Anatomy practical 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Prophase
chromatin condenses and spindle forms

Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the center
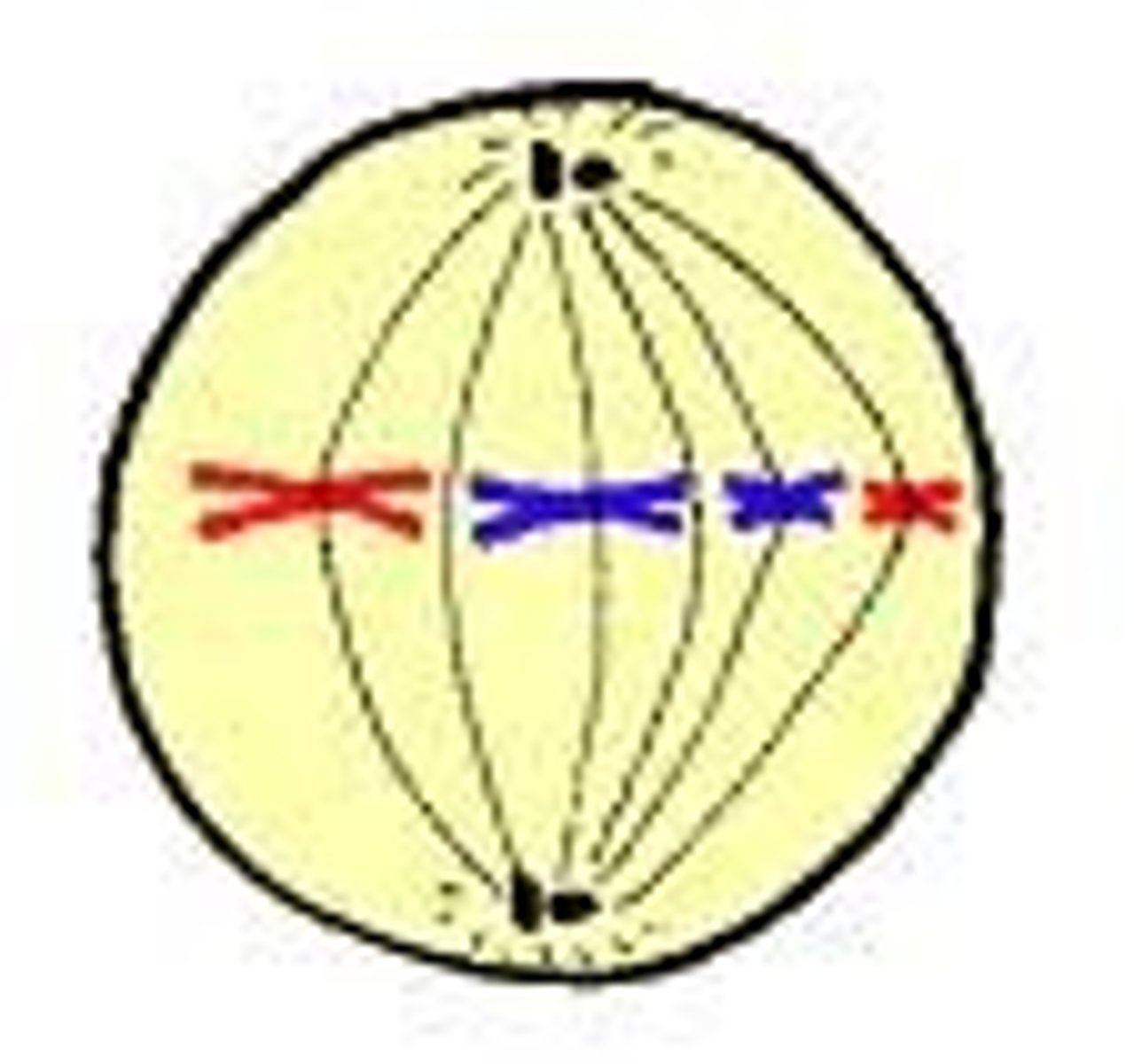
Anaphase
sister chromatids pulled apart
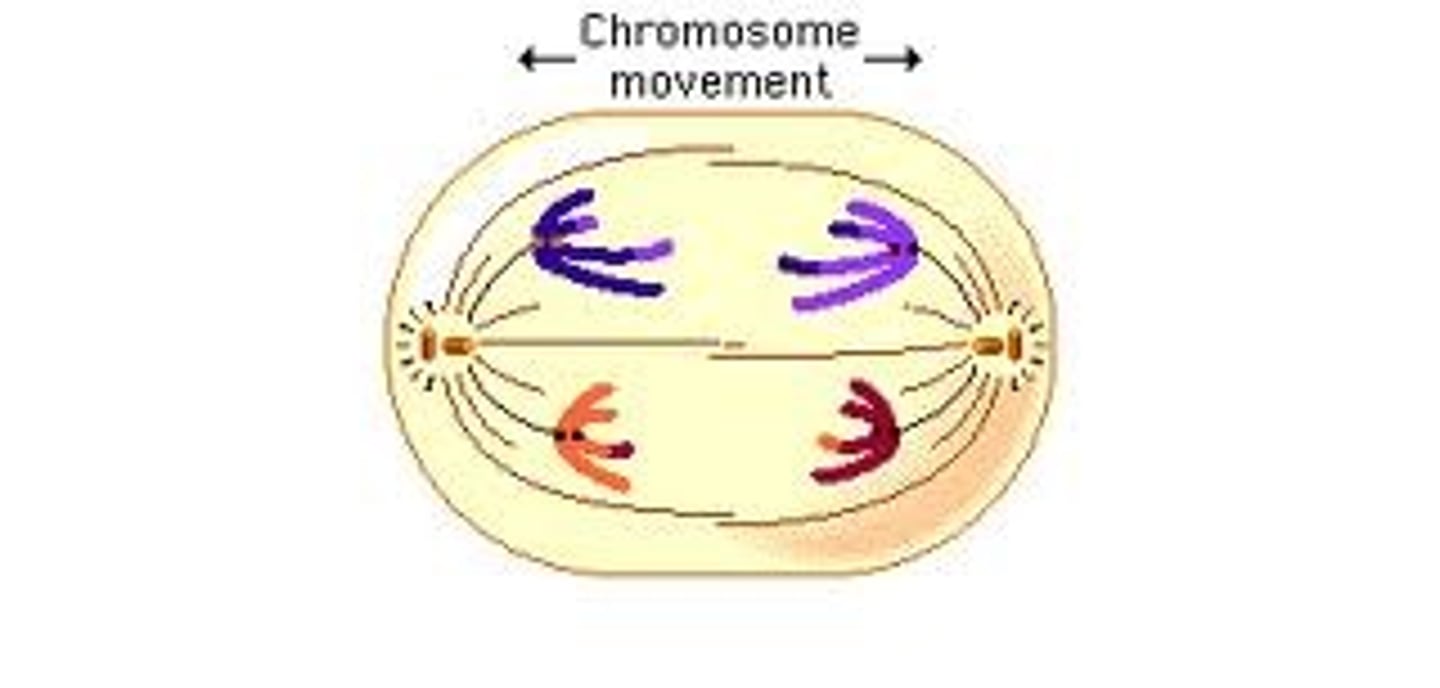
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms
Nervous system supporting cells: Astrocytes
blood-brain barrier, nutrient transport
Nervous system supporting cells: Microglia
Immune defense, phagocytosis
Nervous system supporting cells: Ependymal Cells
Line ventricles, produce cerebral spinal fluid
Nervous system supporting cells: oligodendrocytes (CNS/schwann cells(PNS)
myelinated axons
Satellite cells
support PNS neurons
