Air pollution
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Air Pollution
Introduction of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
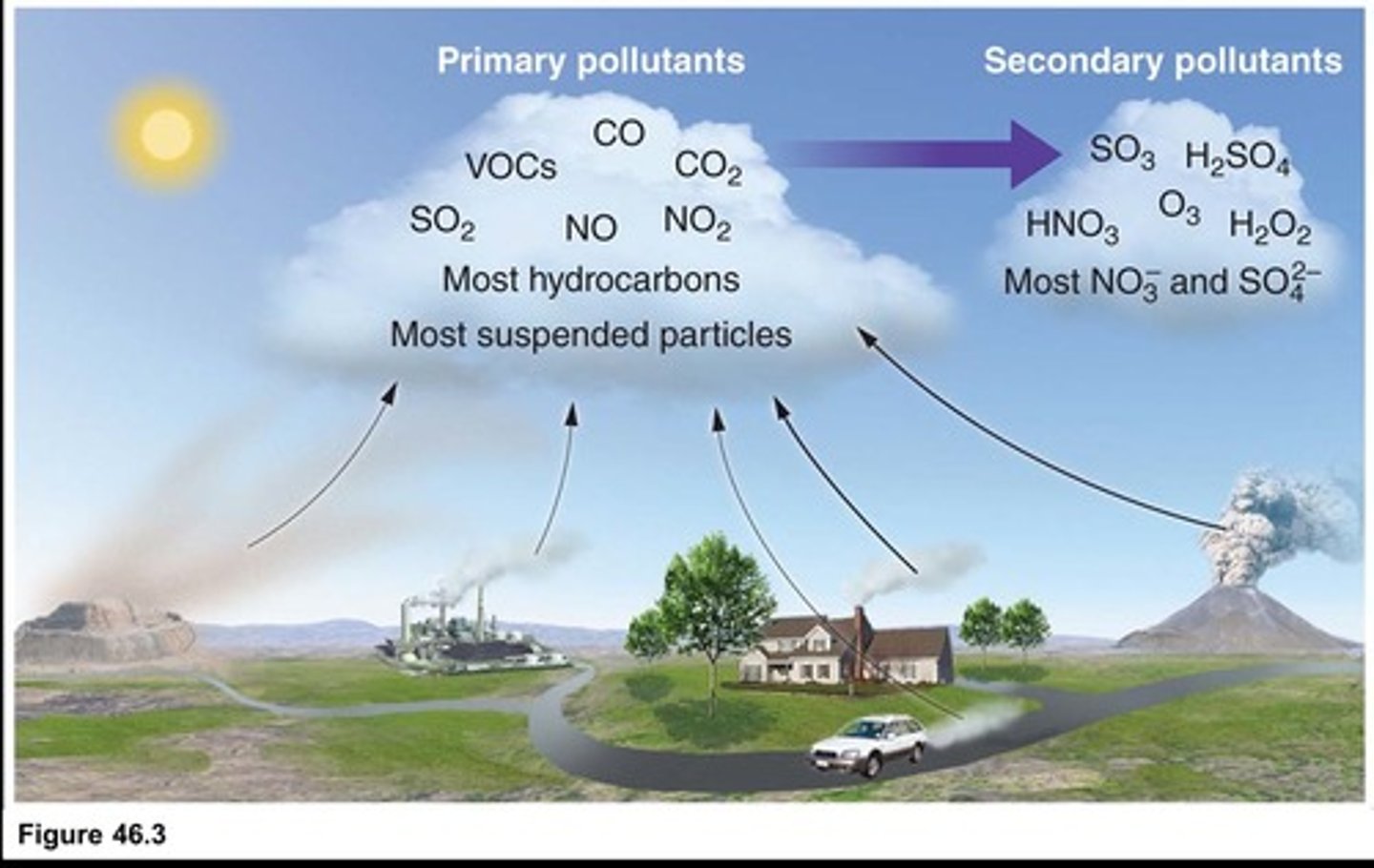
Inputs
Sources contributing to air pollution.
