PSYC 333 test 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:50 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
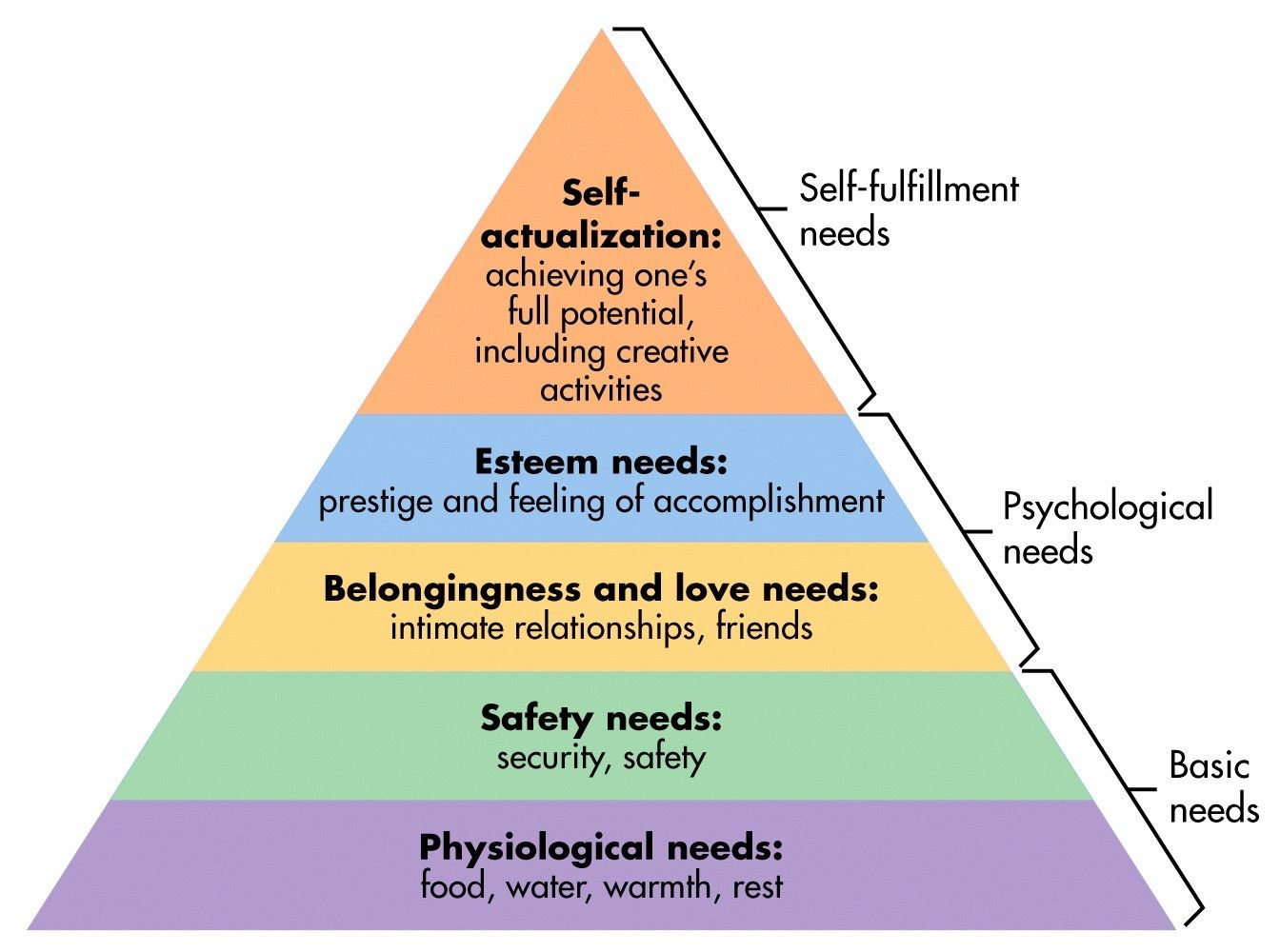
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
* Self-actualization
* esteem needs
* belongingness and love needs
* safety needs
* physiological needs
* esteem needs
* belongingness and love needs
* safety needs
* physiological needs
2
New cards
Big 5 personality traits
* openness
* conscientiousness
* extroversion
* agreeableness
* neuroticism
* conscientiousness
* extroversion
* agreeableness
* neuroticism
3
New cards
Asch’s Conformity Study
How individuals yielded to or defied a majority group and the effect of such influences on beliefs and opinions.
