Atomic Structure | Quizlet
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Nucleus
centre of an atom; contains neutrons and protons
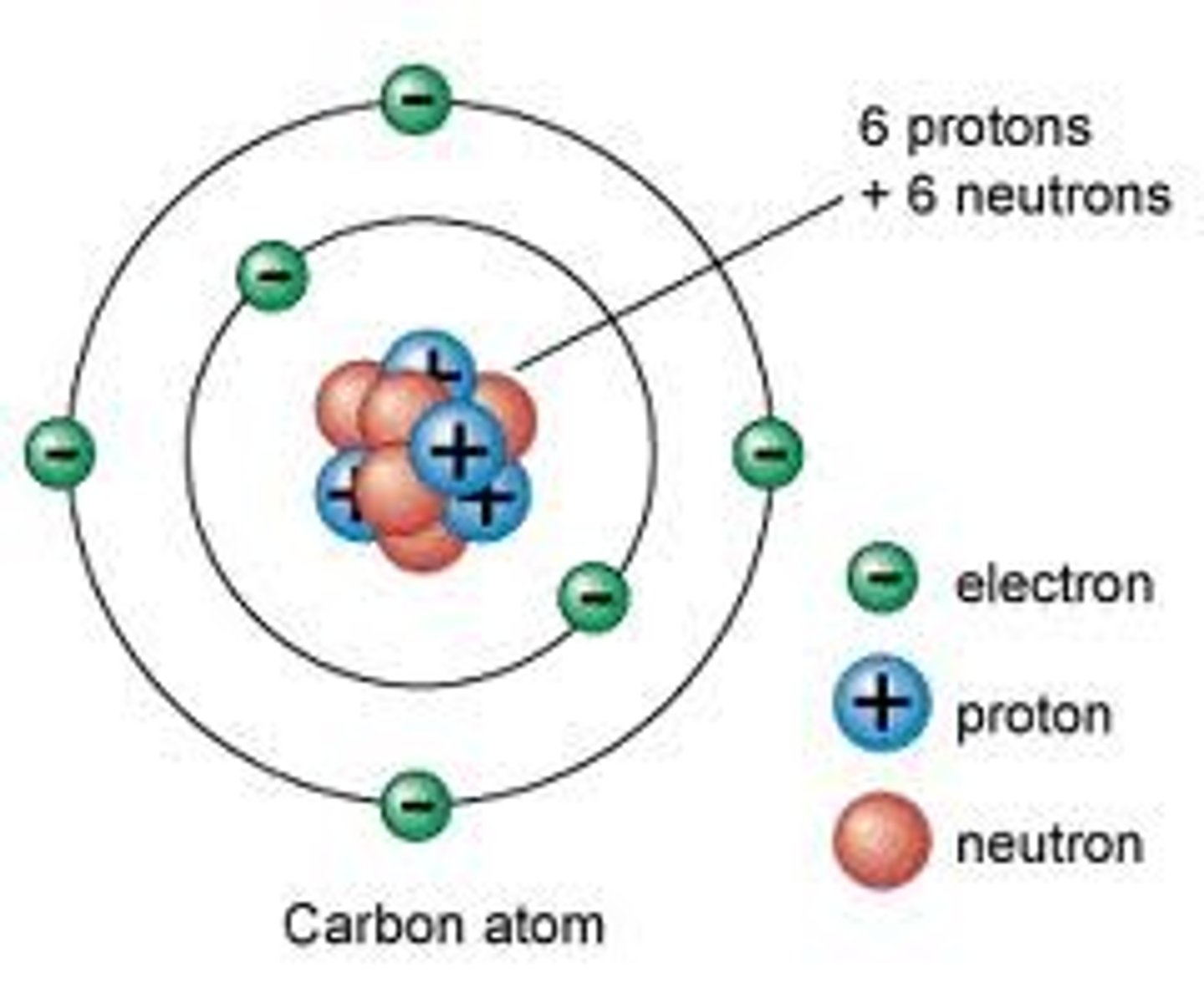
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
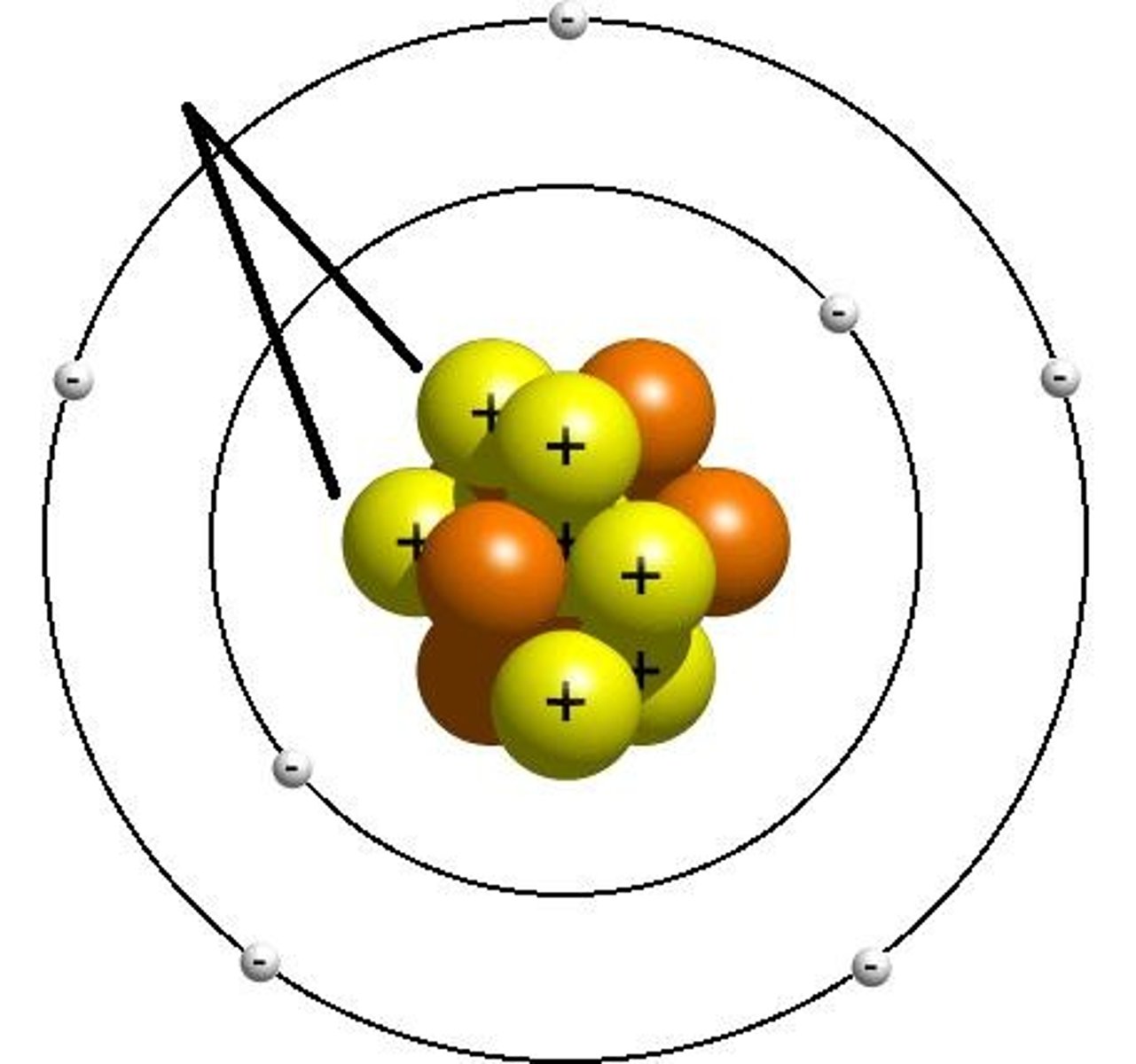
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
