Superposition (Standing waves)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
represents amplitude and depends on x (position)
2 A sin (kx)
represents SHM
cos (ωt)
Nodes
values of x where A = 0
y displacement = 0
these points do NOT move up or down at all (NEVER MOVE)
occur @ all position (x) multiples of λ/2
x = 0, ½ λ, λ, 3/2 λ, 2λ, …
Antinodes
values of x where A = very large #
occur when A of the standing wave is the largest
occur when x is an odd multiple of λ/4
x = ¼ λ, ¾λ, etc.
sin (kx) = ±1
amplitude is largest when?
in a string that is fixed @ both ends, the two ends are nodes
Remember: in a string that is fixed @ both ends, the two ends are nodes
standing waves occur bc of the continuous superposition of waves that are reflected at each end
Remember: standing waves occur bc of the continuous superposition of waves that are reflected at each end
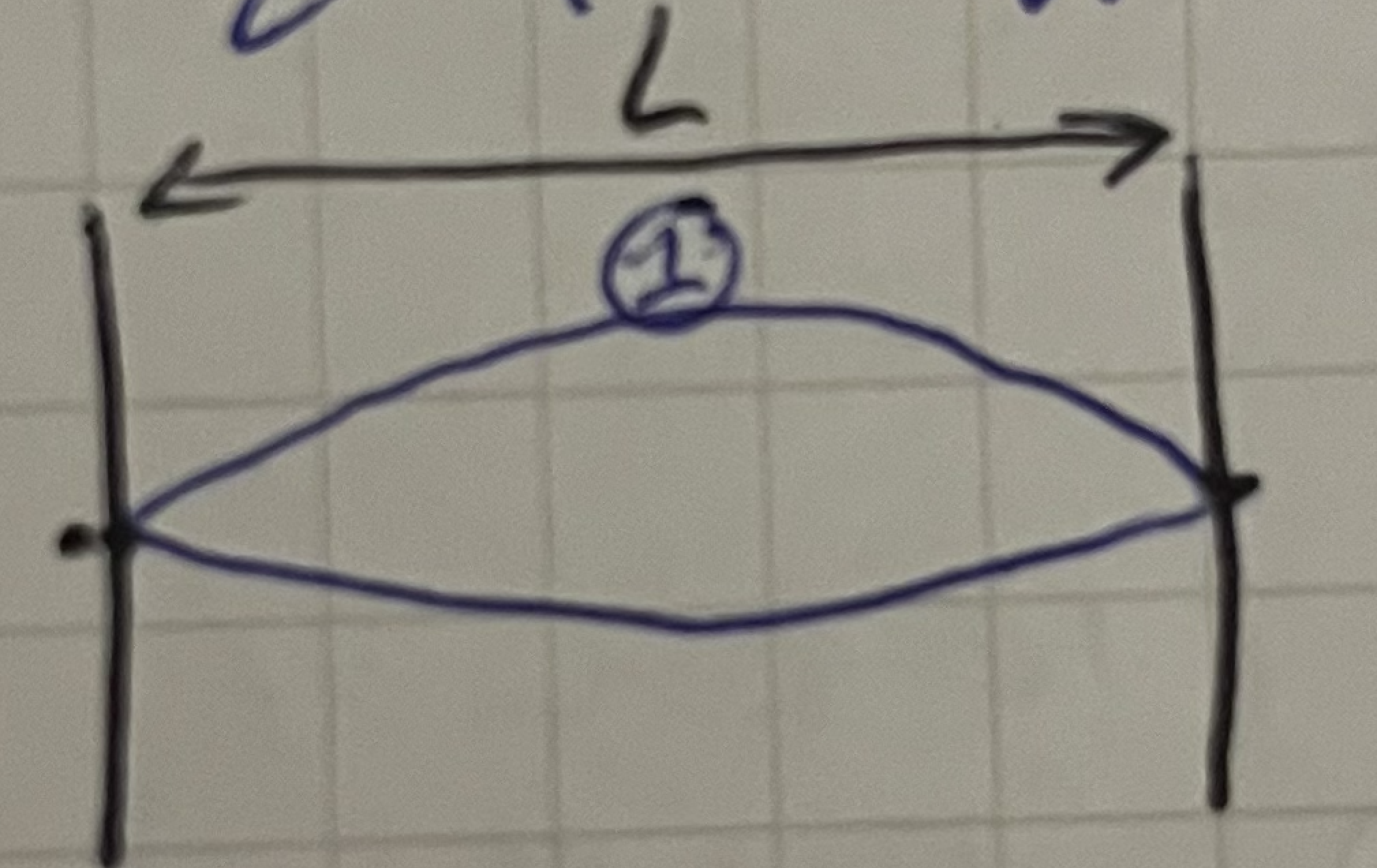
L = ½ λ₁
Given this harmonic mode what is the length of the string equal to?