Connective tissue supporting cells: Mast cells
inflammation, release histamine/heparin
Connective tissue supporting cells: Fibroblast
produce fibers (collagen, elastine, reticular)
Connective tissue supporting cells: Macrophages
engulf pathogens
In Epidermis supporting cells: Keratinocytes
produce keratin
In Epidermis supporting cells: Melanocytes
produce melanin (UV protection)
In Epidermis supporting cells: Langerhans cells
immune surveillance
In Epidermis supporting cells: Merkel Cells
touch receptors
In dermis supporting cells
fibroblasts, mast cells, macrophages, blood vessels, nerve endings
Pressure sensors (integumentary system): meissners corpuscles
light touch (papillary dermis)
Pressure sensors (integumentary system): Pacinian corpuscles
deep pressure/vibration (deep dermis/hypodermis)
Pressure sensors (integumentary system): merkel discs
sustained touch/pressure
Pressure sensors (integumentary system): ruffini endings
stretch and warmth
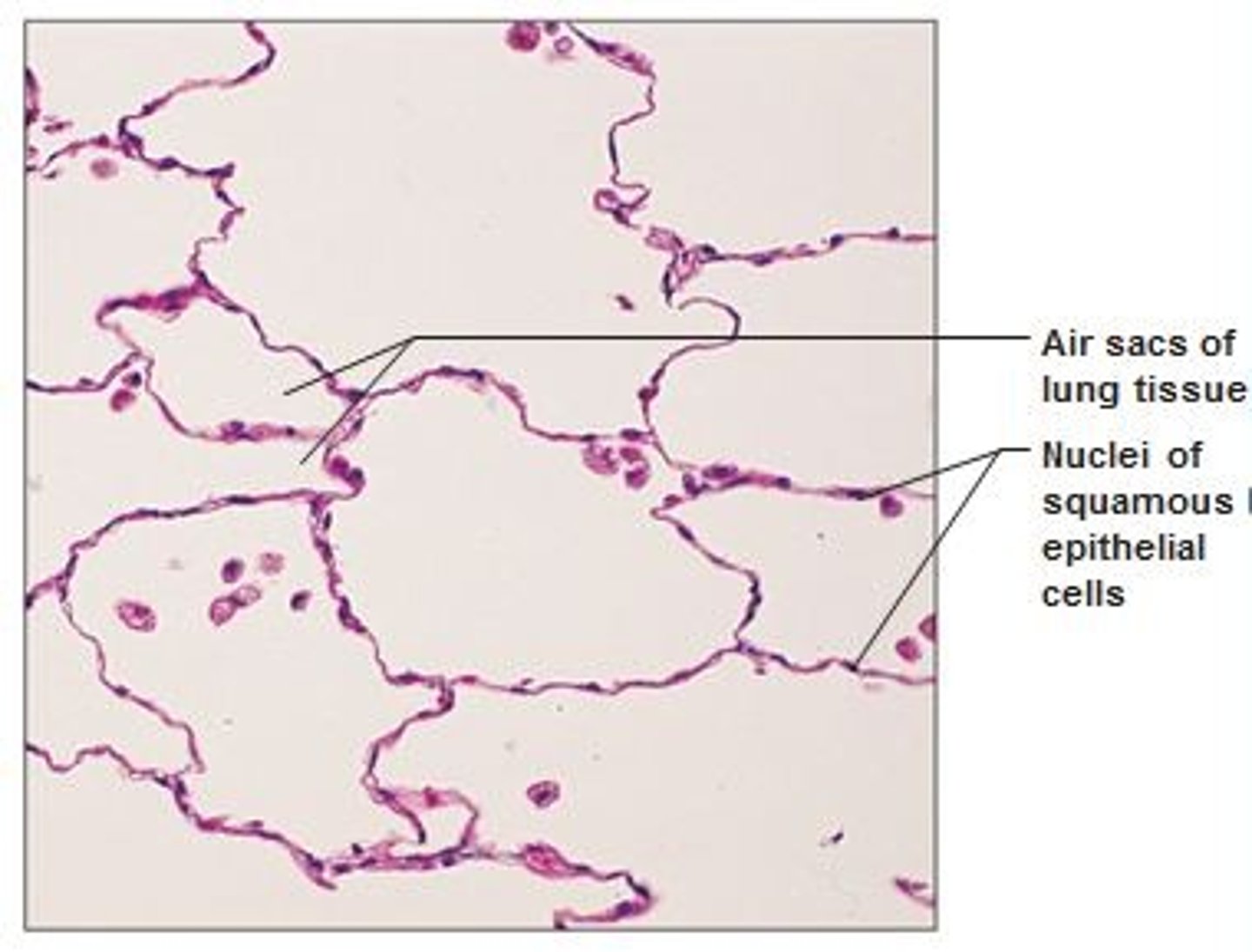
Simple squamous
-Diffusion, filtration
-Lungs (aveoli), blood vessels
simple cuboidal
-secretion, absorption
-kidney tubules, glands
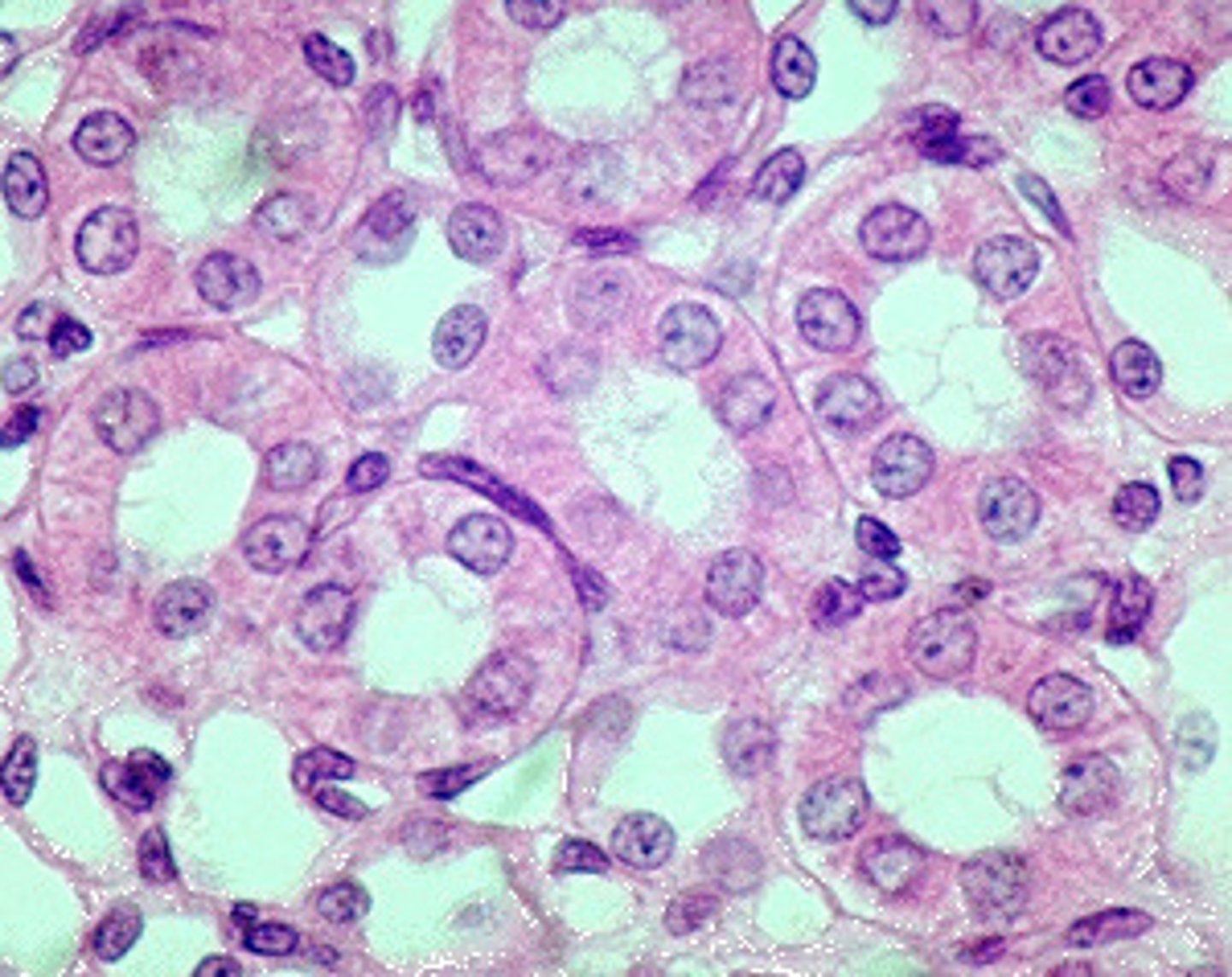
simple columnar
-Absorption, secretion
-Forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine, stomach to rectum
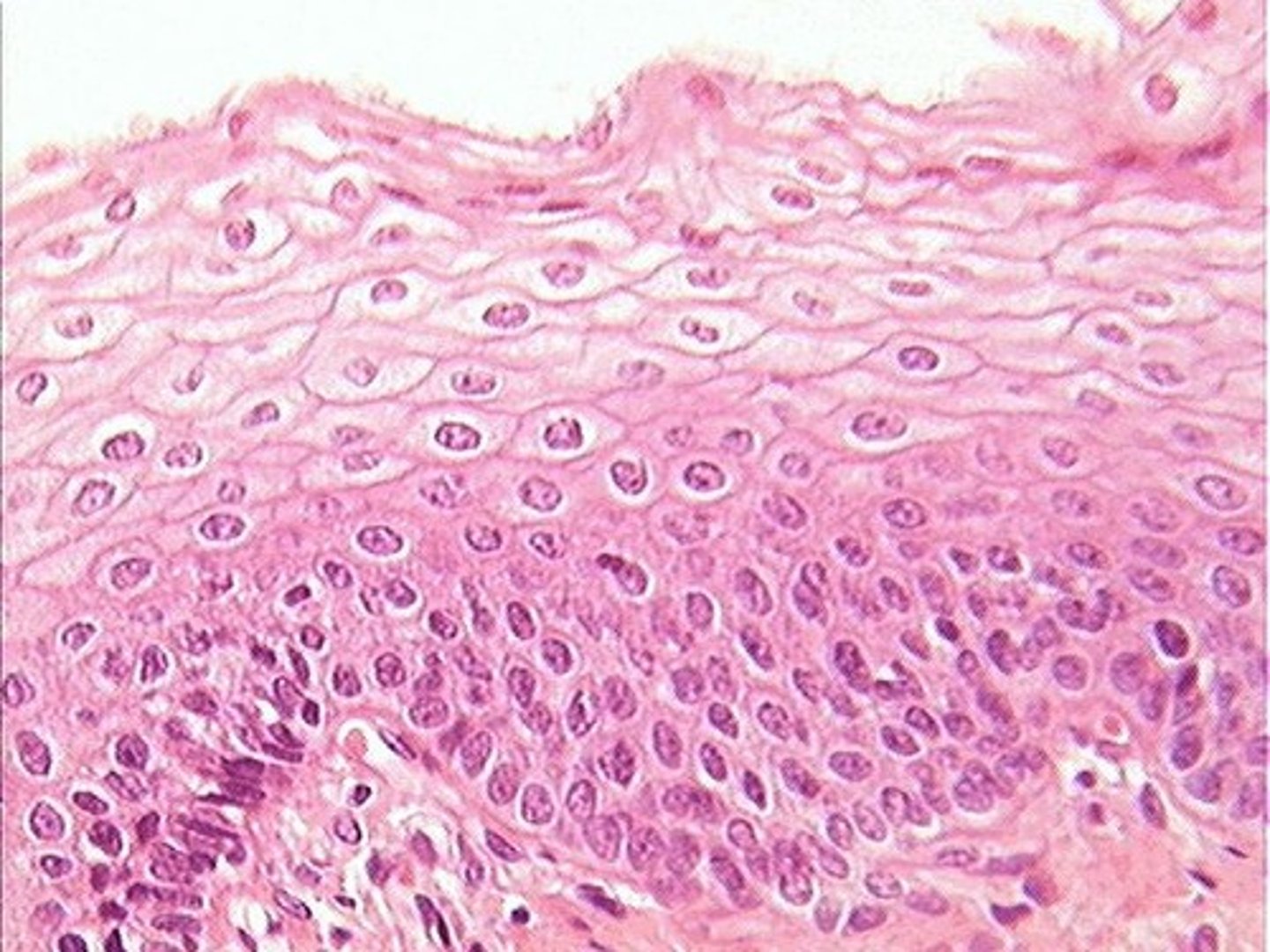
stratified squamous
-protection (abrasion)
-lines the esophagus (non-keratinized), forms the skin epidermis (keratinized
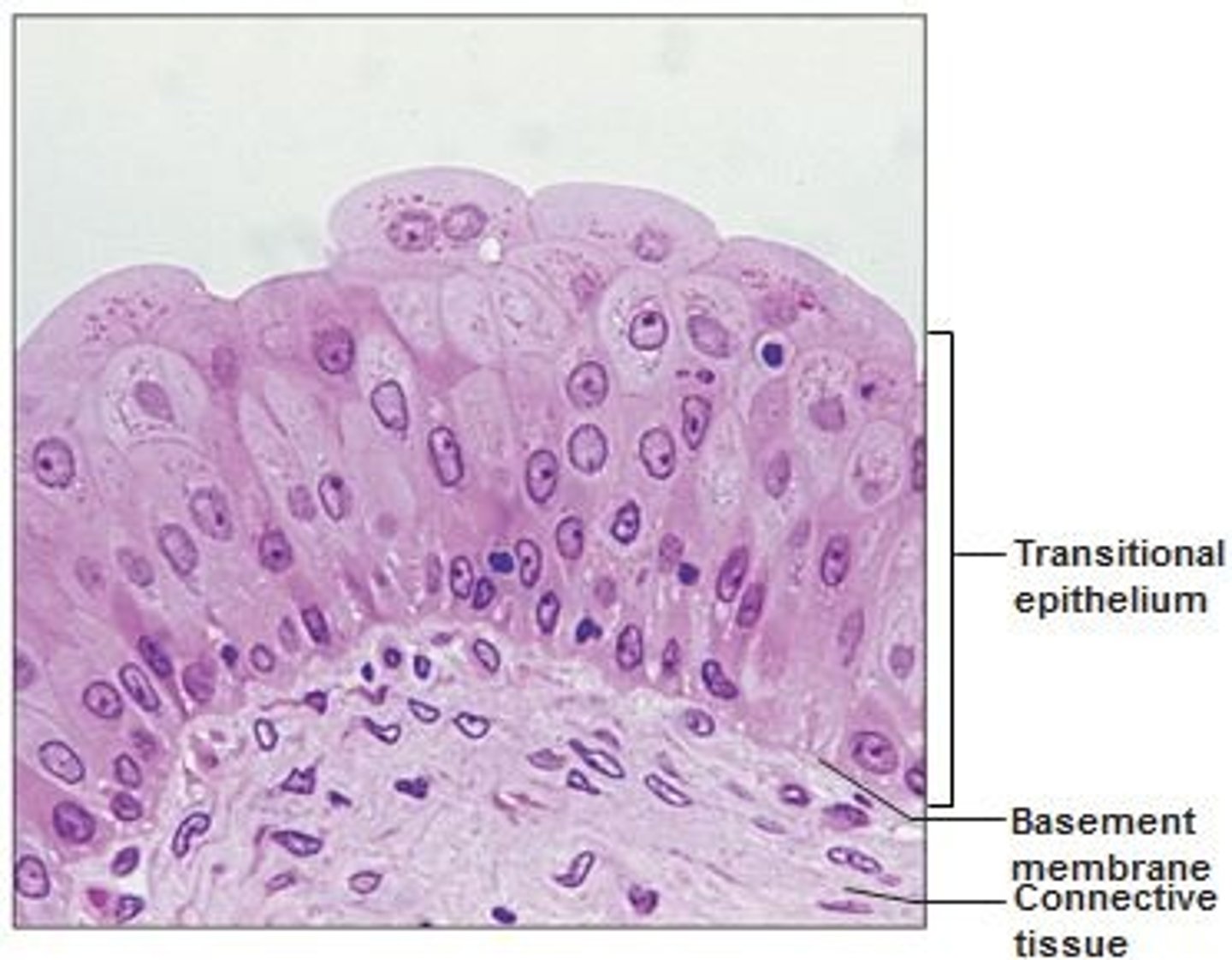
