(draft) BIOL Lecture 4 Microtubule motor proteins Intermediate Filaments
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Describe the role of kinesins and dyneins in cellular transport.
Kinesins and dyneins are microtubule-based motor proteins that transport various types of cargo, along microtubules powered by ATP hydrolysis.
Kinesins typically move cargo toward the (+) end (anterograde).
Dyneins typically transport cargo towards the (-) end (retrograde).
Examples of cargo include
membrane-bound vesicles
proteins
organelles
What direction do kinesins typically move cargo?
Towards the (+) end (anterograde)
What direction do dyneins typically move cargo?
Toward the (-) end (retrograde)
What are some exaples of cargo microtubule-based motor protiens transport.
Membrane bound vesicles
Proteins
Organells
What is a dimer?
A molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together.
Describe the structure of kinesin-1.
Kinesin-1 is a dimer made up of two heavy chains an associated light chains, with a total molecular weight of about 380,000 Da.
It contains a pair of globular N-terminal head domains, connected by a short flexible linker domain to a central stalk, an ends in a pair of small globular tail domains that assocuate with the light chains.
The neck region determines the direction of movement
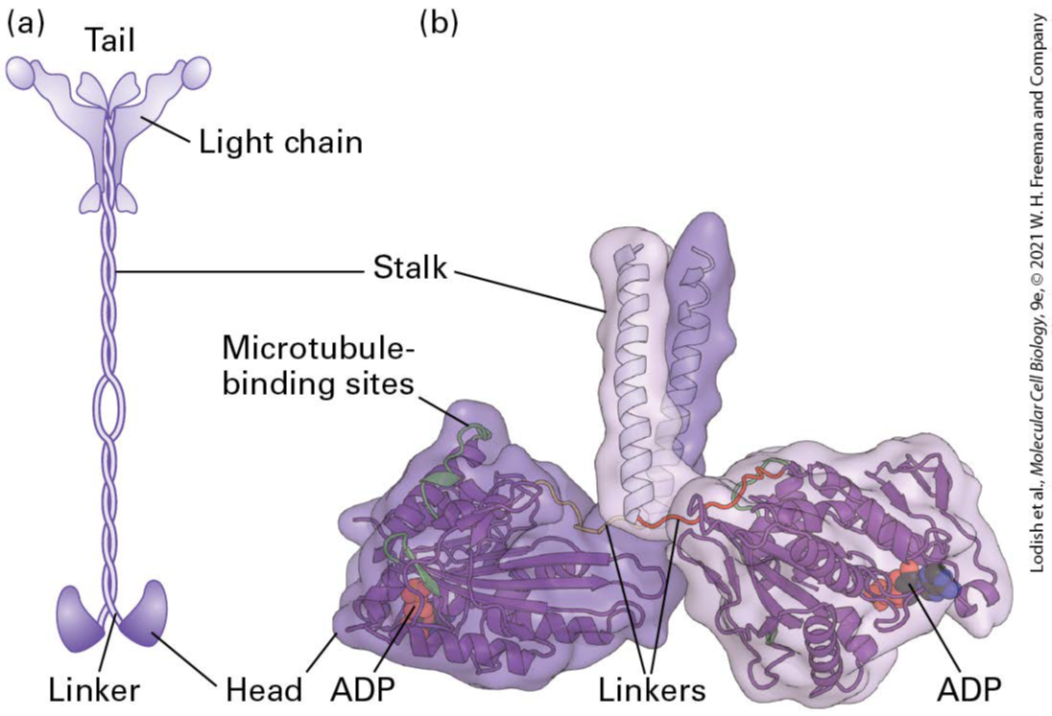
How does kinesin-1 move along the microtubule.
The kinesin family motor (or head domains) contains the ATP binding site and the microtubules-binding site of tthe motor.