MODULE 11 Temporal Lobes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Where is the Temporal Lobe?
Located below Sylvian fissure, anterior (in front of) to occipital cortex.
What are the subcortical temporal lobe structures?
Limbic cortex, Amygdala, and hippocampal formation
Sylvian Fissure
Separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes.
Limbic Cortex
Part of the temporal lobe involved in emotions.
Amygdala
Key structure for emotional processing and memory.
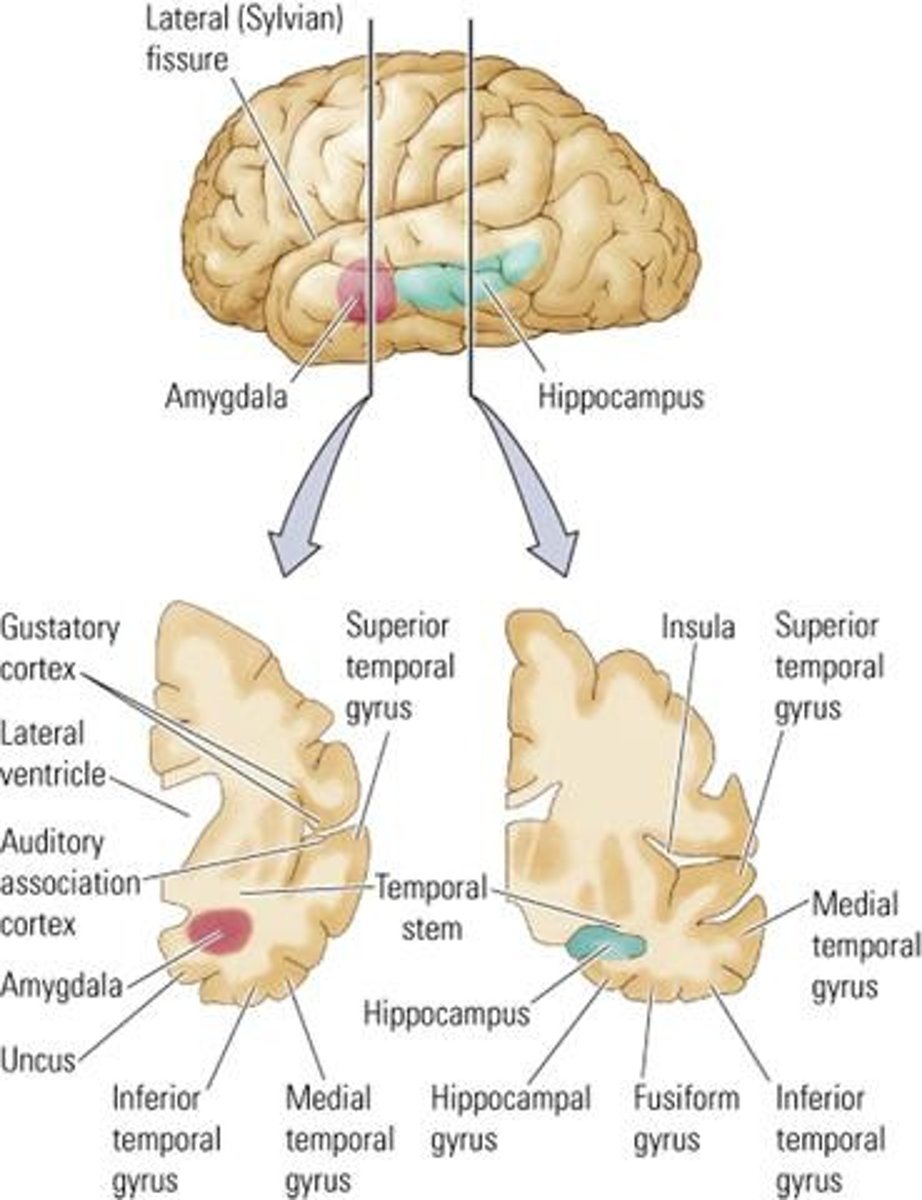
Hippocampal Formation
Critical for memory formation and spatial navigation.
Auditory Areas
Regions in temporal lobe responsible for sound processing.
Ventral Stream
Pathway for visual information processing in the temporal lobe.
Inferior Temporal Cortex
Involved in object recognition and visual perception.
Medial Temporal Cortex
Includes amygdala, hippocampus & surrounding cortex, and fusiform gyrus.