transitional epithelium
-stretching
-bladder
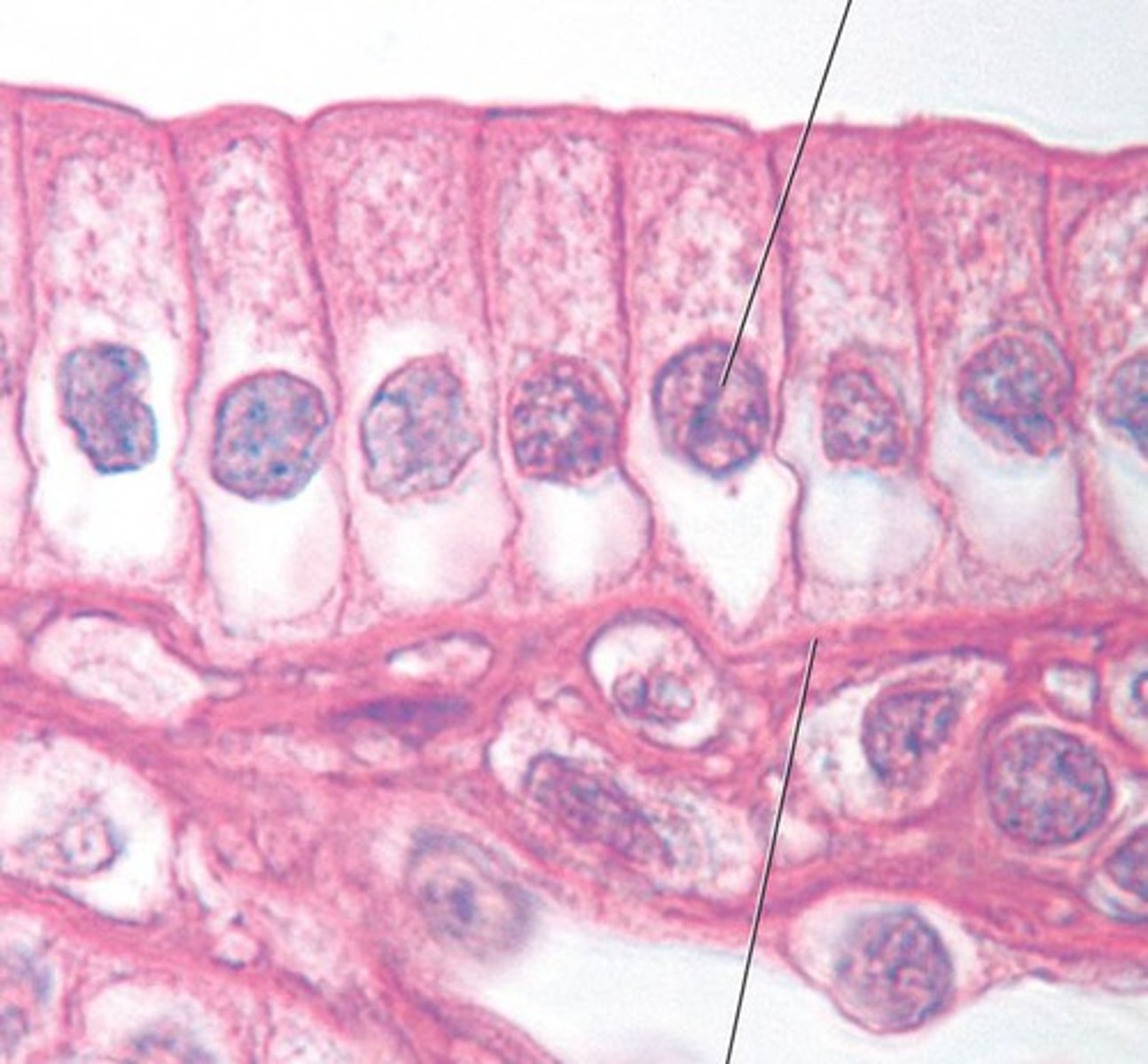
pseudostratified columnar
-secretion, movement (cilia)
-trachea (ciliated)
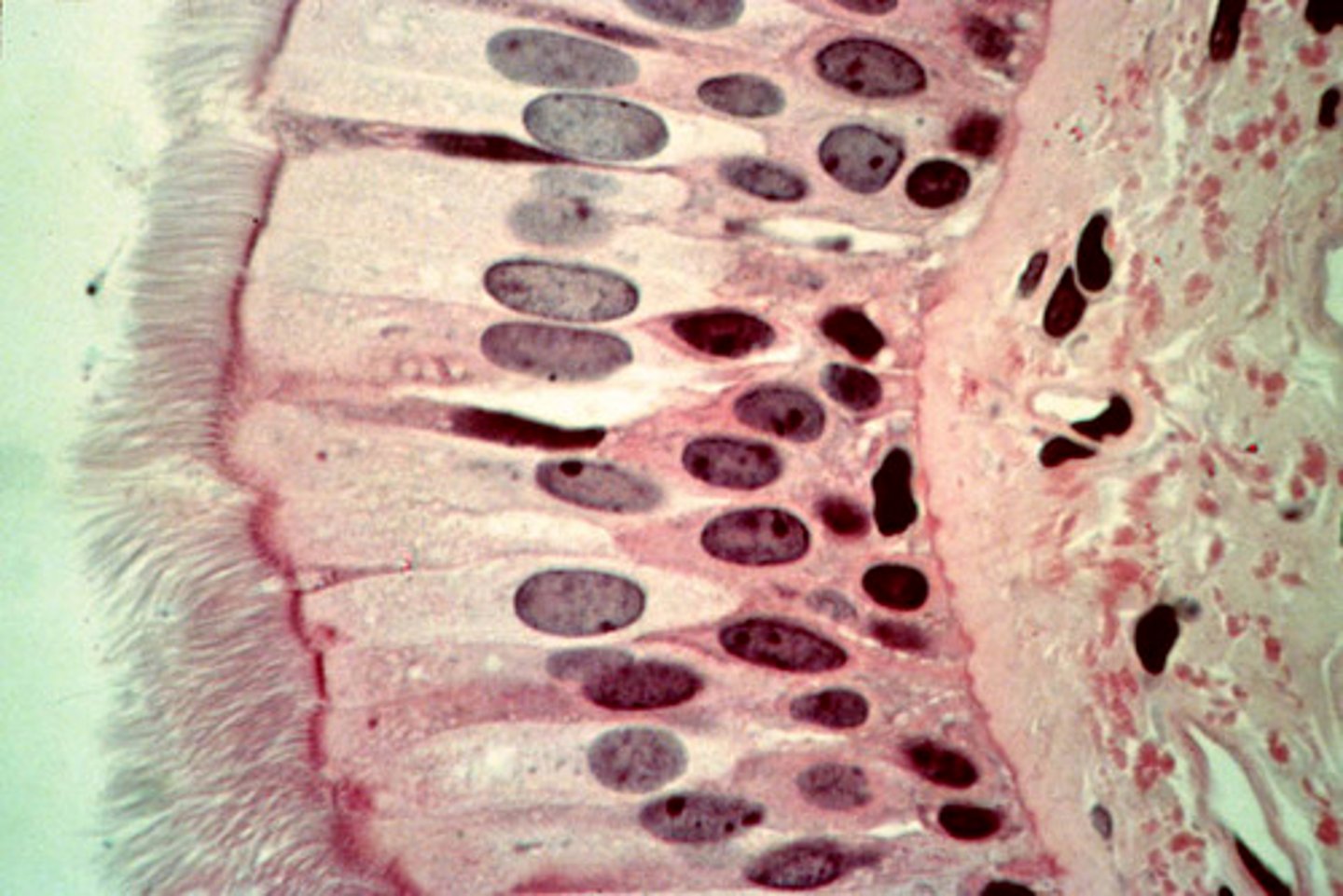
stratified cubodial/columnar
-protection, secretion
-rare in human body, found mainly in ducts of glands
key features of epithelial tissues
- Avascular (no blood supply)
-cells are packed tightly
-high rate of regeneration
mitosis
division of the nucleus PMAT
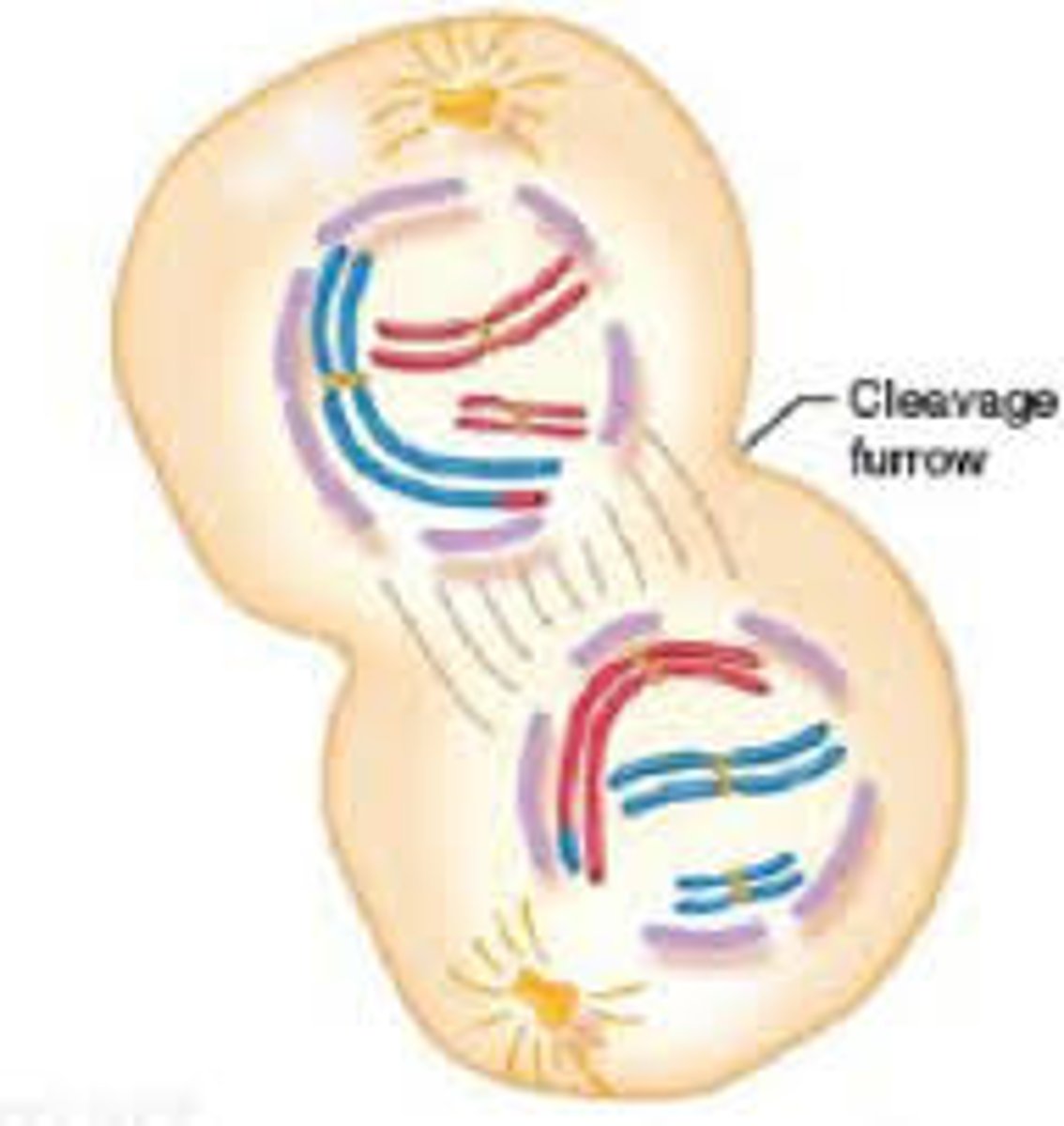
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm
cells that do not undergo mitosis
neurons and skeletal/cardiac muscle cells
Thin skin layers
superficial
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum granulosum
-stratum spinosum
-stratum basale
