Cell Biology & Biochemistry Review Set
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
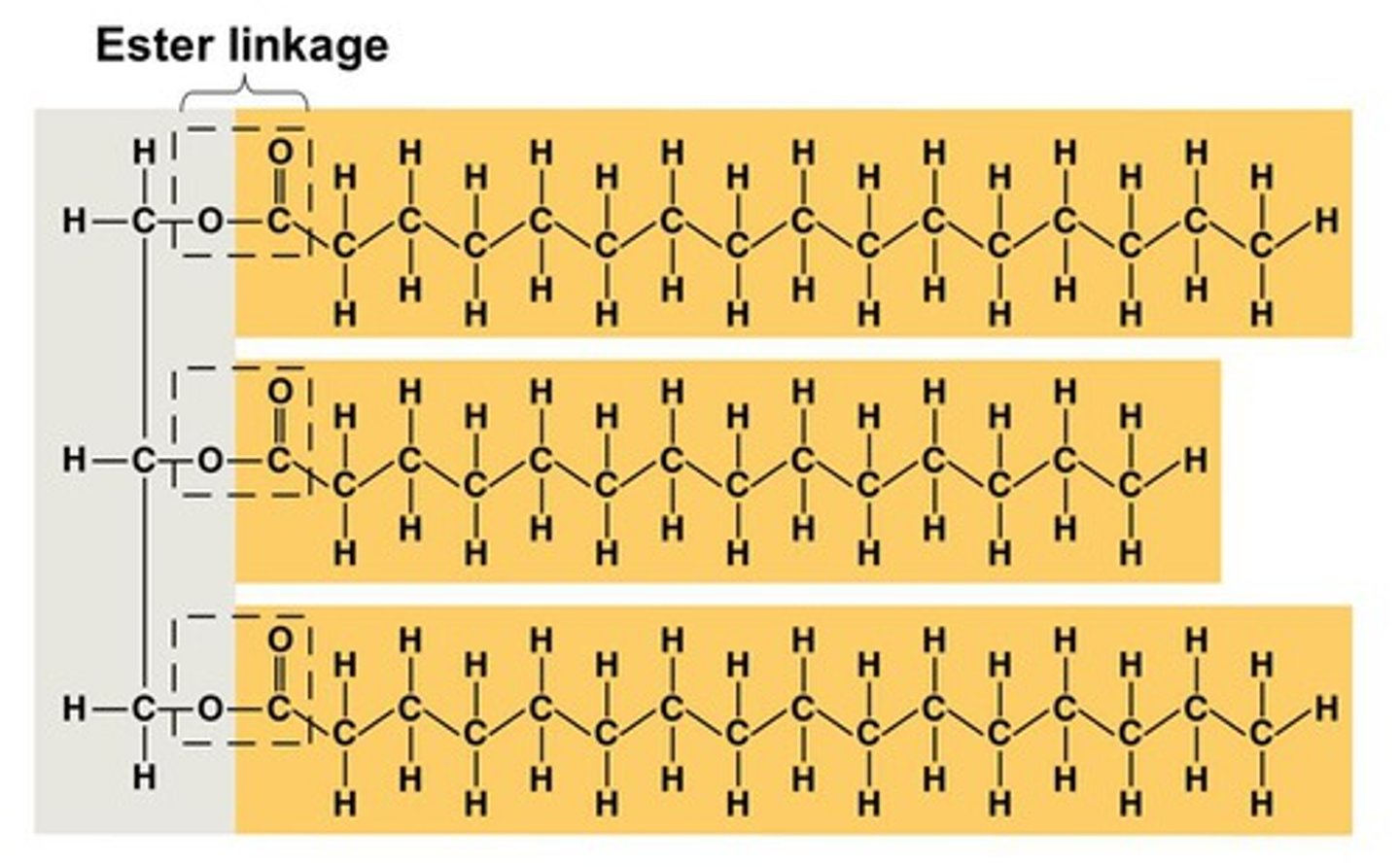
What is the name of the bond that joins glycerol and three fatty acids, and what is the new molecule called?
Ester bond, triglyceride
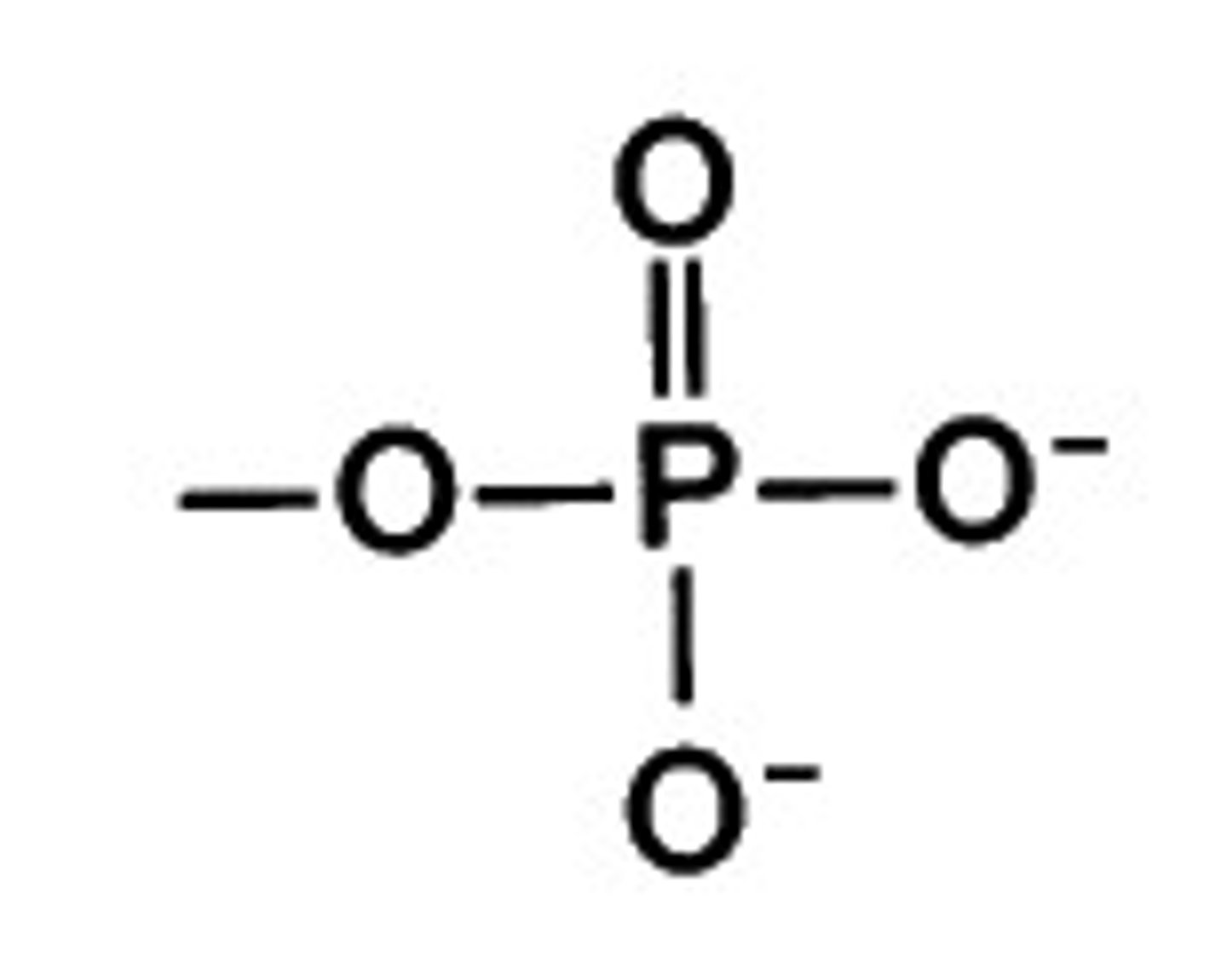
What is the formula for the organic phosphate biofunctional group?
—OPO3 (-2)
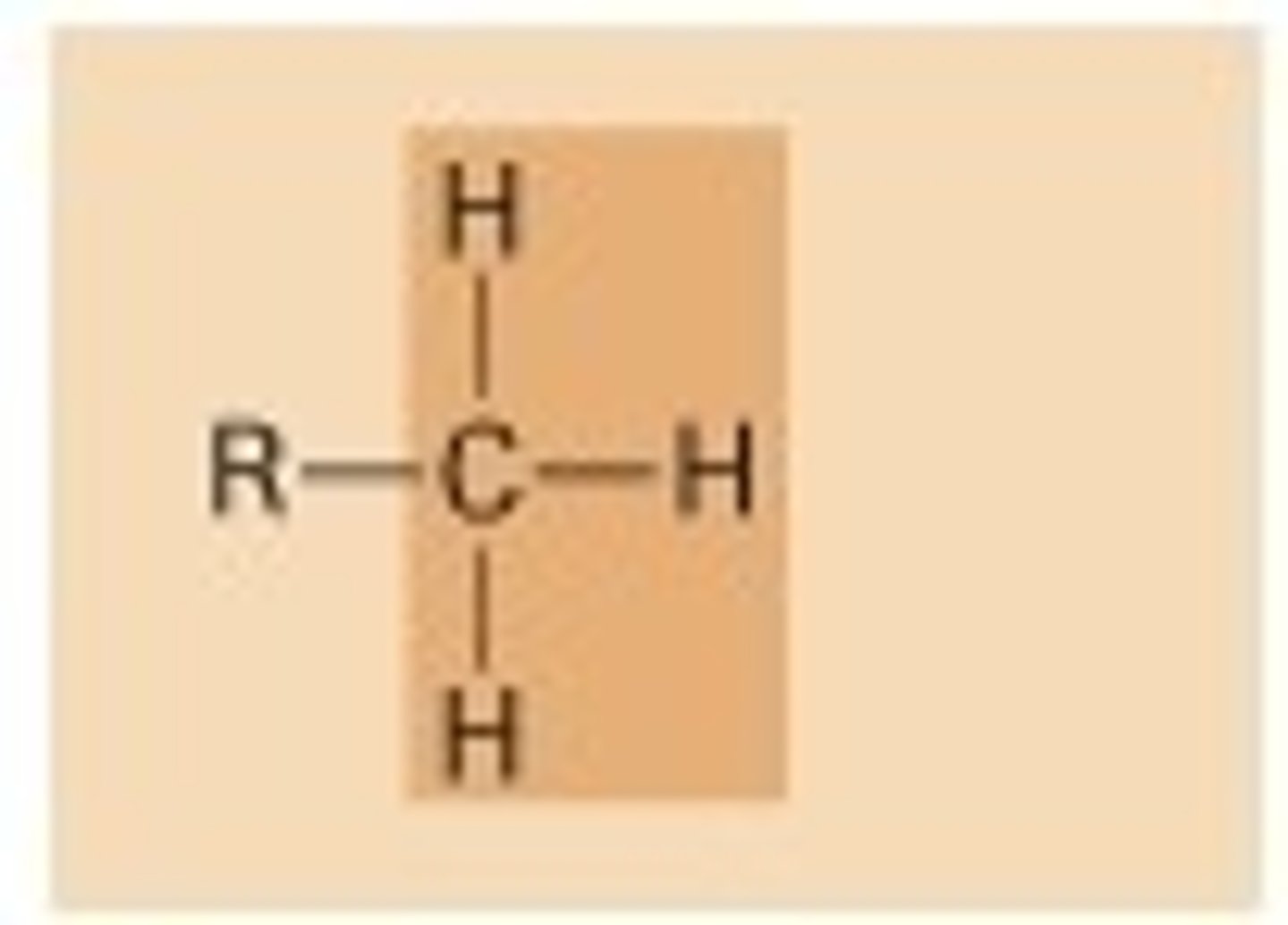
What is the formula for the methyl biofunctional group?
—CH3
What is the importance of water?
Makes up 90% of the cell cytoplasm, excellent solvent for biomolecules, helps for maintaining osmotic pressure, helps transporting molecules in the body, maintains body temperature, solid ice acts as a good thermal insulator

What do the micromolecules have in common? (Hint: Two things.)
All are very small in terms of molecular size, and all are needed in relatively large amounts in the body
What is the name of the bond that joins monosaccharides?
Glycosidic Linkage
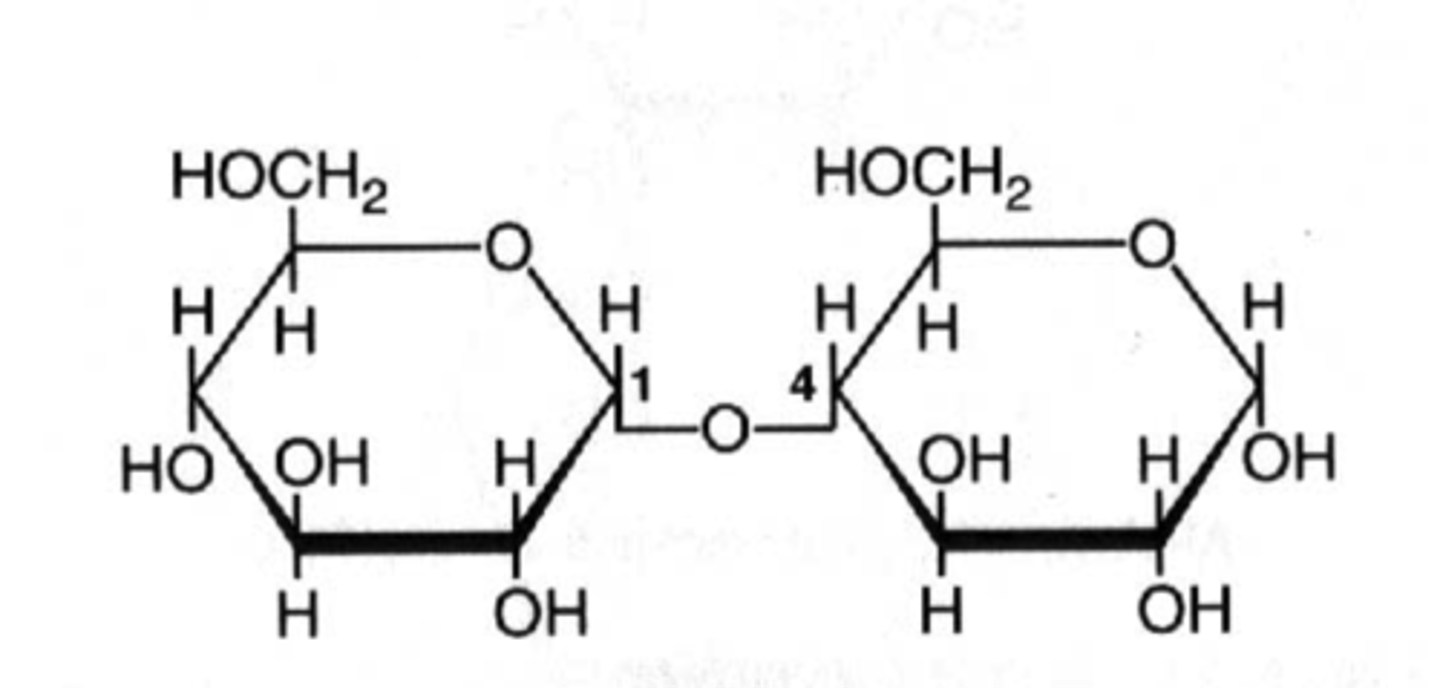
What are the three key polysaccharides?
Glycogen, Starch, Cellulose
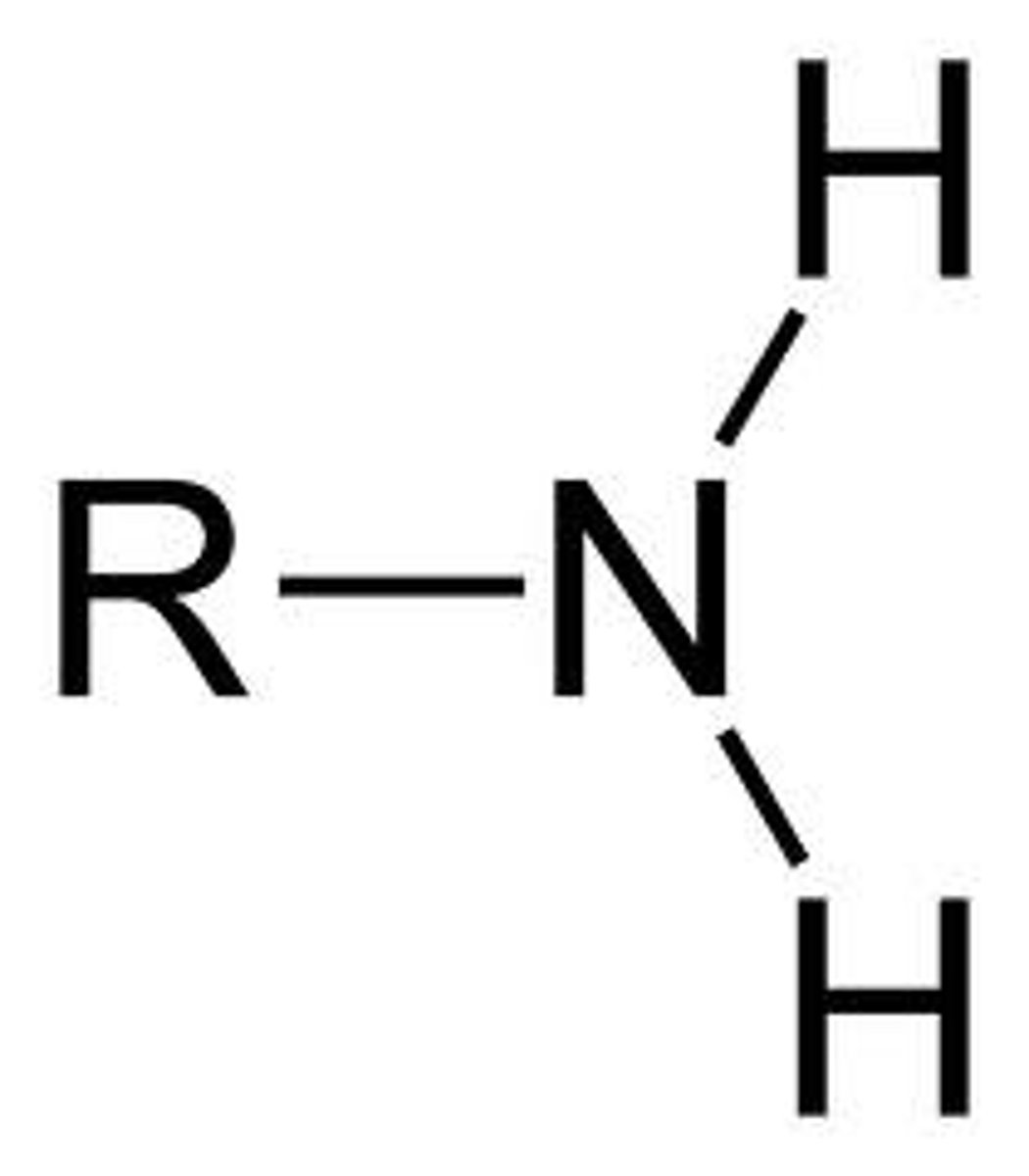
What is the formula for the amino biofunctional group?