Outputs
Components removing pollutants from the atmosphere.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Corrosive gas from fuel combustion and volcanic eruptions.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOX)
Gases from combustion, including NO and NO2.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Colorless gas from incomplete combustion of fuels.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Gas from complete combustion, exceeds 400 ppm.
Particulate Matter (PM)
Solid or liquid particles suspended in air.
PM10
Particulate matter smaller than 10 micrometers.
PM2.5
Particulate matter smaller than 2.5 micrometers.
Photochemical Oxidants
Pollutants formed by sunlight acting on compounds.
Ground-level Ozone (O3)
Secondary pollutant harmful to respiratory function.
Photochemical Smog
Smog dominated by oxidants like ozone.
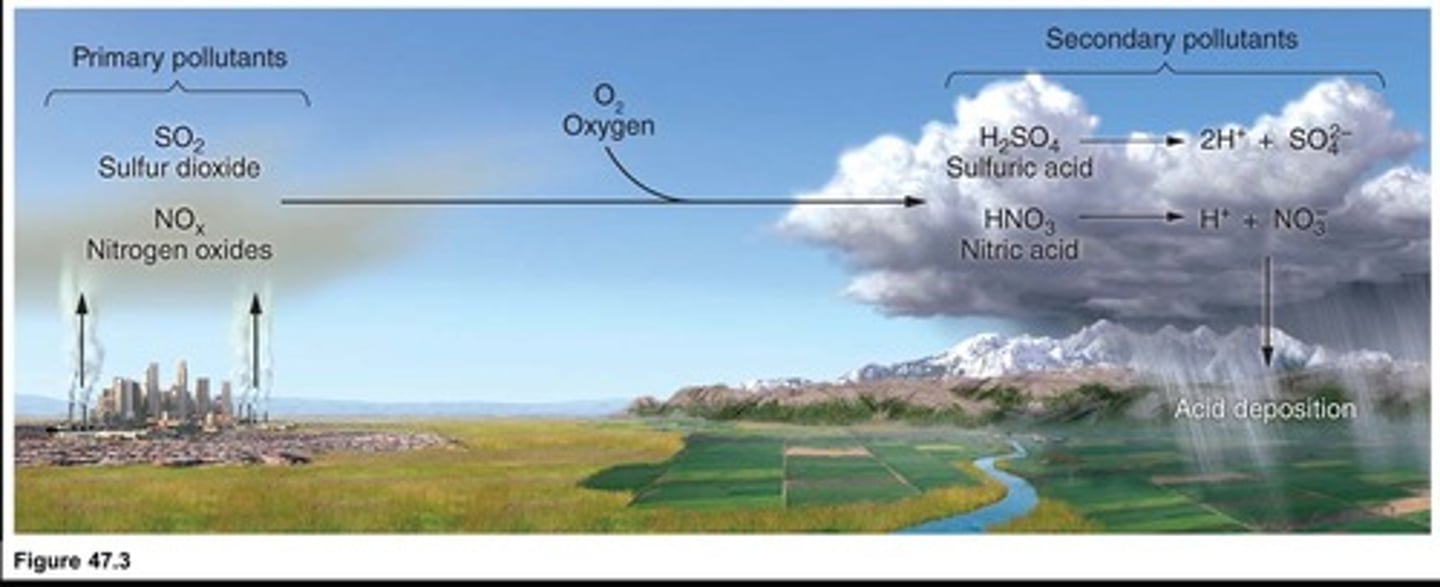
Acid Rain
Rainfall with high levels of sulfuric and nitric acids.
Indoor Air Pollutants
Pollutants found within buildings affecting health.
Noise Pollution
Unwanted or harmful sound affecting human health.
Respiratory Irritant
Substance causing irritation in respiratory system.
Combustion
Chemical reaction producing heat and light.
Volcanic Activity
Natural eruptions releasing gases and particulates.
Forest Fires
Natural fires contributing to air pollution.
Anthropogenic Sources
Pollutants originating from human activities.
Natural Sources
Pollutants originating from natural events.
Nitric Acid
Acid formed from nitrogen oxides in atmosphere.
Ecosystem Alteration
Changes in ecosystems due to pollution.
Respiration
Process of breathing, releasing CO2.