deep
Thick skin (palms and soles, no hair follicles)
superficial
-Stratum corneum
-Stratum lucidum
-stratum granulosum
-stratum sinosum
-stratum basale
deep
Areolar (loose)
-cushions, supports organs
-under epithelia, around organs
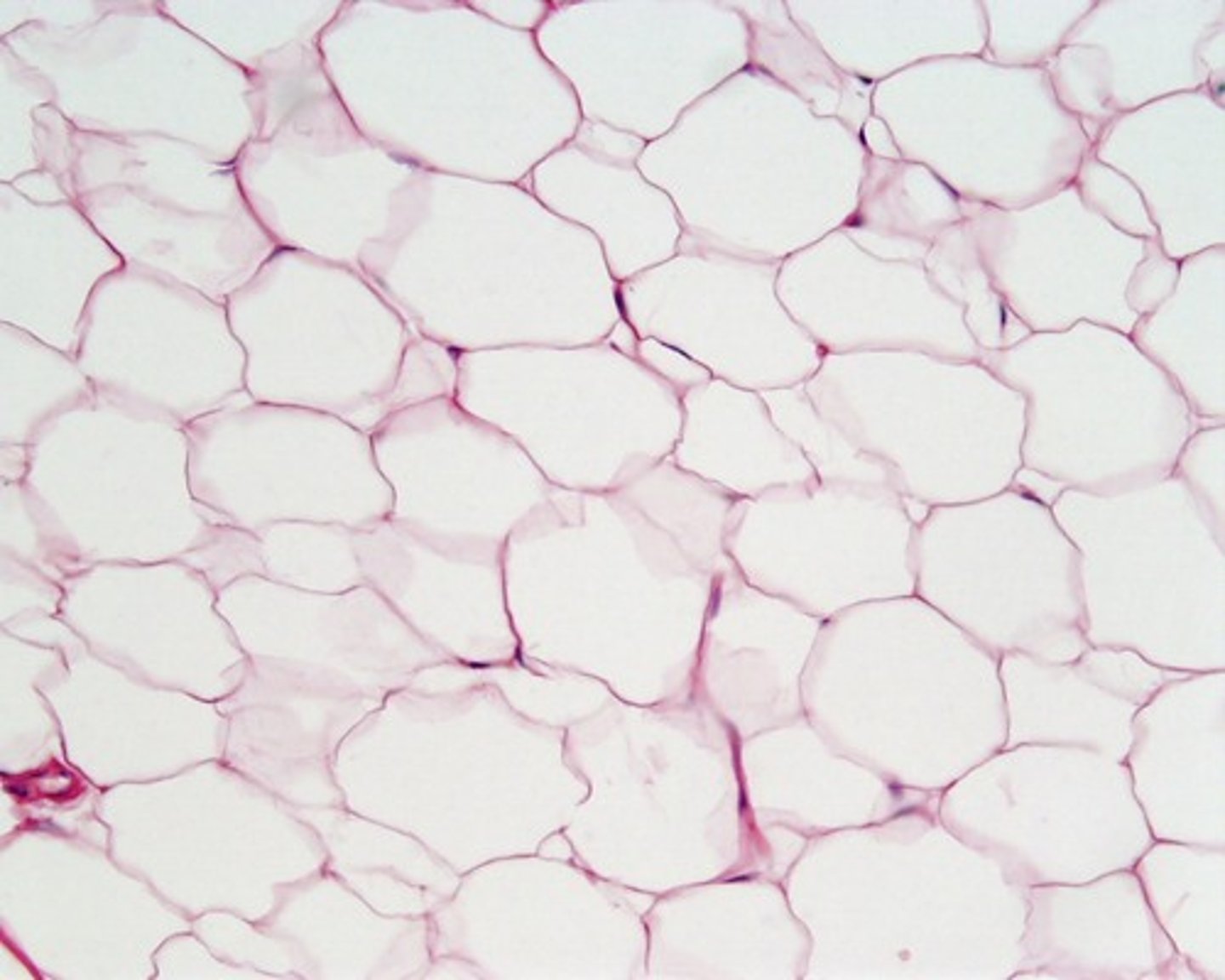
adipose
-stores dat, insulation, protection
-subcutaneous layer, around kidneys
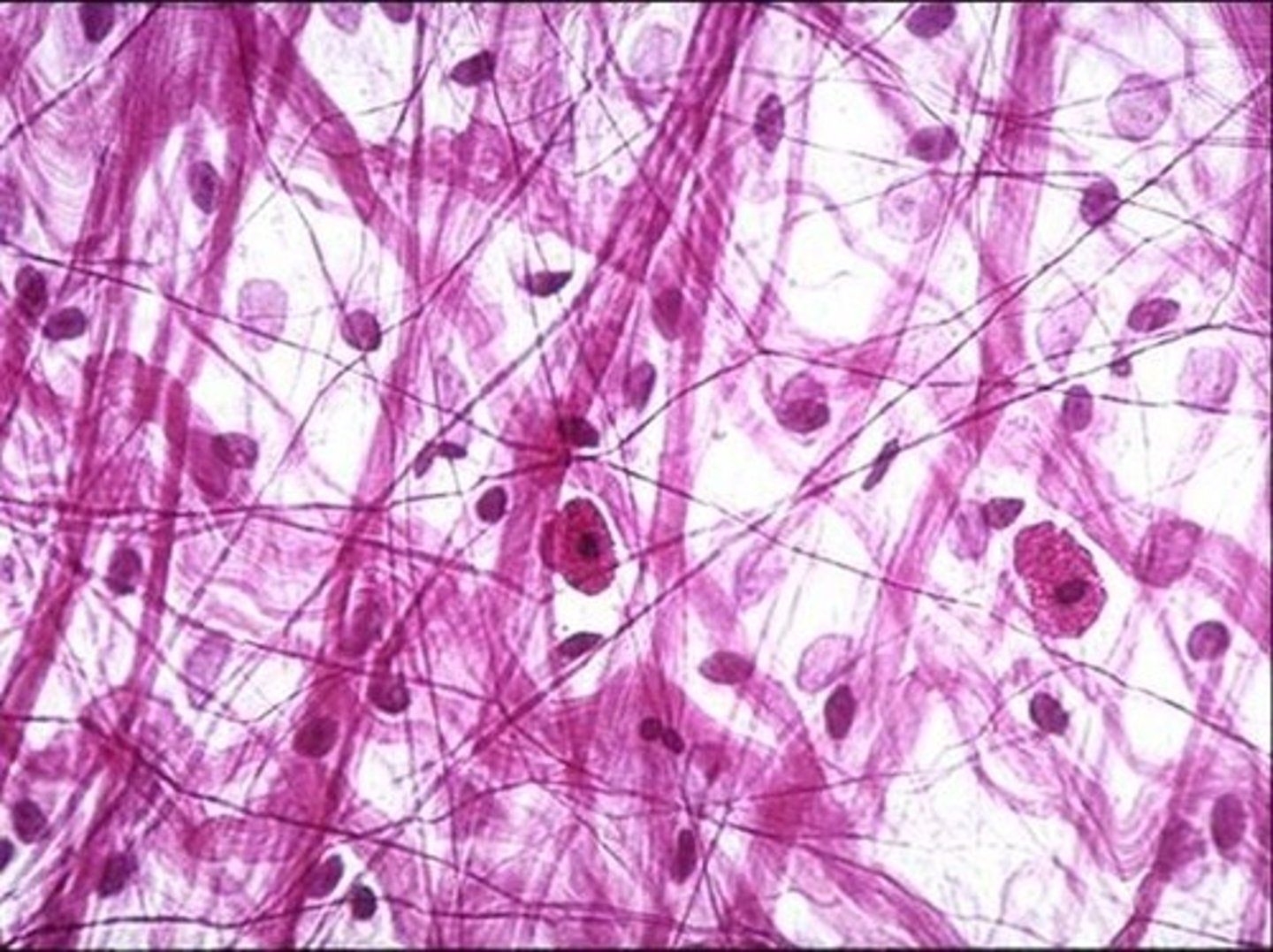
dense regular
-strong attachment (parallel fibers)
-tendons and ligaments
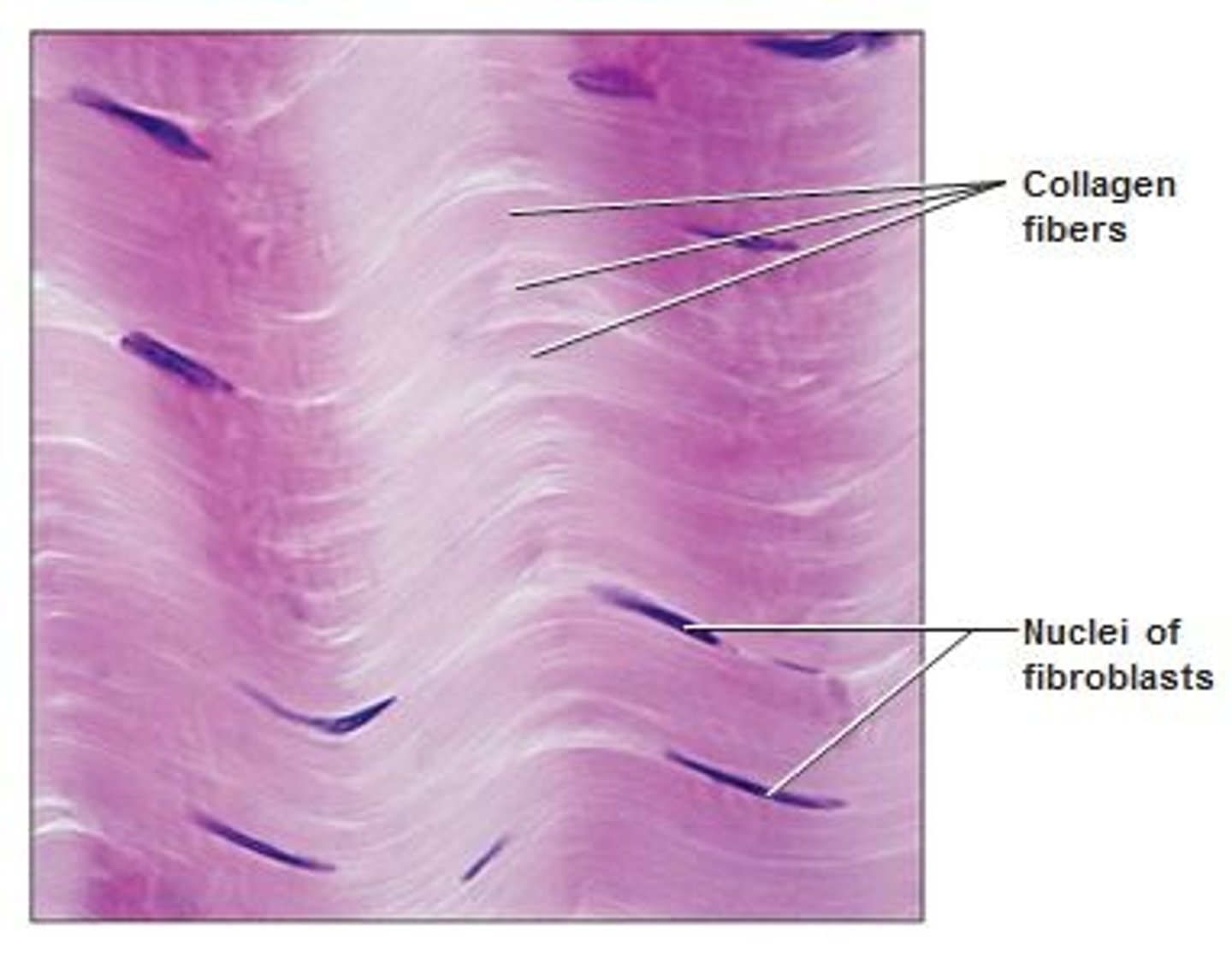
dense irregular
-strength in many directions
-dermis of skin, joint capsules
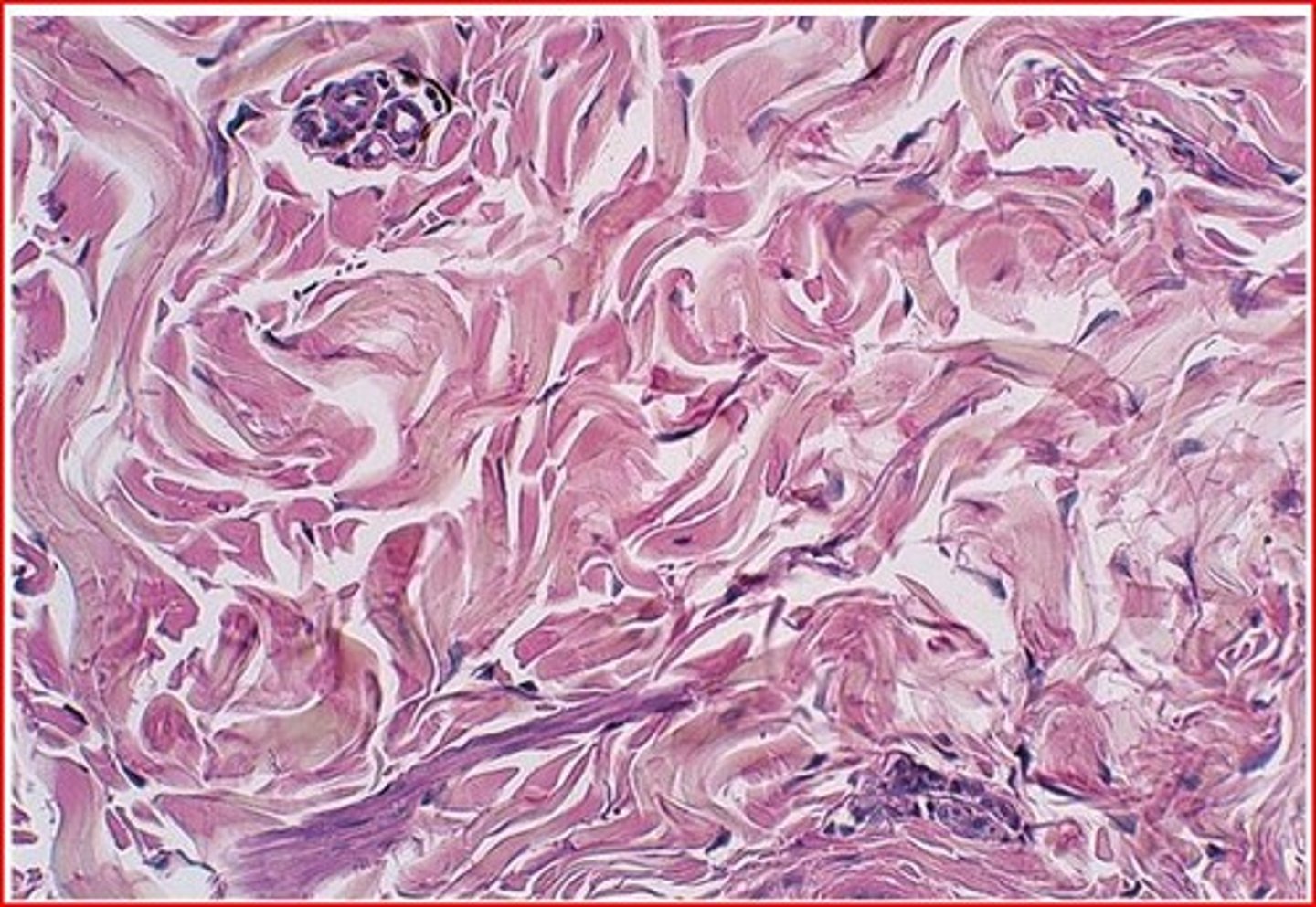
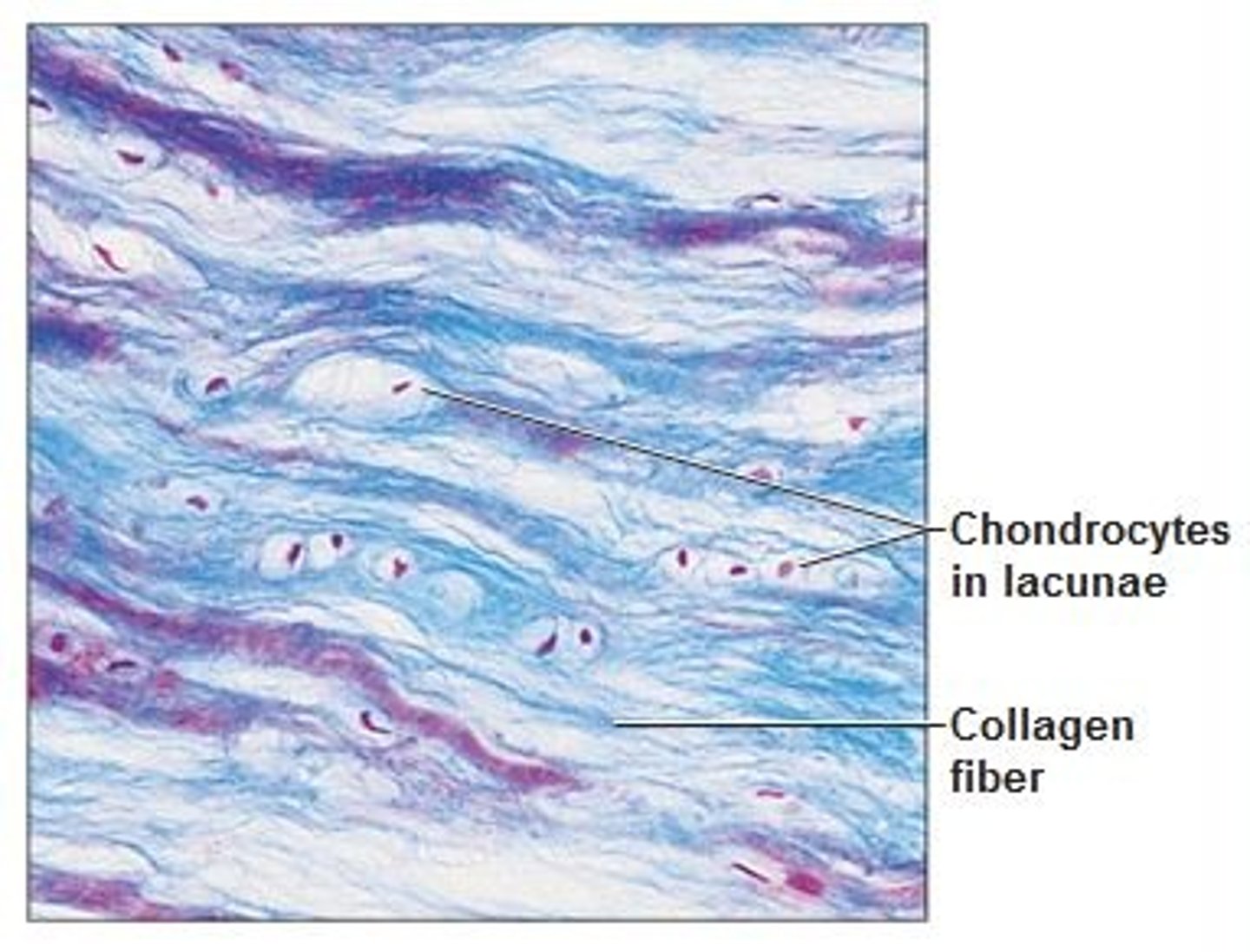
cartilage types: hyaline
-most common, nose, trachea, ends of long bones (smooth support)