—NH2
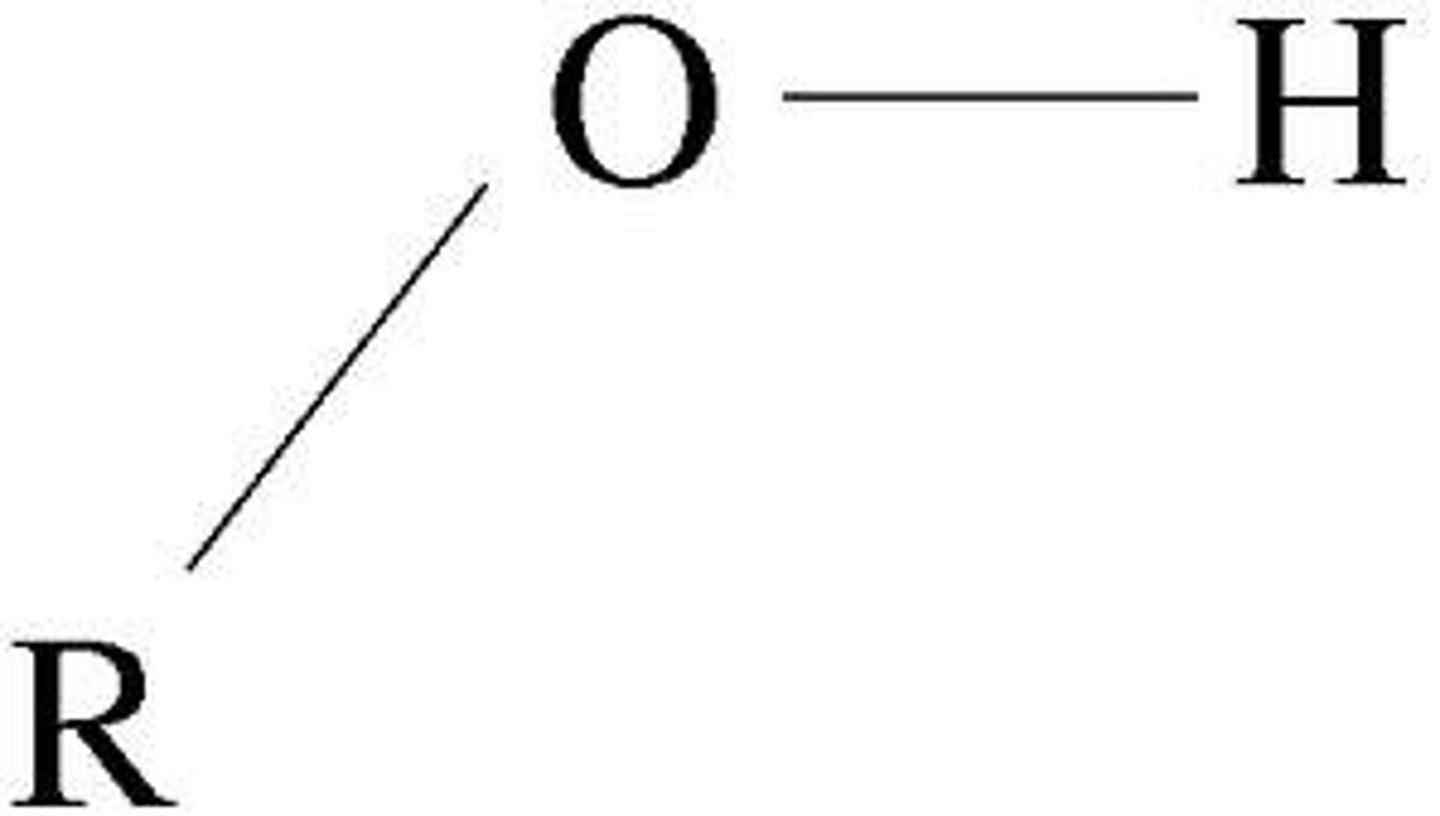
What is the formula for the hydroxyl biofunctional group?
—OH
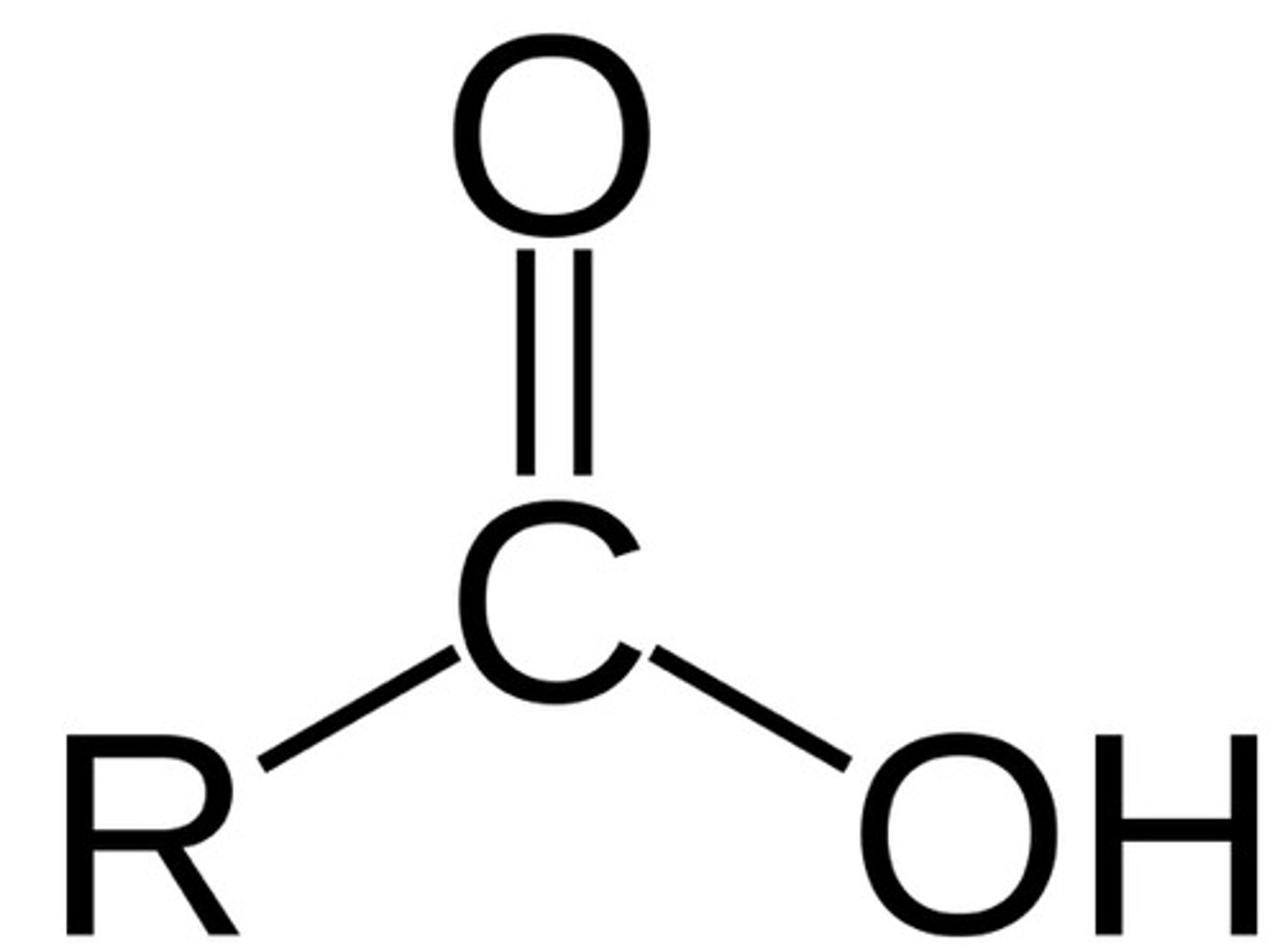
What is the formula for the carboxyl biofunctional group?
—COOH
The nitrogen bases for DNA are what?
Adenine, Thymine, Guamine, Cytosine
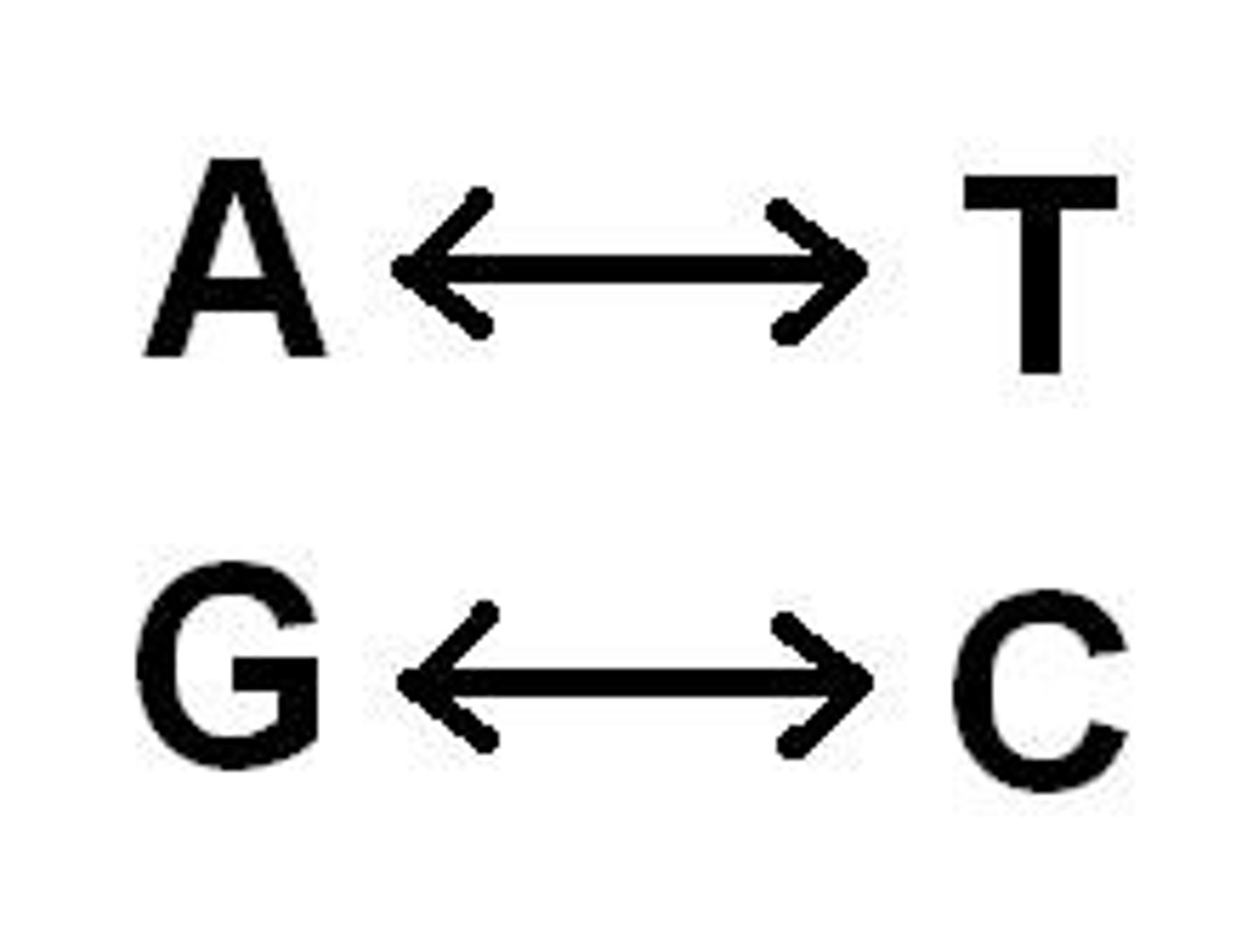
The nitrogen bases for RNA are what?
Adenine, Uracil, Guamine, Cytosine
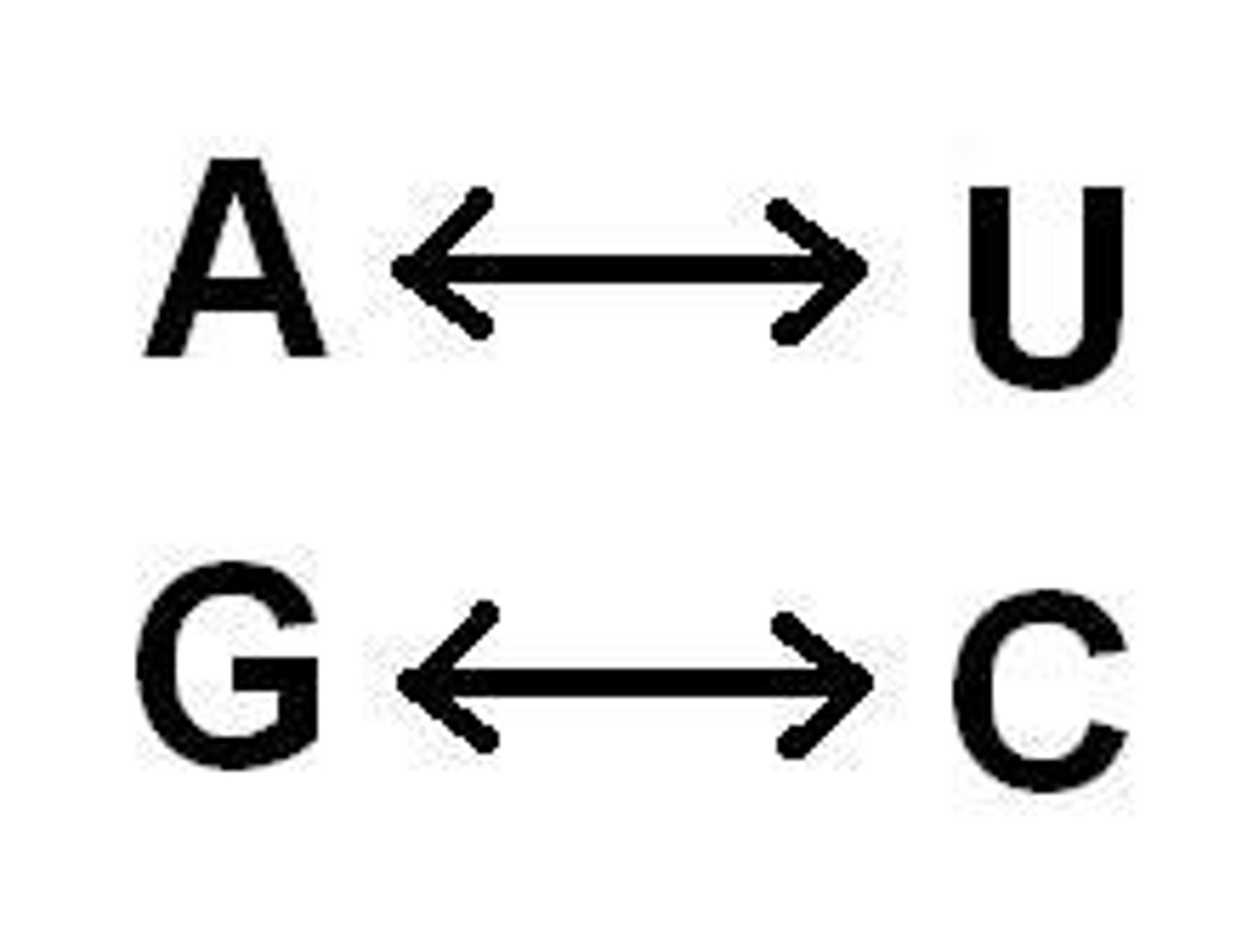
What are the three important micromolecules?
Water (H2O), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Oxygen (O2)
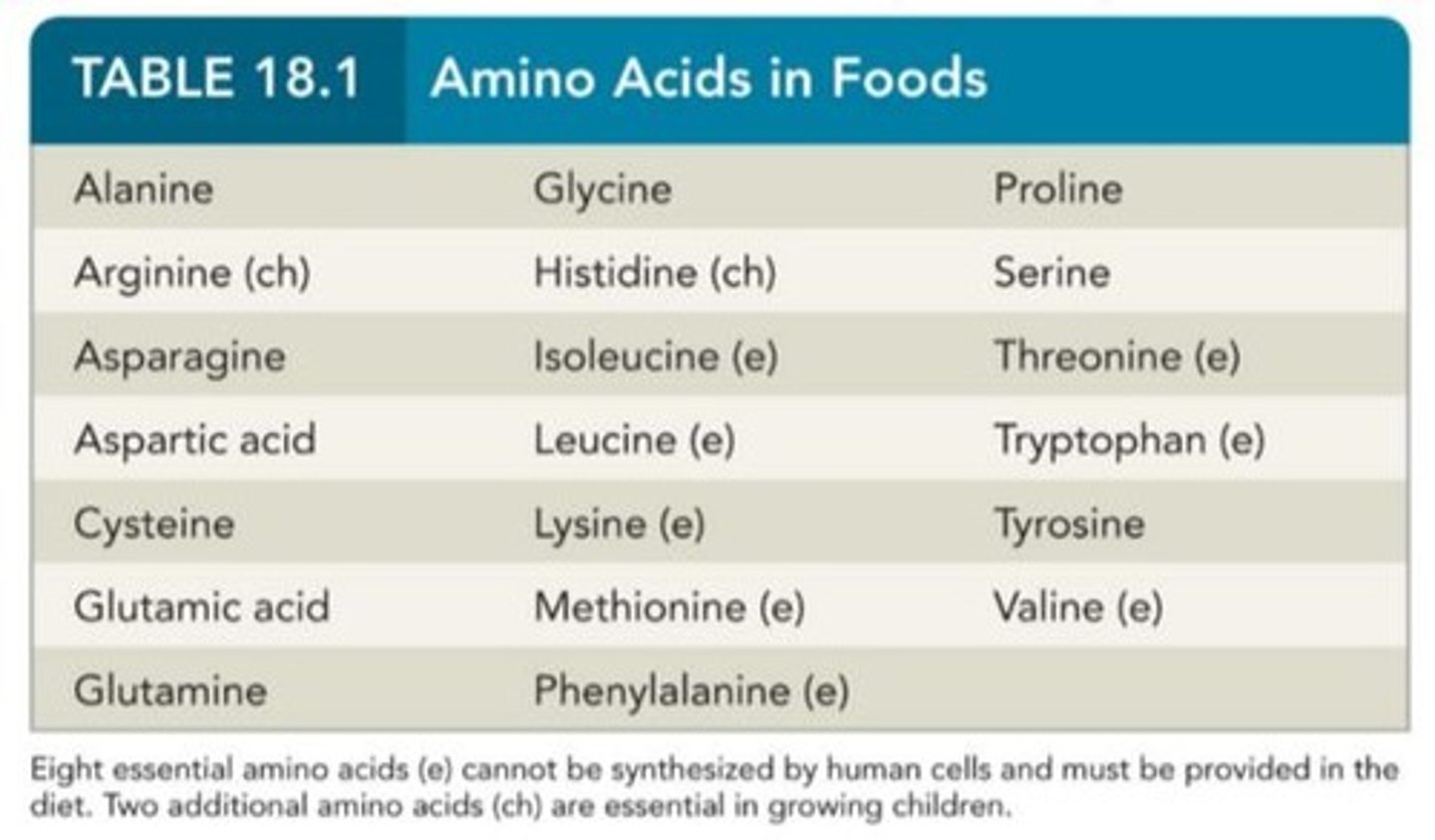
Why are "essential amino acids" called "essential"?
They are not produced by the human body; they must be obtained via diet
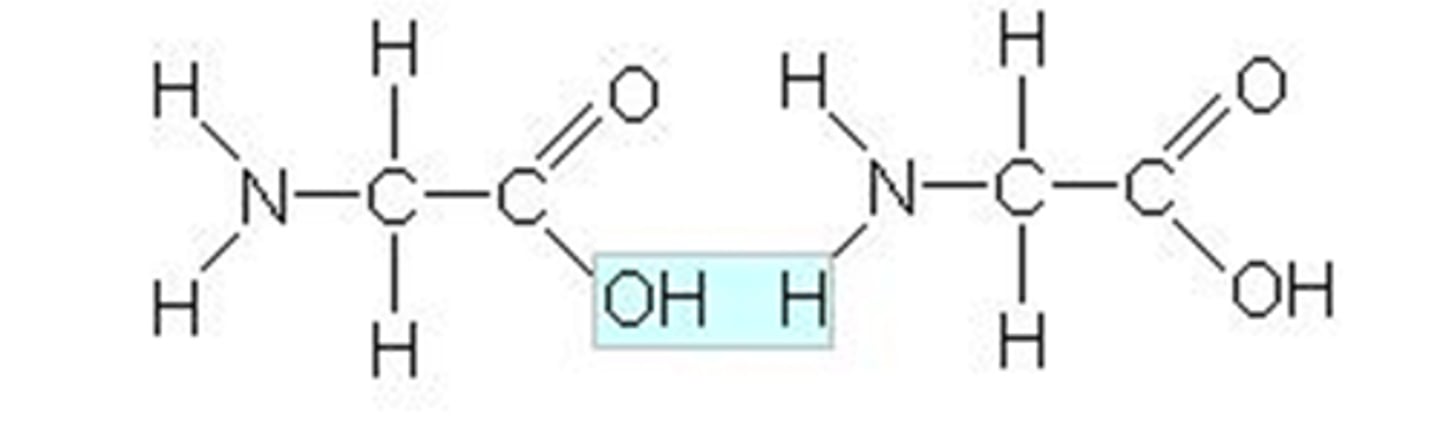
What is the name of the bond that joins amino acids together?
