Topic 5: NERVOUS SYSTEM III – INTERGRATION & CONTROL (BRAIN + SPINAL CORD)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
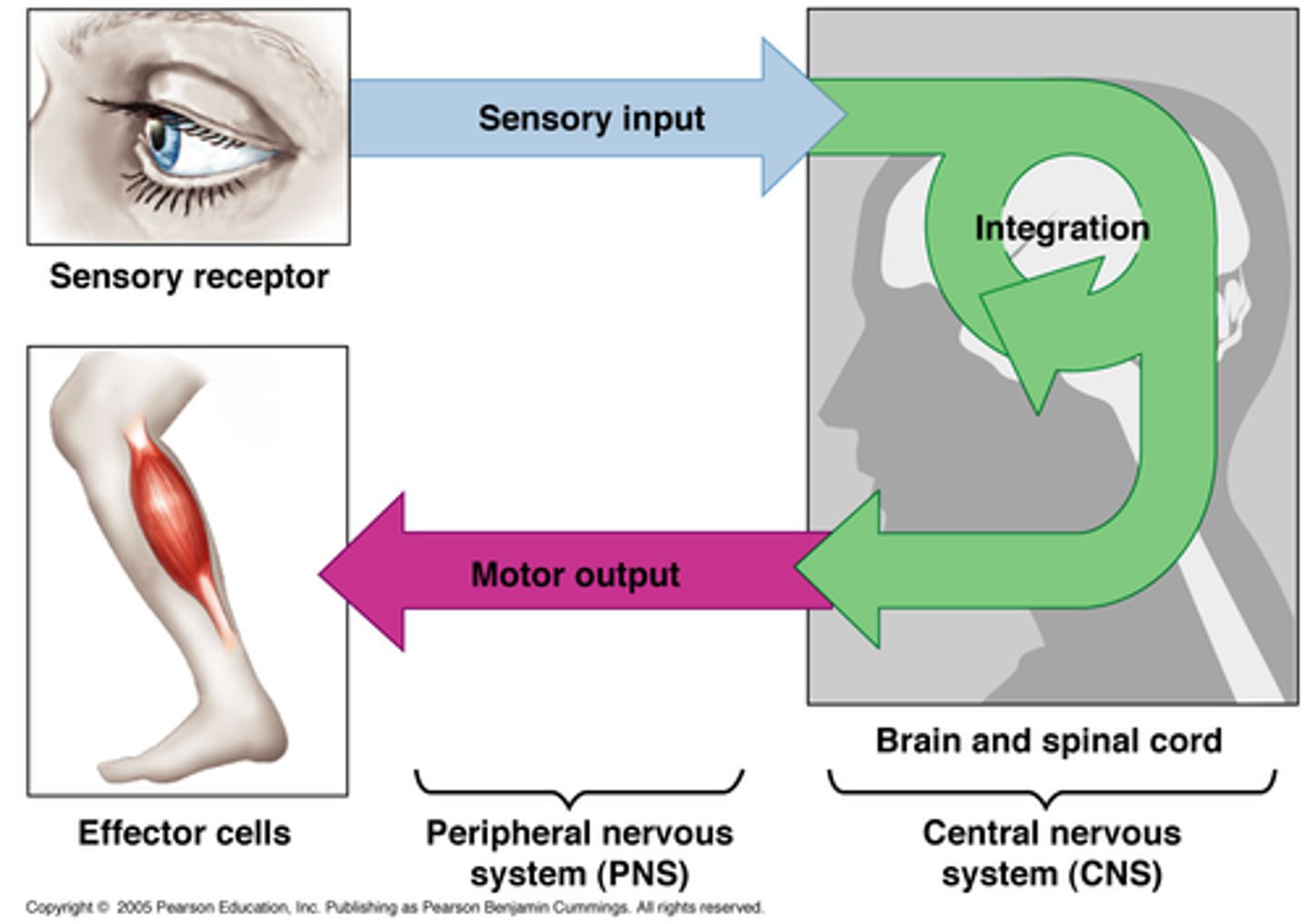
INTRGRATION & CONTROL Overview:
-Sensory (afferent) division “inputs” info to the brain and spinal cord (control centers)
-Brain + spinal cord integrate info and control effectors through motor (efferent) division (“output”)
Spinal Cord: Reflexes
-Rapid automatic, response to stimuli
-Stimulus always causes the same motor response
-Usually protective
-Involve 2 or more neurons
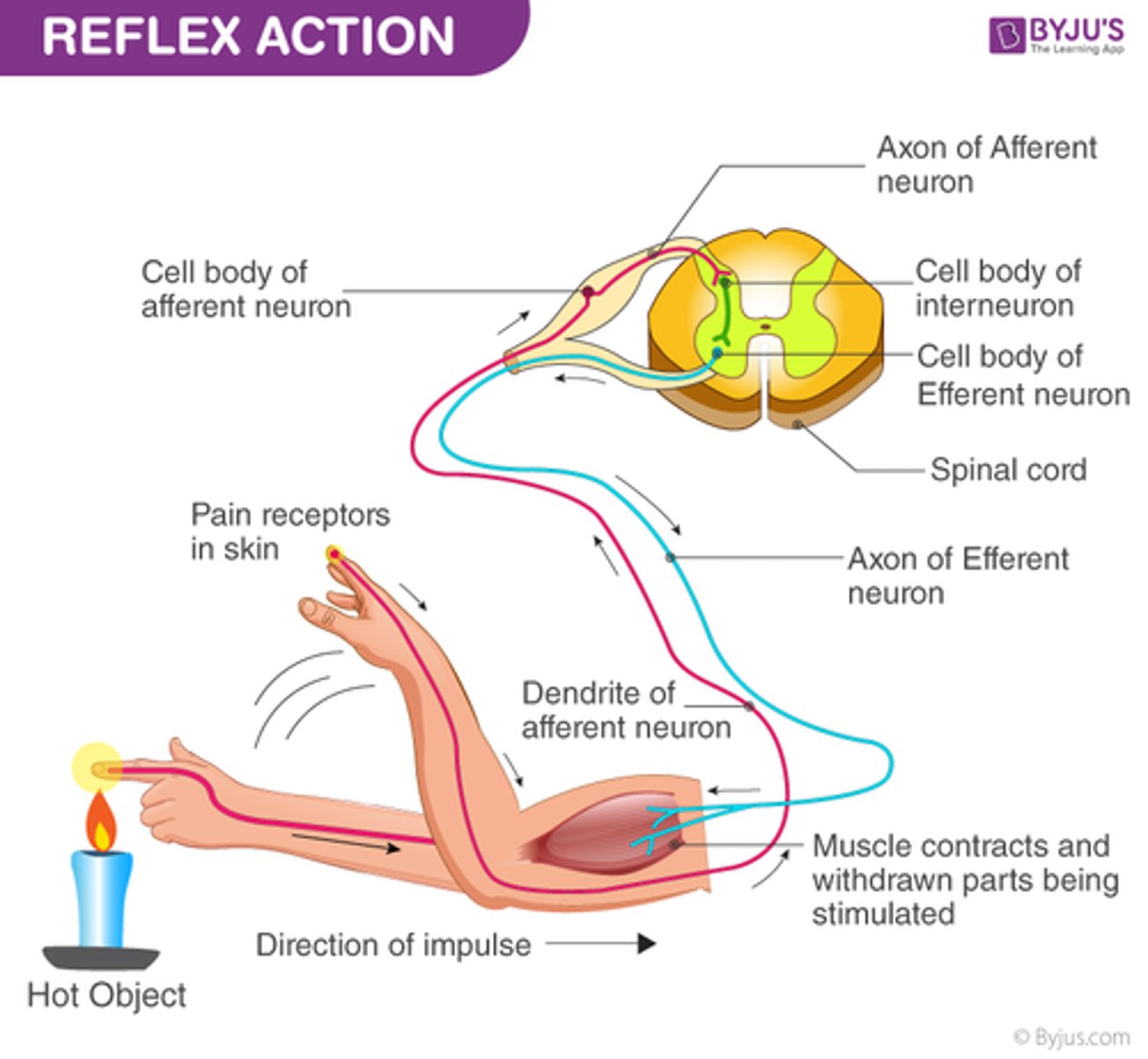
Reflex pathway or arc:
Pathway of impulses
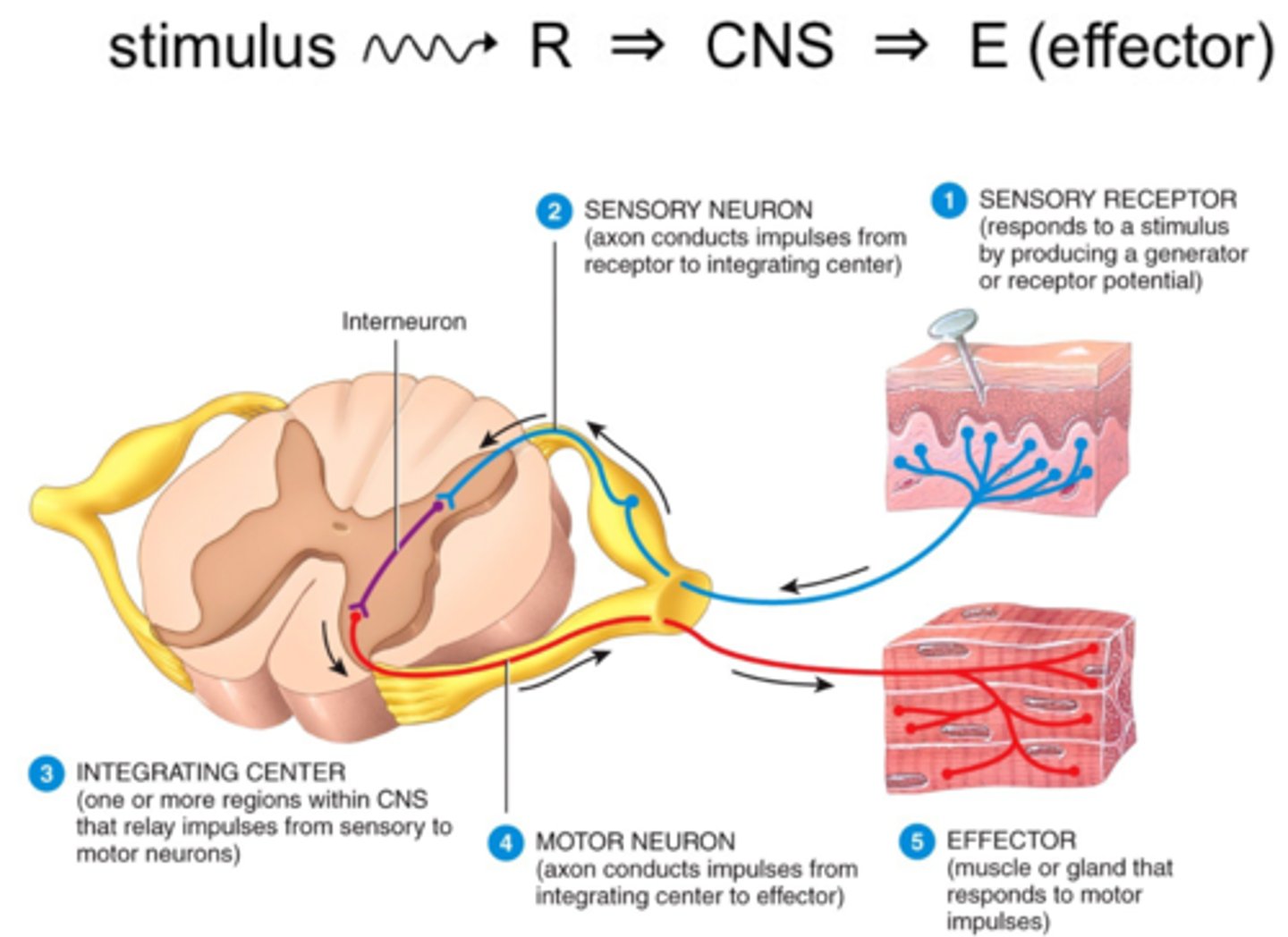
Reflexes are categorized according to:
-Effector
-Which sides of the body the sensory and motor neurons are located
-Number of synapses (and neurons) in arc
Effectors:
Cause responses that alter conditions in the internal environment.