\
**groups had to judge lines*\*
**participants would conform their answers even if they knew it was wrong in order to get along with the group (need to fit in)*\*
\
**groups had to judge lines*\*
**participants would conform their answers even if they knew it was wrong in order to get along with the group (need to fit in)*\*
4
New cards
Bystander Effect
The diffusion of responsibility in emergency situations; the more people the less you feel ‘I’ need to do something (power of the situation)
5
New cards
Stanford Prison Experiment
Two-week simulation of a prison environment that examined the effects of situational variables on participants' reactions and behaviours.
RESULTS: Both groups assumed their roles (the role given dictated their behaviours), guards went overboard (became very aggressive/violent), and prisoners acted like inmates (go by their #).
\
CRITICISMS: unethical, demand characteristics (guards pressured to act a certain way), and more dramatic example of the power of the situation over a science.
\
*****randomly assigned to be guards or inmates*********
RESULTS: Both groups assumed their roles (the role given dictated their behaviours), guards went overboard (became very aggressive/violent), and prisoners acted like inmates (go by their #).
\
CRITICISMS: unethical, demand characteristics (guards pressured to act a certain way), and more dramatic example of the power of the situation over a science.
\
*****randomly assigned to be guards or inmates*********
6
New cards
Person-Situation Debate (personality vs. social psychology)
* personality psychology: behaviour is determined by personality (internal)
* social psychology: behaviour is determined by social situation (extrernal)
\
*****interactional consensus we must understand both and their connection to understand behaviour; behaviour = interaction between personality and the situation*********
* social psychology: behaviour is determined by social situation (extrernal)
\
*****interactional consensus we must understand both and their connection to understand behaviour; behaviour = interaction between personality and the situation*********
7
New cards
Argument towards behaviour due to situation
* correlation of between person’s personality and specific behaviour tested is 0.3 (15% left to personality)
* consistency in behaviour across situations is low
* consistency in behaviour across situations is low
8
New cards
Argument towards behaviour due to person
* personality intuitively exists
* stable across time
* predicts behaviour in general pretty well, but not accurate for behaviour at any one given time
* correlation between well-established situational variables and behaviour is 0.3-0.4 (similar to situation)
* stable across time
* predicts behaviour in general pretty well, but not accurate for behaviour at any one given time
* correlation between well-established situational variables and behaviour is 0.3-0.4 (similar to situation)
9
New cards
Self-concept
A knowledge representation that contains knowledge about us, including our beliefs about personality traits, physical characteristics, abilities, values, goals, and roles, as well as the knowledge that we exist as individuals.
\
****everything a person claims as ‘me’**\*\*
\
****everything a person claims as ‘me’**\*\*
10
New cards
Distinctiveness Theory
A person’s unique, distinctive characteristics are more salient to them than characteristics that they have in common with others.
\
\*what comes to mind first
\*distinctive characteristics are more valuable in distinguishing yourself from others
\
\*what comes to mind first
