AP Psychology: Topic 2.1 - Perception, AP Psychology: Topic 2.2 - Thinking, Problem-Solving, Judgments, and Decision Making, AP Psychology: Topic 2.3 - Introduction to Memory, AP Psychology: Topic 2.4 - Encoding Memories, AP Psychology: Topic 2.5 - S…
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Bottom-up processing
analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory information
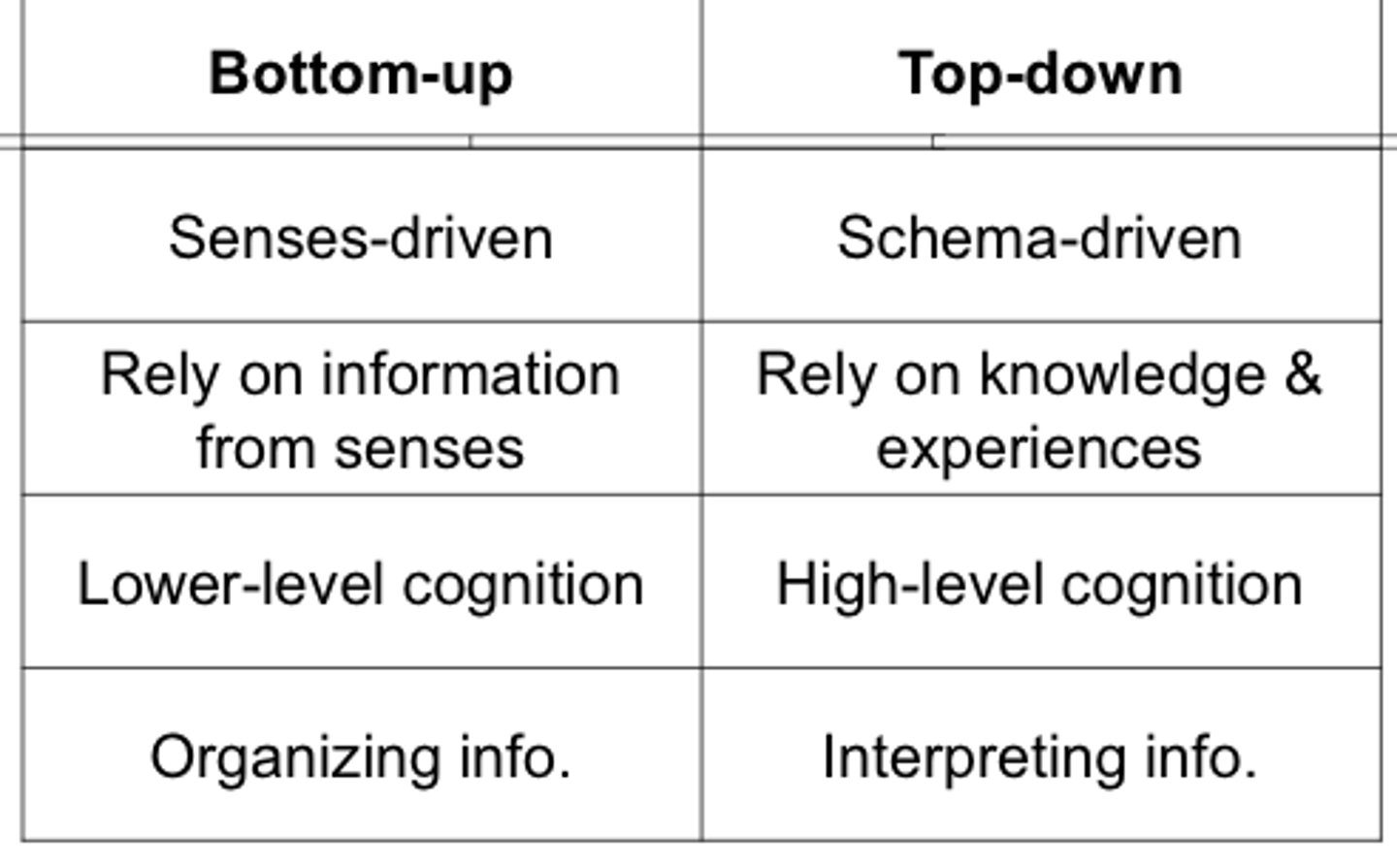
Top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
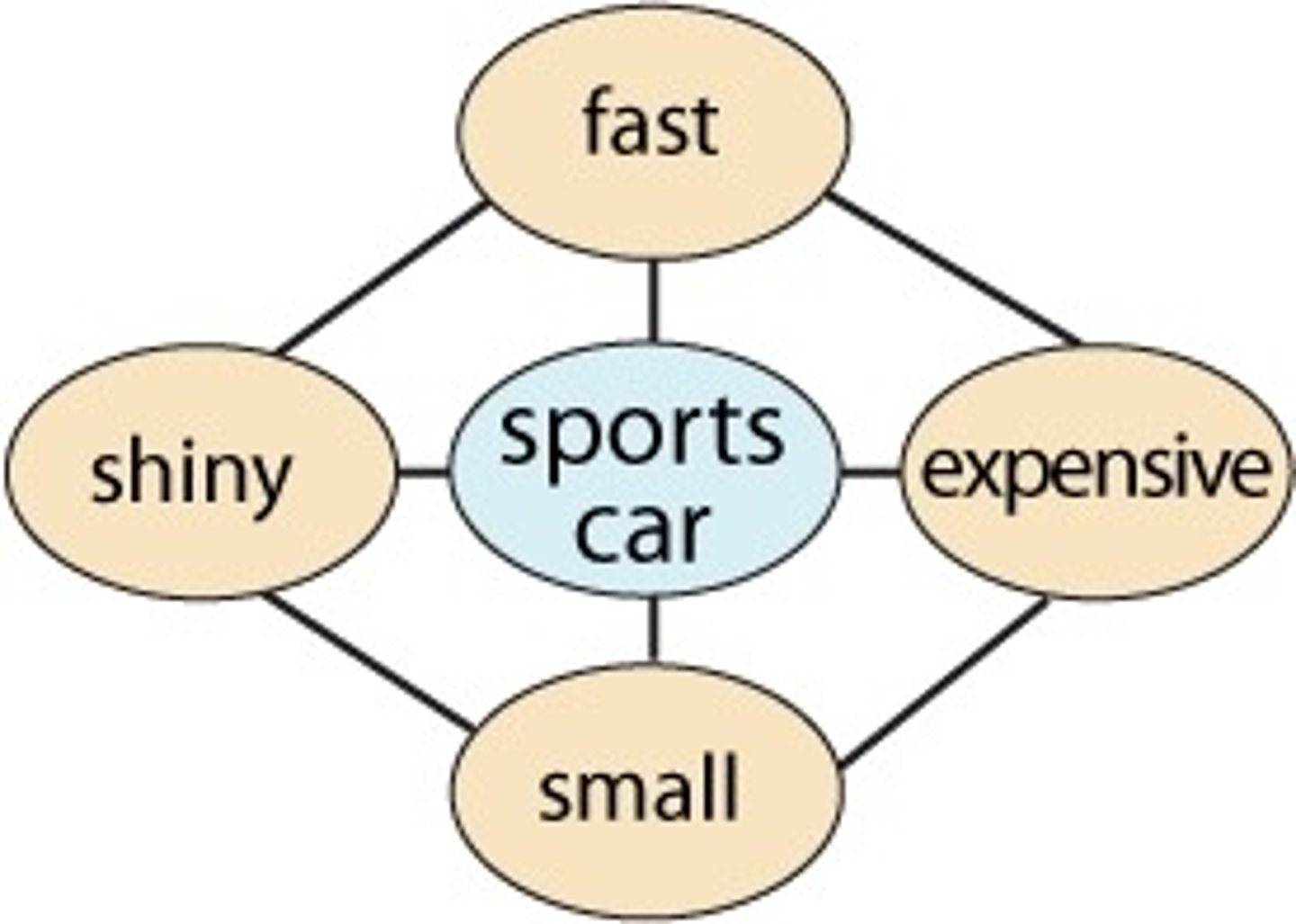
Schema
a conceptual framework a person uses for organizing and perceiving new information
Perceptual set
a predisposition or readiness to perceive something in a particular way and to ignore other perceptions
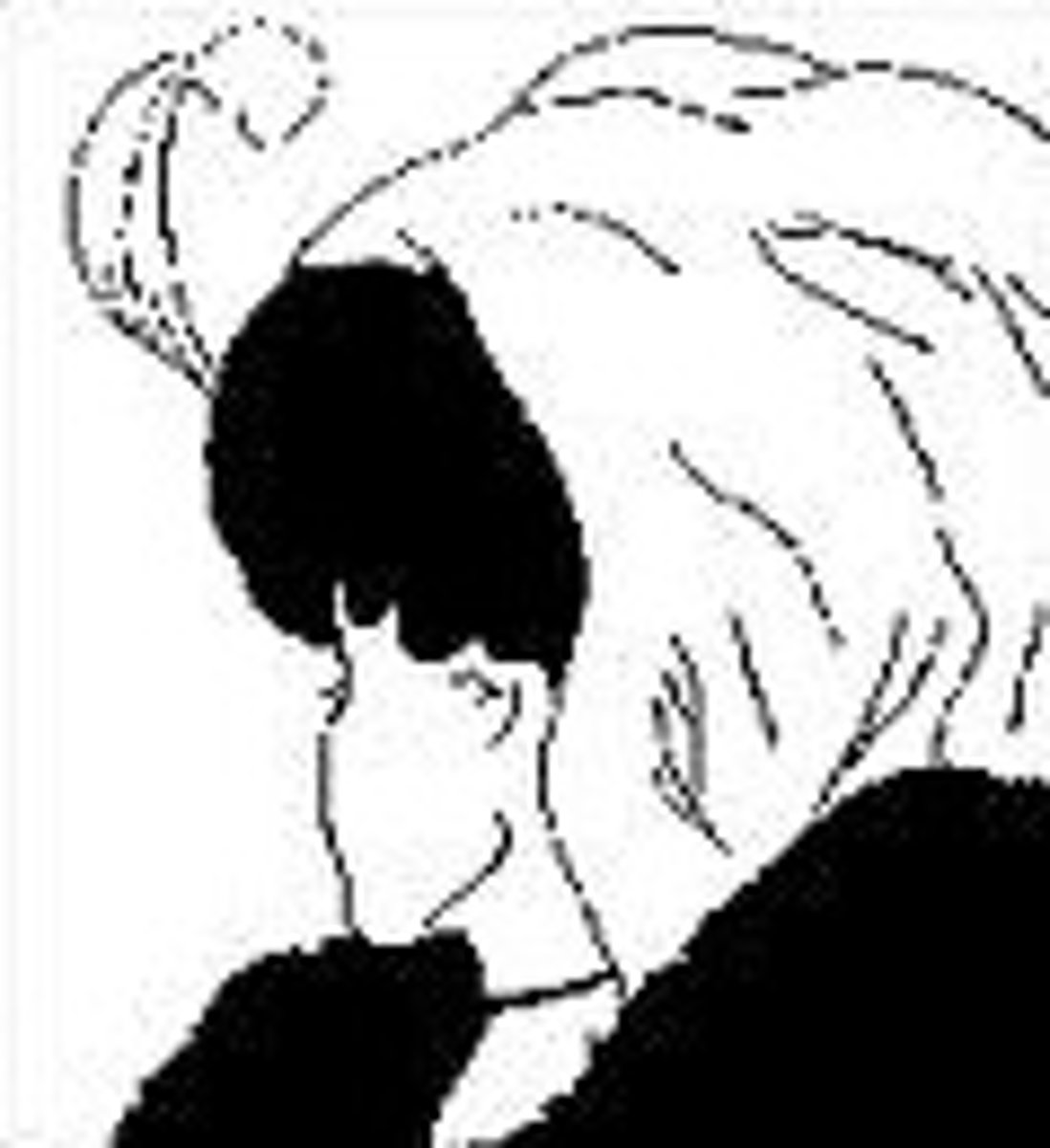

Gestalt psychology
a psychological approach that emphasizes that we often perceive the whole rather than the sum of the parts
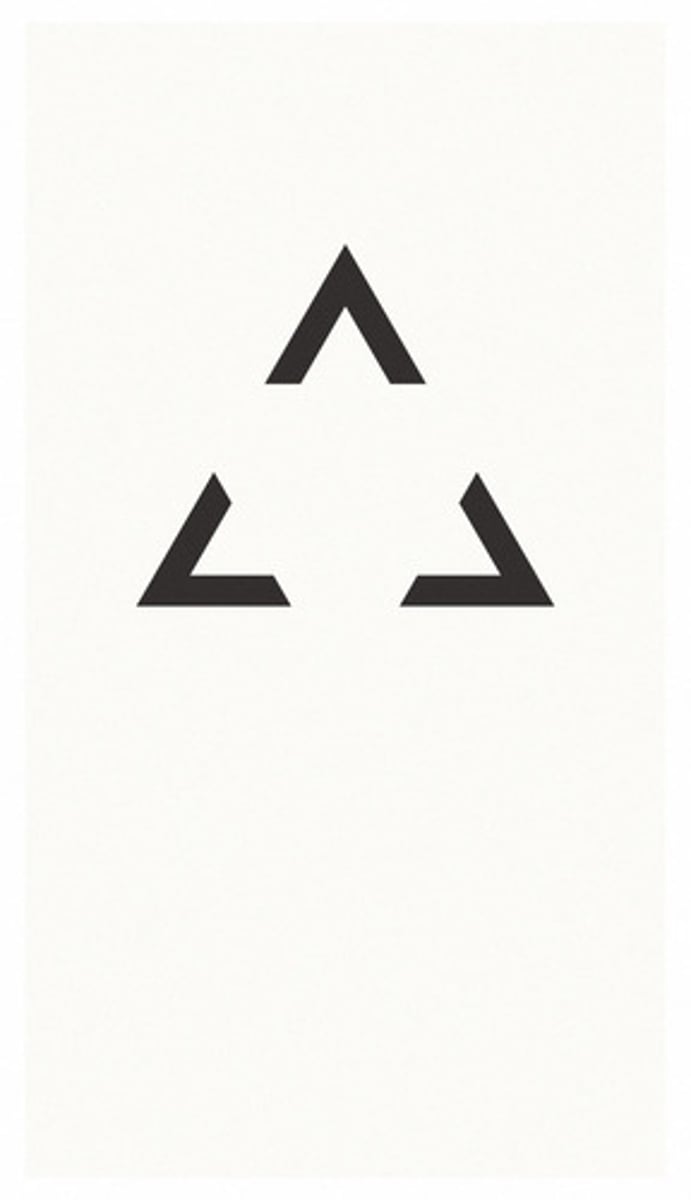

Closure
the tendency of the brain to complete figures that are incomplete

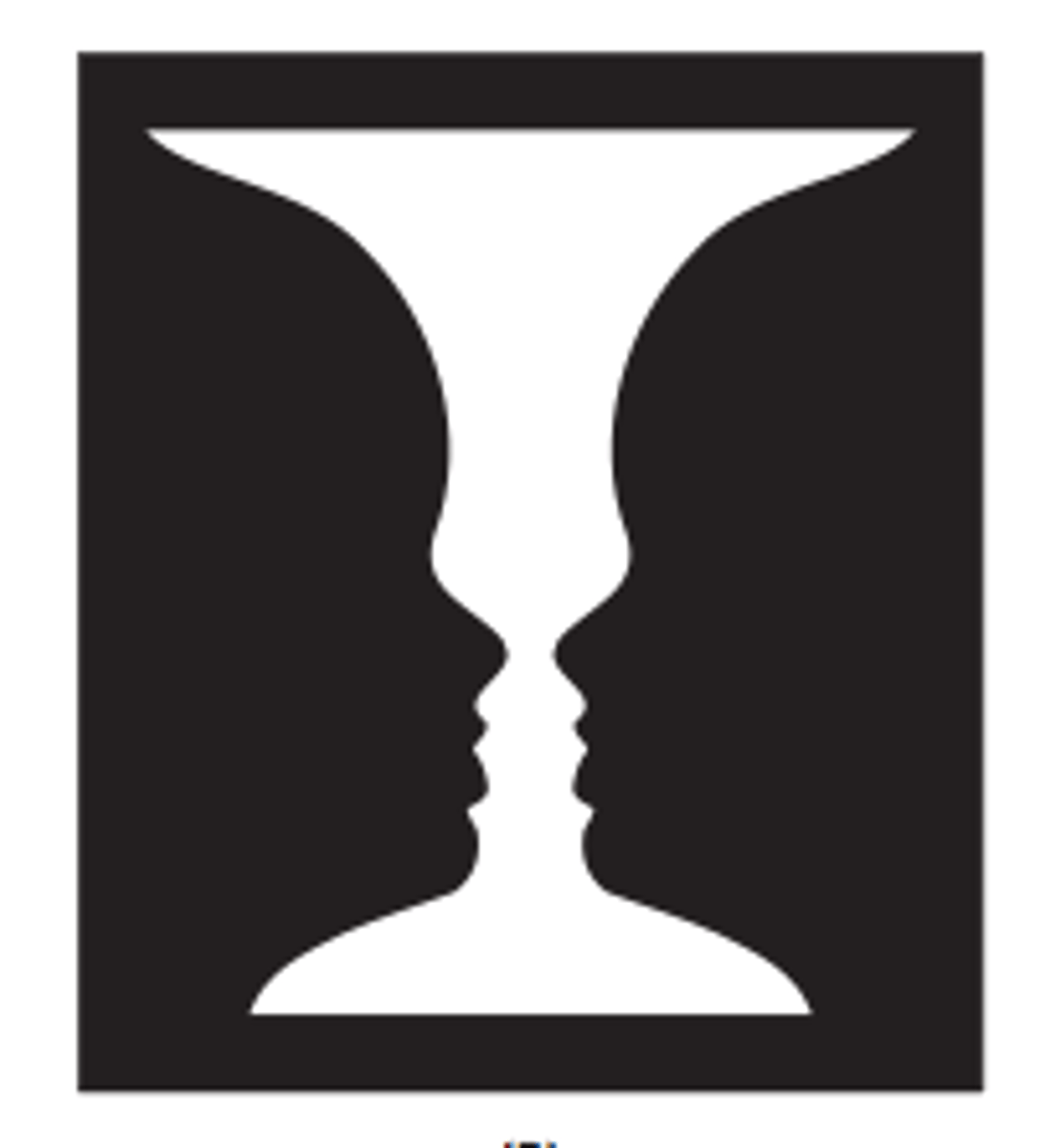
Figure and ground
a human's ability to visually differentiate between an object and its background

