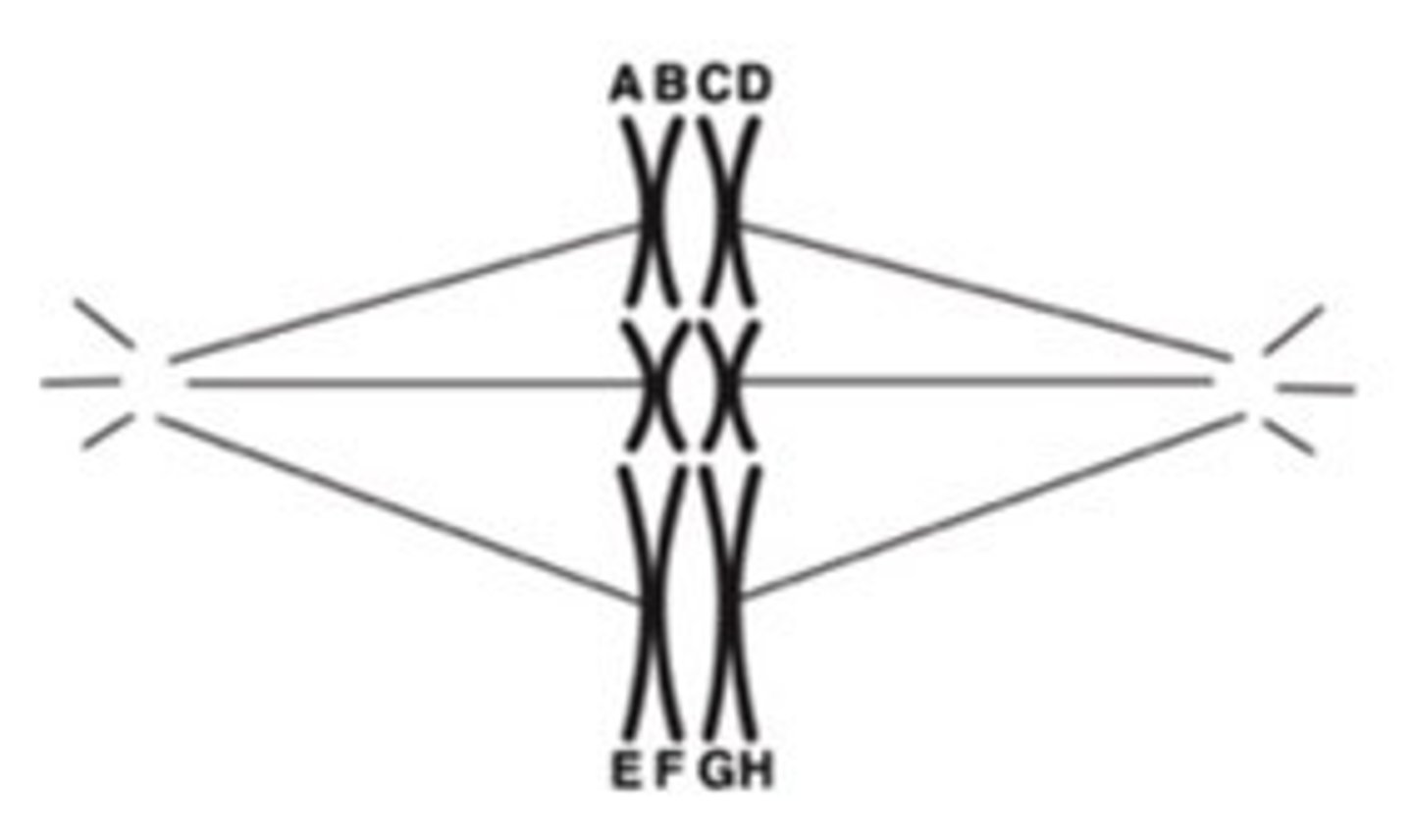
Which following statements about the diagram shown below are true? Check all that apply. Note that the letters are used to mark the chromosomes; they do not refer to alleles/genes carried on the chromosomes
-A and B are sister chromatids
-The image is of a cell in metaphase of meiosis II
-The image is of a cell in metaphase of meiosis
-The image is of a cell in metaphase I of meiosis I
-A and B are identical; A and D are homologous
-A and E are different; E and F are identical.