\*distinctive characteristics are more valuable in distinguishing yourself from others
11
New cards
Distinctiveness Theory Evidence 1: Atypical Attributes (McGuire & Padawer, 1976)
* 6th grades complete “who am i” exercise
* students atypical in age, hair color, eye color, weight and birthplace mentioned these attributes more than other characteristics
* students atypical in age, hair color, eye color, weight and birthplace mentioned these attributes more than other characteristics
12
New cards
Distinctiveness Theory Evidence 2: Ethnicity/Race (McGuire & Padawer, 1976)
* class of 6th graders
* mostly white
* majority of hispanic and black students use this to describe themselves
* difference less salient traits doesn’t come to mind
* mostly white
* majority of hispanic and black students use this to describe themselves
* difference less salient traits doesn’t come to mind
13
New cards
Dynamic self -concept/ Working self-concept
The subset of self-knowledge that is accessible at any one moment
\
\*self-concept is malleable
\*Markus & Wurf
\
\*self-concept is malleable
\*Markus & Wurf
14
New cards
Associative Networks
Knowledge is organized as a metaphorical network of cognitive concepts interconnected by links
\
\*links between concepts vary in strength
\
\*links between concepts vary in strength
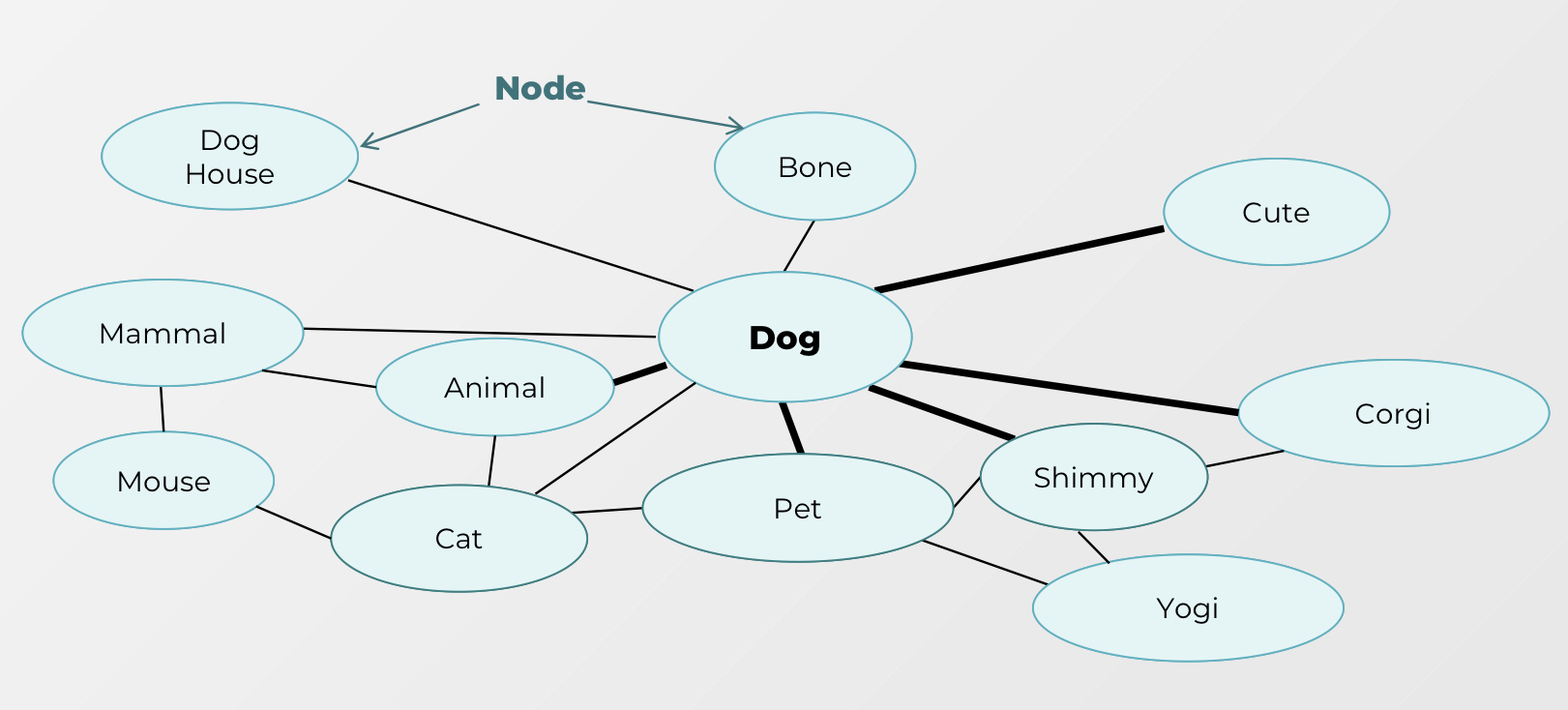
15
New cards
spreading activation
when one piece of knowledge is activated, other concepts that are linked with it are also activated
\
**especially those that are strongly linked (they will be activated more quickly)*\*
\
**especially those that are strongly linked (they will be activated more quickly)*\*
16
New cards
Accessibility of Self-Knowledge
1. Frequency of activation (have more cognitive accessibility)
2. Recency of activation→working self-concept (at the front of mind)
17
New cards
Does situational activated working self-concept impact behaviour?: Evidence 1 (Frazio, Effrein, Falender, 1981)
* participants told they would do a questionnaire to “reveal elements of personality”
* Experimentally manipulated extroversion (what would u do if u want to liven things up at a party) vs. introversion (what things do u dislike about loud parties) \*\****no matter what you are the situations prime E or I*********
\
RESULTS: what participants were primed with had an impact
\*those primed with E described themselves as more E and acted more E in the situation (spoke longer & sat closer to the confederate)
\*shows that working self-concept depends on situational activation and that it influences behaviour (self-monitoring)
* Experimentally manipulated extroversion (what would u do if u want to liven things up at a party) vs. introversion (what things do u dislike about loud parties) \*\****no matter what you are the situations prime E or I*********
\
RESULTS: what participants were primed with had an impact
\*those primed with E described themselves as more E and acted more E in the situation (spoke longer & sat closer to the confederate)
\*shows that working self-concept depends on situational activation and that it influences behaviour (self-monitoring)
18
New cards
Does situational activated working self-concept impact behaviour?: Evidence 2 (Frazio, Effrein, Falender, 1981)
* participants led to believe doing 2 studies on “language ability”
* 1st task: scrambled sentence task (primed with being rude pr polite)
* participants told they must wait for 2nd task because experimenter helping other “participants” with task
* ACTUAL ?: how long does the participant wait to interrupt experimenter and confederate?
