BIO 189: Chapter 9- Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is asexual and sexual reproduction?
Asexual: Without involvement of another organism (genetically identical)
Sexual: Requires combination of genetic material from both
What is a ploidy?
The number of full sets of chromosomes in a cell or an organism
What are haploids and diploids?
Haploid: one set of chromosomes
Diploid: two sets of chromosomes
Most somatic body cells in sexually reproducing organisms are _____?
Diploid
Gametes and asexually reproducing organisms are ___?
Haploids
What are some pros and cons of asexual reproduction?
Pros: No need to find a mate & can maintain “good” genes
Cons: Reduced genetic variety which could lead to extinction
What are some pros and cons of sexual reproduction?
Pros: Increased genetic diversity and allows for evolution
Cons: Need to find/attract a mate and genomes become diluted
The offspring of sexually reproducing organisms are _______ but not identical to parents or siblings
genetically related
Why is genetic diversity good?
Sexual reproduction increases diversity
High genetic diversity allows organisms to adapt to different circumstances
Adaption increases long term survival chances
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis: Somatic cells are created, only used to divide, results in two identical diploid daughter cells, important for growth and development
Meiosis: Germ line cells produce gametes, starts as one diploid cell and ends with four non-identical haploid cells, important for sexual reproduction
Gametes have only _____ ________ instead of 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
23 chromosomes
Meiosis is ___________ while fertilization is ________
Reduction to haploid and return to diploid
DNA duplicates how many times and before what?
Once and before mitosis and meiosis
Mitosis has ____ cell division and meiosis has ___ cell divisions
One and Two
Interphase in a somatic cell comes before what?
Mitosis
Interphase in a germ-line cell comes before what?
Meiosis
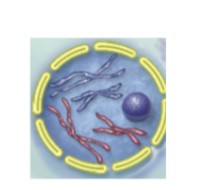
What are the blue chromosomes and what are the red ones?
Red= Maternal
Blue= Paternal
What happens during prophase in both mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis: Chromosomes condense, centrosomes move to opposite poles, and nuclear envelope disintegrates
Meiosis: Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes associate closely, recombination/crossing over occurs
Genes are located at the same part (___) of both homologous chromosomes
locus
What does recombination/crossing over do?
Physically exchanges regions of chromosomes when they associate at this stage
What happens during metaphase in both mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis: All individual chromosomes align single file along metaphase plate
Meiosis: Homologous chromosome pairs align as pairs along metaphase plate
What happens during anaphase in both mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis: Sister chromatids are pulled apart becoming daughter chromosomes
Meiosis: Homologous chromosomes are pulled apart
What happens during telophase & cytokinesis in both mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis: Daughter chromosomes are enclosed in two nuclei and chromosomes decondense
Meiosis: Chromosomes are enclosed in two nuclei and chromosomes decondense (becoming haploids)
What does cross-over/recombination do?
Increases genetic diversity by making unique chromosomes with new combinations of maternal and paternal alleles
During metaphase I homologous pairs are in what?
Random alignment and independent assortment
What is the difference between the formation of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins
Monozygotic: A single zygote produces two embryos
Dizygotic: Two zygotes form two different embryos at the same time
What are most chromosomal disorders caused by?
Errors during Meiosis
What is an error during meiosis (nondisjunction in meiosis I)?
All 4 gametes and 100% of zygotes will have abnormalities
What is an aneuploidy?
An unbalanced chromosome number (extra or fewer)
What is monosomic/monosomy and what is it represented by?
A cell is missing a chromosome (n-1)
What is trisomic/trisomy and what is it represented by?
A cell contains an extra chromosome (n+1)
What is an error during meiosis (nondisjunction in Meiosis II)?
2 gametes and 50% of zygotes will have abnormalities
What does having a trisomy 21 and 18 mean?
Trisomy 21: Down Syndrome
Trisomy 18: Edwards Syndrome
What are the different sex chromosome abnormalities?
XXX- Triplo-X
XXY- Klinefelter or XXY syndrome
XYY- Jacobs or XYY syndrome
XO- Turner Syndrome
What does polyploidy mean?
Entire extra sets of chromosomes (most animals do not survive and more tolerated in plants)
Total nondisjunction, occurs in stressful conditions