dental embryology, histology, and anatomy ch 1-2 quiz
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
oral cavity divisions
the oral cavity is divided into the
vestibules
jaws with alveolar processes
teeth
and oral cavity proper
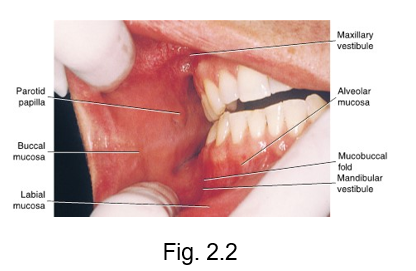
oral vestibules
upper and lower horseshoe-shaped spaces in the oral cavity between the lips and cheeks anteriorly and laterally
maxillary and mandibular vestibule
lined by oral mucosa (labial and buccal)
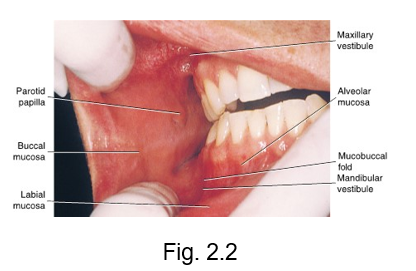
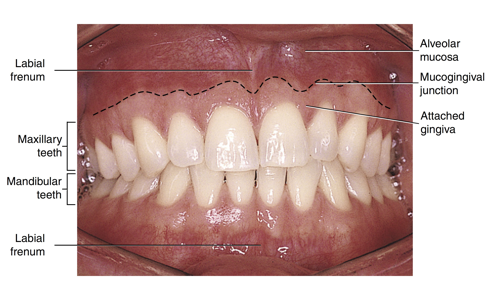
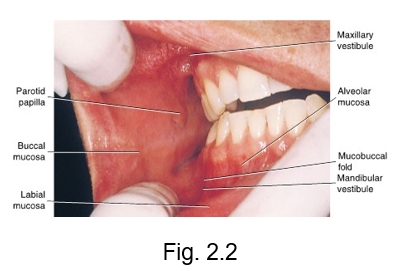
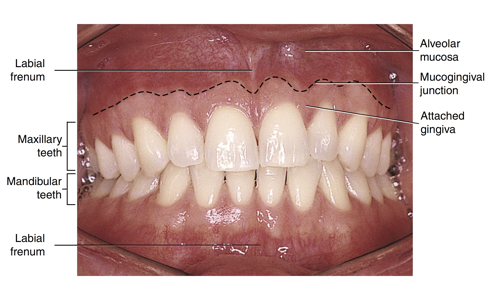
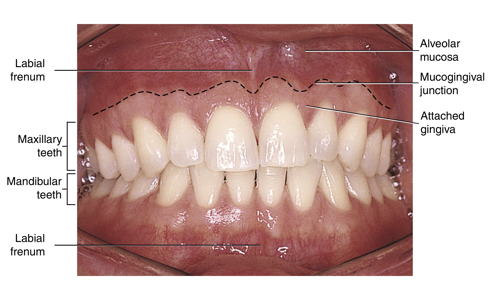
labial frenum
a fold of tissue located at the midline between the labial mucosa and the alveolar mucosa on the upper and lower dental arches
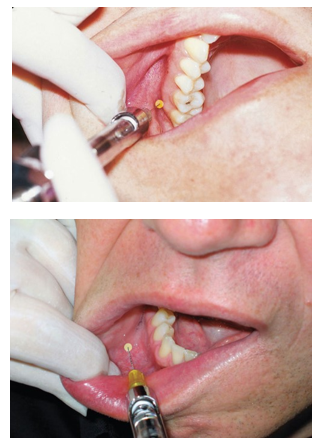
important to locate labial frenum because it is a primary injection site for local anesthesia
mucobuccal folds
the fold formed by the oral mucosa where it passes from the mandible or maxilla to the cheek
many of the local anesthesia injections for patient pain control and hemostasis are administered at the height or depth of the mucobuccal fold
parotid ducts
protected by the parotid papilla
also known as the stensen duct
