Chapter 3 - Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Democritus
Who coined the term "atom", which means "indivisible"?
2
New cards
Aristotle
Who did not believe in atoms and believed that all matter was continuous?
3
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass, Law of Definite Proportions, Law of Multiple Proportions
What are the 3 laws the describe how matter behaves in chemical reactions?
4
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
Law that states that matter is neither created or destroyed during ordinary chemical reactions of physical changes.
5
New cards
matter, created, destroyed, chemical, physical
Law of Conservation of Mass - states that _____________________ is neither _____________________ or _____________________ during ordinary _____________________ reactions or _____________________ changes.
6
New cards
Law of Multiple Proportions
Law that states that if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a small ratio of whole numbers.
7
New cards
elements, proportions, size
Law of Definite Proportions - states a chemical compound contains the same _________________ in exactly the same ______________________ by mass regardless of the ___________ of the sample or source of the compound.
8
New cards
Law of Definite Proportions
Law that states a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound.
9
New cards
different, elements, small, whole
Law of Multiple Proportions - states that if two or more _____________________ compounds are composed of the same two _____________________, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a _____________ ratio of _____________ numbers.
10
New cards
atoms, size, mass, properties
Summary of Dalton's Theory:
1) ALL matter is composed of extremely small particles called _____________. (✓)
2) Atoms of a given element are identical in __________, ____________, and other ____________; Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. (x)
3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. (x)
4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. (✓)
5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. (✓)
1) ALL matter is composed of extremely small particles called _____________. (✓)
2) Atoms of a given element are identical in __________, ____________, and other ____________; Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. (x)
3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. (x)
4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. (✓)
5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. (✓)
11
New cards
differ, subdivided, different, combined
Summary of Dalton's Theory:
1) ALL matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. (✓)
2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms of different elements ______________ in size, mass, and other properties. (x)
3) Atoms cannot be ______________, created, or destroyed. (x)
4) Atoms of ______________ elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. (✓)
5) In chemical reactions, atoms are ______________, separated, or rearranged. (✓)
1) ALL matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. (✓)
2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms of different elements ______________ in size, mass, and other properties. (x)
3) Atoms cannot be ______________, created, or destroyed. (x)
4) Atoms of ______________ elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. (✓)
5) In chemical reactions, atoms are ______________, separated, or rearranged. (✓)
12
New cards
divisible, masses, matter, properties
Modern Atomic Theory:
a) Atoms ARE _____________________ into even smaller pieces (protons, neutrons, electrons)
b) A given element can have atoms with different _______________ (isotopes).
c) ALL _______________ is composed of atoms
d) Atoms of any one element differ in ____________________ from atoms of another element.
a) Atoms ARE _____________________ into even smaller pieces (protons, neutrons, electrons)
b) A given element can have atoms with different _______________ (isotopes).
c) ALL _______________ is composed of atoms
d) Atoms of any one element differ in ____________________ from atoms of another element.
13
New cards
Atom
Smallest complete part of an element that can exist alone or in combination with others.
14
New cards
Nucleus
Part of an atom:
Positively charged central part of the atom
- Very dense
1 x 10^-13 cm in diameter
Positively charged central part of the atom
- Very dense
1 x 10^-13 cm in diameter
15
New cards
Electron cloud
Part of an atom:
Negatively charged region around the nucleus where electrons exist
Negatively charged region around the nucleus where electrons exist
16
New cards
(electrically) neutral
What is the charge of all atoms?
17
New cards
Total negative charge of the electron cloud
The total POSITIVE charge of the NUCLEUS of an atom equals what?
18
New cards
electrons
What are located in the electron cloud?
19
New cards
negative, light, shells, energy levels, equal
Electrons:
- __________________ charge
- Very _________________ particles (9.109 x 10^-28 g); (1/1837th the mass of a proton)
- They exist in regions called _________________ or _________________ ___________________
- They are always _______________ to the number of protons in the nucleus
*All electrons are IDENTICAL*
- __________________ charge
- Very _________________ particles (9.109 x 10^-28 g); (1/1837th the mass of a proton)
- They exist in regions called _________________ or _________________ ___________________
- They are always _______________ to the number of protons in the nucleus
*All electrons are IDENTICAL*
20
New cards
Shell/Energy level
Regions of probable locations of electrons [K-L-M-O-P-Q]
*All electrons are IDENTICAL*
*All electrons are IDENTICAL*
![Regions of probable locations of electrons [K-L-M-O-P-Q]
*All electrons are IDENTICAL*](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/edb3ad44224b4409a55ce8bd2ce9c432.jpg)
21
New cards
JJ Thomson, Robert Millikan
Discovery of the Electron:
1) ________________________ - cathode-ray tube experiments measured the charge-mass ratio of an electron
2) ________________________ - oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the mass of an electron*
1) ________________________ - cathode-ray tube experiments measured the charge-mass ratio of an electron
2) ________________________ - oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the mass of an electron*
22
New cards
cathode-ray tube, charge-mass
Discovery of the Electron:
1) J.J. Thomson - ___________________________________ experiments measured the _______________________ ratio of an electron
2) Robert Millikan - oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the mass of an electron*
1) J.J. Thomson - ___________________________________ experiments measured the _______________________ ratio of an electron
2) Robert Millikan - oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the mass of an electron*
23
New cards
oil drop, charge, mass
Discovery of the Electron:
1) J.J. Thomson - cathode-ray tube experiments measured the charge-mass ratio of an electron
2) Robert Millikan - ________ ______________ experiment measured the ________________ of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the _____________ of an electron*
1) J.J. Thomson - cathode-ray tube experiments measured the charge-mass ratio of an electron
2) Robert Millikan - ________ ______________ experiment measured the ________________ of an electron
*Both discovered enabled scientists to determine the _____________ of an electron*
24
New cards
Ernest Rutherford, 1911
Which scientist discovered the nucleus and in what year?