Proximity
a tendency of the brain to perceive that things which are closer to each other as more related than things farther apart
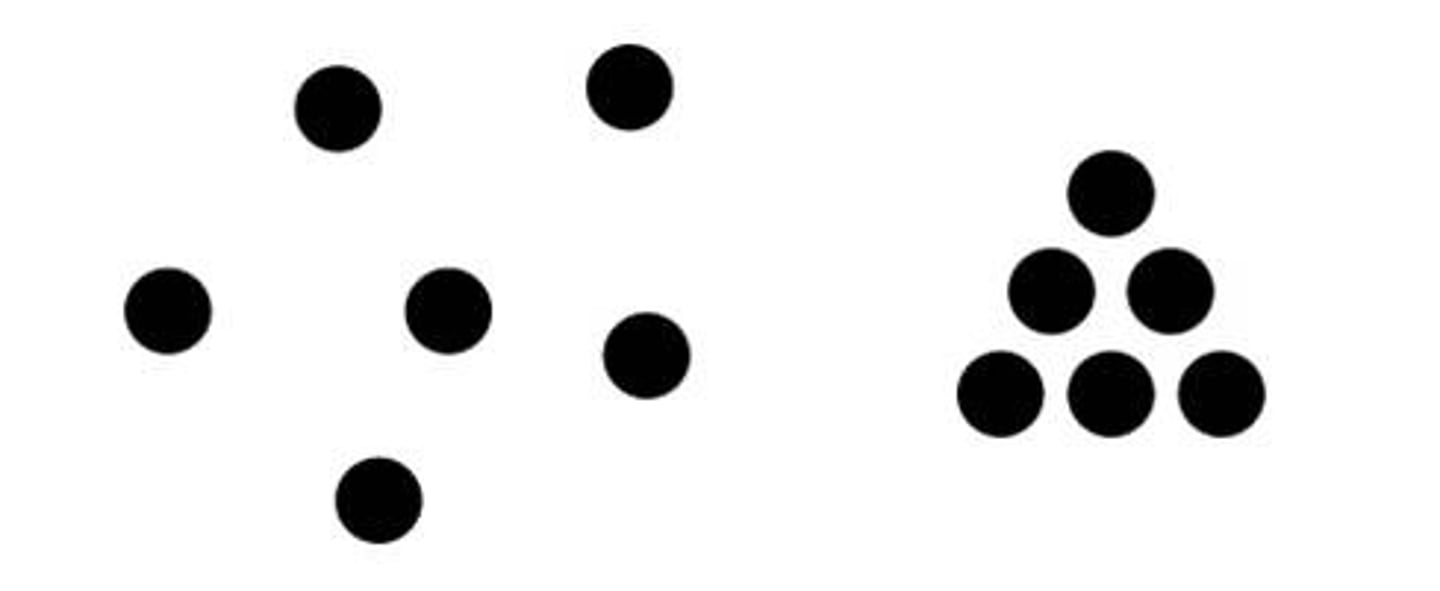
Similarity
when things appear similar to each other, the brain tends to group them together and perceive that they have the same function
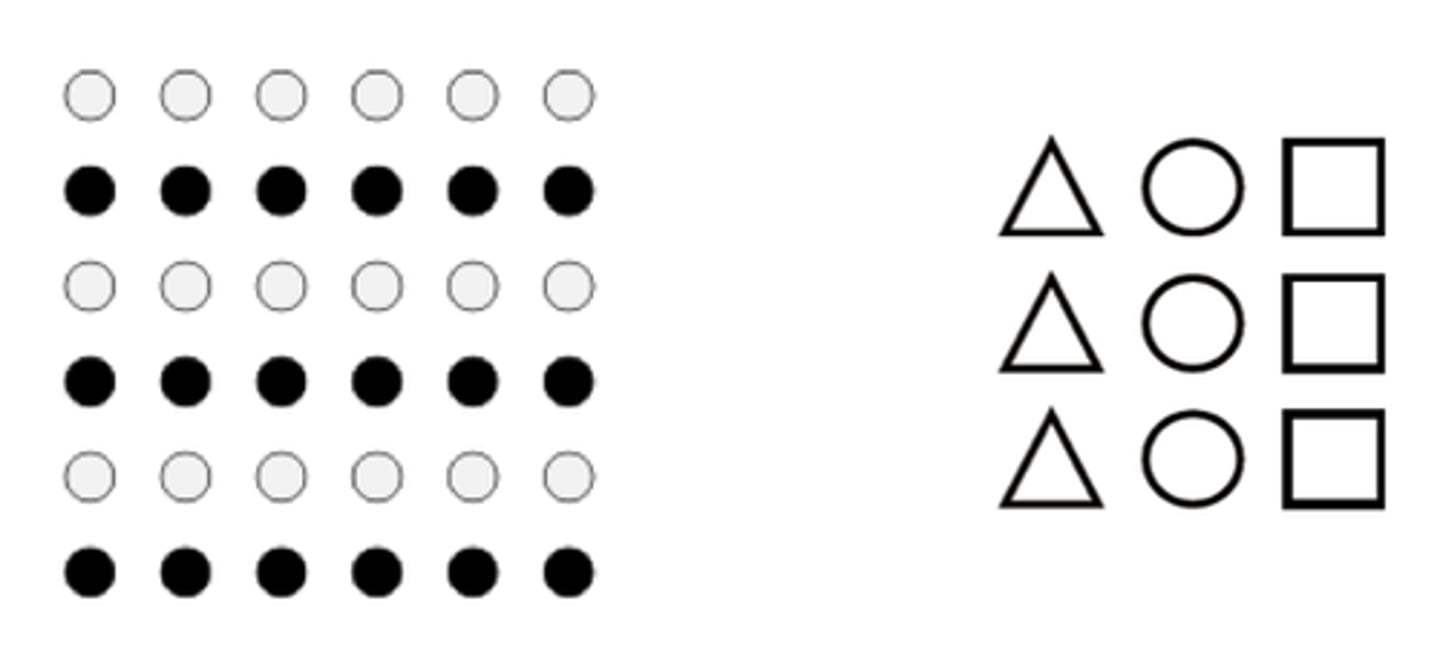
Attention
focusing awareness on a narrowed range of stimuli or events

Selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus and not others

Cocktail party effect
the ability to attend to only one conversation among many

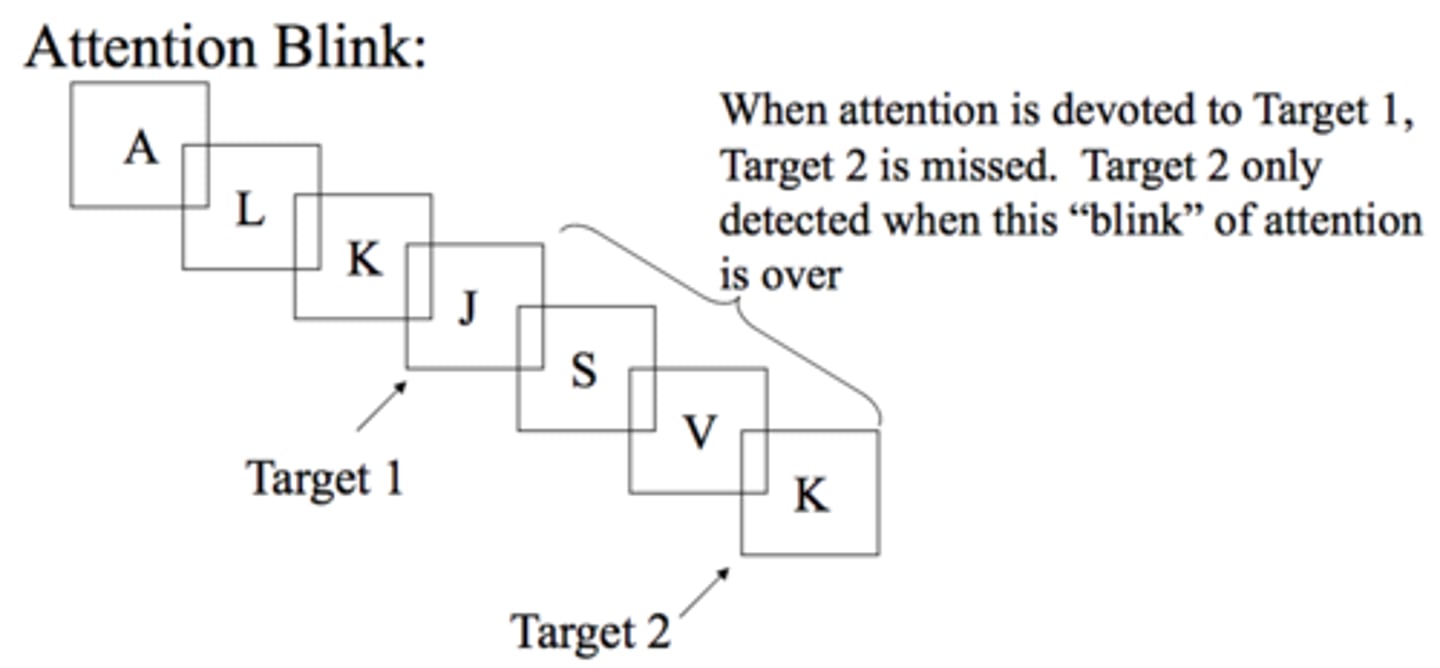
Inattentional blindness
a failure to perceive stimuli that are not the focus of attention

Change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
Binocular depth cues
cues of depth perception that arise from the fact that people have two eyes

Retinal disparity
a binocular cue used to perceive depth between two near objects

Convergence
a binocular cue for depth resulting from the eyes converging inward when looking at an object

Monocular depth cues
cues of depth perception that are perceived by one eye, rather than by both working together

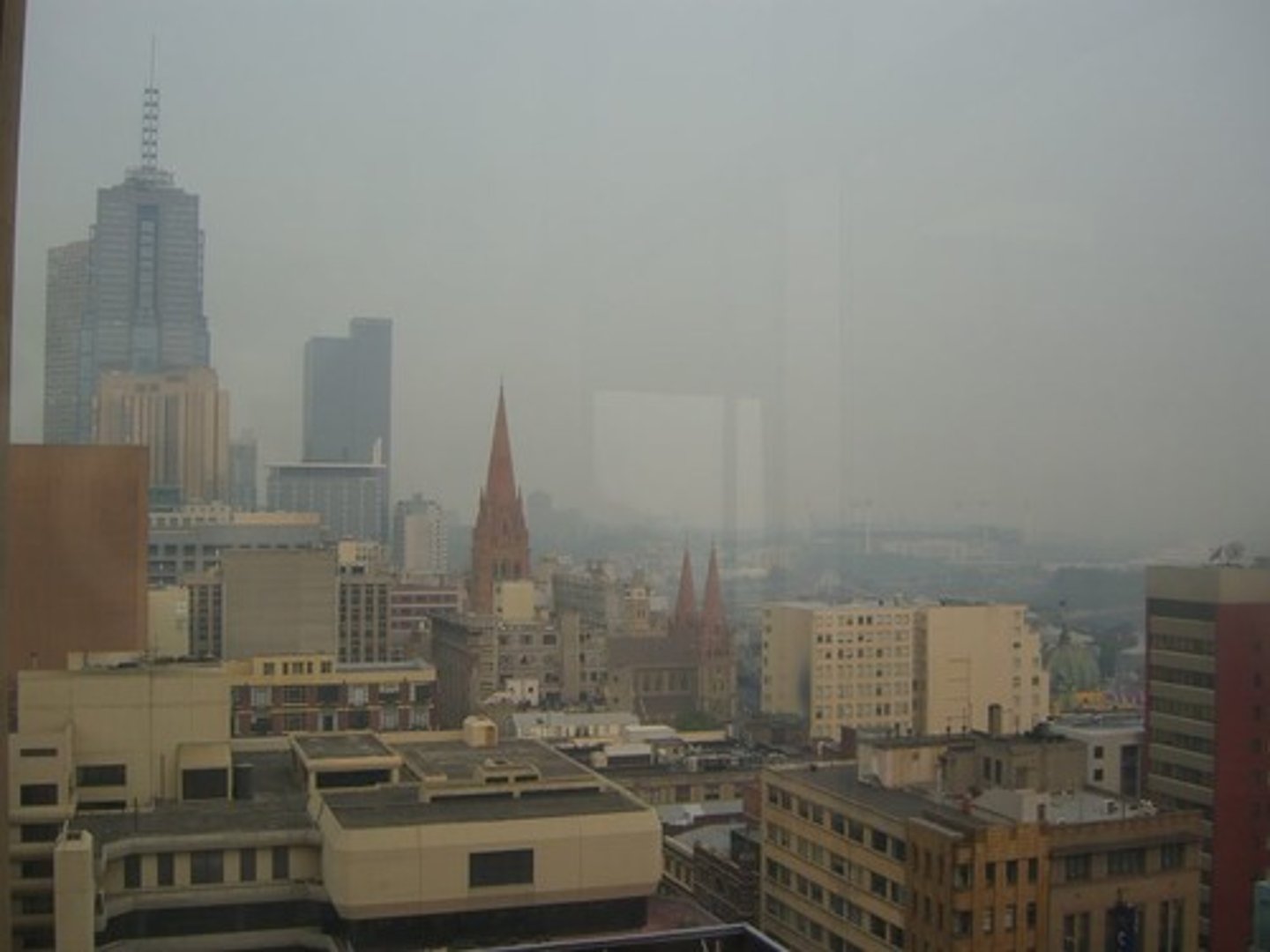
Relative clarity
a monocular cue for perceiving depth in which distant objects appear hazy or blurry while near object are sharp and clear

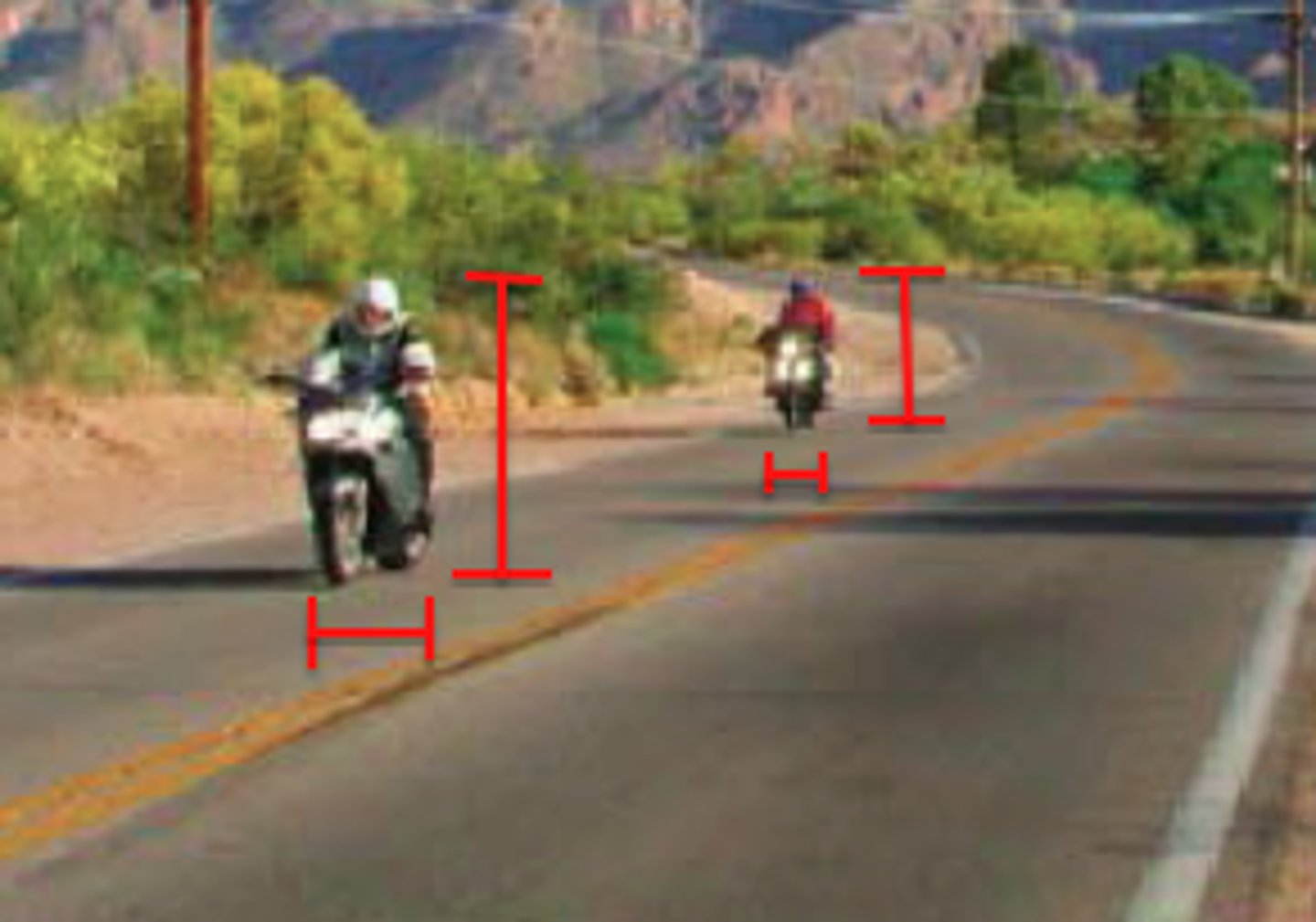
Relative size
a monocular cue that perceives objects of a known size to be farther away because they appear to be small

