Mid Semester Exam
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What is animal welfare?
Animal welfare refers to the state of an individual as it attempts to cope with its environment.
What are the five freedoms?
Freedom from hunger and thirst
Freedom from discomfort
Freedom from pain, injury or disease.
Freedom to express normal behaviour
Freedom from fear and distress.
What are the five domains?
Nutrition, environment, health, behaviour, mental state.
What a stereotypies?
Repetitive behaviours with no obvious purpose.
What are some ways we can measure animal welfare?
Behaviour
physiological measures
environmental assessment
We can also assess welfare by looking at input versus output. What are some examples of inputs and some examples of outputs?
Inputs measure indirect parameters such as housing, provision of food and water, medical records. Outputs assess the animals including body condition, lesions, lameness, foot conditions and assessment of dead animals in post-mortems.
What is biosecurity?
The strategic and integrated approach to analysing and managing relevant risks to human, animal and plant life and health and associated risks for the environment.
What are some examples of personnel biosecurity precautions?
PPE
hand hygiene
vaccination
What are some examples of engineering controls with respect to biosecurity?
Facility design
Facility decontamination, cleaning and disinfection
Fences, gates, foot baths, vehicle decontamination
Specialist facilities
What are some administrative controls with respect to biosecurity?
Quarantine, triage, isolation, standard operating procedures, guidelines, disposal of sharps and clinical waste.
What kind of PPE would protect against inhaled zoonoses?
P2 masks or respirators
face shields and eye goggles
How long is cow gestation?
283 days
What are the main dairy breeds?
Holstein (Friesian)
Brown Swiss
Guernsey
Illawarra
Ayrshire
Jersey
Why is the term dry cow used?
To indicate that a cow is greater than seven months pregnant
What is the Springer?
A cow who is in the last three weeks before calving. Also called transition and close-up.
What is a fresh cow?
A cow who has just calved. Can be use for up to 41 days post calving.
How long is the lactation cycle of a cow?
305 days
What are the different housing systems for dairy cows?
Pastoral, free stalls, compost barns
What is the difference between this budding and dehorning?
Disbudding is done with calves that are less than two months old. It is the removal of horn producing cells. The buds are not attached to the skull. Dehorning is the removal of the horn and horn producing tissues. The horn is attached to the skull.
Where are some of the diseases that dairy cows are vaccinated against
Clostridial diseases such as tetanus malignant oedema, back leg Enterotoxaemia, black disease
Leptospirosis
Botulism
Bovine ephemeral fever
Tick fever
What is an act?
Acts generally take the form of a legal instruments of writing that have probative value and executory force.
What is the code of practice?
A written document, published by a professional organisation that establishes ethical standards.
What are guidelines?
General rules, principles, or advice.
Describe the animal care and protection Act.
It is legislation promotes the responsible care and use of animals.
Provide standards for the care and use of animals.
Protects animals from unjustifiable, unnecessary or unreasonable pain.
Ensures the use of animals for scientific purposes is accountable, open and responsible.
What advice would you give someone considering new pet ownership?
Suitable species or breeds
information on desexing and vaccination
Breed specific potential health issues
costs
Responsible pet ownership
What are some methods of identification?
Breed, gender, age, markings, physical characteristics such as colour, size, weight, tattoos, microchips, collars and tags
How do you identify cross breed dogs?
Dominant breed first.
How many teeth does an adult cat have?
30
How many teeth does an adult dog have?
42
What are the seven basic needs of all animals to ensure physical and mental well-being?
Warmth, comfort and security
companionship
protection from disease and injury
protection from fear and distress
exercise
Provision of appropriate feed and water
opportunity to defecate and urinate away from sleeping and eating areas.
What the exercise requirements depend on?
Breed, age, health status, life stage.
What five things to feed need to be?
Complete, balanced, digestible, palatable, acceptable.
What are the four attributes of the environment, which together meat and animals psychological needs
Security, complexity, achievement, novelty
What is the most important of the environmental factors?
Security
Give an example of complexity.
Climbing apparatus, a patch of dirt, sand to dig in, varieties food, a maze to wander through, the rubber innards of a tyre to wrestle with.
What are the four elements of an affective sanitation program?
Clean and disinfect, use effective products, clean where it counts and be meticulous, minimise stress and fomite transmission
What is a carrier?
An animal, which is infected and infectious to other animals, but not currently showing signs of disease.
What are five forms of modes of disease transmission.
Vectors
direct contact
droplet
airborne
Fomite
Aircon completely in activate an envelope to viruses, true or false.