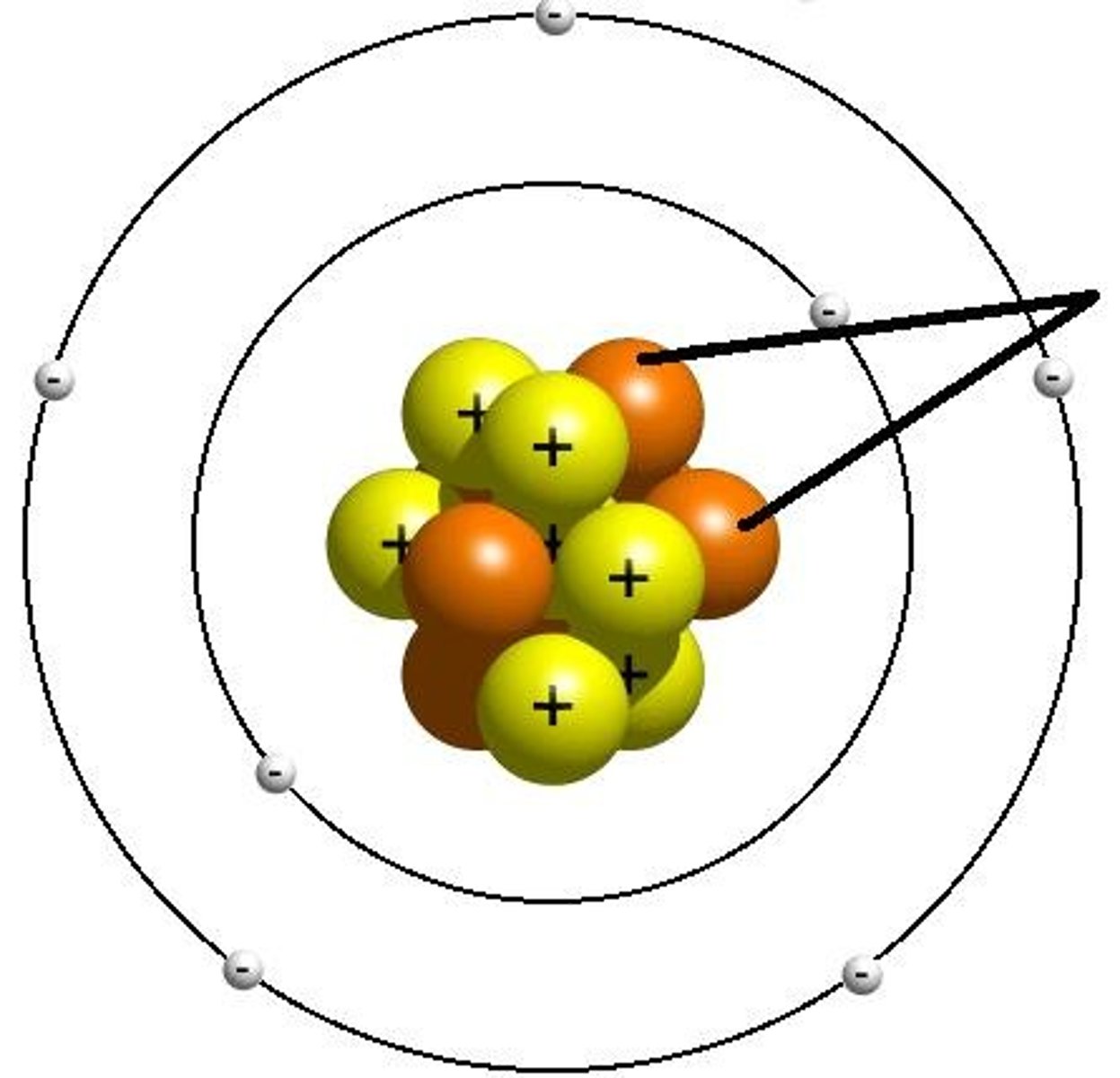
Electron
negatively charged particle; located outside the atomic nucleus, orbits the nucleus in energy shells
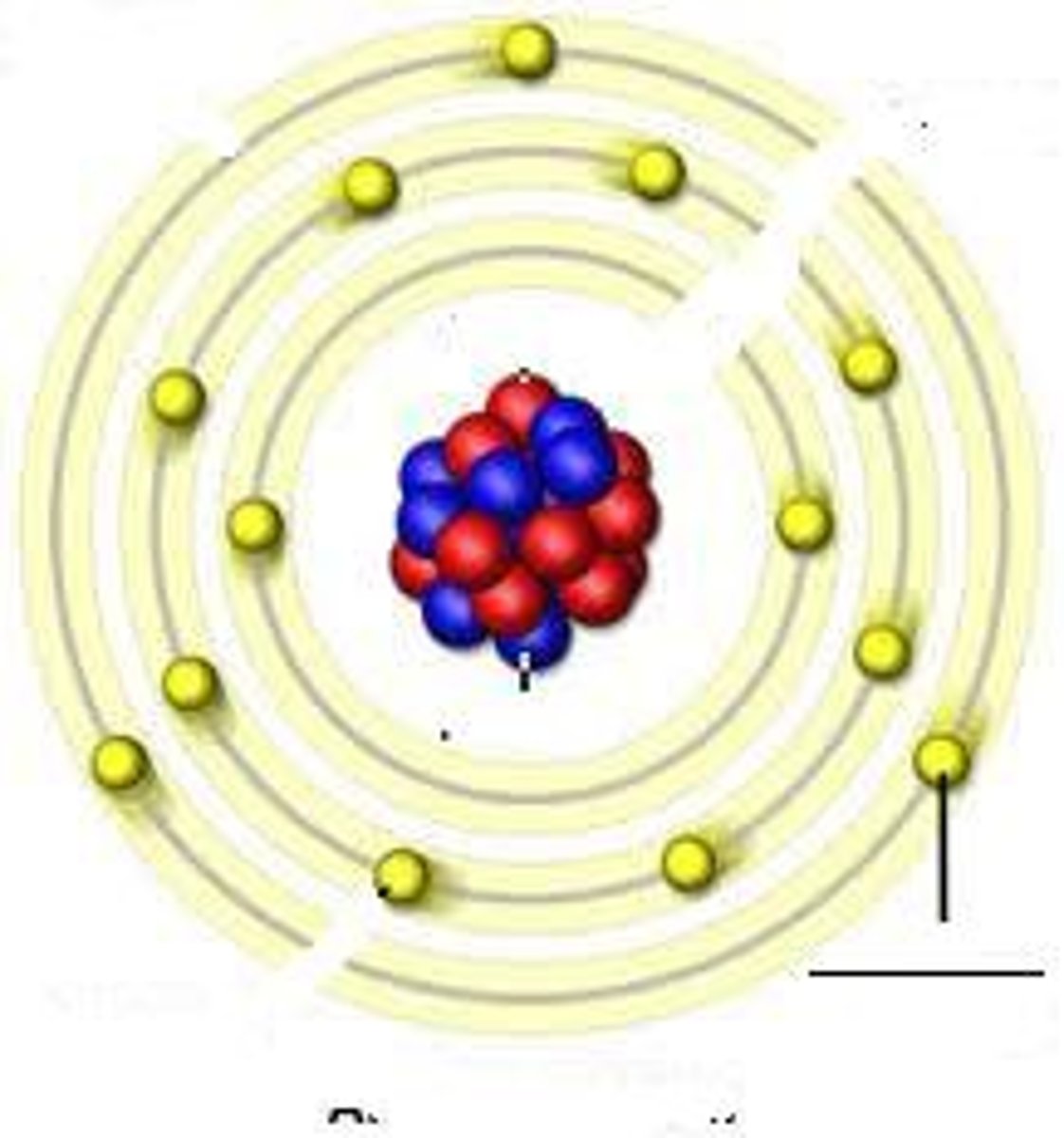
Atom
The basic unit of matter
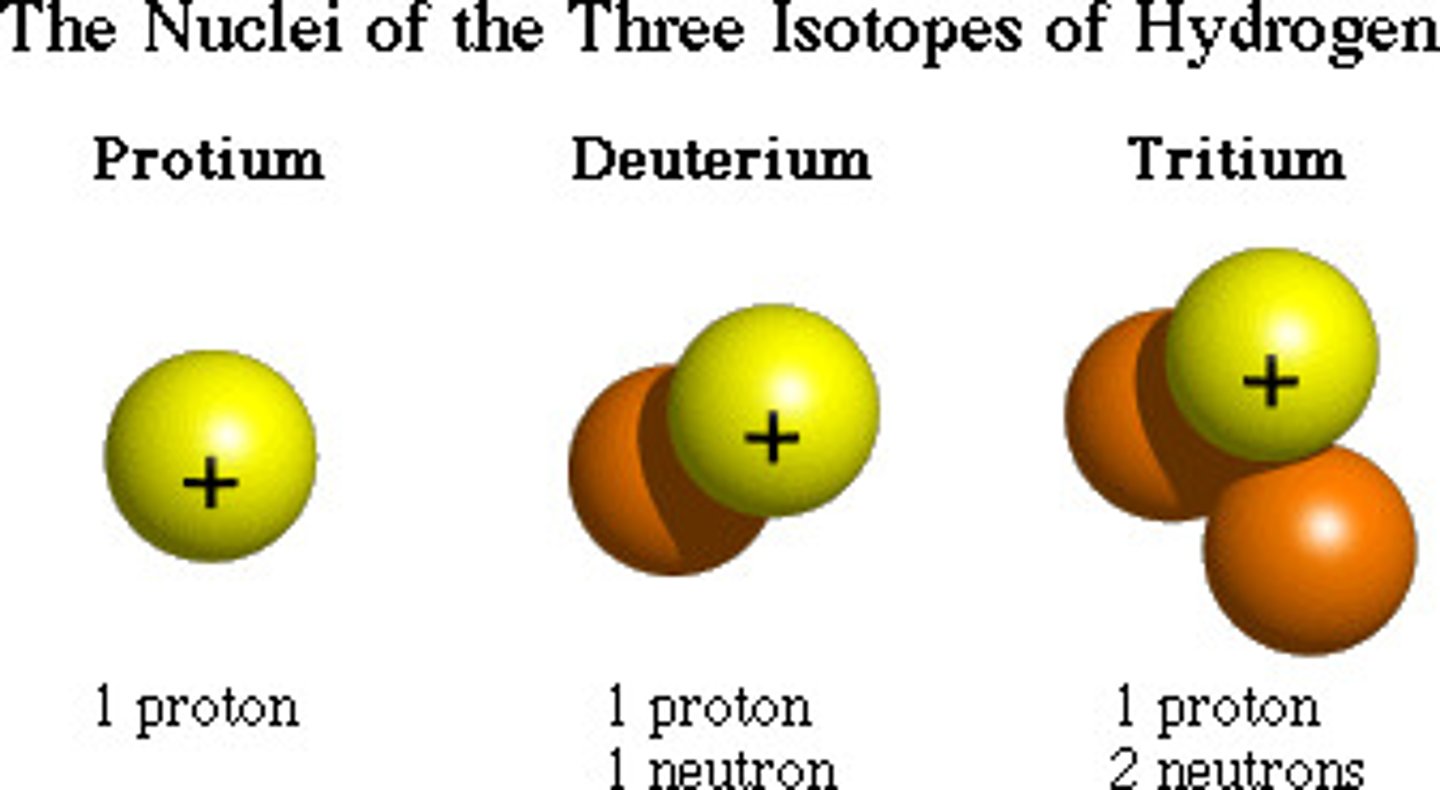
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