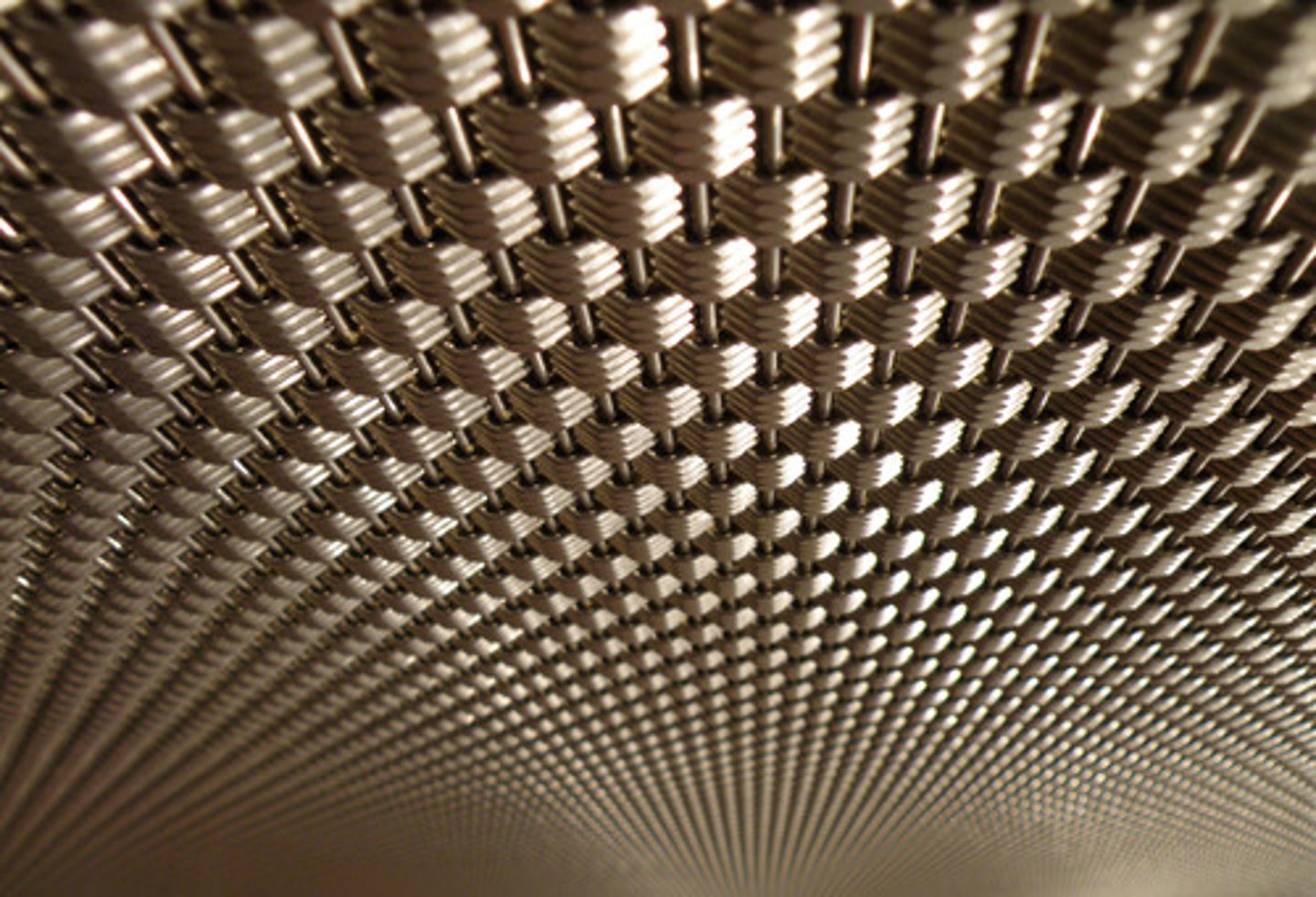
Texture gradient
a monocular cue in which a gradual change from a coarse distinct texture to a fine, indistinct texture signals increasing distance (e.g., objects far away appear smaller and more densely packed)
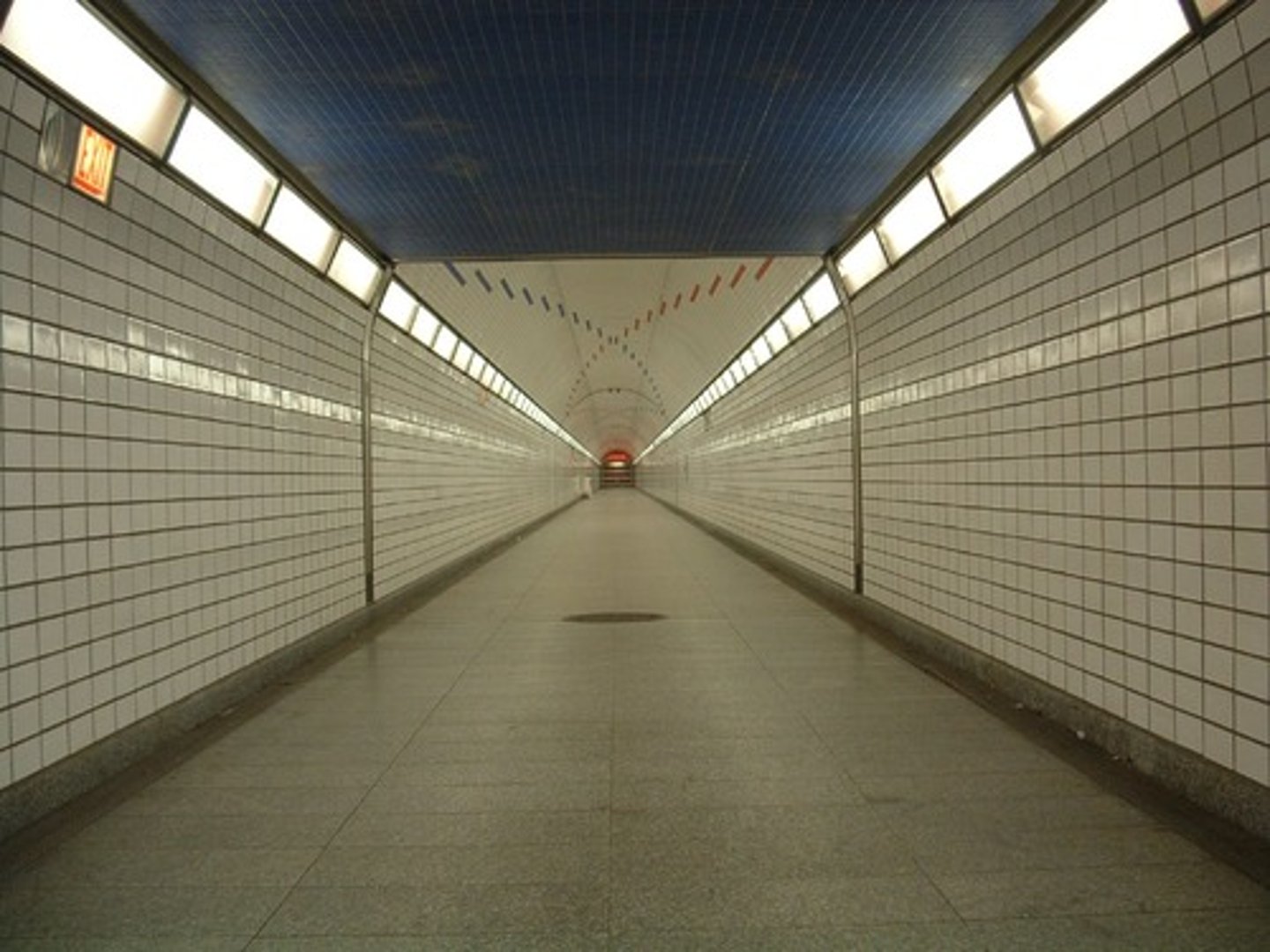
Linear perspective
a monocular cue that perceives two parallel lines appearing to meet, thus signaling increasing distance

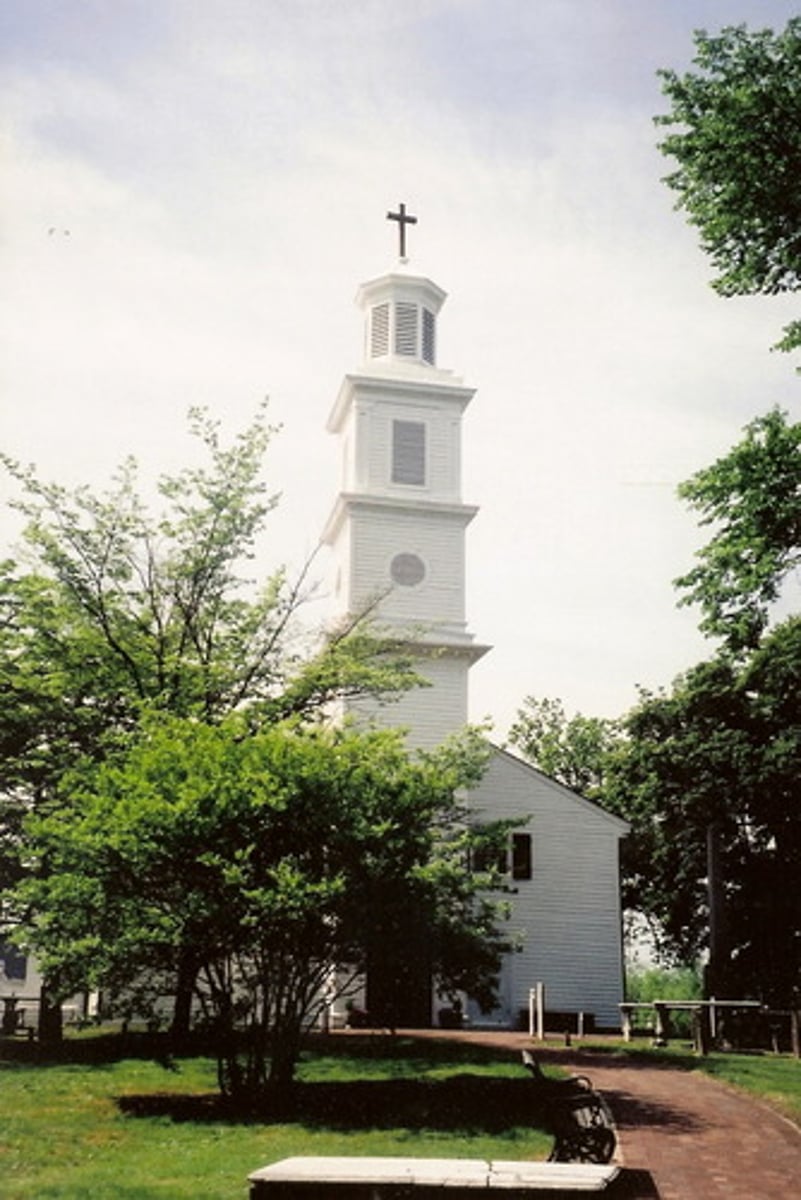
Interposition
a monocular cue in which the distances of two separate objects are judged based on the fact that one object partially obscures or overlaps the other object

Apparent movement
an illusion of movement that occurs when stimuli in different locations are flashed one after another with the proper timing

Prototypes
a mental image or best example that incorporates all the features we associate with a category

Assimilation
making new information fit in with an existing understanding of the world (existing schema)

Accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information

Algorithms
a methodical problem-solving routine that attempts all possible solutions until the correct one is found
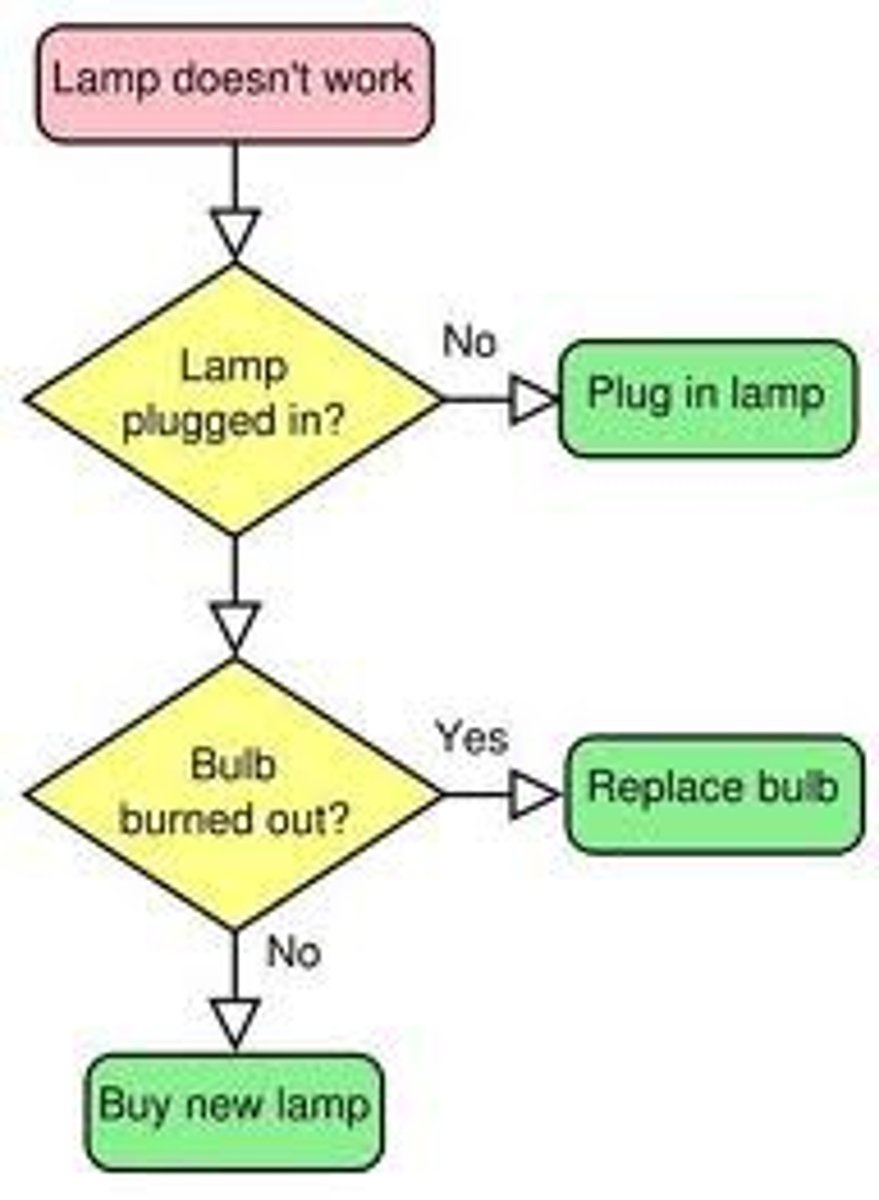
Heuristics
tools of thinking that address problems by using mental shortcuts to make judgments

Representativeness heuristic
a mental shortcut whereby people classify something according to how similar it is to a stereotypical case or prior expectation

Availability heuristic
a mental shortcut that bases a decision on the first or most vivid example that comes to mind

Mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way that has been successful in the past

Priming
a technique in which the introduction of one stimulus influences how people respond to a subsequent stimulus

Framing
a cognitive bias in which people decide between options based on whether the options are presented with positive or negative connotations

Gambler's fallacy
the belief that the chances of something happening with a fixed probability become higher or lower as the process is repeated

Sunk-cost fallacy
the tendency to continue with a decision we've invested resources into even if the costs outweigh the benefits