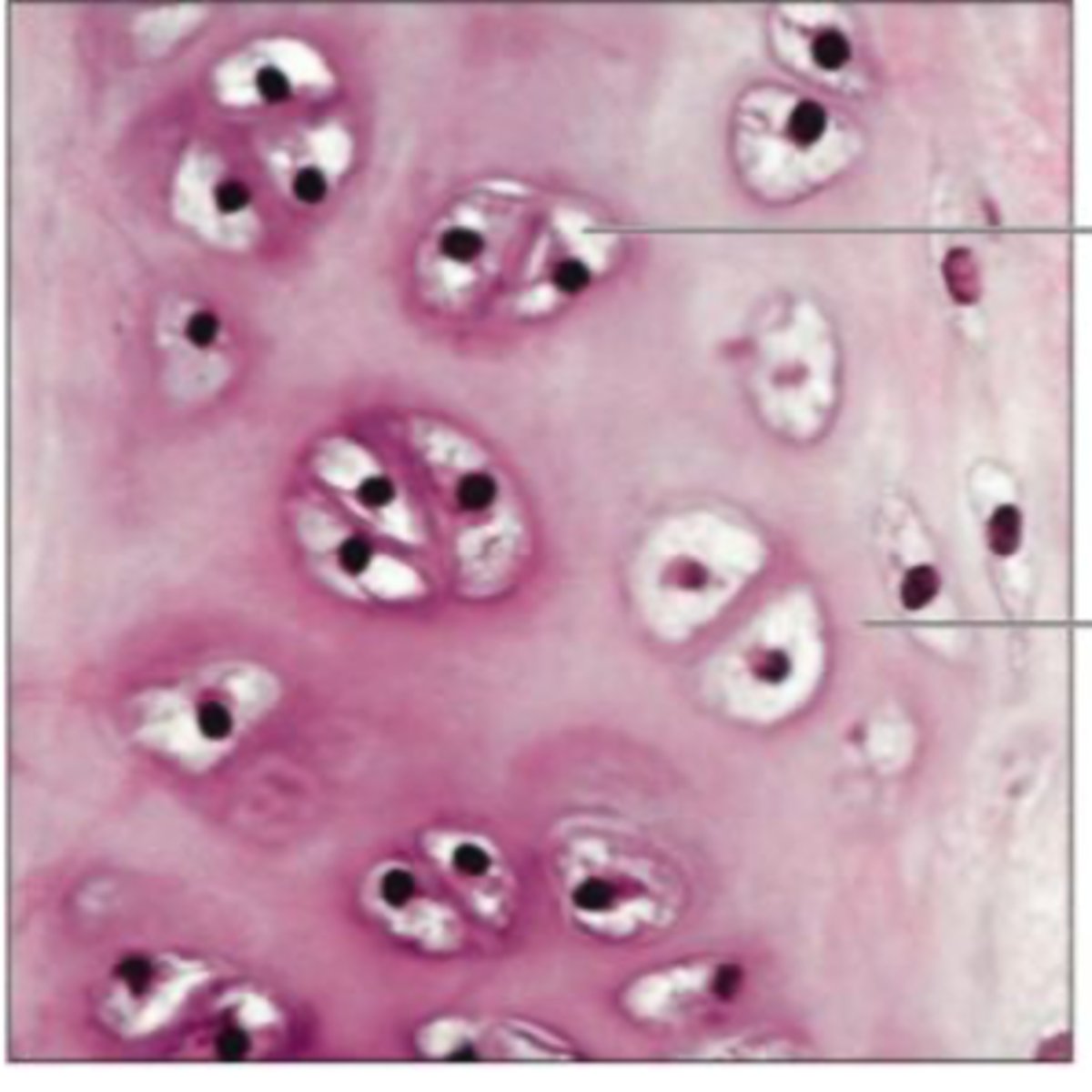
cartilage types: elastic
-flexible
-ear, epiglottis
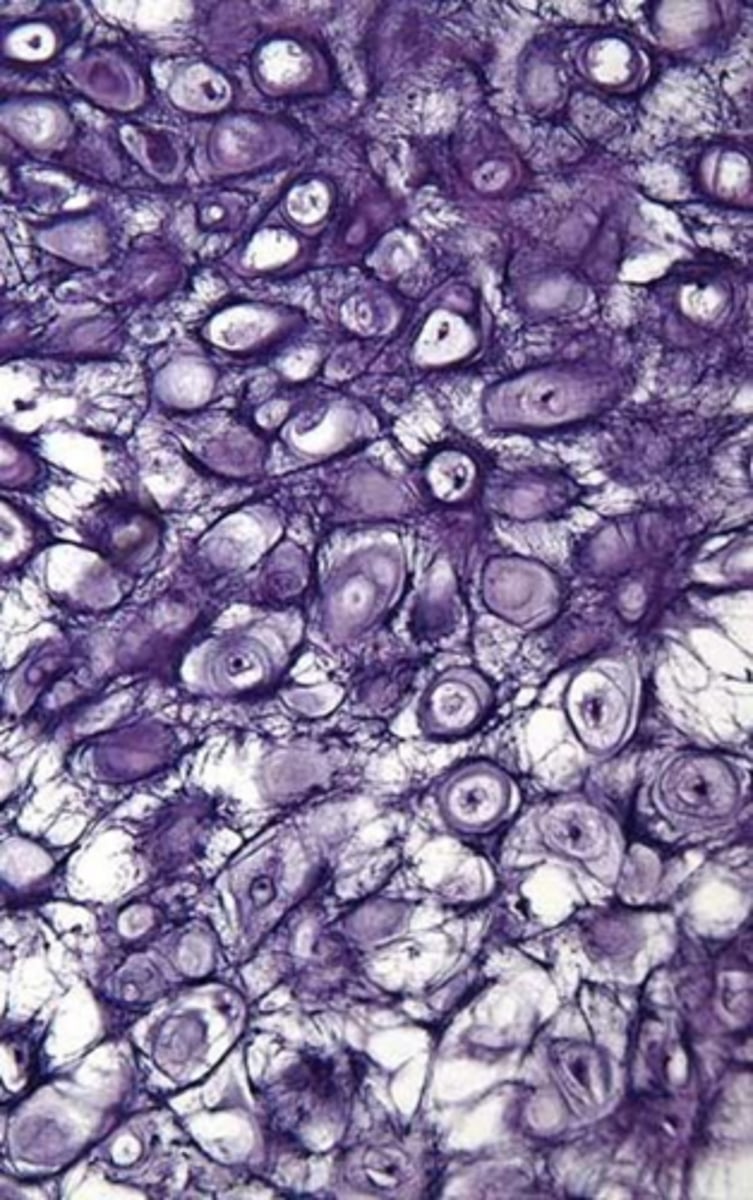
cartilage types: fibrocartilage
-stong
-intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
bone
-supports, protection, mineral storage
-skeleton
blood
-transports nutrients gases and waste
-within blood vessels
Cells of connective tissues
fibroblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, osteocytes, blood cells
Matrix
fibers (collagen, elastic, reticular) and ground substance
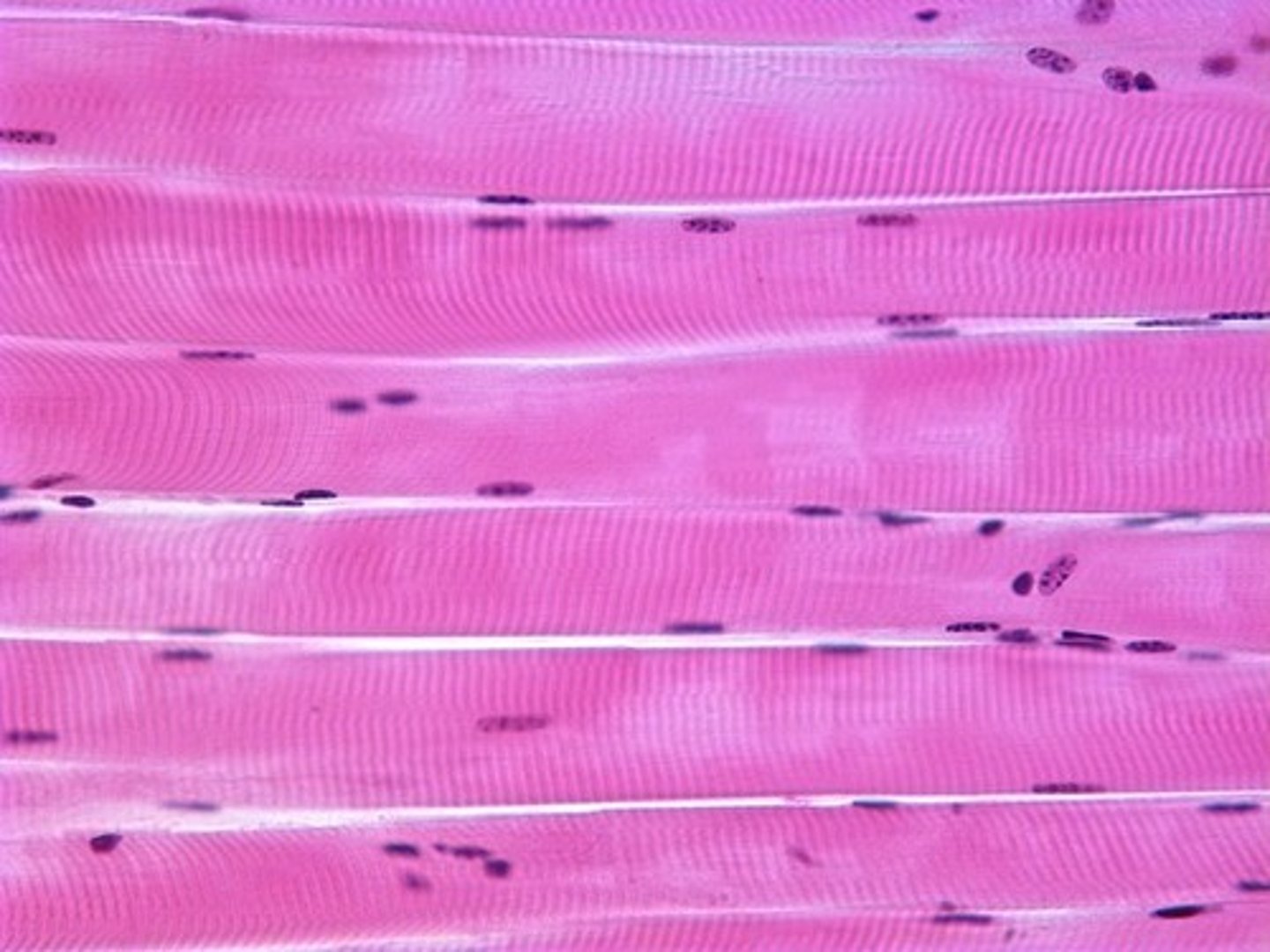
Skeletal muscle tissue
-striated, multinucliated, long cells
-attached to bones
-voluntary control
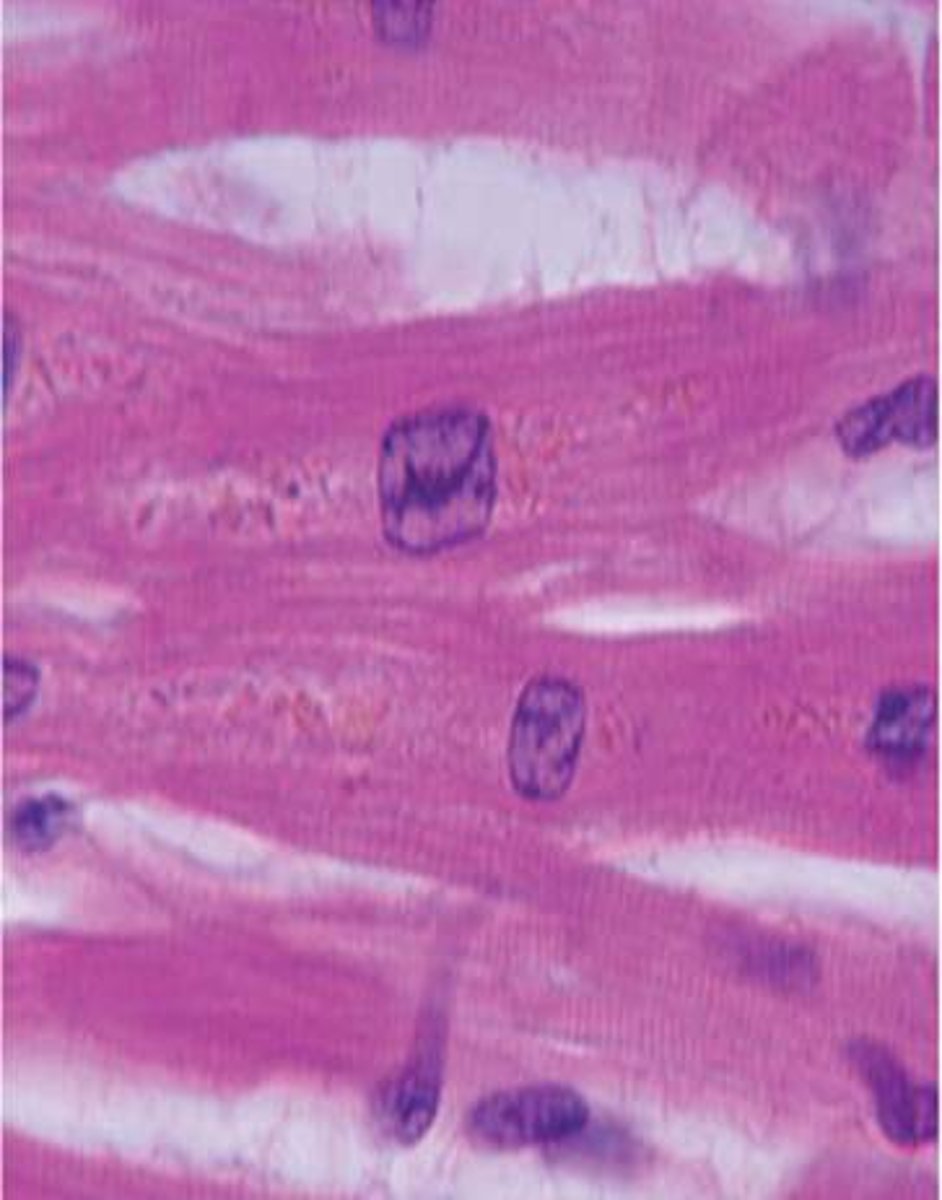
Cardiac
