Biology 1.1 Enzymes
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are enzymes?
They are biological catalysts. These biological catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently changed themselves.
What is an advantage of enzymes in the body?
They enable cellular reactions to take place at lower temperatures.
What group of chemicals do enzymes belong to?
Proteins.
Describe how DNA controls the production of a specific enzyme (Higher).
DNA codes for a specific sequence of amino acids.
The order of amino acids determines how the enzyme folds and its structure.
The shape of the enzyme determines its function.
What is the chemical that an enzyme works on called?
Substrate.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region of an enzyme to which a substrate molecule binds, and the reaction takes place.
Why are enzymes described as having a ‘high specificity’ for their substrate?
Only substrates with a specific, complementary shape can fit into an enzyme’s active site.
What must happen between an enzyme and its substrate for a reaction to occur?
Enzyme and substrate must collide.
Describe the ‘lock and key’ model (Higher).
Substrate collides with the active site of an enzyme.
Substrate binds, enzyme-substrate complex forms.
Substrate is converted to products.
Products are released from the active site, which is now free to bind to another substrate.
What factors affect the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction?
Temperature
pH
Explain how increasing temperature initially affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
As temperature increases, molecules have more kinetic energy.
Movement of molecules increases.
Probability of a successful collision increases.
More enzyme-substrate complexes form.
Rate of reaction increases.
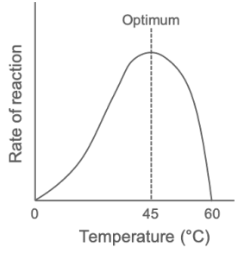
Explain how increasing temperature above the optimum affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
Temperature increases above the optimum.
Increased vibrations break bonds in the enzyme’s structure.
The active site changes shape, and the enzyme is denatured.
No more enzyme-substrate complexes can form.
Rate of reaction decreases.
Draw a graph to show the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
Explain how pH affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
Enzymes have an optimum pH.
pH shifts from the optimum.
Bonds in the enzyme’s structure are altered.
The active site changes shape, and the enzyme is denatured.
Rate of reaction decreases.
Draw a graph to show the effect of increasing pH on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
pH