-Somatic reflex
-Visceral (autonomic) reflex
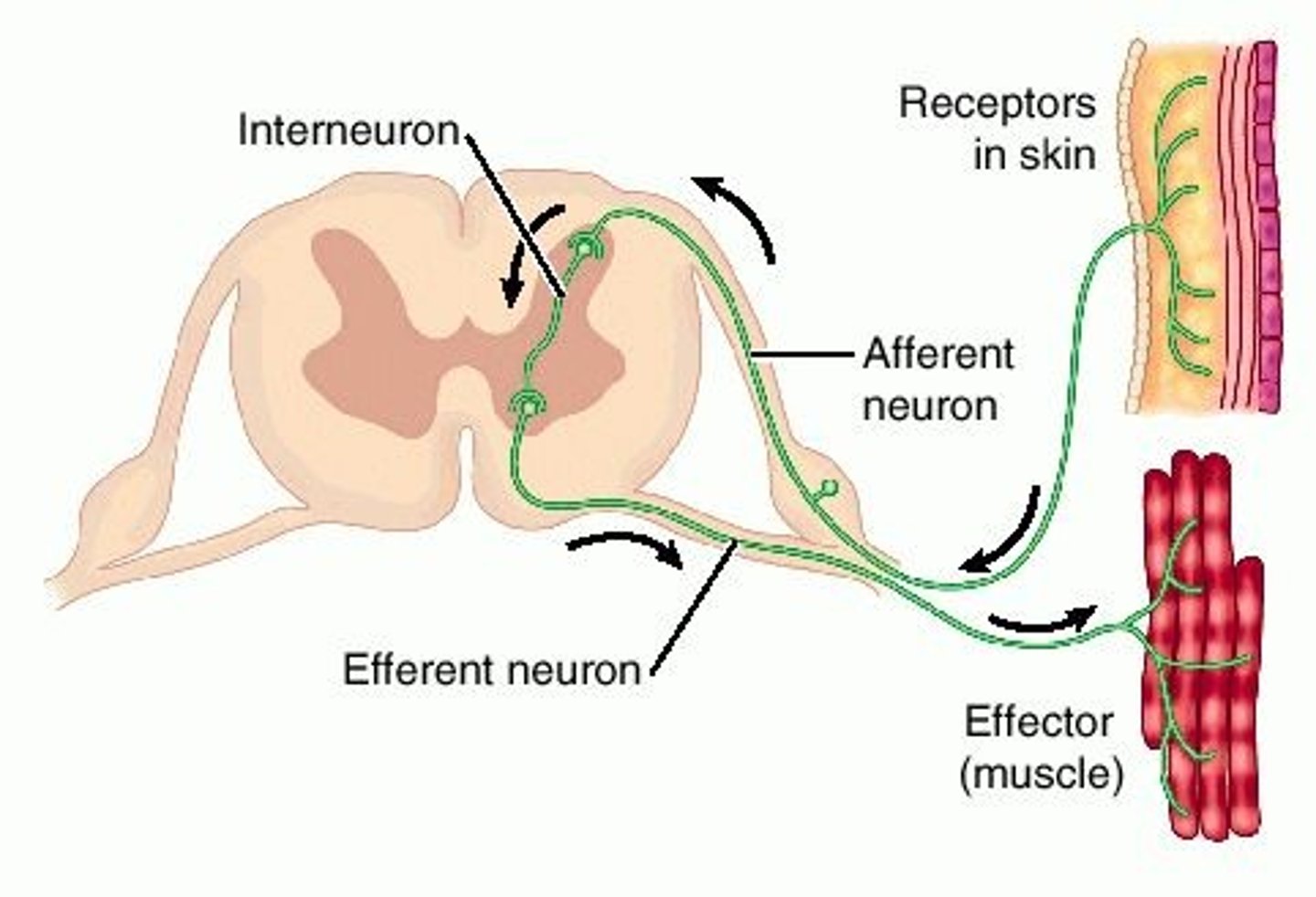
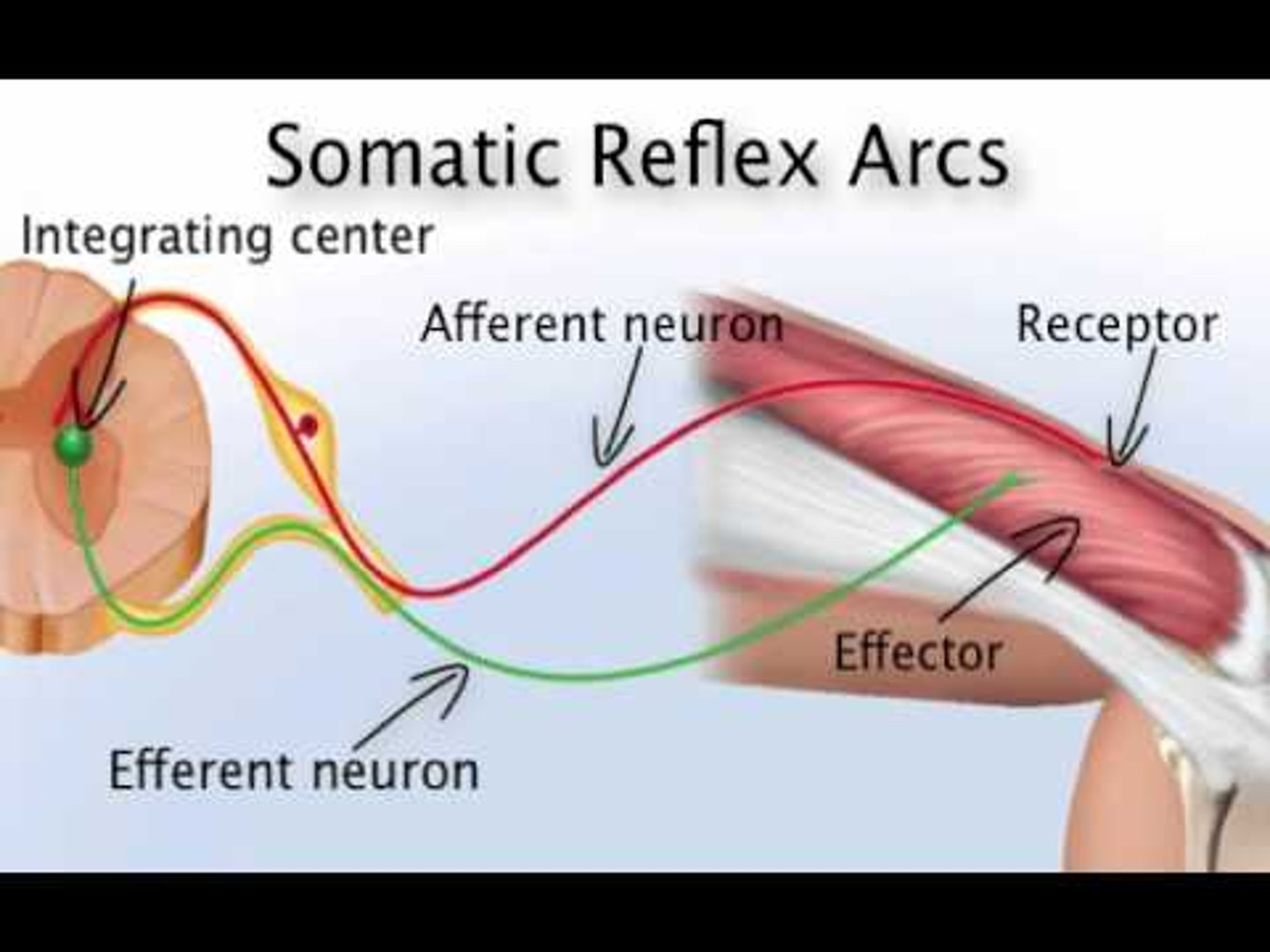
Somatic Reflex
Effector is skeletal muscle
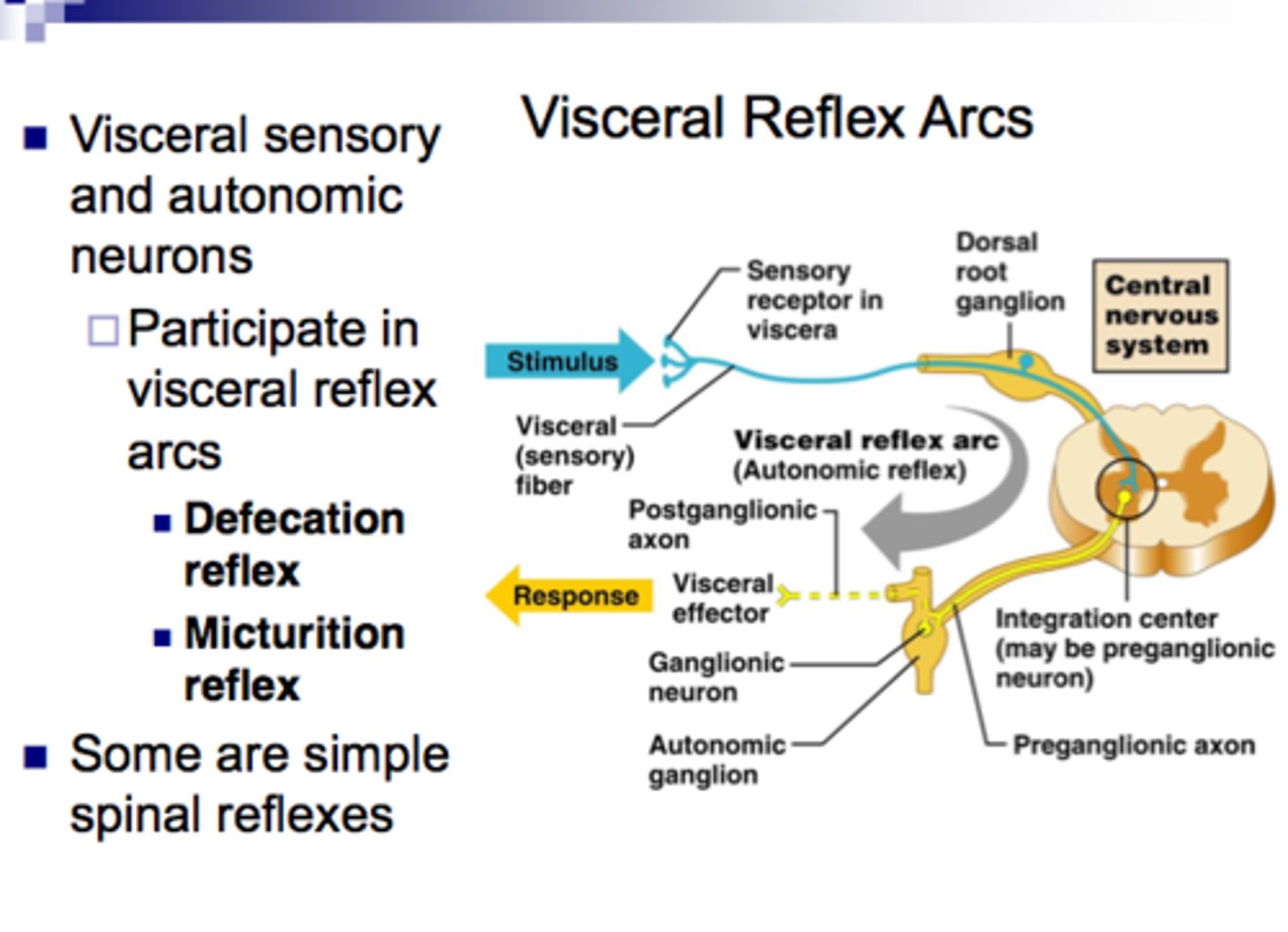
Visceral (autonomic) Reflex
Effector is smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or glands
Which sides of the body the sensory and motor neurons are located:
-Ipsilateral Reflex
-Contralateral Reflex
Ipsilateral Reflex
Sensory and motor neurons on the same side of body
Contralateral Reflex
Sensory and motor neurons on opposite sides
Number of synapses (+ neurons) in arc
-Monosynaptic Reflex
-Polysynaptic Reflex
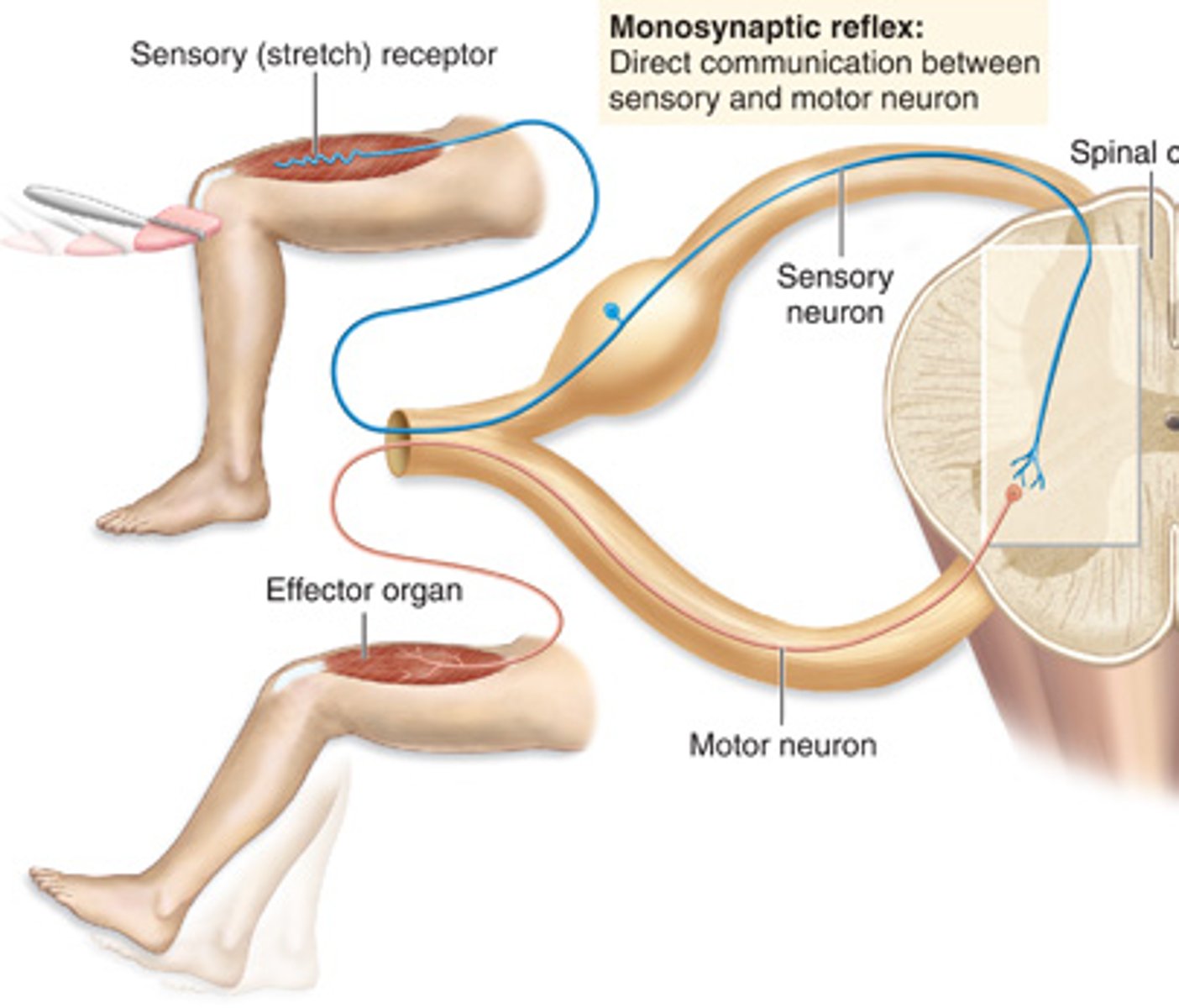
Monosynaptic Reflex
1 synapse between 1 sensory + 1 motor neuron
-one synapse / two neurons involved.