Peptide Bond
How many amino acids are there, and how many are essential vs. non-essential?
20 amino acids (8 essential, 12 non-essential)
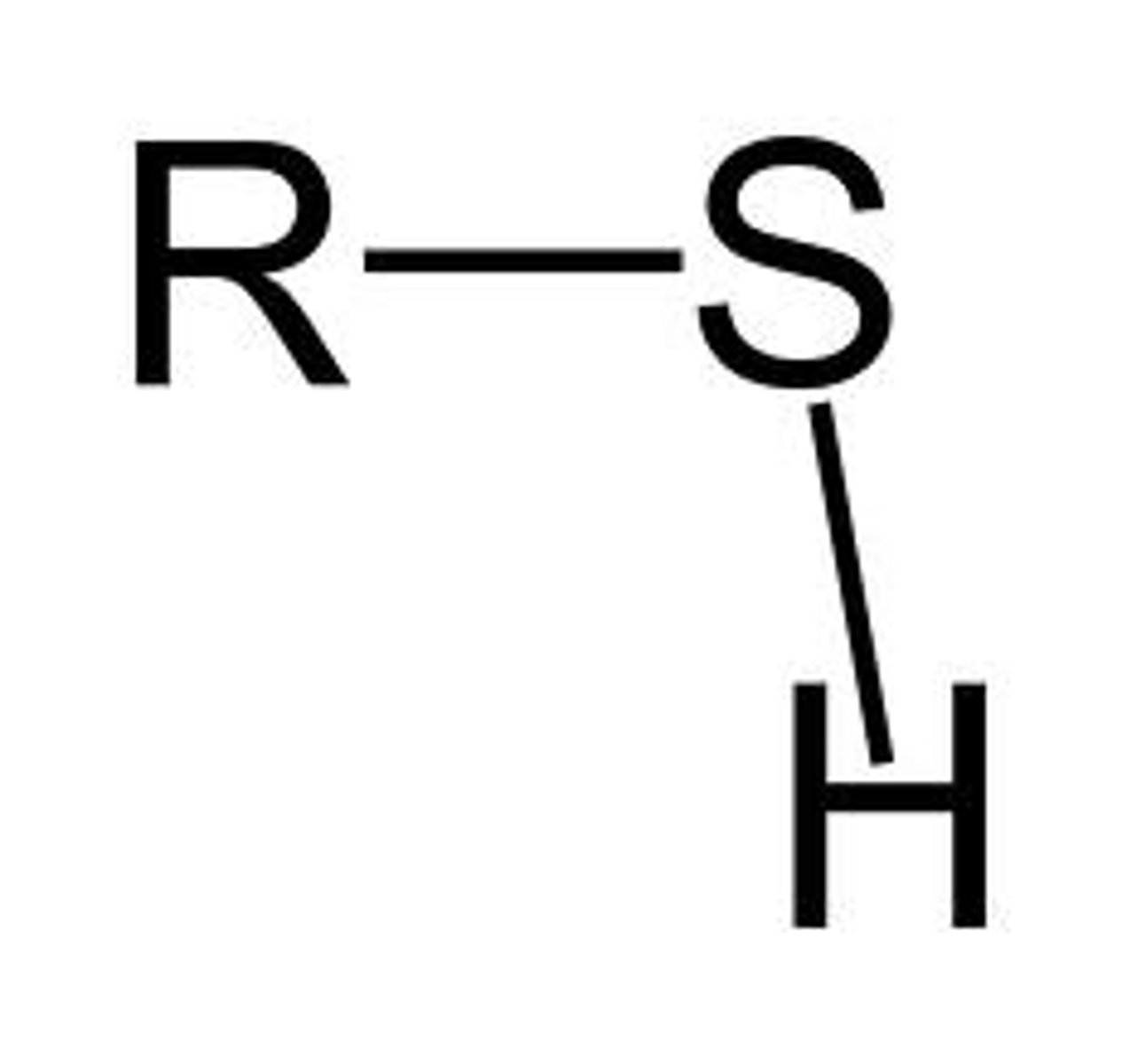
What is the formula for the sulfhydryl biofunctional group?
—SH
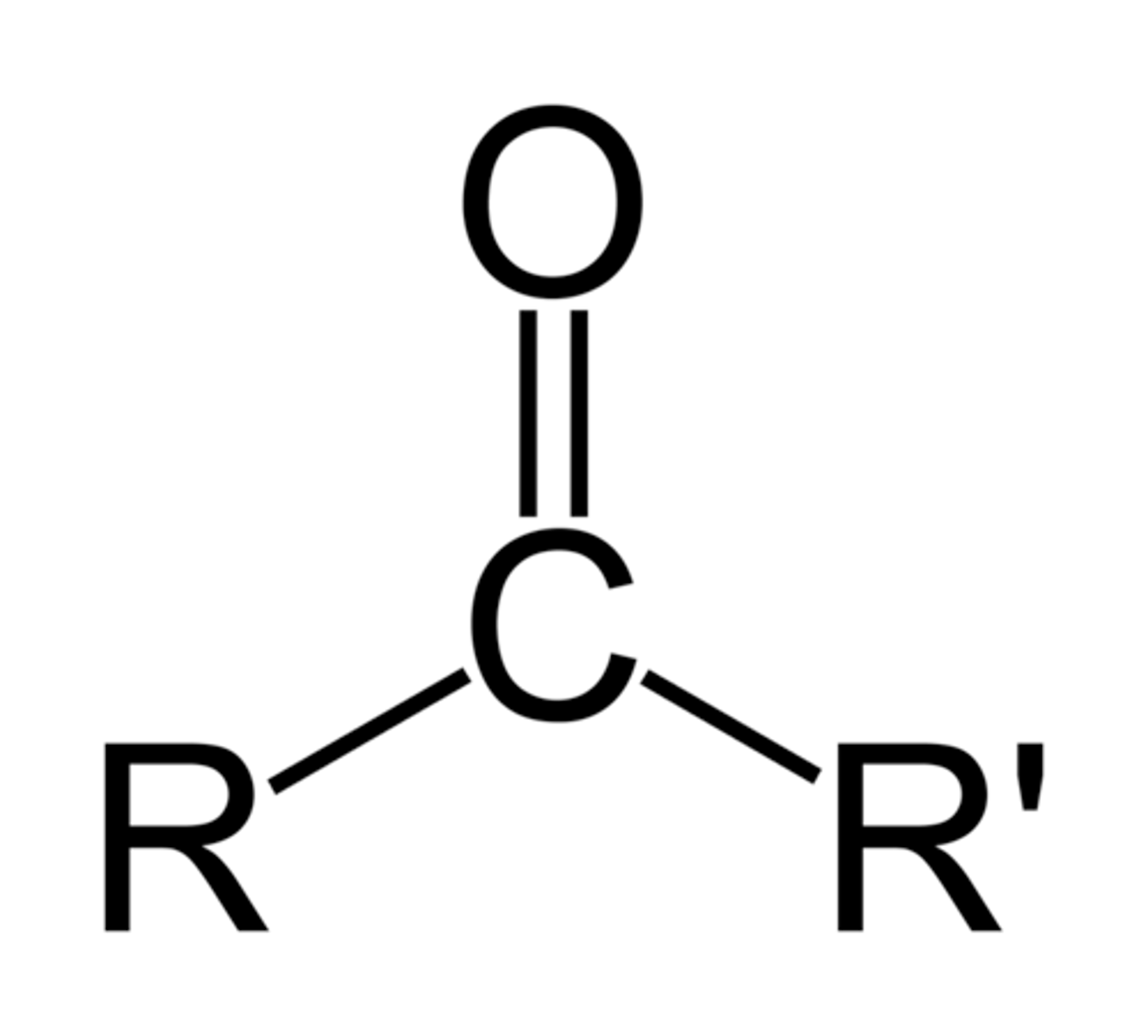
What is the formula for the carbonyl biofunctional group?
>CO
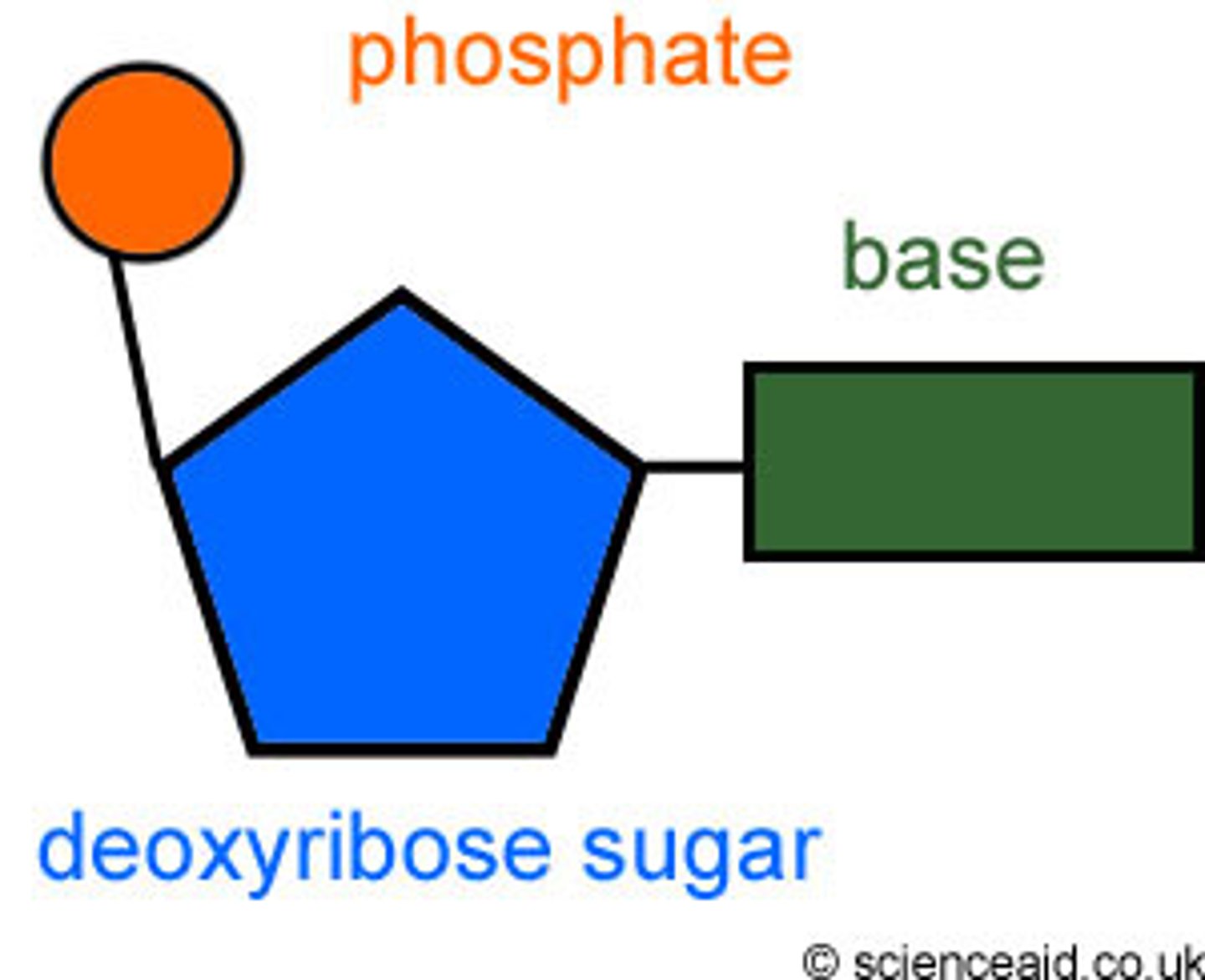
A nucleotide is made up of what three parts?
Nitrogen Base, Pentose Sugar, Phosphate Group
What are the four important macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids

What are the properties of water?
Liquid at room temperature & highly electronegative
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ——> 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
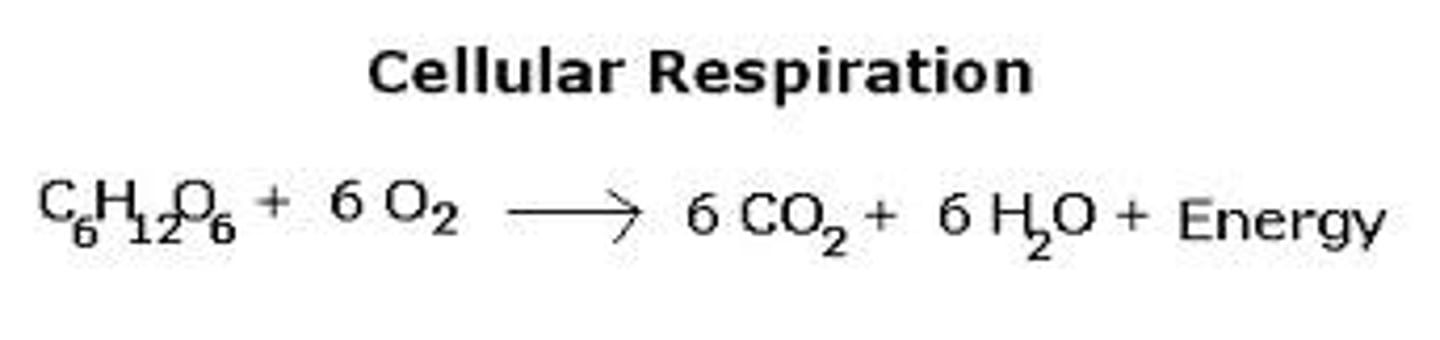
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2.
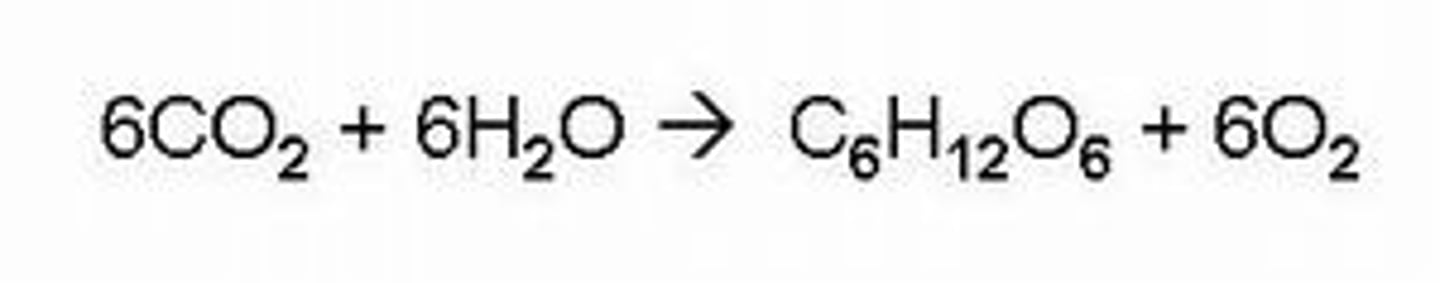
What is the importance of carbon dioxide?
Waste product of cellular respiration, starting molecule in photosynthesis

What is the importance of oxygen?
Facilitates cellular respiration, eliminate "free radicals" (products of biochemical reactions, which can harm cells)

What do the marcomolecules have in common? (Hint: Two things.)
All are much larger than the macromolecules in terms of molecular size, and are needed in relatively small amounts in the body.
What is the importance of carbohydrates?
Short term energy source (mono + disaccharides), long term energy source (polysaccharides), plant structural component (cellulose)
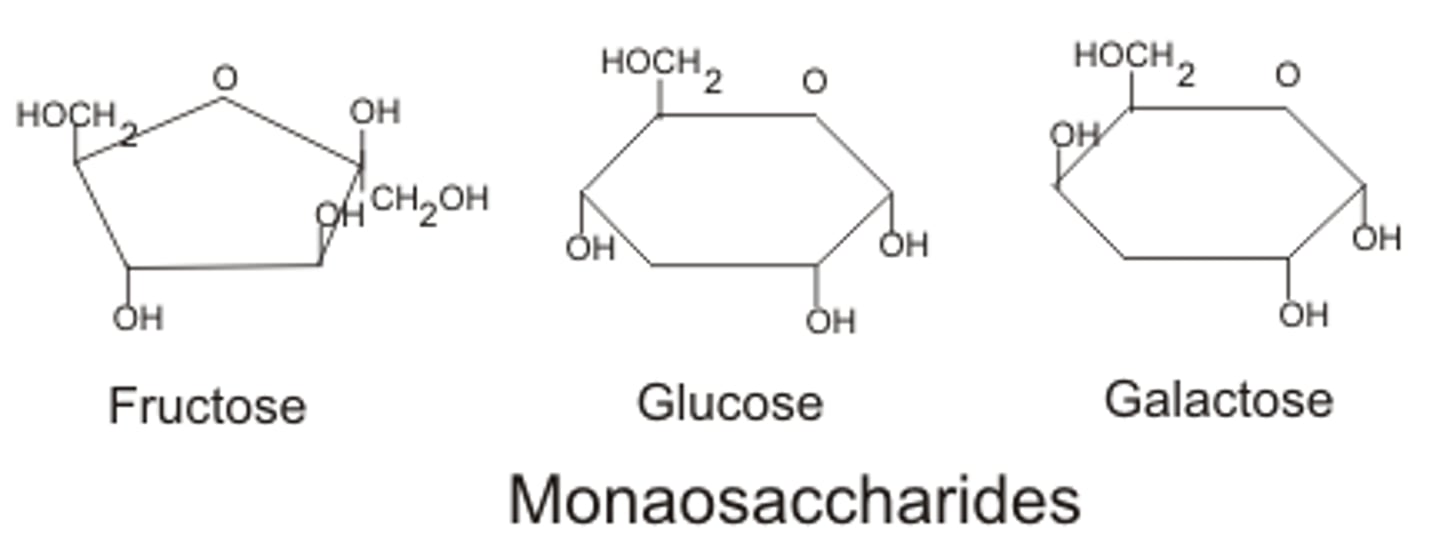
How can you tell the difference between the three monosaccharides based on their chemical structure?
Fructose is five-sided, glucose has an —OH group on the bottom left, galactose has an —OH group on the top right instead
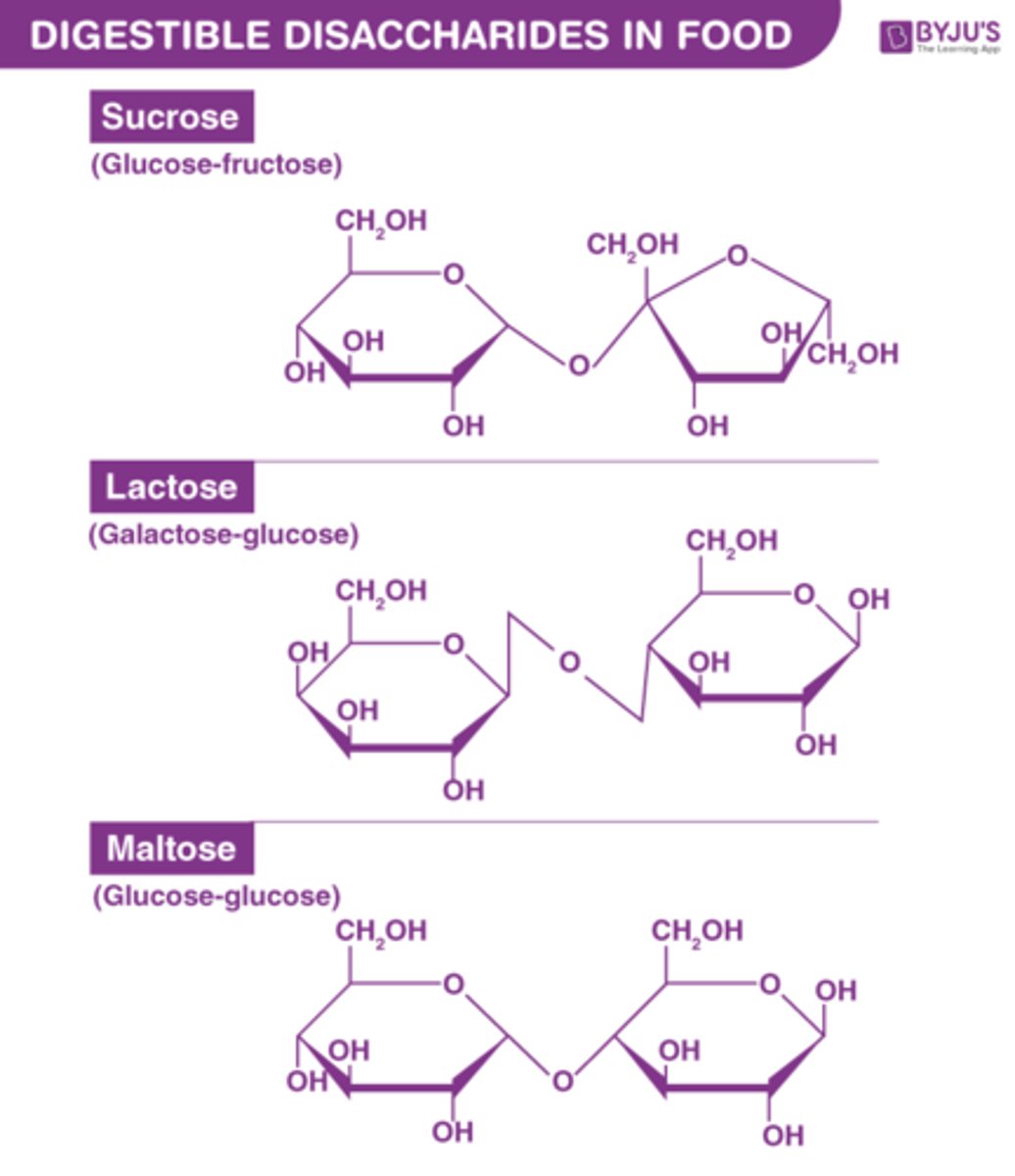
What are the three disaccharides, and what monosaccharides are they made up of?