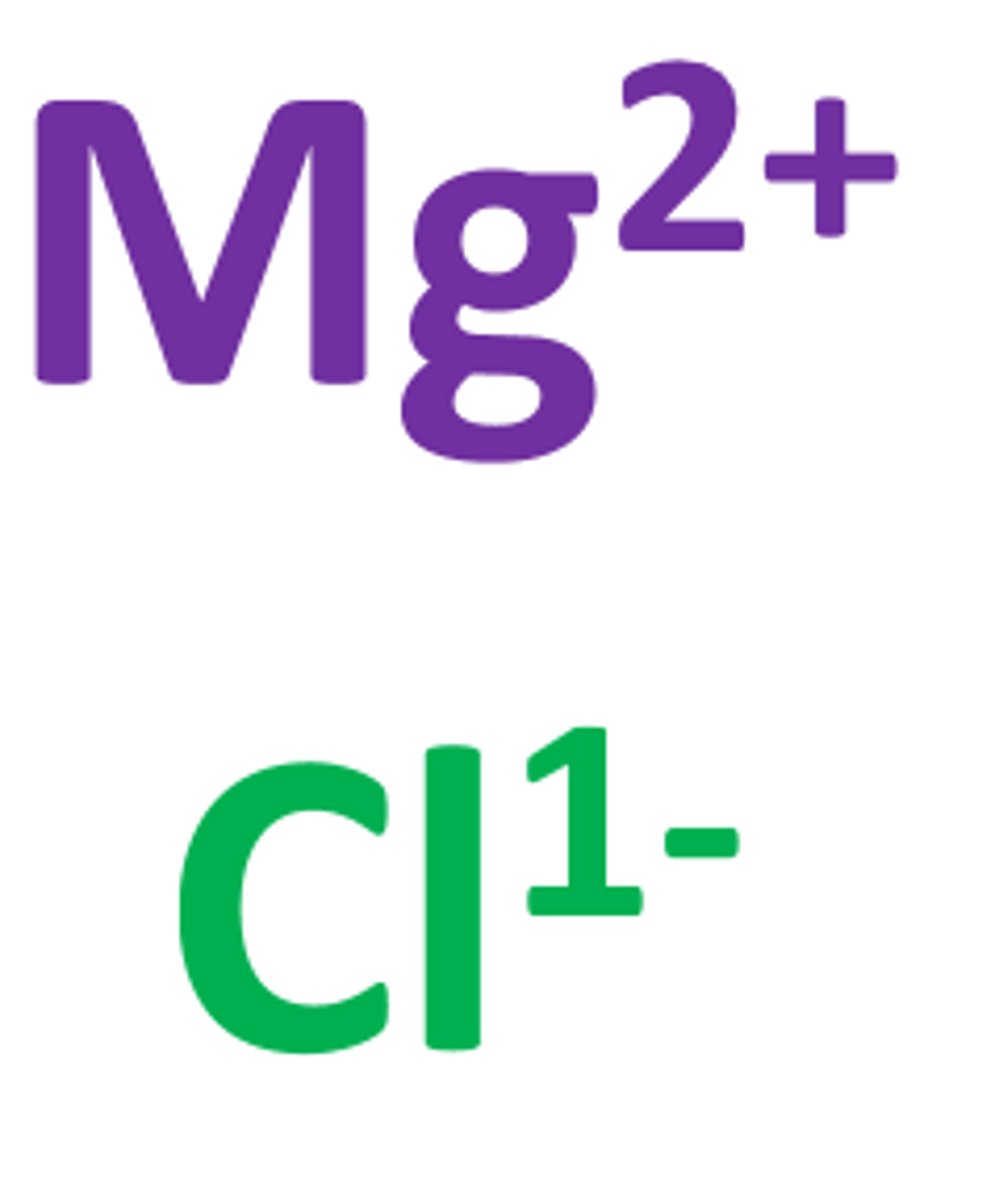
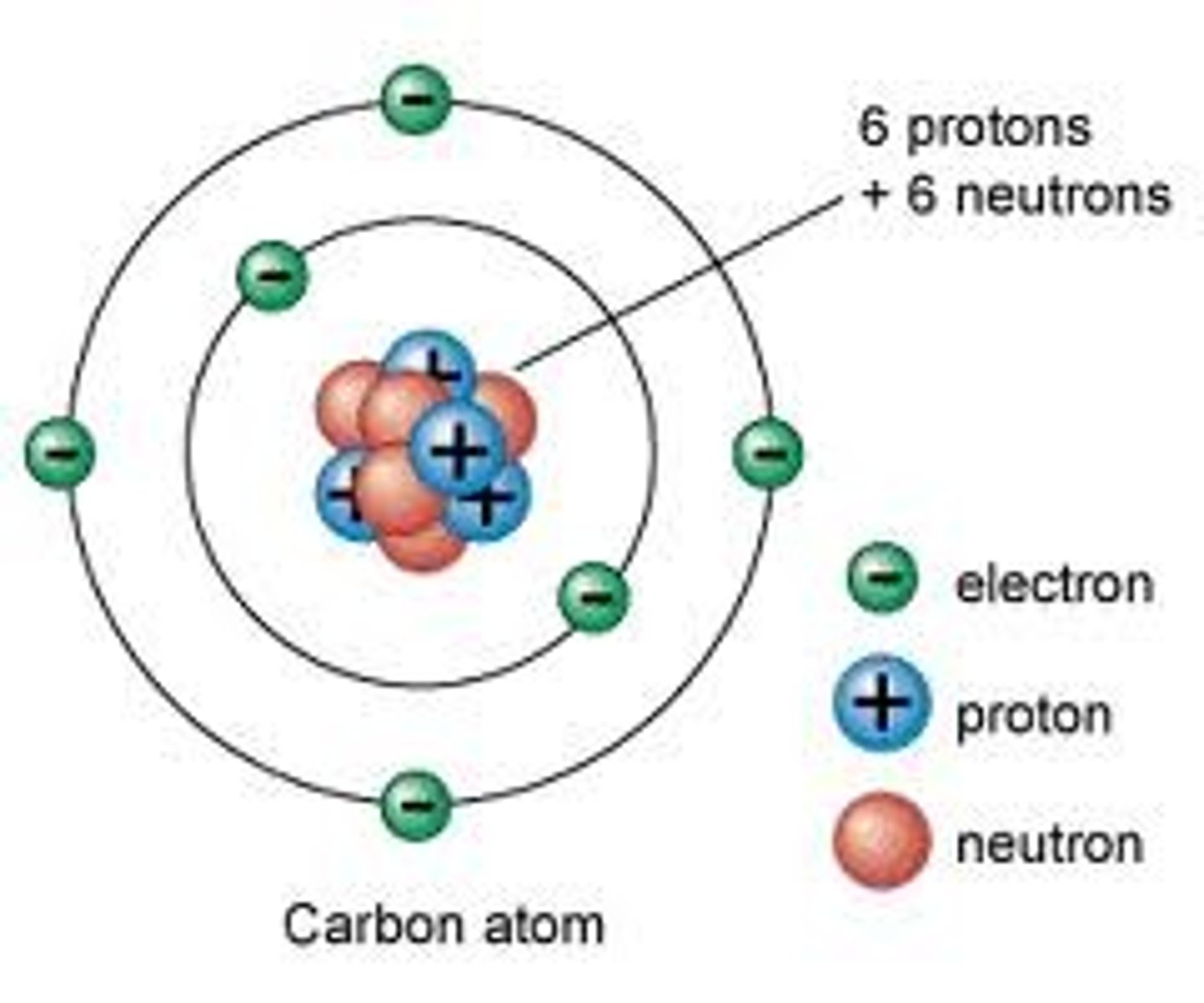
Bohr Atomic Model
Atoms described as electrons orbiting the nucleus in well defined paths.
Proton (atomic) number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom

Mass (nucleon) number
The number of particles (protons and neutrons) in the nucleus.