\
RESULTS: 65% in rude prime interrupted vs 15% in polite prime; and those in rude prime interrupted 3 minutes faster
* 1st task: scrambled sentence task (primed with being rude pr polite)
* participants told they must wait for 2nd task because experimenter helping other “participants” with task
* ACTUAL ?: how long does the participant wait to interrupt experimenter and confederate?
\
RESULTS: 65% in rude prime interrupted vs 15% in polite prime; and those in rude prime interrupted 3 minutes faster
19
New cards
self-schemata / Core-self
Aspects of the self that are more central that then guide how we process new information about the self.
\
****explain consistency in self-descriptions and behaviours across situations. → suggests how core self-concept can change**\*\*
****all new info related to self is filtered through this**\*\*
\
****explain consistency in self-descriptions and behaviours across situations. → suggests how core self-concept can change**\*\*
****all new info related to self is filtered through this**\*\*
20
New cards
Study evidence for Self-schemata/Core-self (Markus, 1977)
* which traits 1. describe you and 2. are important to you?
* independent vs. dependent
* categorized participants by Schematic(extreme on attribute + very important) or Aschematic (attribute does not apply).
* participants come back to lab 3-4 weeks later
* participants complete me/not me task (traits presented one at a time)
* they are asked to answer as quickly as possible
\
RESULTS:
core self traits = faster RTs
Reaction time indicates how accessible a trait is to you (faster RTs = more frequently activated and slower RTs = less frequently activated)
dependents = faster RTs for dependent traits
independents = faster RTs for independent traits
* independent vs. dependent
* categorized participants by Schematic(extreme on attribute + very important) or Aschematic (attribute does not apply).
* participants come back to lab 3-4 weeks later
* participants complete me/not me task (traits presented one at a time)
* they are asked to answer as quickly as possible
\
RESULTS:
core self traits = faster RTs
Reaction time indicates how accessible a trait is to you (faster RTs = more frequently activated and slower RTs = less frequently activated)
dependents = faster RTs for dependent traits
independents = faster RTs for independent traits
21
New cards
Self-perception theory
some aspects of our self-concept are formed by making inferences about ourselves while observing our own behaviour
22
New cards
The role of social interactions (3 concepts)
self-concept critically depends on social interactions (there is not self without other people)
\
1. looking glass self
2. social comparison
3. social identity
\
1. looking glass self
2. social comparison
3. social identity
23
New cards
looking glass self
how we see ourselves comes from how others see us
* we internalize their judgments of us
* rely on how we think other see us
\
EVIDENCE: how we see ourselves is often similar to how other people, especially close others, see us (Beer et al., 2013)
* we internalize their judgments of us
* rely on how we think other see us
\
EVIDENCE: how we see ourselves is often similar to how other people, especially close others, see us (Beer et al., 2013)
24
New cards
social comparison
We compare ourselves with others to form conclusions about our relative standing on attributes, abilities, opinions, etc..
\
EX: this person is like this ….. so then I must be more like this
(I must be more extroverted because I like have people over more than my partner who is introverted)
\
EX: this person is like this ….. so then I must be more like this
(I must be more extroverted because I like have people over more than my partner who is introverted)
25
New cards
social identity theory
We draw part of our identity from the social groups we belong to
* important social groups we belong to
* broad (ethnic) or specific (family)
* EX: my family is E, because im part of this group i must also be E
* important social groups we belong to
* broad (ethnic) or specific (family)
* EX: my family is E, because im part of this group i must also be E
26
New cards
Where does our sense of self come from?
* self-perception
* largely based on social interactions (looking glass, social comparison, social identity)
* largely based on social interactions (looking glass, social comparison, social identity)
27
New cards
whats the difference independent vs. dependent variables?
* Independent variable (x): the cause
* Dependent variable (y): the effect
\
**independent variable affects the dependent variable*\*
* Dependent variable (y): the effect
\
**independent variable affects the dependent variable*\*
28
New cards
How does extroversion affect talkativeness?