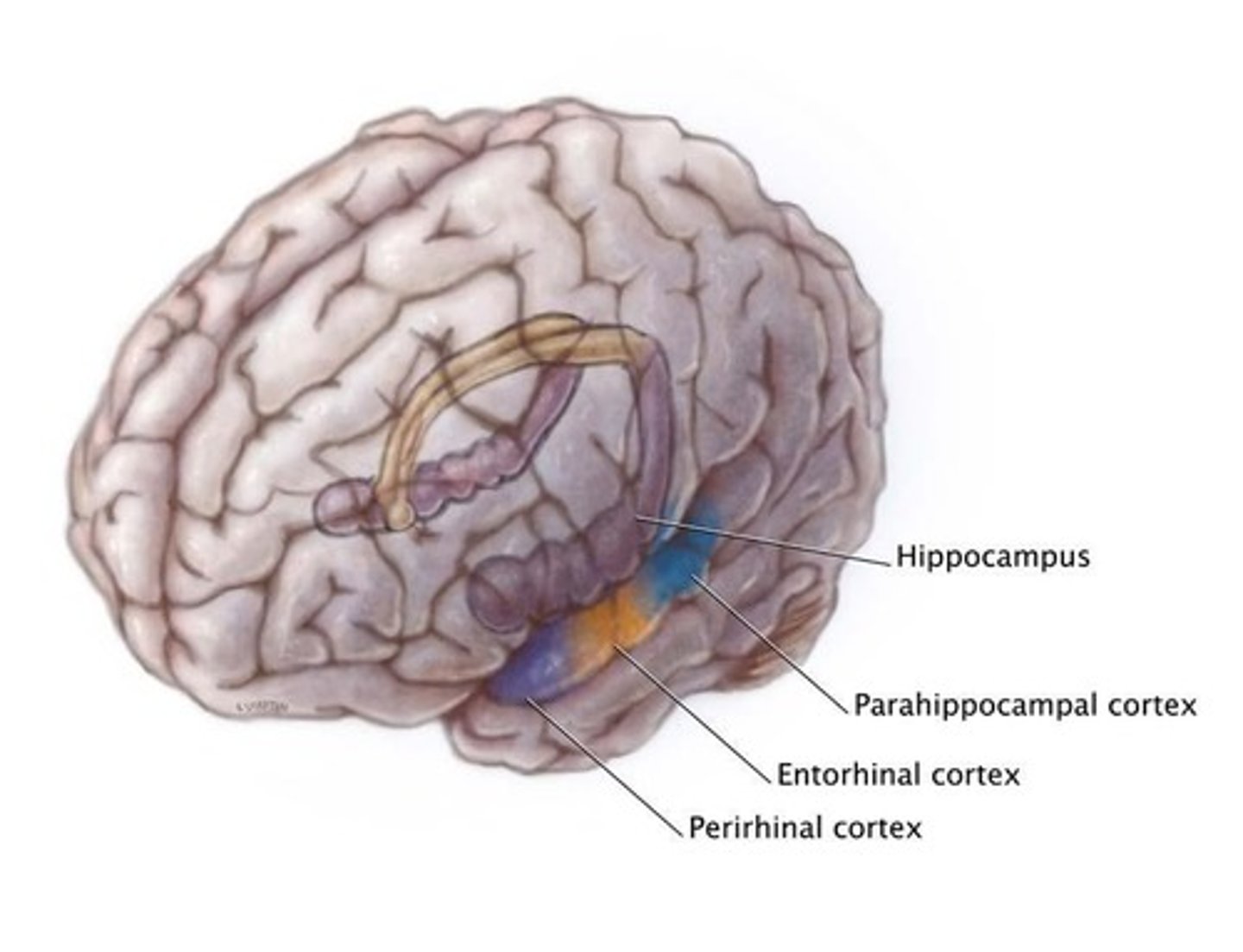
Parahippocampal cortex
Where is it located?
What role does it play?
Region for landmark and scene recognition.
E.g., watch movie and watch people doing things -- when we are looking at sweeping scenes, we see activation in this area
- located at the posterior end of medial temporal lobe
Insula
Where is it located?
What role does it play?
