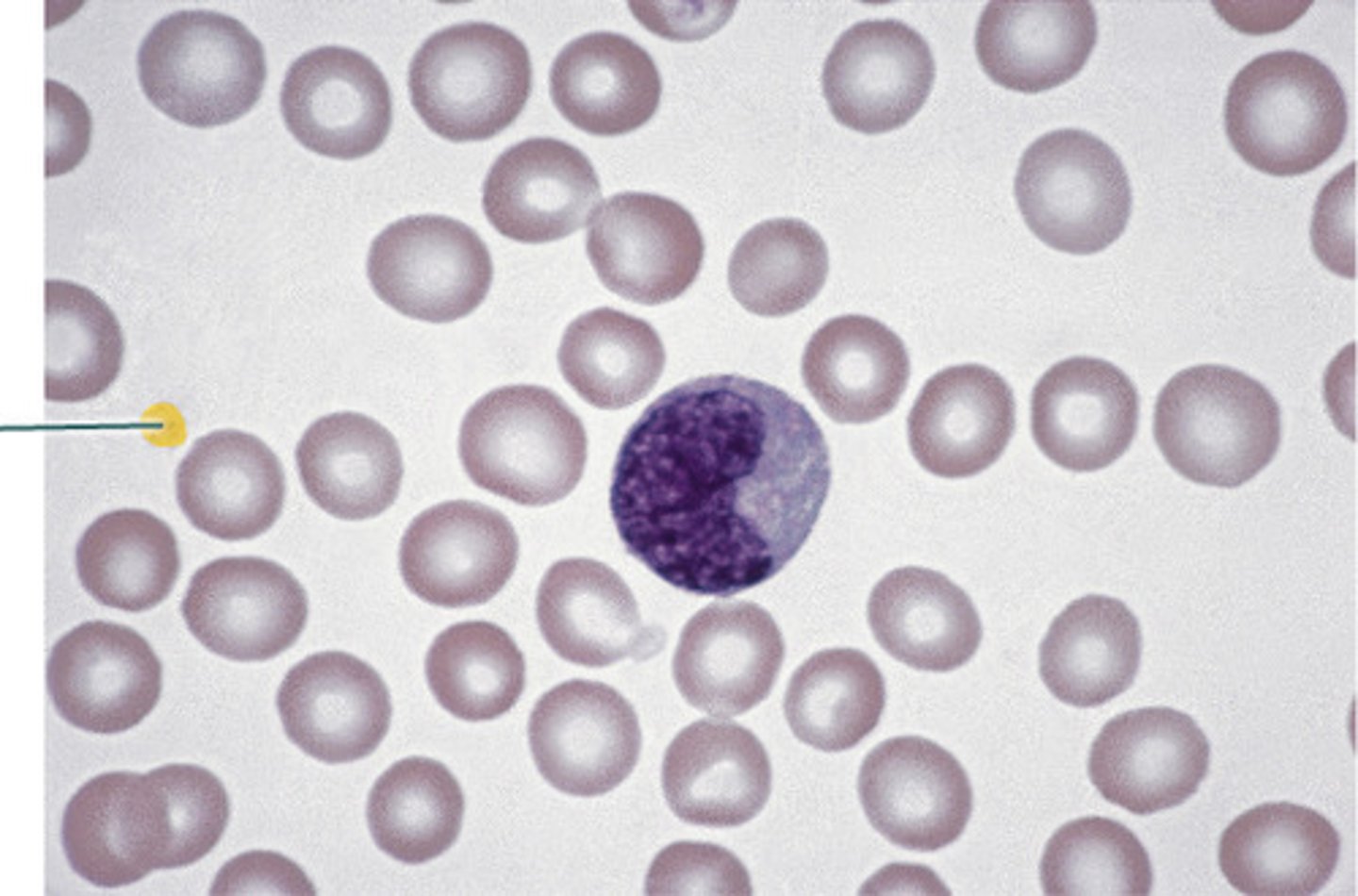
Non-Specific Defences - Phagocytosis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What are phagocytes?
Specialised white blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens
What are the 2 types of phagocytes?
Neutrophils and macrophages
Difference between neutrophils and macrophages
Neutrophils have multi-lobed nuclei, which makes it easier for them to squeeze through small gaps to get to the site of infections. It also has granular cytoplasm, containing many lysosomes that contain enzymes used to attack pathogens.
