ARTERIAL - SEGMENTAL PRESSURES AND PLETHYSMOGRAPHY
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
analog doppler
graphical recording of pulsatile doppler signal in a nonspectral or strip chart recording
analog doppler displays _____ as a single line, not _____
average shift, a range of frequency shifts
t/f: analog doppler displays turbulence/spectral broadening
false
analog doppler uses a ______ MHz ______-style transducer
8-10, pencil
limitations of lower extremity CW doppler exam
bandages, casts, wounds
room temp affects resistance
CANNOT properly localize an area of obstruction
underestimates high velocities and overestimates low velocities
in an le segmental pressure exam, the probe should be at an angle of _____ with the skin
45 degrees
le segmental pressure exam - pressures are obtained from _____ to _____
ankle, thigh
cuff width should be _____% wider than the diameter of the part being measured
20
if the cuff is too wide, the segmental pressure is ______
underestimated
if the cuff is too narrow, the segmental pressure is ______
overestimated
what cuff is used for the brachial, ankle, calf
10-12 cm
what cuff is used for thigh and patients with a larger body habitus
12 cm or larger
what size cuff is used for the digits
2.5 cm
what size cuff is used for the wrists
7 cm
the _____ cuff method is most common
4
the _____ cuff method provides a more accurate mid thigh pressure
3
the 3 cuff method cannot differentiate _____ disease from _____ disease
distal femoral, popliteal
<_____mmHg between adjacent levels on the same leg is normal
30
<_____mmHg difference between same level of both legs is normal
20
rest pain is seen in patients with an ankle pressure of <_____ mmHg
50
>_____ reduction in ABI on serial exams indicates disease progression
.15
an abi of over _____ indicates noncompressibility
1.3
ankle pressures over _____ indicates noncompressibility
200
ankle pressures _____% higher than brachial indicates noncompressibility
30
an abi over over 1.0 is considered
normal
an abi of .9-1.0 is considered
asymptomatic/minimal disease
an abi of .5-.9 is considered
claudication/mild to moderate disease
an abi under .5 is considered
rest pain/severe disease
strandness criteria: an abi of over .5 means
single vessel disease
strandness criteria: an abi of under .5 means
multiple vessel disease
ankle pressures under _____mmHg are associated with non-healing wounds
80
when calculating abi, the _____ of the two brachial pressures should be used
higher
when calculating abi, the _____ of the pta or dpa pressures should be used
higher
toe pressures under _____mmHg are associated w non-healing wounds
30
a normal finger/brachial index is above
.8
normal toe/brachial index is
.6-.8
a toe/brachial index indicating claudication is
.2-.5
a toe/brachial index under _____ indicates rest pain
.2
treadmill exercise testing helps differentiate
true claudication from pseudoclaudication
exercise induces peripheral vaso_____ and can be used to evaluate autoregulation
dilation
diminished pulsatility in flow pattern is _____ after exercise
normal
how does the treadmill test work
take pre measurements then post exercise, take measurements every 2 minutes until pre exercise baseline pressures have been returned to
exercise results (normal)
pressures decrease to normal in 5 min
exercise results (single-level obstruction)
pressures and abi drop, increase to normal baseline 2-6 min post exercise
exercise results (multi-level obstruction)
pressures and abi drop, increase to normal baseline 6-12 min post exercise
after exercise, if the patient has pseudoclaudication, what will the results look like
increased or no change in the abi
reactive hyperemia
transient increase in blood flow that occurs after a brief period of ischemia
when is reactive hyperemia testing needed
patients w poor cardiac output
history of angina
difficulty walking or breathing
amputation of leg
how is reactive hyperemia testing done
elevate legs to 45 degrees to drain venous blood
inflate thigh cuff to 30-50 mmHg above brachial pressure
lower legs back onto table and maintain pressure in thigh cuff for up to 5 min
pressures are obtained upon releasing the cuff
obtain pressures every 30 seconds until pressures return to baseline
reactive hyperemia (normal) results
ankle pressure drops under 35%, returns to baseline in a minute
velocity of flow increases over 100% from resting velocity when cuff released
reactive hyperemia (single level disease) results
ankle pressure drops 35-50%
reactive hyperemia (multi level disease) results
ankle pressure drops over 50%
pulse volume recording is also known as
arterial plethysmography or volume plethysmography
how is a pvr obtained
patient lies supine w a wedge under their ankles to prevent cuff compression
12 cm cuffs placed on thighs, calves, ankles, 7 cm on foot. for the upper extremity, 12 cm cuff is placed on the upper arm, 10 cm on forearm, 7 cm cuff wrist. inflated to 50-60 mmHg, held constant
pvr tracings are performed thigh to ankle on both legs at the same time
volume changes under the cuffs are recorded by the machine
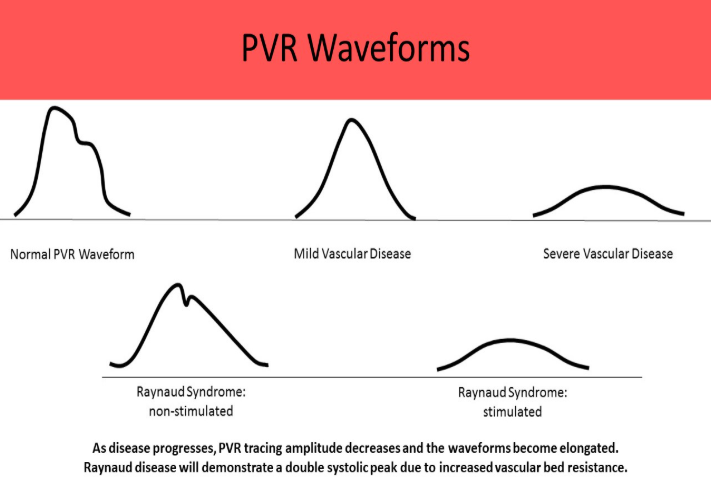
in pvr, increased peripheral resistance will lead to _____ amplitude
increased
calf pvr tracings will have a _____ amplitude than thigh pvr tracings
higher
photoplethysmography
infrared light is released into tissues, red blood cells reflect light to photocells where it is measured, detecting cutaneous blood flow/volume changes
t/f: ppg recordings are not affected by calcified vessels
true