Deep within lateral fissure area under sylvian fissure
Region or cortex that plays a role in:
- conscious urges (e.g., cue induced drug urges)
- processing taste information as well as auditory information
- plays a role in association affects of pain
- possible role in nicotine addiction/addiction pathways
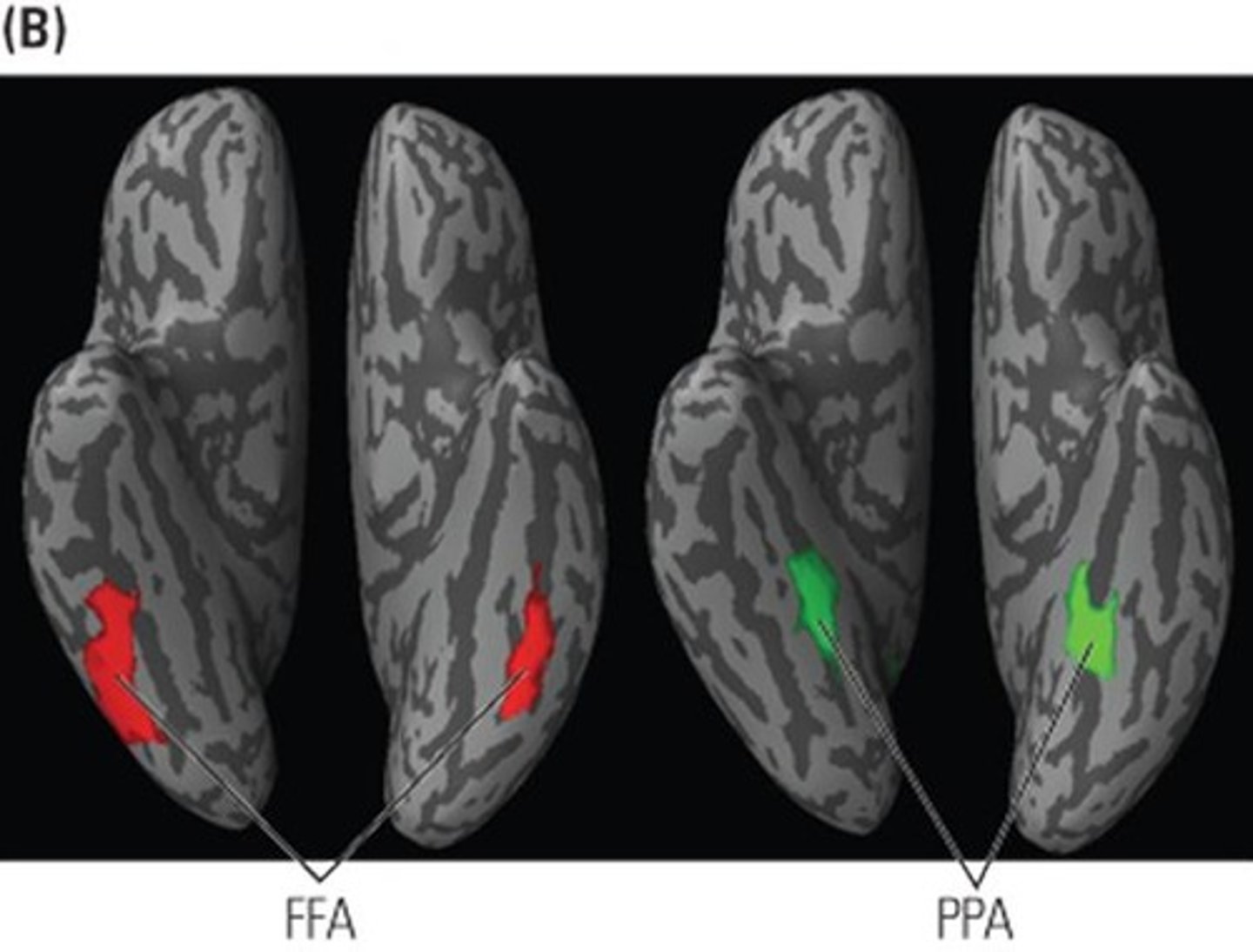
PPA
Parahippocampal Place Area for spatial recognition.
What are Afferent Projections?
- projectiosn coming with sensory information TO the brain
Incoming sensory information to the temporal cortex
- recieves info. from primary motor cortex
indo. fro, visual systems
What are Efferent Projections?
Outgoing signals to other brain regions from temporal cortex.