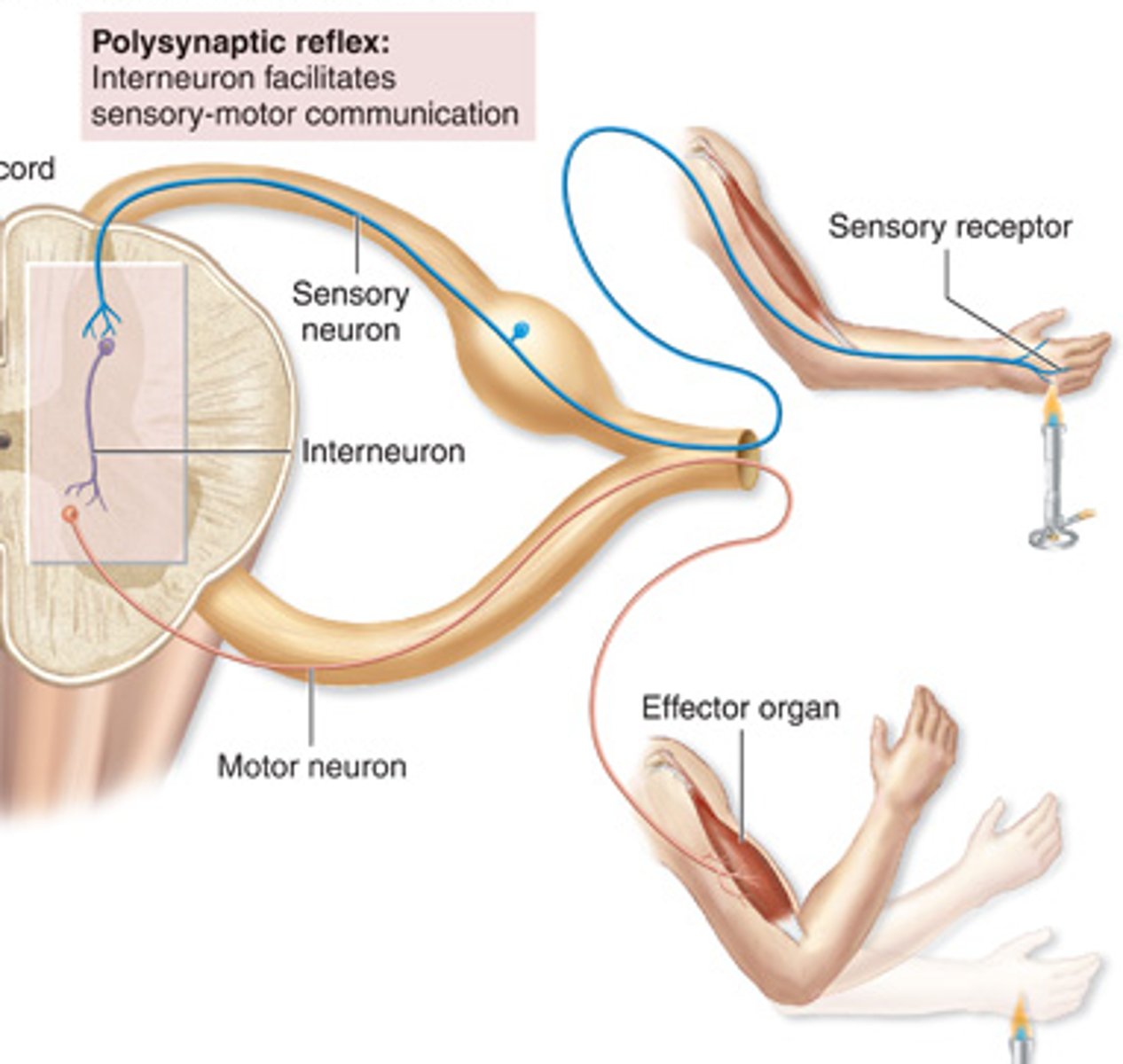
Polysynaptic Reflex
2+ synapses between 3+ neurons
-Two or more synapses / three or more neurons involved

Somatic Spinal Reflexes: EXAMPLES
-Stretch Reflex
-Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex
-Crossed Extensor Reflex
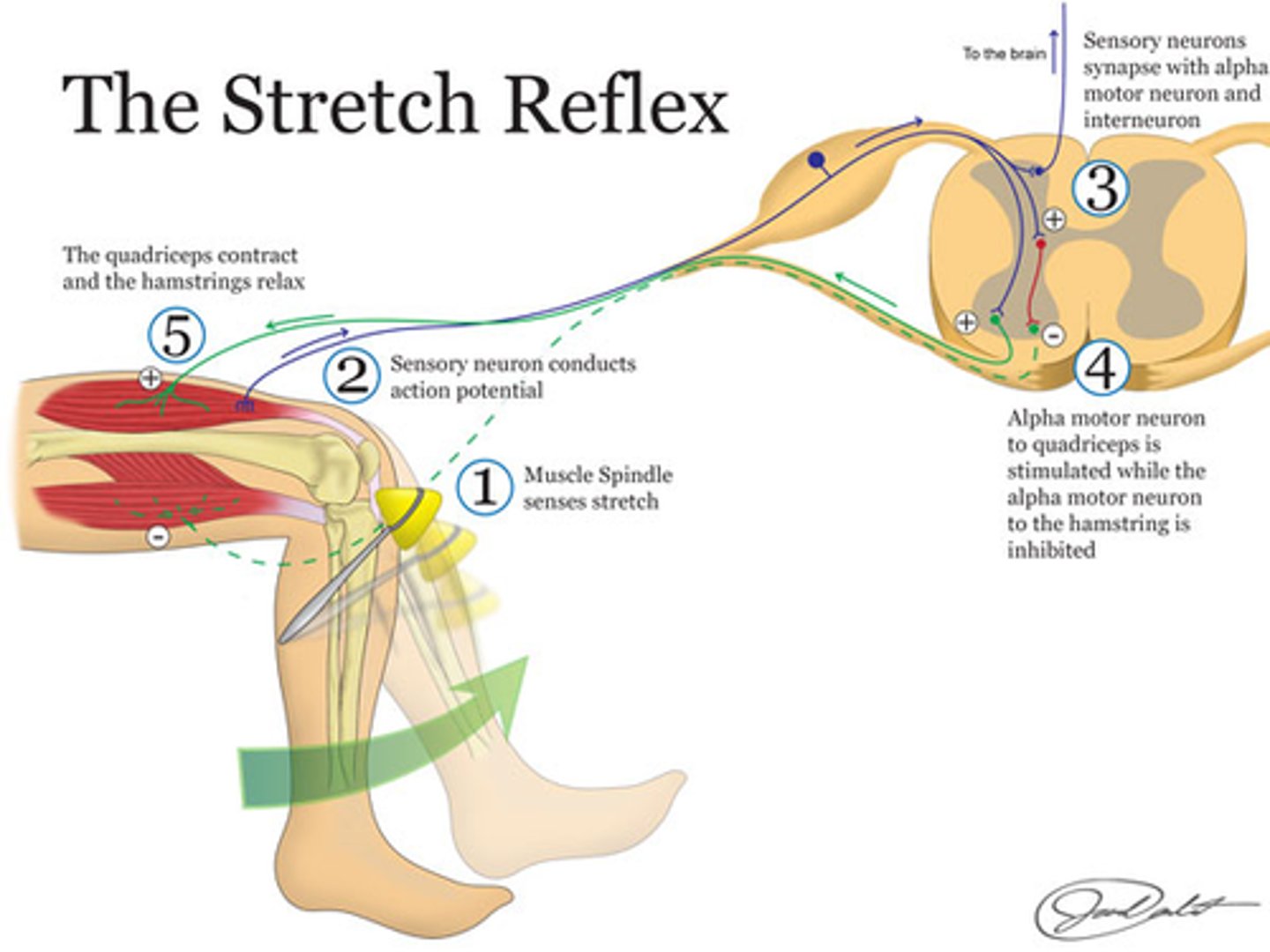
Stretch Reflex
E.g Knee Jerk
Extensor muscle contracts
↓
Stimulus = Tapping patellar ligament, which stretches the quadriceps femoris muscle
↓
Receptor = Muscle spindle (in quad.)
↓
Effector = skeletal muscle (quad.) – it contracts
↓
Ipsilateral, monosynaptic
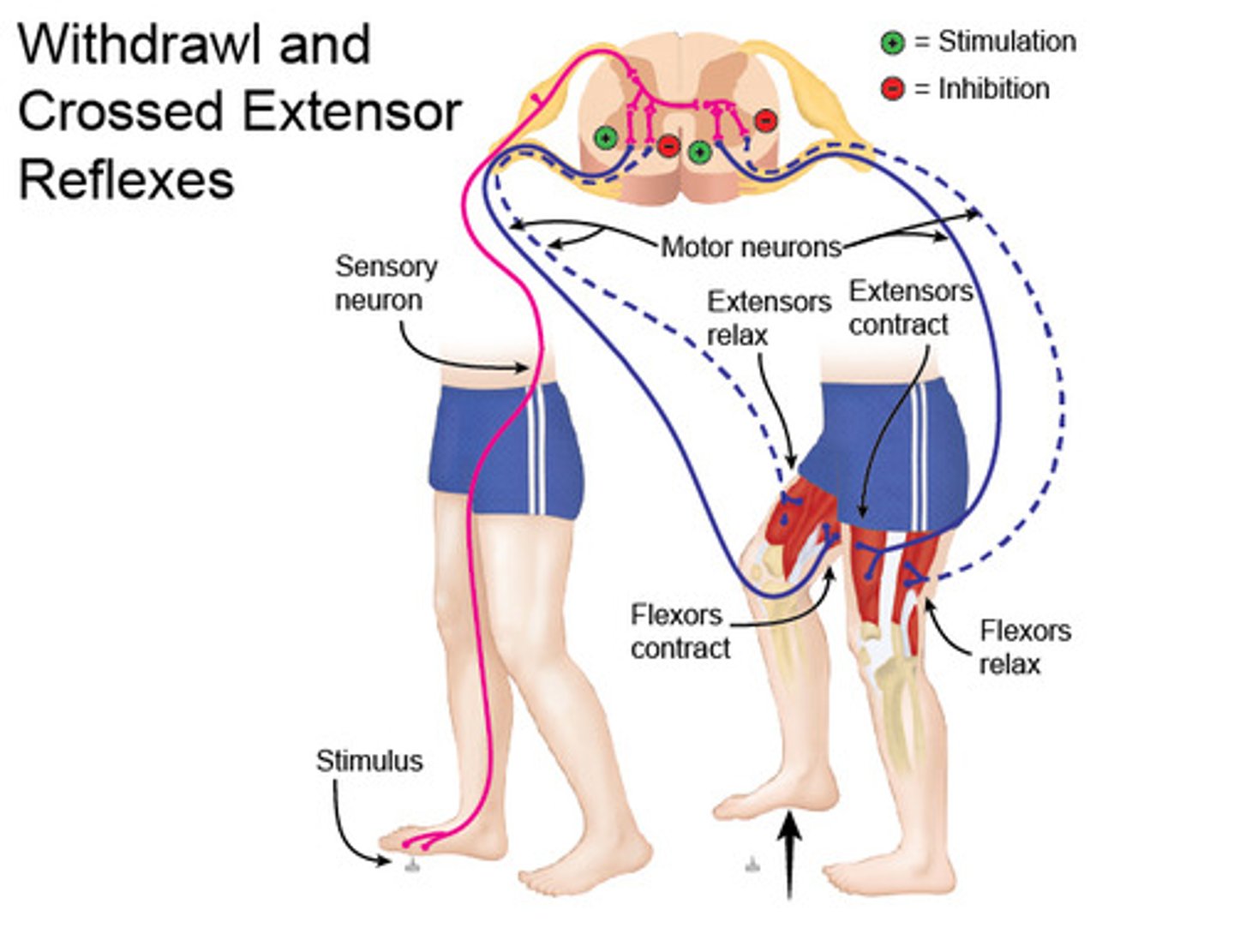
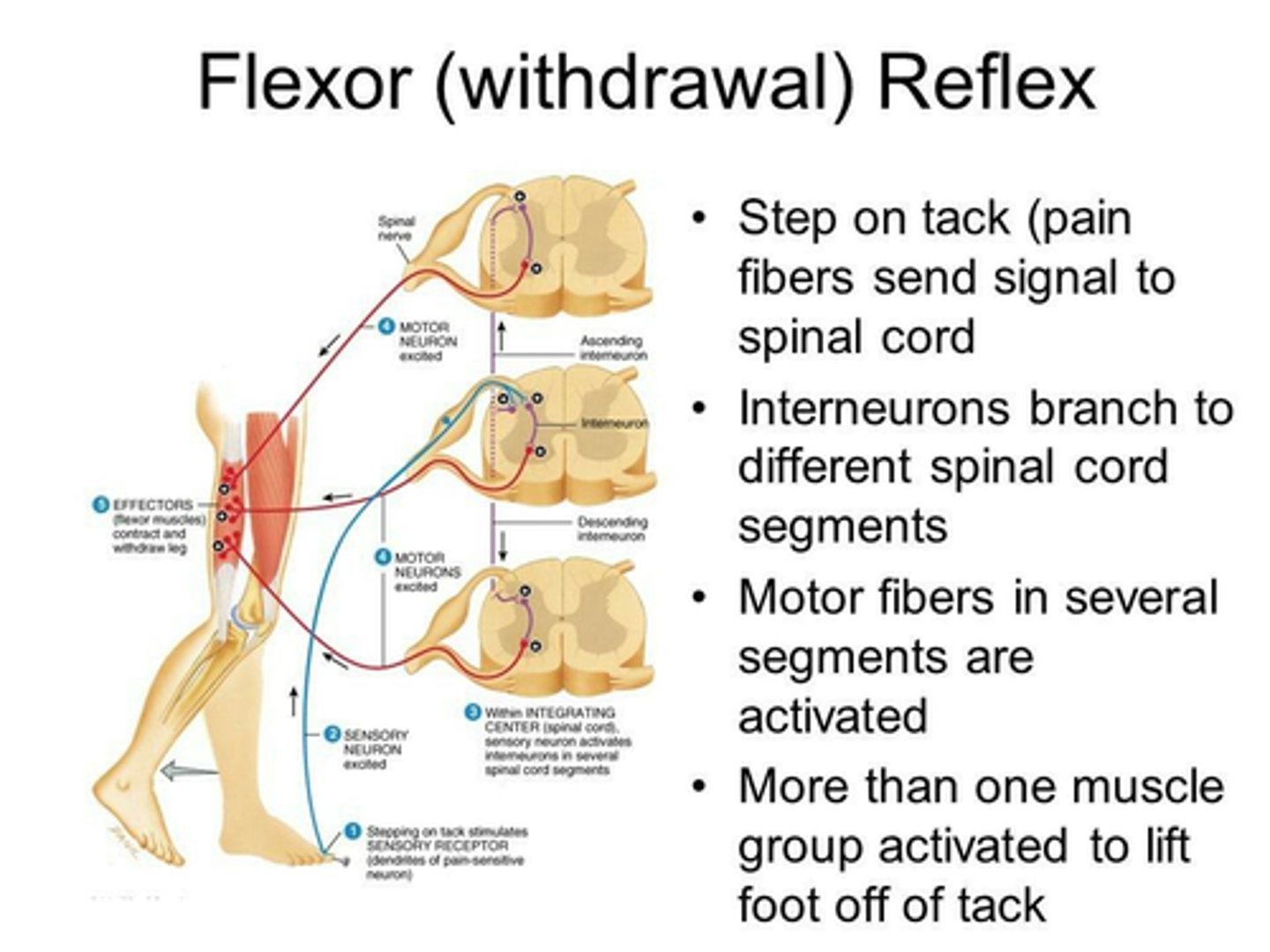
Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex
E.g Leg
Stimulus = stepping on nail
↓
Receptor = touch, pressure, pain
↓
Effector = hamstrings (= flexors) ⇒ contract
↓
Ipsilateral, Polysynaptic
Crossed Extensor Reflex
E.g Leg
Stimulus = stepping on nail
↓
Receptor = touch, pressure, pain
↓
Effector = quadriceps femoris in the opposite leg(= extensor) ⇒ contracts
↓
Contralateral, Polysynaptic
↓
Keeps you from falling down.