True
Describe dose effect
Often a disease needs millions of germs. When you increase in the dose you increase the likelihood of the disease, faster transmission and more severe disease. When looking at sanitation methods we do not need to attain zero dose, just lower the dose enough of the animals immune system can ward off the rest
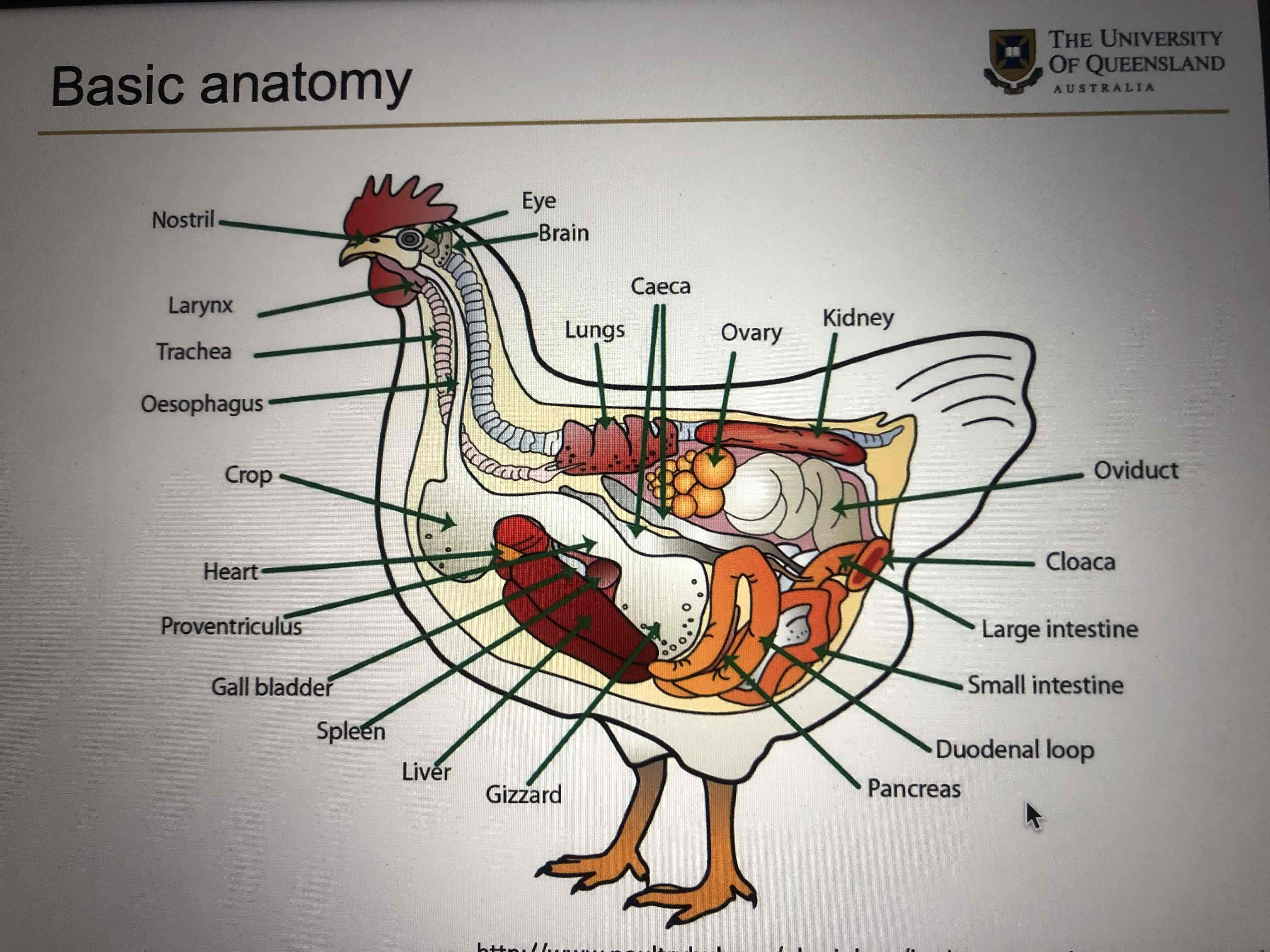
What does anatomy and physiology have to do with husbandry and management?
Influences diet, influences housing, influences type and management of environmental enrichment, influences management and pregnancy prevention and shows whats normal.
What does does the vomeronasal organ do in cats?
It detects pheromones.
What are the three methods of feeding?
Ad Lib
time restricted
food restricted
Amino acids are classified as either essential or non essential. Define what is meant by each of these terms.
