Molecular Biology
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Define metabolism
The collection of enzyme catalyzed chemical reactions that occur in a living thing and require a solvent
Define cohesion
hydrogen bonds between polar water molecules cause them to cohere to each other
Explain cohesion in plants
Allows for transpiration in plants moving water against gravity from the roots up the xylem to the leaves
If a molecule evaporates at the leaf another is pulled up
Define adhesion
water molecules form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules
Explain adhesion in plants
Water adheres to cellulose in plants which prevents the water column from breaking and assists in transpiration
This is an example of capillary action
Define capillary action
The adhesion of water to the walls of a narrow tube, drawing the water upwards
State the solvent properties of water
Water dissolves polar molecules
This is necessary for metabolism
Enzymes catalyze reactions in aqueous solutions
Non polar substances are hydrophobic
Explain an example of a non-polar substance
Steroid hormones can diffuse through membranes because they are hydrophobic and not repelled by fatty acid tails of membranes
membrane proteins have hydrophobic regions allowing them to contact the hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails
Explain adaptations for the thermal properties of water
water has a high thermal conductivity so warm blooded animals that live in water need a layer of fat to prevent heat loss
high specific heat capacity
high viscosity selects for animals with streamlined bodies
high buoyancy allows air breathing animals to remain near surface
State the chemical properties of carbon
Forms four covalent bonds leading to a diversity of possible stable compounds
Can form single or double bonds allowing for long chains or rings
Monomer
The individual units of a polymer
Polymer
A long chain of monomer units covalently bonded
Explain anabolic reactions
Turn monomers into polymers by linking them together through condensation synthesis
Require energy in the form of ATP
Produce water as a byproduct
What is the polymer for a monosaccharide + example
polysaccharide
Glucose links together to form glycogen
Outline catabolic reactions
digest polymers by turning them into monomers
Requires water
Requires energy
Describe glucose
Hexose monosaccharide
Alpha glucose has a hydrogen at the top of carbon 1
Beta glucose has the hydroxyl at the top of carbon 1
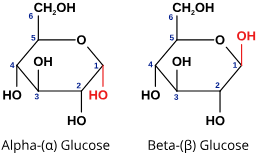
Outline the form and function of glucose as an example of a monosaccharide
glucose is polar covalent
Polar = soluble in water and easy to transport
Covalent bonds = stable but a lot of energy released when bonds are broken in cell respiration
What is an example of a pentose monosaccharide
DNA/ RNA
Describe the structure of starch
alpha glucose linked at carbons one and four
All glucoses oriented the same way
Curved chain
Amylose: unbranched helix
Amylopectin: branched globular shape due to additional links at carbons 1 and 6
Short term energy storage in plants
Describe the structure and function of glycogen
similar to amylopectin with more branching
Short term energy storage in animals
Stored in the liver
How are polysaccharides suited to storage
insoluble due to size
Linked with a bond called a glycosidic bond
They can be broken down into monosaccharides through hydrolysis
Describe the structure and function of cellulose
provides rigidity and strength in plant cell walls
B glucose linked at 1 and 4
Glucoses alternate
Unbranched chain
Chains can be grouped in bundles and linked with hydrogen bonds for more strength
Describe the hydrophobic properties of lipids
lipids include long carbon chains
Steroids found in animals are cholesterol based but they are still lipids
They are not very soluble
Outline the formation of triglycerides
three separate condensation reactions linked three fatty acid monomers to a glycerol
This forms one triglyceride and three waters
Stored as fate in adipose tissue used for long term energy storage and insulation
What is the structure of a phospholipid
The same as a triglyceride but with one phosphate group instead of a fatty acid group
What is the function of unsaturated fatty acids in membranes
In phospholipids: preventing phospholipids from packing as tightly allowing for membrane fluidity
Draw an amino acid
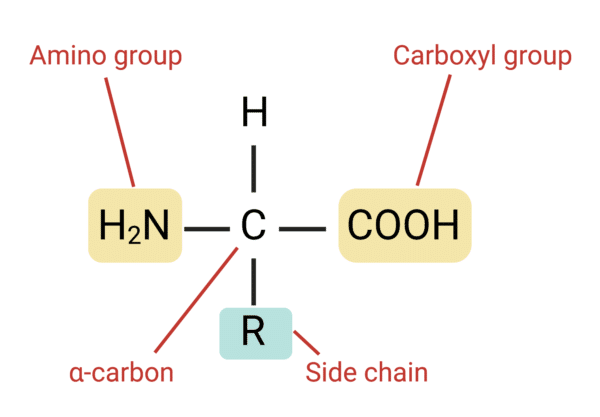
Explain the formation of an amino acid Chain (polypeptide)
two amino acids are linked by condensation synthesis producing a protein
Outline the different amino acids
there are 20 amino acids
Humans require all 20
About half of the amino acids are essential meaning they must be ingested and we cannot produce them
Explain the variety of proteins possible
every protein has a different sequence of amino acids
Because proteins can be any length there is an infinite variety of possible polypeptide chains
Outline the denaturation of proteins
changes in the 3d structure of a protein due to changes in the bonds holding its shape
Structure dictates function so changes in the structure alter or halt the function
High temps and extreme ph can cause denaturation
How do enzymes affect metabolic reactions
catalyse them
Unique enzymes exist for thousands of unique metabolic reactions
Reactions can be controlled by activating or deactivating enzymes
Contrast the activation energy of metabolic reactions
catabolic: exergonic release energy
Anabolic: endergonic require energy
