Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Law of demand
As price ↓, quantity demanded ↑ (inverse relationship)
Law of Supply
As price ↑, quantity supplied ↑ (direct relationship).
What happens to total revenue when demand is elastic and price increases?
Total revenue decreases
What happens to total revenue when demand is inelastic and price increases?
Total revenue increases
∣Ed∣>1
Demand is elastic
∣Ed∣<1
Demand is inelastic
What causes a movement along the demand curve?
A change in a price
What causes a shift of the demand curve?
Changes in income, tastes, prices of related goods, number of buyers, or expectations.
What causes a shift of the supply curve?
Changes in input prices, technology, number of sellers, expectations, or taxes/subsidies.
Qd=Qs
market equilibrium
What happens if price is above equilibrium?
Surplus
Shortage
price is below equilibrium
What is the effect of a price ceiling below equilibrium?
shortage
What is the effect of a price floor above equilibrium?
surplus
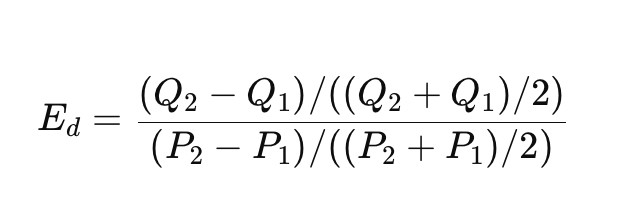
What is it
Price elasticity of demand
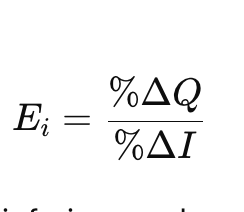
Formula for which elasticity
Income elasticity of demand
Positive → normal good
Negative → inferior good.
Income elasticity
Normal good(IED)
A good for which demand increases when consumer income rises.
Inferior good(IED)
A good for which demand decreases when consumer income increases.
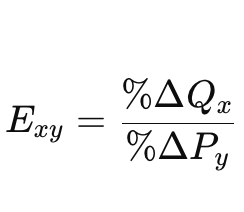
Formula for which elasticity
Formula for cross-price elasticity
Positive → substitutes; Negative → complements.