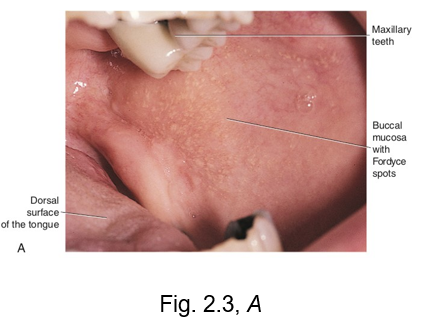
fordyce granules
on the surface of the labial and buccal mucosa is a common variation, fordyce granules
these are visible as small yellowish elevations in the oral mucosa
they represent deeper deposits of waxy sebum from trapped or misplaced sebaceous gland tissue
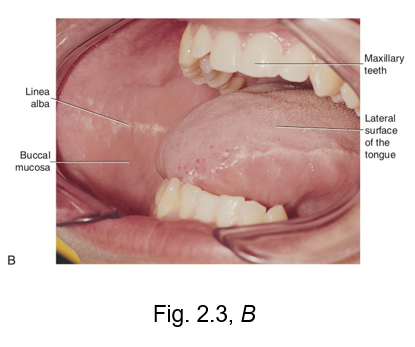
linea alba
LINEa alba - looks like a line
this is a white ridge of calloused tissue (hyperkeratinization) that extends horizontally at the level where the maxillary and mandibular teeth come together to occlude
can occur on the buccal mucosa or the lateral surface of tongue
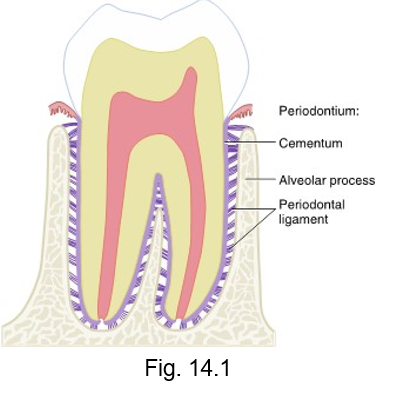
periodontal ligament (PDL)
all of the teeth are attached to the bony surface of the alveoli by the fibrous __ __
allows some slight tooth movement within the alveolus while still supporting tooth
attaches to cementum of root and the alveoli of bone, holding the tooth in the socket
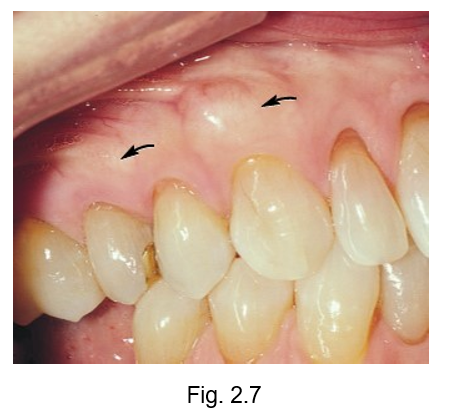
exostoses
facial surface of the alveolar process of maxillary arch may contain ___
they are extra localized developmental growths of bone covered in oral mucosa with a possible hereditary etiology and which may be associated with occlusal trauma
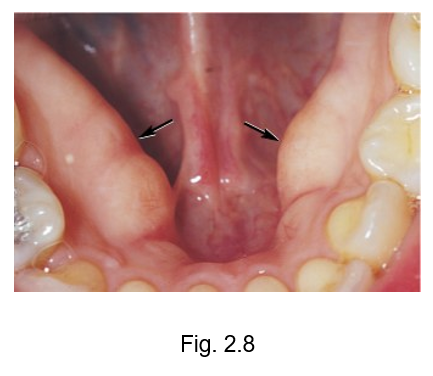
mandibular torus
