Chemical formulae, equations, and calculations
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is relative atomic mass (Ar)?
The average mass of all the isotopes of that element
Where is the relative atomic mass located on each element?
The top number
How do you find the relative formula mass which is the same as relative molecular mass (Mr)?
number of atoms of that element x their relative atomic mass
What is the unit for the amount of substance?
mol
What is the equation linking mass, Mr and moles
moles = mass / Mr
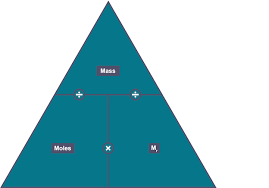
What is the molar ratio and what is the rule?
The ratio between the moles of the reactant and product in a balanced equation.
Just the big number on the left side of the element, never the subscript
e.g. N2 + 3H2 —> 2NH3
molar ratio : 1:3:2
What is percentage yield?
The actual yield of a reaction compared to the maximum theoretical yield
(meaning how much product you produce compared with how much you thought you should produce based on your calculations)
What is the formula for calculating percentage yield?
% yield = (actual yield/ theoretical yield) x 100
Suggest 3 reasons why the percentage yield may be less than 100%
Reactants may not all react (e.g. slow reaction or reaches equilibrium)
side reactions, maybe other products produced instead
products may be lost (e.g. gases may float off or some solids left on the filter paper)
How can you obtain formula of metal oxides experimentally? Describe example of aluminium oxide.
Through electrolysis
e.g. Aluminium oxide (2Al2O3 —> 4Al + 3O2)
Anode - O2 would be formed (2O2- —> O2 + 4e-) (Oxidised - loss of electrons)
Cathode - Al would form (Al3+ + 3e- —> Al) (Reduced - gain of electrons)
How can you obtain formula of aqueous solutions? And what are the rules?
Electrolysis
H+ and OH- ions are always present
OH- ions are always oxidised at the anode unless a halide ion (group 7) is present in solution
H+ ions are always reduced at the cathode unless a less reactive element than H is present (e.g. Cu2+)
What is water of crytallisation?
It is the water molecules which are incoporated in a crystal lattice
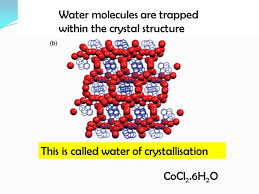
What is a hydrated salt?
When the solid crystal contains water of crystallisation
What is an anhydrous salt?
When the solid crystal does NOT contain water of crystallisation
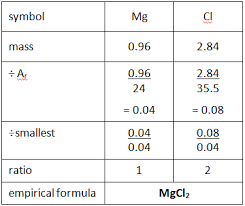
What is the empirical formula and how do you find it?
It is the smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each element within a compound
e.g. empirical formula of N2O4 would be NO2
Find out number of moles with moles = mass/ Mr
Then divide each mole number by the smallest one out them to find the molar ratio.
Substitute ratio into compound
What is the molecular formula and how do you find it?
It is the exact number of atoms of each element within a compound
Use the empirical formula
molecular mass = n x empirical formula
n = the subscript found in the empirical formula
e.g. CH2O x 2 —> C2H4O2
State the equation linking concentration, moles and volume
concentration = moles / volume
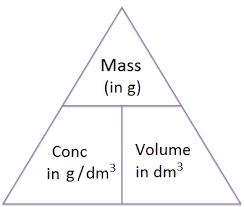
What is the unit for volume?
dm3
What is the unit for concentration?
mol / dm3
What is 1 dm3 in m3
1 dm3 = 1000 cm3
State the equation linking number of moles and the volume of a gas
volume of gas = number of moles x 24
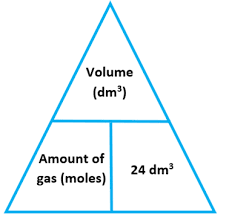
What are the conditions needed to use the equation volume of gas = moles x 24
Room temperature
Room pressure