Maltose (Glucose + Glucose), Lactose (Glucose + Galactose), Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose)
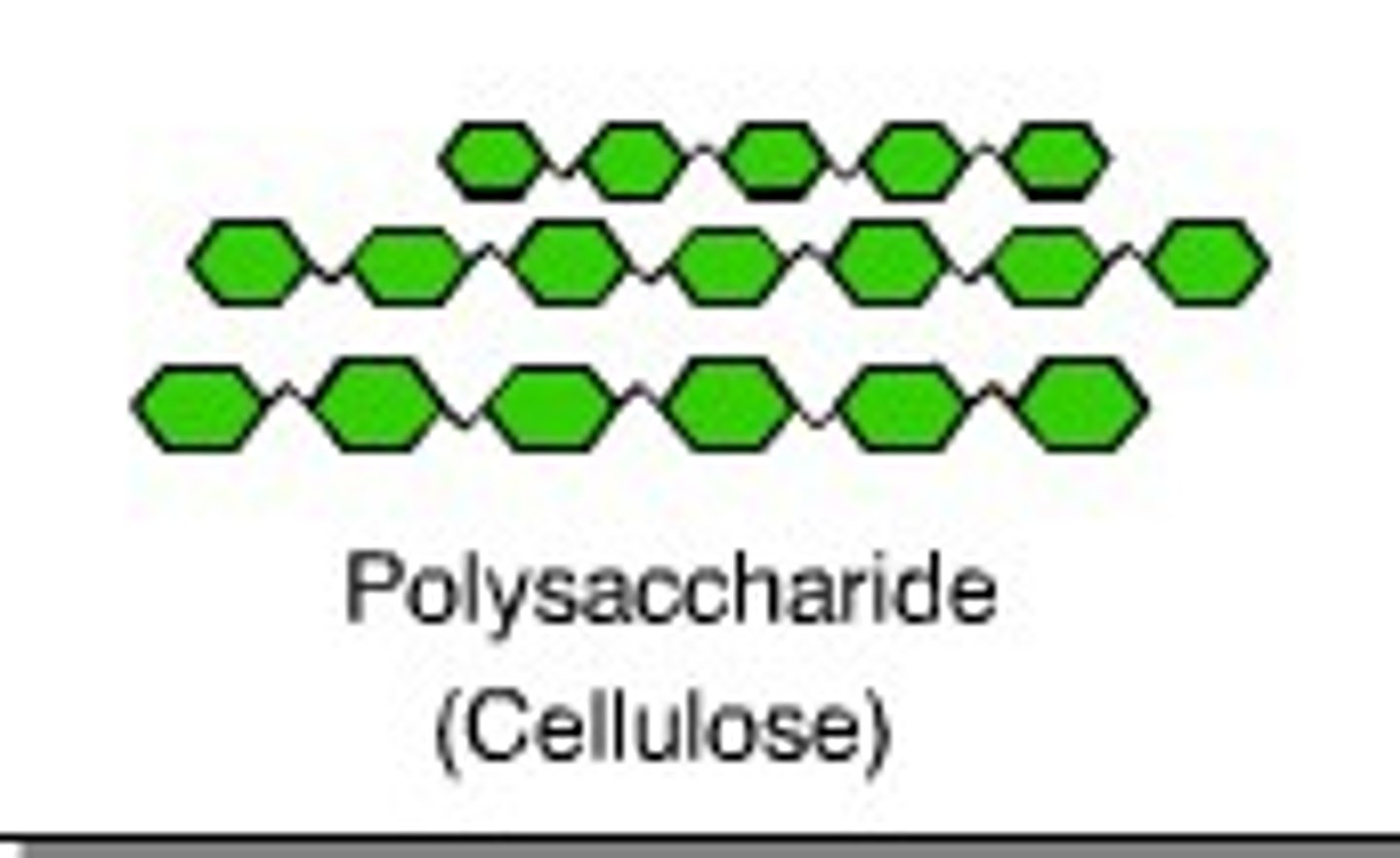
Which polysaccharides can humans NOT break down?
Cellulose
What is the importance of proteins?
Protein channels regulate entry/exit into cells, transport proteins move molecules throughout the body, structural proteins (i.e., muscles, tendons, ligaments), and surface proteins involved in the immune response
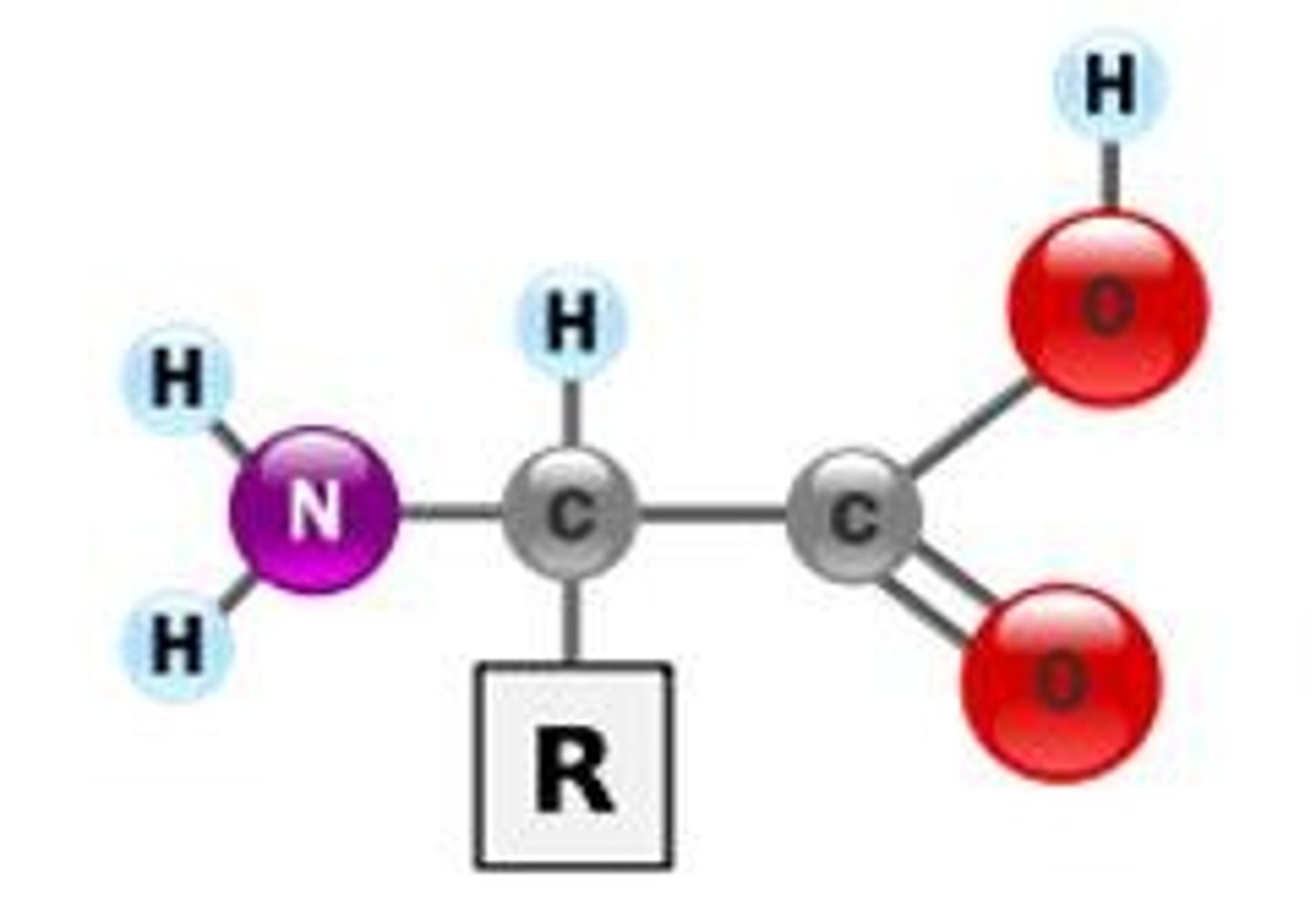
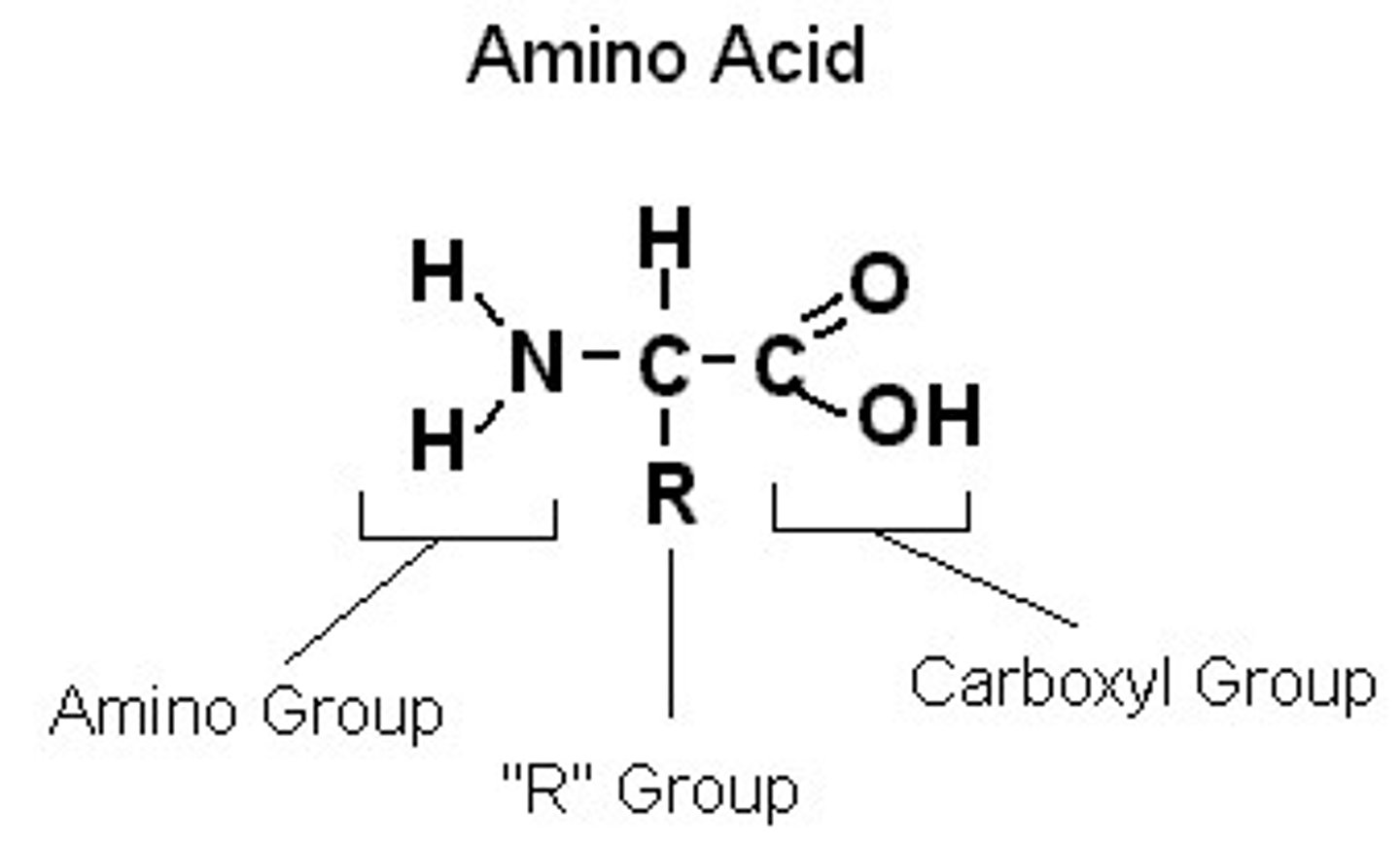
What is the structure of an amino acid (the fundamental building block of proteins)?
—NH2 amino group bonded with a central carbon bonded with a —COOH carboxyl group and the rest of the molecule
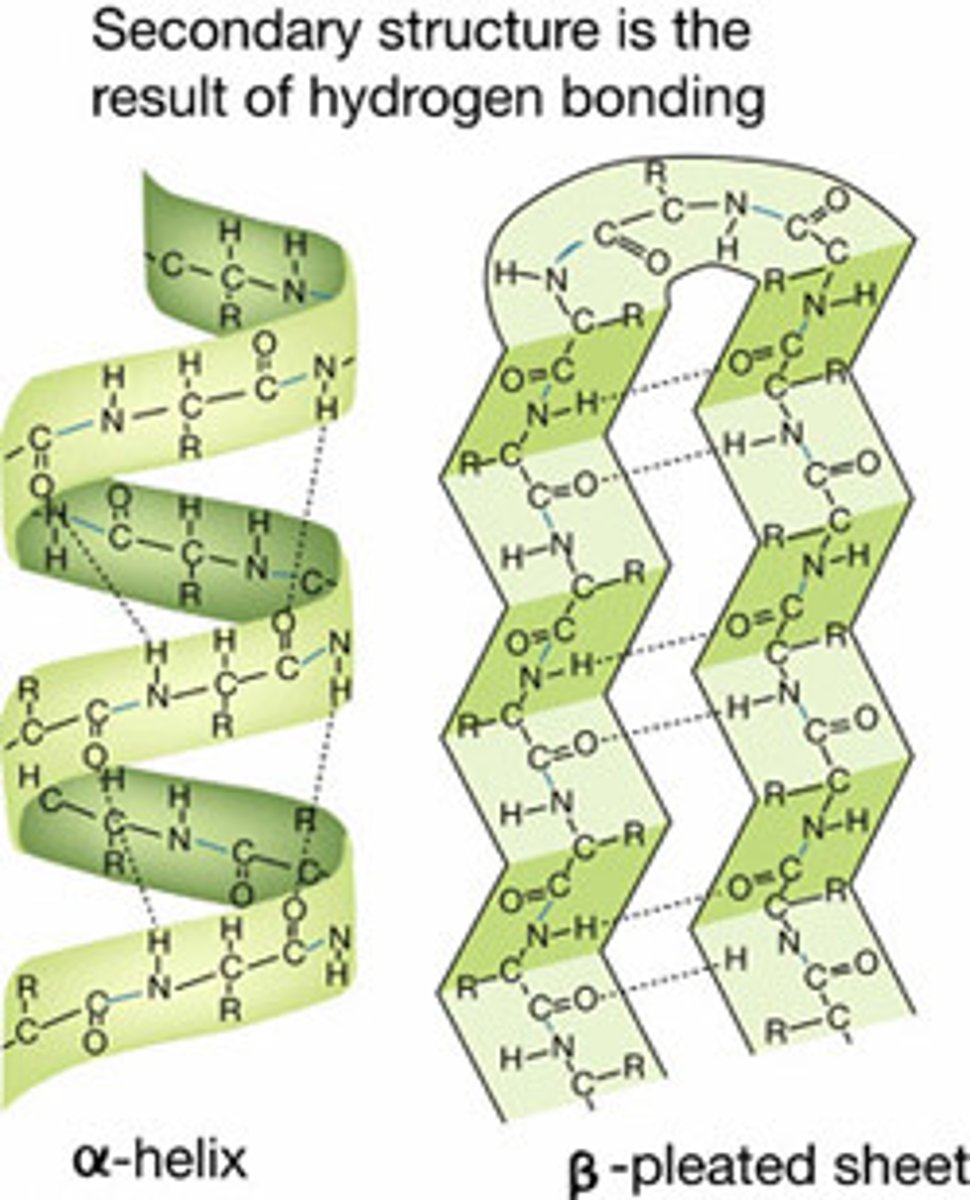
Secondary protein structures include what 2 primary shapes?
Alpha helixes & Beta sheets
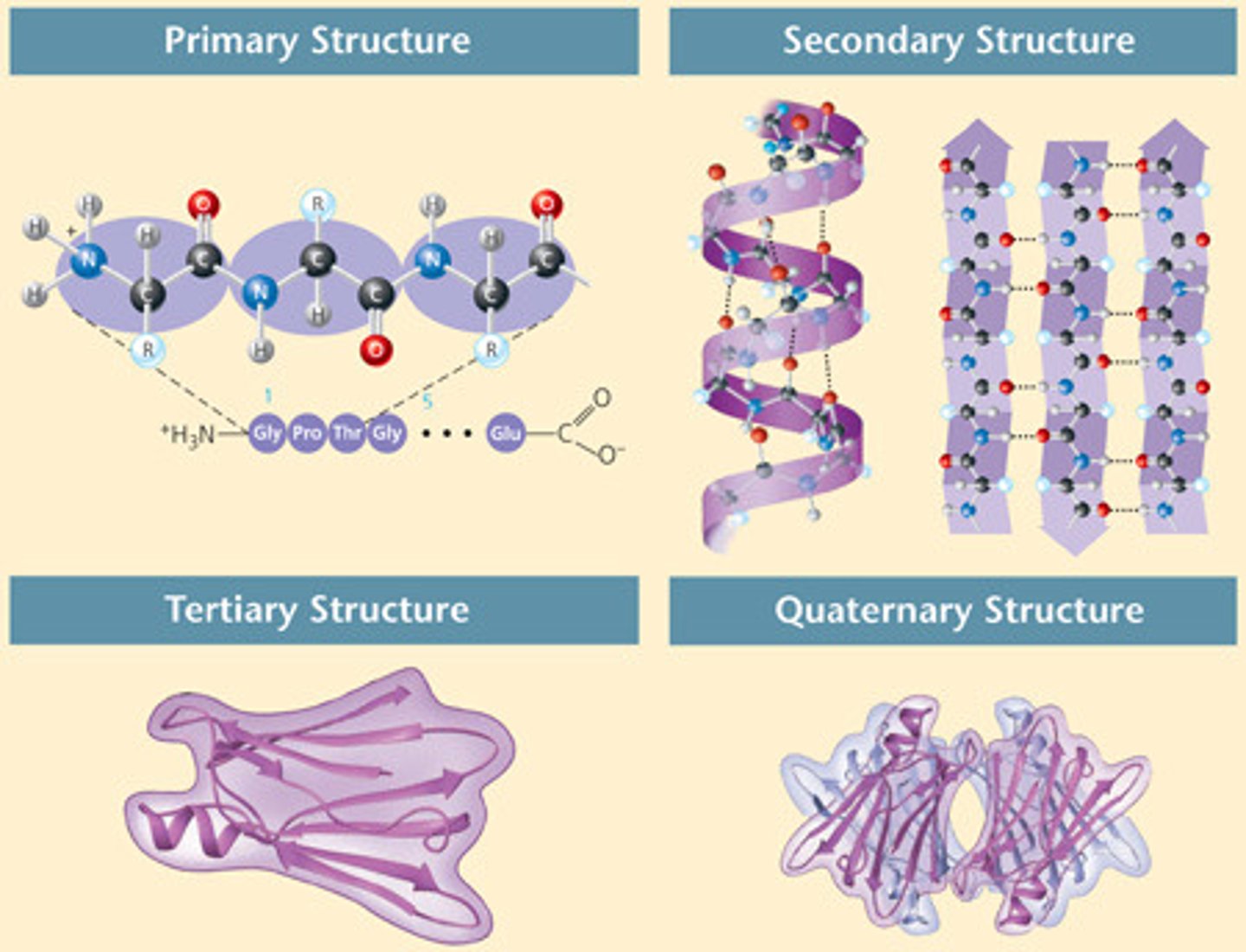
What are tertiary & quaternary protein structures?