developmental growth of bone present on the lingual surface of the mandibular arch with a possible hereditary etiology similar to exotoses
may be associated with grinding, also known as bruxism
gingival tissue
labial frenum
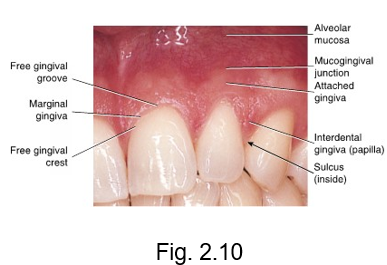
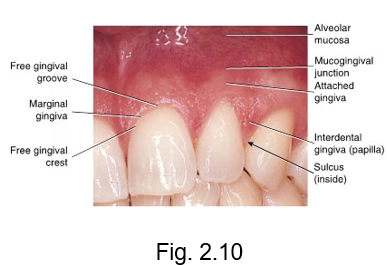
alveolar mucosa
mucogingival junction
attached gingiva
maxillary tuberosity
retromolar pad
attached gingiva
attached to something
gingival tissue that tightly adheres to the alveolar process surrounding the roots of the teeth
mucogingival junction
the line of demarcation between the firmer and pinker attached gingiva and the moveable and redder alveolar mucosa that lines the vestibules is the scalloped-shaped ___
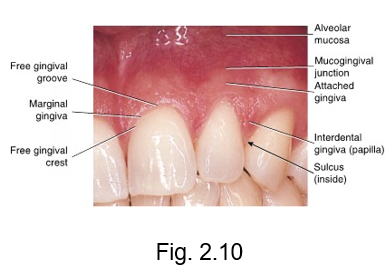
marginal gingiva
at the gingival margin of each tooth is the __ or free gingiva
forms a cuff above the neck of the tooth
gingiva that creates a MARGIN around the tooth
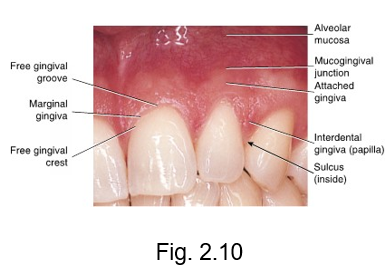
free gingival groove
separates the marginal gingiva from the attached gingiva
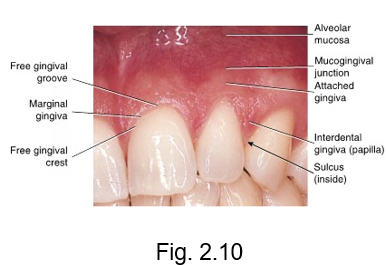
free gingival crest
at the most coronal part of the marginal gingiva
crest is at the TOP
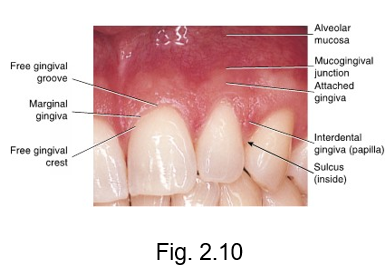
sulcular epithelium
epithelium that line pockets
sulcus = hole or pocket
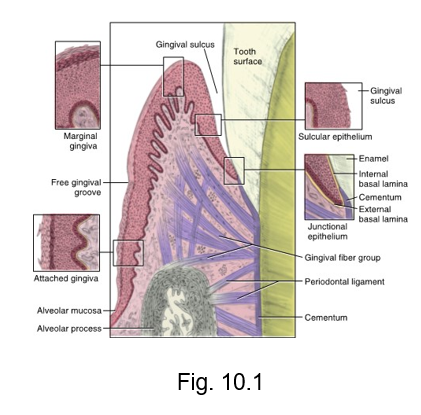