Decomposition
Breakdown of organic matter, releasing CO2.
Haze
Reduction of visibility due to particulate matter.
Photochemical smog
Smog dominated by ozone and oxidants.
Sulfurous smog
Smog dominated by sulfur dioxide and sulfates.
Lead (Pb)
Toxic trace metal found in fuels and paint.
Mercury (Hg)
Toxic trace metal from fossil fuel combustion.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic compounds that evaporate at atmospheric temperatures.
Primary pollutant
Pollutant emitted directly from sources.
Secondary pollutant
Pollutant formed from primary pollutants' transformation.
Clean Air Act (CAA)
Federal law regulating air emissions and pollutants.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
Standards to protect public health from air pollutants.
Ozone (O3)
Ground-level pollutant formed by nitrogen oxides and VOCs.
NO2
Nitrogen dioxide, a precursor to ozone formation.
Ozone destruction
Natural process reforming O3 into O2 and NO2.
Anthropogenic emissions
Pollutants originating from human activities.
Trace metals
Metals present in small concentrations, often toxic.
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Ground-level ozone
Ozone formed at Earth's surface, harmful to health.
Photochemical oxidants
Pollutants formed from reactions involving sunlight.
Industrial smog
Smog resulting from industrial emissions, often gray.
Brown smog
Another term for photochemical smog, often seen in cities.
Gray smog
Another term for sulfurous smog, typically in industrial areas.
