Biological Molecules
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Macromolecule
Many same micromolecules joined together to make one giant molecule
Monomer
Small basic molecular unit
Polymer
Many same type monomers joined together in a chain (repeated monomers)
Anabolism
The process of building up smaller molecules into bigger molecules
Catabolism
Process of breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body
Condensation reaction
This joins 2 molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water.
Hydrolysis reaction
Breaking a chemical bond between 2 molecules and involves the use of a water molecule
Examples of monomers
Monosaccharides, amino acids, nucleotides
Polymers and their monomers
carbohydrates-monosaccharides
nucleic acid-nucleotide
protein-amino acids
lipids-fatty acids and glycerol
water - no monomer
How does hydrogen bonding work?
A molecule with an uneven distribution of charge is polarised. The negative region of the polar molecule and the positive region attract each other to make an electrostatic bond. These bonds collectively can form a force that alters the physical properties of molecules
3 Monomers for carbohydrates you need to be able to draw
Alpha glucose, beta glucose, galactose. (You dont have to be able to draw fructose but you need to know it)
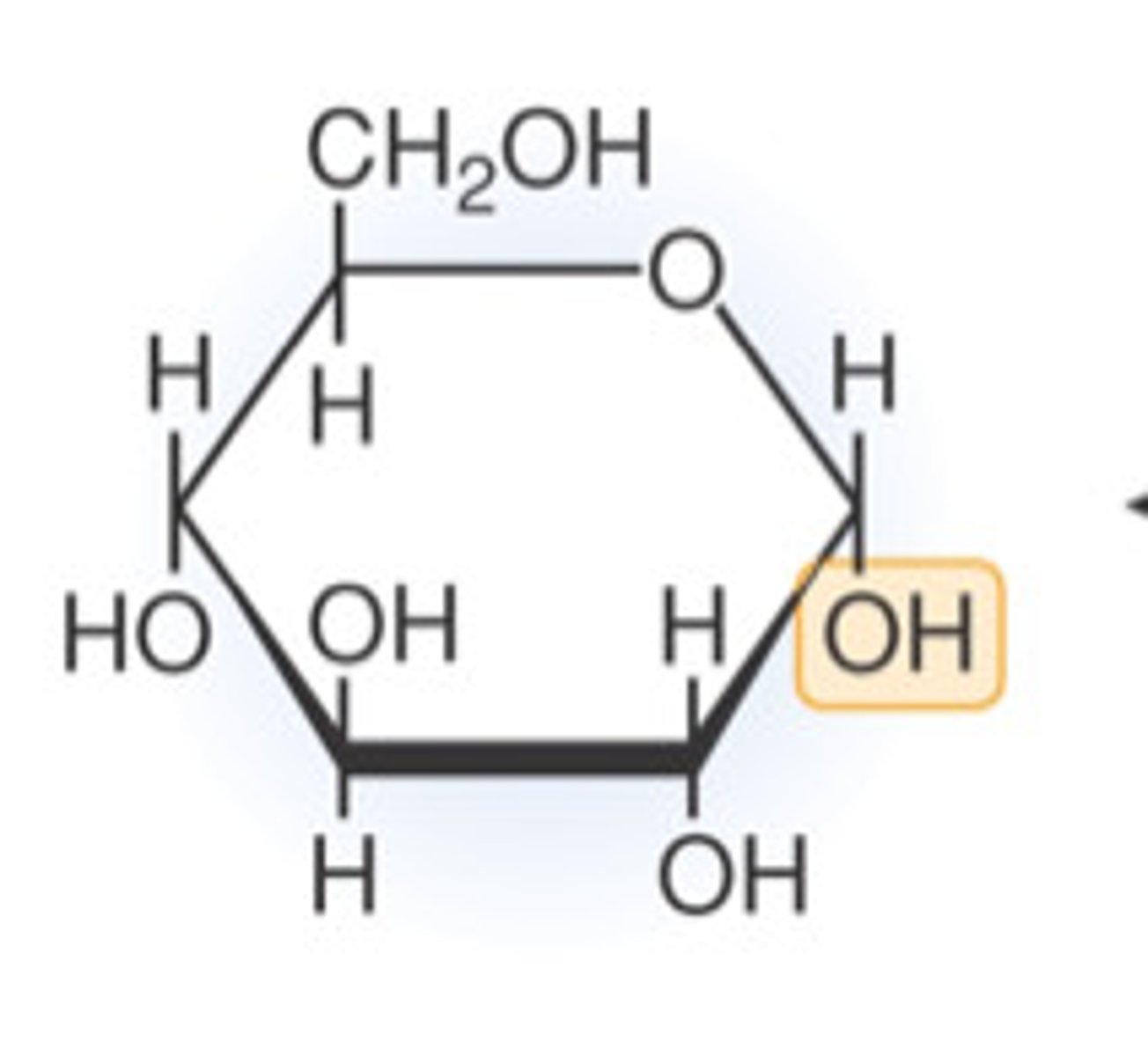
Alpha Glucose (Image)
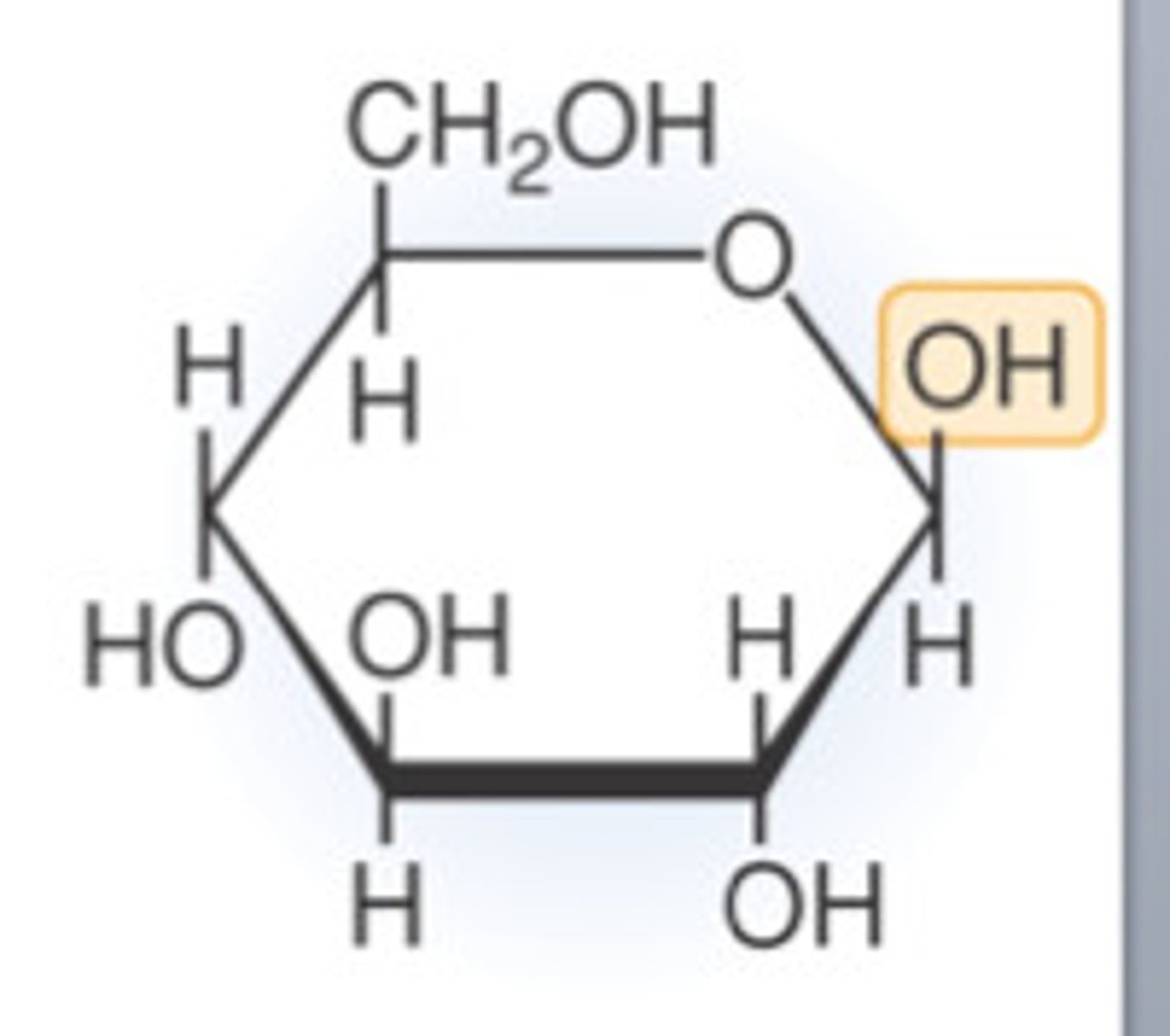
Beta Glucose (Image)
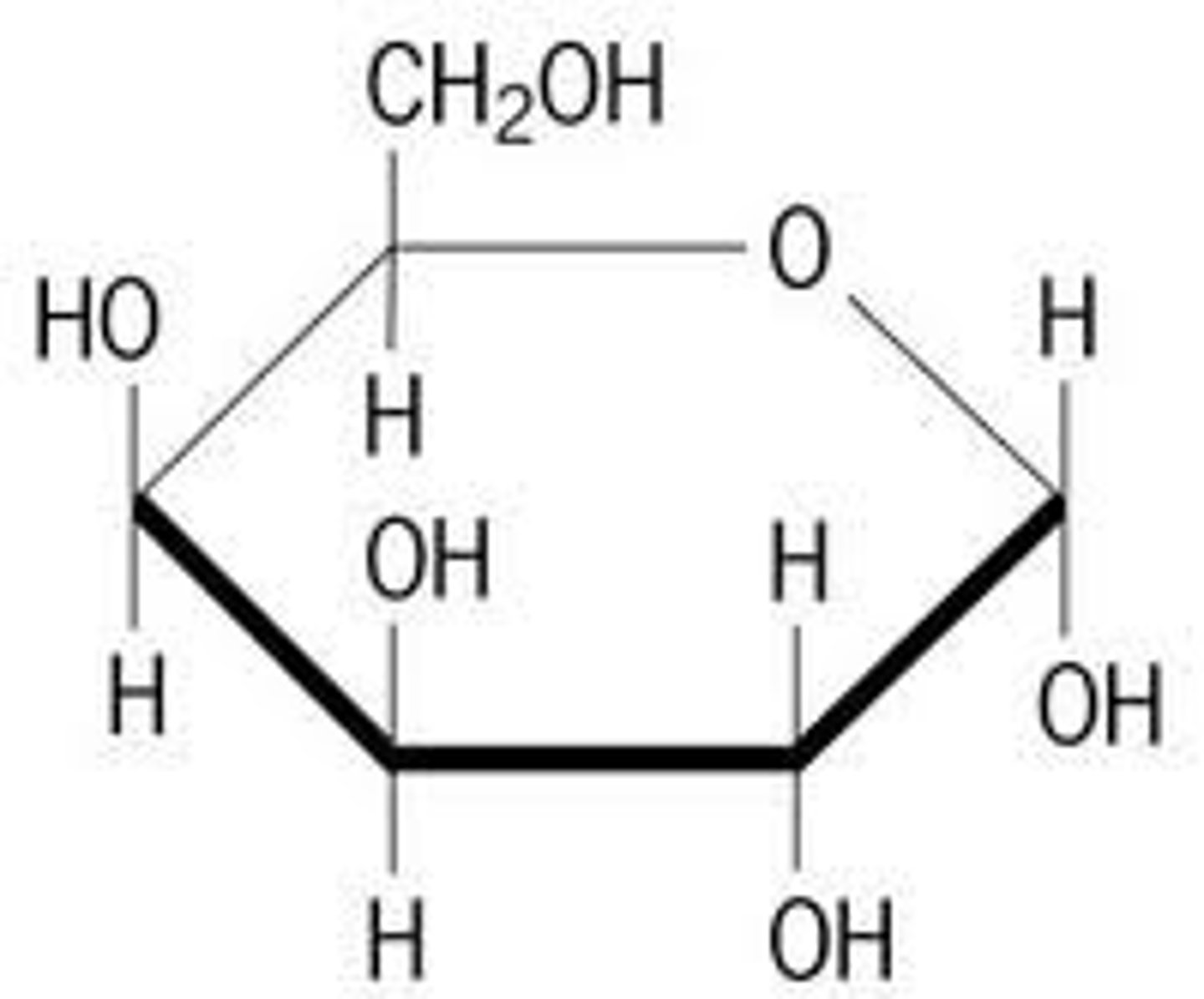
Galactose (image)
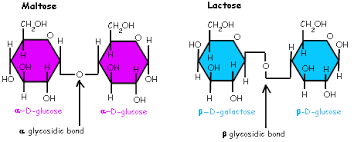
What 2 monomers is the disaccharide maltose made from
Condensation of 2 glucose molecules
What 2 monomers is the disaccharide sucrose made from?