-striated, branched, intercalated discs
-heart
-involuntary
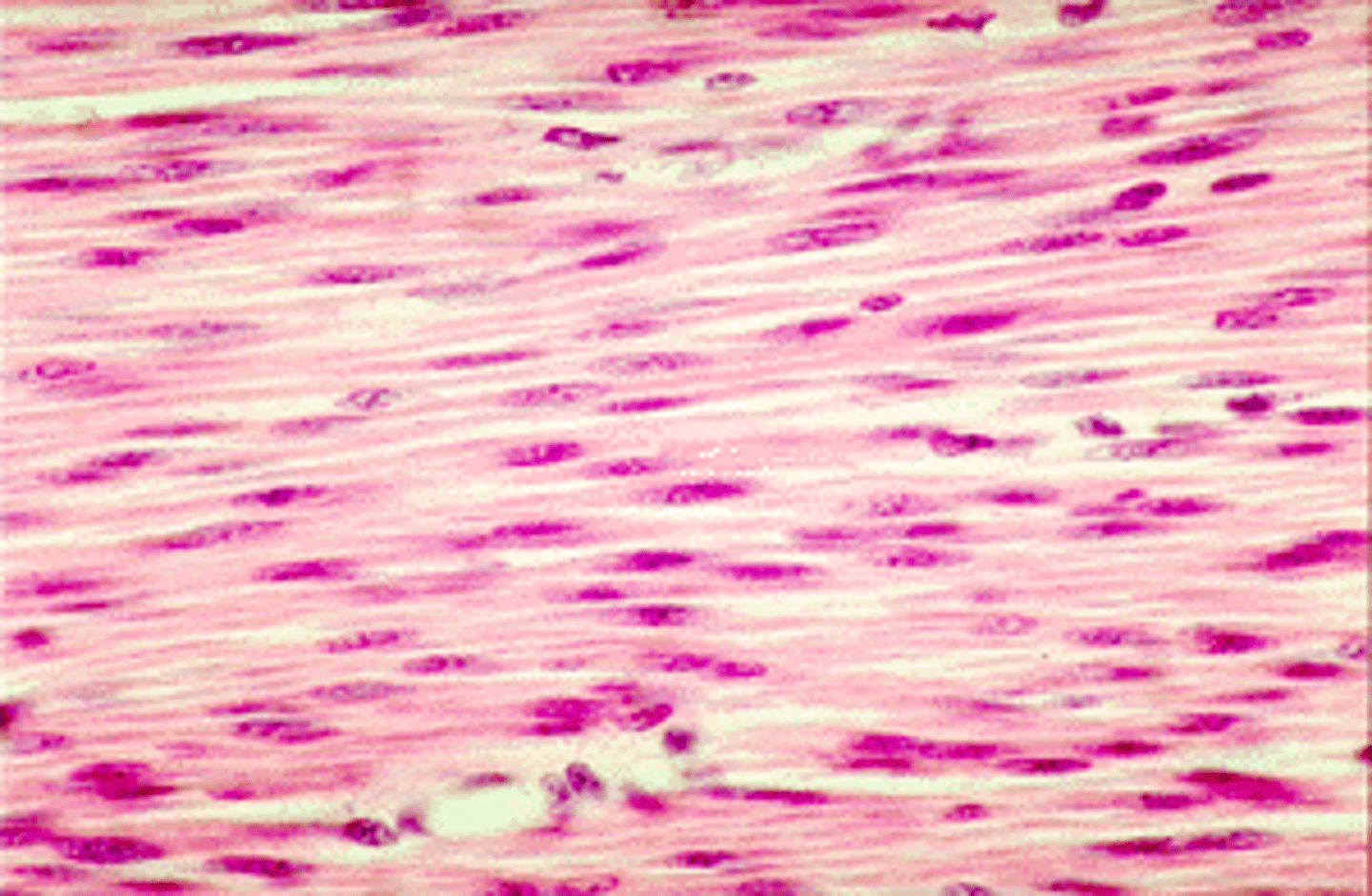
smooth
-non-striated, spindle shaped
-walls of organs/vessels
-involuntary
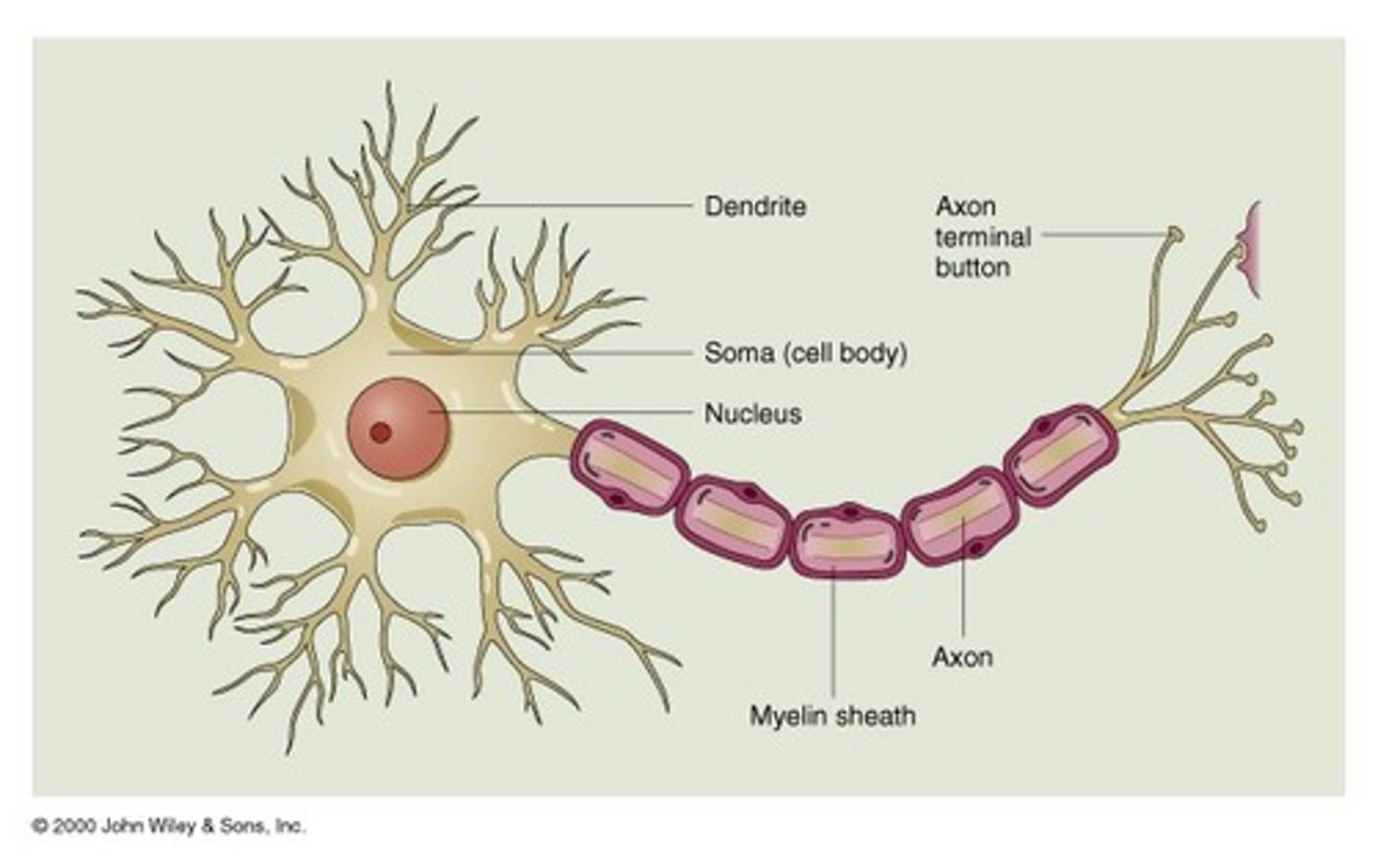
Neurons + Neuroglia (glial cells)
-transmit electrical impulses
-dendrites recieve, axons sens
-brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
-supports, nourish, protect neurons
Brownian movement
random motion of particles due to kinetic energy
Passive transport
movement of substance without energy (ATP), from high to low concentration
Diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a semi permeable membrane from high to low water concentration
active transport
movement of substances againt the concentration gradient (low to high) using ATP