Evaporation
Process of a substance transitioning from liquid to gas.
Sublimation
Transition of a substance from solid to gas.
Combustion
Chemical reaction producing heat and light, often with pollutants.
Ozone concentrations
Levels of ozone, peaking in afternoons during summer.
Natural sources of VOCs
Vegetation like trees releasing organic compounds.
Urban air pollution
Pollution concentrated in cities, often from vehicles.
Forest fires
Natural events contributing to air pollution and VOCs.
Photochemical Smog
Air pollution caused by sunlight and pollutants.
VOCs
Volatile Organic Compounds that increase with temperature.
NOX
Nitrogen oxides produced from fuel combustion.
Ozone (O3)
A photochemical oxidant formed from chemical reactions.
Respiratory Problems
Health issues caused by photochemical smog exposure.
Thermal Inversion
Warm air traps cooler air and pollutants below.
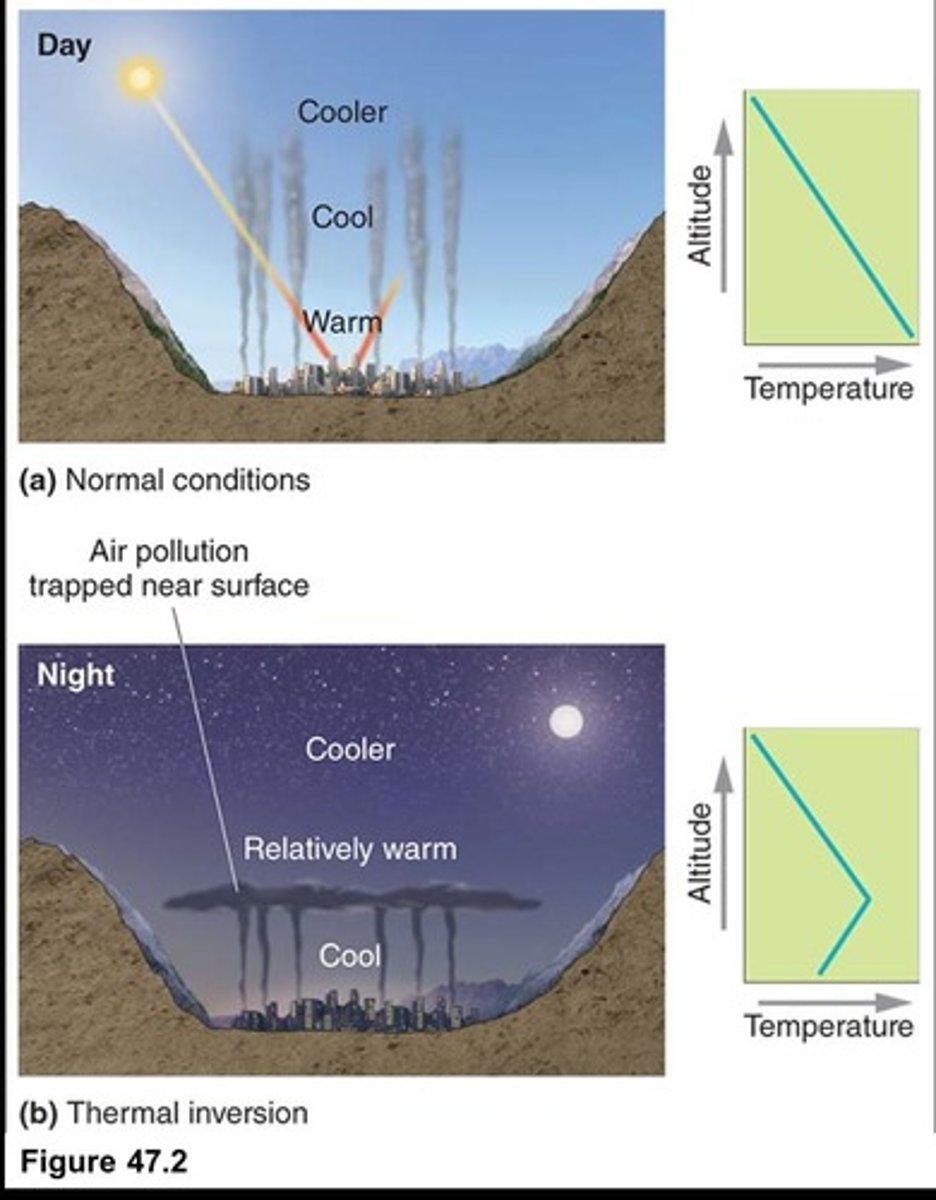
Inversion Layer
Warm air layer preventing pollutant dispersion.
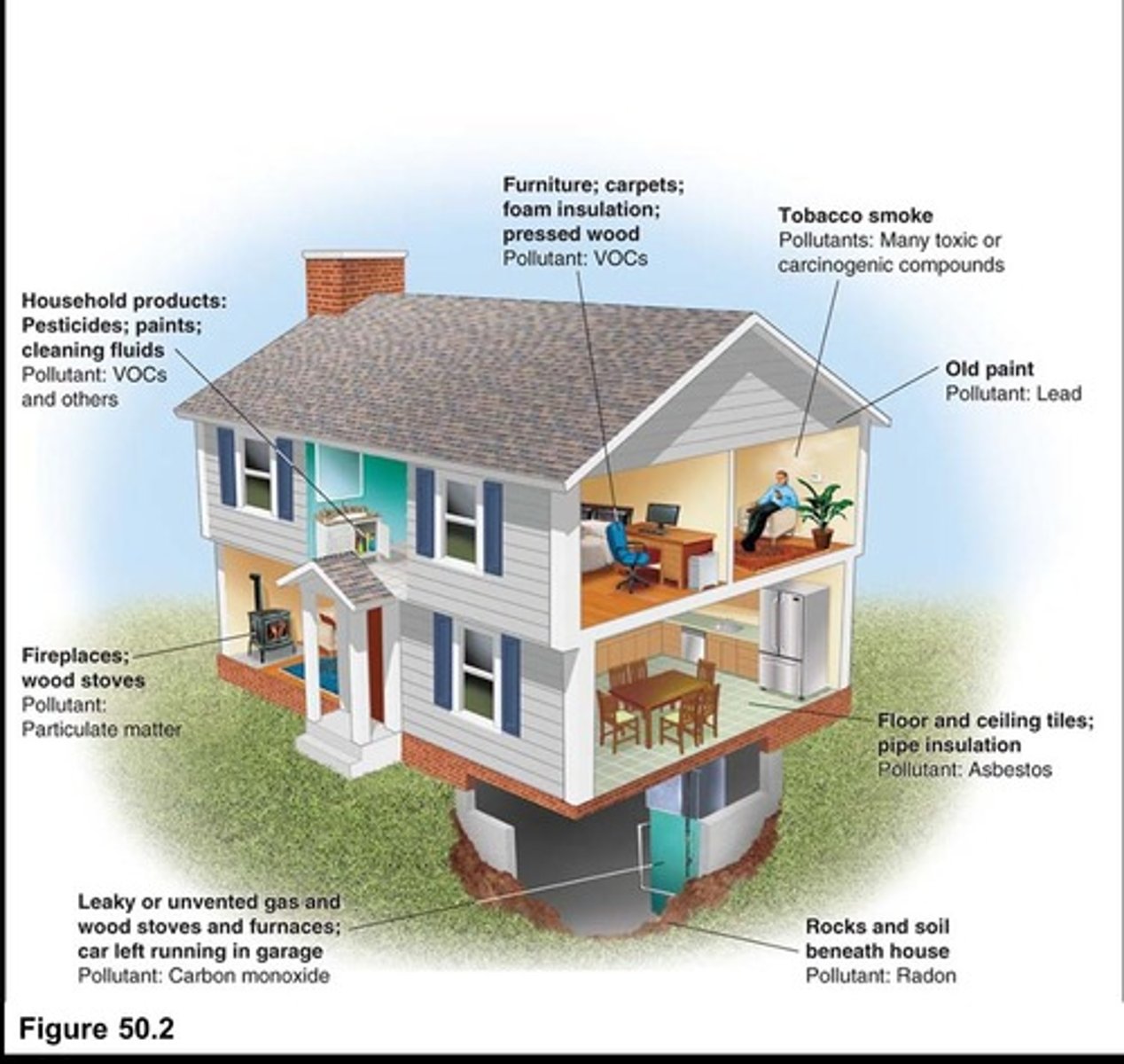
Indoor Air Pollution
Pollution occurring within buildings, affecting health.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Colorless gas from malfunctioning heating systems.
Asbestos
Fibrous mineral causing cancer when inhaled.
Radon
Radioactive gas from uranium decay, lung cancer risk.
WHO Indoor Pollution Deaths
4 million deaths annually from indoor air pollution.
Biomass Energy
Fuel from organic materials, often poorly ventilated.
Pollutant Trapping