Condesnation of a glucose molecule and fructose
What 2 monomers is the disaccharide lactose made from?
Condensation of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule
How is glycogen and starch formed?
The condensation of alpha glucose
How is Cellulose formed?
The condensation of beta glucose.
What is a reducing sugar
A sugar that can donate electrons to another chemical
Molar solution
A solution that contains one mole of solute in each litre of solution
Isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
Bonds that form between monomers
Glycosidic bond
What is a condensation reaction
When two molecules bond through the loss of a water molecule.
What is a hydrolysis reaction
A covalent bond is broken by adding a molecule of water.
Where is glycogen found?
In animal s liver and muscle cells
What are the monomers of glycogen
Alpha glucose
Structure of glycogen
Chains of glucose in 1-4 glycosidic bonds and highly branched with alpha glucose in alpha-glucose in 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Function of glycogen
Stores sugar and an energy source its more soluble so can be broken down rapidly
Where is starch found
plants starch grains in plastids ( green chloroplasts and amyloplasts)
Monomers of starch
alpha glucose
Structure of starch
Glucose molecules are arranged in 2 different ways amalyse and amylopectin. These are built up in the chloroplasts or inn storage oragns
Amylase structure in starch
Unbranched chain of alpha glucose in a 1-4 glycosidic bond a compact vertical structure
Amylopectin structure in starch
Chain of alpha glucose in a 1-4 glycosidic bond with many more chains of alpha glucose 1-6 glycosidic bonds - compact
Function of starch
Used as storage ibn plants as starch granules are insoluble in water
Where is Celluose found
Cell wall of plants , monomers: beta glucose
Structure of Cellulose
Every other glucose molecules is rotated 180 degrees so that the hydrogen group on each molecule are adjacent to each other. Made up of about 10,000 beta glucose molecules in an unbroken chain
Function of Cellulose
Hydrogen bonds between chains gives cellulose great tensile strength cellulose is strong and prevents cell from bursting
Testing for carbohydrates (Starcg)
Potassium iodide is utilised as a solution starch-iodide complex forms a strong blue-black colour
Test for reducing sugar
Add benedicts solution to the sample in a water bath that has been boiled to 100 degrees for 5 minutes, positive test blue to orange/brick red
Test for non reducing sugars
Hydrolyse, dilute HCL is added to sample - breaks glycosidic bond . neutralise it by adding sodium hydrogen carbonate. Then add benedicts reagent in a water bath thats been brought to a boil of 100 degrees Celsius. Positive test blue to orange/brick red.
What type of bond is formed together when monosaccharides join together
glycosidic bond
What type of raection joins together proteins
condensation reactions
What are the advantages of storing glucose as starch
Starch is insoluble and therefore does not affetc water potential so water is not drawn into the cell via osmosis. Starch is also compact so alot of it can be stored in a small space.
