3.1 - heat and cold
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
hot/cold packs
ice massage, contrast bath
fluidotherapy
paraffin
infrared lamps
whirlpool
list of thermal agents tfor superficial thermal agents
continuous ultrasound
continuous shortwave diathermy
list of thermal agents for deep heating
1-3cm
skin, subcutaneous tissue/fluids
superficial heating goes about ________ deep and targets….
3-5cm
large muscles, joins
deep heating goes about ________ deep and targets….
conduction
convection
radiation
conversion
what are the 4 types of heat
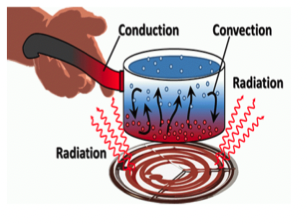
conduction
what type of heat involves direct contact to transfer heat
hot packs
paraffin
cold modalities
what are some types of conductive modalities (3)
fast; slow
with conduction, objects get warm (slow or fast) and get cold (slow or fast)
thermal conductivity
_____________ is the rate that material transfers heat
((area of contact) x (thermal conductivity) x (temp difference)) / tissue thickness
what is the rate of heat transfer equation
more
does a high water content of more or less conductivity
muscle (this means it transfers heat faster - conductivity)
does muscle or fat have a higher thermal conductivity
area of contact
larger = faster transfer
temp difference of the 2 materials
large gradient = greater change
conductivity
high is fast, low is slow
tissue depth
deep = slower to change temp
what are the four principles for conduction
true
T/F: In applying paraffin to a patient’s hand, it is important to remove any jewelry due to the high thermal conductivity of metal.
false
T/F: The total amount of heat transferred is the same when comparing a thermal agent applied to the entire quad muscle with the biceps muscle
true
T/F: Placing 6-8 layers of towels between hot pack and skin decreases the heat conduction
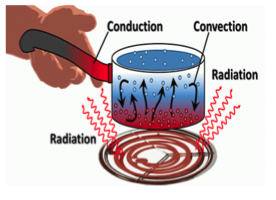
convection
what type of heat involves a circulating medium and a material of a different temperature
convection
which is faster process, conduction or convection
fluidotherapy
whirlpool
what are two types of convection modalities
motion
convection is a thermal agent that is in _________
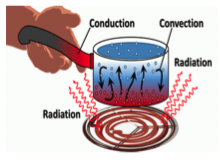
radiation
what type of heat involves energy transfer without contact or intervening material
radiation intensity
size and source of radiation
treatment area
distance and angle between source and treatment area
radiation depends on what 4 factors
infrared lights
what is a clinical modality for radiation
radiation
what type of heat is a thermometer an example of
radiation
what type of heat is this an example of

conversion
what type of heat involves changing nonthermal into heat
ultrasound; diathermy; cold packs activated by striking
an example of conversion heat:
mechanical: ____________
electrical: ______________
chemical: _____________
false
T/F: conversion heat involves direct contact
evaporation
____________ is a process where a liquid changes into a gas
true
T/F: evaporation is cooling ONLY
lower (contact with warm skin causes liquid to change to gas and leaves skin cooler)
vapocoolant spray evaporates at a (lower or higher) temp than water
specific heat
_______________ is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a unit of mass of a material by one degree celcius
more
a high specific heat means (less or more) energy is required to heat up, this also means it can hold (less or more) energy at a given temp
water
what has a higher specific heat, air or water
1. More rapidly
Immersion in a whirlpool will heat a patient’s skin _________ than/as immersion in a bowl of water of the same temperature.
1. More rapidly
2. Less Rapidly
3. The same rate
2. Convection
Blood circulating in the body also transfers heat by ___________ to reduce local changes in tissue temperature.
