Non-Renewable Energy
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Fossil Fuels
the remains of ancient organisms that changed into coal, oil, or natural gas
Coal is made up of ________________
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and varying amounts of sulfur
What is the precursor to coal?
Peat
Peat
organic plant material; can be used as fuel
What is the softest type of coal that has the lowest amount of carbon?
Lignite
What is the coal that is “in-between” and has a medium level of carbon?
Bituminous (also known as soft coal and black coal)
What is the hardest type of coal that is the richest in carbon and burns the cleanest?
Anthracite
What are 4 advantages of coal?
Energy-dense
Plentiful
Cheap
Easy to handle and transport
What are 4 disadvantages of coal?
Ash is left behind
Contains impurities
Carbon is released into the atmosphere which contributes to climate change
Releases impurities into the air when burned
What habitat is coal formed in?
A swamp
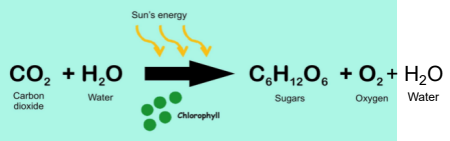
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
Think: Energy + gas + water in ——> Energy + gas + water out
How is coal formed?
300 million years ago, many giant plants died in swamps. This dead plant material accumulated, and over millions of years the plants were buried under water and dirt. When buried deep underground, the peat experienced increasing pressure and temperature, causing it to lose moisture and become more densely packed, eventually turning into coal.
What is oil also known as?
Petroleum and crude oil
How are oil and gas formed?
Tiny sea plants and animals died and were buried on the ocean floor. Over time, they were covered by layers of sand and sediment, which turned into sedimentary rock. Over millions of years, the remains were buried deeper and deeper. The enormous heat and pressure from inside the earth and the rock above turned them into oil and gas.
What are 4 advantages of oil?
Energy-dense
Cleaner-burning than coal
Convenient to transport and use
Creates jobs
What are 4 disadvantages of oil?
Possibility of leaks when extracted and transported
Releases carbon-dioxide into the atmosphere when burned, which contributes to climate change
Releases sulfur, mercury, lead, and arsenic into the atmosphere when burned
Releases sulfur dioxide; the sulfur dioxide and water turn into sulfuric acid, contributing to acid rain
Electric generator
machine that converts mechanical energy (motion) into electrical energy
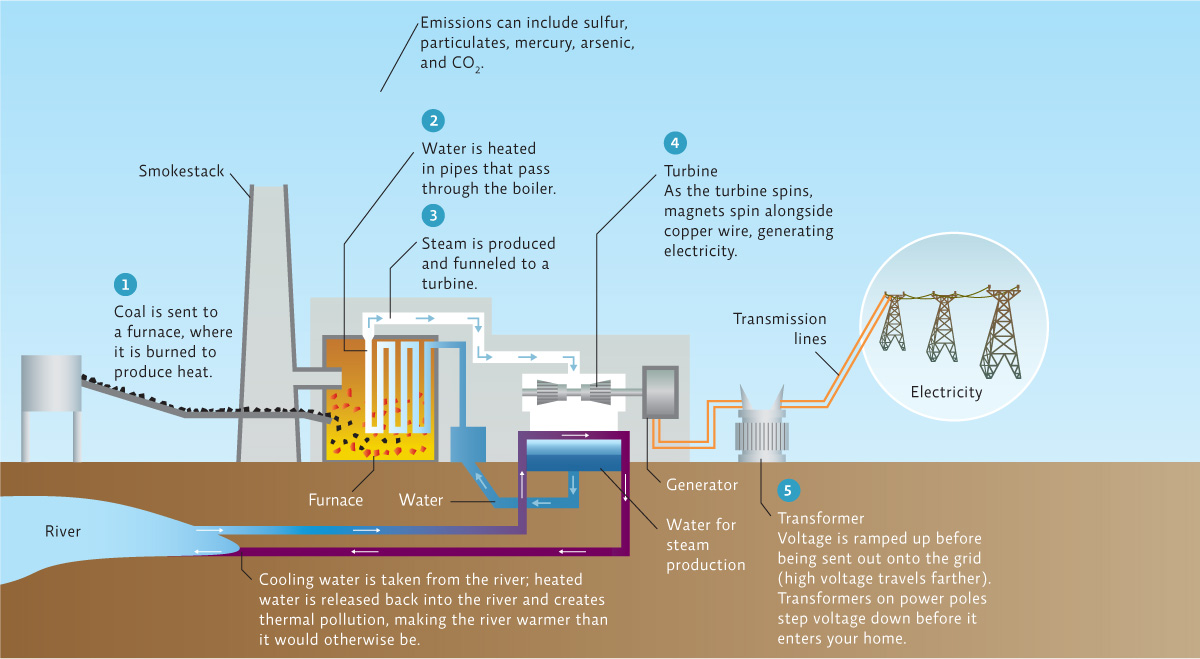
What is happening in this picture?