- info. goes to parietal (Dorsal Stream; Where pathway) -->
- auditory location
- frontal association regions (highest level of association integrating info. from all lobes)
- limbic system (emotion and memory), and basal ganglia (motor regulation)
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right temporal lobes.
Anterior Commissure
Another connection between the temporal lobes
- primarily linking limbic systems (e.g., amygdala)
What is the Hierarchical Sensory Pathway?
Processes incoming auditory and visual information
- stimulus recognition
- ventral pathways for vision and audition (what a sound is)
What is the Dorsal Auditory Pathway?
Detects spatial location and movement of sounds.
- from auditory cortex to posterior parietal
Polymodal Cortex
Integrates auditory and visual information for stimulus categorization.
- located under the STS
- E.g., McGurk effect
What is the McGurk effect? What is it an example of?
It is an example of cross-modal matching (STS)
a perceptual phenomenon that demonstrates an interaction between hearing and vision in speech perception.
- The illusion occurs when the auditory component of one sound is paired with the visual component of another sound, leading to the perception of a third sound.
E.g., Hearing "Ba Ba Ba" when the mouth is moving "Fa Fa Fa"
What is the Medial Temporal Projection?
- from auditory and visual areas to medial temporal lobe (hippocampal formation, limbic cortex, and amygdala (strong emotions))
What is the Frontal Lobe Projection?
Links auditory and visual cortex to frontal lobe
- deals with movement control, short-term memory, and affect
Biological Motion
Movements that convey social intentions and cognition.
What are the three basic sensory functions of the temporal lobes?
1) Processing auditory input
2) Visual object recognition
3) Long-term storage of information
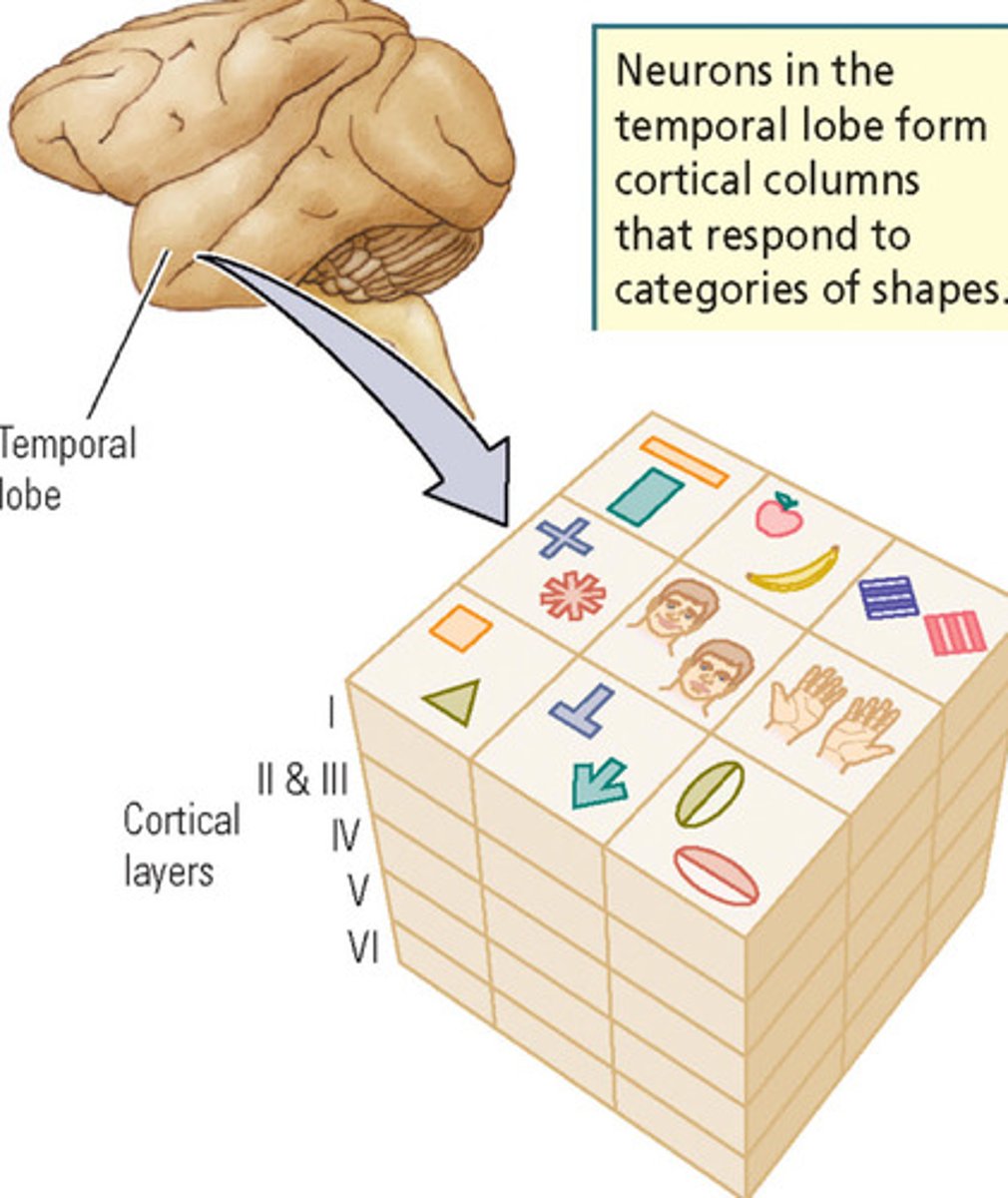
What do neurons in the temporal lobe form?