Executive functions
higher order mental processes that allow individuals to generate, organize, plan, and carry out goal-directed behaviors and experience critical thinking
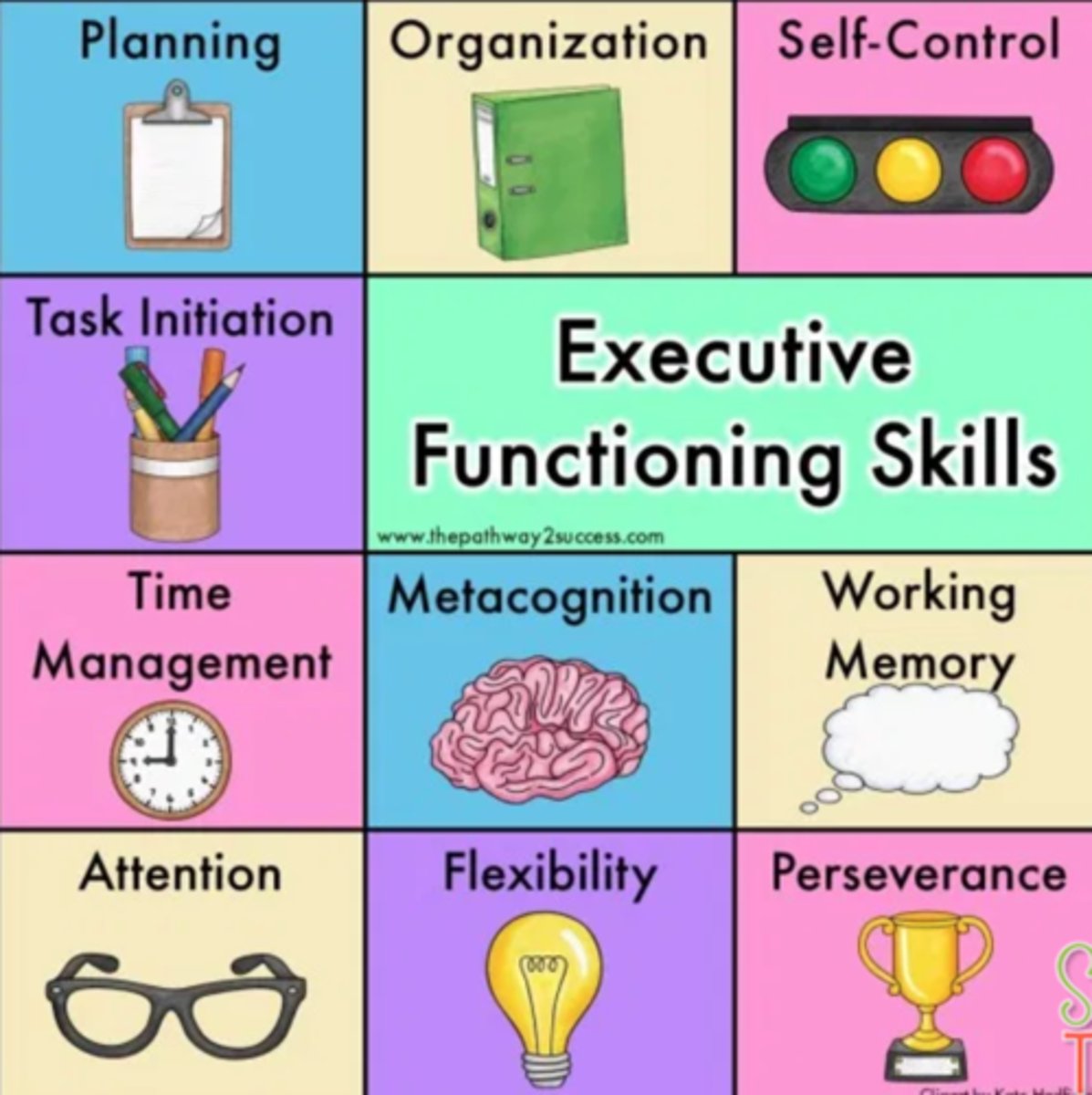
Creativity
a way of thinking that includes generating novel ideas and engaging in divergent thinking

Divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; thinking that flows in different directions

Convergent thinking
reapplying prior learning to quickly and accurately solve problems that do not require novel thinking
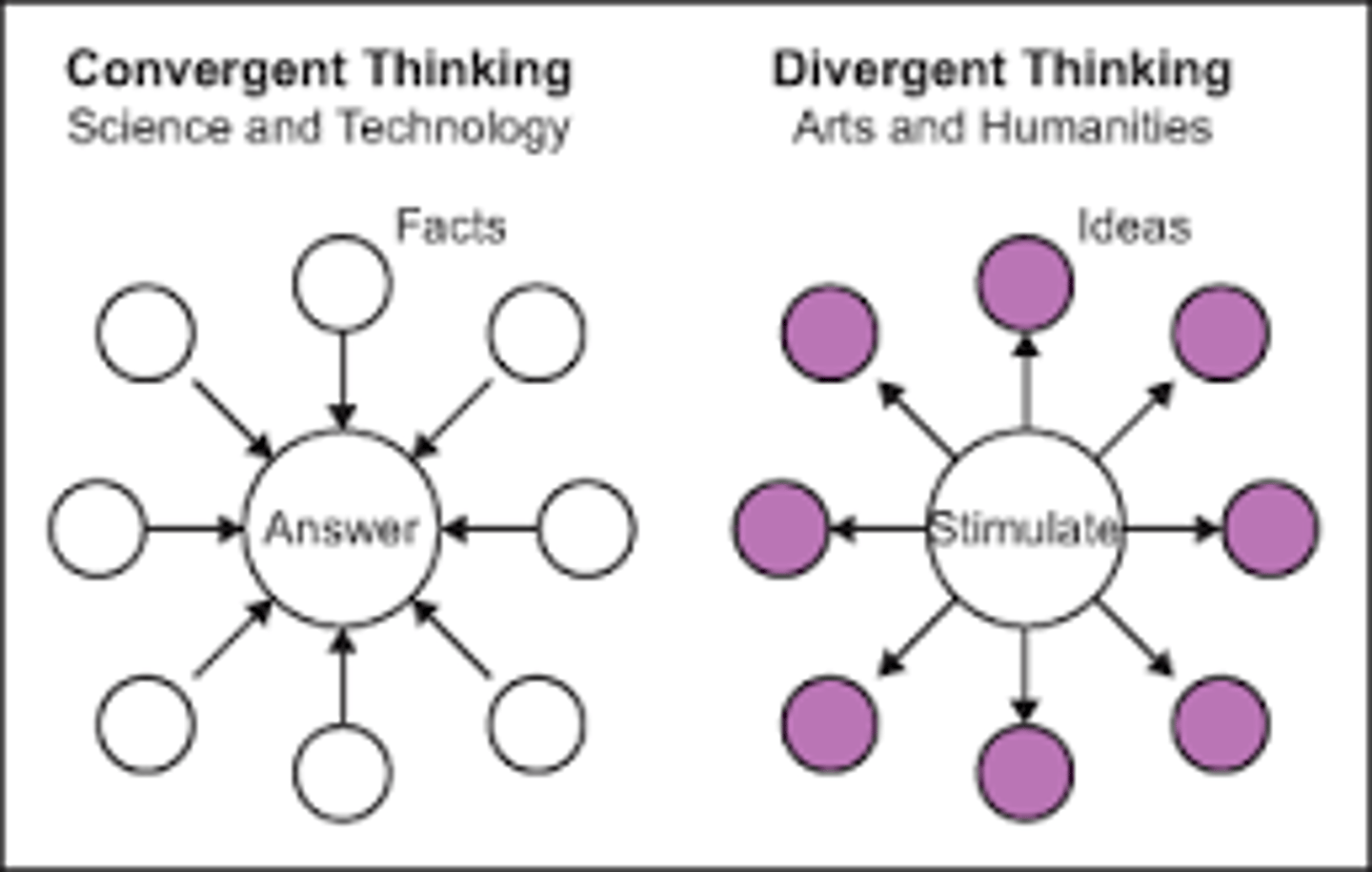
Functional fixedness
a block to problem solving that comes from thinking about objects in terms of only their typical functions

Storage
the process of retaining encoded information over time

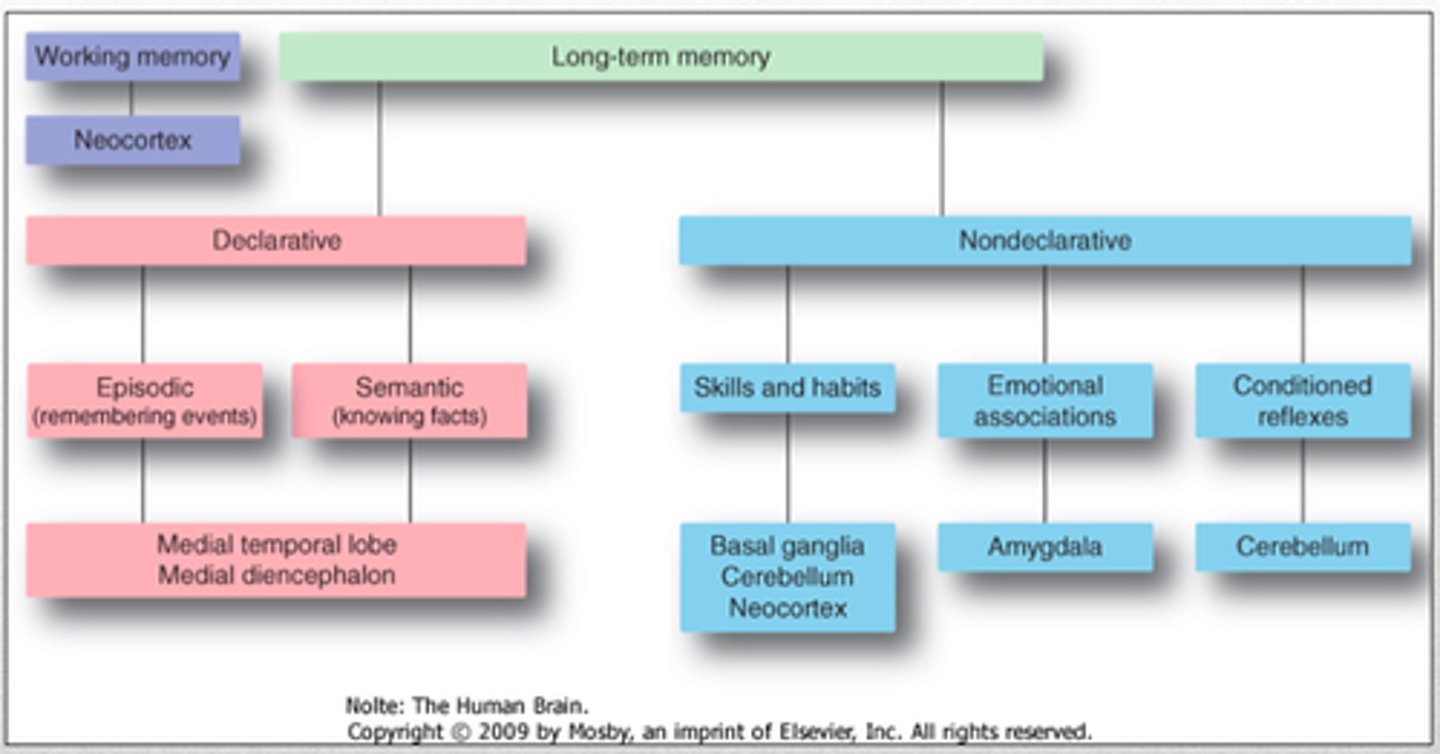
Explicit memory
facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare" (i.e., describe or explained) to others
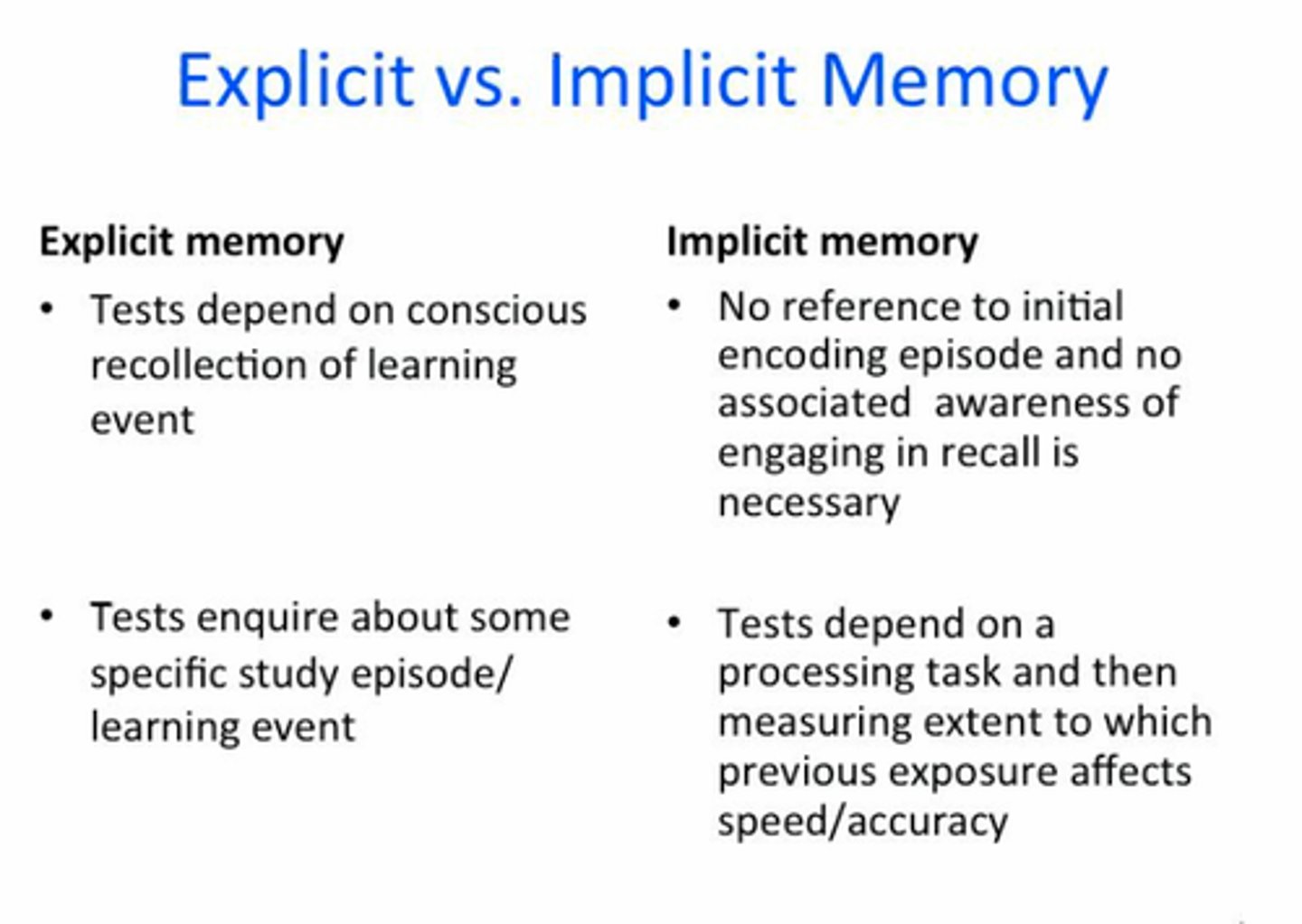
Episodic memory
the recollection of personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place

Semantic memory
the recollection of general knowledge and facts about the world

Implicit memory
automatic memories and processes that operate outside of conscious awareness or control

Procedural memory
a type of implicit memory used in everyday tasks
Prospective memory
remembering to do something at some future time