junctional epithelium
where free tissue is attached to tooth
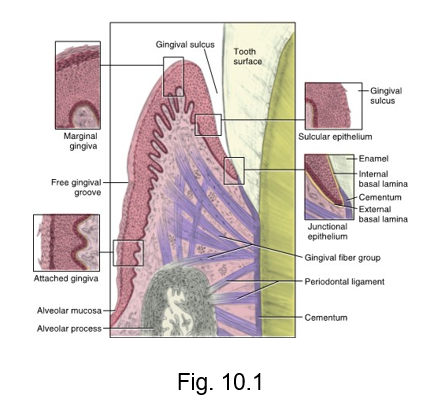
gingival sulcus
the circular inner surface of gingival tissue of each tooth faces an equally rounded space
the __ ___
interdental gingiva
is the gingival tissue between adjacent teeth adjoining the attached gingiva
(papilla)
inter = between
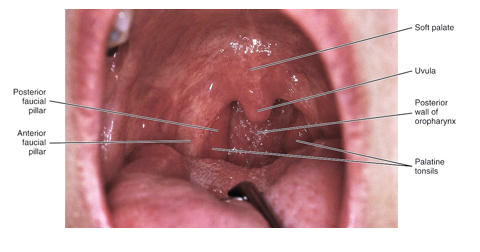
fauces
are formed laterally on each side by the anterior faucial pillar and the posterior faucial pillar
palatine tonsils are located between these folds of tissue created by underlying muscle
important to know locations
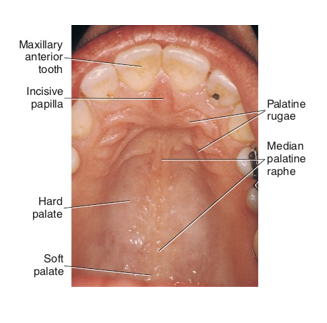
palate
located within oral cavity proper
separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity
hard palate shows an absence of mucogingival junction on the palatal aspect because there is not an attachment of tissue, only bone
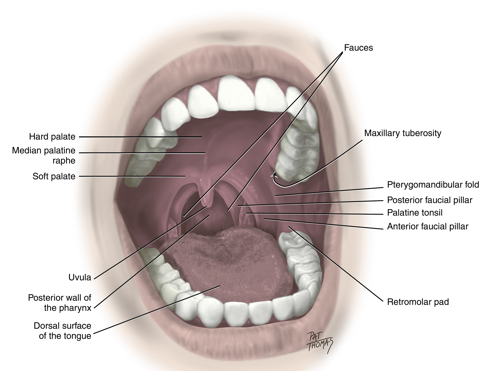
the pterygomandibular fold
extends from the junction of hard and soft palates down to the mandible
posterior to the most distal mandibular tooth and stretches when the mouth is open wider
important to know location for injections
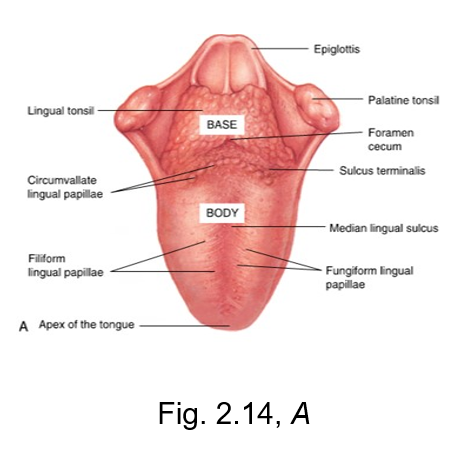
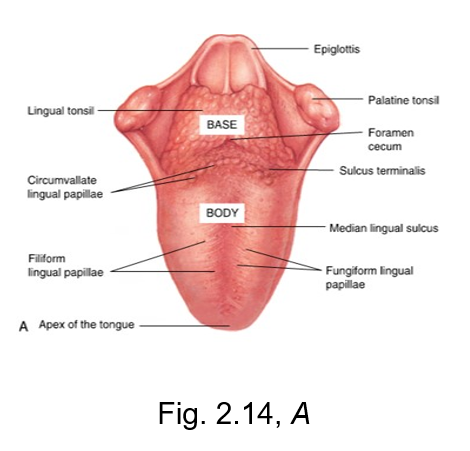
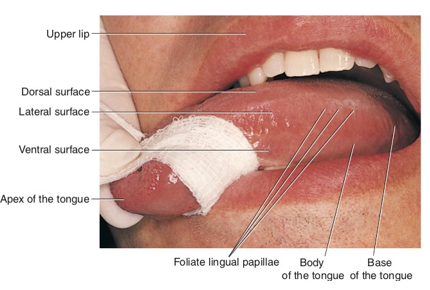
filiform lingual papillae