Inversion layers trap pollutants near Earth's surface.
Health Effects of Smog
Includes lung damage, asthma, and eye irritation.
Low Birth Weights
Adverse health outcome linked to air pollution.
Pollution in Cities
Inversion layers more common in mountainous cities.
CO Detectors
Devices to detect harmful carbon monoxide gas.
Asbestosis Symptoms
Shortness of breath and persistent dry cough.
Radon Testing
Recommended to identify radon levels in homes.
EPA Radon Estimates
21,000 deaths annually from radon-induced lung cancer.
Pollution Sources
Includes VOCs, NOX, and indoor pollutants.
Chemical Compounds
Various substances that can pollute indoor air.
Ozone Formation
Accelerated by heat and sunlight conditions.
Air Quality
Influenced by temperature, emissions, and pollution levels.
Ventilation Importance
Crucial for reducing indoor air pollution exposure.
VOCs
Volatile Organic Compounds found in home products.
Formaldehyde
Toxic VOC used in adhesives and wood products.
Sick Building Syndrome
Health issues from toxic pollutants in airtight buildings.
Inadequate Ventilation
Insufficient airflow causing pollutant buildup indoors.
Chemical Contamination
Pollutants from indoor sources like cleaning agents.
Biological Contamination
Pollutants from mold and pollen indoors.
Outdoor Sources
Pollutants entering buildings from external environments.
Pollution Control Methods
Strategies to reduce air pollution emissions.
Cleaner Fuels
Fuels that produce fewer emissions when burned.