L = λ₂
Given this harmonic mode what is the length of the string equal to?

L = 3/2 λ₃
Given this harmonic mode what is the length of the string equal to?
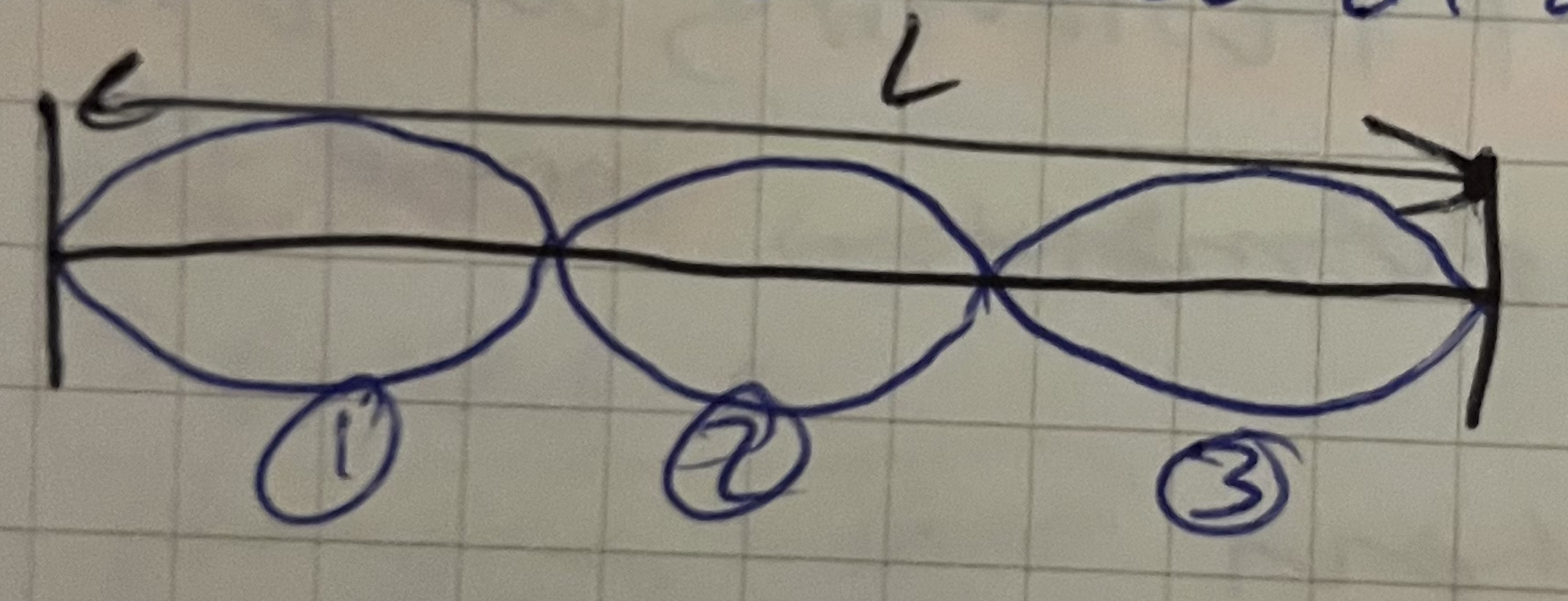
fundamental frequency (f₁)
f₁ = V / 2L
can be changes by:
changing the strings length
changing the strings tension (thus the wave speed)
fm = mf₁
equation for frequency depending on harmonic modes?
Sound waves that oscillate @ diff frequencies, sound diff
Remember: Sound waves that oscillate @ diff frequencies, sound diff
a music note from a string is defined by its fundamental frequency (harmonic mode = 1)
Remember: a music note from a string is defined by its fundamental frequency (harmonic mode = 1)
closed end of pipe
displacement node
pressure antinode
open end of pipe
displacement antinode
pressure node
open-open pipe
two pressure nodes
f₁ = V / 2L
fm = mf₁
m = 1, 2, 3 …
open-closed pipe
1 pressure node, 1 pressure antinode
f₁ = V / 4L
fm = mf₁
m = 1, 3, 5 …
m = only odd multiples bc of the antinode