Tertiary: combination of secondary structures interacting; Quaternary: combination of tertiary structures interacting
What are the functions of lipids?
Long term energy storage (adipol cells, adipol tissue), organ protection, starting molecule for modification into steroids/hormones

What is a fatty acid?
Hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end, which can be broken down to release energy (Fatty acid metabolism)
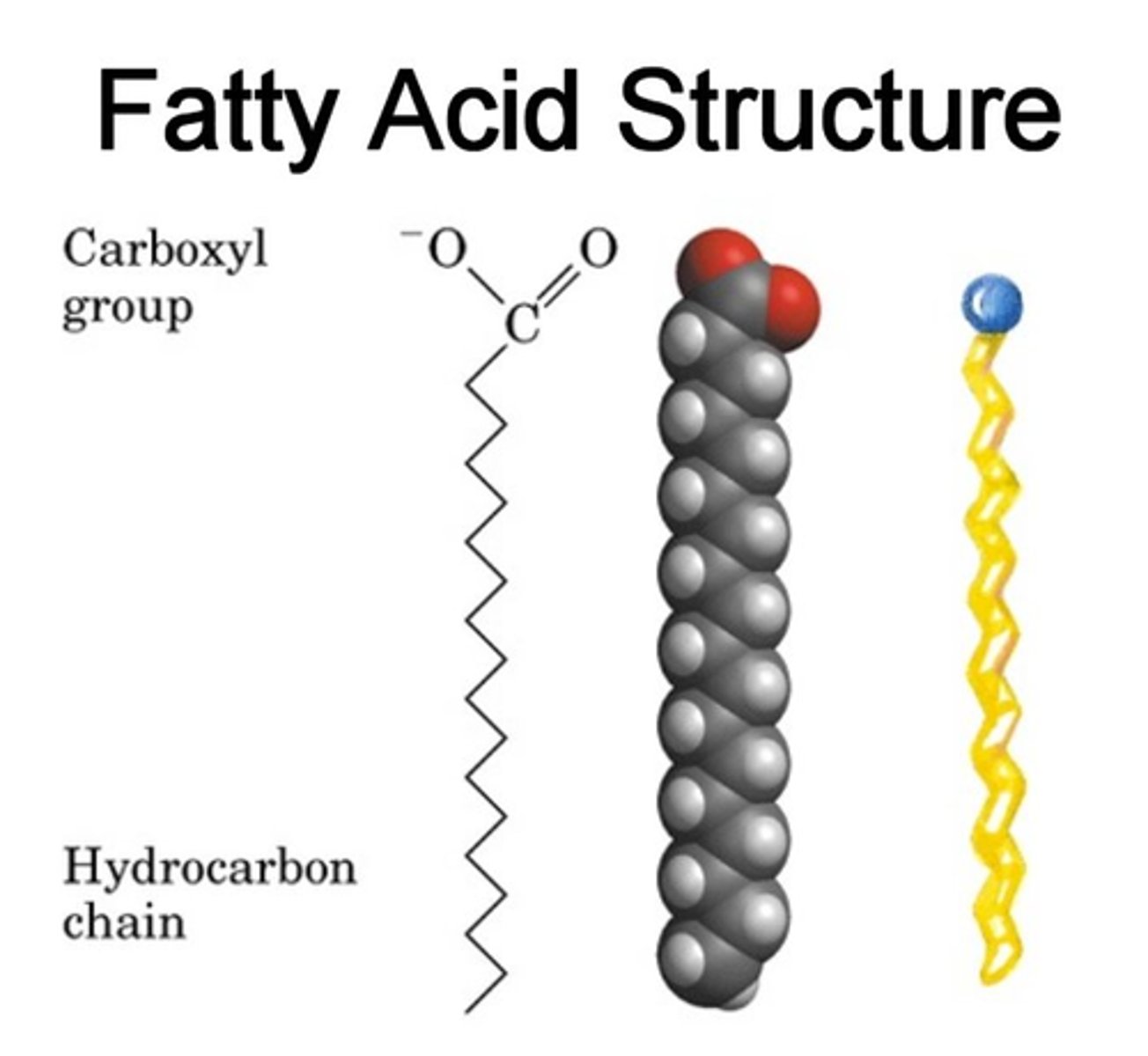
How many carbons can a fatty acid chain be made up of?
20 - 80 carbons
Why are saturated fats called saturated?
All carbons saturated with hydrogen, no carbon double bonds present
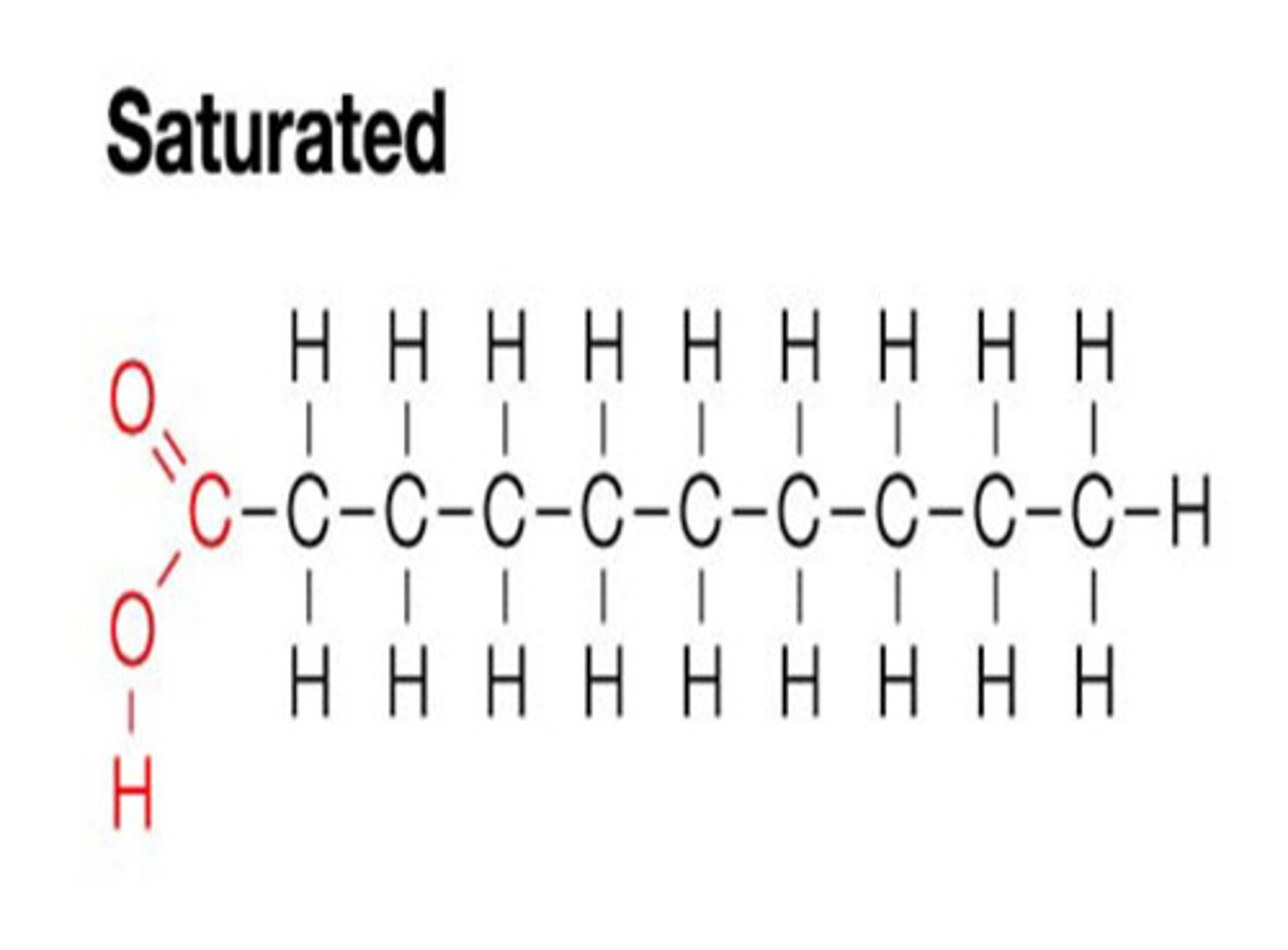
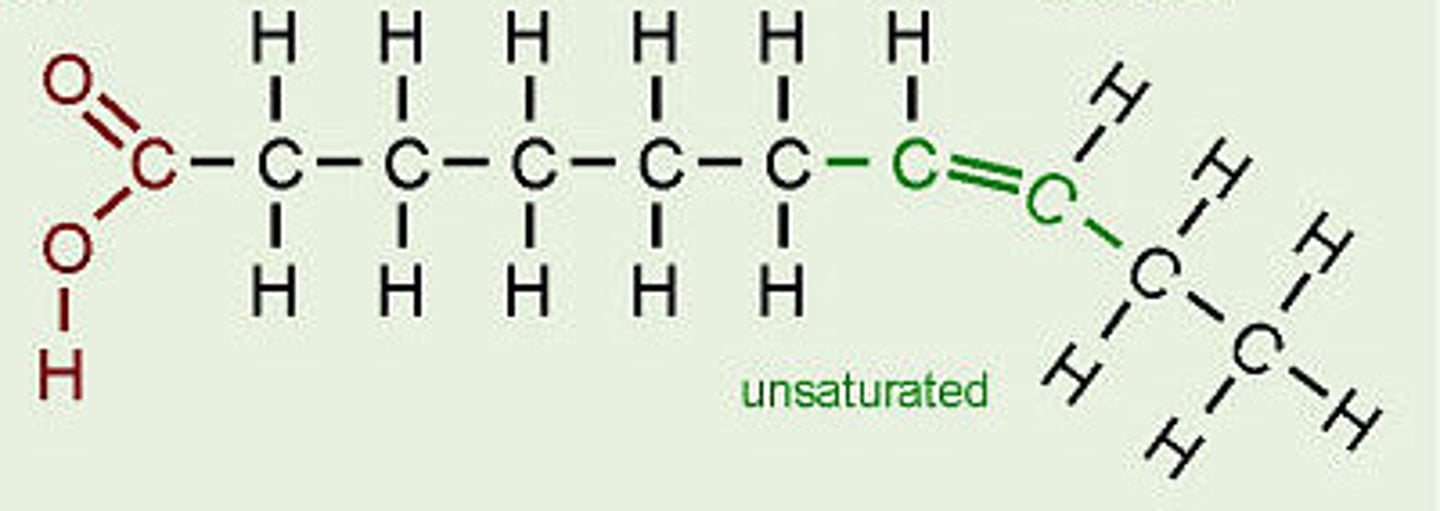
Why are unsaturated fatty acids called unsaturated?
One or more carbon double bonds present, limiting the amount of hydrogen present and thus reducing total energy units available
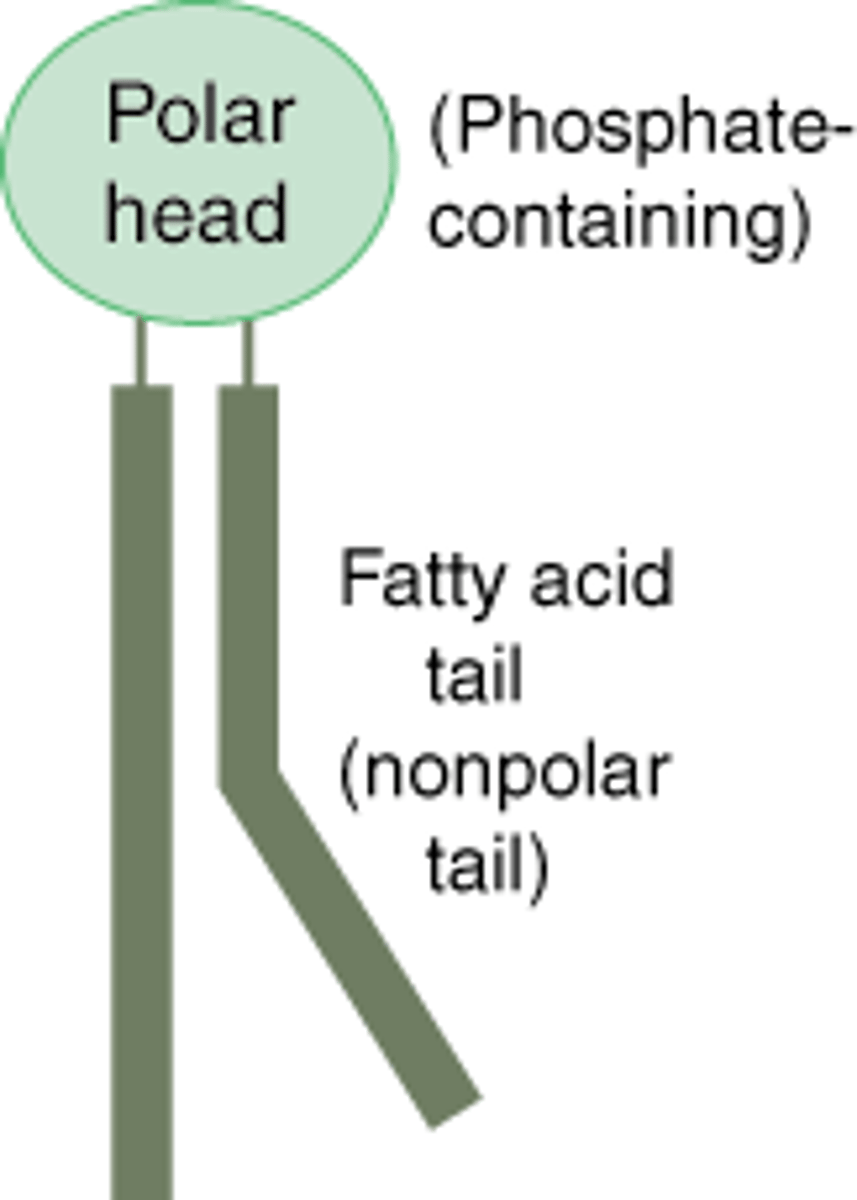
What is a phospholipid, and what is their most important property?
a modified lipid where the glycerol is bonded to a phosphate group, making a molecule responsible for forming biological membranes; important property is having a polar phosphate head and non-polar fatty acid tail
What is the function of nucleic acids?
DNA stores genetic info, RNA does protein synthesis

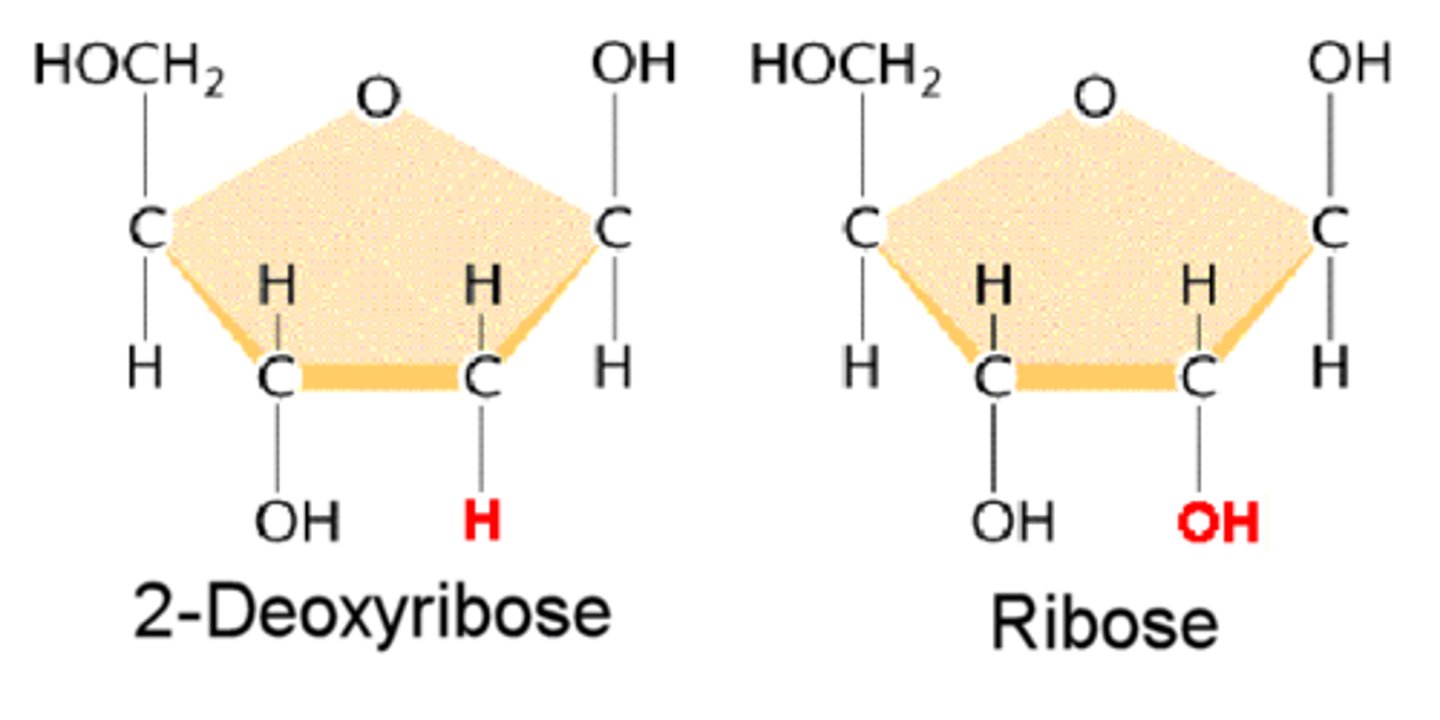
What are the sugars that make up the DNA and RNA nucleotides?
DNA: 2-deoxyribose; RNA: ribose
What are the two main types of cells and what are their differences?