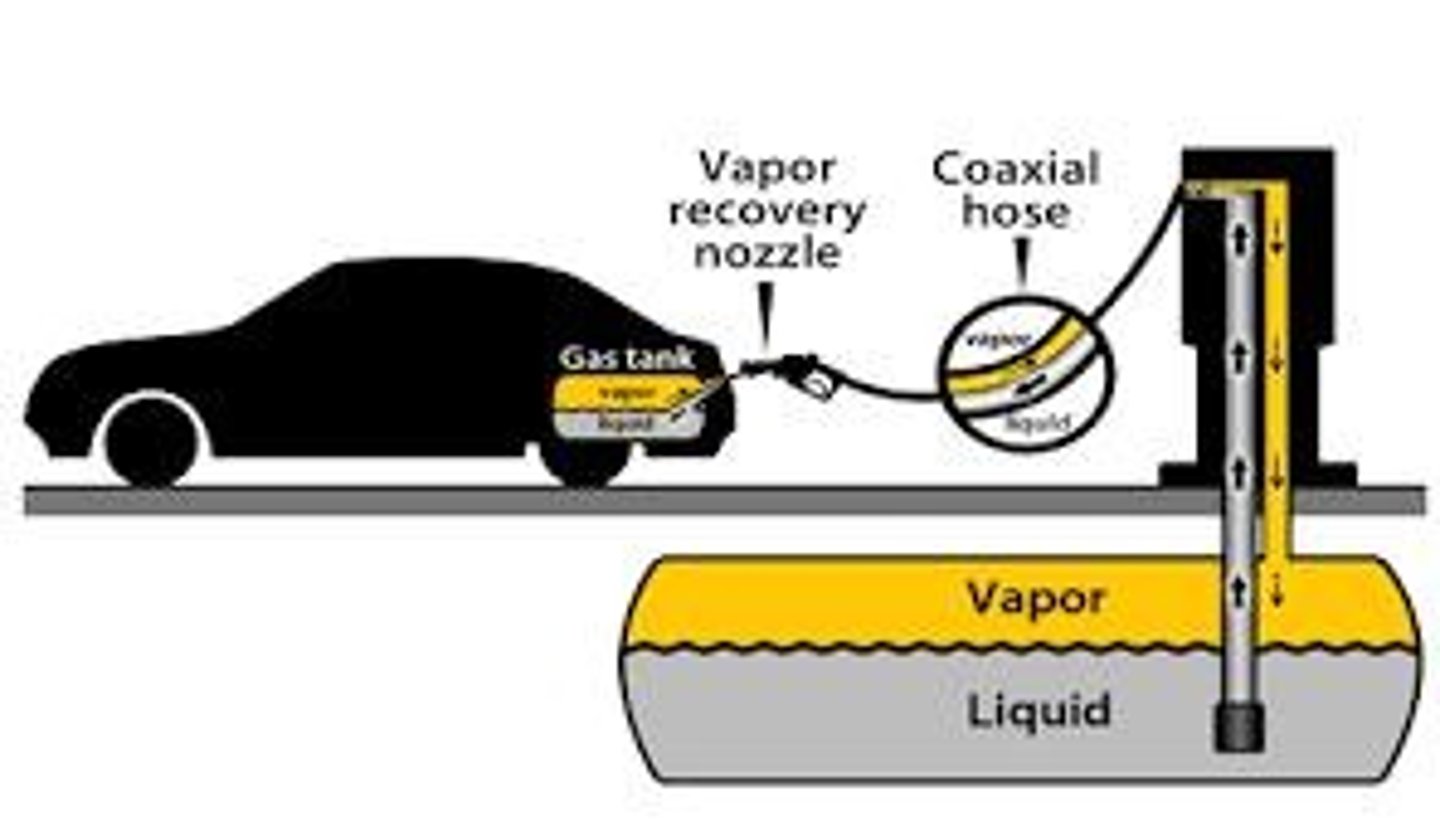
Vapor Recovery Nozzle
Device preventing gasoline fumes during refueling.
Fluidized Bed Combustion
Process reducing sulfur dioxide emissions from coal.
Catalytic Converters
Devices converting exhaust pollutants into less harmful gases.
Gravitational Settling
Process where gravity causes particulates to settle.
Baghouse Filters
Fabric filters trapping particulates from exhaust gases.
Electrostatic Precipitator
Device using electric charge to remove particles.
Scrubber
Device using water to remove particles from exhaust.
