Solids, Liquids & Gases Flashcards
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the key concepts of solids, liquids, and gases, including kinetic theory, states of matter, pressure, temperature, and diffusion.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the Kinetic Theory of Matter and how does it explain the properties of different states of matter?
A theory that explains the physical properties of solids, liquids, and gases by referring to the arrangement and motion of particles. It posits that all matter is composed of constantly moving atoms or molecules.
Describe the properties of a solid in terms of volume, shape, density, particle movement, kinetic energy, and intermolecular forces.
- Has a fixed volume and shape.
- High density due to particles being closely packed.
- Particles vibrate in a fixed position with limited movement.
- Particles have low kinetic energy compared to liquids and gases.
- Strong intermolecular forces hold particles in place.
- Particles in a solid are arranged in a regular lattice.
Explain the characteristics of a liquid, including its volume, shape, density, particle arrangement, and intermolecular forces.
- Has a fixed volume but takes the shape of its container.
- Less dense than solids; particles are more spread out.
- Particles move and slide past each other, allowing the liquid to flow.
- Medium density and moderate kinetic energy.
- Particles have a random arrangement with weaker intermolecular forces than solids.
- Particles in a liquid are arranged irregularly.
Outline the properties of a gas, including its volume, shape, density, particle movement, compressibility, and intermolecular forces.
- Does not have a fixed volume or shape, expands to fill its container.
- Very low density; particles are widely dispersed.
- Particles move randomly and quickly with high kinetic energy; they are also far apart.
- Particles can be easily compressed due to the large spaces between them.
- Irregular arrangement with minimal intermolecular forces.
- Gas particles are arranged irregularly.
Describe the process of melting in terms of energy transfer, particle behavior, and the role of intermolecular forces.
- The change of state from solid to liquid.
- Requires heat energy to increase the kinetic energy of particles.
- Occurs at a specific melting point, where the solid's particles gain enough energy to overcome intermolecular forces.
- Heat energy is absorbed as the solid's particles gain energy and vibrate more rapidly, breaking intermolecular bonds, increasing kinetic energy.
Explain the process of freezing, including how temperature affects particle energy and the formation of a solid structure.
- The change of state from liquid to solid.
- Requires a significant decrease in temperature to reduce the kinetic energy of particles.
- Occurs at a specific freezing point where particles lose energy and intermolecular forces become strong enough to arrange them into a solid structure.
Outline the process of boiling, including the conditions required, the role of vapor pressure, and the formation of gas bubbles.
- The change of state from liquid to gas.
- Requires heat and occurs at a specific temperature (boiling point), where the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
- Bubbles of gas form throughout the liquid, allowing liquid particles to escape from the surface and transition into the gaseous state rapidly.
Describe the process of evaporation and what factors increase the rate of evaporation.
- The change of state from liquid to gas at the surface of the liquid.
- Occurring over a range of temperatures below the boiling point; the rate increases with temperature.
- Occurs only at the surface of the liquid, where particles gain enough kinetic energy to overcome intermolecular forces and escape into the air.
- Particles can escape from the liquid at any temperature if they have sufficient kinetic energy.
- When the surface area increases, the rate of evaporation increases because more particles are at the surface.
Explain the process of condensation and what happens on a molecular level.
- The change of state from gas to liquid on cooling.
- Occurring over a range of temperatures as gas particles lose kinetic energy.
- Gas particles lose energy when they collide; if they have no energy to bounce back, intermolecular forces cause them to condense into a liquid.
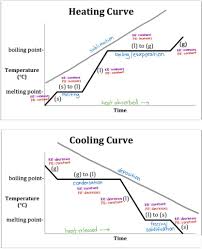
What is a heating curve and what key information does it tell you?
A graph showing the changes in temperature and state of a substance as it is heated, indicating melting and boiling points as plateaus where temperature remains constant while the state changes.
Explain the relationship between gas volume and temperature when pressure is constant. What law describes this relationship?
At constant pressure, the volume of a gas increases as temperature increases (Charles's Law), because higher temperature means greater kinetic energy, causing particles to move more and occupy more space.
Describe the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. What law describes this relationship?
At constant temperature, pressure increases as volume decreases (Boyle's Law), because reducing the volume increases the frequency of collisions between gas particles and the container walls.
What causes gas pressure inside a closed container, and how do collisions affect it?
The pressure that a gas creates inside a closed container is produced by the gaseous particles hitting the inside walls of the container; more frequent and forceful collisions result in higher pressure.
What is diffusion and how does it distribute particles and provide an example?
The process where particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration due to random motion, aiming to evenly distribute particles throughout the available space.
occurs in gases and liquids due to random movement of particles
The diffusion of bromine gases
The diffusion of color of potassium magnate crystals in water
What is the relationship between molecular mass and diffusion rates?
- Lighter particles diffuse faster than heavier particles.
- At the same temperature, lighter particles move at higher speeds, covering more distance in the same amount of time compared to heavier particles.
- Heavier particles move slower and cover less distance in the same amount of time.