the slender threadlike whitish lingual papillae
give the dorsal (top) surface of the tongue its velvety texture
has no taste buds, but makes up a majority of the tongue
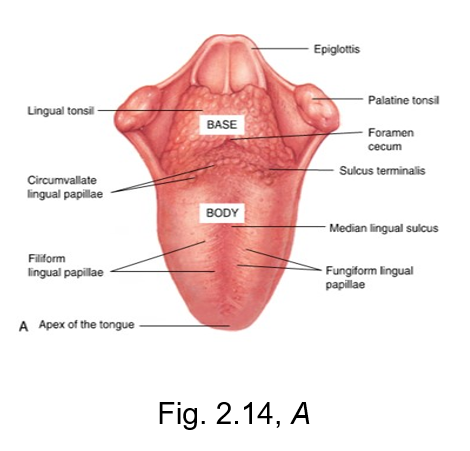
fungiform lingual papillae
The reddish, small, mushroom-shaped dots on the dorsal (top) surface of the tongue
crucial for taste perception
tasting is FUN
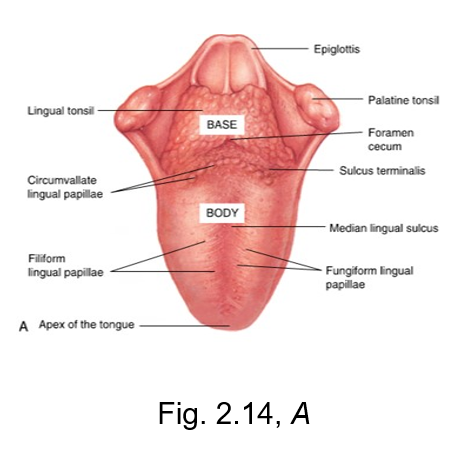
sulcus terminalis
v-shaped groove
separates the base from the body of the tongue
located posterior to body of tongue
terminal = end
dorsal surface of the tongue
top of the tongue
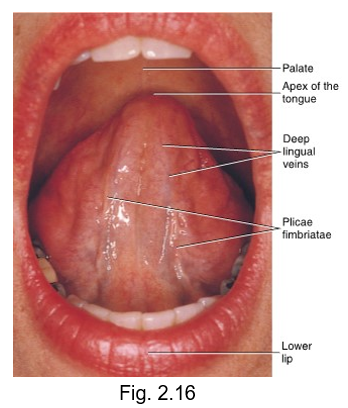
ventral surface of the tongue
bottom of the tongue
has large visible blood vessels and deep lingual veins
submandibular duct
also known as wharton duct
sublingual duct
also known as bartholin duct
Sialolithiasis or ranula
blocked salivary duct
is a condition where mineral deposits (sialoliths) form in the salivary glands or their ducts
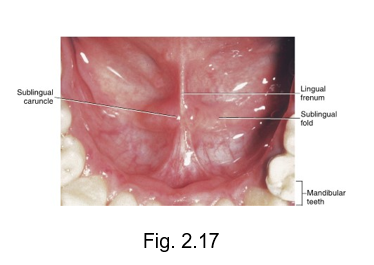
Ankyloglossia
commonly known as being “tongue tied”
tight lingual frenum attachment
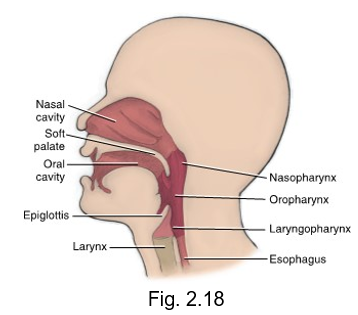
pharyngeal divisions
nasopharynx (nose)
oropharynx (oral)
laryngopharynx (larynx - voicebox)
buccal fat pad
covered in buccal mucosa
dense pad of underlying fat tissue