Category of Reflex Summary:
Stretch Reflex: Ipsilateral, monosynaptic
-The contraction of a muscle in response to stretch of that muscle
Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex: Ipsilateral, Polysynaptic
-Causes withdrawal of a limb to avoid injury or pain.
Crossed Extensor Reflex: Contralateral, Polysynaptic
-Opposite limb supports body during withdrawal of injured limb
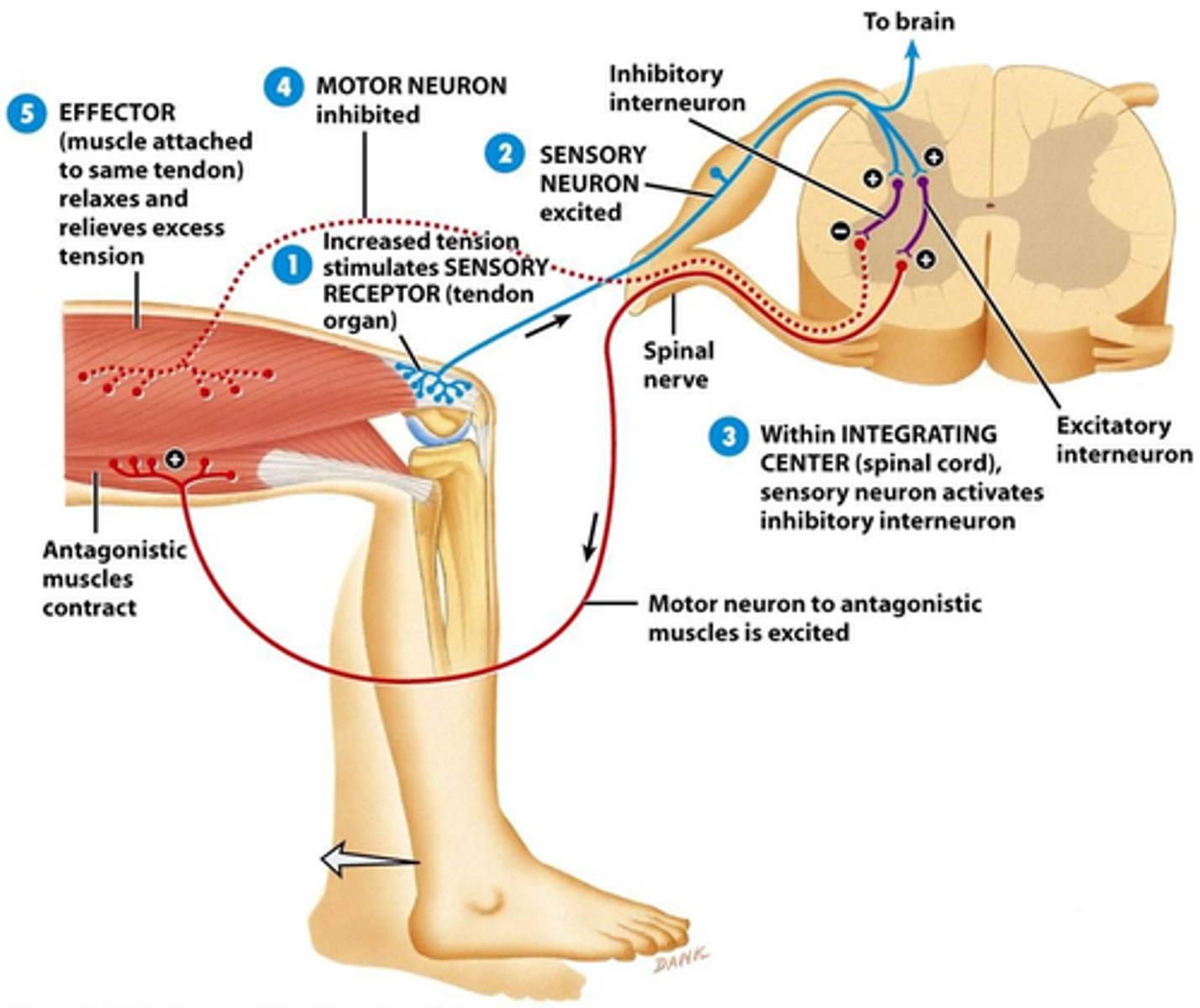
Reciprocal Inhibition
-Skeletal muscle (or groups) that contract are known as Agonists.
-Antagonists are prevented from contacting (inhibitory neurons firing).
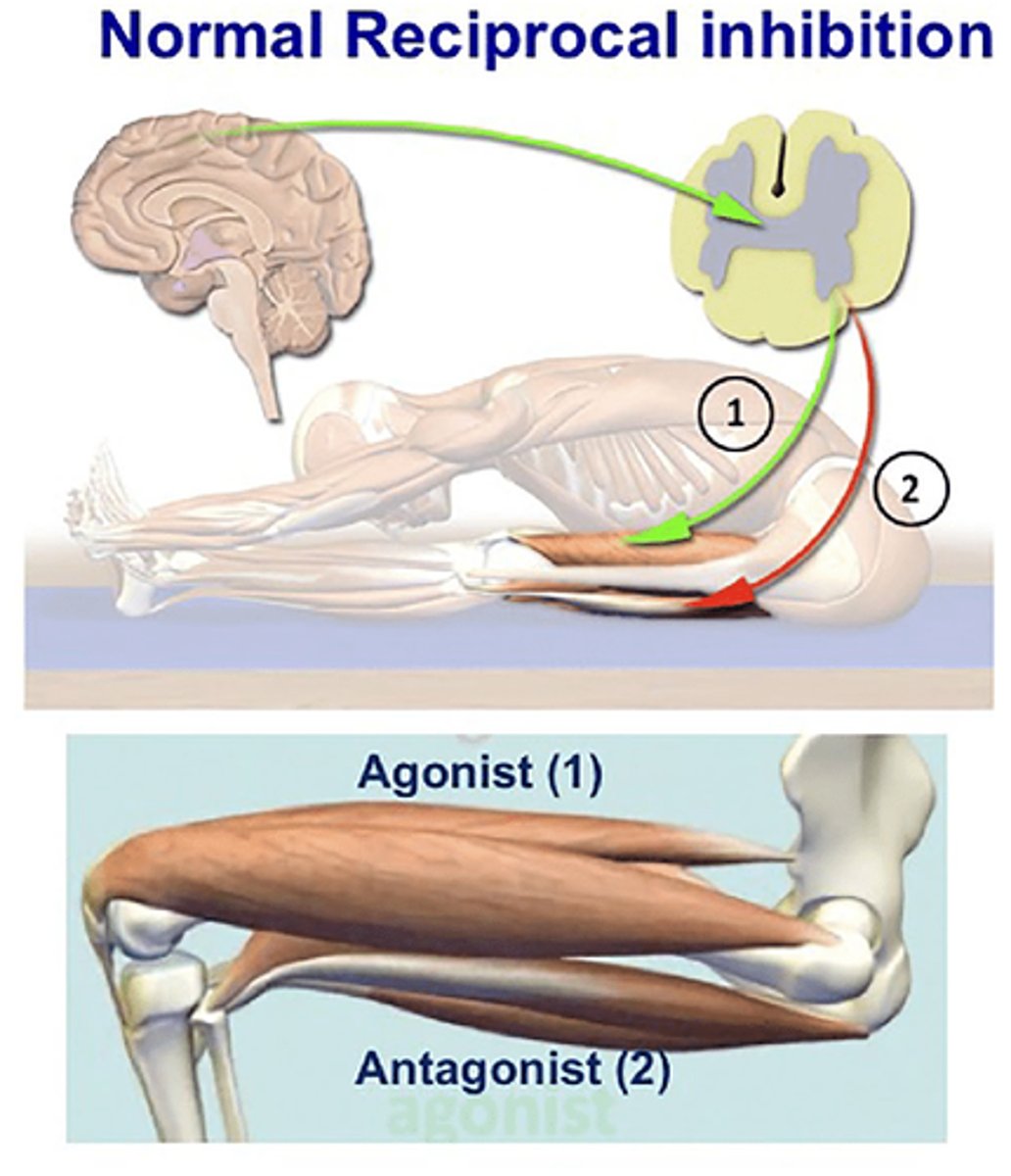
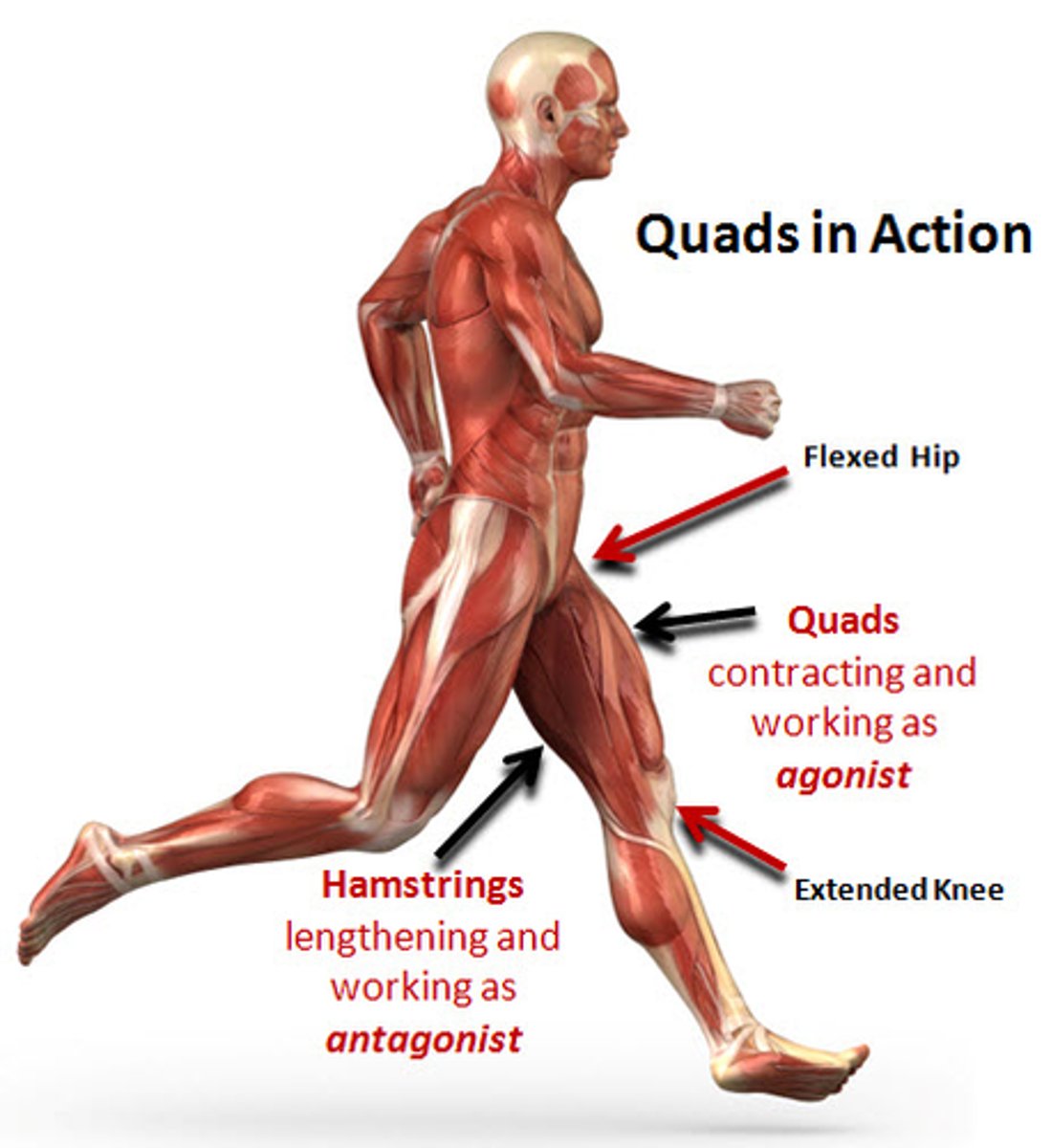
Reciprocal Inhibition: Example
e.g. in stretch reflex
-Quadriceps femoris (agonist) contracts
-Hamstrings (antagonists) contraction inhibited
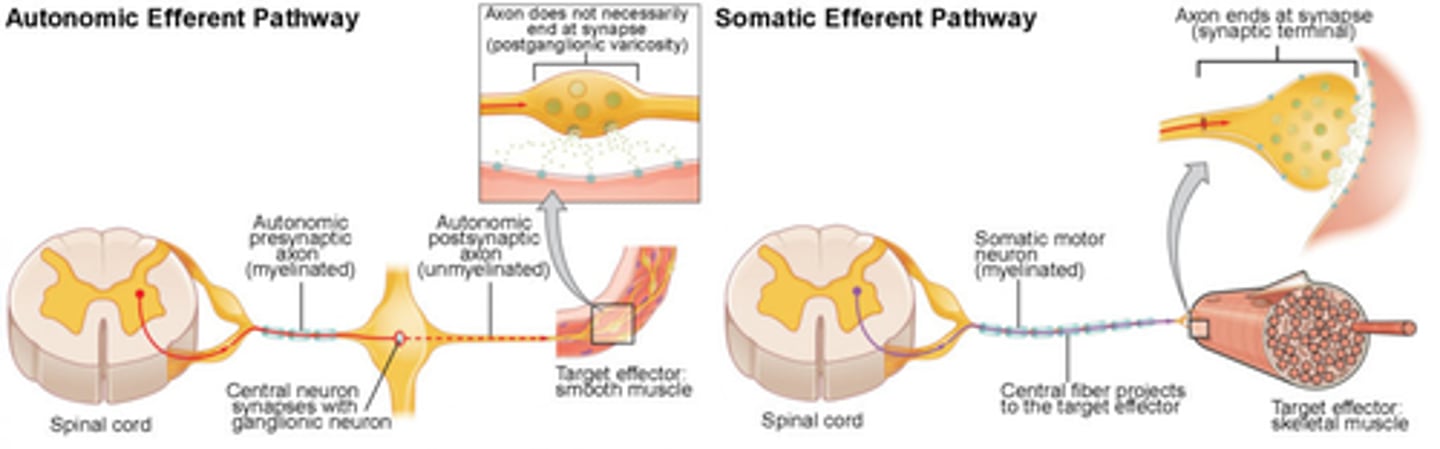
Autonomic Spinal Reflexes
Effector = cardiac m., smooth m., or glands.