25
New cards
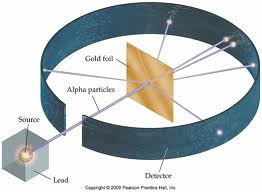
Gold Foil Experiment
What experiment did Ernest Rutherford conduct in 1911 that led to the discovery of a very DENSLY packed bundle of matter with a POSITIVE charge (nucleus)?
26
New cards
protons, neutrons
What are the nuclear particles?
27
New cards
positive, heavy, electrons, nucleus
Protons (p+):
a) _______________ charge (equal in magnitude to the charge of an electron)
b) Relatively _______________ particles (1.673 x 10^-24 g)
c) Always EQUAL the number of _______________
d) Found in the _______________
a) _______________ charge (equal in magnitude to the charge of an electron)
b) Relatively _______________ particles (1.673 x 10^-24 g)
c) Always EQUAL the number of _______________
d) Found in the _______________
28
New cards
neutral, proton, nucleus
Neutrons (n^0):
a) No electrical charge (________________)
b) Same weight as a ________________ (1.675 x 10^-24 g)
c) Found in the ________________
a) No electrical charge (________________)
b) Same weight as a ________________ (1.675 x 10^-24 g)
c) Found in the ________________
29
New cards
repel, attract
LIKE charges ________________ and UNLIKE charges ________________.
30
New cards
Nuclear Forces
Short range p+ -- p+ , p+ -- n^0 , n^0 -- n^0, attraction forces which hold the nucleus together
- The nucleus accounts for most an atom's mass, while most of an atom's volume is due to the size of its electron cloud
- The nucleus accounts for most an atom's mass, while most of an atom's volume is due to the size of its electron cloud
31
New cards
nucleus, mass, volume, cloud
Nuclear forces - short range p+ -- p+ , p+ -- n^0 , n^0 -- n^0, attraction forces which hold the _______________ together
- The NUCLEUS accounts for most an atom's __________, while most of an atom's ______________ is due to the size of its electron ___________
- The NUCLEUS accounts for most an atom's __________, while most of an atom's ______________ is due to the size of its electron ___________
32
New cards
Atomic Number (Z)
Refers to the number of protons found in the nucleus of an element
*In the periodic table, the elements are placed from left to right in order of INCREASING atomic numbers*
*____________________________ = # of protons = # of electrons*
*In the periodic table, the elements are placed from left to right in order of INCREASING atomic numbers*
*____________________________ = # of protons = # of electrons*

33
New cards
Mass Number
Refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
34
New cards
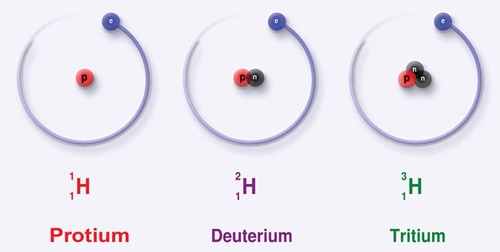
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different masses; They differ in their number of NEUTRONS
35
New cards
hyphen, nuclear, mass, atomic
Methods of Designating Isotopes:
1. _______________ Notation: Hydrogen -- 3 (3 refers to the mass number)
2. ________________ Symbol: mass # is superscript and the atomic # if subscript
*Number of neutrons = ___________ # - ___________ number
1. _______________ Notation: Hydrogen -- 3 (3 refers to the mass number)
2. ________________ Symbol: mass # is superscript and the atomic # if subscript
*Number of neutrons = ___________ # - ___________ number
36
New cards
Atomic Mass Unit (AMU)
A unit of the relative mass scale.
1 amu = 1/12 of C-12 = 1.660 540 2 x 10^-24 g
1 amu = 1/12 of C-12 = 1.660 540 2 x 10^-24 g
37
New cards
C-12
Which element is used to compare the atomic mass of any atom?
38
New cards
1/12
1 amu = __________ of C-12 = 1.660 540 2 x 10^-24 g
39
New cards
Atomic Mass
The mass of an atom expressed in atomic mass units.
40
New cards
Average Atomic Mass
The sum of the atomic masses of EACH isotope multiplied by the DECIMAL of its percentage abundance.
41
New cards
Avogadro's Number
The number of atoms there are in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12.
**6.022 x 10^23**
**6.022 x 10^23**
42
New cards
6.022 x 10^23
What is Avogadro's Number?
43
New cards
Mole (mol)
The amount of substance that contains the Avogadro's number of chemical units
- The SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
**1 ___________________ = 6.022 x 10^23**
- The SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
**1 ___________________ = 6.022 x 10^23**
44
New cards
Molar Mass
(Gram-atomic-weight): the mass in GRAMS of one mole of an element
- Contain equal numbers of atoms
- Has the units of grams per mole (g/mol)
- Contain equal numbers of atoms
- Has the units of grams per mole (g/mol)