What happens when starch is hydrolysed
It forms an alpha glucose which is both easily transported and readily used in respiration
What are the adaptations of glycogen
it is insoluble and is more branched than starch so has more ends that can be acted on simultaneously by enzmes. It is therefore more rapidly broken down to form glucose monomers.
What are the adaptions of celluose
celluose has straight unbranced chains. These run parallel to one another allowing hydrogen bonds to form cross-linkages between and adjacent chains. While each individual hydrogen bond adds very little strength. Then combine contributes heavily to strenght
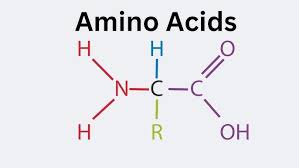
what does a amino acid look like?
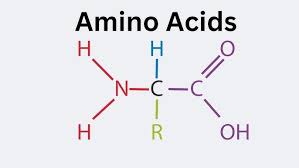
Diagram of a phospholipid

Why are phospholipids polar molecules.
They have a hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic taail of 2 fatty acis. This means that phosphoplipids form a bilayer within cell surface memvrabes.
What are some examplesthat lipids are used for
Insulation secondary food storage.
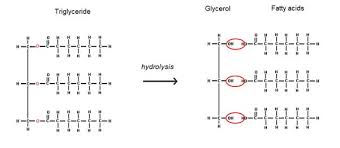
Triglyceride diagram
Simple way to denotew a general fatty acid moleucle
R-COOH (R represents the hydrocarbon chain)
Ester bond (image)
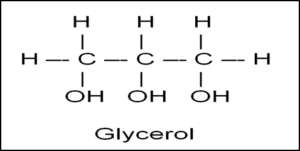
glycerol (image)
Saturated fats
Fats dont have any bonds between their carbon atoms. No kinks, less fluid
Unsaturated fats
Fats that have at ;easy one double bond between carbon atoms causing the chain to kink, more fluid
How many glycosidic bonds are between 3 monosaccharides
2
Give 2 features that may be found in a prokaryotic cell which would not be found in a plant cell
Peptidoglycan cell wall (celluose in plant cells). 70s ribosomes compared to 80 s in plant cells. Circular DNA compared to linear DNA in plants.
How many carbon atoms does a molecule of fructose contain?
2
How are triglycerides formed?
Through the reactions of 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol. It is formed through a type of condensation reaction called esterification due to formation of ester bonds
What does the “R” represent on a fatty acid
The hydrocarbon chain
What 2 parts make up a phospholipid
A hydrophilic head (Attracted to water) and a hydrophobic tail (afraid of water)
diagram of phospholipid
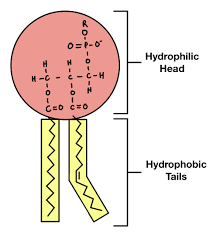
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer within cell-surface membranes
They are polar molecules, having a hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic tail of 2 fatty acids. This means that in an aqueous environment, phospholipid molecules form a bilayer within cell -surface membranes. As a result a hydrophobic bbarrier is formed between the inside and outside of a cell.
How do hydrophilic heads of phosphate molecules help the phopsholipid molecule
It helps to hold at the surface of the cell surface membrane
How are glycolipids formed at a cell surface membrane
The phospholipid structure allows them to form glycolipids by combinding with carbohydrates within the cell surface membrane
What bond forms between fatty acid and glycerol
ester bond
E coli has no cholesterol in its cell surface membrane. Despite this the cell maintains a constant shape
it has a peptidoglycan cell wall.
What are the roles of proteins
Defence, - Structural, -carriers, hormones, enzymes
amino acid
NH2 = Amine group COOH = carboxylic acid group
The structure of haemaglobin explained
Globular, soluble in water, many different amino acids 4 polypeptide chains, 4 haem groups containing iron.
The structure of collagen explained
Fiborous, insoluble in water, lots of smallest amino acids (glycine). 3 Polypetide chains Helix Rope like and strong.