1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Conversion
4. Radiation
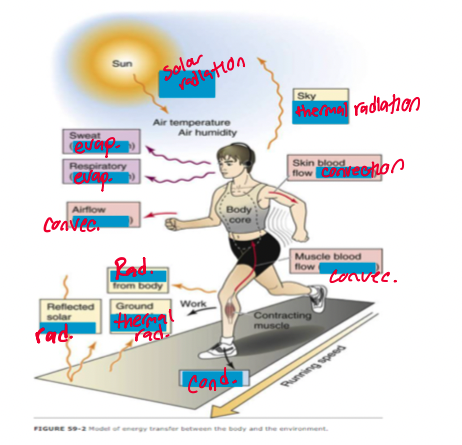
label all the energy sources/thermal types
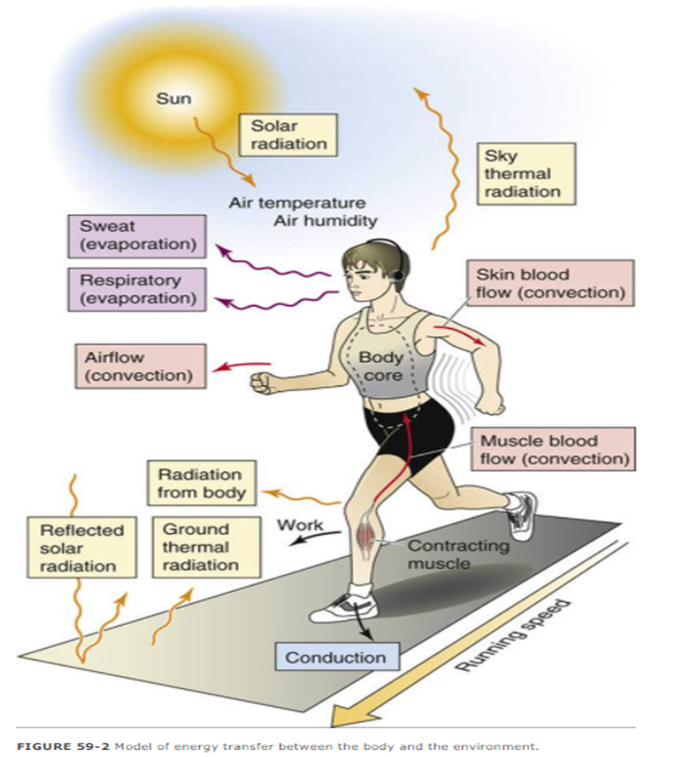
decrease pain
muscle spasm
joint stiffness
increase soft tissue extensibility and ROM
general relaxation
MIGHT decrease effects of DMOS
indications for using therapeutic heat (6)
104-113 degrees farenhiet
the tissue temp must be elevated to __________ to provide a therapeutic effect
vascular/hemodynamic effects
neuromuscular effects
metabolic effects
altered tissue extensibility
what are the 4 effects of heat
dilation; smooth
heat causes vaso_________ and it relaxes ___________ muscle
inc metabolic rate, chemical mediators
inc oxygen for repairs
in what ways does heat increase metabolic reactions
exercise
what is the best way to heat deep muscles
inc; inc; dec
the neuromuscular effects of applying heat
(inc or dec) nerve conduction velocity
(inc or dec) thermoreceptors at skin
(inc or dec) nociceptive afferents at dorsal horn
dec alpha mn → GTOs relax → relax muscle contraction
how can heat decrease muscle spasms through neuromuscular effects
decreases muscle performance → strength for 30mins after heat → gradually increase up to 2 hours
what is the timeline of muscle performance when applying heat and considering the neuromusclar effects
113-122
past ________ degrees is when tissue is subject to burning
104-113; 5-10 minutes
to increase tissue extensibility of soft tissue with heat, the tissue temperature must be maintained at ________ degrees for ________ (duration)
no
is there good evidence behind heat increasing flexibility
yes
is there good evidence behind heat reducing pain
kinda… limited but shows positive outcomes by using “heat-wrapped”
is there good evidence behind heat decreasing DOM
impaired sensation (can burn)
vascular disease/insufficiency
thrombophlebitis
over recent or potential hemorrhage (can inc bleeding)
over area of known malignancy
over infected area
over lidocaine patches
impaired cognition
list the contraindications for therapeutic heat (8)
over area of acute injury or inflammation
over abdomen or low back during pregnancy
impaired circulation
metal in area (only superficial
area of edema
over area where liniments or heat rubs were recently applied
cardiac insufficiency
over an open wound (nerve with paraffin, closely monitor)
demyelinated nerves
precautions of therapeutic heat (9)
burns
_________ is the second most common suit for malpractice in PT
158-167
hot packs are stored at ____________ degrees
6-8; 2-3
must use _______ layers of toweling with therapeutic heat; note that a hot pack cover equals _________ layers of toweling
5 minutes
you must check in with the patient after ________ when using therapeutic heat
125-134 fahrenheit
what is the appropriate temperature for paraffin
dip-wrap
painting
what are the 2 techniques for paraffin
6-10 times
when you do the dip-wrap method with paraffin, how many times do you dip, lift and allow wax to dry
6-10 layers
how many layers do you use for the painting paraffin technique
100-118 fahrenheit
what is the appropriate temp for fluidotherapy
20 minutes
how. many times is fluidotherapy applies for
explain purpose, procedure, expectations to patient
clear contraindications
check sensation
apply agent
perform a 5 min check
after treatment: inspect skin and document results
what is the 6 step process of therapeutic heat application
5 min
when does a patient reach “peak heat” when getting therapeutic heat
heat (doesn’t add cold)
cryotherapy removes (cold or heat)
inflammation
pain
edema
reduce spasticity
facilitation of movement
increase pain threshold
clinical indications for using cryotherapy
temp difference between objects
time of exposure
conductivity of tissue