In a coal-fired electric generator, coal is burned to produce heat, which turns water into steam; this high-pressure steam then drives a turbine that spins a generator, creating electricity; the steam is then cooled and condensed back into water to be reused in the process.
What are 4 advantages of natural gas?
Contains fewer impurities and therefore emits almost no sulfur dioxide or particulates
Emits only 60% as much carbon dioxide as coal
Burns cleaner than other fossil fuels
Efficient storage and transportation through pipelines
What are 4 disadvantages of natural gas?
When unburned, methane escapes into the atmosphere
Exploration of natural gas has the potential of contaminating groundwater
Risk of explosions due to its flammability
Non-renewable resource
Proton
a stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with a positive electric charge.
Electron
a stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity.
Neutron
a subatomic particle of about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge, present in all atomic nuclei except those of ordinary hydrogen.
Nuclear energy
The energy within the nucleus of an atom.
Nucleus
The cluster of protons and neutrons in the center of an atom.
Atomic Number
the number of protons in an atom
Atomic Mass (amu)
the number of protons and neutrons
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different atomic masses (different number of neutrons)
Radioactive
atoms that emit particles and energy as they decay
Unstable →→Stable
Radiation
The alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays given off in the decaying of unstable nuclei.
Radioactive Decay
When atoms lose alpha particles and become different elements.
Half Life
The amount of time in which half the atoms in a sample decay
Nuclear Fission
A reaction in which the nucleus of a large atom is split into smaller nuclei and energy is released
Nuclear Fusion
a nuclear reaction in which atomic nuclei of low atomic number fuse (together) to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy.
Chain Reaction
process in which the products themselves promote or spread the reaction
Nuclear Reactor
an apparatus or structure in which fissile material can be made to undergo a controlled, self-sustaining nuclear reaction with the consequent release of energy.
Control Rods
“rods” made of cadmium, boron or other elements that absorb neutrons.
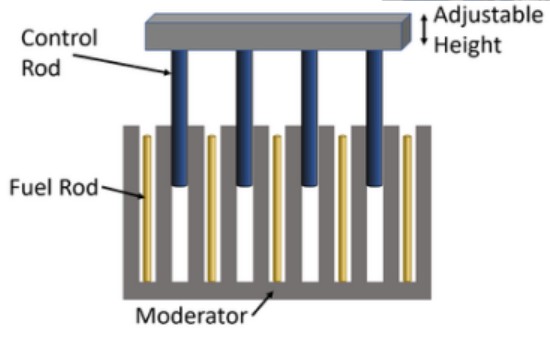
Breeder Reactor
a reactor that generates (creates) fuel
Radioactive Waste
Waste that emits larger amounts of radiation.
Fission
the splitting of a large atom into smaller ones.
reactions do not normally occur in nature.
produces many highly radioactive particles
the energy released is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions
Fusion
the fusing (putting together) or two or more lighter atoms into a large one.
occurs in stars, such as the sun.
produces few radioactive particles.
the energy released by fusion is three to four items greater than by fission.
What isotope is used for fission in nuclear reactors?
Uranium-235
What is used to start a chain reaction?
A neutron
What is one of the three nuclear disasters, and where was it located?
Three Mile Island near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, in March 1979. There was major fuel damage,and radioactive gases and contaminated cooling water filled the containment building. Some radioactivity was released into the atmosphere.
What is the second nuclear disaster, and where was it located?
1986 at Chernobyl in the Ukraine (former Soviet Union). The reactor was built with no containment system. The reactor core was severely damaged and a large amount of radioactivity was released into the environment.
What is the third nuclear disaster, and where was it located?
Fukushima Daiichi in Japan; March 11th 2011. After the earthquake and tsunami there was a core meltdown (heat generated exceeds the heat removed), loss of coolant (the pumps stopped working) which caused it to overheat and therefore there was the potential for the release of radioactive material. Additionally, there were hydrogen explosions at the plants
What are 4 advantages of nuclear energy?
Clean energy source
Creates jobs
Energy-dense
Low carbon footprint
What are 4 disadvantages of nuclear energy?
Radioactive waste
Possibility of nuclear accidents
High construction cost to build nuclear power plants
Uranium is nonrenewable