Where along the ventral stream does this occur?
What happens if a person has damage in certain columns?
They form cortical columns that respond to categories of specific shapes
- This occurs far down the ventral stream in more anterior regions
- If certain columns are damaged, a person may have difficulty in object recognition for particular shaped objects that are categorized in the column of damage
- This is also called Category-Specific Agnosia
Amusia
Deficit in music processing and pitch perception.
- cannot process music
What areas of the temporal lobe process certain parts of music?
What special function does the right temporal lobe have?
Left Temporal Lobe - temporal grouping for rhythm
Right Temporal Lobe - meter (base/more global aspects)
*Right temporal lobe has special function in extracting pitch from sound, regardless if sound is speech or music
What do musicians have a larger volume of?
They have a larger amount of grey and white matter in Heschl's Gyrus
- broader perception of music
Fill in the blanks:
Fundamental pitch listeners have a _________ asymmetry Heschl's gyrus.
Spectral-pitch listeners have a _________ asymmetry in their Heschl's gyrus.
leftward
rightward
What are fundamental pitch listeners?
People who understand and perceive the frequency of sound
What are spectral-pitch listeners?
People who perceive pitch as the perceptual correlate of frequency
Prosody
Tone of Voice or pitch
- larger Heschl's gyrus in right hemi. to do so
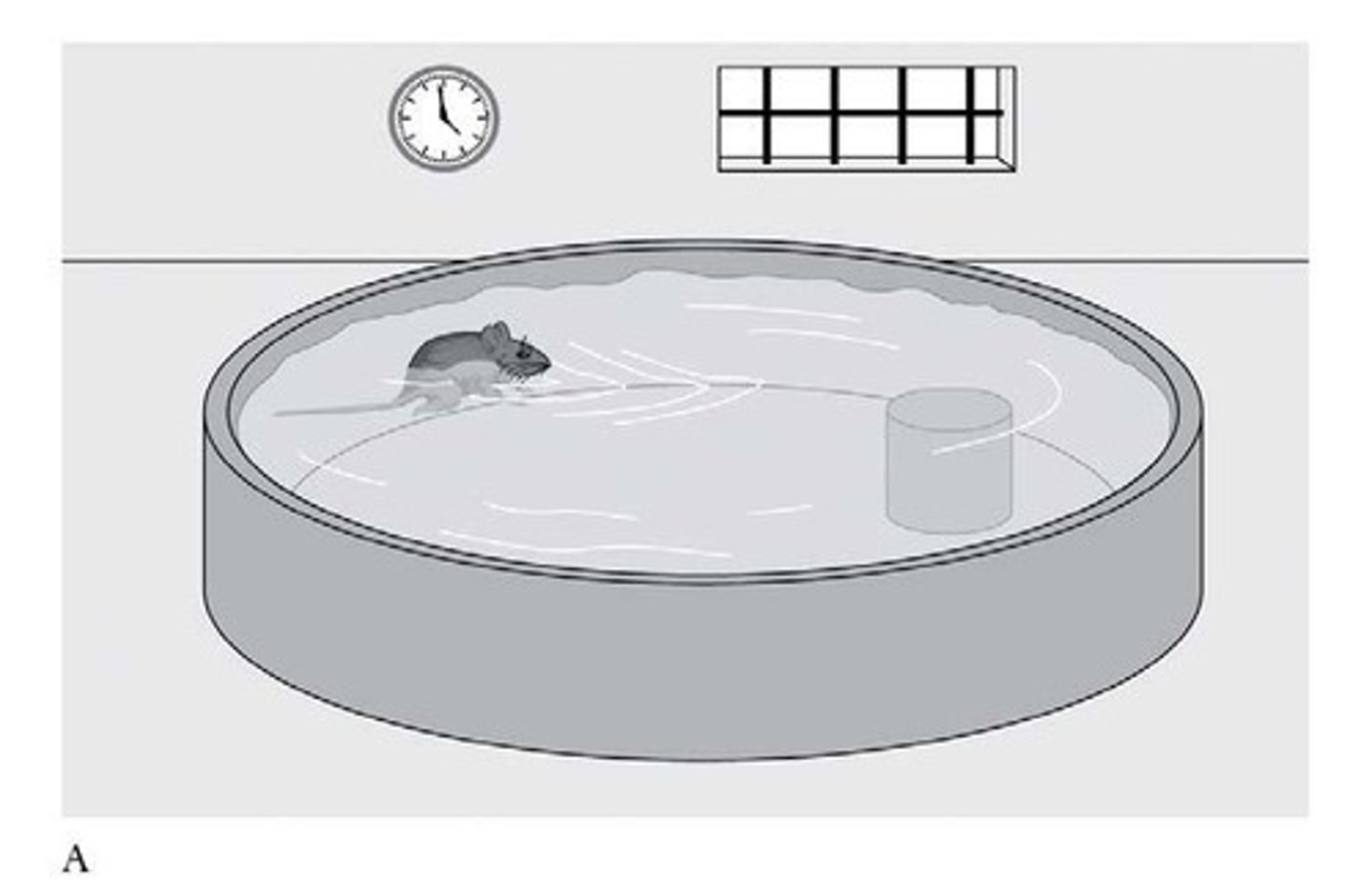
Morris Water Maze Task
Test for spatial memory using a water maze
- circular pedestal placed in pool
- allow rat to learn where pedestal is by practice (swimming around in clear water)
- During testing: Make water opaque so they will have to use memory to find where pedestal is
- allows rat to use external cues to know where it is
Intact Hippo: Rat will be able to find pedestal easily (spatial map)
Lesioned Hippo: Once water made opaque, rats are unable to find where the pedestal is (inability to create spatial map)
What are affective responses?
Emotional responses associated with particular stimuli
- Frontal lobe (Cingulate cortex) and limbic system (amygdala) play a role