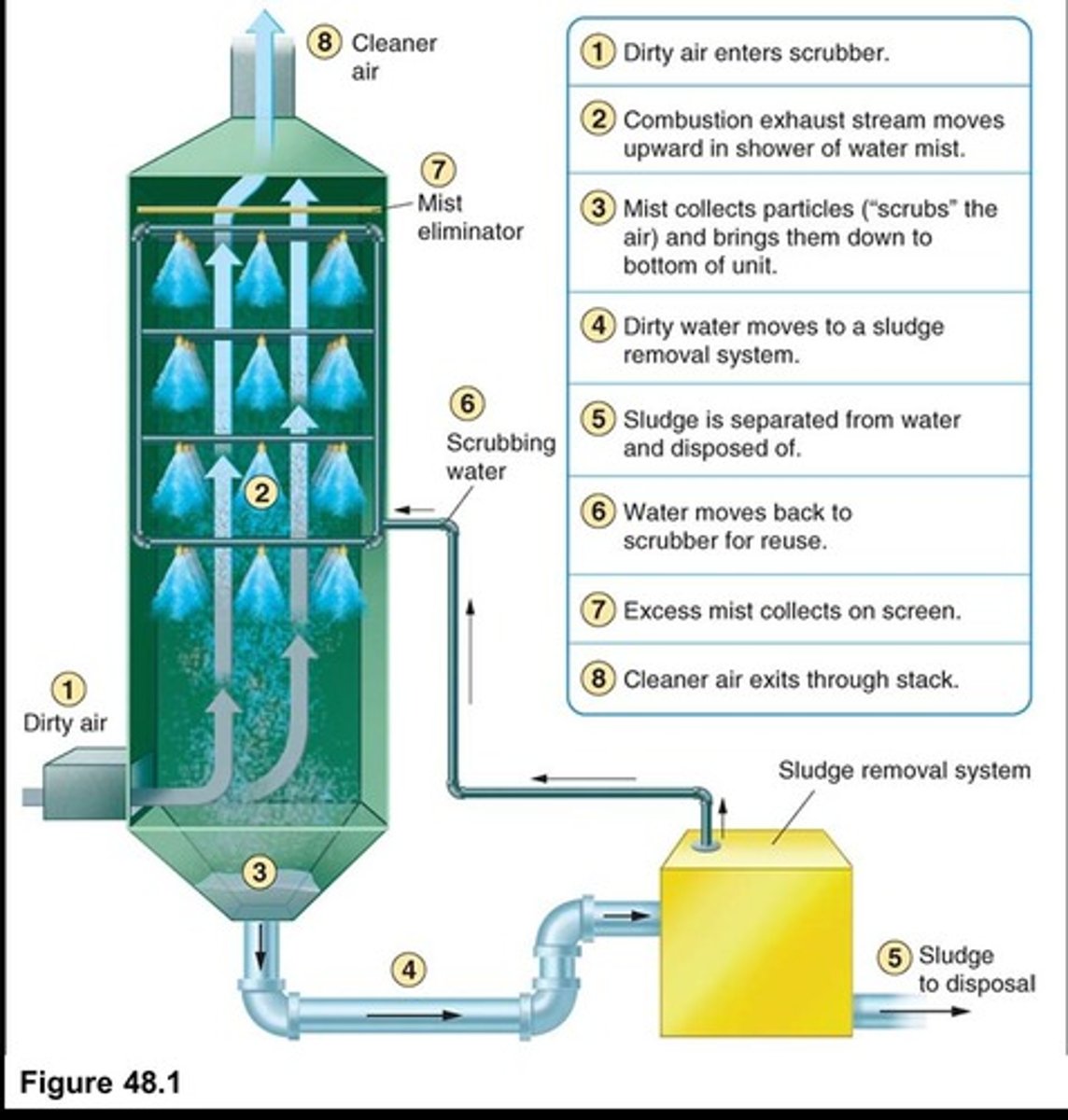
Water-Particle Sludge
Mixture collected from scrubbers for disposal.
Smog
Air pollution primarily composed of ozone.
Nitrogen Oxides
Pollutants reduced by catalytic converters in vehicles.
Sulfur Dioxide
Pollutant from coal, reduced by fluidized bed combustion.