PROKARYOTES: no nucleus, chromosomes in cytoplasm, bacteria cells; EUKARYOTES: has nucleus, chromosomes (chromatids) in nucleus, animal & plant cells
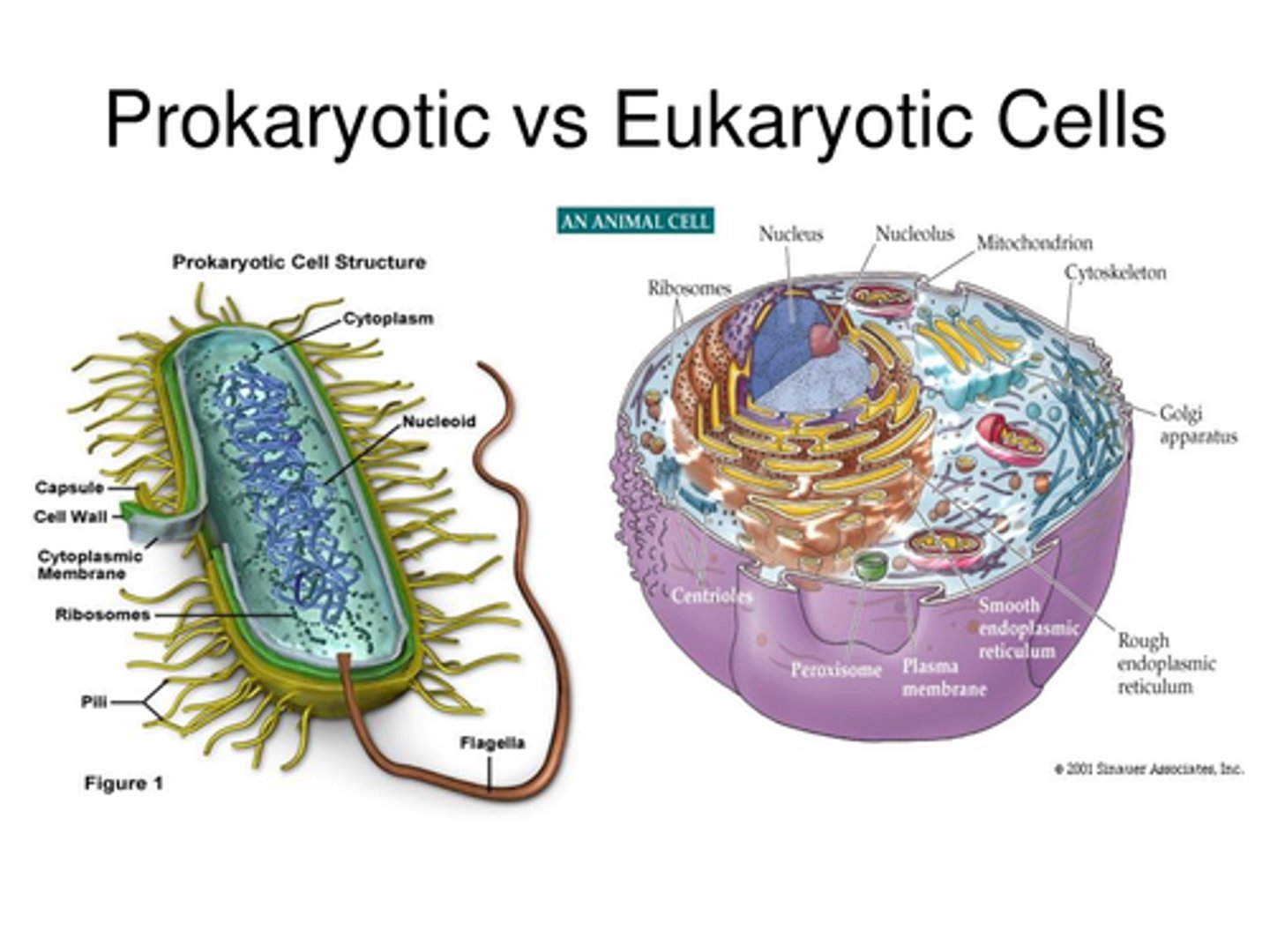
What are the two main types of bacteria and what are their properties?
ARCHAEABACTERIA: unique cell wall composition to adapt to harsh conditions; EUBACTERIA: simple cell wall composition allows for growth in more favourable environments; make up 90% of bacteria species; cell wall composition allows fast growth & metabolism
What are the four types of primitive archaeabacteria?
Halophiles (salt-loving), Methanogens (methane-loving), Acidophiles (low-pH-loving), Thermophiles (like high temps, +40ºC)

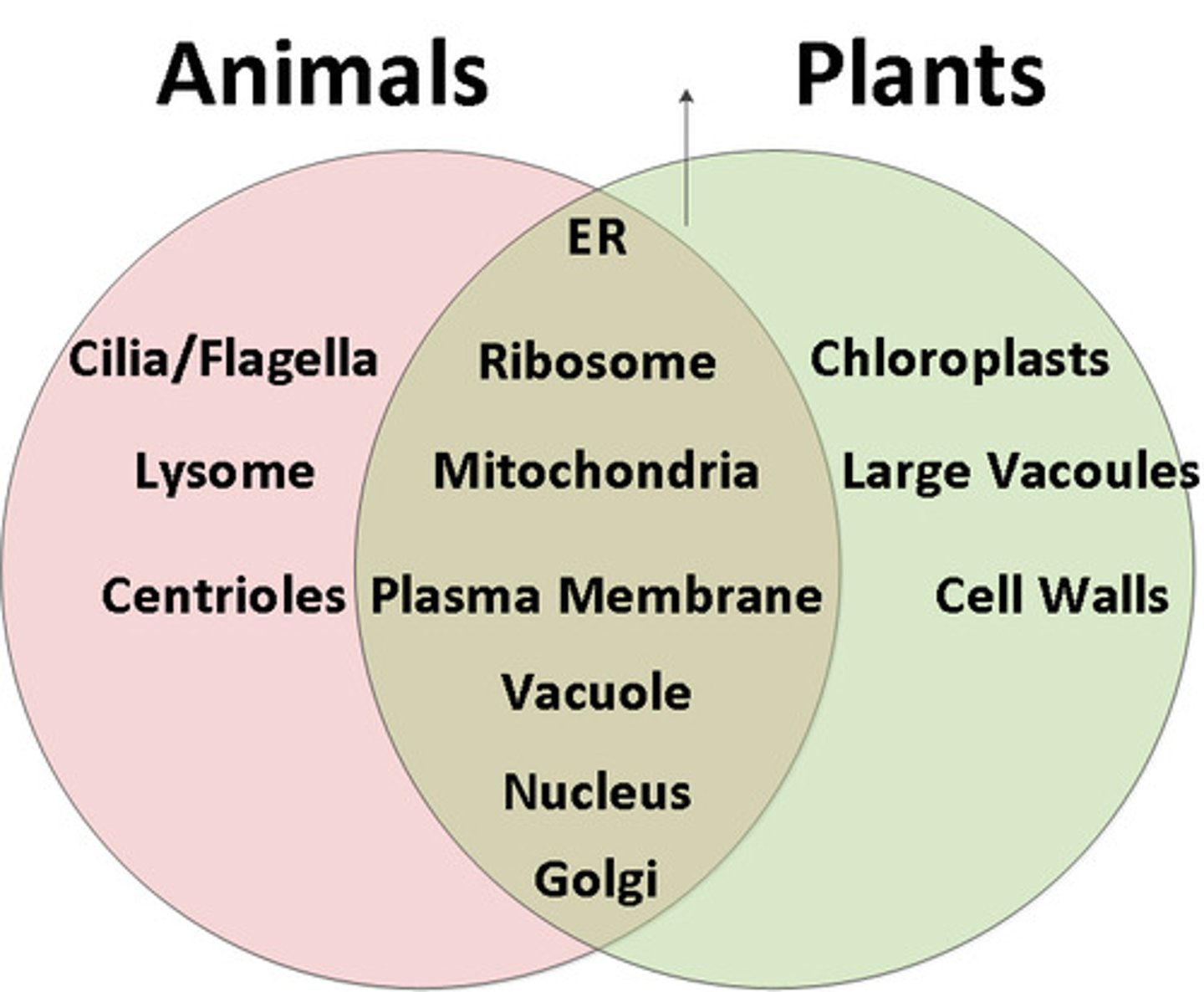
What are the differences between plant & animal cells?
PLANT CELLS: Contain a cell-wall & photosynthesis-specific organelles; ANIMAL CELLS: No cell wall, digestion-specific organelles
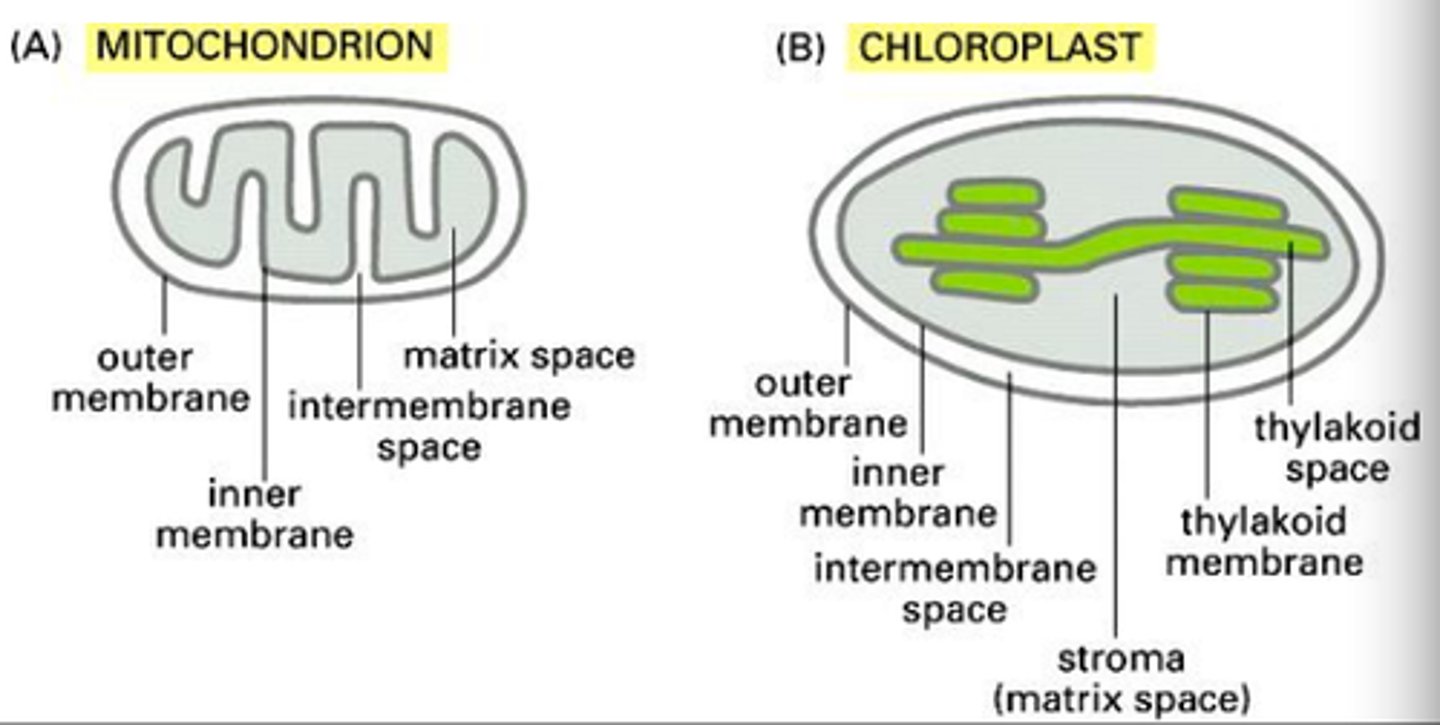
How are the chloroplasts & mitochondria unique amongst organelles?
Both organelles resulted from symbiotic relationship between primitive photosynthesizing/metabolizing bacteria and primitive eukaryotic cells
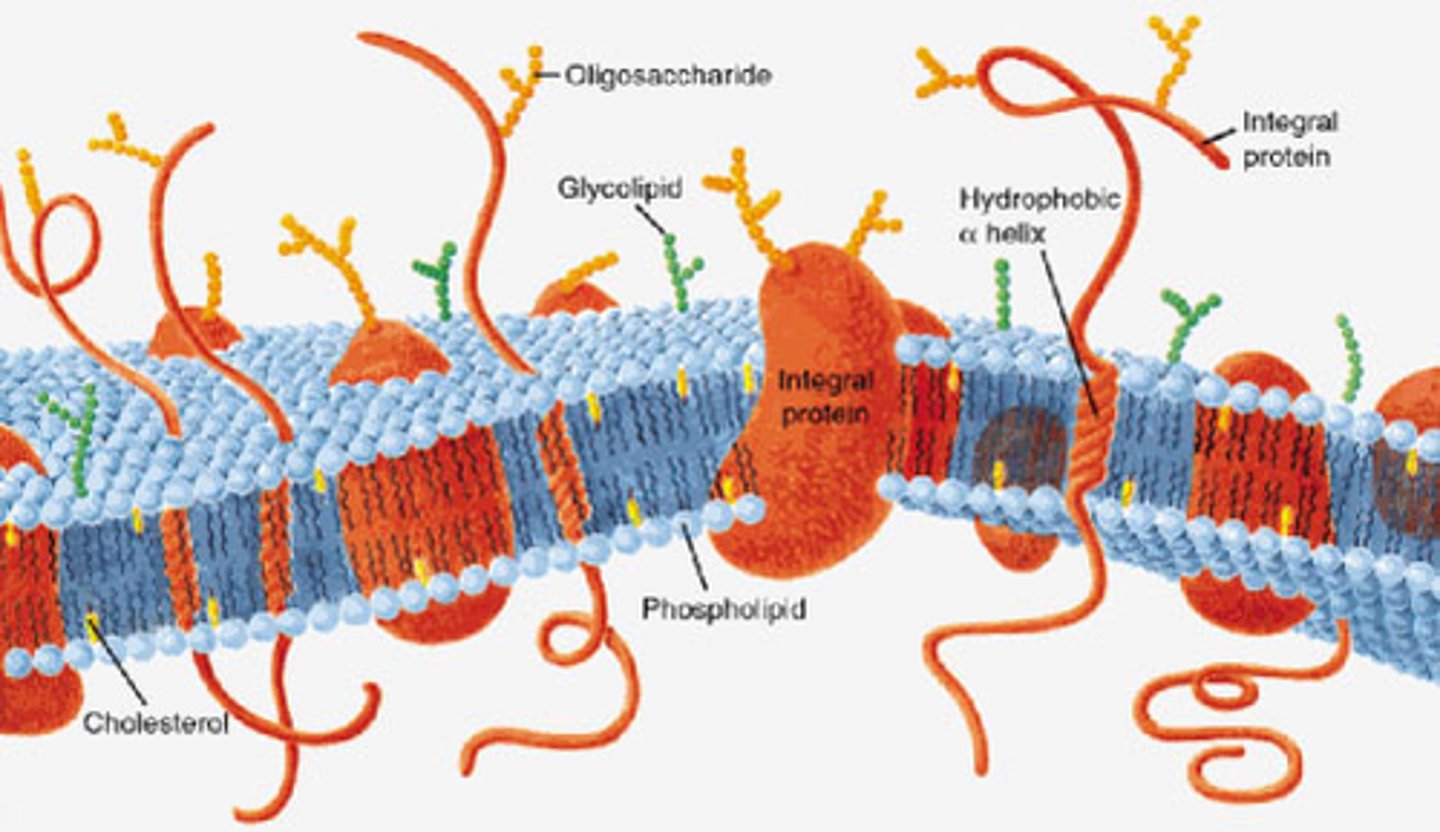
What is a plasma membrane made up of?
phospholipid bilayer with various proteins and other molecules embedded within
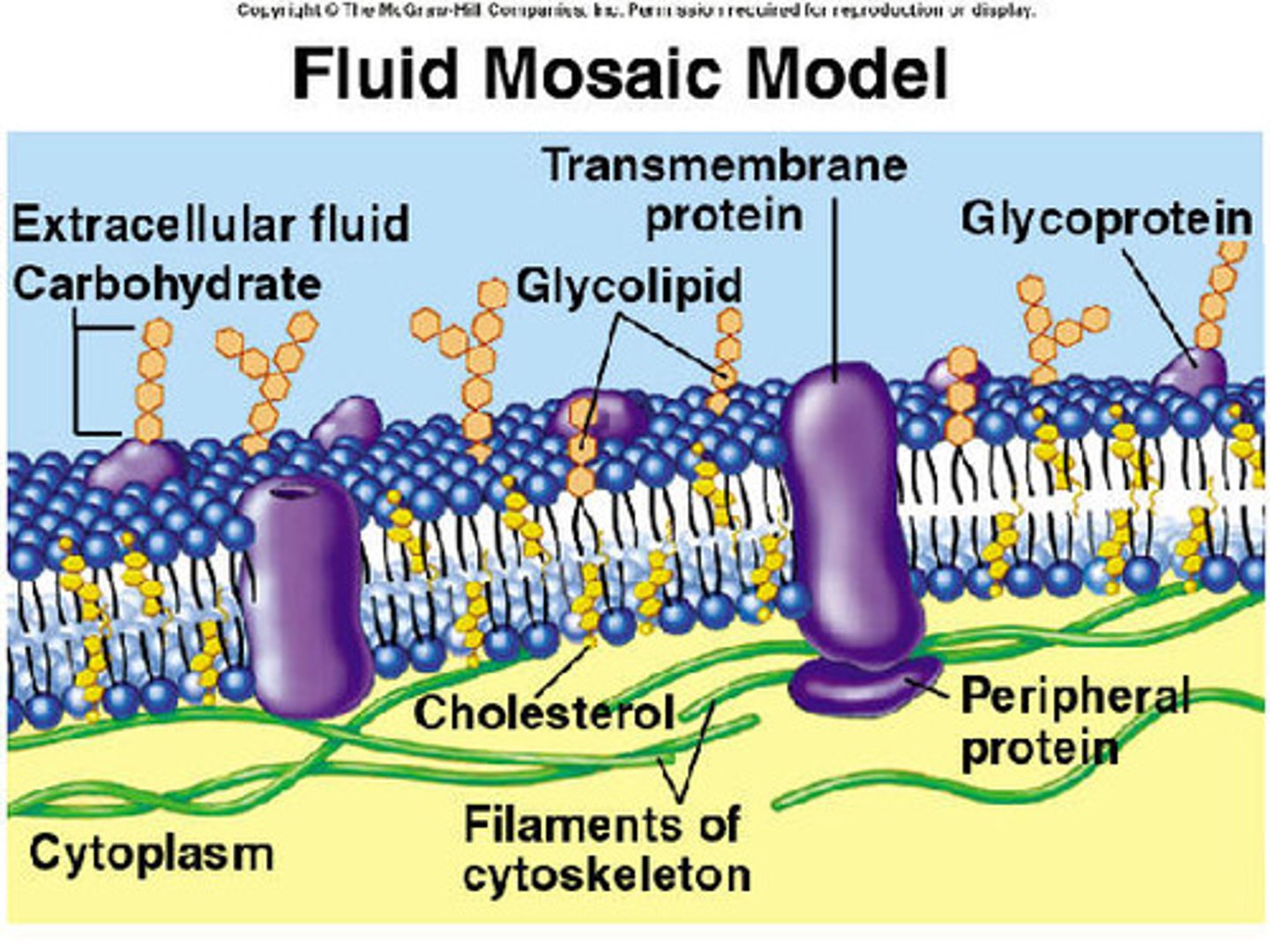
What are the objects embedded on and/or within the plasma membrane, and what are their functions?
Transport proteins (moves molecules in/out of cell), Globular proteins (anchors in cell membrane to help in cell adhesion), Glycoprotein (for the immune system to recognize 'self' cells), Carbohydrates (arrangement indicates if cell belongs to body; sequence indicates compatibility), Cholesterol (keeps membrane fluid), Glycolipids (attaches to ECF molecules), Peripheral protein (allows cell organelles to bind to inner membrane), Integral protein (binds hormones to alter cell physiology without entry), Cytoskeleton + Surface protein (maintains cell shape & volume) & Alpha helix protein (Cell signalling via electrical stimuli)
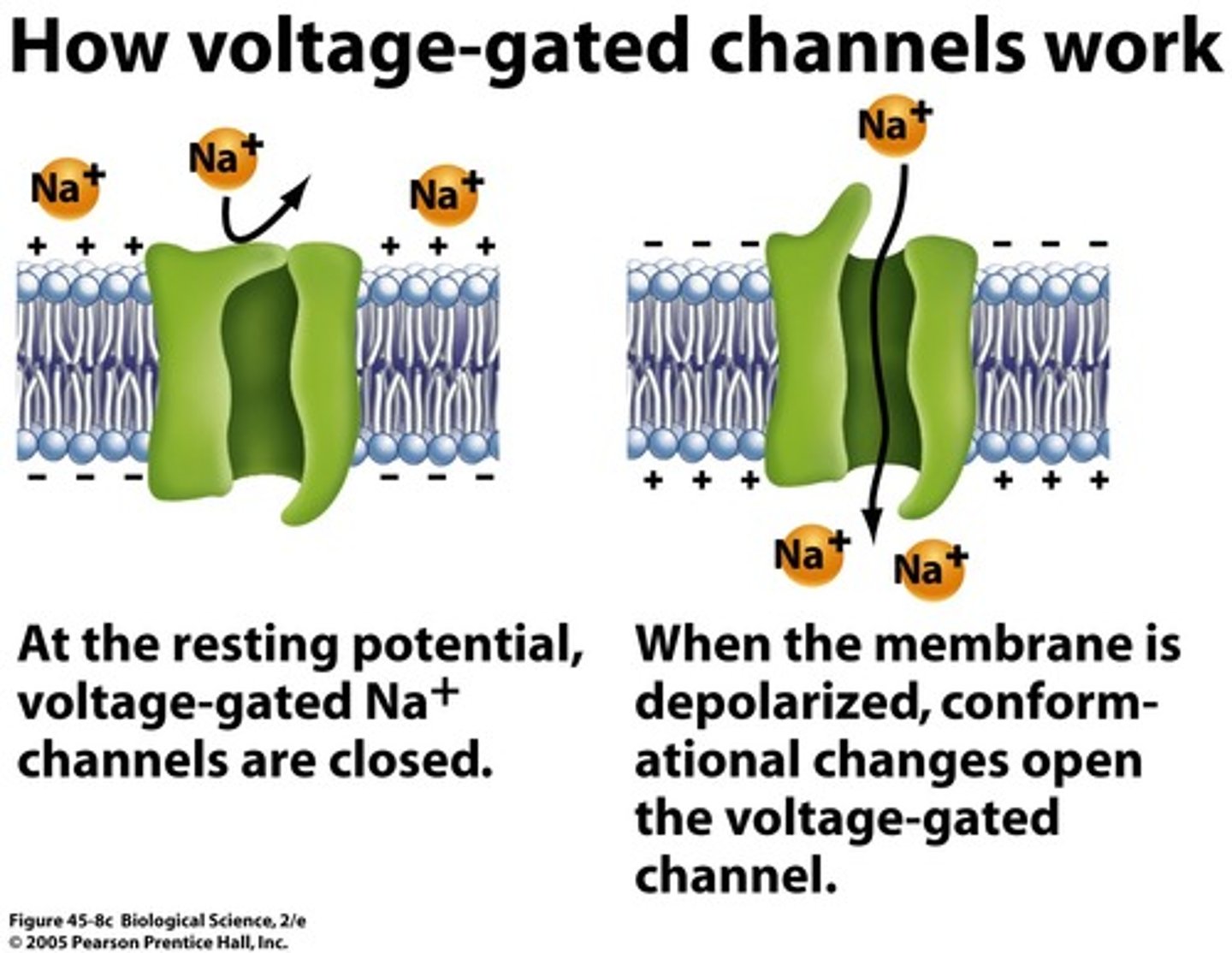
What are the four main cell channel types?