-A and B are homologous; A and D are identical
-A and B are sister chromatids
-The image is of a cell in metaphase I of meiosis I
-A and B are identical; A and D are homologous
-A and E are different; E and F are identical.
Which of the following could account for incomplete dominance?
sex-linkage
polygenic inheritance
environmental effects
linkage
the product of a gene is present in limited quantities
the product of a gene is present in limited quantities
In a cross AaBbCcDd x AaBbCcDd, what is the probability that one of the offspring will have the genotype aaBBCCDd? Assume the genes are unlinked.
1/32
1/16
1/128
1
1/64
1/128
Match each of the following with the correct definition:
-dominant
-autosome
-genotype
-phenotype
-the appearance of an organism
-a chromosome other than a sex chromosome
-the allele that determines the appearance of an organism
-the genetic makeup of an organism
dominant-the allele that determines the appearance of an organism
autosome-a chromosome other than a sex chromosome
genotype-the genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype-the appearance of an organism
A male mouse with brown fur is crossed to a female mouse with white fur. All the male progeny have white fur while all the female progeny have brown fur. What is the most likely explanation for these data? Assume that the data are highly reproducible and large numbers of progeny were examined.
-The brown allele is dominant
-The brown allele is recessive
-The coat color gene is X-linked
-The coat color gene is autosomal
-The female parent is homozygous for the white allele
-The brown allele is dominant
-The coat color gene is X-linked
-The female parent is homozygous for the white allele
The purple (P) allele of a flower color gene is dominant to the white (p) allele. If two heterozygous plants are crossed, ____ % of their progeny will have purple flowers
75%
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). Of 32 progeny of the cross BbTt x BbTt, approximately how many will have brown fur and short tails? (assume the genes are not linked)
- 16
- 18
- 0
- 32
- 6
6
Given the parents AABBCc x AabbCc, what proportion of the progeny will phenotypically resemble the first parent (assuming the genes involved are on different chromosomes)?
- 1/4
- 9/16
- 3/4
- all of them
- 3/16
- 0
- 1/2
3/4
Two parents are healthy carriers of the mutations that cause sickle-cell disease and cystic fibrosis. What fraction of their children will have sickle cell disease and cystic fibrosis. The genes that cause the two diseases are unlinked.
- 1/16
- 3/4
- 3/16
- 1/4
- 9/16
- 1/2
1/16
A healthy man and a healthy woman have a son. The woman's father had hemophilia. What is the probability that their son will also have hemophilia?
- 75%
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%
50%
Which of the following genetic diseases are caused by an autosomal recessive mutation? Check all that apply
Huntington's Disease
sickle cell disease
Tay-Sachs Disease
Hemophilia A
sickle cell disease
Tay-Sachs Disease
Mutations in a gene encoding a chloride transport protein cause:
- Cystic fibrosis
- Tay Sachs disease
- Sickle cell disease
- Hemophilia
- Huntington's disease
- Cystic fibrosis
________ is a chromosome disorder that can be caused by meiotic nondisjunction.
Down Syndrome
Which of the following statements about genetic testing for BRCA1 and 2 mutations are true? (check all that apply)
-it will reveal if a woman will definitely develop breast or ovarian cancer
-it can rule out the possibility that a woman will develop breast or ovarian cancer
-is recommended for individuals who belong to certain ethnic groups or have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer
-it may reveal if a woman has an elevated risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer
-is recommended for individuals who belong to certain ethnic groups or have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer
-it may reveal if a woman has an elevated risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer