Biochemistry flashcards - Grade 12 Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:56 AM on 5/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
intramolecular bonds
1. covalent bonds - 2 non metals sharing e- equally
2. ionic bonds - 1 atom loses e- and the other gains the e-
3. polar covalent bonds - sharing of e- less equally
type of intramolecular bond is distinguished by difference in electronegativity (∆EN):
covalent = ∆EN < 0.4 → share equally
ionic = ∆EN > 1.7 → atom w greater EN takes e- from atom w lesser EN, both become charged
polar covalent = ∆EN = 0.5-1.7
\
2
New cards
polar covalent bonds
* one atom has a stronger hold on shared e-
* one end of molecule gets slightly + charged, one end gets slightly - charged
δ- = stronger EN end gets - charge
δ+ = weaker EN end gets + charge
influences attraction & biological interaction
* one end of molecule gets slightly + charged, one end gets slightly - charged
δ- = stronger EN end gets - charge
δ+ = weaker EN end gets + charge
influences attraction & biological interaction
3
New cards
water is polar, has polar covalent bonds
e- spend more time near the O than the H, difference in charge btwn poles of the molecules
δ- = O
δ+ = H
due to its polarity, it forms H bonds w itself → a lot of H bonds = a lot of strength
δ- = O
δ+ = H
due to its polarity, it forms H bonds w itself → a lot of H bonds = a lot of strength
4
New cards
water forms bonds through
* H bonding w itself
* cohesion: water molecules are attracted to other water molecules
* adhesion: water is a polar molecule and thus attracts other polar molecules
* cohesion: water molecules are attracted to other water molecules
* adhesion: water is a polar molecule and thus attracts other polar molecules
5
New cards
intermolecular forces
1. London dispersion forces: v weak attraction btwn all molecules, even non polar ones. increase w molecule size
2. dipole dipole attraction: attractive force btwn 2 polar molecules
3. H bonding: special kind of dipole dipole attraction btwn 2 polar molecules w H bonded to N, O, F
6
New cards
carbon, the backbone of nearly every bio molecule except for water
* organic compound = compound containing C-H bonds and maybe other elements too such as N, O, etc.
* often found in organisms
* C-H is non polar bond → hydrocarbons are non polar but polarity can be achieved by adding other atoms called functional groups
* often found in organisms
* C-H is non polar bond → hydrocarbons are non polar but polarity can be achieved by adding other atoms called functional groups
7
New cards
functional groups (FG)
molecules interact w eo at specific regions of their molecules and classifies molecule types
after a rxn btwn 2 molecules’ functional groups, a linkage will be formed
after a rxn btwn 2 molecules’ functional groups, a linkage will be formed
8
New cards
alcohols
* FG: -OH \~ hydroxyl
* simplest = CH3OH
* simplest = CH3OH
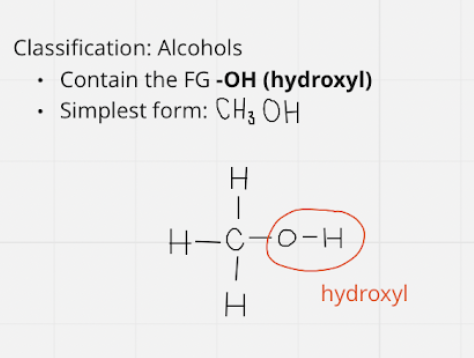
9
New cards
aldehydes
* end group of fg -CO \~ carbonyl
* simplest = HCOH
* simplest = HCOH
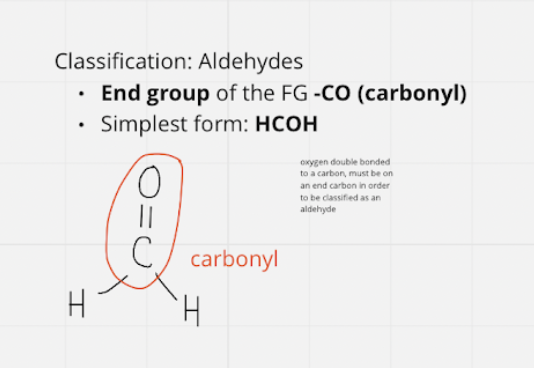
10
New cards
ketones
* middle fg -CO ; middle carbon
* simplest = CH3COCH3
* simplest = CH3COCH3
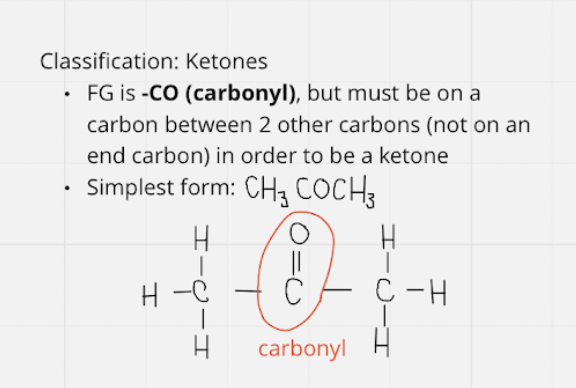
11
New cards
organic acids
* fg: -COOH \~ carboxyl; end group
* simplest = HCOOH
* simplest = HCOOH
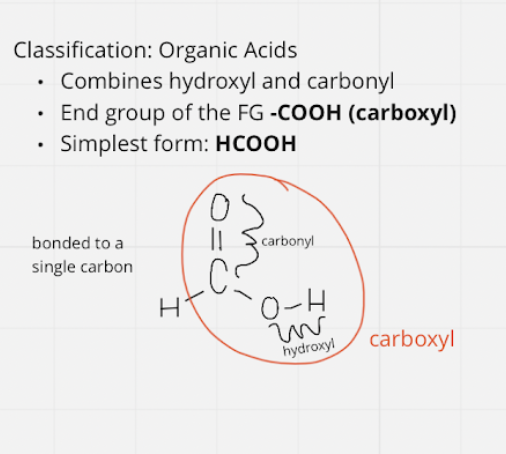
12
New cards
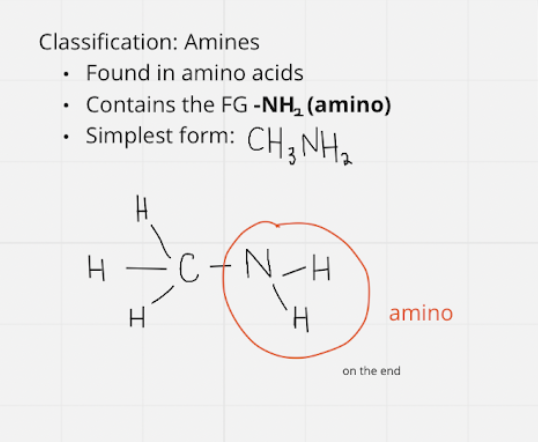
amine
* fg: -NH2 \~ amino
* simplest = CH3NH2
* simplest = CH3NH2
13
New cards
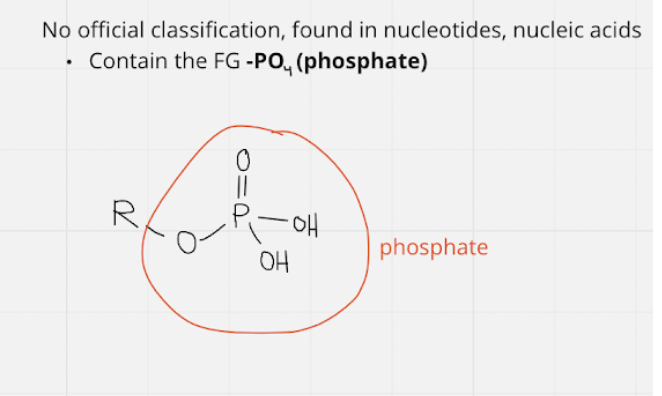
phosphate group
* fg: -PO4 \~ phosphate ; no official classification
14
New cards
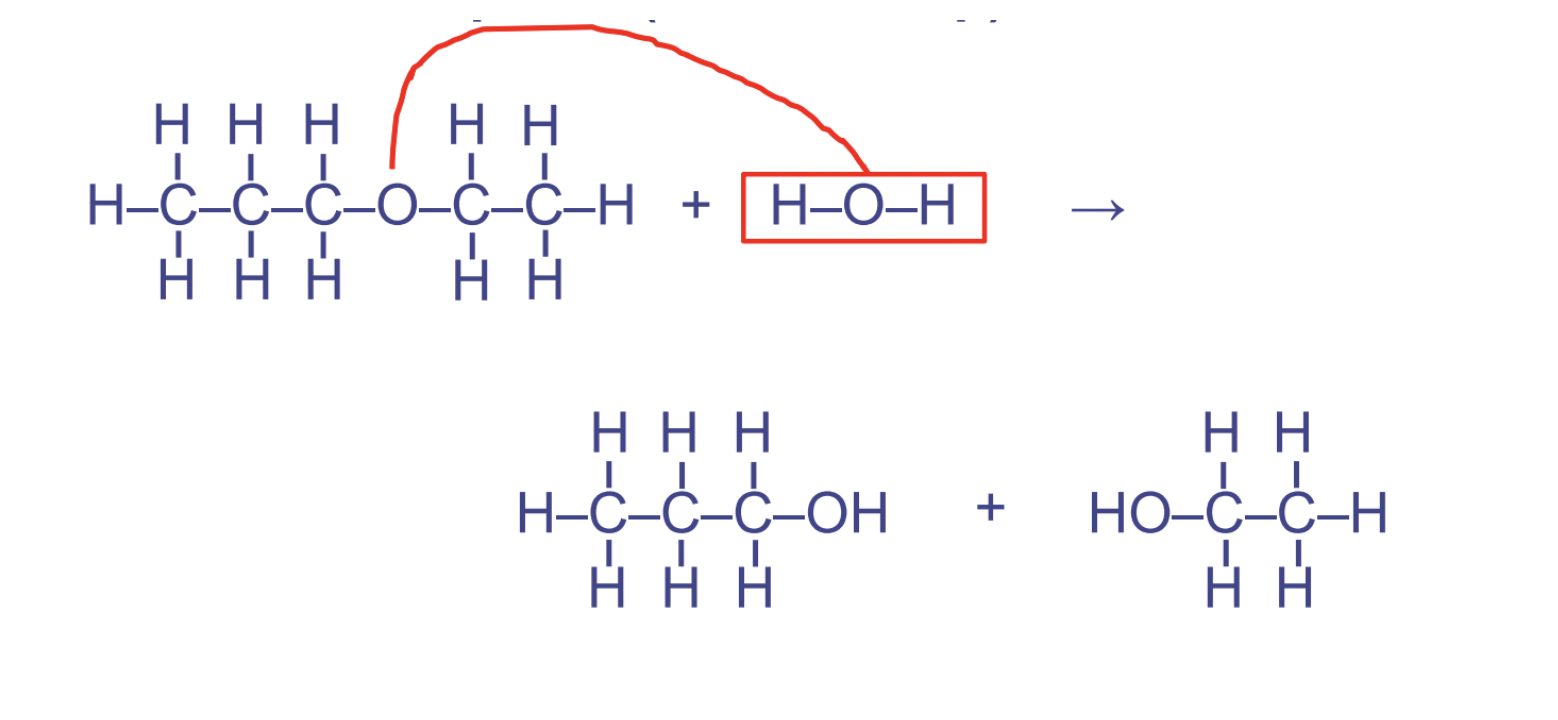
hydrolysis rxns
rupture, use of water to rupture/break down, catabolic, splits a larger molecule apart \~ water required and used up
15
New cards
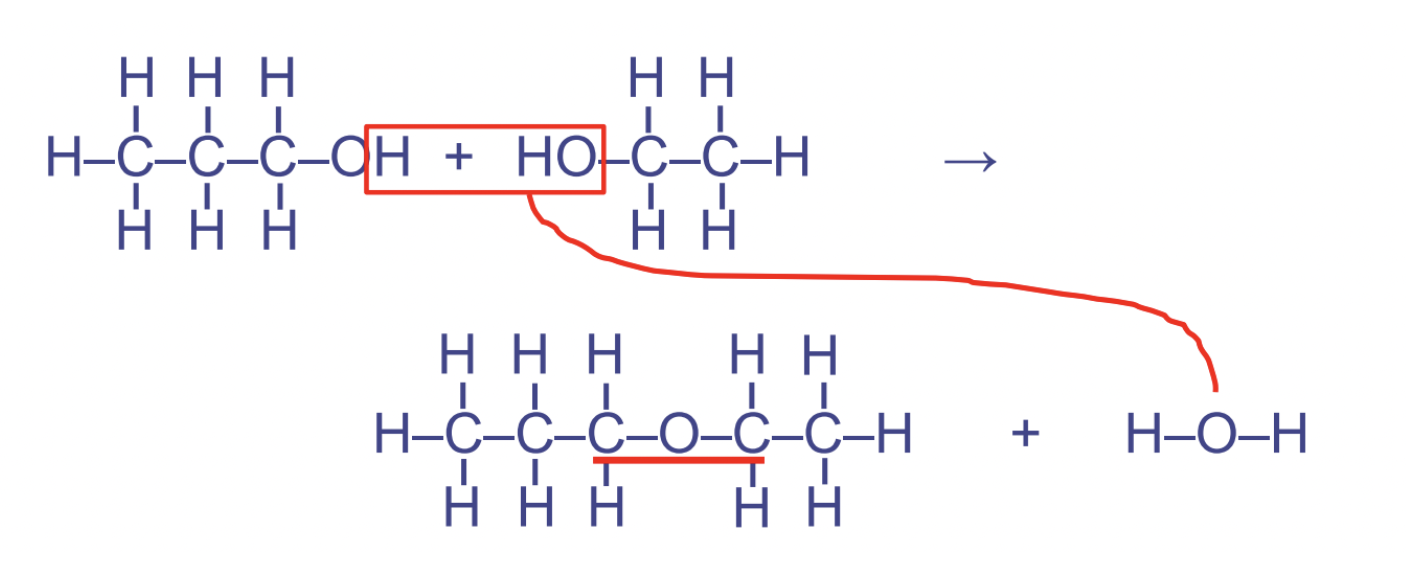
dehydration synthesis rxns
condenses smaller particles into larger ones. anabolic and builds up molecules \~ water is released as a product
16
New cards
ether linkages
* glycosidic link btw sugars when it occurs btwn sugar molecules
* btwn 2 hydroxyl groups
* used in carbohydrates
* pattern COC
* btwn 2 hydroxyl groups
* used in carbohydrates
* pattern COC
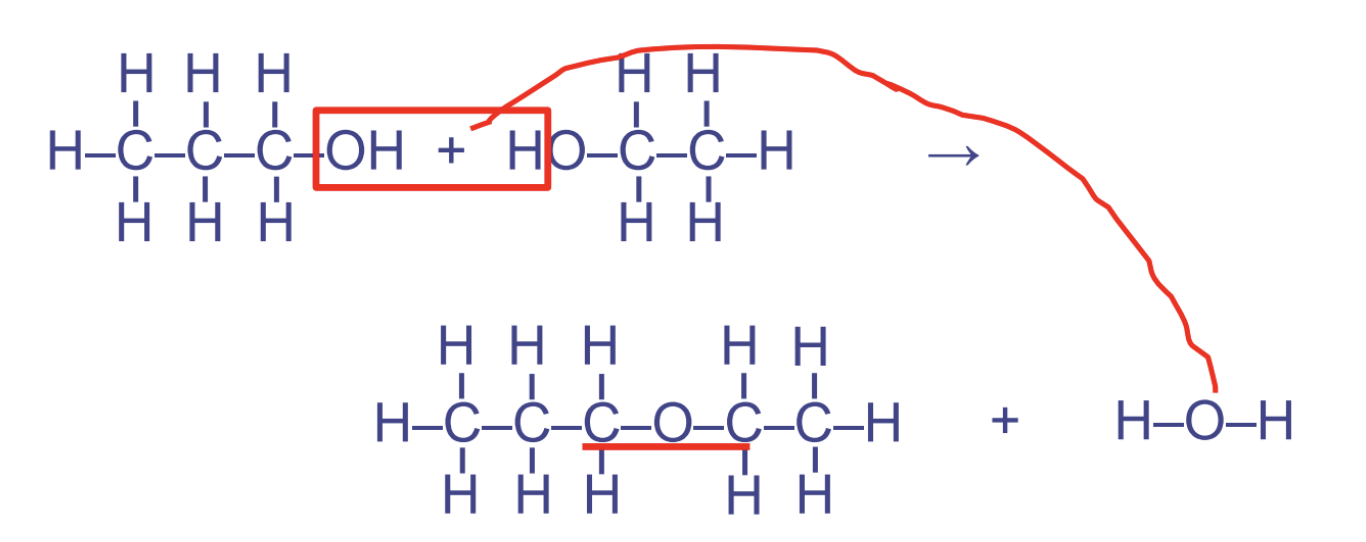
17
New cards
ester linkages
* btw hydroxyl and carboxyl
* used in triglycerides
* pattern OCO
* used in triglycerides
* pattern OCO
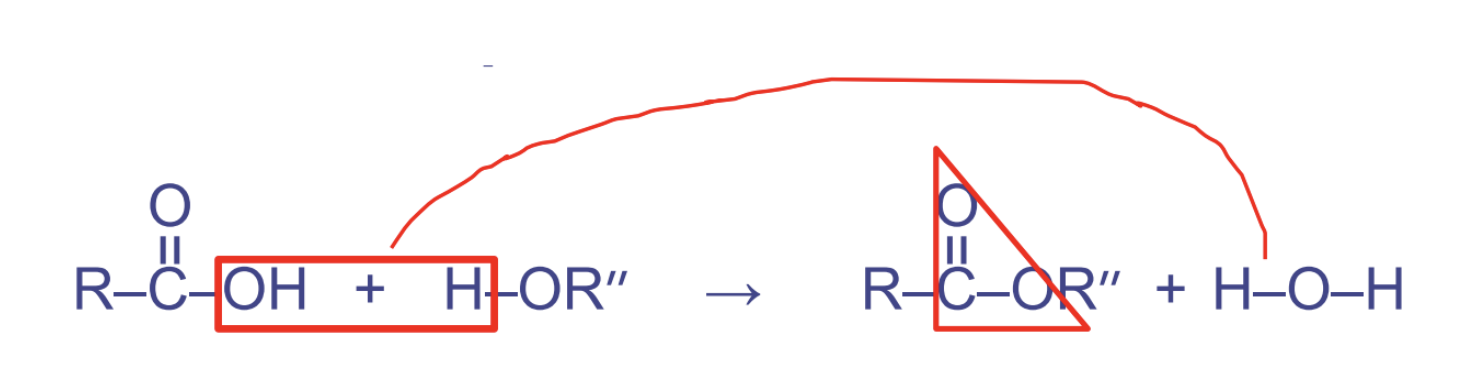
18
New cards
phosphate ester linkages
* btwn hydroxyl (1st) and phosphate (2nd)
* used in phospholipids and nucleic acid - instructs DNA and RNA
* pattern OPO
* used in phospholipids and nucleic acid - instructs DNA and RNA
* pattern OPO
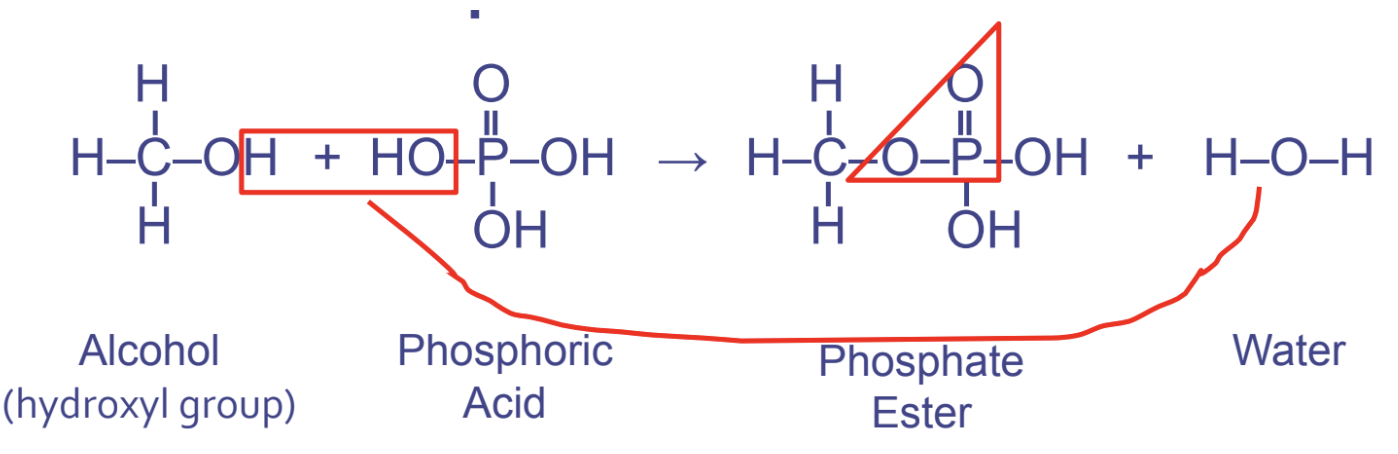
19
New cards
peptide linkages
* btwn carboxyl (1st) and amino (2nd)
* links amino acids together
* pattern OCNH
* links amino acids together
* pattern OCNH
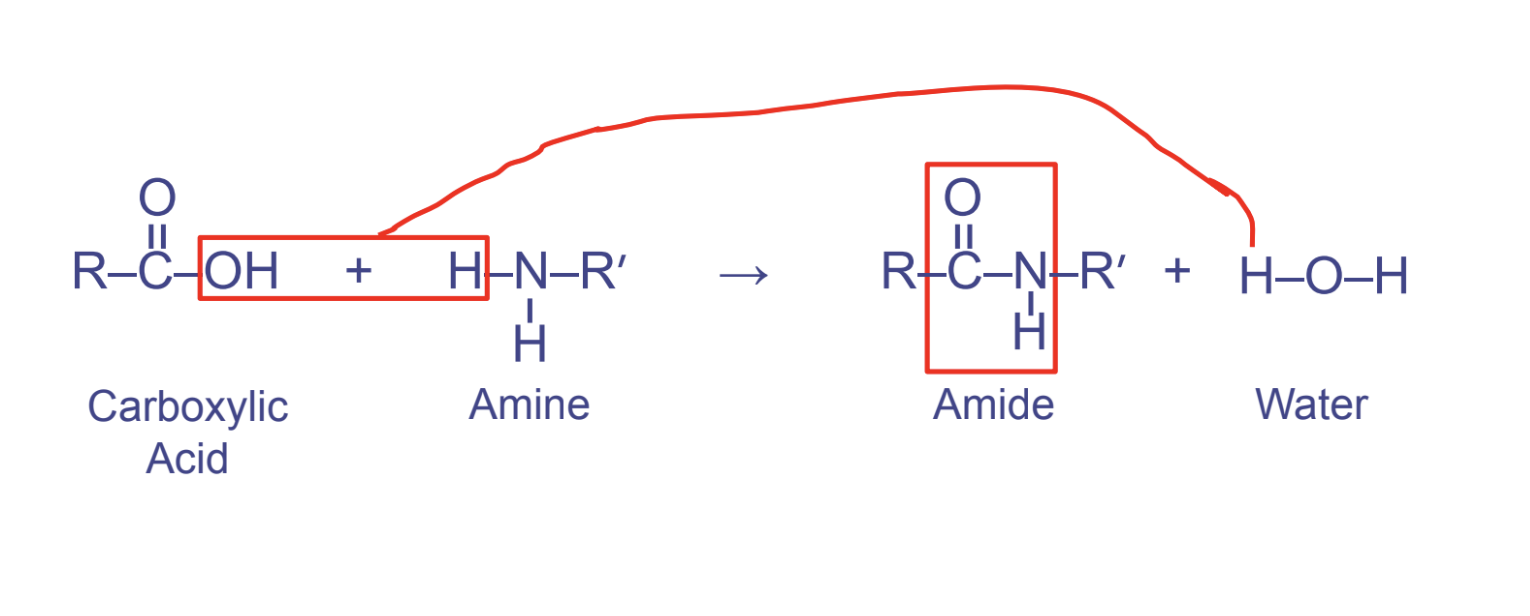
20
New cards
carbohydrates
* made of C, H, O - ratio 1:2:1
* formula - (CH2O)n where n is # of carbons
* short term energy source, building blocks, cell surface markers
* 3 kinds - monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
* formula - (CH2O)n where n is # of carbons
* short term energy source, building blocks, cell surface markers
* 3 kinds - monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
21
New cards
monosaccharides
* chain of carbons w hydroxyl groups attached
* contain carbonyl groups
* have diff #s of carbons - commonly 3, 5, 6 carbon sugars
* isomers = compounds with same empirical formula but diff configurations
* glucose, galactose, fructose are isomers - C6H12O6
* contain carbonyl groups
* have diff #s of carbons - commonly 3, 5, 6 carbon sugars
* isomers = compounds with same empirical formula but diff configurations
* glucose, galactose, fructose are isomers - C6H12O6
22
New cards
glucose
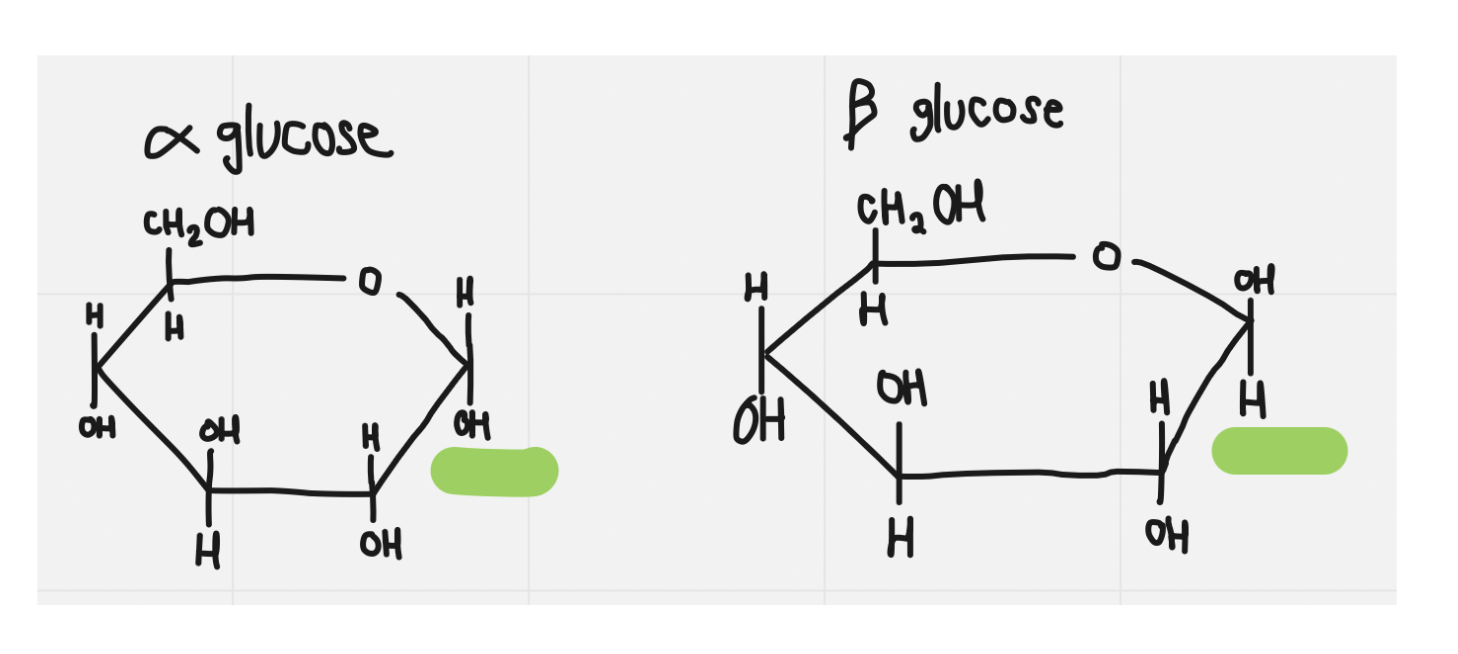
23
New cards
galactose
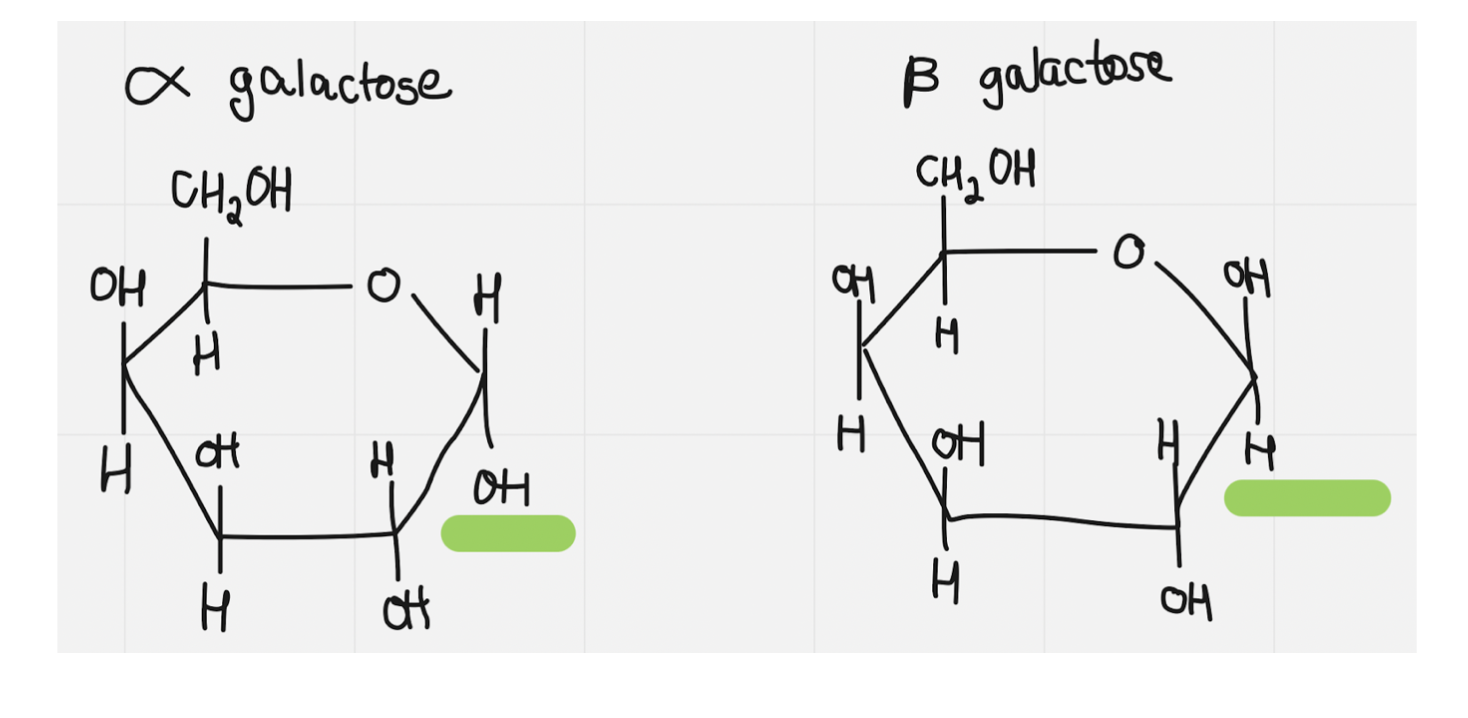
24
New cards
fructose
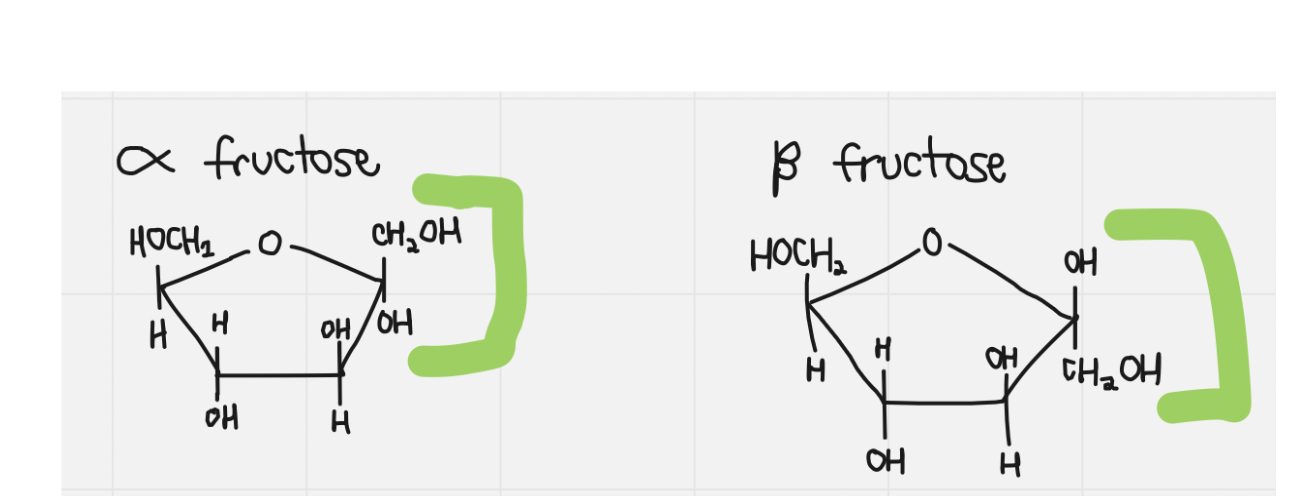
25
New cards
disaccharides
* 2 simple sugars attached by ether/glycosidic linkage, dehydration synthesis rxn - 2 OH linked together
26
New cards
maltose
glucose + glucose → maltose + water
* linkage btw c1 on glucose 1 and c4 on glucose 2
* a 1-4 glycosidic linkage
* linkage btw c1 on glucose 1 and c4 on glucose 2
* a 1-4 glycosidic linkage
27
New cards
lactose
b galactose + glucose → lactose + water