Essential amino acids are those that are not synthesised by the body and are required to be consumed through food. Nonessential amino acids are those manufactured by the body.
What are five factors that affect water intake.
Temperature, type of diet, exercise, physiological state, health.
What does digestibility mean?
The proportion of food digested by an animal. The difference between the content of the nutrient in food and quantity in faeces.
What is meant by bioavailability?
The relationship between the amount of nutrient absorbed and the amount used by the body.
What factors influence food requirements for optimal health?
Individual variation
environmental temperature, humidity, and air movement
stress
physical activity
stage of life
health status.
What is animal behaviour?
Anything an animal does including movement, activities, and underlying mental processes. Behaviour is how an animal acts in response to a particular situation or stimulus.
What is neurotypical behaviour?
Neurotypical behaviour conforms to common behaviour for the species.
What are the three R’s of animal research?
Replace, reduce, refine.
What are the some of the main differences between birds and mammals?
Birds have a very high metabolic rate.
Birds have a high oxygen demand.
Birds have a high efficiency of converting feed to growth or eggs.
What is one of the key differences between third respiratory anatomy and mammal respiratory anatomy?
The avian lung has a flow through system with small at capillaries. The mammalian lung has reciprocating ventilation with large terminal airspaces called alveoli.
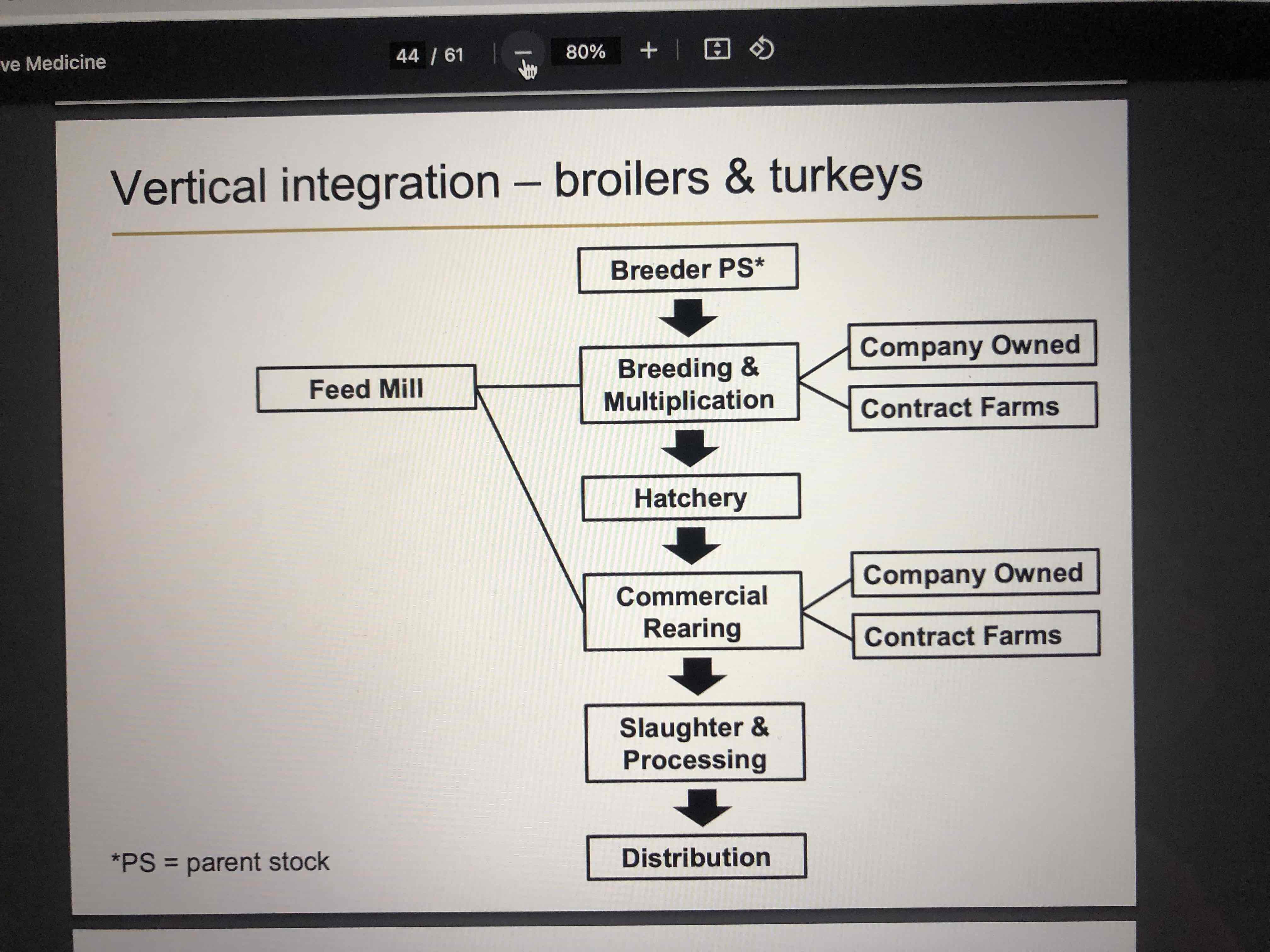
The Australian poultry industry is highly vertically integrated. What does this mean?