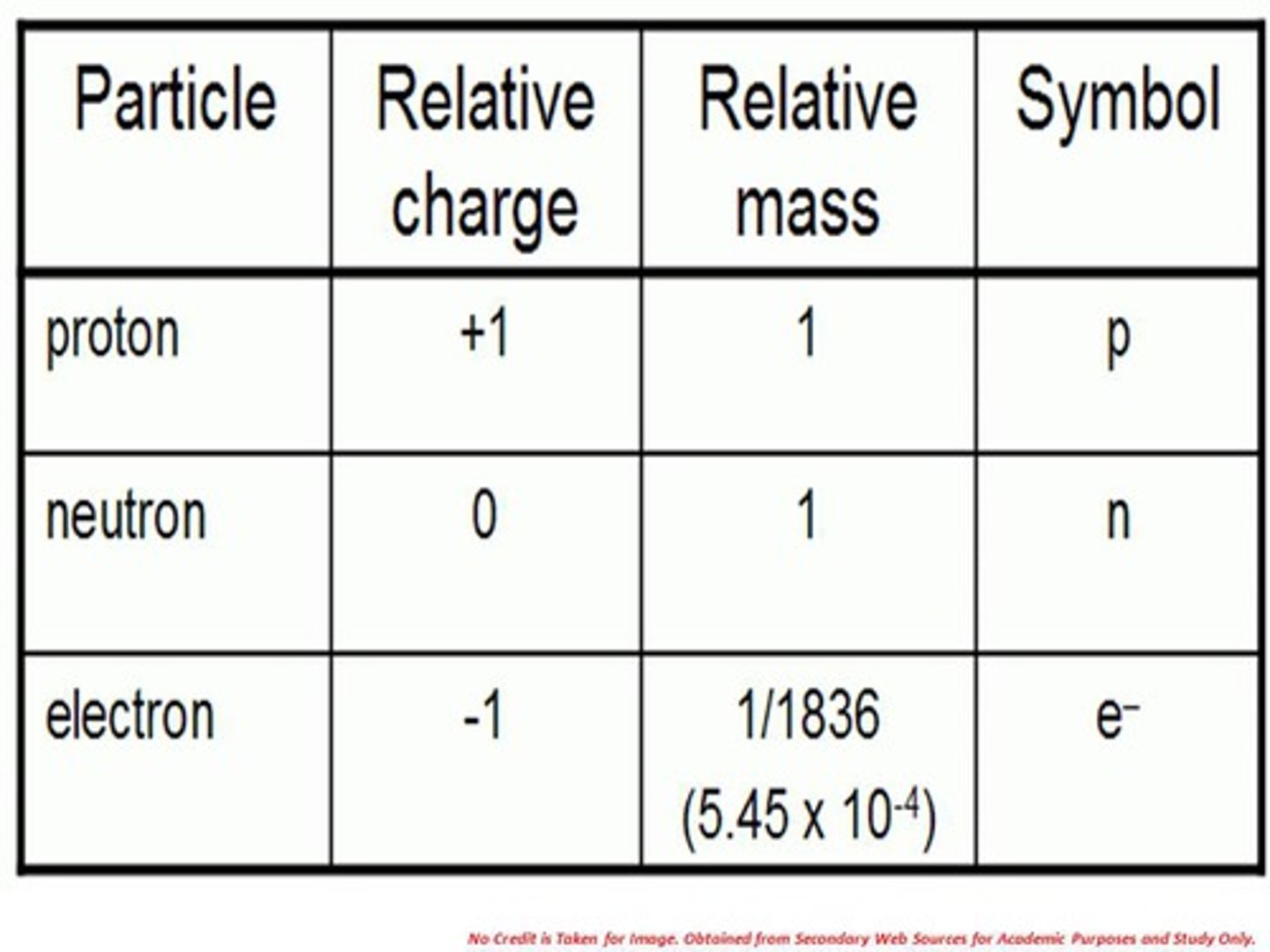
Properties of electrons
- Negatively charged particles
- Relative mass = 1/1836
- Found in the energy shells
- (e-)
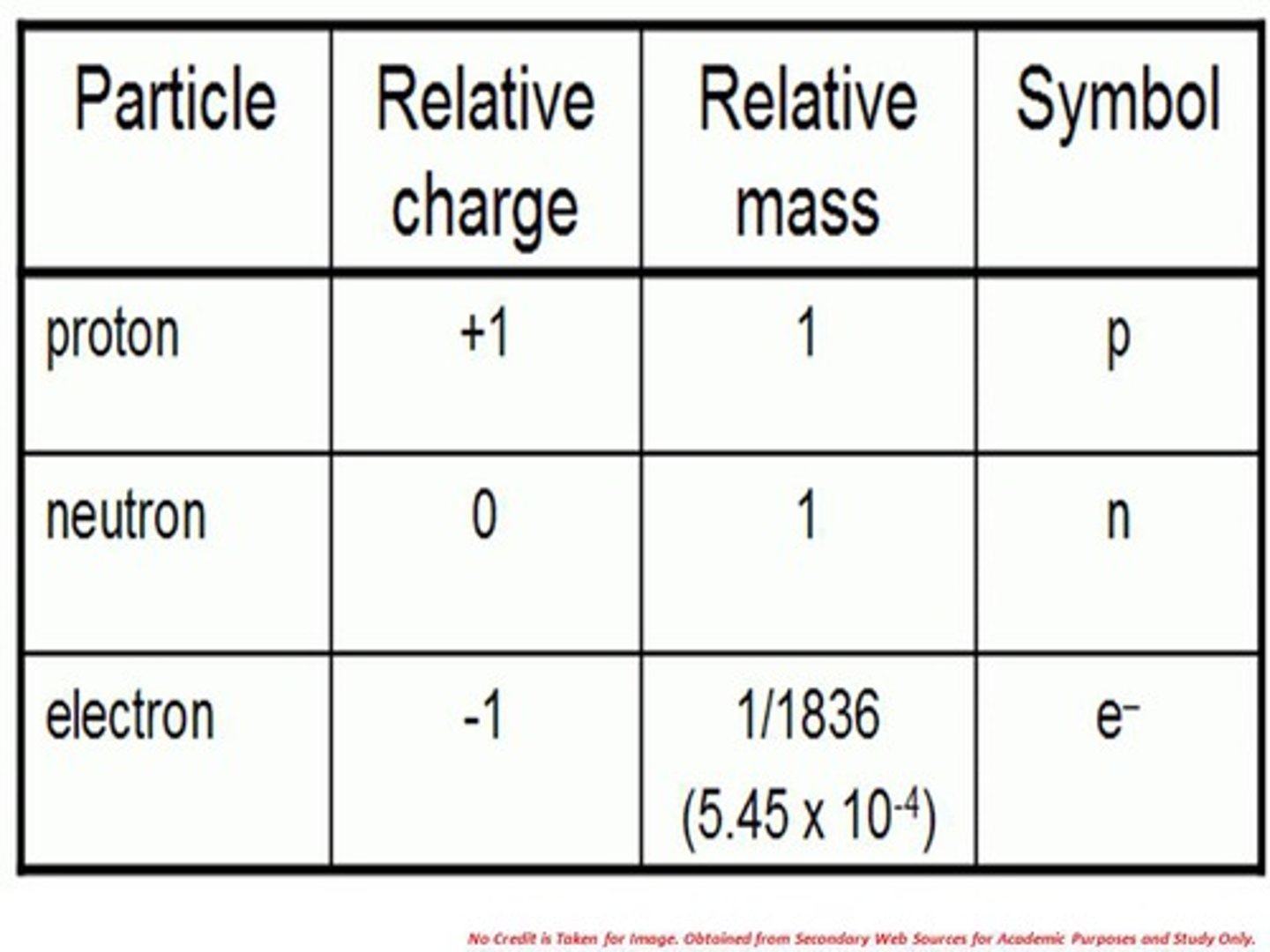
Properties of neutrons
- Particles with no charge
- Relative mass = 1
- Found in the nucleus of the atom
- (n0)