Macrophages have simpler round nuclei
Phagocytosis Process
Pathogens produce chemicals that attract phagocytes
Pathogen is engulfed and phagosome is formed
Lysosome fuse with the phagosome to form a phagolysosome
Hydrolytic enzymes in the phagolysosome break down (hydrolyse) the pathogen
Harmless products like the amino acids are absorbed into the cytoplasm
The digested pathogen combines with MHC in the cytoplasm. The MHC-antigen complex is displayed on phagocyte membrane, making an antigen presenting cell (APC)
What are cytokines?
Released from T helper cells to trigger clonal expansion of B cells
What are opsonins?
Opsonins are molecules that bind to antigens on the surface of pathogens, making them easier for phagocytes to recognize and engulf, thereby increasing the rate of phagocytosis
Neutrophil Structure
Multi-lobed nuclei, which makes it easier for them to squeeze through small gaps to get to the site of infections.
Granular cytoplasm, containing many lysosomes that contain enzymes used to attack pathogens.
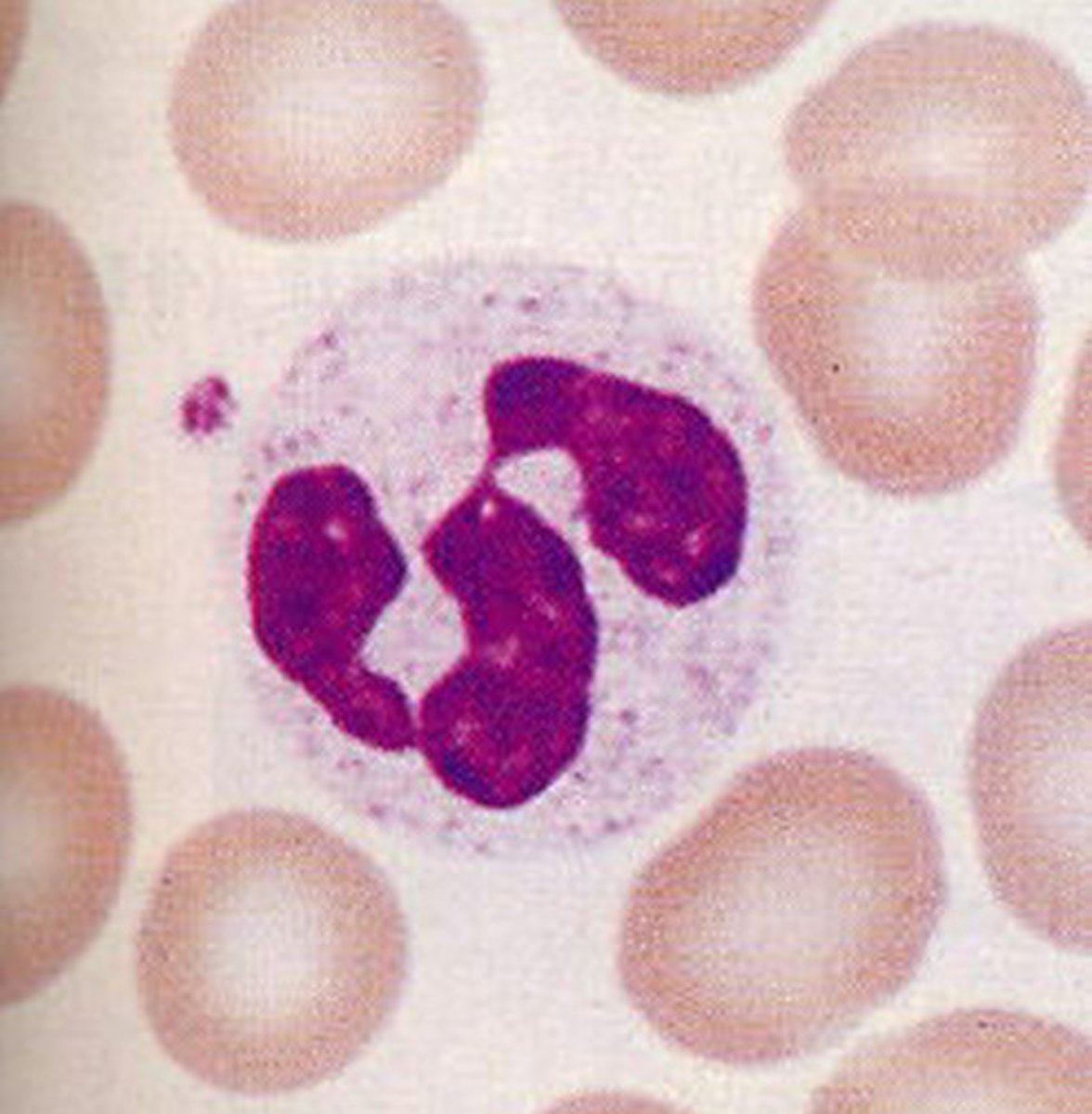
Lymphocyte Structure
Spherical nucleus
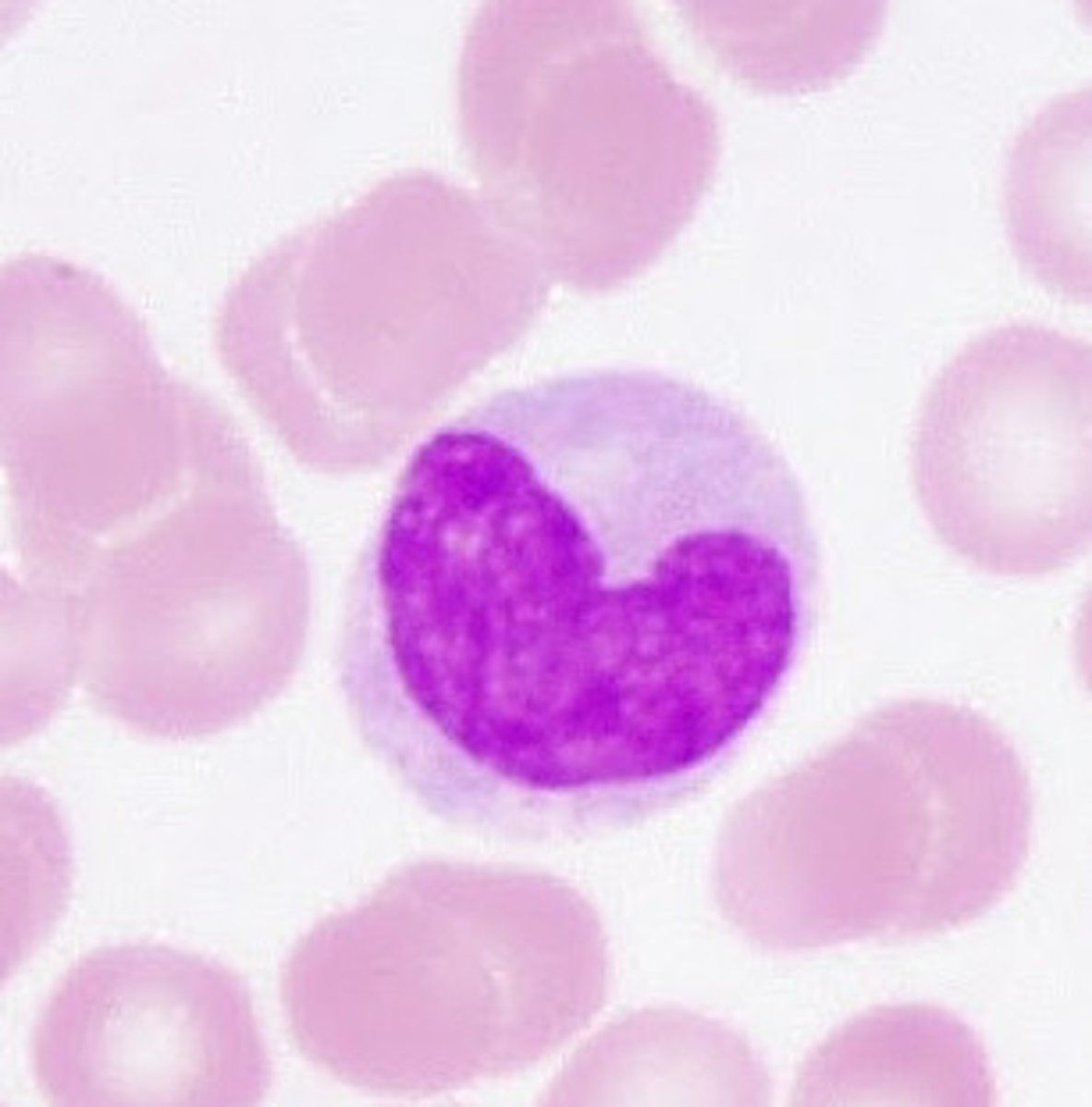
Monocyte Structure
Unilobular nuclei (kidney shaped - different to neutrophil)
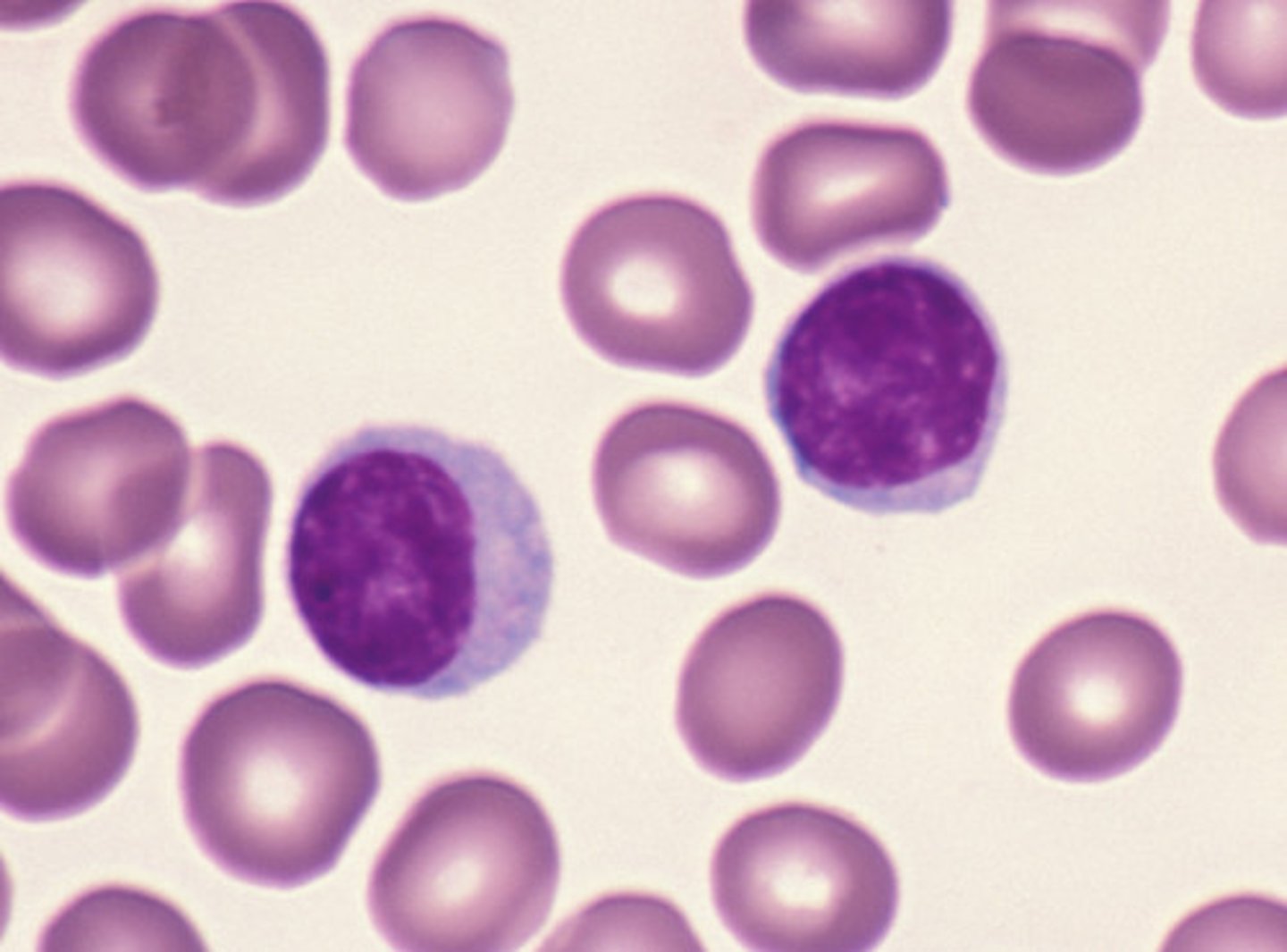
Erythrocyte Structure (red blood cell)
Biconcave disc