It means that a small number of large integrated companies supply the majority of chickens for meat consumption. In the case of Australia, there’s six large integrated companies which supply up to 95% of the total chicken meat for consumption. Two of them supply 70%.
What is the definition of vertically integrated?
That the company controls two or more steps of production, processing and marking. They also control the management decisions in the production system.
When does candling of eggs occur?
At 7 to 10 days, if it’s clear the eggs infertile , if there’s a red ring, the embryo died at some point and if there are blood vessels, there is a live embryo.
When is in ovo vaccination?
18 days
What diseases are vaccinated for during in ovo vaccination?
Marek’s disease, infectious latyngotracheitis, infectious bursal disease, Newcastle disease
Brooding chicks require supplementary heat, until what age?
2 to 3 weeks
What is the target for carbon dioxide in chicken sheds?
Less than 2500 ppm
What is the target carbon monoxide in chicken sheds?
Less than 10 ppm
What are the percentages of protein for starter grower and layer feeds?
Starter, 22% grower, 14 to 16% layer 15 to 18%
Free range birds must have meaningful and regular access to an outdoor range during daylight hours and be free to roam and forage outside. How many birds per square metre in free range?
One bird per square metre which equals 10,000 birds per hectare.
The stocking density according to the RSPCA for broiler chickens is 34 kg/m² for tunnel ventilated or extractive systems. How much is it for mechanically ventilated systems and non-mechanically ventilated systems?
32 kg/m² for mechanically ventilated system 28 kg/m² for non-mechanically ventilated systems
How long should you isolate in quarantine with incoming poultry stock?
Two weeks
What disease do rodents carry?
Fowl cholera
What kind of internal parasites are likely to cause harm in poultry?
Round worm, caecal worms, tapeworms
What at Tinbergen’s questions?
What is the adaptive value or selective advantage of the trait? What mechanisms cause the trait to occur in an individual?How is the trait acquired during the course of development? From what did it evolve?

What is meant by a co-opted behaviour?
A behaviour that was previously used for one thing, but is now use for something else
What is meant by an adaptive trait?
Characteristics or features of an organism that enhances it survival or reproductive success in a particular environment
Allopatric speciation occurs when a barrier is formed in an original population. Given example of allopatric speciation
The Darwinian finches are an example of allopatric speciation. Their isolation on the islands over long periods of time, made them undergo changes in their beaks due to the different types of food sources.
Parapatric speciation occurs when explorer populations, find new resources, and do not return to the parent population. This leads to different species with different behaviours, and eventually leads to different species. What is the other form of speciation and give an example?
Sympatric speciation occurs when females diverge in their preference for male characteristics and the divergence becomes genetic, and eventually there will be two different gene pools
What are the five theories that explain Sue social cooperation within a group?
Kin selection, group selection, reciprocal altruism, selfish teamwork, stolen help
What are some of the social grouping reasons that animals group together?
exploitation of public information, shared defences or vigilance, giving or receiving aid
Why do animals participate in kin selection?
This is for the protection of their offspring, so that their genes are passed on
What are some examples of group selection?
Confusion of predators by the groups motions and cooperative hunting
What are some of the limitations to group size?
Food supply
increase chance of predator attraction
plateau with shared vigilance
reproductive success
What are some of the benefits of being highly ranked and some of the constraints
Benefits are preferred access to food, mating, grooming and protected positions the constraints are that the group leader is in a more risky position and will eventually will be out ranked. It is also physically and cognitively taxing.
What is the difference between intersexual selection and intra sexual selection?
Intersexual selection is the affect that the mating preferences of females I has on the characteristics of males (such as peacocks tails). Intrasexual selection are features due to effects of competition of males to secure females (such as fighting tools - antlers).
What is the handicap signal?
It is an honest signal that animal cannot pretend to pay that cost
The index hypothesis predicts that dishonest signals cannot be faked. The handicap principle predicts that dishonest thing signals are too costly to fake.