Lecture 1
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gas Laws
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
List four general properties of gases.
Large free space between molecules.
Can expand infinitely.
Fill containers uniformly and completely.
Diffuse and mix rapidly.
It states that gases are point particles in ceaseless random motion.
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
According to KMT, what are gas molecules considered to be?
Point particles in ceaseless random motion.
It states that the average kinetic energy (translational) varies proportionally with temperature.
kinetic molecular theory of gases
How is the average kinetic energy of a gas related to temperature?
directly proportional
What type of collisions do gas molecules undergo?
elastic
In this type of colission, there is no net loss of kinetic energy.
elastic
What assumption does KMT make about intermolecular forces in gases?
Attractive and repulsive forces are negligible (ideal gas assumption)
It is a mathematical function that involve measurable gas properties like pressure, volume, temperature. and amount in moles.
equation of state
State the ideal gas law.
PV = nRT
Under what conditions is the ideal gas law most accurate?
At low pressure and high temperature, where intermolecular forces are minimal.
What does 1 mole represent?
6.022×1023 particles (Avogadro’s number)
What instrument is used to measure pressure?
barometer
Who developed the barometer and in what year?
Evangelista Torricelli in 1643
How does a barometer measure atmospheric pressure?
Mercury (Hg) rises in a tube until the downward force of the mercury column balances the upward force of atmospheric pressure.
What two factors determine the height of the mercury column in a barometer?
density of mercury (ρ)
atm pressure pushing on it
It states that at constant temperature (T) and amount of gas (n), the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
Boyle’s Law
What is Boyle’s Law
At constant temperature (T) and amount of gas (n), the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
What is the mathematical formula for Boyle’s Law?
P1V1=P2V2
PV = c
If gas volume doubles at constant T, what happens to pressure?
Pressure is halved (inverse relationship).
Who discovered Boyle’s Law?
Robert Boyle
Give some applications of Boyle’s Law.
Syringe - When you draw the liquid, the volume increases and the pressure decreases.
Dead-sea fish die when brought to the surface due to expansion of gases inside their bodies.
Scuba diving - Exhaled bubbles grow in size as a diver ascends (less pressure, more volume); rapid ascent can cause decompression sickness (“the bends”)
It states that at constant pressure (P) and amount of gas (n), the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K).
Charles’s Law
What does Charles’ Law state?
At constant pressure (P) and amount of gas (n), the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K).
Write the mathematical formula for Charles’s Law.
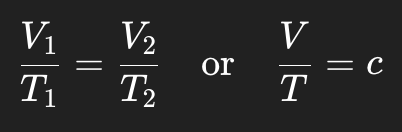
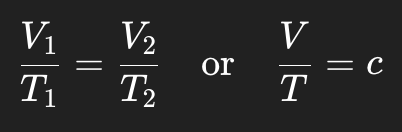
Who discovered Charles’s Law and what else was he known for?
Jacques Charles, who isolated boron, studied gases, and was also a balloonist.
Give real-life applications of Charles’ Law.
A football inflated inside and then taken outdoors on a winter shrinks slightly.
An underinflated raft expands in sunlight.
The plunger on a turkey syringe thermometer pops out when the turkey is done.
It states that at constant volume (V) and amount of gas (n), the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K).
Gay-Lussac’s Law
What does Gay-Lussac’s Law state?
At constant volume (V) and amount of gas (n), the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K).
Write the mathematical formula for Gay-Lussac’s Law.
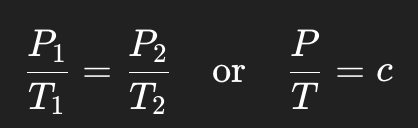
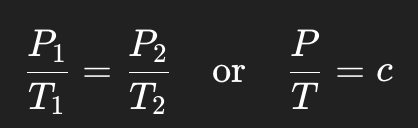
What happens to gas pressure when temperature increases at constant volume?
Gas pressure increases
Who formulated Gay-Lussac’s Law?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Give applications of Gay-Lussac’s Law.
Pressure cookers: As temperature rises inside, pressure also rises, allowing food to cook faster.
Aerosol cans: Heated cans may burst because increased temperature raises pressure inside.
Tire pressure variation: Tire pressure increases during long drives due to heating of air inside.
Gas cylinders: Storage and handling must consider temperature to prevent accidents.
What does the Combined Gas Law combine?
Boyle’s
Charles’
Gay-Lussac’s
What is the formula for the Combined Gas Law?
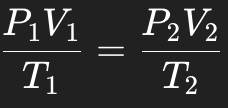
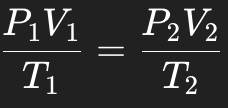
It states that at constant pressure and temperature, volume (V) is directly proportional to the amount of gas (n).
Avogardro’s Law
What does Avogardo’s Law state?
At constant pressure and temperature, volume (V) is directly proportional to the amount of gas (n).
Formula of Avogadro’s Law.
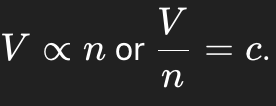
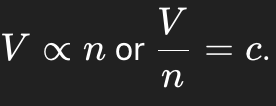
If the amount of gas increases, what happens to the volume (at constant P and T)?
increases