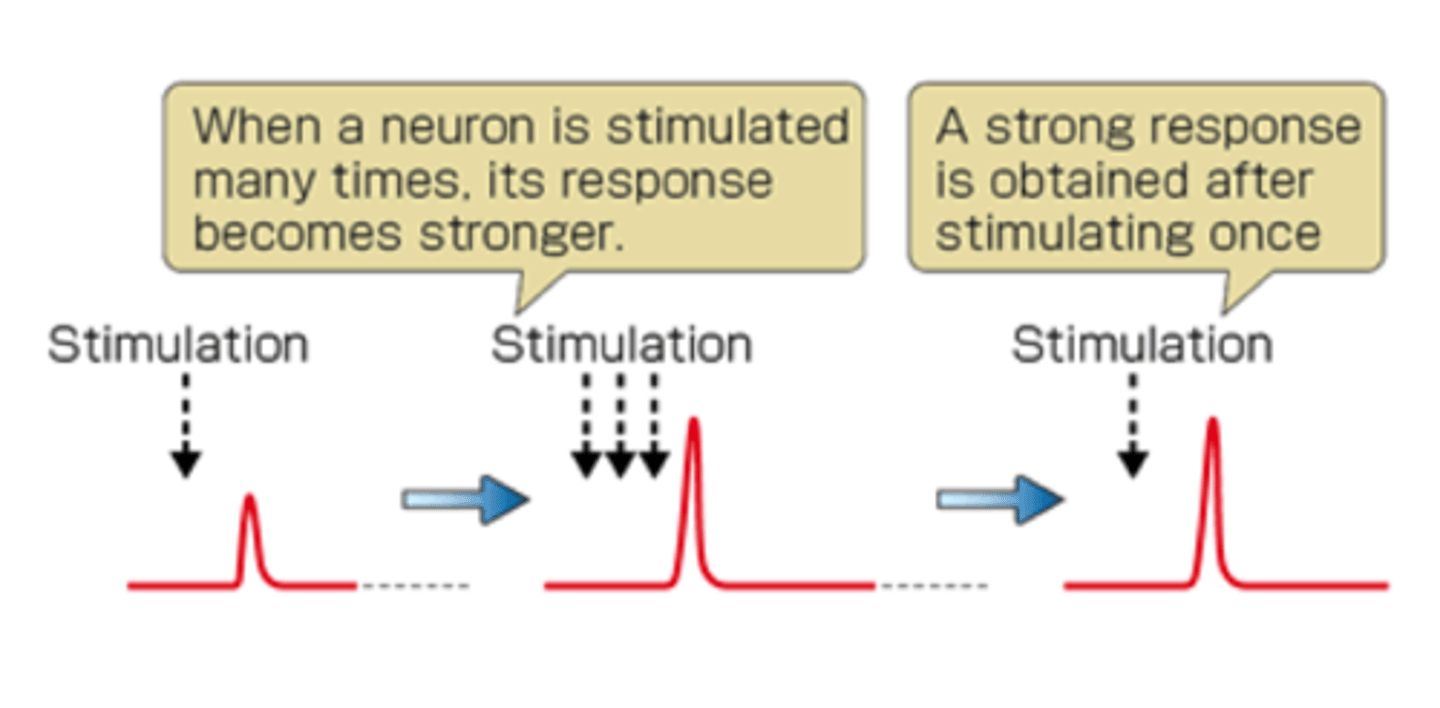
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a cell's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; related to learning activities that turn short-term memories into long-term memories
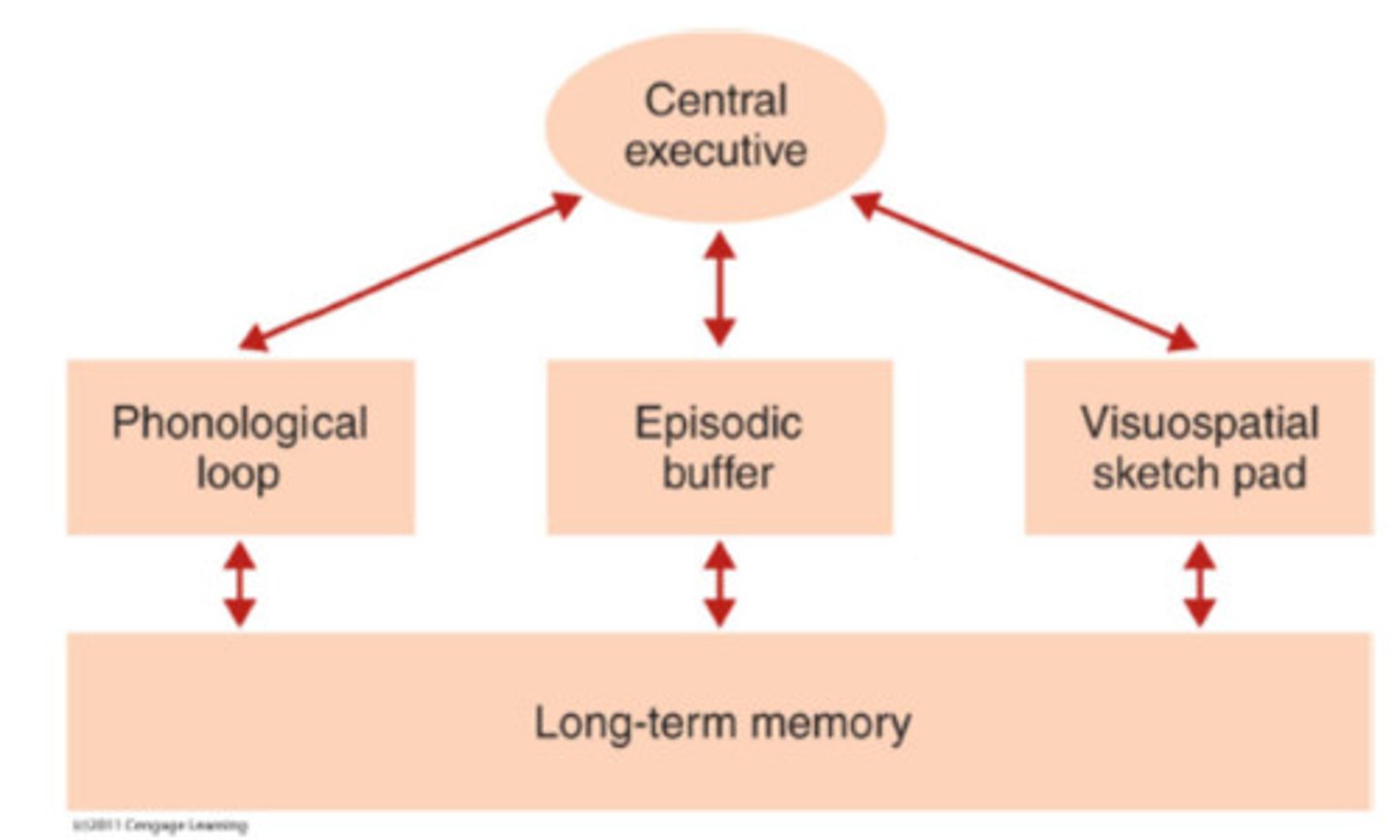
Working memory model
the theory that short-term memory is not a single store but consists of sub-categories
Primary memory system
the part of memory that retains a few items for only several seconds

Central executive
the "boss" of the working memory model that directs the two slave systems (the phonological loop and the visuo-spatial sketchpad)
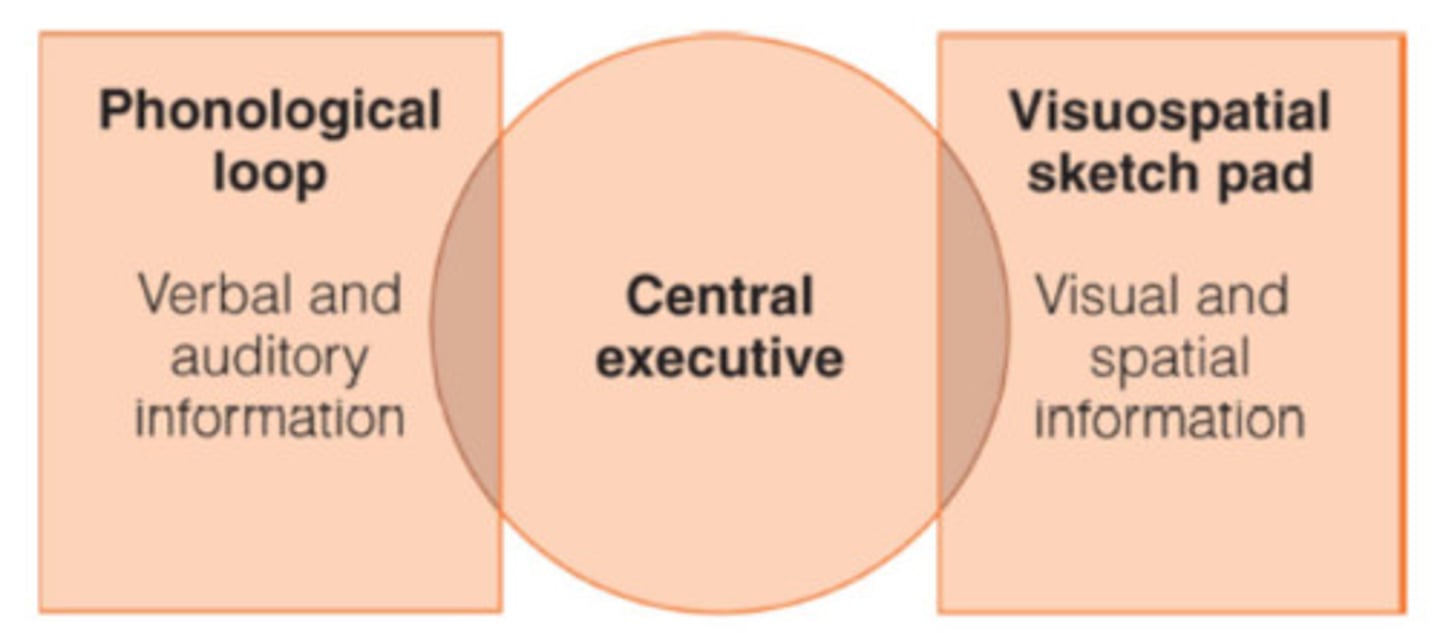
Phonological loop
the part of working memory that holds and processes verbal and auditory information
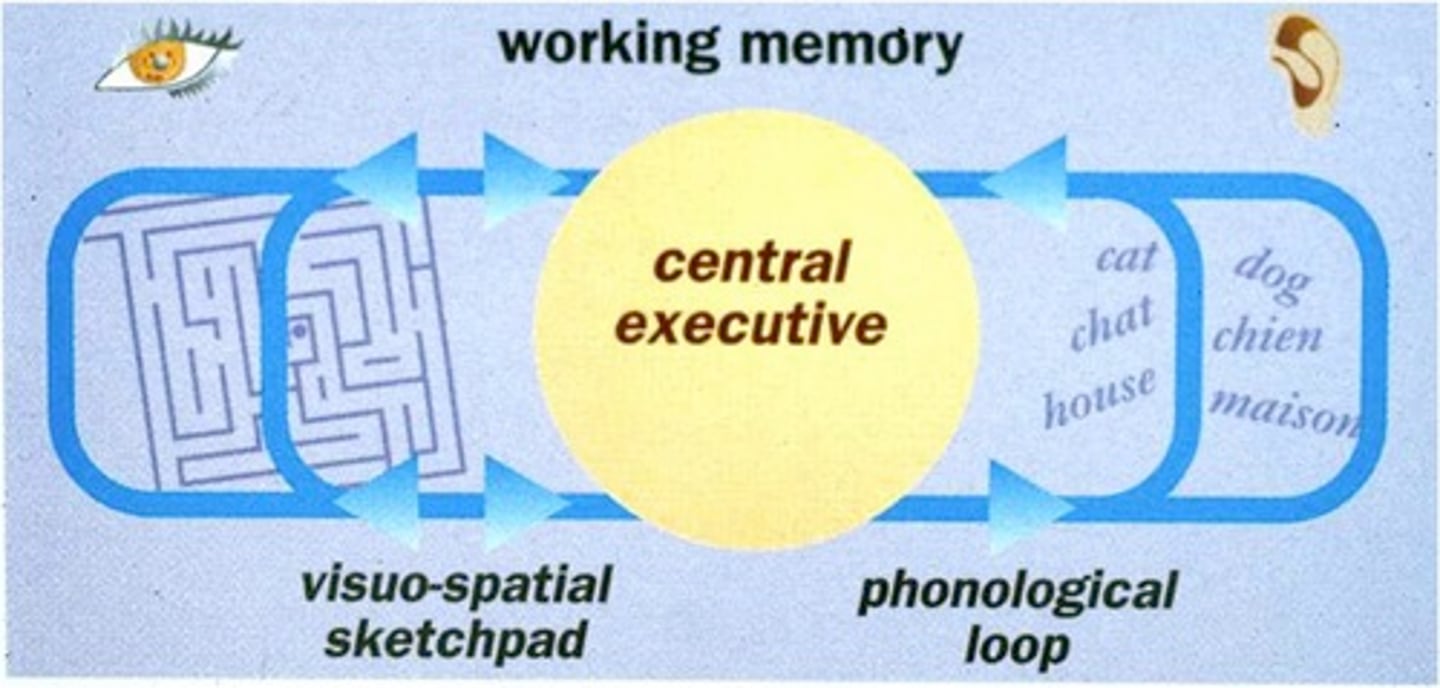
Visuospatial sketchpad
the part of working memory that creates mental images to remember visual information