type of agent
total body surface being cooled
cooling depends on what 5 factors
hemodynamic
neuromuscular effects
metabolic effects
what are the 3 effects of cold therapy
constriction
hemodynamic effects of cold causes immediate vaso___________
smooth muscle of blood vessel walls contract
decreased production of vasodilator mediators
increased blod viscosity
reflexes causing vasoconstriction
what are the 4 effects of vasoconstriction from the hemodynamic effects of cold
5-10 minutes
after __________(duration) of cold application, the possibility of cold induced vasodilation can occur
10-15 minutes
limit cold therapy applications to _________ to limit vasodilation
dec; inc; force; dec; proprioception
neuromuscular effects of cold:
(dec or inc) nerve conduction velocity
(dec or inc) pain threshold
alters muscle _________ generation
(dec or inc) spasticity
alters _______________
A delta
neuromuscular effects of cold is especially effective for ________ nerve fibers
true
T/F: cold therapy can treat myofascial pain and trigger points
inc; dec; isometric
the temporarily altered muscle strength from the neuromuscular effects of cold:
< 5 minutes = (dec or inc)
> 5 minutes = (dec or inc)
cooling 10-20 → decreased _________ muscle strength initially
10-30 minutes
cooling for _________(duration) decreases spasticity, clonus, resistance to PROM, and some reflexes
false
T/F: cold therapy is recommended when healing is delayed
true
T/F: cold therapy can treat inflammatory joint disease: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
20 minutes; 1 hour
when using cold therapy, never apply longer than _______ and at least _________ apart
1+ hours
cold therapy applied for 10-15+ minutes can control pain for _________
true
T/F: cold therapy can reduce spasticity
upper
cold therapy can treat spasticity with (lower or upper) motor neuron dysfunction
false (MS sx are aggravated in the heat)
T/F: it is better to treat MS with heat rather than cold
cooled; takes longer when vessels are vasoconstricted, it’s faster when they are vasodilated
it takes longer for a (cooled or warmed) area to return to normal temperature; why
PRICE(s) = protection, rest, ice, compression, elevation, stabilization
POLICE = protection, optimal loading, ice, compression elevation
what does PRICE(s) and POLICE stand for
PEACE = protection, elevation, avoid anti-inflammatories, compression, education
LOVE = load, optimism, vascularization, exercise
what does PEACE and LOVE stand for
acute (remember the A stands for avoid anti-inflammatories)
what stage of healing would you use the acronym PEACE
cold urticaria
cold intolerance
cryoglobulinemia
raynaud’s disease/phenomenon
paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
over regenerating peripheral nerve
over area of circulatory compromise
over area of PVD (esp. PAD)
contraindications for cold therapy (8)
HTN - monitor
thermoregulatory disorders
over a superficial peripheral nerve
over an open wound
poor sensation
poor cognition
the very young and very old
persons with aversion to cold
precautions for cold therapy
tissue death
frostbite
nerve damage
what are the three adverse effects to using cold therapy
59 fahrenheit (skin should be between 59 and 113)
always keep tissue temperature above __________ degrees
2 cm
cold packs reduce temperature of skin/tissues up to _______ deep
with
what is more effective: ice bag with or without water
water/alcohol bag
what is more effective:
ice bag with water
water/alcohol bag
1
you should be using _______ towel layers if the agent is < 30 degrees fahrenheit
10-15 min
general treatment time for cold packs
intense cold
burning
aching
numbness
anesthesia
what are the normal reactions/sensations to cryotherapy
small
ice massage application is typically done over a (small or large) area