Therapeutic potential of regulatory RNAs
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What can siRNAs be used for?
to knock down a harmful mRNA expressed from a particular mutated gene
treatment of situations where the disease is caused by a harmful exogenous element
What does dicer do?
Processes siRNAs to allow them to be taken up by the RISC complex
What does RISC stand for?
RNA Induced Silencing Complex
siRNA pathway
guiding strand of siRNA scans cytoplasm for sequence complimentarity
when perfect match is found (base pairing between guide RNA and mRNA), enzymatic components of RISC activated + degrade the mRNA.
How long are the siRNAs and why?
22 nt so they can be recognised by the RISC complex
What is this pathway used for?
in humans: regulates translation of mRNA
in plants: defense
exists in all cells
What is manipulation of the pathway used to study?
genetic function
design siRNAs that are complementary to a gene of interest
transfect into cells
destruction of mRNA
study phenotypic effects.
one potential target
oncogenes
e.g. BCR-ABL fusion → Philadelphia chromosome 22
chromosomal translocation causing leukaemia.
how can siRNAs be used against BCR-ABL fusion
design siRNA against the fusion point → destruction of fused mRNA and not the normal ones → reduce potential of leukaemia
example against a virus
design siRNA against mutations that might occur in the virus
obtain virus → sequence → detect mutations → redesign siRNA to target mutated strain of virus
Issues with siRNAs
quickly destroyed by exonucleases bloodstream, kidneys (bc small size) + stomach and by immune cells
don’t naturally cross plasma membranes because they are negatively charged so repel
need to target to specific cell/tissue type - need to trigger receptor-mediated endocytosis
What do exonucleases do?
Destroy foreign genetic material e.g. from viruses
Present in bloodstream
How can you protect siRNAs from exonucelase attack?
add a 2’O-methyl group to the base ring
because most exonucleases are 5’ → 3’ and this modification blocks it.
How to reduce attack of siRNAs from the immune system?
Phosphorothioate linkages - replace phosphodiester bonds with a sulphur.
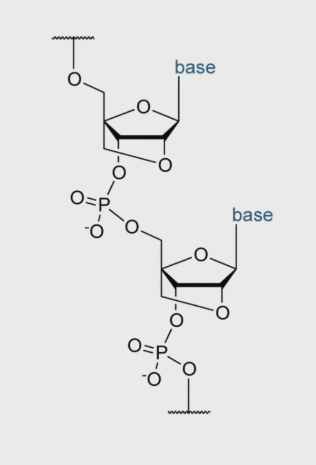
What are locked nucleic acids?
Oxygen linked from the 2’ to the 4’ position
it is a synthetic nucleic acid - not DNA or RNA
Reduces attack from exonucelases and immune system.
Binds to target mRNAs more potently
How to make the siRNAs cross the plasma membrane
Encase them in lipid nanoparticles (LNP)
Mixtures of cationic and neutral lipids - form spherical structure
neutralises negative charge on siRNA
increases molecular weight to stop it being cleared by the kidneys
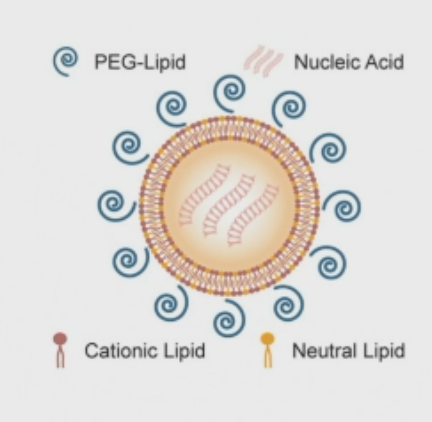
What does adding PEG groups do?
Polyethene groups
increases molecular weight even further
How do LNPs help siRNAs cross the cell membrane?
Made of the same thing so they fuse and siRNA released into cytoplasm.
Good for systemic delivery - to deliver to lots of cells in the body.