What area of the brain that is associated with the temporal lobe is associated with spatial memory?
Hippocampus
Fill in the blank:
Depending on where damage occurs in the temporal lobes, you can see very ____________ symptoms.
different
What are Hippocampal Place Fields?
- shows specificity of single-cells in hippocampus
- preferential locating is occurring
- rats placed in circular environment
- the more the rats spend time in this environments, the more their cells start to fire specifically to when rats are in certain location in environment
- cells fire most in bottom right region over numerous trials
rats then placed in larger space
- see similar cells being fired as smaller circle (expanded)
What is the Superior Temporal Sulcus and its relation to biological motion?
Imaging reveals activation in STS during perception of biological motion
- allows us to guess others intentions
- also part of mirror neuron system
Explain the Visual Processing in the Temporal Lobe using the study of the viewing for "The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly"
- used fMRI data
- extensive activity in auditory and visual regions in the temporal lobes, STS (Biological movement), and cingulate regions (emotional processing)
- selective activation in FFA (when faces shown) and PPA (in processing sweeping scenes)
- Regions of parietal and frontal lobes showed no intersubjective coherence
What is intersubjective coherence?
What study showed this?
Every person has their own subjective experience, thought processes etc. and so results in activation may differ from person to person
The study that showcased this was in the fMRI data from the viewing of "The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly"
RESULTS: No intersubjective coherence in parietal and frontal lobes!
What symptoms occur in temporal-lobe lesions?
- Auditory disturbance
- Disturbance in selection of visual and auditory input
- impaired organization and categorization
- inability to remember prior experiences (contextual information)
- long-term memory issues
- altered personality (damage to amygdala/limbic systems) and affective behaviour