protein pump
a membrane protein that uses ATP to move substances against their gradient
endocytosis
process of taking substances into the cell by forming vesicles from the cell membrane
exocytosis
process of releasing substances from the cell by merging vesicles with the membrane
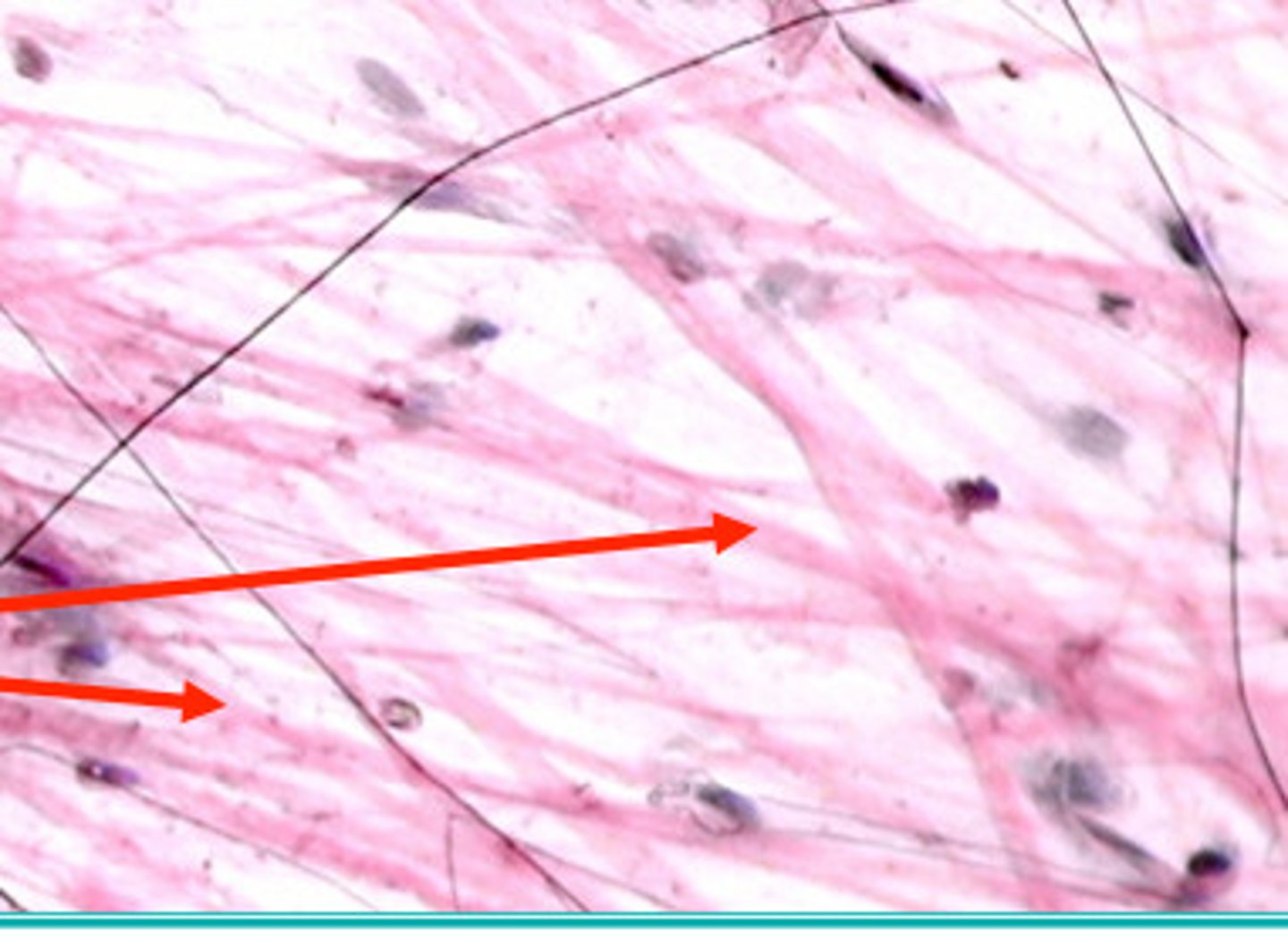
collagen fibers
strong, thick (tendons and ligaments)
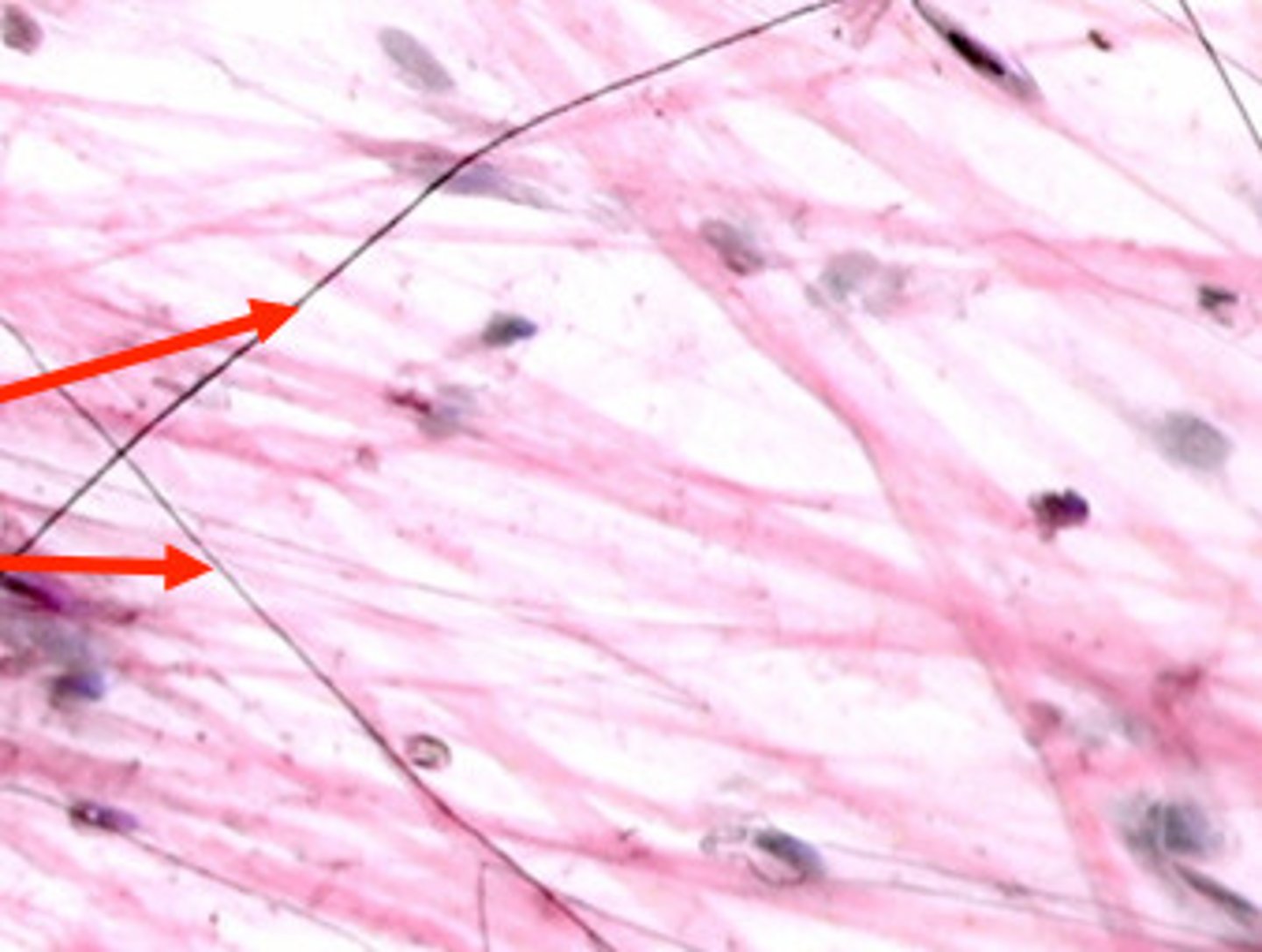
elastic fibers
stretchy (skin lungs and arteries)
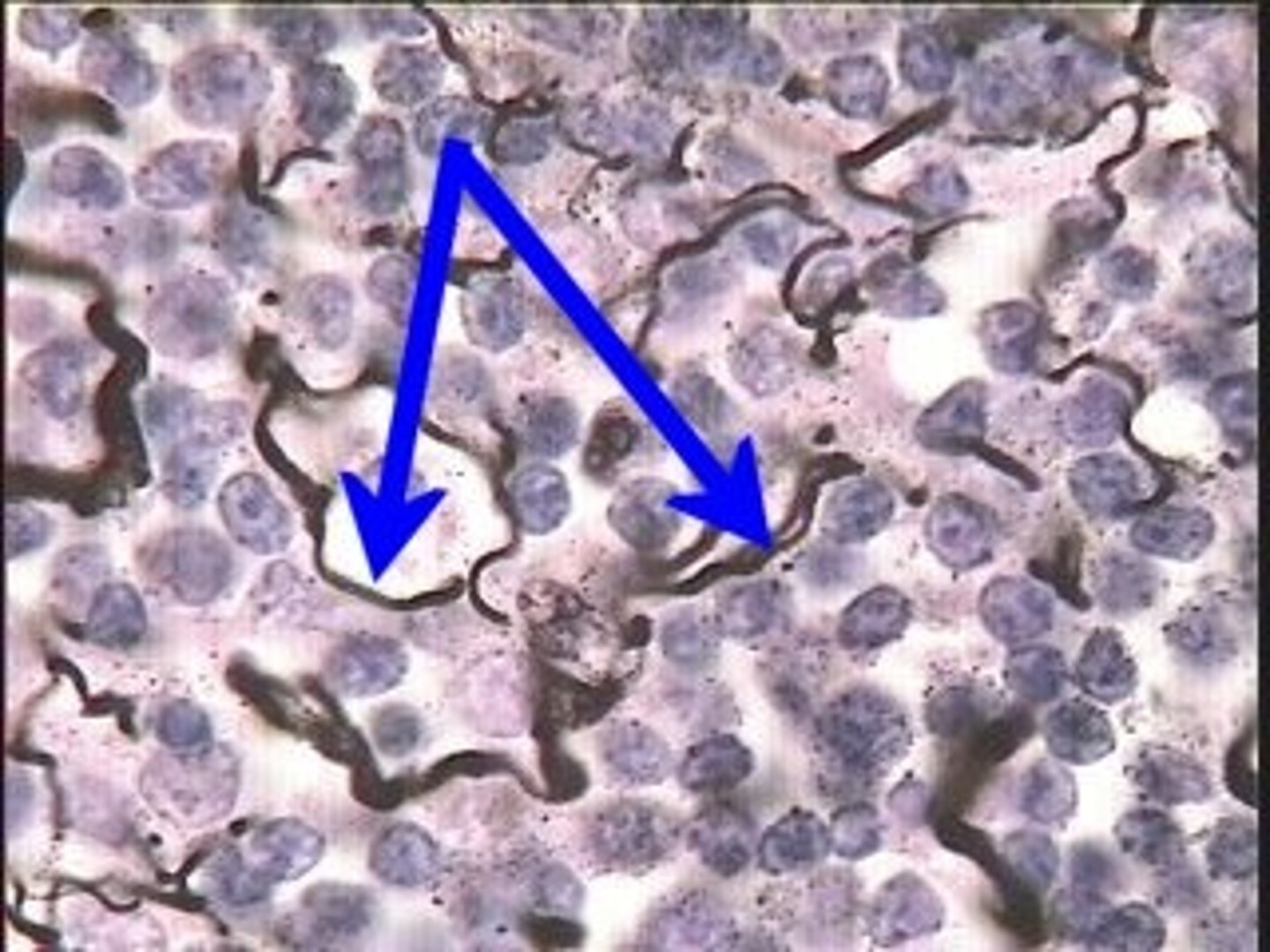
reticular fibers
mesh like, support (spleen, lymph nodes)
Jaundice
yellowing of the skin due to bilirubin buildup
cyanosis
bluish tint caused by low oxygen
erythema
redness from increased blood flow
pallor
pale, low perfusion