* glucose can be a or b
* linkage btw c1 on galactose 1 and c4 on glucose 2
* b 1-4 glycosidic linkage
* glucose can be a or b
* linkage btw c1 on galactose 1 and c4 on glucose 2
* b 1-4 glycosidic linkage
28
New cards
sucrose
glucose + fructose → sucrose + water
* flip fructose so hydroxyl on the side for bonding
* linkage btw c1 on glucose 1 and c2 on fructose 2
* 1-2 glycosidic linkage (either a or b depending on the glucose)
* flip fructose so hydroxyl on the side for bonding
* linkage btw c1 on glucose 1 and c2 on fructose 2
* 1-2 glycosidic linkage (either a or b depending on the glucose)
29
New cards
polysaccharides
* large molecules - same linkage used to make a strand, several hundred-thousand monosaccharides bonded w glycosidic linkages
* straight chain = a 1-4 glycosidic linkages or brained chains = a 1-6 glycosidic linkages
* energy storage and structural support
* all a or all b linkages
* straight chain = a 1-4 glycosidic linkages or brained chains = a 1-6 glycosidic linkages
* energy storage and structural support
* all a or all b linkages
30
New cards
starch
* plant energy storage
* straight chains - amylose
* branched chains - amylopectin
* stored in leaves and roots
* straight chains - amylose
* branched chains - amylopectin
* stored in leaves and roots