acts as a protective cushion during mastication
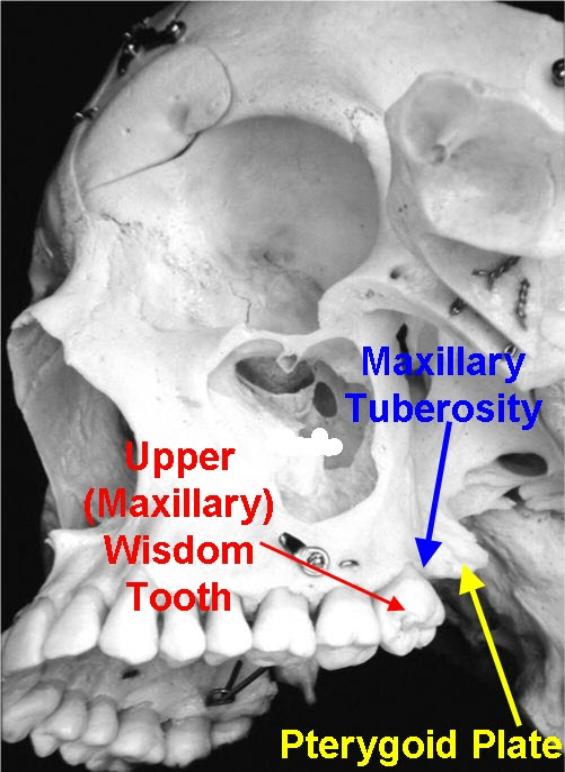
maxillary tuberosity
rounded bony process located in the posterior section of the alveolar maxilla ridge
retromolar patch
retro = behind
mass of soft tissue located in the posterior portion of the mandibular alveolar ridge
alveolus
LUS = less bone
bony socket in the upper and lower jaws that teeth sit in
foliate papillae
located on the lateral surface of the tongue
vertical ridges
the lips of the face mark the __ boundary of the oral cavity
lips
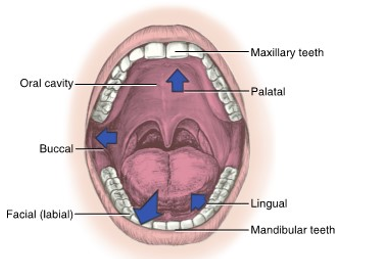
the __ is the posterior boundary of the oral cavity
throat
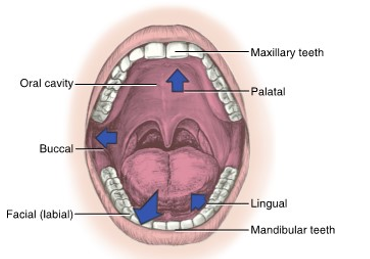
the __ of the face mark the lateral boundaries
cheeks / buccal
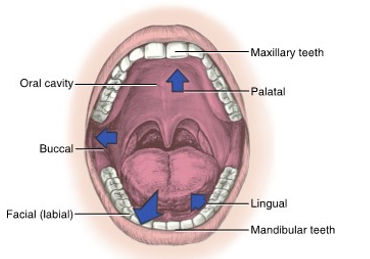
the __ of the oral cavity marks the superior boundary
palate
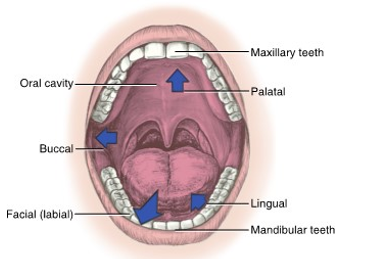
the __ of the mouth is the inferior border of the oral cavity
floor
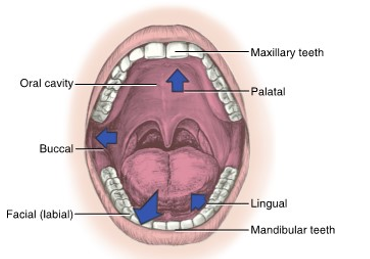
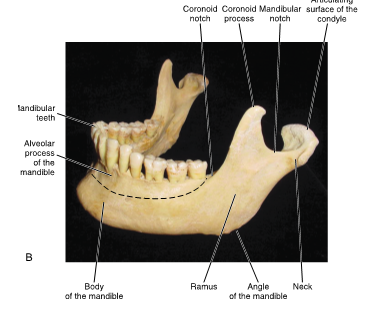
condyle of mandible
con people are always behind
posterior structure on mandible
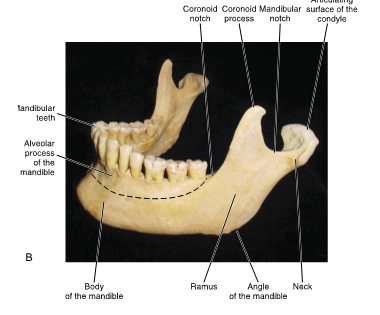
coronoid process
crown on top
anterior structure of mandible
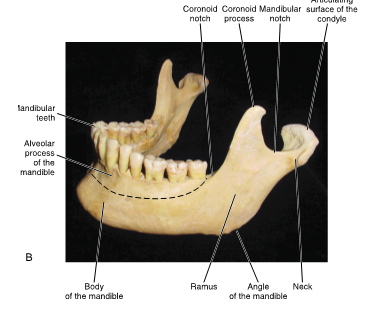
mandibular notch
located in between coronoid process and condyle