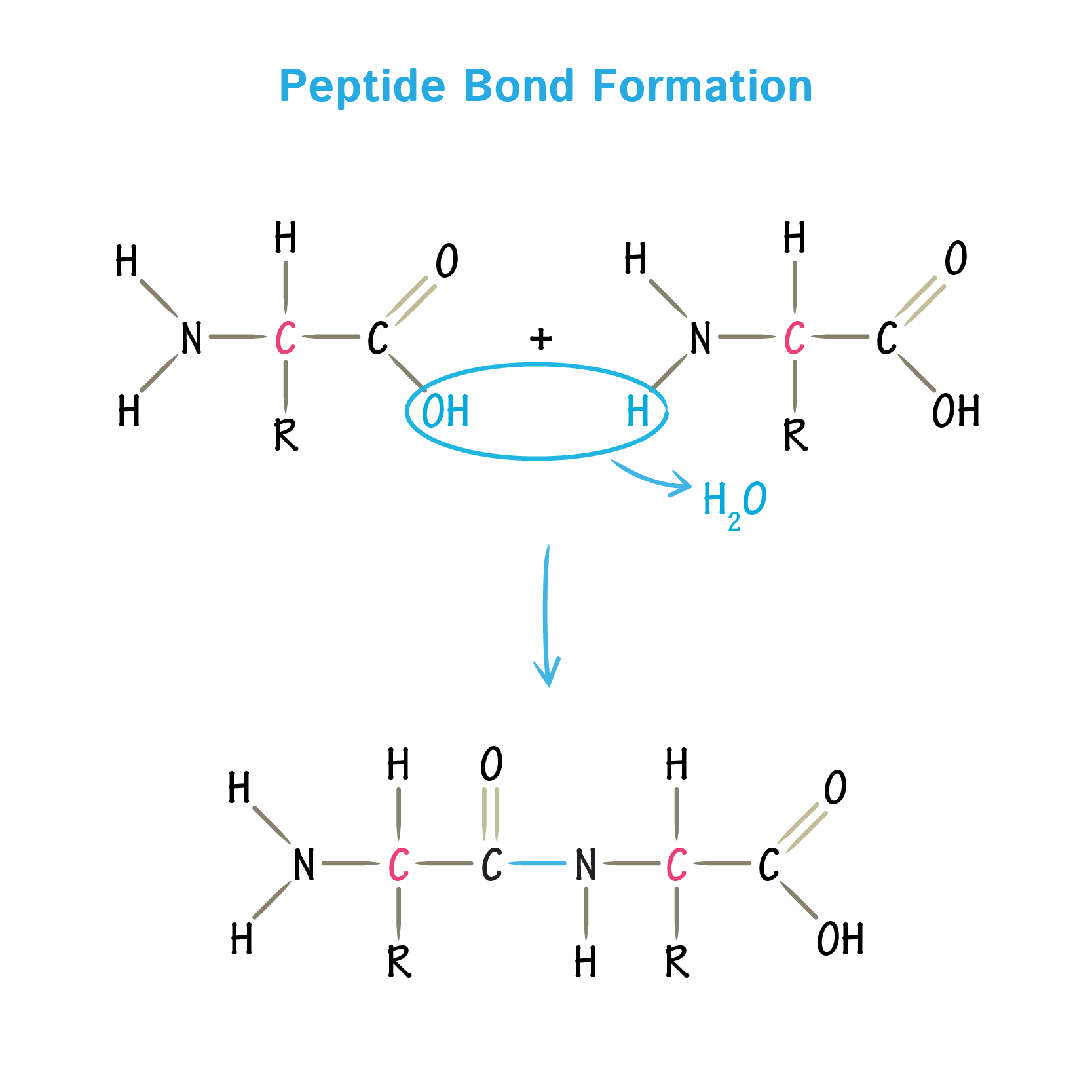
How is a peptide bond formed
the C-N is the chemical bond formed but the peptide bond is the C=O , H-N and C-N
What type of protein is Insulin
Globular protein
What 2 substances are formed when 2 amino acids join together
watrer and polypeptide
Primary structure of protein explained
The sequencee of amino acids provides the primary structure
Secondary structure of protein explained
This is how the polypeptide chain is folded. It may form an alpha helix or beta fold or pleated sheet. It is held together by hydrogen bonding.