31
New cards
glycogen
* animal energy storage
* many side branches
* made in liver, muscle, fat cells
* many side branches
* made in liver, muscle, fat cells
32
New cards
cellulose
* plant structural support
* in cell walls
* H bonds btw chains from fibres, strong
* straight chain of b glucose units - b 1-4 linkages
* in cell walls
* H bonds btw chains from fibres, strong
* straight chain of b glucose units - b 1-4 linkages
33
New cards
chitin
* animal structural support and fungi as well
* polymer of straight chain b-N-acetylglucosamine
* 2nd most abundant organic material
* no branches
* polymer of straight chain b-N-acetylglucosamine
* 2nd most abundant organic material
* no branches
34
New cards
lipids
* mostly C and H, with few O
* hydrophobic - repel water
* few polar O-H bonds & more non polar C-H bonds
* long term nrg storage, membranes, dissolving fat soluble vitamins ADEK
* fats, phospholipids, sterols, waxes
* hydrophobic - repel water
* few polar O-H bonds & more non polar C-H bonds
* long term nrg storage, membranes, dissolving fat soluble vitamins ADEK
* fats, phospholipids, sterols, waxes
35
New cards
nucleic acid
* molecules that are polymers made of nucleotides
* 3 components - pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
* 3 components - pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
36
New cards
proteins
* structural support, storage, transport, signalling, cell response, movement, defence, catalysis of rxns
* amino acids make these up
* side chains determine function
* 4 levels of folding:
* 1º - N → C terminus
* order determines folding
* 2º - coils and folds ; stabilized by H bonds btw amino and carboxyl groups
* a helixes and b pleated sheets
* 3º - super coiling involving side groups
* 4º - many polypeptide chains come together
* amino acids make these up
* side chains determine function
* 4 levels of folding:
* 1º - N → C terminus
* order determines folding
* 2º - coils and folds ; stabilized by H bonds btw amino and carboxyl groups
* a helixes and b pleated sheets
* 3º - super coiling involving side groups
* 4º - many polypeptide chains come together
37
New cards
enzymes
* bio catalysts - assist in chemical rxns
* distort substrate chemical bonds
* sometimes need cofactors
* distort substrate chemical bonds
* sometimes need cofactors
38
New cards
cell membrane and transport
* fluid mosaic model
* phospholipids = main molecule
* membrane fluidity
* proteins - integral and peripheral
* phospholipids = main molecule
* membrane fluidity
* proteins - integral and peripheral