-Involuntary
-Automatic
Autonomic Spinal Reflexes: Example
e.g. Urinary bladder
Stimulus = Stretch of bladder
↓
Receptor = Stretch receptors in bladder wall
↓
CNS = Sacral segment of spinal cord (PSNS)
↓
Effector = Detrusor muscle (wall of bladder): wall contracts and internal sphincters open.
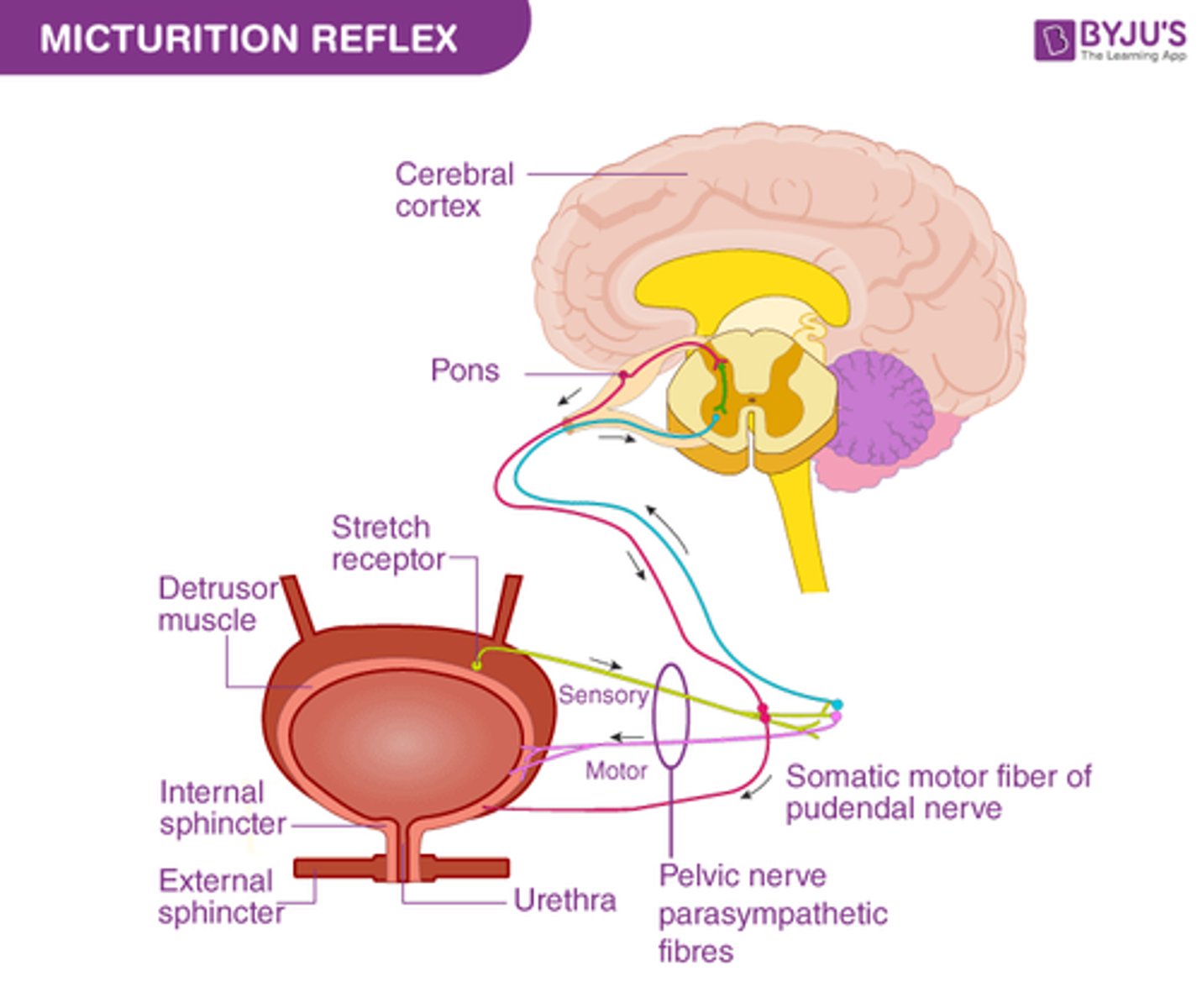
What reflex from the Urinary Bladder is it called?
Micturition Reflex
*Remember autonomic
Cerebrum
The area of the brain is responsible for all voluntary activities of the body.
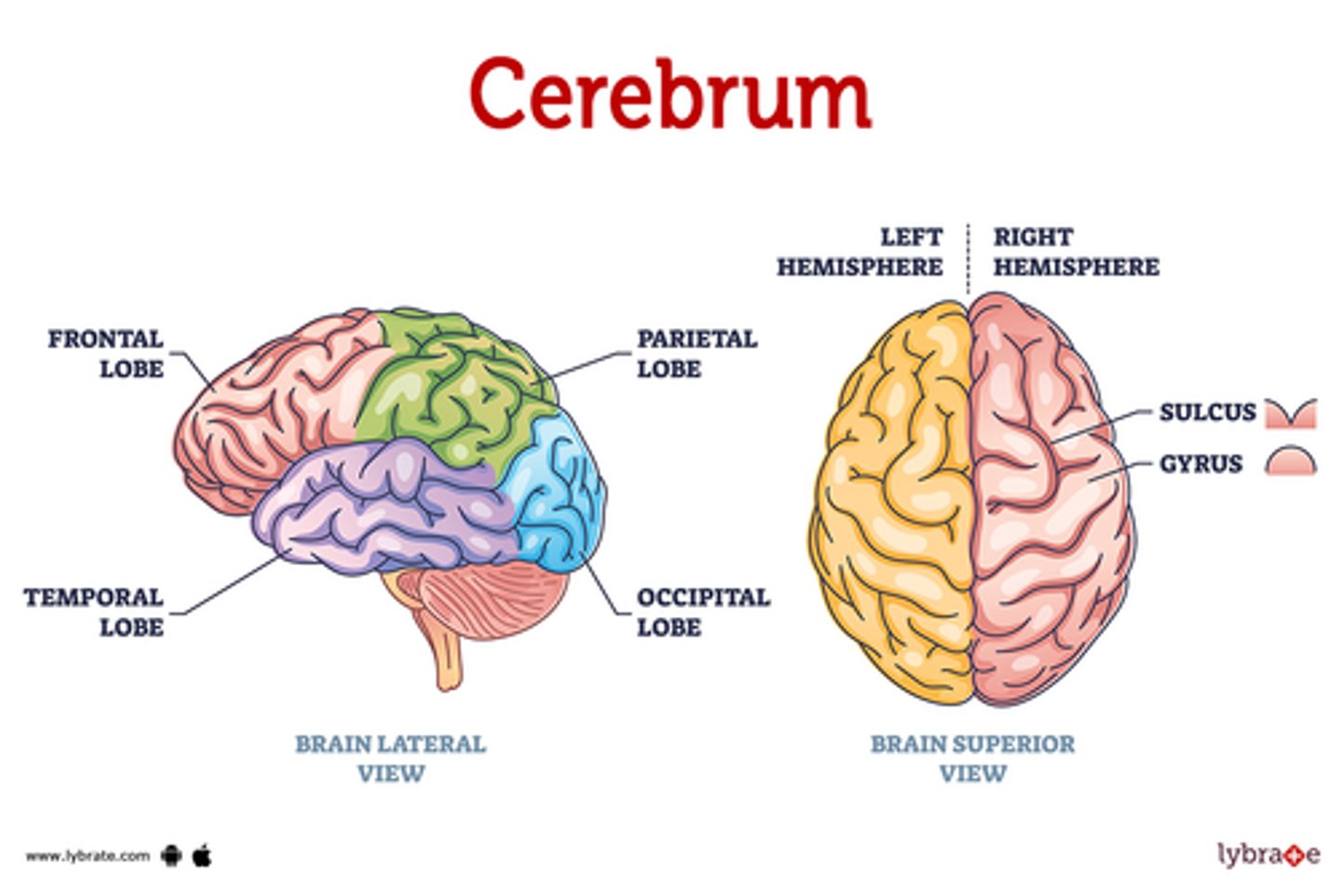
Cerebrum Role:
-Interpreting sensory info from senses (general and special)
-Initiating/controlling skeletal muscle movement
-Memory, intellect, etc.