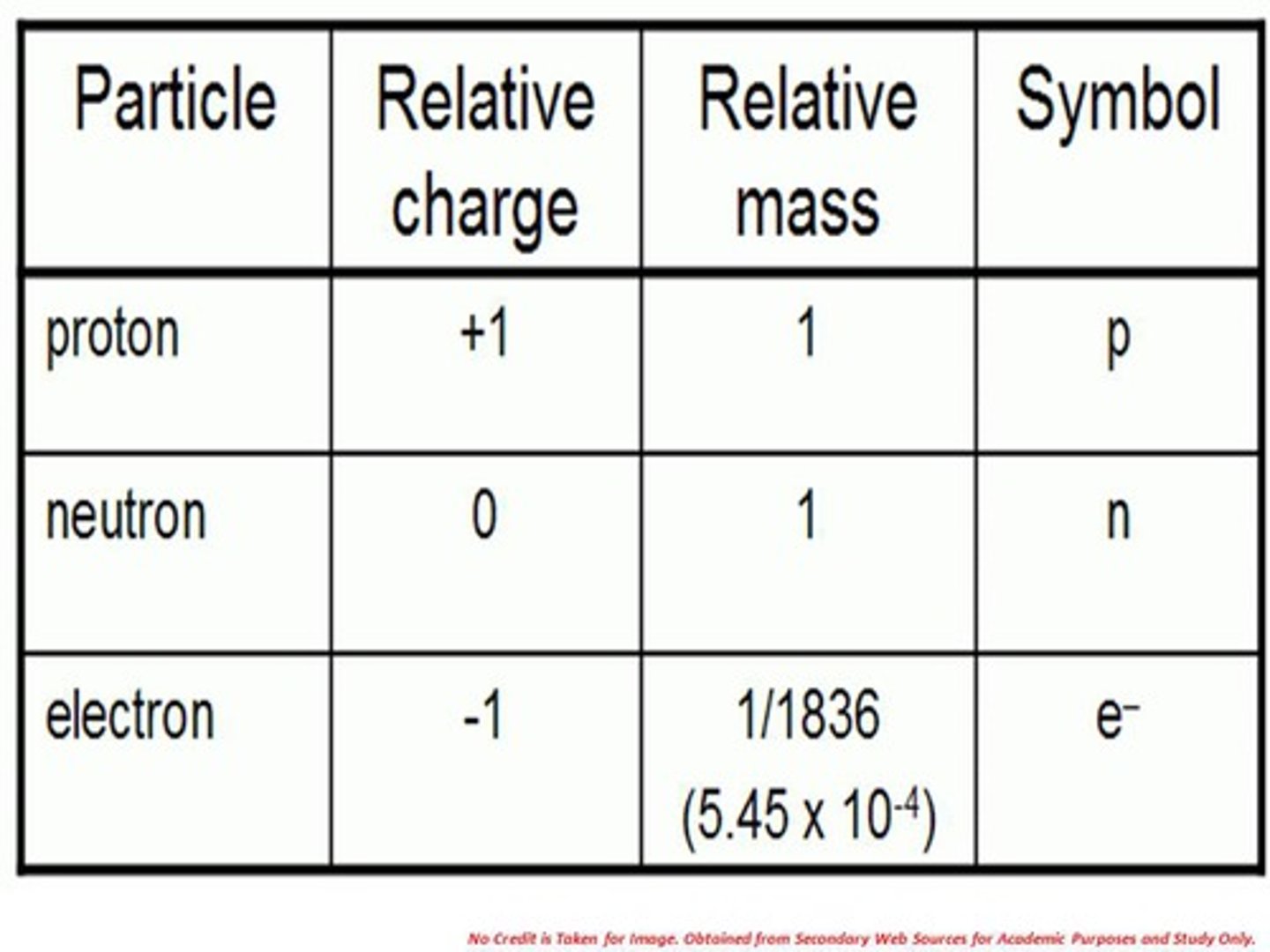
Properties of protons
- Particle with a positive charge
- Relative mass = 1
- Found in the nucleus of the atom
- (p+)
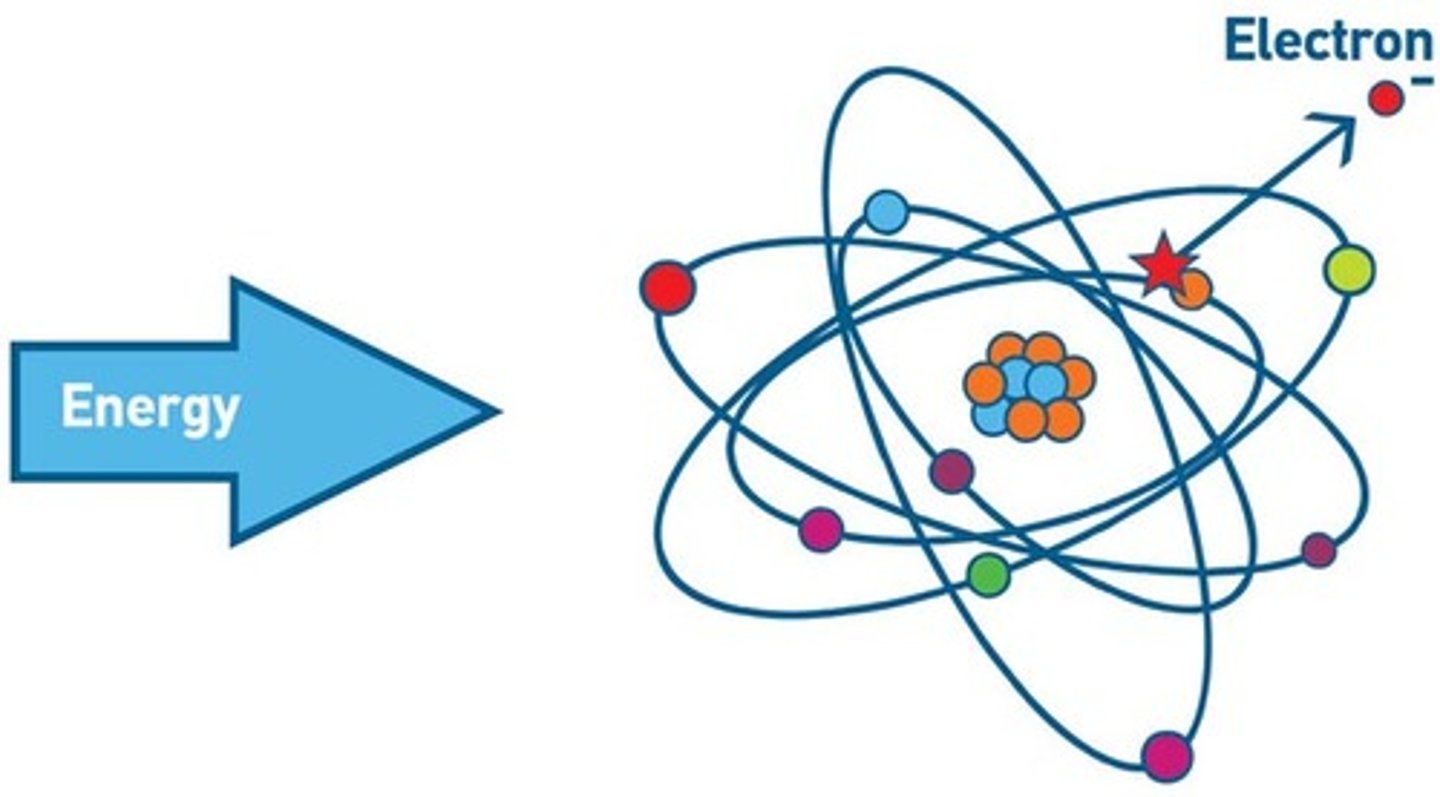
Ionisation
The removal of one or more electrons from an atom.
Radioactive decay
A spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation
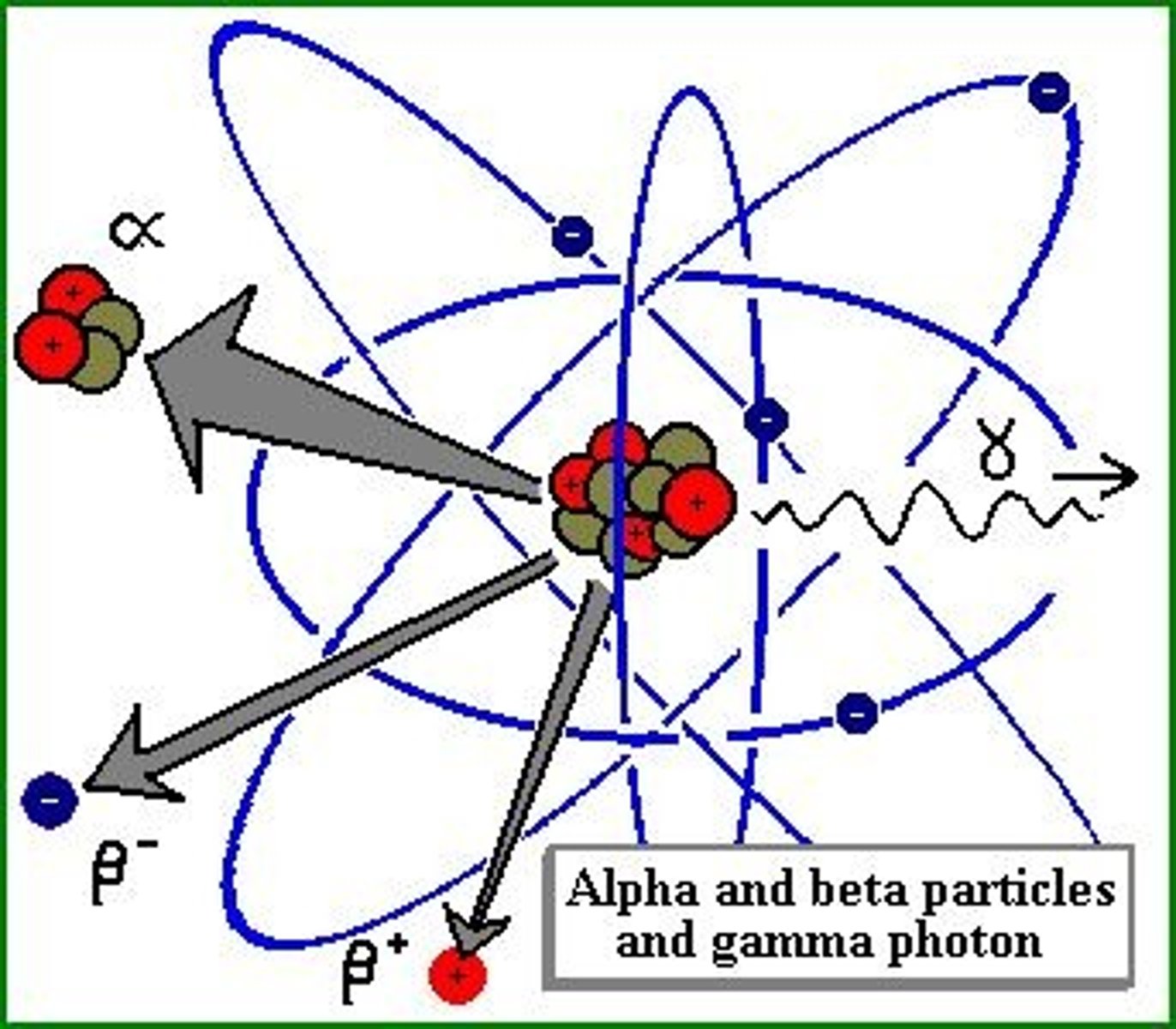
Alpha decay
A nuclear reaction in which an atom emits an alpha particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. This increases the atomic number by 2 and the mass number by 4.
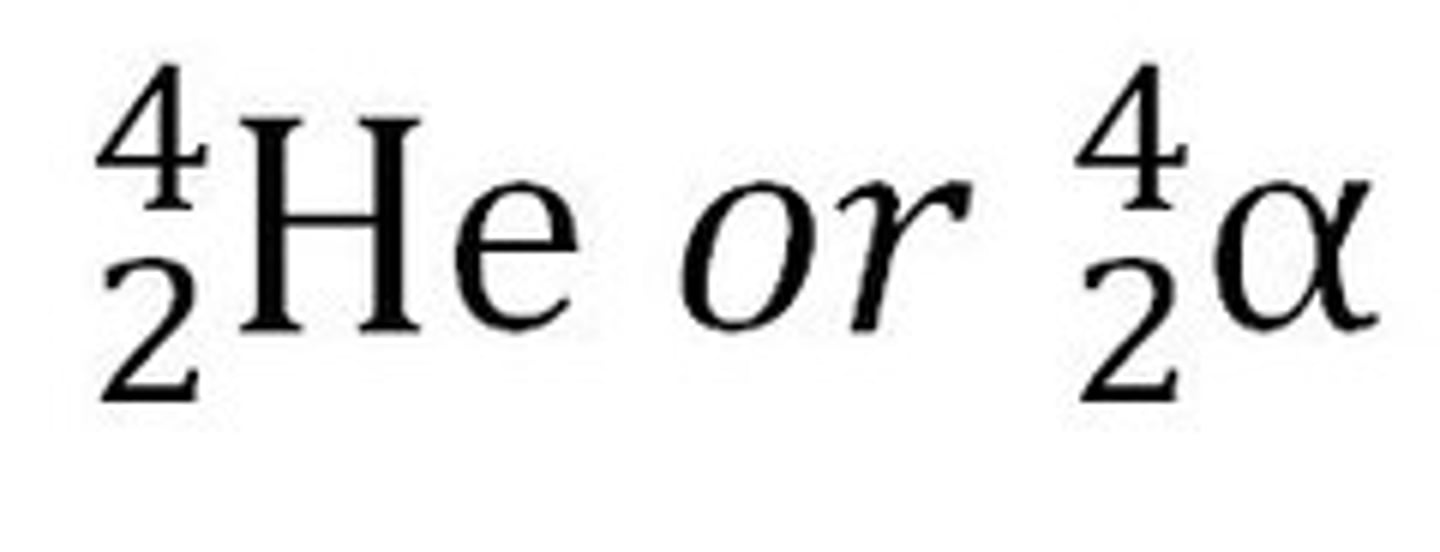
Beta decay
radioactive decay in which an electron is emitted.
