Lecture 7: Neuronal Conduction
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
“The speed of AP propagation is determined by how fast the next segment of membrane gets depolarised to threshold’ state what two factors determine this
Space constant (aka length constant). Time constant.
Define space\length constant
Describes how far current can spread passively along the axon before it decays to a fraction of its initial value.
Define ‘passively’ in the context of electrical current
Electrical charges moving according to laws of electricity rather than opening or closing of ions channels.
State the equation for space constant (aka length constant)
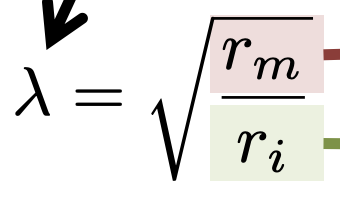
Define membrane resistance
Current flowing spreads further if the membrane is less leaky.
Define internal resistance
Current spreads further if there is little resistance to it moving down the axon.
What would happen to the space constant value if the membrane resistance is higher?
Longer/higher space constant.
What would happen to the space constant value if the internal resistance is lower?
Longer/higher space constant = easier for current to travel along the axon.
Why do wider axons have a longer space constant?
Membrane resistance is inversely proportional to SA of the membrane (ie more area = more leaks) + axon’s circumference. Internal resistance in inversely proportional to the cross sectional area of the axon.
State the time constant equation

What does myelin do to membrane resistance + what does this cause?
Causes it to increase. Longer space constant = current can spread farther down the axons.
What does myelin do to capactiance + what does this cause?
Causes it to decrease. Counteracts the effect of increased membrane resistance on the time constant = membrane can still charge up as quickly as possible.
Define conduction velocity
How fast signal propagates down the axon.
What does merlin do to the conduction of APs?
Speeds them up.
Describe the process of saltatory conduction
Current enters through Na+ channels at nodes of ranvier = depolarisation spreads passively down the axon (this is sped up by a long space constant) = at next node of ranvier depolarisation triggers VG Na+ channels to regenerate the AP.
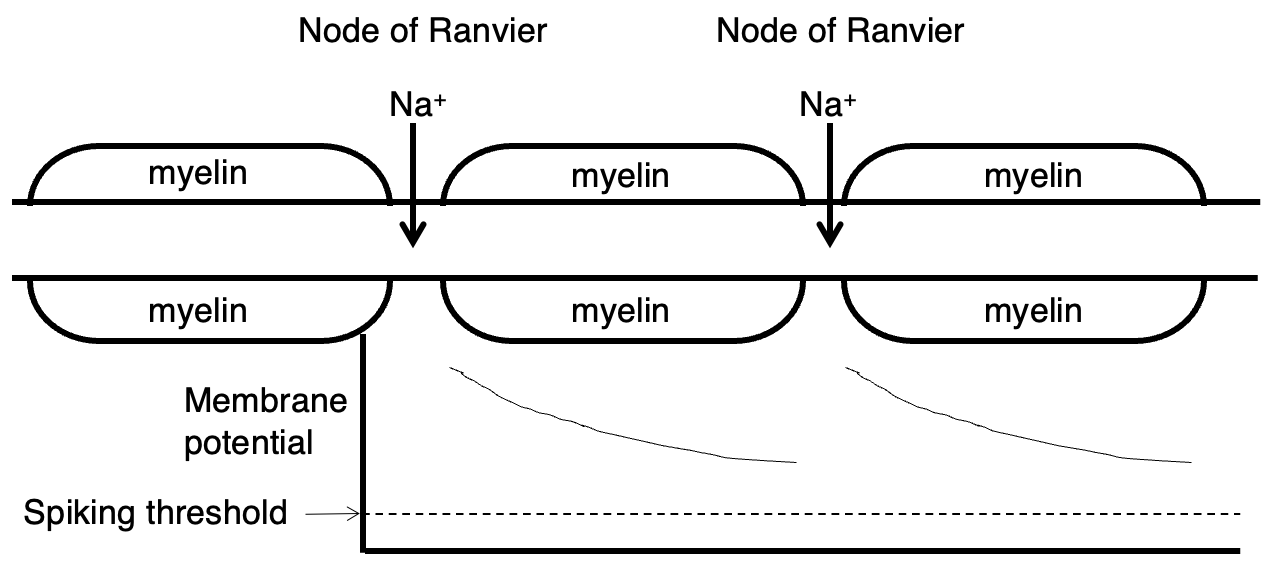
How does saltatory conduction save energy?
Means Na+ only enters at nodes of ranvier (instead of all along axon) = less work for Na/K pump to restore Na+ gradient.
What happens as a result of myelin + wide axons being costly?
Only myelinate + widen axons that need to carry info quickly, e.g proprioception, motor axons.
Define proprioception
Neurons that sense position of muscles.
Why does demyelination lead to neurological problems?
Axons aren’t made to work without myelin.
Describe multiple sclerosis
Auto-immune disorder (immune system attacks myelin). Episodic. Diverse neurological problems (e.g vision problems, numbness, muscle spasms). Symptoms may get worse under stress or at high temps (neural conduction is safer at low temps as Na+ channels inactivate more slowly).
Describe Guillain-barre syndrome
Auto-immune disorder affecting PNS myelin. Symptoms are numbness, tingling, weakness. Patients usually recover because PNS myelin can regenerate (unlike CNS myelin).