-Relaying info between different parts of the brain/spinal cord
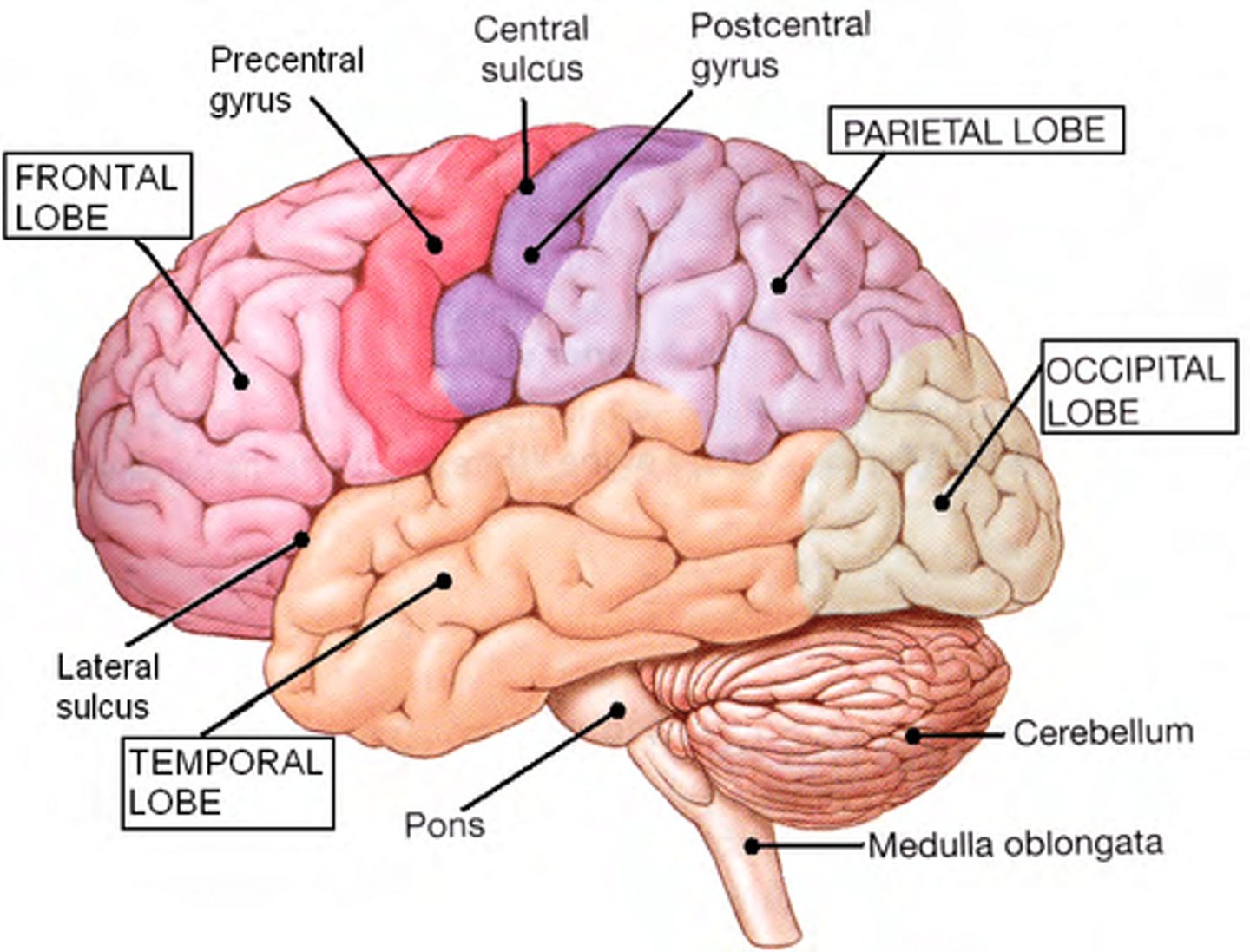
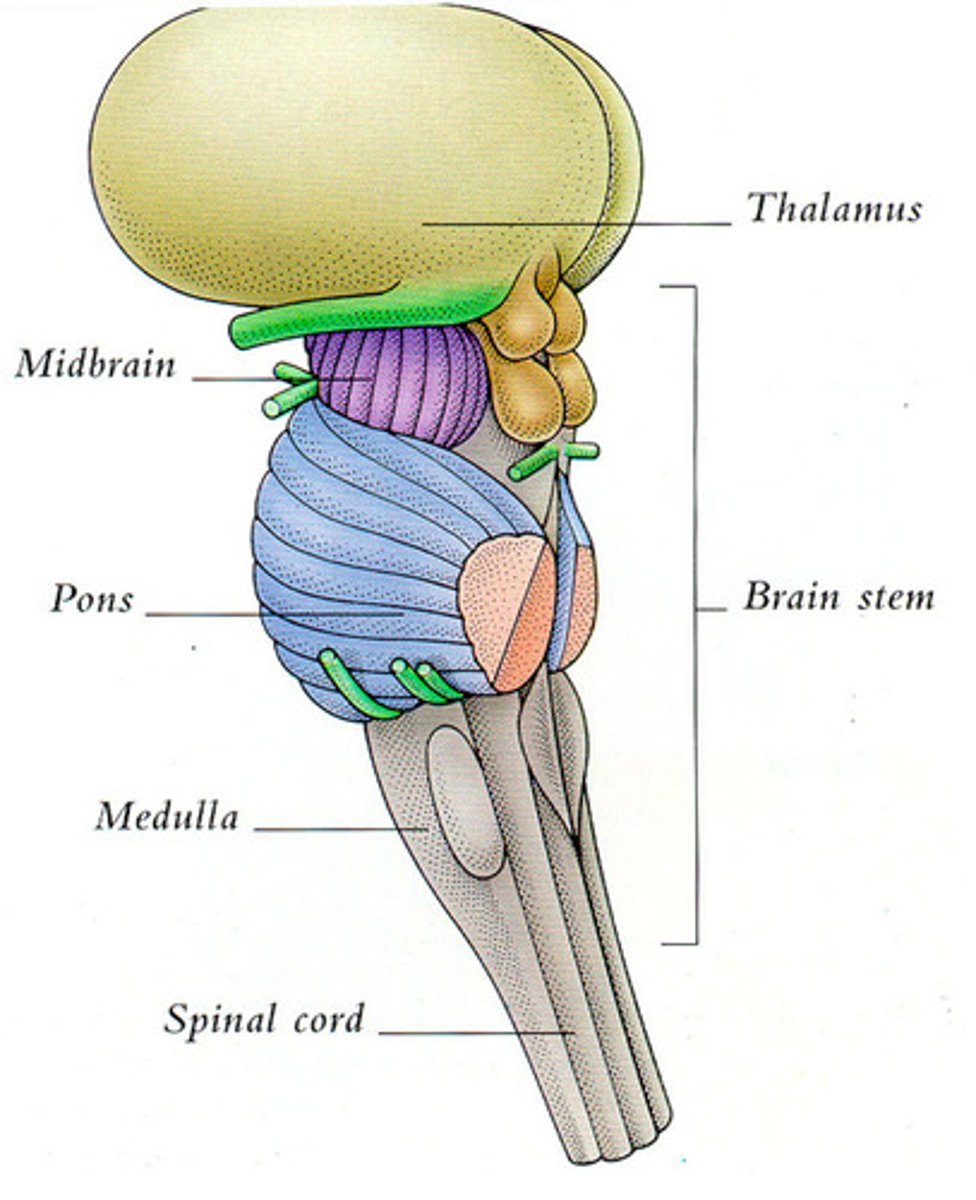
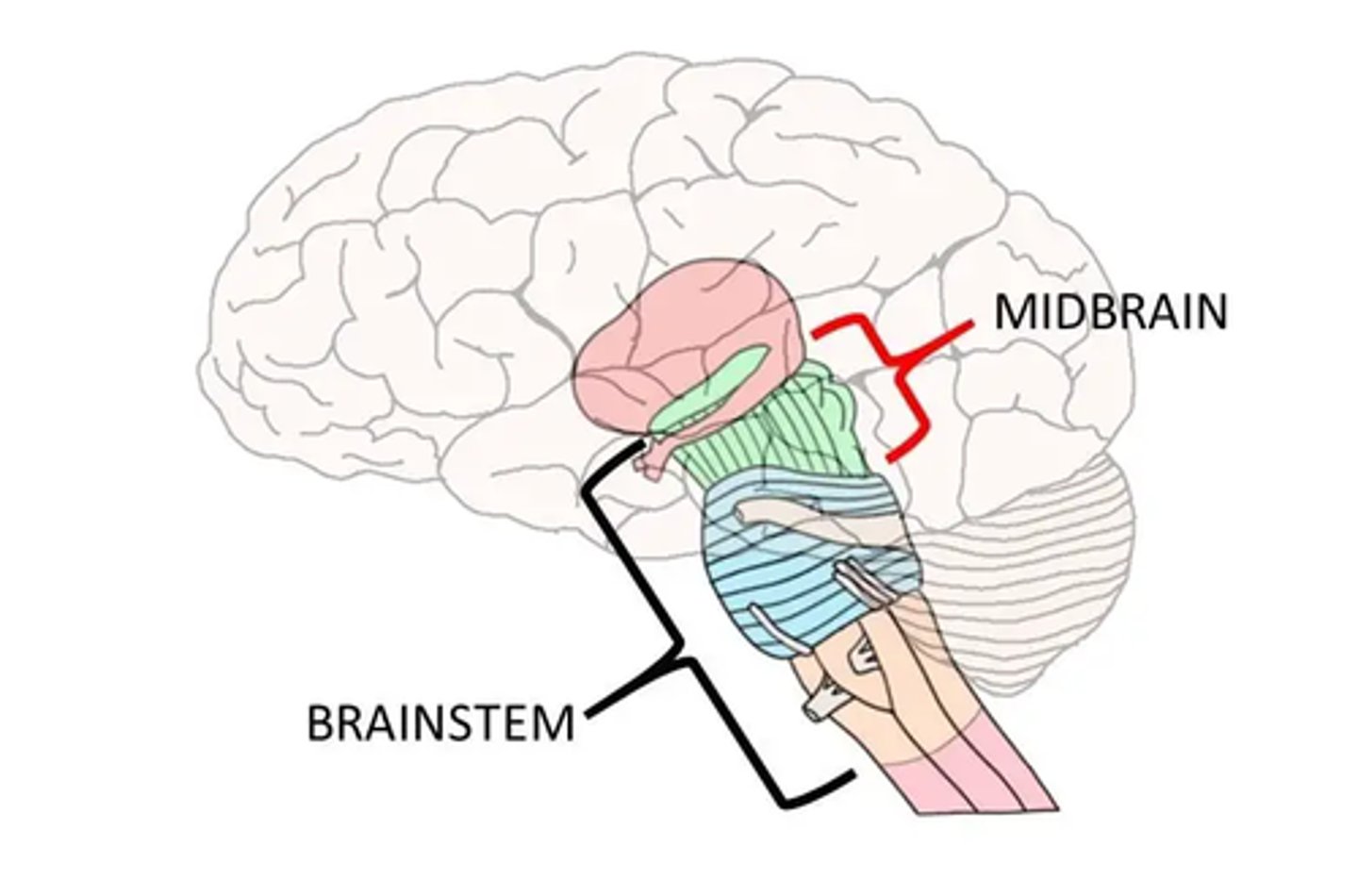
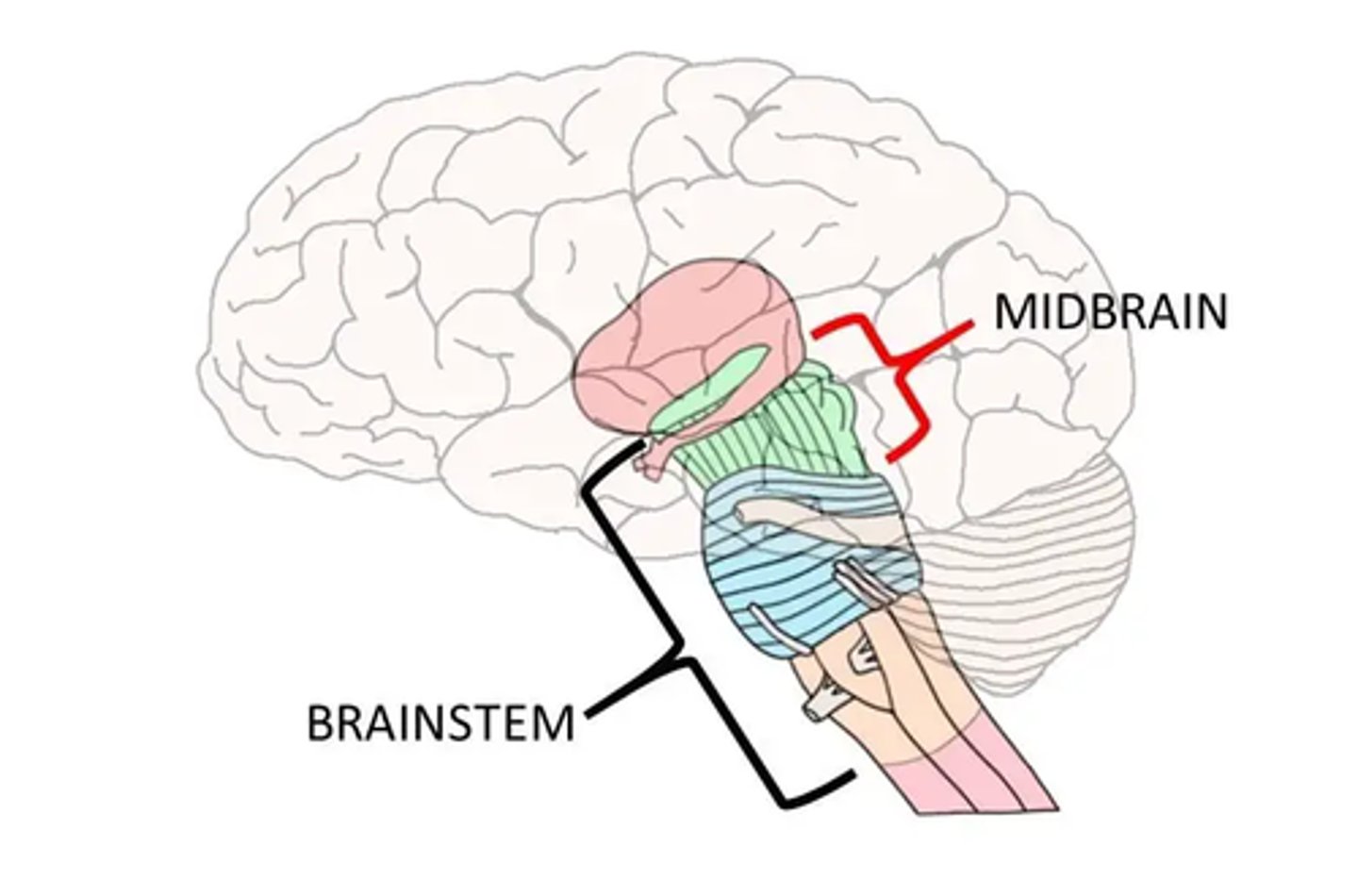
Brain Stem
Controls life-‐sustaining processes
e.g. breathing, circulation.
-Connects the CNS.