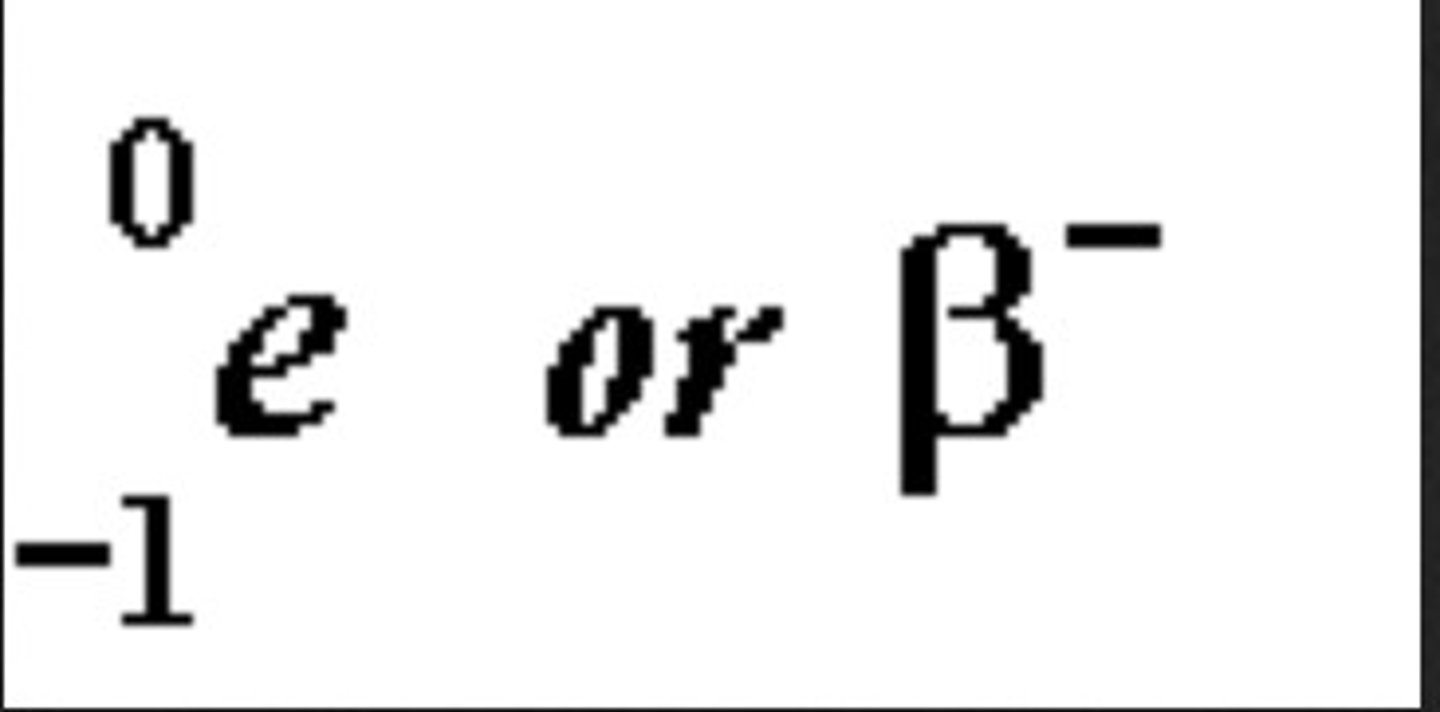
Gamma decay
radioactive decay by emission of a gamma ray
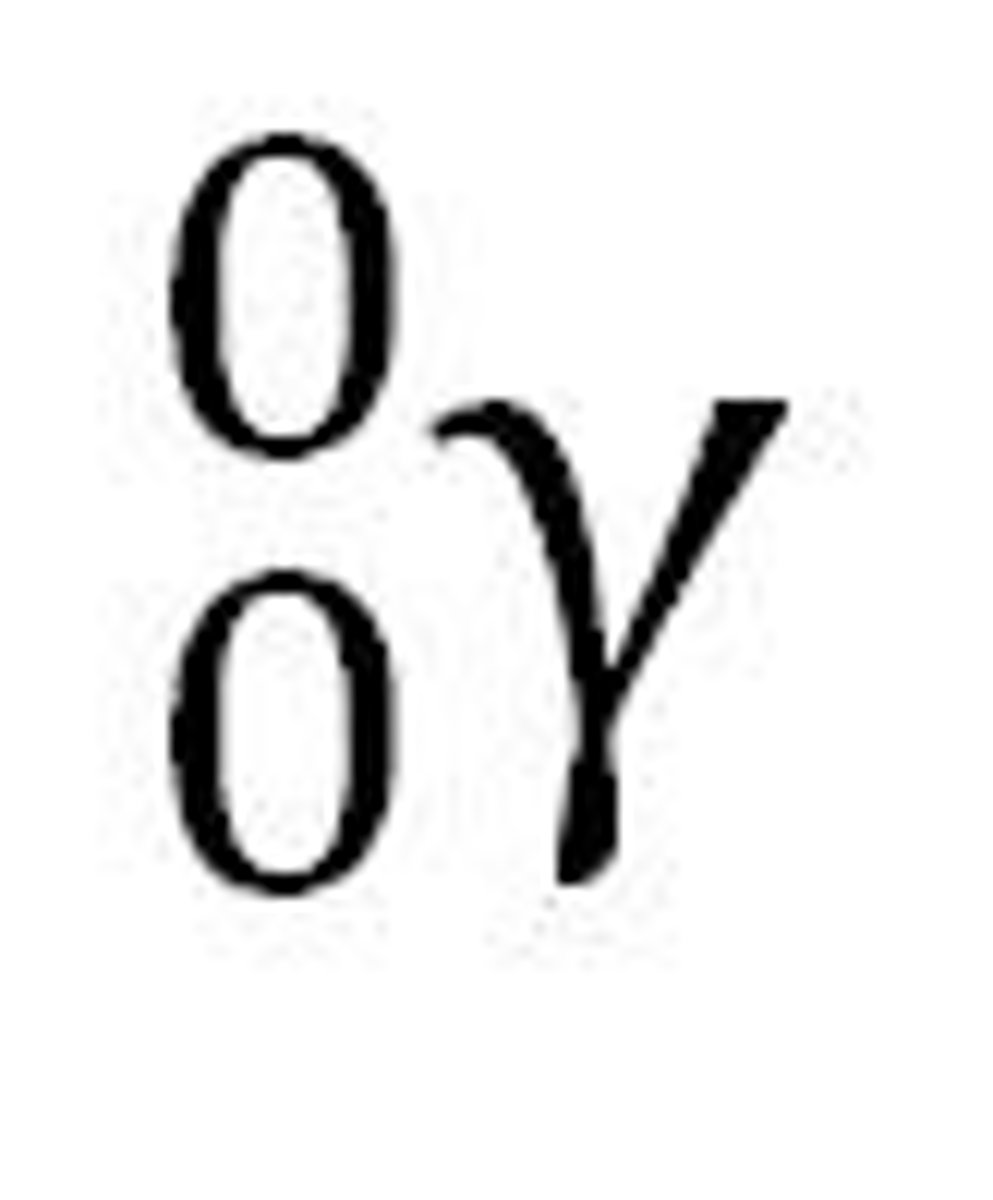
Background radiation
nuclear radiation that occurs naturally in the environment