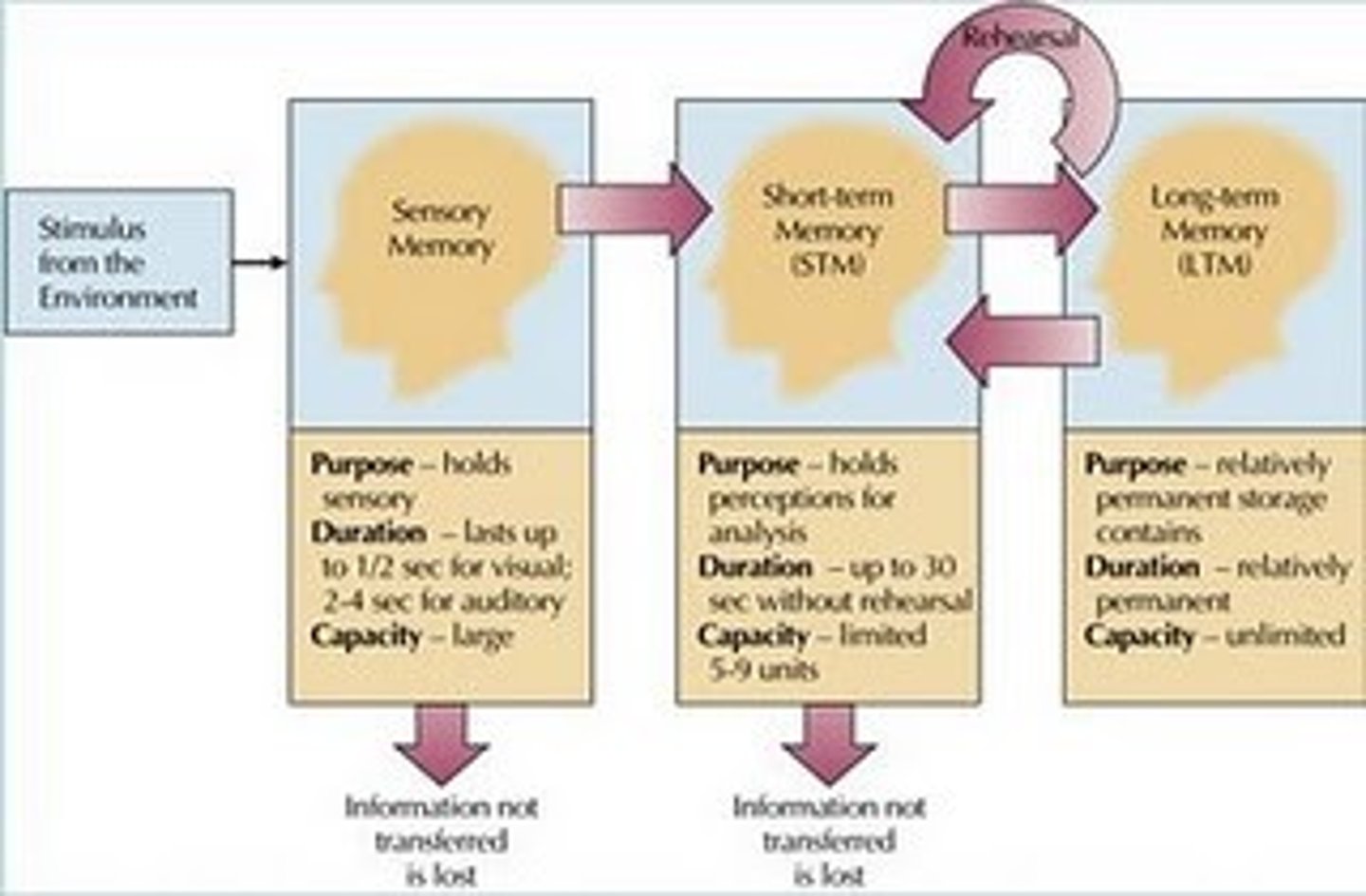
Multi-store model
an explanation of memory based on three separate memory stores, and how information is transferred between these stores
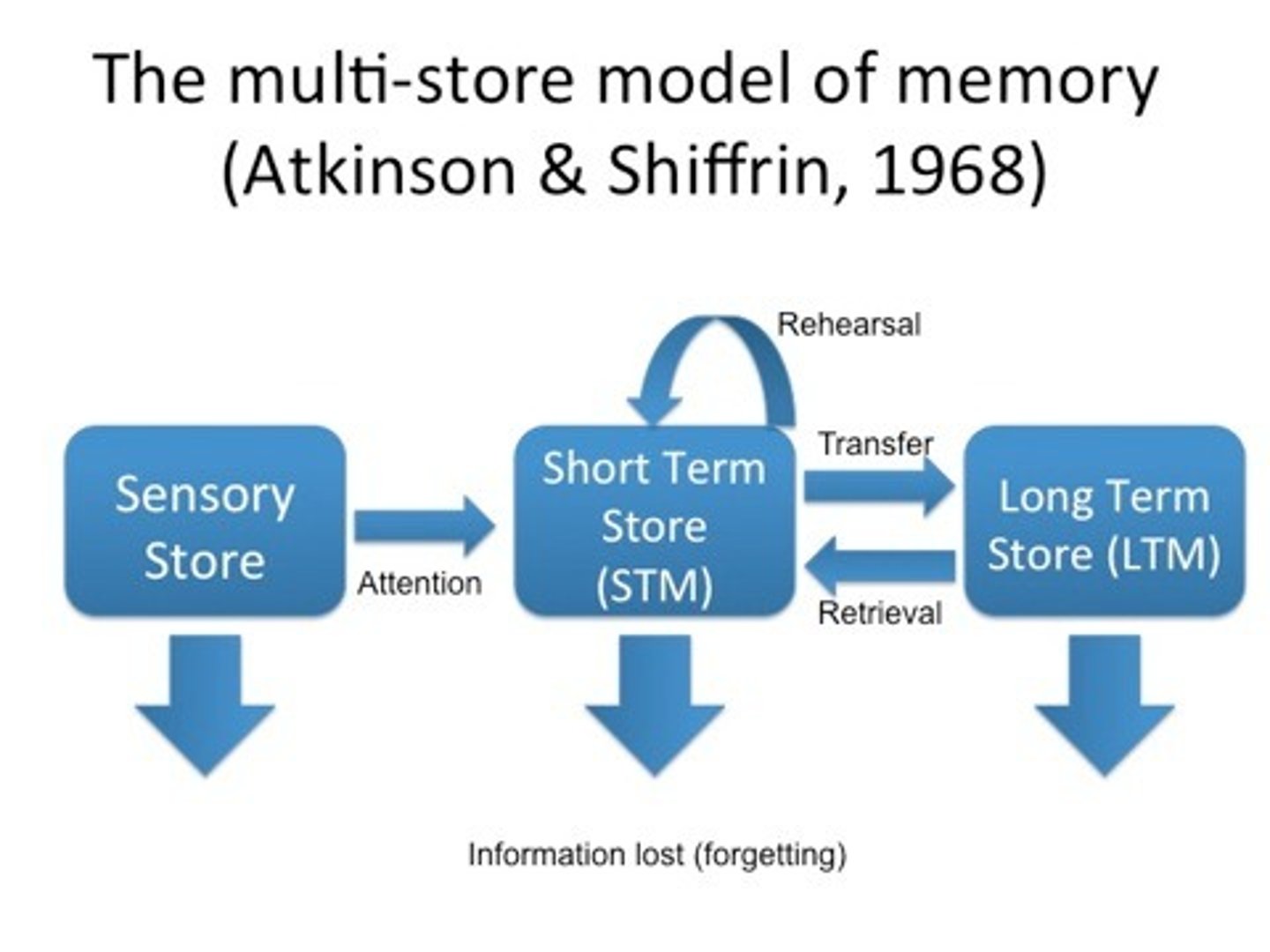
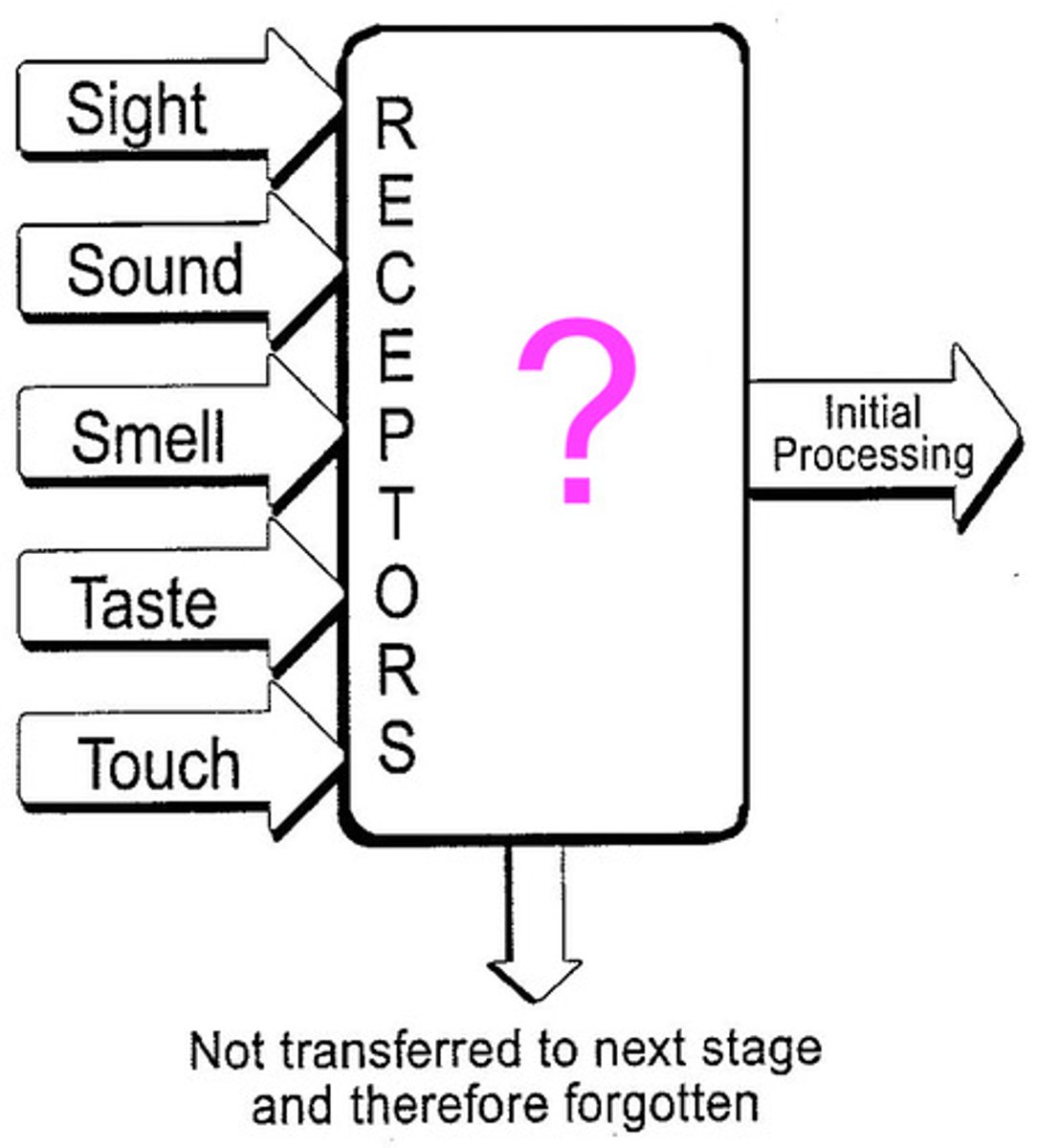
Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system

Iconic memory
a type of short-term sensory memory in which one can recall visual images for just a few milliseconds after the physical image has disappeared
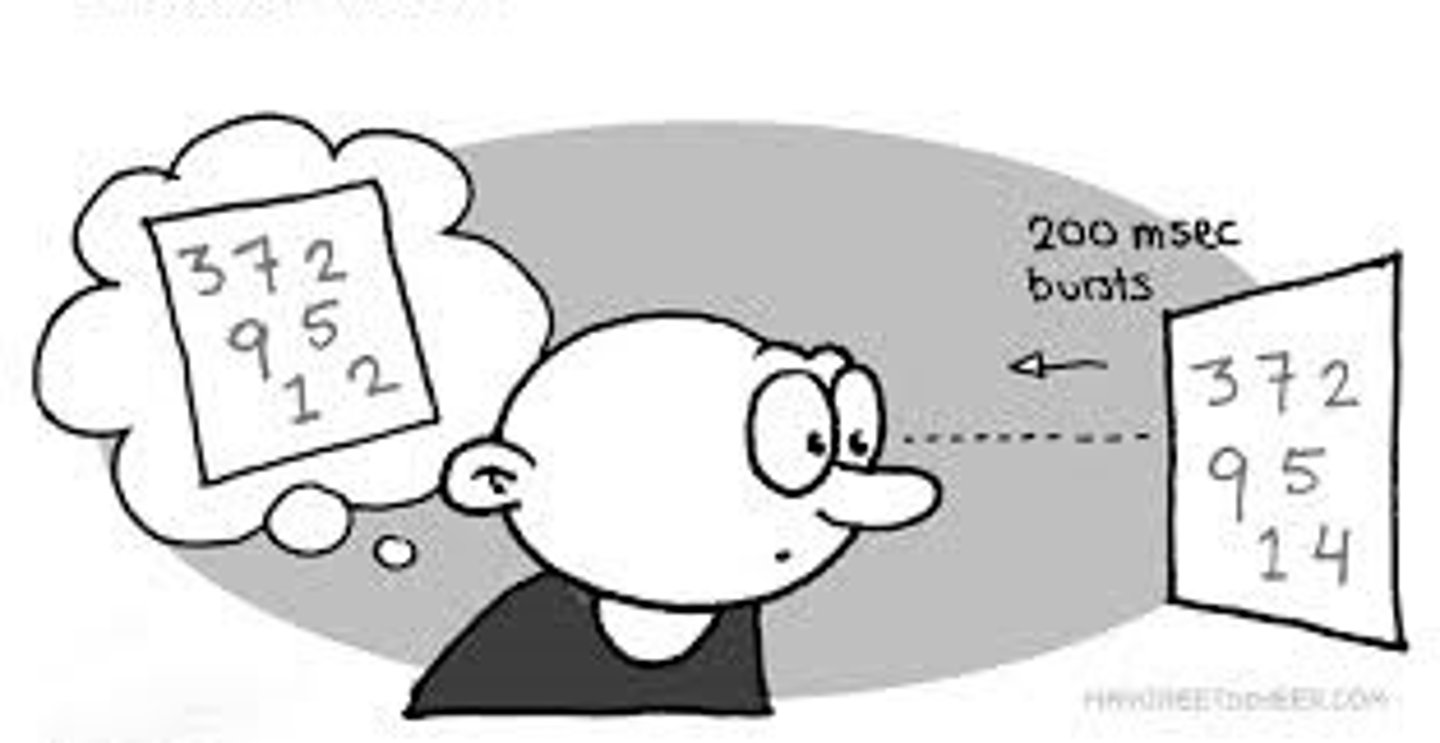
Echoic memory
a type of short-term sensory memory in which one can recall auditory stimuli for about 3 or 4 seconds

Automatic processing
any information processing that occurs involuntarily and without conscious intention or control
Effortful processing
encoding information through conscious attention and effort

Storage
the process of retaining encoded information over time

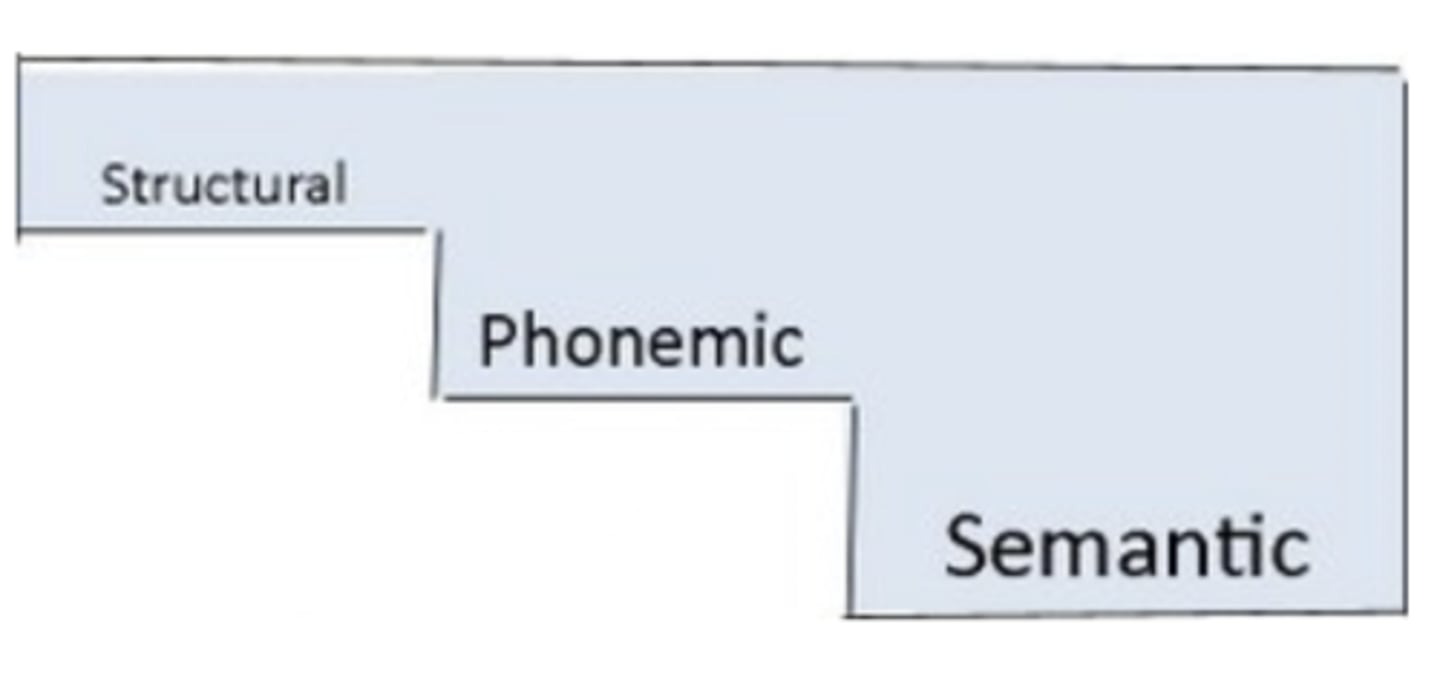
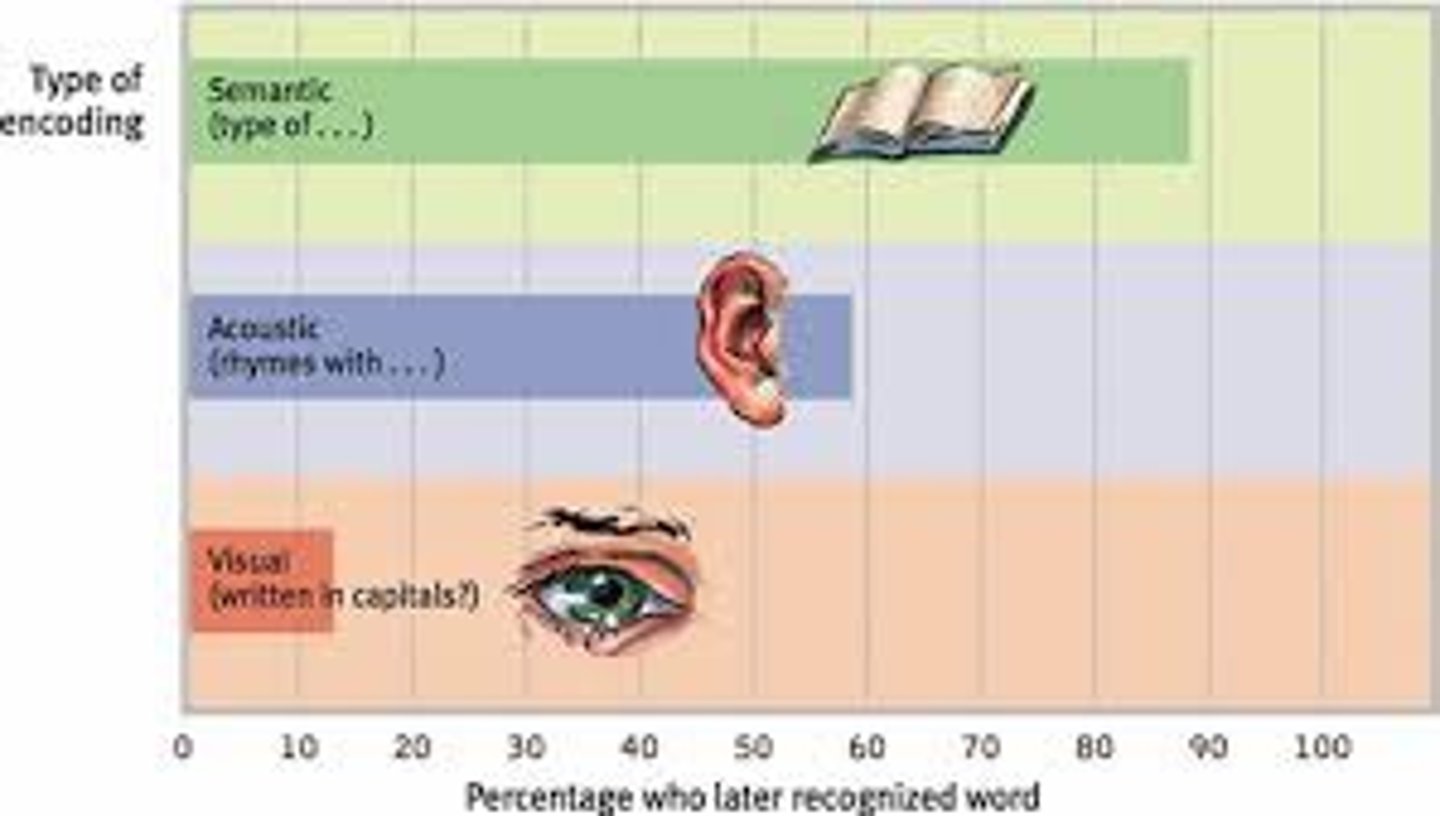
Levels of processing model
a theory that deeper processing of information increases the likelihood that the information will be recalled
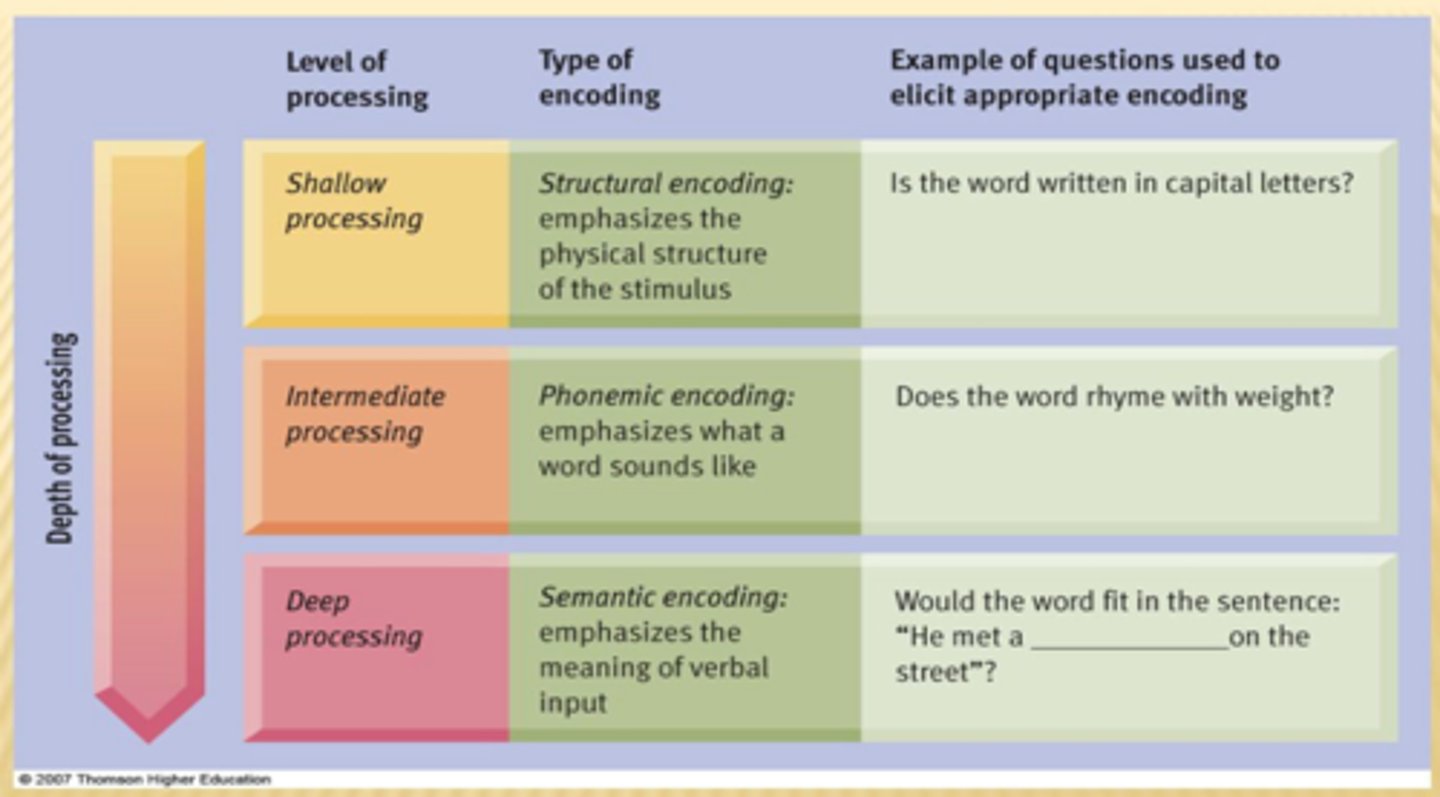
Structural, phonemic, semantic
the three levels of the levels of processing model
Shallow encoding
encoding based on sensory characteristics, such as how something looks or sounds