Voltage gated, Extracellular ligand-gated, Intracellular ligand-gated, stress-activated
Explain each of the four cell channel types.
Voltage-Gated: Difference in ionic concentration of + and - ions causes it to open, otherwise it stays closed; ECF & ICF Ligand-Gated: Ligands (anything that binds to the channel) binds to proteins on the channel to open it; Stress-activated: opens when membrane is deformed (i chose the image of the one that confuses me the most)
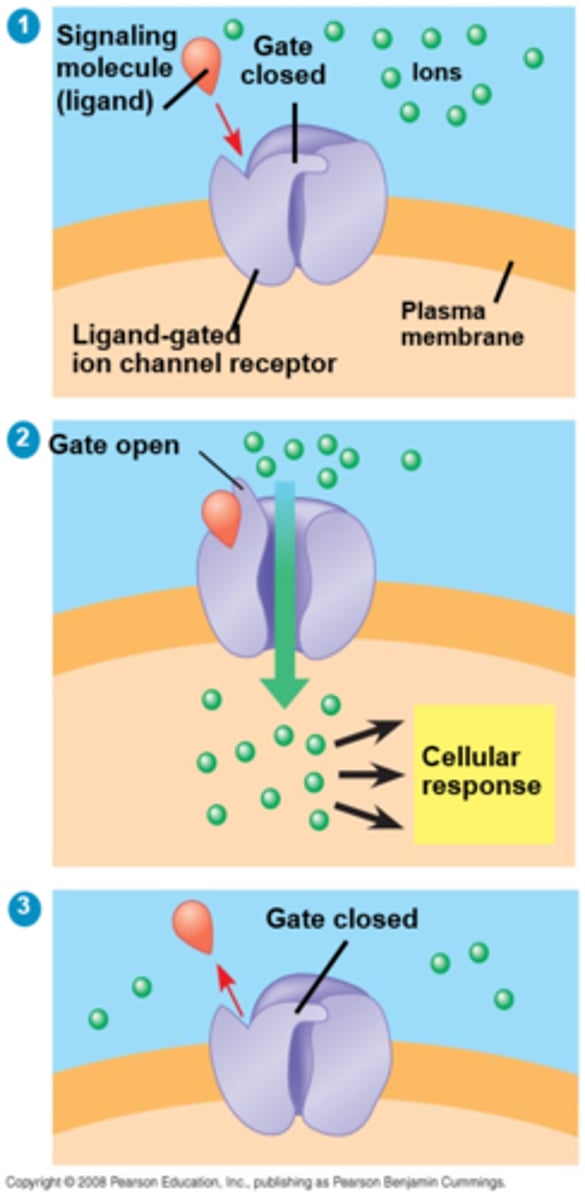
Name & explain all of the methods of cell transportation through channels.
Simple Diffusion: Uses concentration difference to move small non-polar molecules through; Ion/Water (Aquaporin) Channel: Allows polar water through membrane; Gated Ion Channels: Opened/closed by ligands; Uniporter: moves one specific molecule in one direction; Symporter: two difference molecules move in the same direction; Antiporter: two different molecules move in opposite directions; ATP-coupled: ATP used for active transport of molecules
What are the two main categories of membrane transport, and what are their characteristics?
Passive Transport: Uses no energy; relies on concentration gradient to move molecules, Active Transport: Uses energy (ATP) to move molecules against concentration gradient
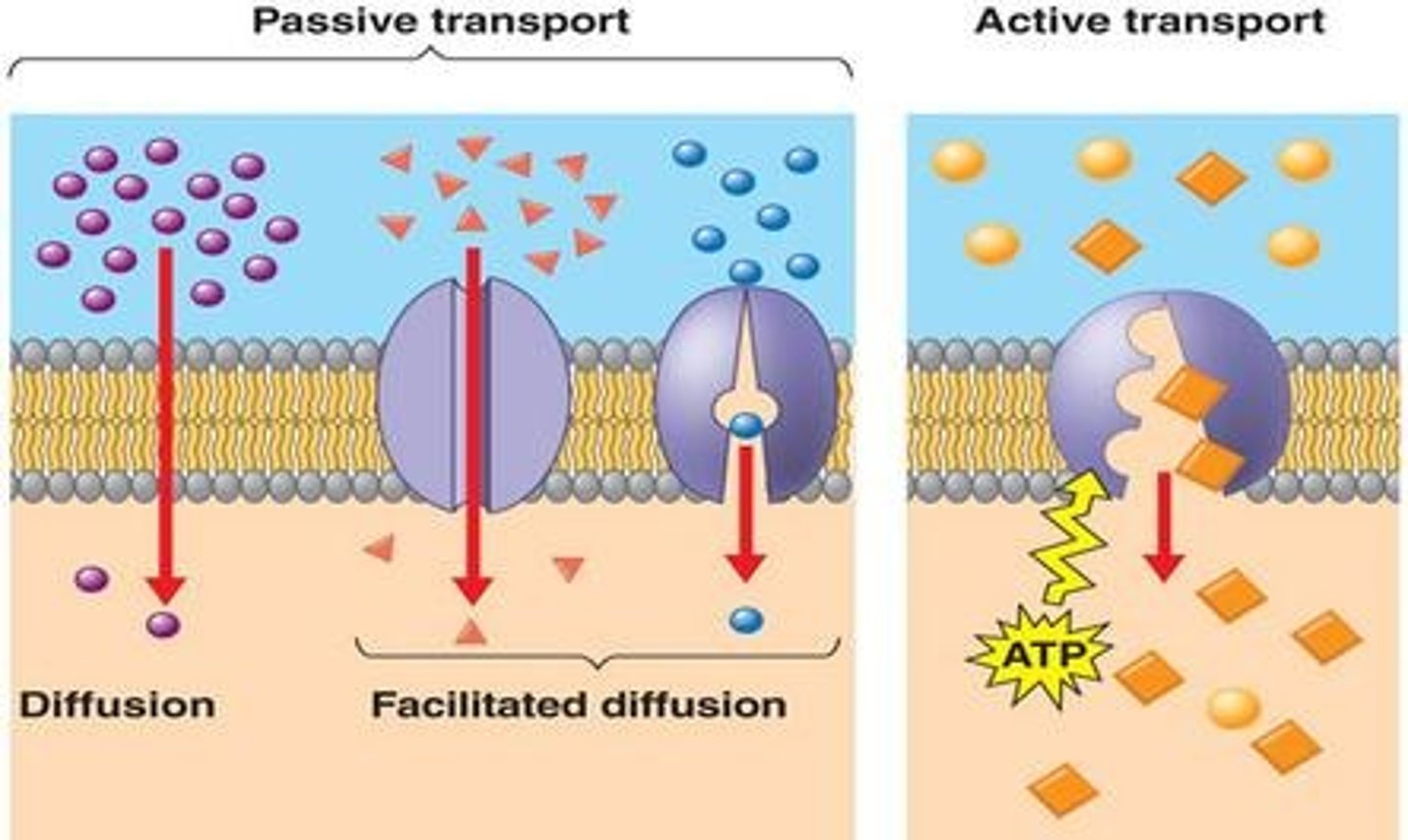
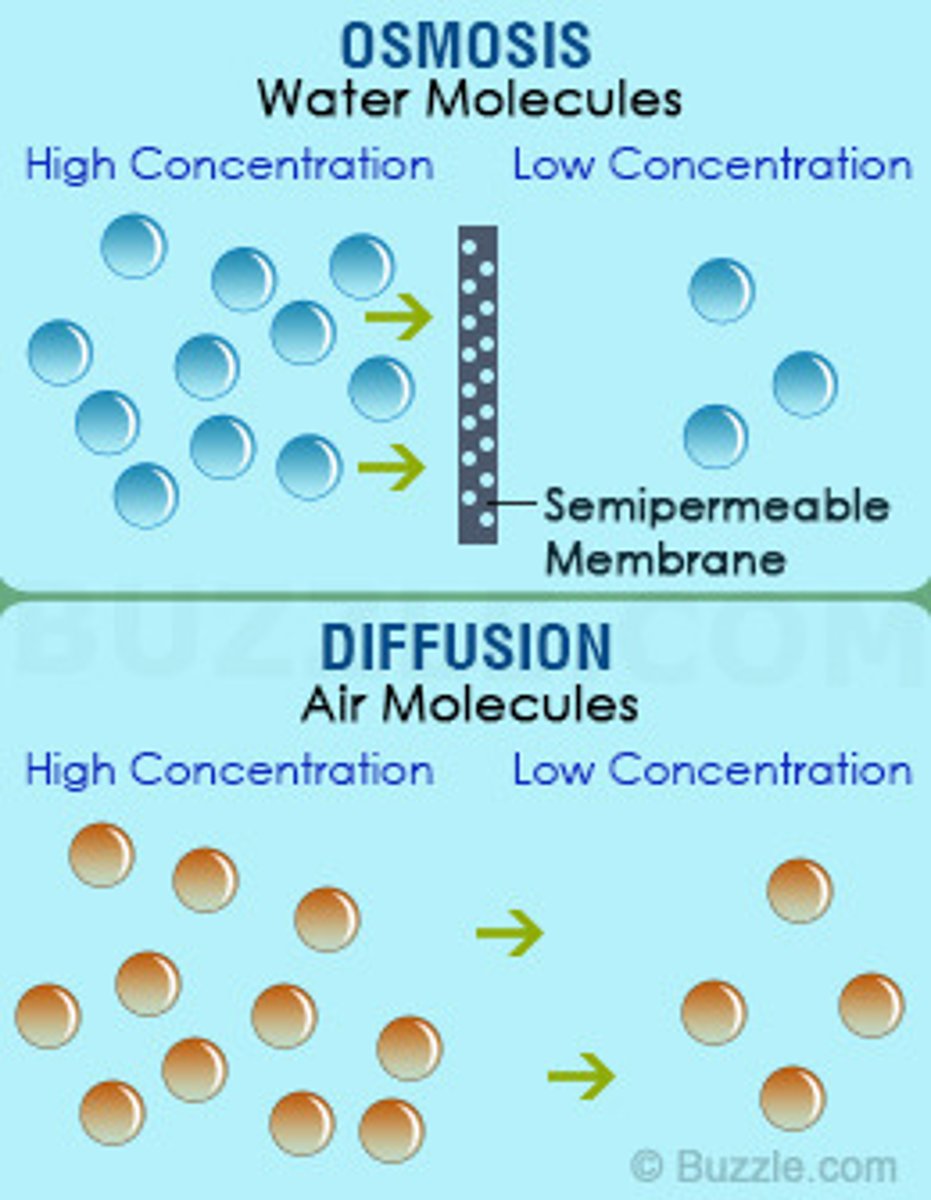
What are the two types of passive transport, and how do they differ?
DIFFUSION: movement of molecules from high to low concentration gradient; OSMOSIS: movement of water only via concentration gradient of solute in water
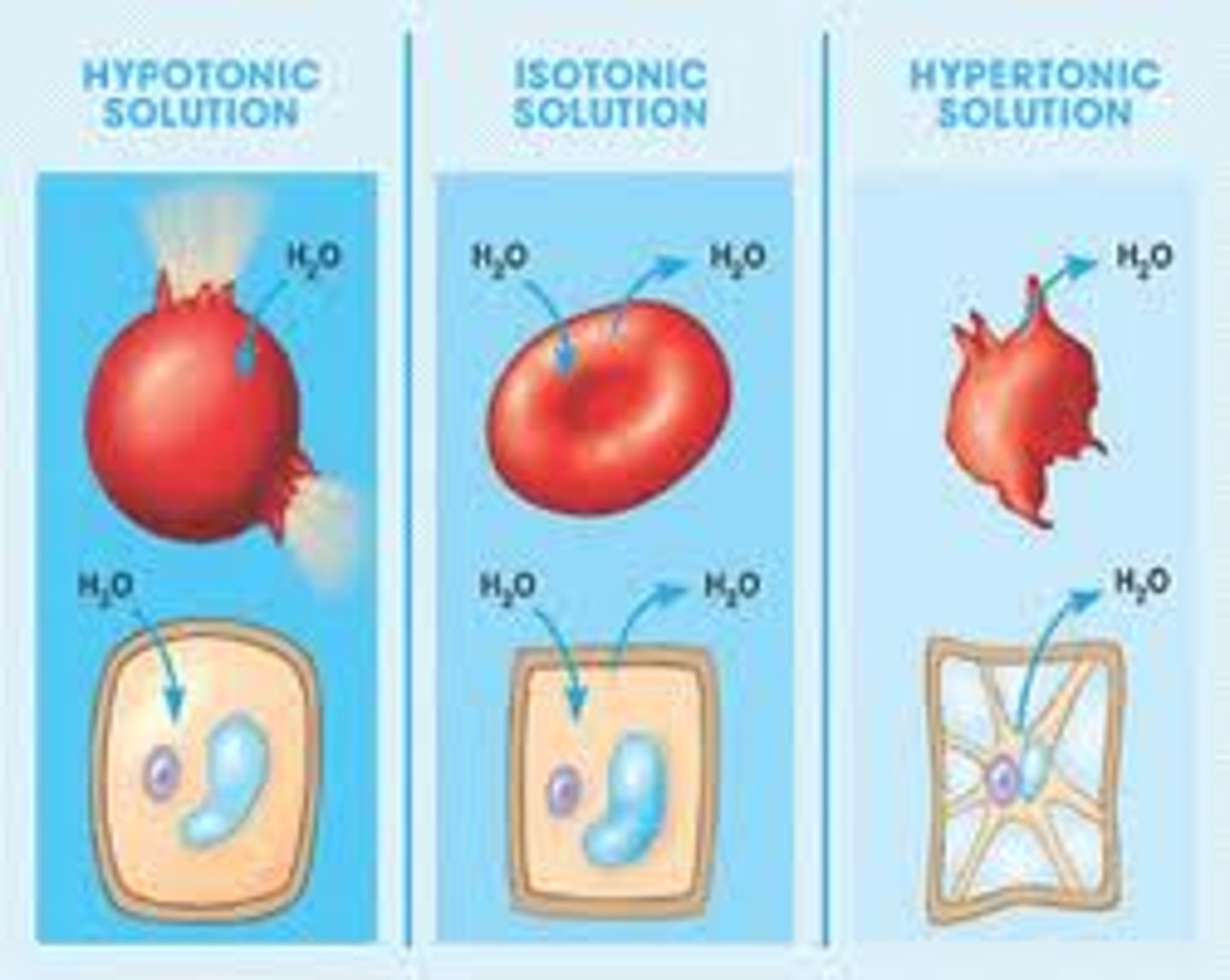
Explain the three scenarios of osmosis.
ISOTONIC: Solute concentration is equal in ECF & ICF, resulting in no water movement; HYPOTONIC: Solute concentration in ICF is greater than ECF, causing water to move in; HYPERTONIC: Solute concentration in ICF is less than ECF, causing water to move out
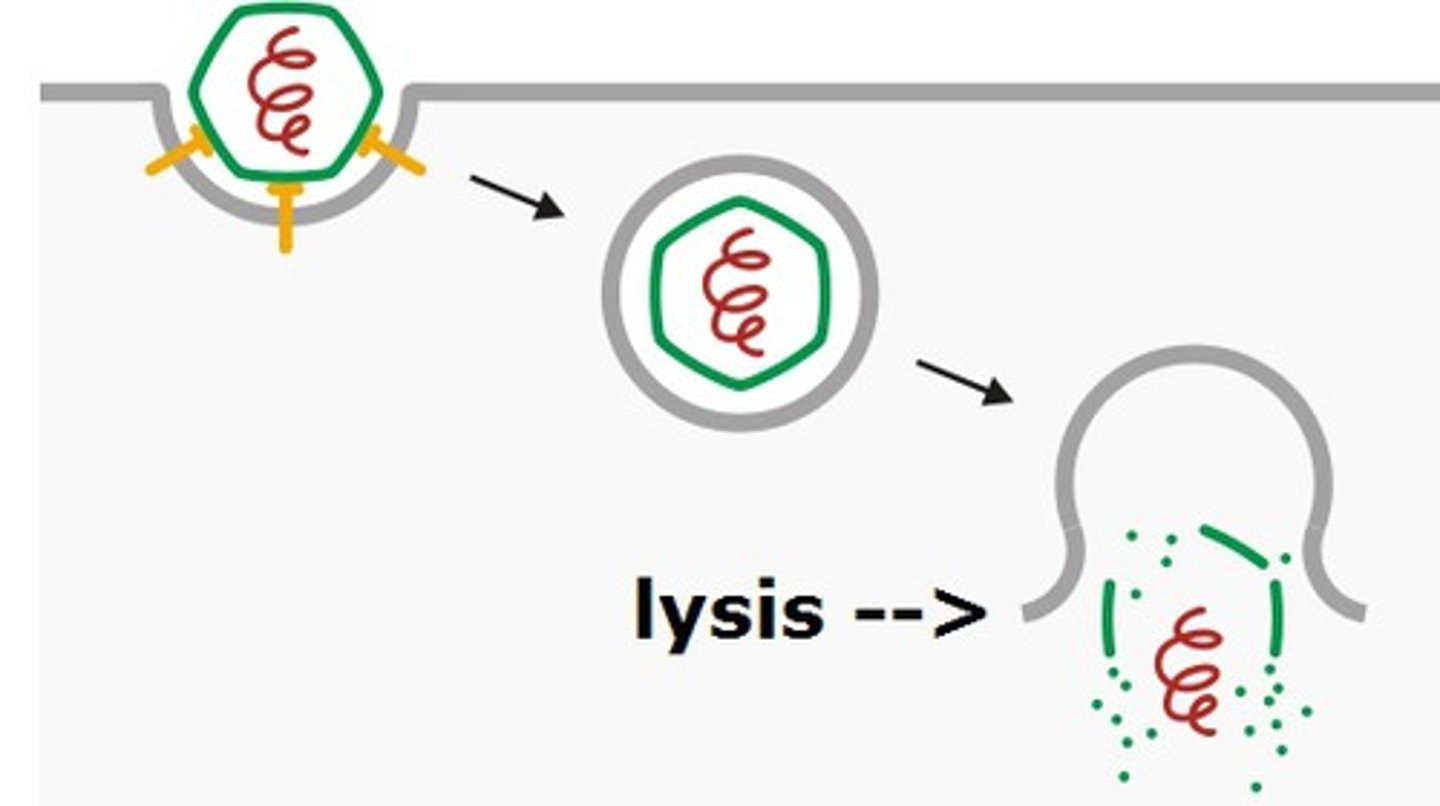
What is the name of the process where a cell bursts from excess water gained from hypotonic osmosis?