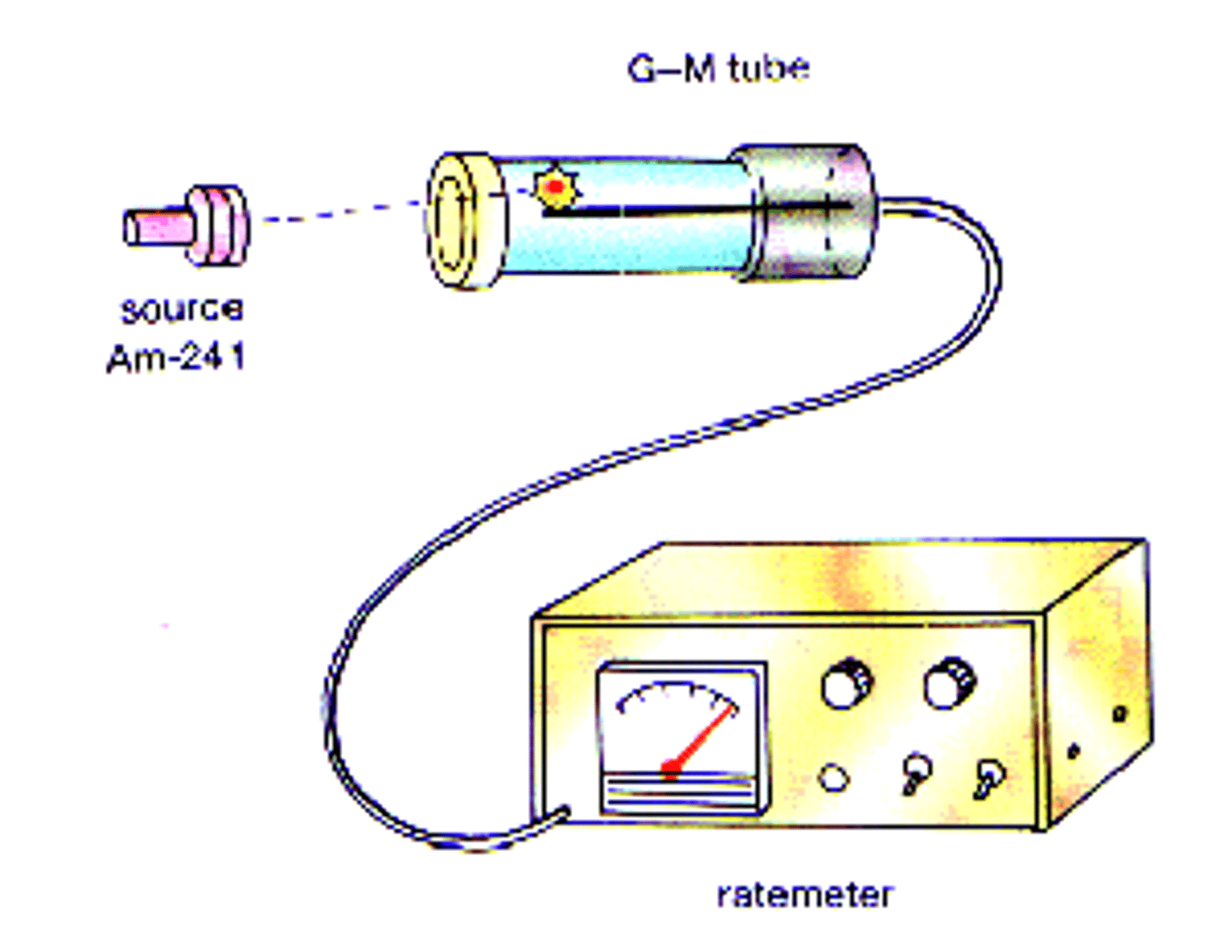
Geiger counter
instrument that measures radiation output
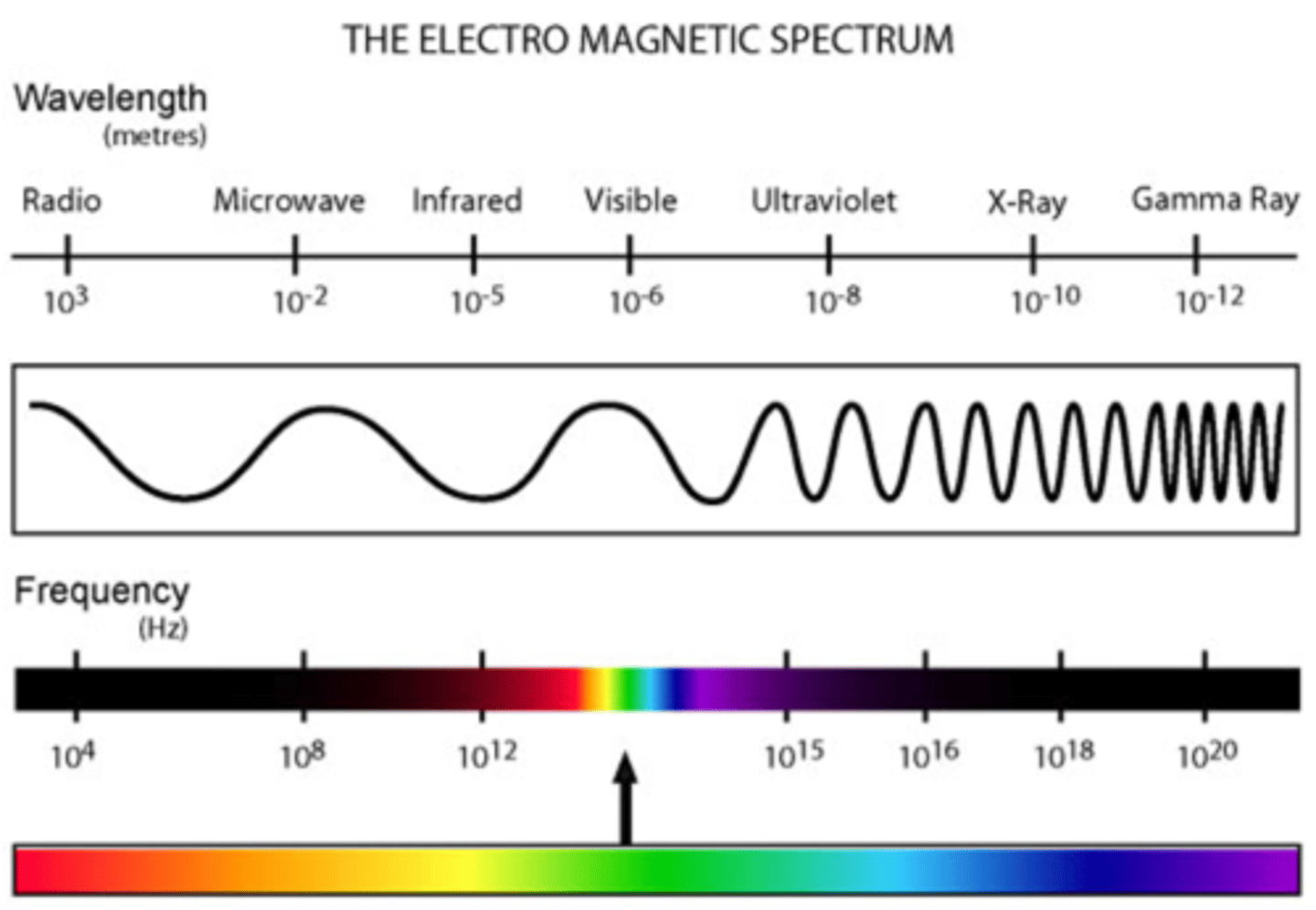
Electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space