Tertiary structure of protein explained
Further folding of the polypeptide chain, it is held by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulphide bridges and ionic bonds
Quaternary structure of protein explained
Furyjer folding of the polypeptide chain, it is held by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulphide bridges ionic bonds
What is meant by a receptor molecule
A molecule that is on the surface of a protein and receives signals.
Explain how a proteins tertiary structure might allow a protein molecule to act as a receptor molecule
Folds into specific shape which can be complimentary to specific substances.
What is the relationship between enzymes and substrates in terms of reactions
Ezymes enable substrate to react but it is not used during the reaction
What are enzyme’s structures
They are proteins, large macromolecules, proteins with tertiary structures
Why can enzymes not catalyse multiple reactions
The active site of the enzyme is complimentary to a specific substrate
Enzyme induced fit diagram
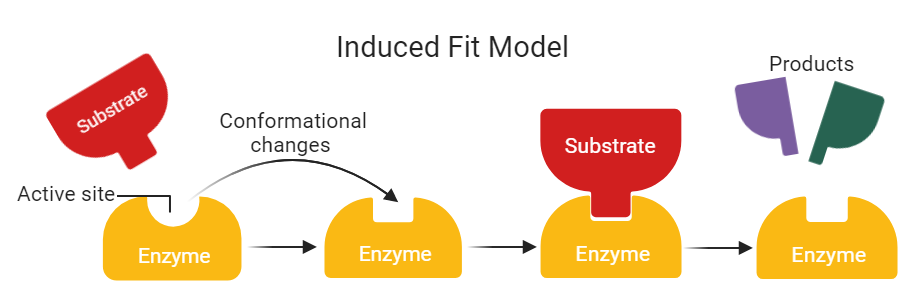
What type of reactions do enzymes catalyse?
They catalyse both anabolic and catabolic reactions
Investigating the effect of enzymes practical
First add 10ml of 30% powder milk solution in tube C and T and draw an x on tube T
1) In one tube add 4ml of pH7 buffer (test tube C) in another add 2ml of pH7 and 2ml of 0.5trypsin solution (Test tube T)
2)Place tets tubes in water bath until tubes reach 40oc
3) In tube labelled T add trypsin enzyme tube and in the tube labelled C add tube without enzyme trypsin
4) Then start timer and record the time it takes for x to appear on the T tube
Rate of teaction = 1/time(s)
What is the induced fit model
The active site shape is not initially complimentary to the substrate. The active site moulds itself around the substrate. The change of shape alters the substrate, putting stress on the bonds and therefore lowers the activation energy required for the reaction
Graph for rate of reaction with pH
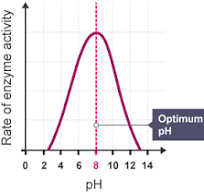
Graph for rate of reaction with temperature
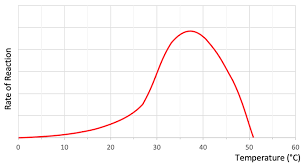
Rate of reaction and enzyme graph
This is the same as the substrate concentration and rate graph. Sometimes the graph is shown with the rate decreasing at high enzyme concentration this is due to the fact that if there is too many enzymes, then enzymes will collide with one another instead of binding with the substrate to create an enzyme substrate complex

What is an advantage of using a pH meter rather than a pH indicator in an experiment
It is more objective than subjective
Why does the pH decrease when lipase is added ti milk
Lipase breaks down fat in milk to fatty acids and glycerol. The fatty acids decrease the pH
What type of biological molecule are enzymes
proteins
How do inhibitors prevent reactions?
through blocking the active site or changing the active site shape so enzymes can not bind to substrates
How do competitive inhibitors work?
They have a similar shape to the normal substrate so compete with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme and block the active site preventing a reaction from occuring.
How does a non competitive inhibitor work?
The inhibitor binds to the allosteric site causing a confirmational change so that the active site no long has an induced fit with the substrate and no reaction occurs.