Lysis
What is the name of the process where a cell stops functioning from too much water lost from hypertonic osmosis?
Plasmolysis
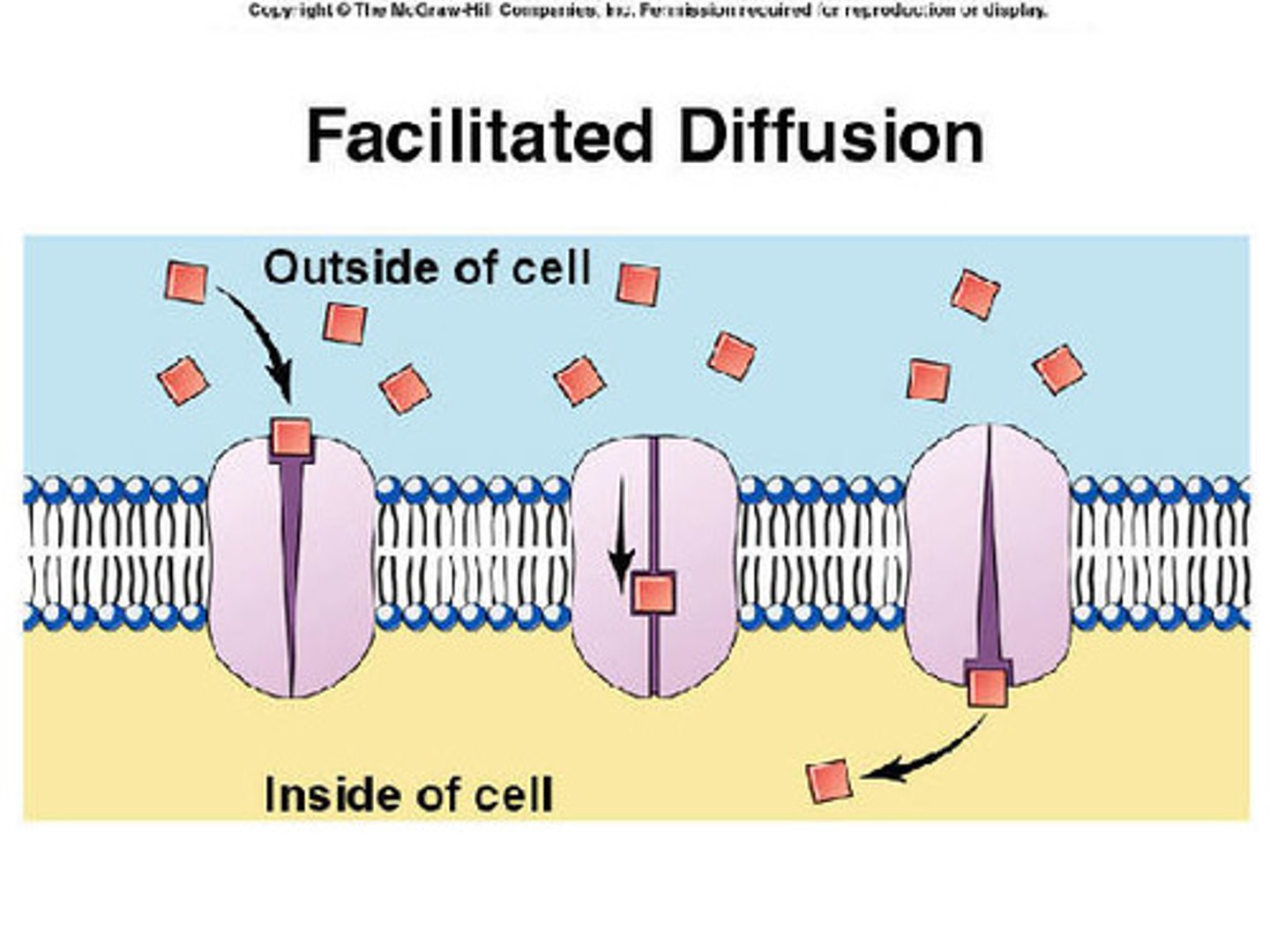
What is facilitated diffusion?
Passive movement of larger molecules across the cell membrane via transport channels (i.e., ECF ligand channels)
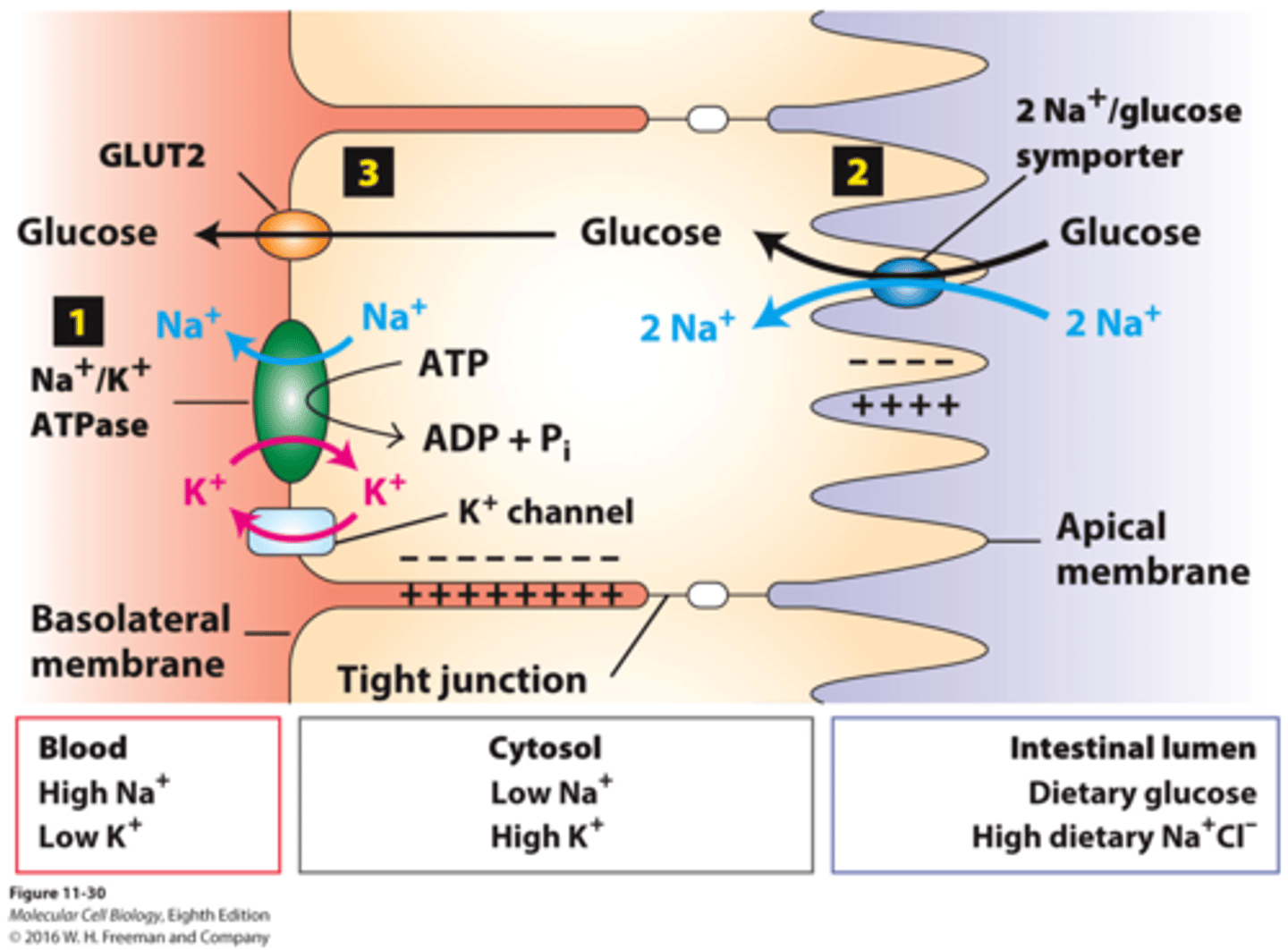
Explain the process of the active transport method: Sodium-Potassium Pump & Glucose Transporter
ATP activates (ATP -> ADP + Pi) antiporter Na-K pump to move 3 sodium ions (Na+) out and 2 potassium ions (K+) into ECF, creating concentration & electrical gradient. For the sodium ion to get back in, it binds to a glucose molecule and activates the glucose transporter. One in, negative electrical environment dislodges sodium from glucose, and the glucose has successfully been moved in
What is bulk membrane transport?
Form of active transport where ATP modifies internal cytoskeleton to create "pockets" on cell surface to take in ECF fluid and any solutes within it at the time; non-specific on what is taken in aside from receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME)
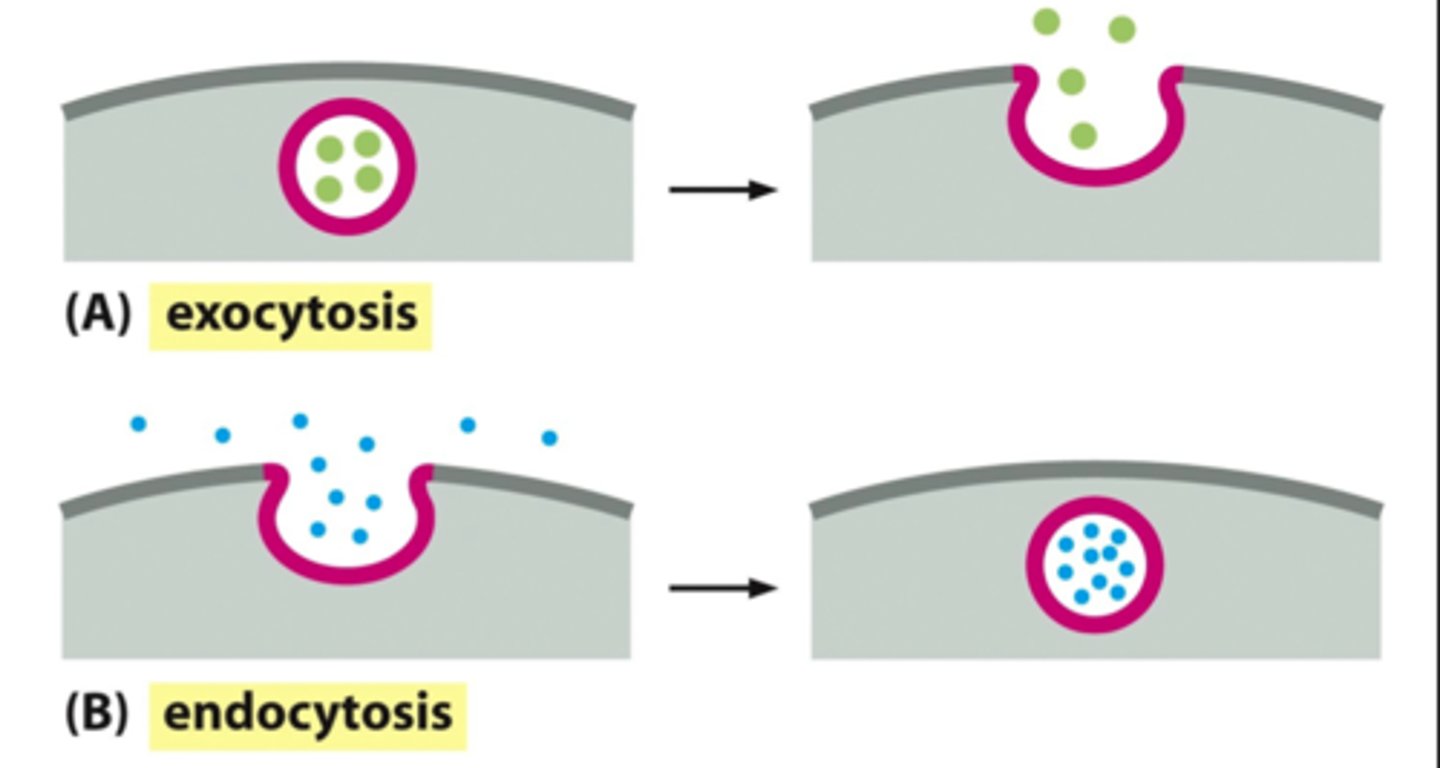
What are the types of bulk membrane transport?
ENTRY: Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis (RME), Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis; EXIT: Exocytosis
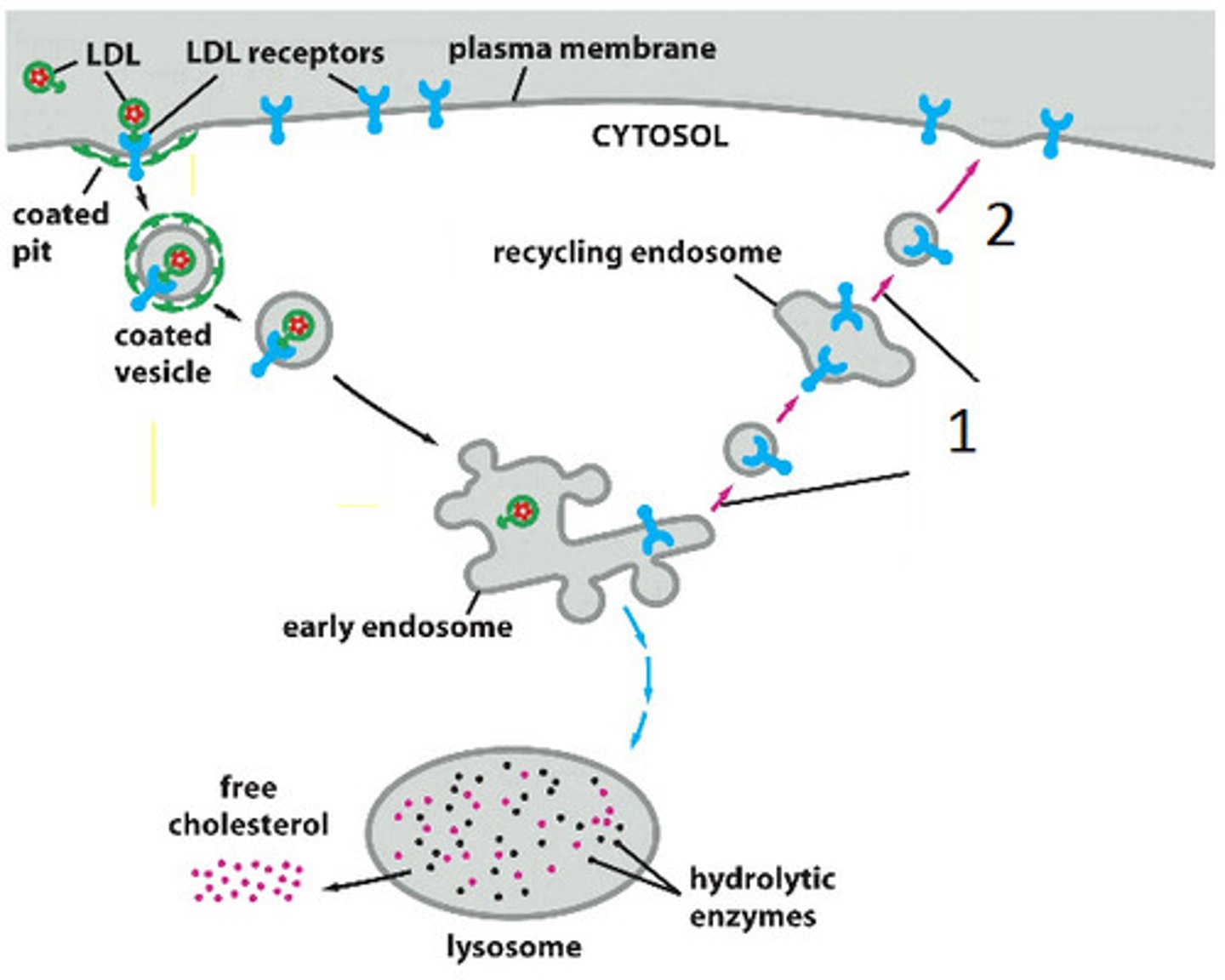
Explain the process of Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis (RME).
1. Receptor is activated by molecule of compatible shape; 2. ATP used to modify clathrin protein to make "pits" in plasma membrane; 3. Big pit created with ECF fluid, plasma membrane joins to create closed vesicle with receptor inside; 4. Clathrin is recycled; 5. Vesicle breaks in two, one with receptor recycled and other (called endosome) which contains ligand goes to lysosome or Golgi for processing
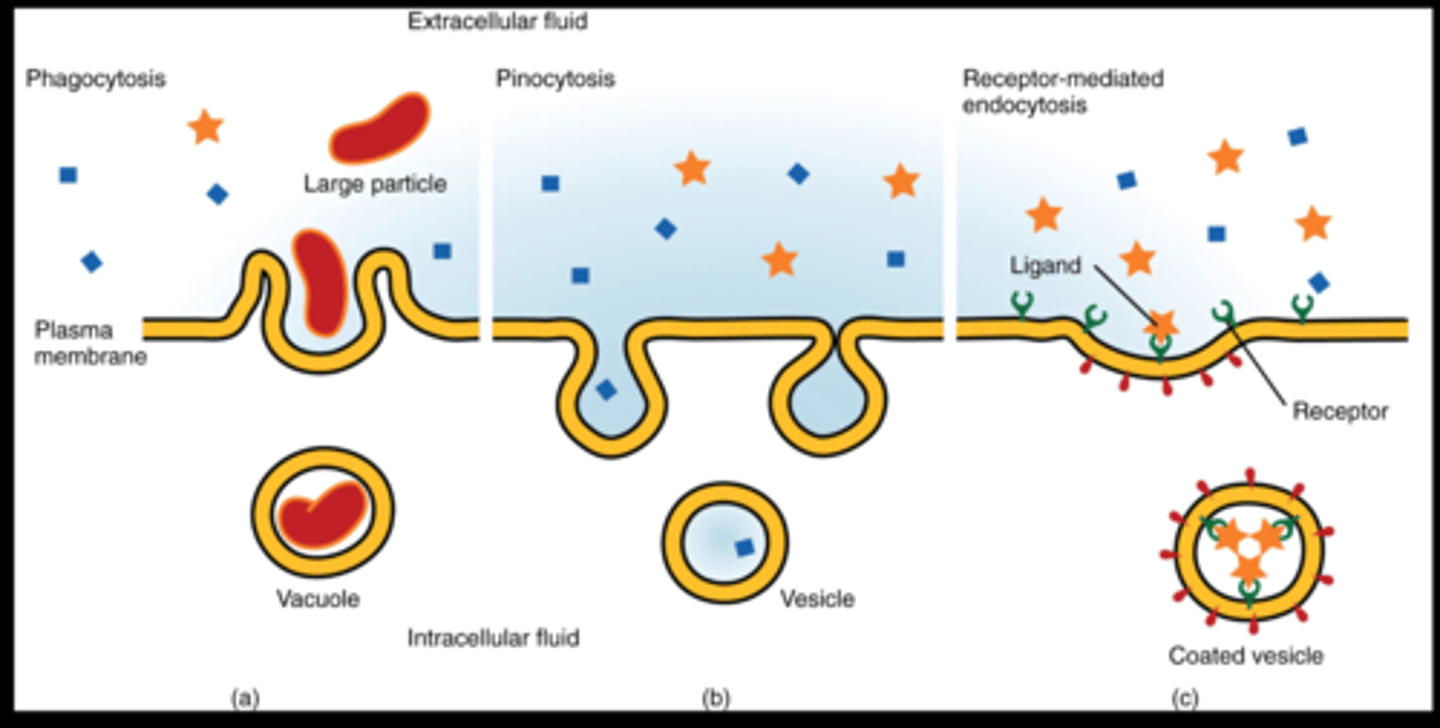
What is the key difference between phagocytosis and pinocytosis?
Phagocytosis uses large pits to take in large amounts of ECF (able to taken in very large objects), while pinocytosis makes small pits to take small amounts of ECF
What do excretory cells mainly release through exocytosis?
Hormones, proteins & growth factors
Why is bulk membrane transport a form of active transport?
ATP is used to modify the cytoskeleton of the cell (In the case of exocytosis, ATP is also used to separate secretory proteins from Golgi Apparatus)
What is the general process (or key ideas) behind cell signalling pathways?
1: Insulin (& hormones) never physically enter a cell; 2: Cell surface receptors are involved; 3: Through cascade of protein pathways, the nuclear expression of genes involved