If brain stem functional but higher centers damaged:
Alive but not aware,
-no conscious control

Brain Stem Parts:
-Midbrain
-Pons
-Medulla
"MPM"
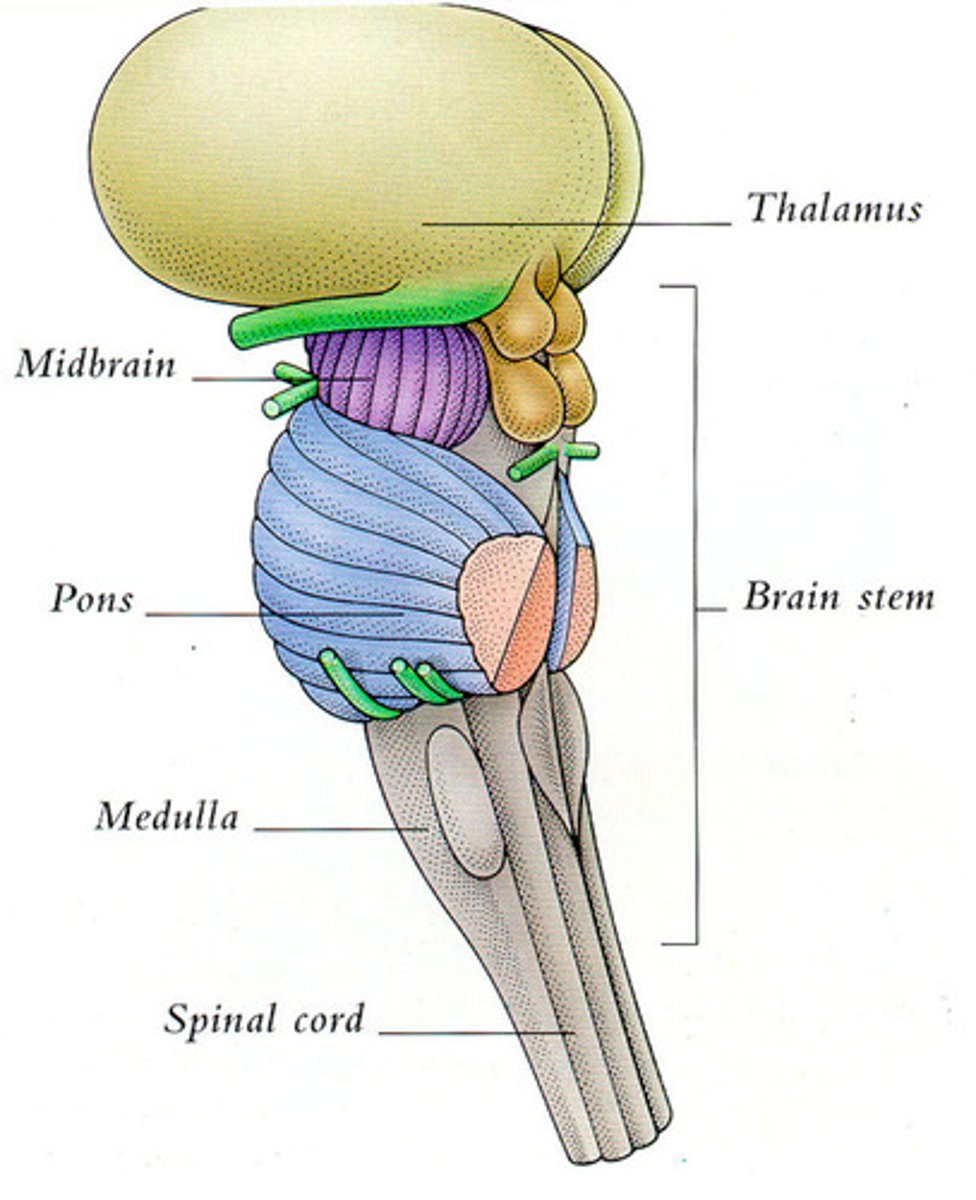
Midbrain
Auditory and visual reflexes ⇒ movement of eyes (vision), head and neck in response to visual/auditory stimuli
Pons
Pontine Respiratory Centres
-Functions with the medulla to regulate breathing
Medulla
Functional regions:
-Decussation
-Autonomic Vital Reflex Centers
other non-‐vital areas - control swallowing, coughing, sneezing, vomiting, etc.
Medulla: Decussation
Decussation (crossing over) of sensory and motor tracts
↓
Right brain receives/controls left side
↓
Left side receives/controls right side
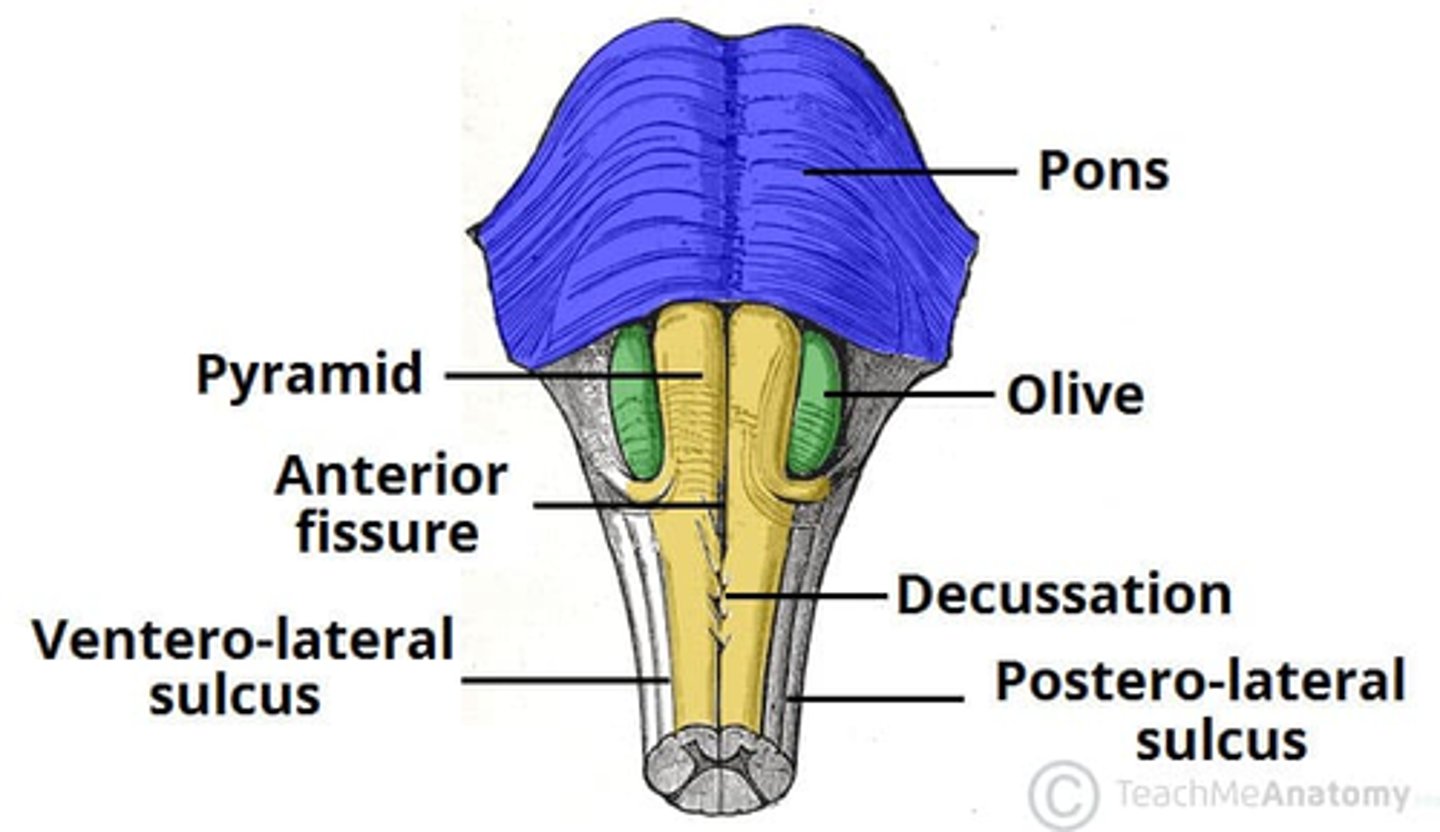
Medulla: Autonomic Vital Reflex Centers
Respiratory Area
-Drives breathing rate
Cardiovascular Centre
-Cardiac area: Modifies heart rate
-Vasomotor area: Controls blood vessel diameter
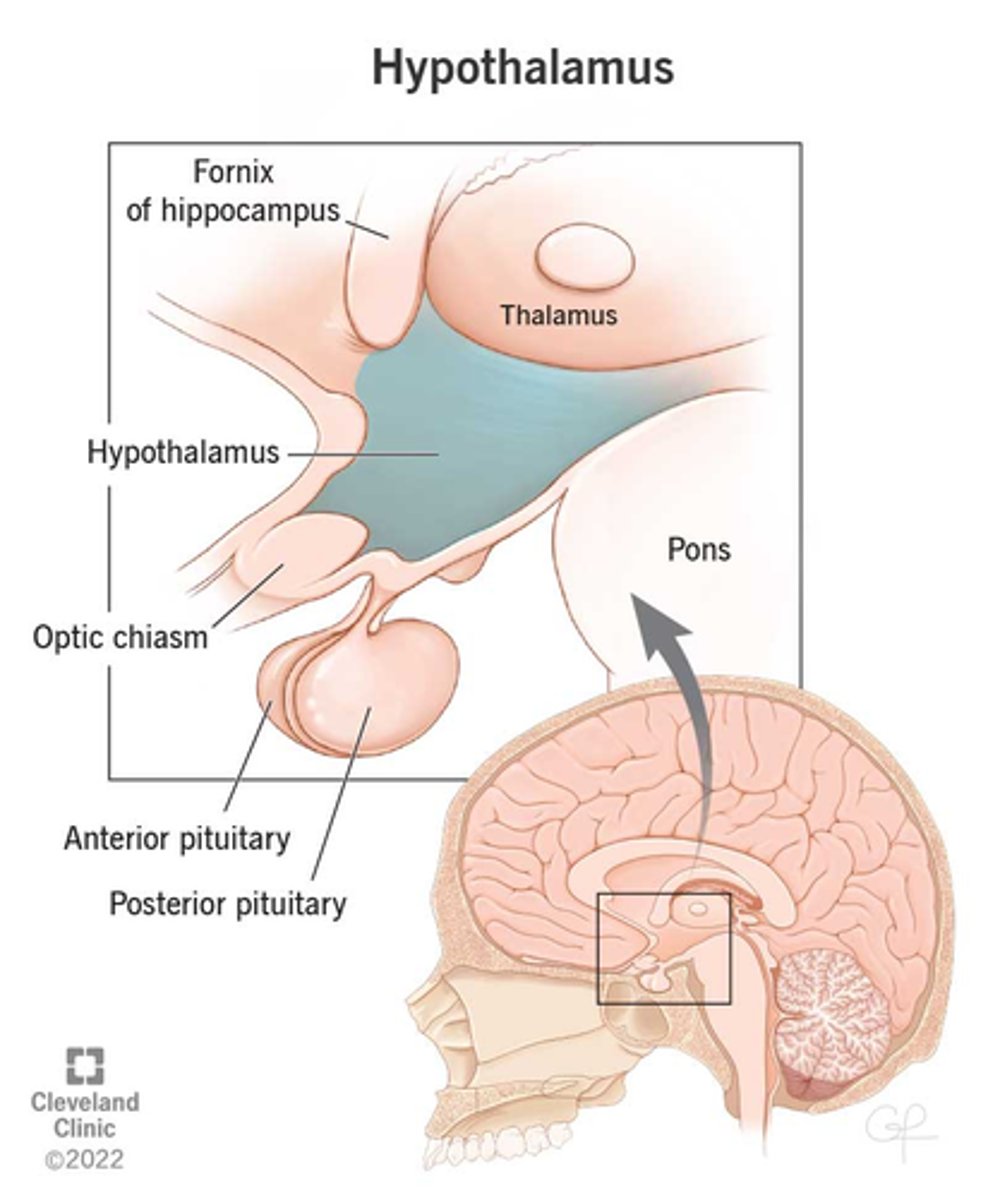
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion.
-Brain region controlling the pituitary gland.
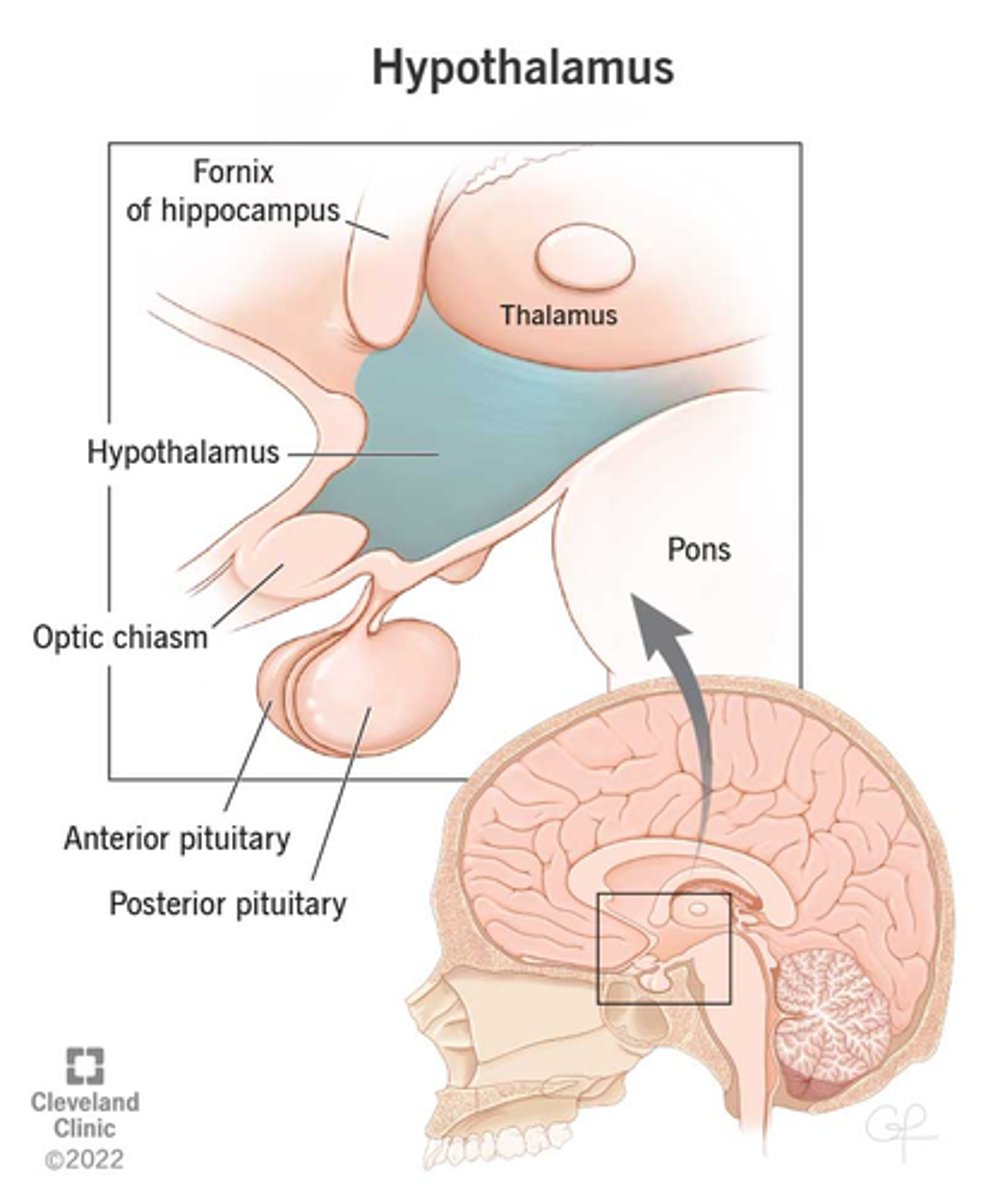
Hypothalamus Major Functions:
-Regulates ANS (sm. + card. muscle, glands)
-Regulates parts of the endocrine system
-Regulates temp: “thermostat cells"
-Regulates food and water intake, body fluid conc.