Deep encoding
encoding based on an event's meaning as well as connections between the new event and past experience

Encoding
the act of getting information into the memory system through automatic or effortful processing
Mnemonic devices
techniques for using associations to help memorize and retrieve information

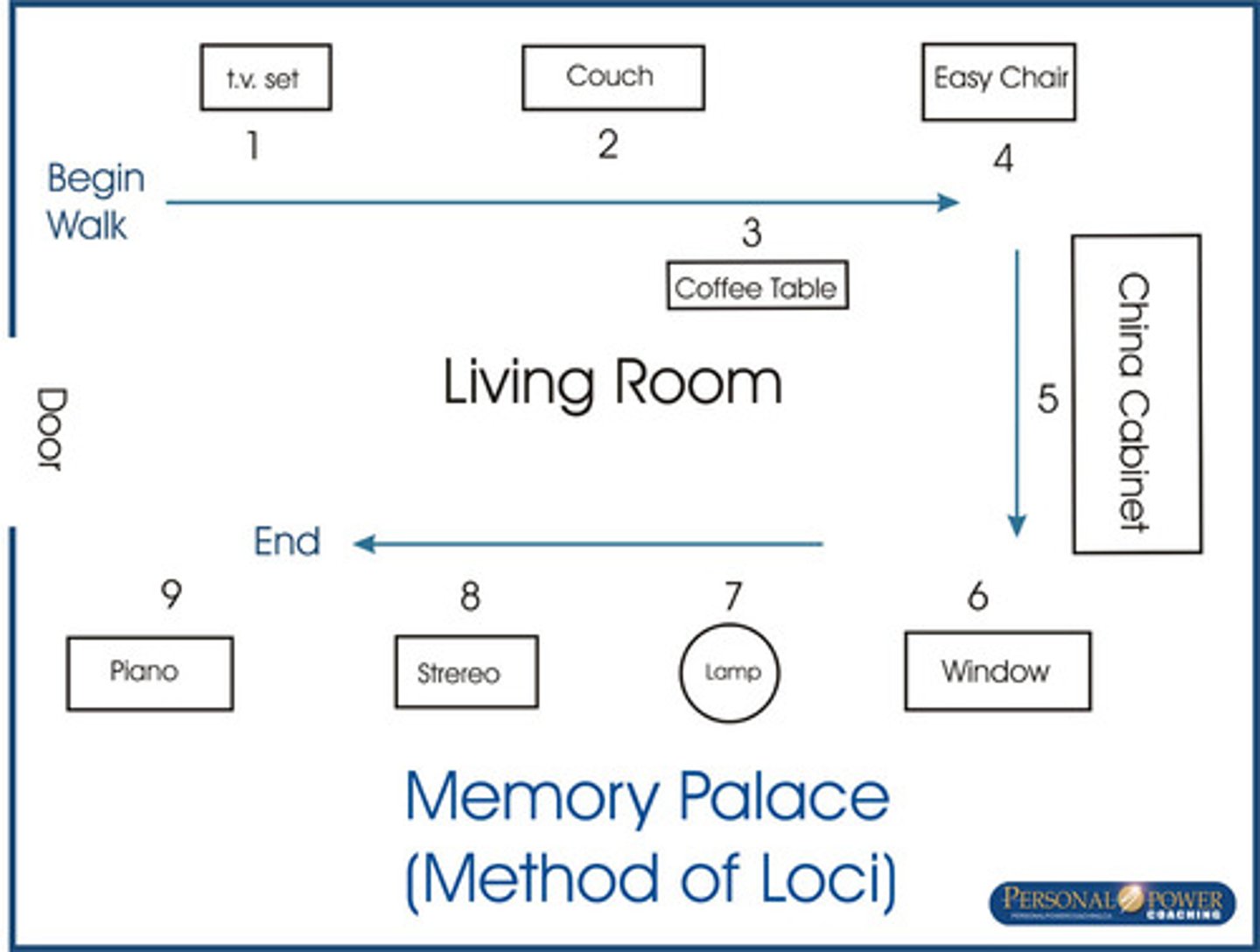
Method of loci
a mnemonic technique that involves associating items on a list with a sequence of familiar physical locations
Chunking
a mnemonic that arranges information as in acrostics, acronyms, and grouping of digits in a phone number
Categories
a memory strategy that clusters interrelated concepts to aid in learning
Hierarchies
a system of complex information broken down into broad concepts and further subdivided into categories and subcategories
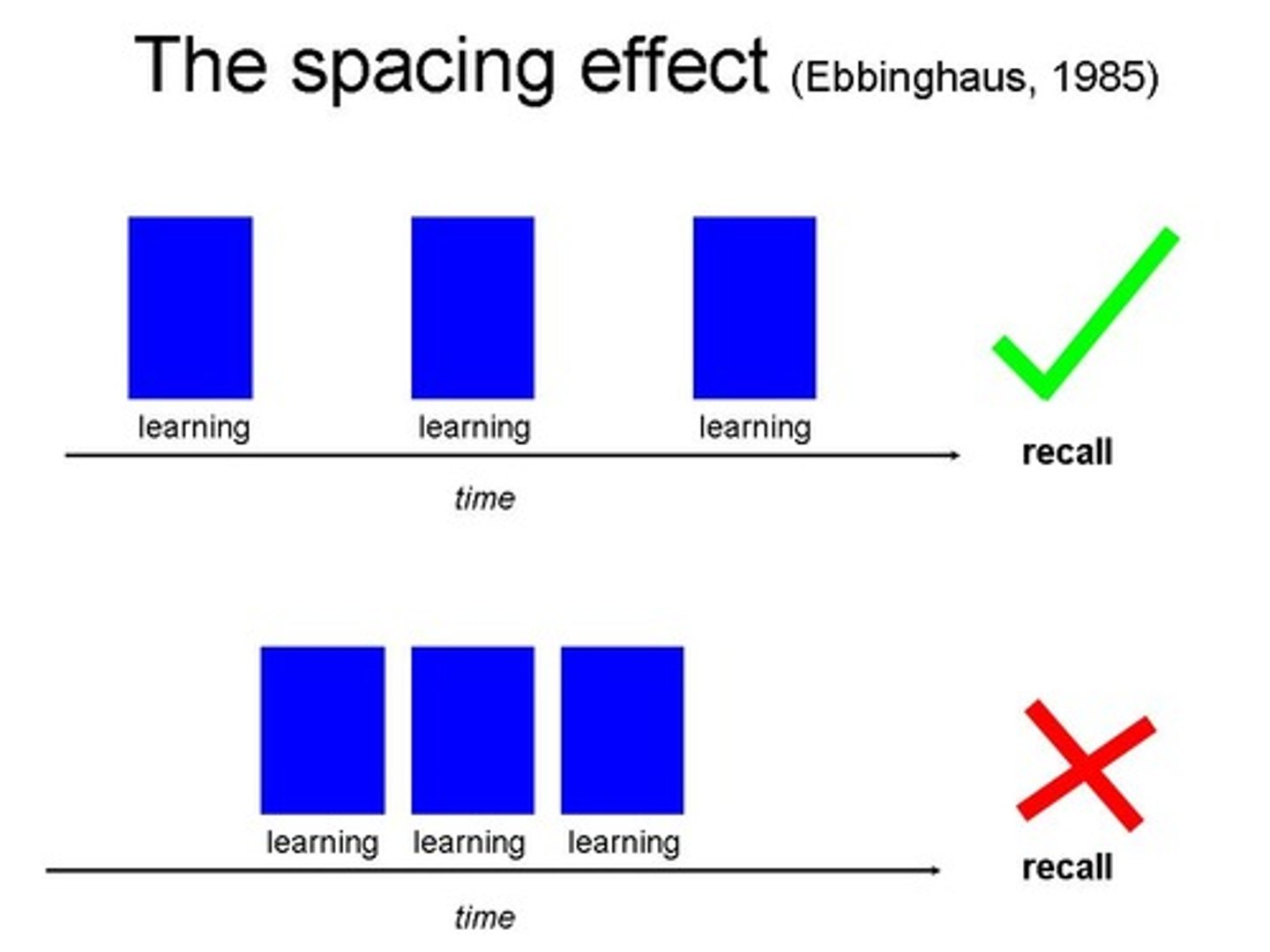
Spacing effect
information is retained better if there is a period of time between study sessions
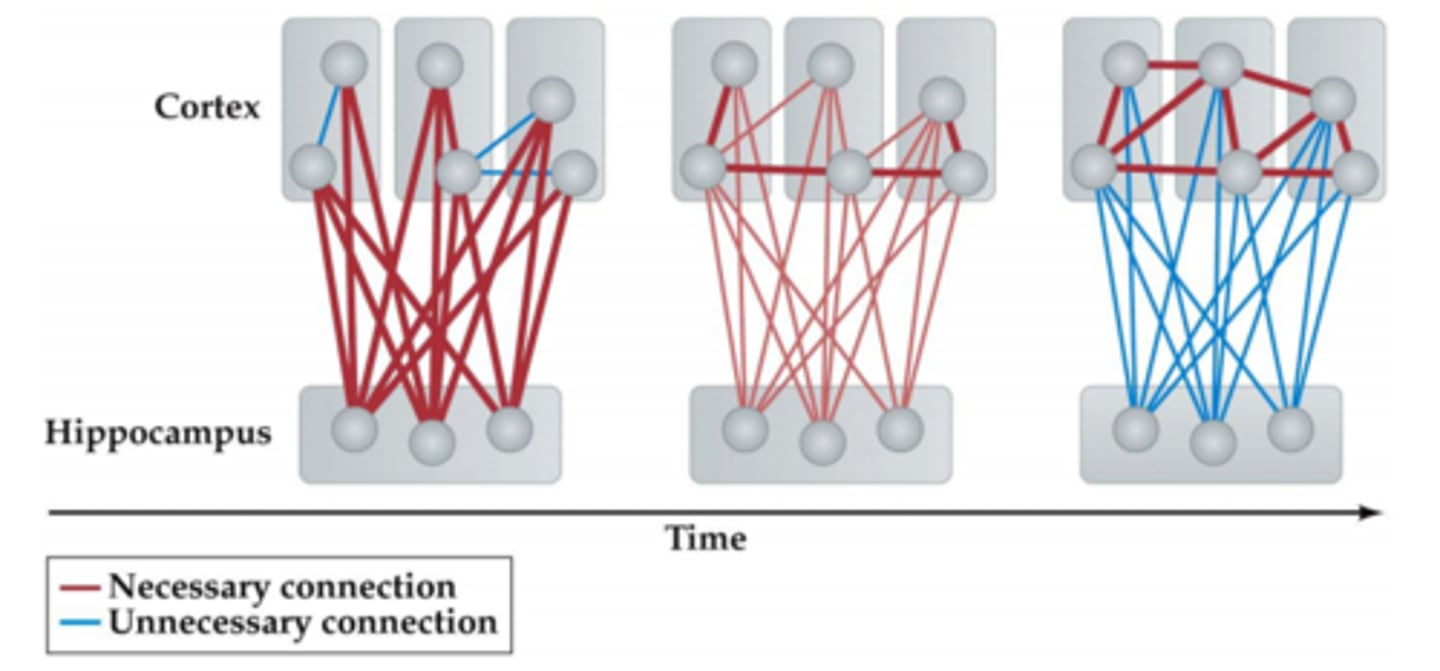
Memory consolidation
the gradual process of converting new long-term memories to stable, enduring memory codes; sleep is useful for organizing and consolidating memories
Massed practice
studying a large amount of information over a short or uninterrupted period of time

Distributed practice
breaking practice or study into several short sessions over a longer period of time

Serial position effect
the brain's tendency to best recall the last and first items in a list

Primacy effect
the brain's tendency to remember information at the beginning of a body of information better than the information that follows
Recency effect
the brain's tendency to remember the most recent information better than earlier information
Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten
Working memory
the part of memory that holds a limited amount of information at the ready for immediate use

Long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system; includes knowledge, skills, and experiences

Maintenance rehearsal
repeatedly verbalizing or thinking about a piece of information; allows information to be held from 20-30

Elaborative rehearsal
transferring something to long-term memory by thinking about its meaning, as opposed to simply repeating it over and over
Memory retention
the ability to retain and use information

Autobiographical memory
a form of episodic memory consisting of a person's recollections of his or her life experiences