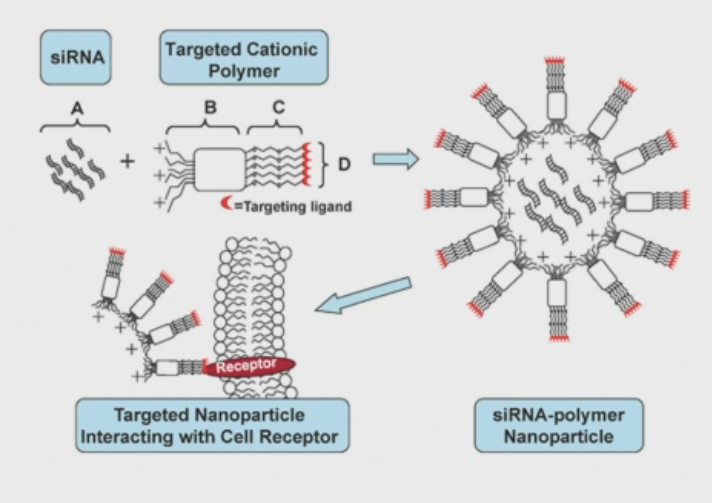
How to do a targeted delivery
Use polymer nanoparticles
Structure of polymer nanoparticles
A: siRNA
B: polycationic groups (neutralise negative charge)
C: PEG to increase molecular weight
D:targeting ligand - made specific to a receptor on the cell type of interest
How is it taken up in targeted delivery?
receptor-mediated endocytosis
siRNAs encased in endosomes → lysosome
need endosomal escape to stop them being transferred to lysosome.
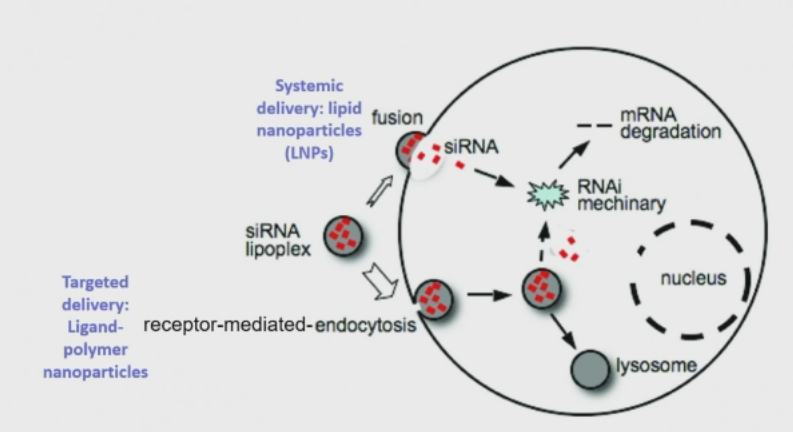
How does endosomal escape occur?
Add proton sponge groups to lipid nanoparticle
induces pumping of hydrogen ions into endosome → osmotic swelling → endosome ruptures → siRNA released → taken up by RISC complex.
How have siRNAs been used to treat haemophilia?
clotting factors + anti-clotting factors produced in liver
haemophilia = mutation in a gene encoding a clotting factor → profuse bleeding
If you can knock down an anti-clotting factor e.g. antithrombin, it restores the balance.
How to target liver cells for haemophilia?
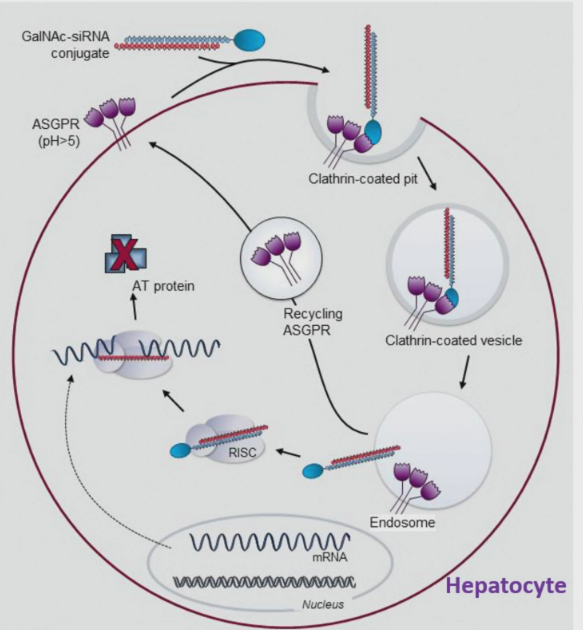
Use GaINAc ligands - high affinity for ASGPR receptor on hepatocytes
targets the antithrombin mRNA
binds to glycoprotein receptors on liver cell → taken up by receptor mediated endocytosis → endosomal escape → siRNA binds to antithrombin mRNA → RISC destroys it → reduced production → restoration of balance between clotting and anticlotting factors.
Shown to work in mouse models.
How did siRNAs help with ebola?
siRNA designed for new strain of virus
used lipid nanoparticle (LNP) approach for systemic delivery
showed efficacy on monkeys
virus mutates quickly but can redesign in response to this for an effective countermeasure.