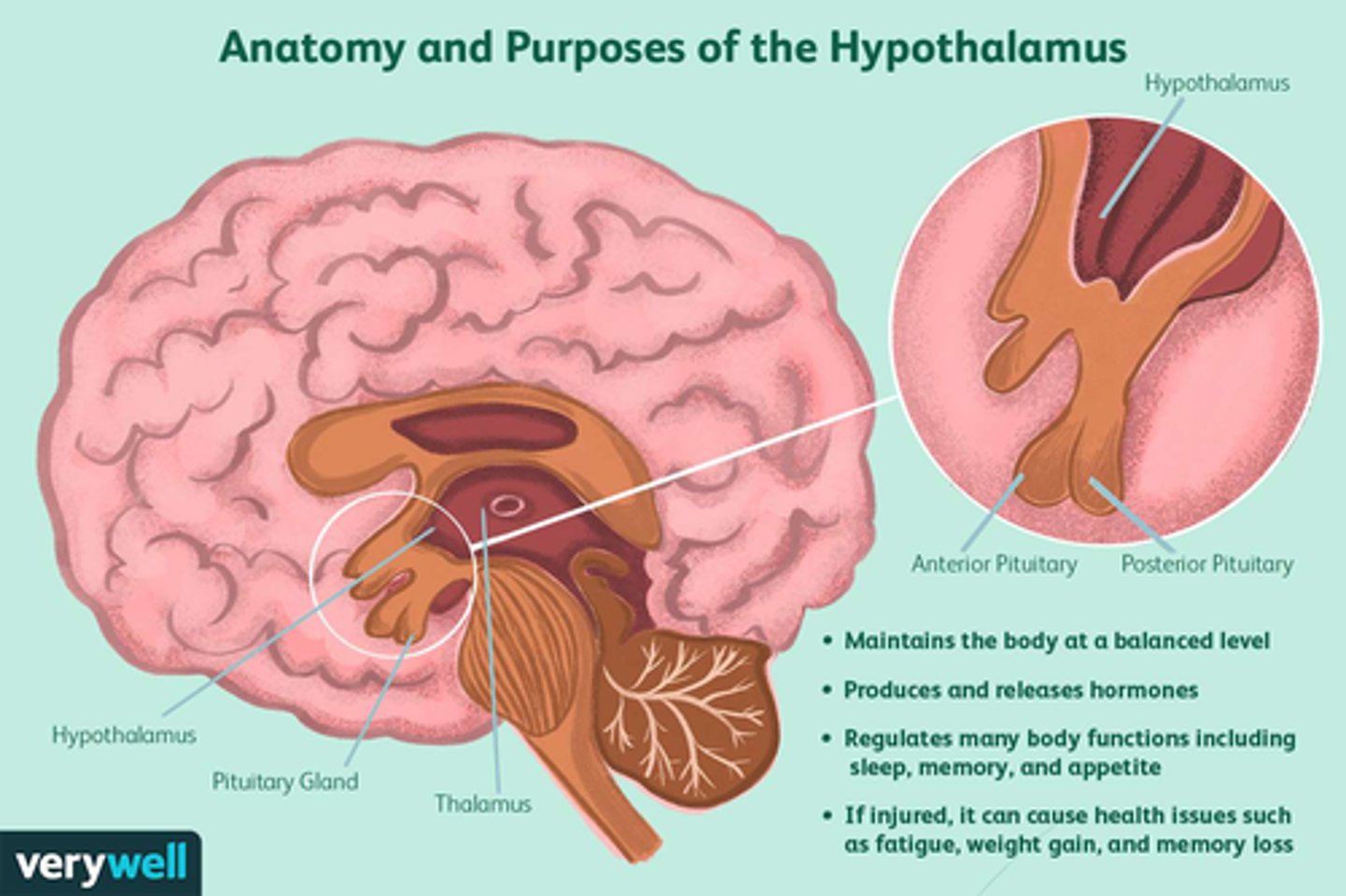
Hypothalamus is part of the:
Limbic System (composed of cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus)
-basic emotions regulated here (e.g. fear)

Limbic System
-Regulates emotions (laughing, crying, etc.)
-Memory (memories evoke emotional responses)
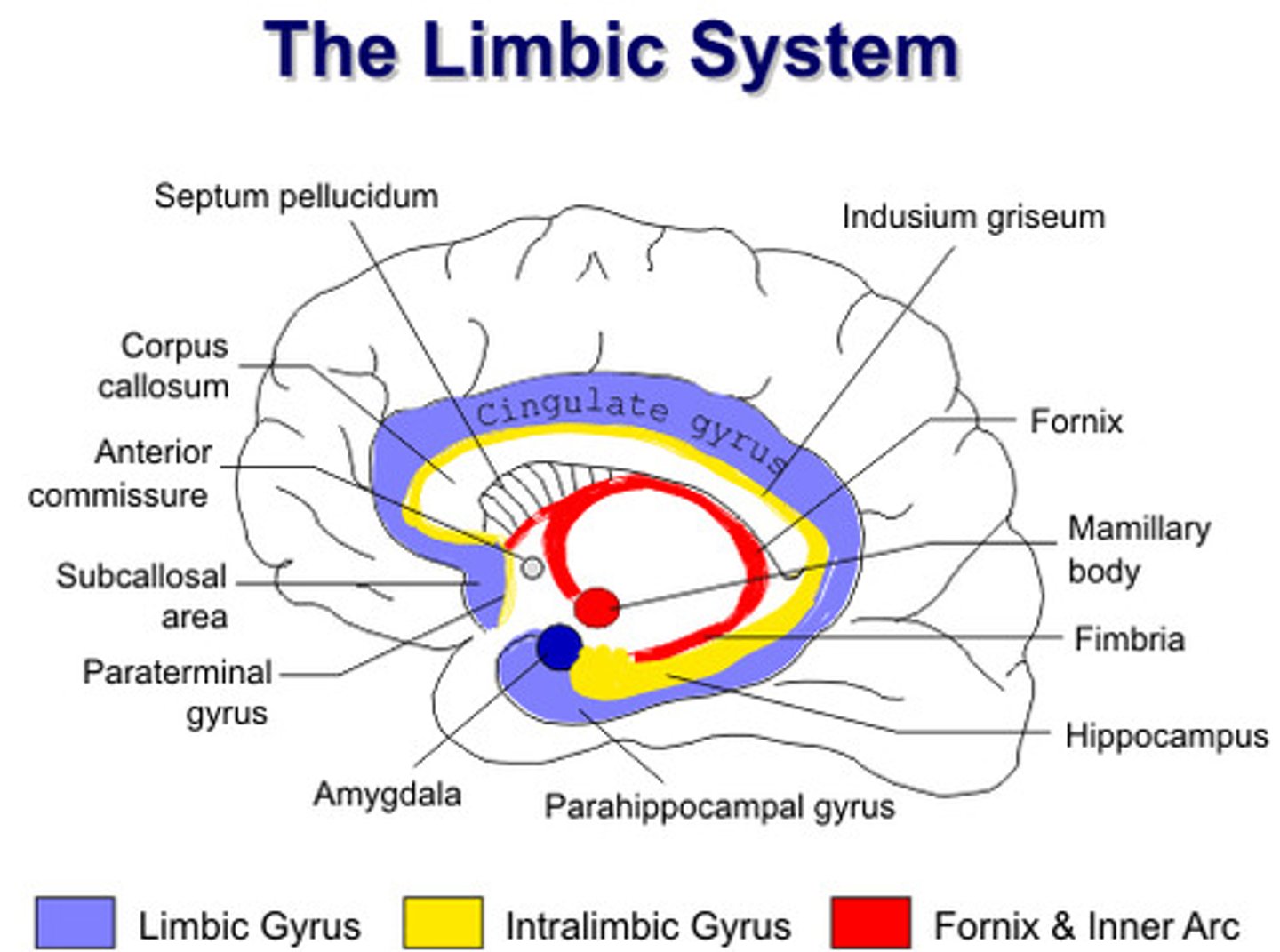
Hypothalamus also plays a part on:
Coordinating the Reticular Activating System
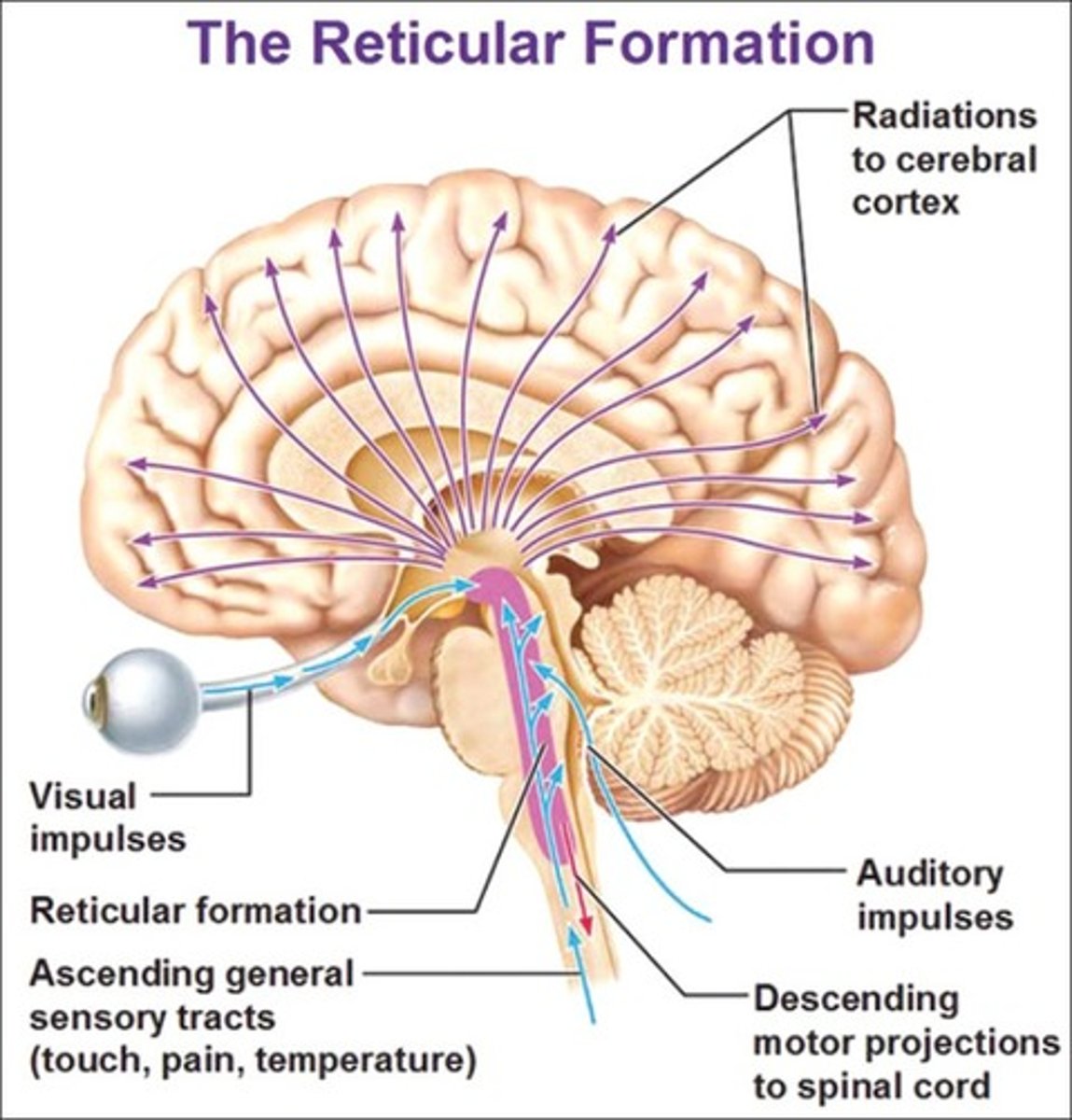
Reticular Activating System
In reticular formation (functional area of brain stem) – Alerts rest of brain
Receives sensory input for awakening ⇒ Sets daily rhythms (sleep/awake)
Overall, Hypothalamus is known for:
All major homeostatic functions! ⇒ Damage = Loss of homeostasis