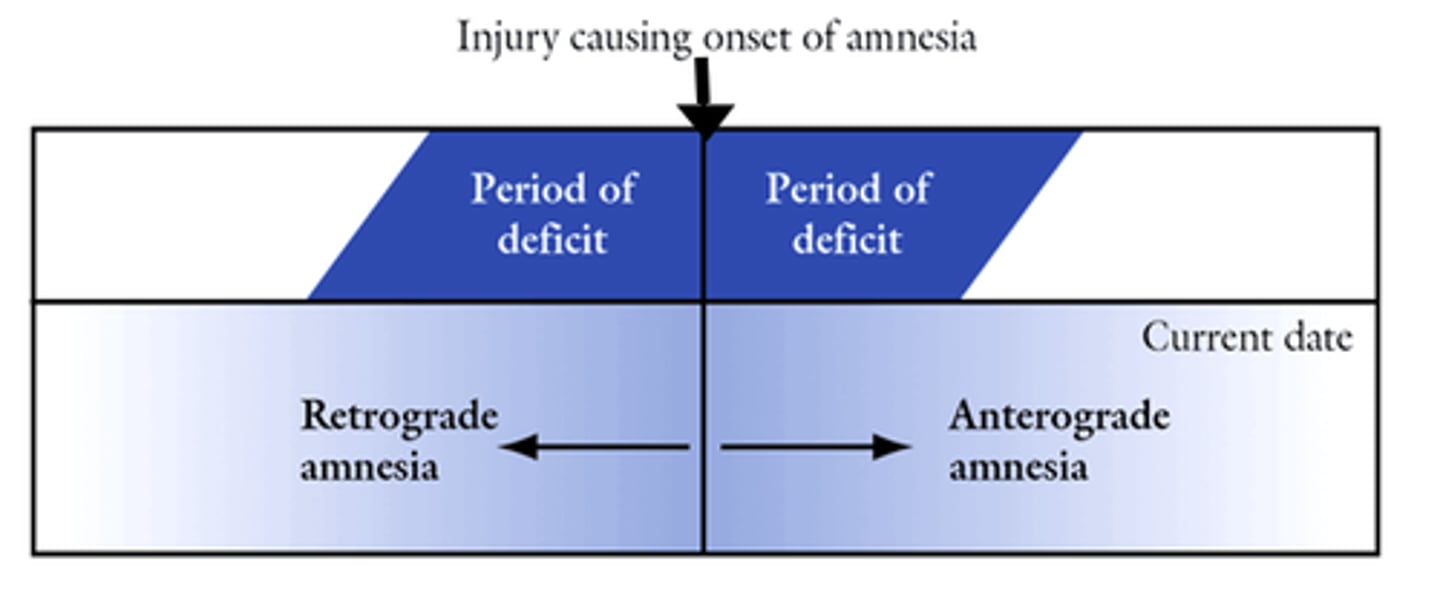
Retrograde amnesia
loss of memory from the point of some injury or trauma backwards, or loss of memory for the past
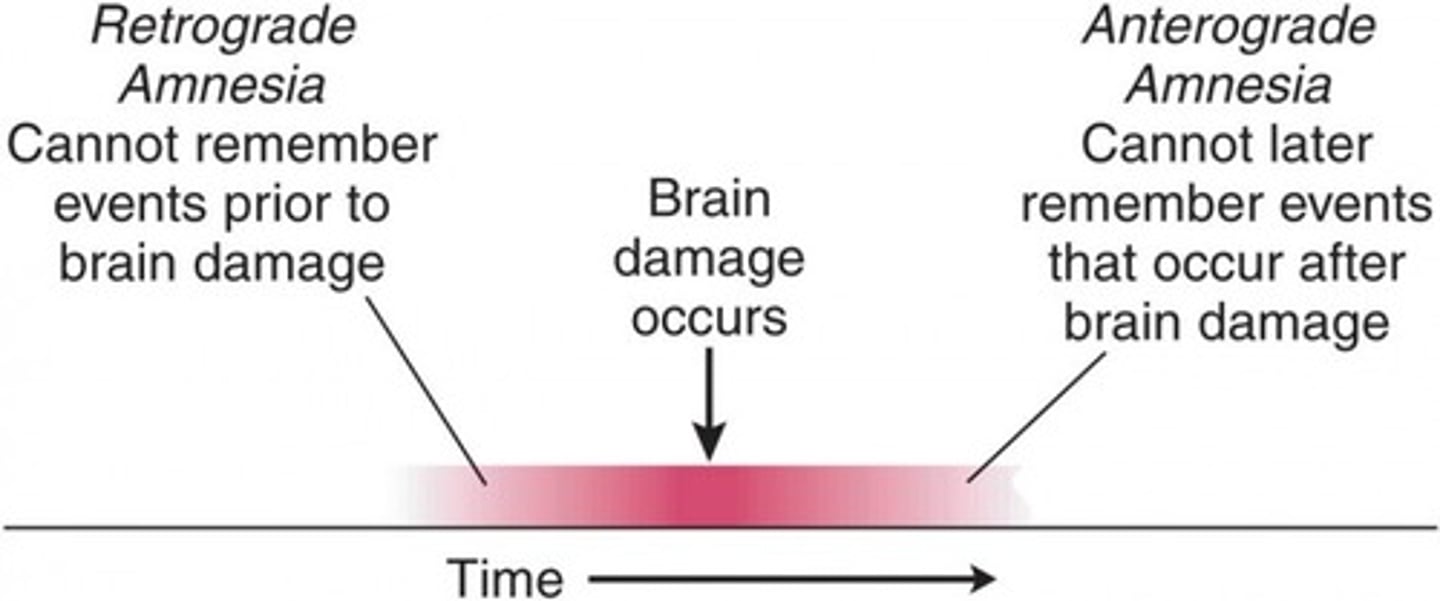
Anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories while still maintaining past memories
Alzheimer's disease
a specific type of dementia characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline

Infantile amnesia
inability of adults to remember personal experiences that took place before an early age

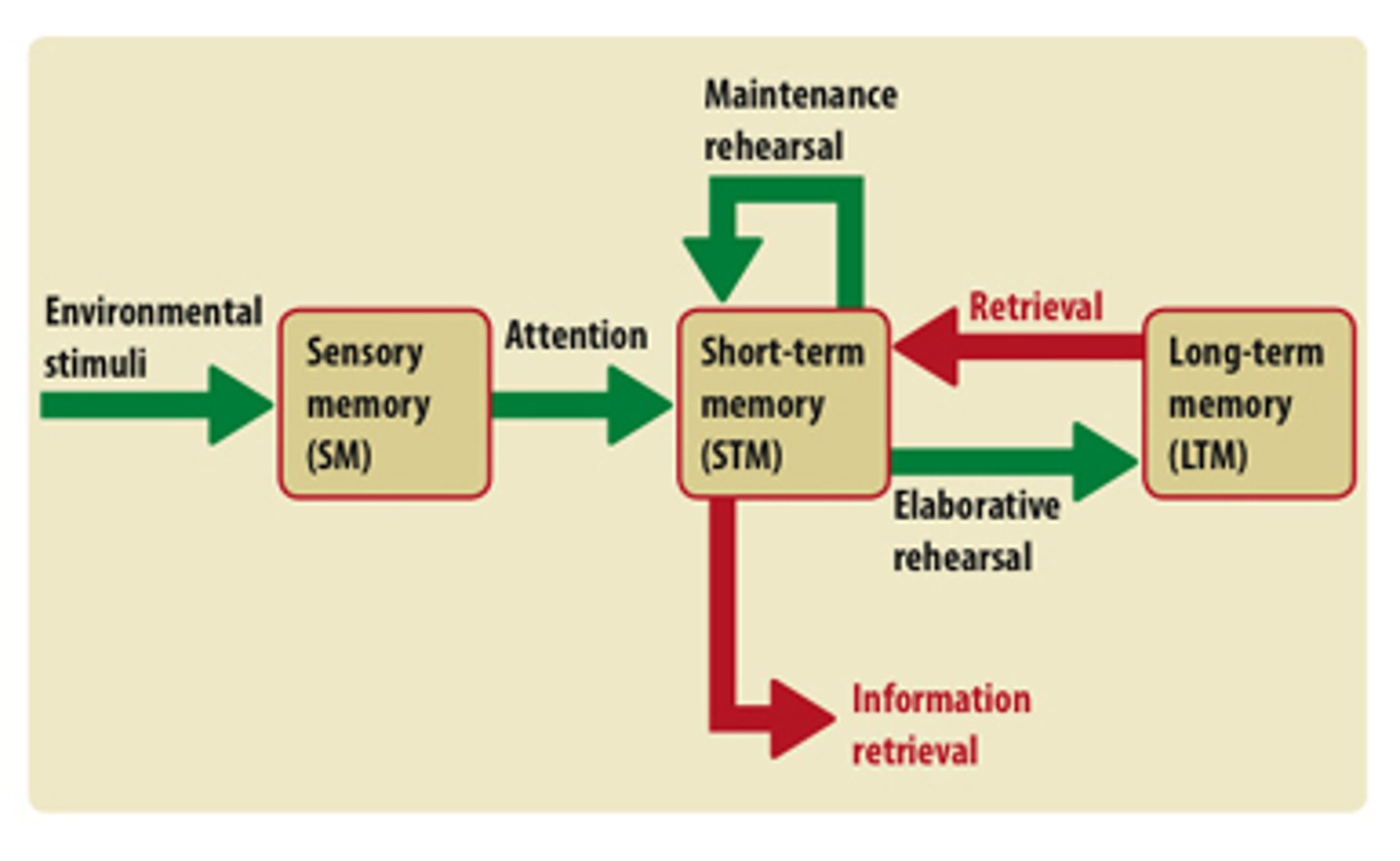
Retrieval
the process of bringing to mind information that has been previously encoded and stored
Recall
retrieving information from past learning or experience without a memory cue

Recognition
identifying information previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test

Retrieval cues
stimuli that aid the recall or recognition of information stored in memory

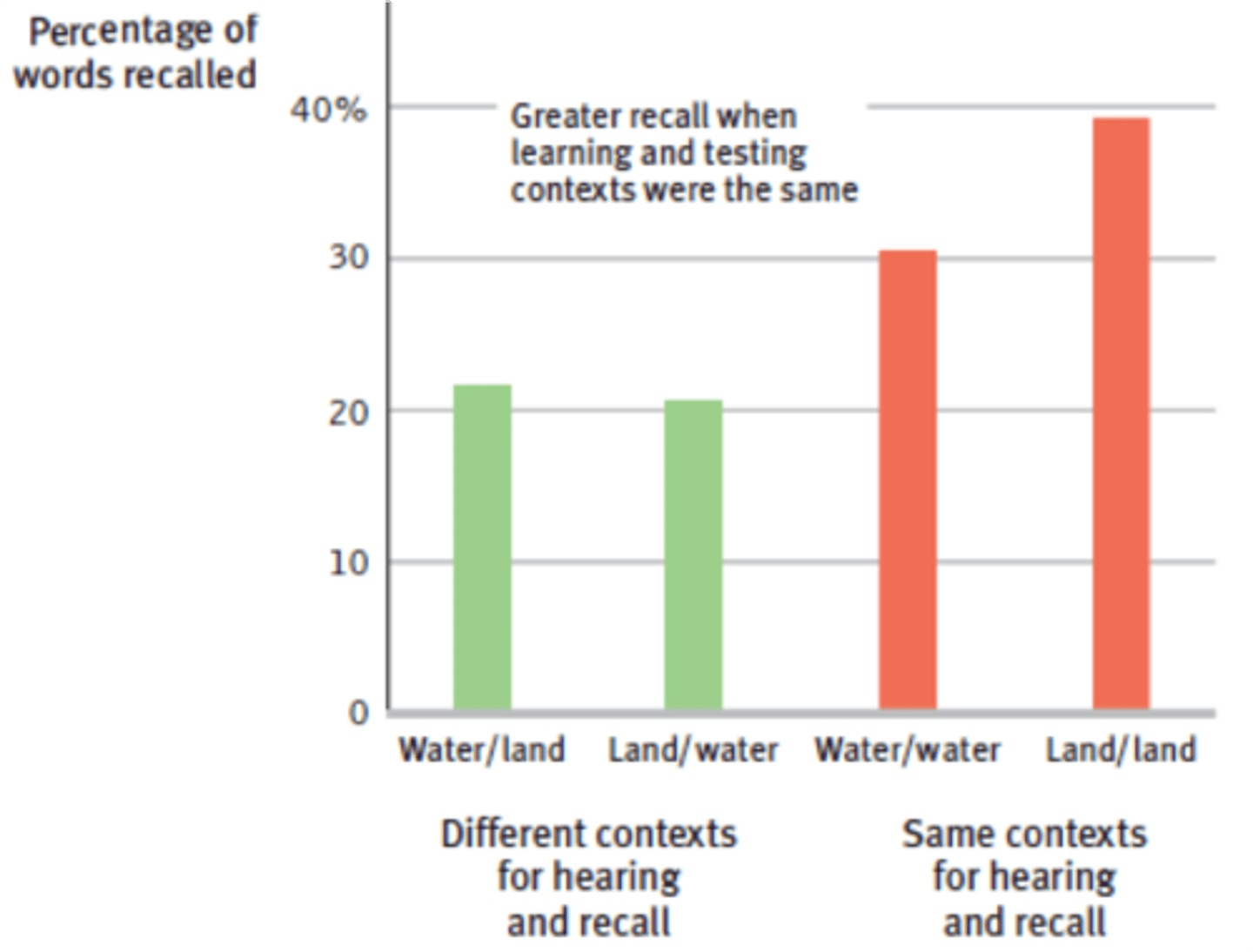
Context-dependent memory
the theory that information is better remembered when when a person is present in the same environment in which the original memory was formed
Mood-congruent memory
a phenomenon that explains how a person is able to recall a memory in more detail if it coincides with their mood at the current time

State-dependent memory
a phenomenon that explains why a memory is improved when the person is in the same biological or psychological state as when the memory was initially formed

Testing effect
the phenomenon that testing an individual's memory makes the memory stronger and easier to retrieve

Metacognition
the phenomenon that learners can improve retrieval by understanding and regulating their own learning process, including their beliefs about learning

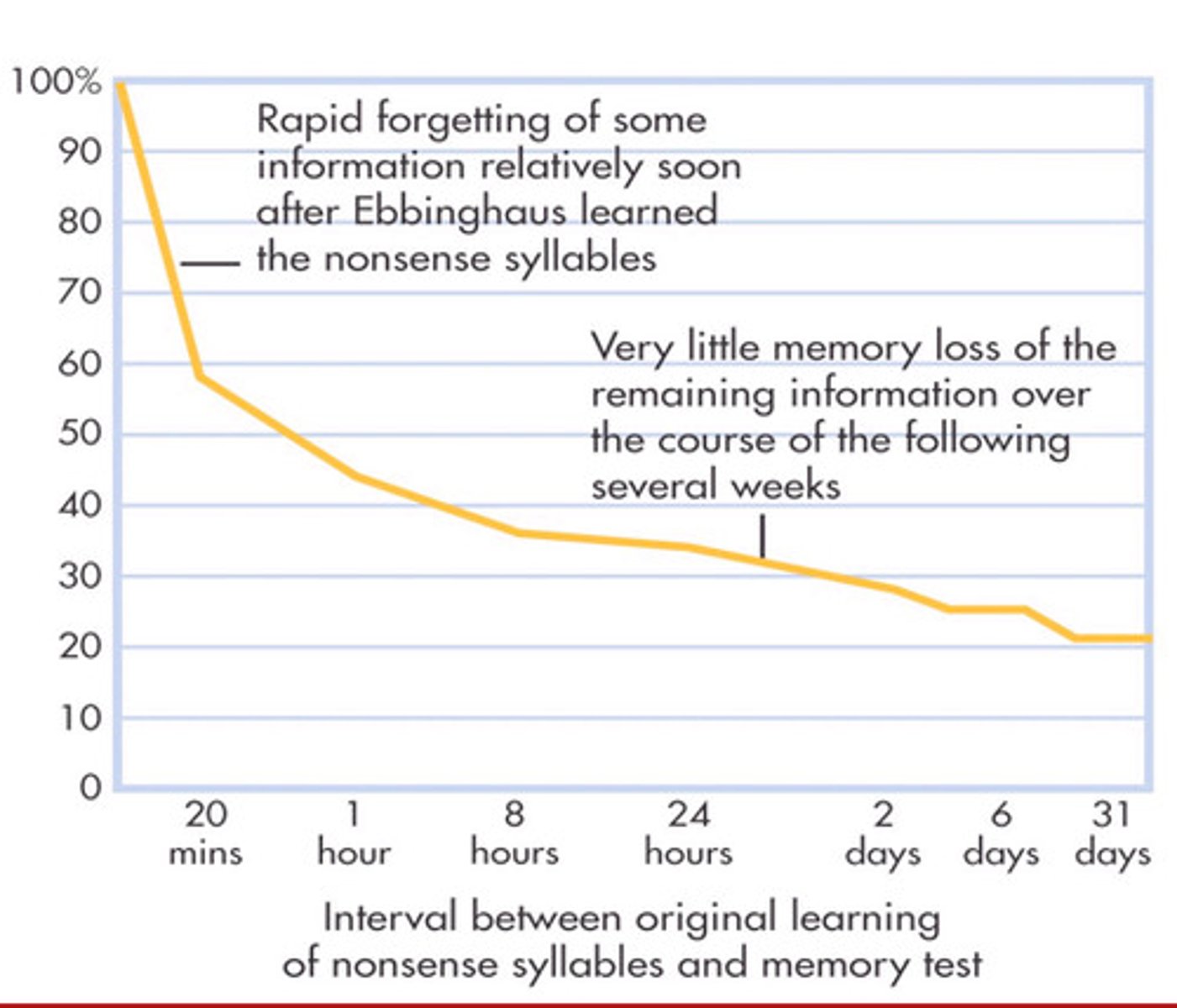
Forgetting curve
a mathematical formula by Ebbinghaus that demonstrates the rate at which information is forgotten over time if there is no attempt to retain it