The transition state of an enzyme catalyzed reaction has a lower energy than non enzyme catalyzed, lowering activation energy
Net energy absorbed or released is not changed
Define enzyme
A globular protein functioning as a biological catalyst speeding up metabolic exactions by lowering the activation energy
Explain active sites
the site on the surface of an enzyme to which a substrate binds and catalyses a chemical reaction
When a enzyme binds to substrate it is referred to as an enzyme-substrate complex
Diff enzyme for almost every substrate
Specificity of the enzyme is determined by the shape and chemical composition of the active site
Determined by the amino acids making up the enzyme
As the substrate approaches the active site the shape of the active site changes slightly to fit the shape of the substrate
Bonds of the substrate weaken and it changes shape too
This is the induced fit model explaining broad specificity
How does kinetic molecular theory relate to enzymes
molecular motion increases with increasing temperature
In order for an enzyme to catalyse it must collide with reactant molecules
Increased frequency of catalyst and reactant molecules leaves to an increase in enzyme activity up to the optimal temp where it is denatured
The catalyst may be immobilized in a membrane
What is an optimal pH
The pH at which the active site best fits the substrate (not denatured)
Explain the relationship between substrate concentration and activity
more substrate = more collisions = more product formed
Until the saturation point at which all of the active sites are occupied
State two ways to measure the rate of enzyme catalysed reactions
production of product per unit time
Reduction of reactant per unit time
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cell respiration
complementary processes
The products of photosynthesis are used for cellular respiration and vice versa
Photosynthesis is performed in choroplasts
Cellular respiration is performed in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells
What is atp
cells require energy in the form of atp
A nucleotide that can diffuse to any part of the cell and release energy
Every cell produces its own atp
State three functions atp is used for
Anabolic reactions like synthesizing polymers
Active transport using membrane pumps
Movement within a cell or as the entire cell
Relationship between adp and atp
energy from cell respiration attaches an inorganic phosphate to adp making atp
The high energy bond of atp is hydrolyzed then adp and phosphate are reformed and energy is released
What compounds can be used for cellular respiration
glucose/fatty acids or other organic compounds
Aerobic versus anaerobic respiration
aerobic: uses oxygen and make a lot of atp slowly
Anaerobic: does not involve oxygen and makes a little atp quickly
Outline anaerobic respiration
Glucose is converted to pyruvate in the cytoplasm producing a small amount of atp
If no oxygen is available the pyruvate remains in the cytoplasm and is converted into a waste product (lactate in humans)
Outline aerobic respiration
Glucose is converted to pyruvate in the cytoplasm producing a small amount of atp
if oxygen is available the pyruvate is absorbed into a mitochondrion and broken down into co2 and water producing a large amount of ATP
Higher yield of ATP per gram of glucose
Define photosynthesis
The process by which algae and some bacteria produce organic carbon compounds
Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy
What is photolysis
light energy is used to split water into oxygen gas and hydrogen used for carbon fixation
Photosynthetic pigments absorb light energy and convert it into atp
Energy from atp is used to fix carbon dioxide (turn it into organic molecules) by combining it with the hydrogen
What happens to the oxygen produced by photolysis
waste product
Diffuses out of the plant
All atmospheric oxygen is a result
Describe photosynthetic pigments
absorb light and convert it into chemical energy
Chlorophyll is green and the most common
Other pigments are called accessory pigments
Describe the visible light spectrum
em radiation of wavelength 400 to 700 nm
400 - 525 violet - blue
525 - 625 green - yellow
625 - 700 orange - red
Outline chlorophyll’s absorption
Greatest absorption of violet - blue
High absorption of red
Green to yellow not absorbed and reflected
Explain photoactivation
absorbed light energy excites electrons
Jump to higher energy level
This is photoactivation
Diff pigments are activated by diff wavelengths
What is an absorption spectrum
wavelengths or frequency of light absorbed by each pigment
What is an action spectrum
the rate of photosynthesis for each wavelength or frequency measured in o2 produced or co2 consumed
Strong correlation to pigment absorption peaks
Explain the relationship between co2 concentration and photosynthesis rate
Low levels = less carbon for fixation
Increase = increase in rate up to max
At the max another factor is usually limiting
Co2 is usually liming factor at atmospheric levels
Why is there a maximum in the relationship between light and rate of photosynthesis
chlorophyll cannot absorb any more light
Usually not a limiting factor
Why are co2 rich lab experiments not accurate for photosynthesis
higher co2 concentration is shown to lead to more photosynthesis in the lab
Not accurate in the field because high co2 = high temp which decreases rate of photosynthetic activity (denaturation)
Rf formula
distance moved by pigment/distance moved by solvent