Extroversion is associated with more talkativeness (main effect)
* extroversion (independent variable)
* talkativeness (dependant variable)
* extroversion (independent variable)
* talkativeness (dependant variable)
29
New cards
Interaction Effect = Moderation
The relationship between the independent and dependent variable is affected by another variable (moderator)
\
\*A moderator influences the strength or direction of a relationship between variables\*
\
\*A moderator influences the strength or direction of a relationship between variables\*
30
New cards
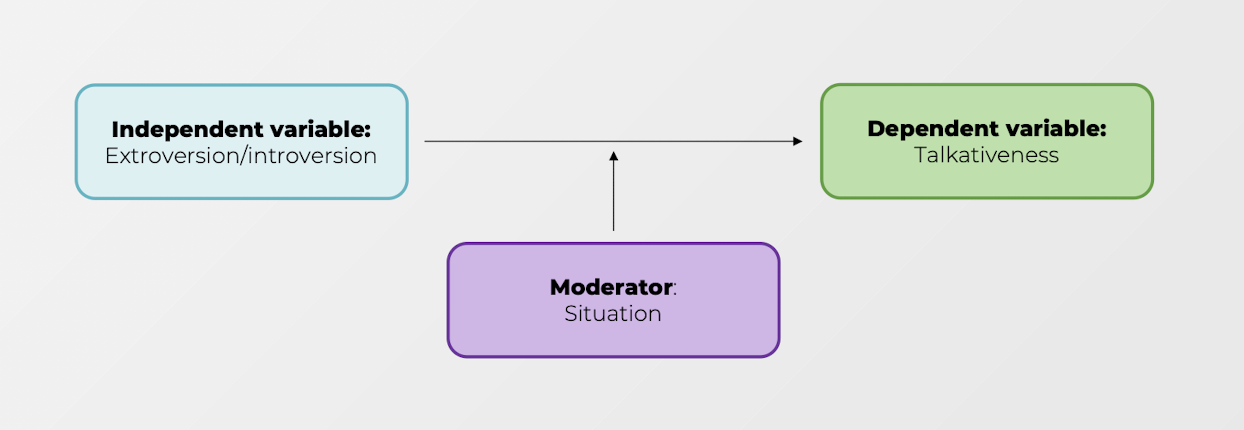
Does the situation moderate the effect of extroversion on talkativeness? (framing)
* Extroversion has more of an effect on talkativeness when at a party and less of an effect when with close friends
* More social media use leads to worse well-being, but only for adolescents
* The strength of the relationship between work experience and salary depends on gender
* More social media use leads to worse well-being, but only for adolescents
* The strength of the relationship between work experience and salary depends on gender
31
New cards
Self-concept contains? (ARRAG)
* Attributes
* roles
* relationships
* activities
* goals
* roles
* relationships
* activities
* goals
32
New cards
Self-complexity
* High self-complexity: many self-aspects that are relatively distinct from each other
* Low self-complexity: few self-aspects that have a high degree of overlap with each other
* Low self-complexity: few self-aspects that have a high degree of overlap with each other
33
New cards
People’s self-concepts differ in 2 ways; what are they?
1. # of self-aspects (attributes, roles, relationships, goals, etc.)
2. degree to which these self-aspects are distinct from each other (overlap)
34
New cards
What are the Implications of Self-Complexity?
* affective spillover
* affective extremity for low self-complexity
* high self-complexity as a stress buffer
* affective extremity for low self-complexity
* high self-complexity as a stress buffer
35
New cards
Affective Spillover
Because of links between self-aspects, emotions associated with one self-aspect will “spillover” to other self-aspects
\
****more affective spillover for people with low self-complexity because of high degree of overlap between self-aspects****
\*more aspects & fewer connections = less spillover (less emotionally reactive because it affects global self-esteem less)
\*negative affect not only activates other connecting aspects but spreads the negative affect to them aswell
\
****more affective spillover for people with low self-complexity because of high degree of overlap between self-aspects****
\*more aspects & fewer connections = less spillover (less emotionally reactive because it affects global self-esteem less)
\*negative affect not only activates other connecting aspects but spreads the negative affect to them aswell
36
New cards
Affect Extremity; how does it affect low and high self-complexity?
* Low self-complexity: Greater spillover causes more extreme emotional reactions and changes in self-esteem (In response to both negative and positive life events)
* High self-complexity: Less spillover allows for more emotional stability
* High self-complexity: Less spillover allows for more emotional stability
37
New cards
self-complexity study 1: Linville
Does self-complexity moderate the relationship between failure and emotional reactions?
* participants told they were doing an analytic task that measures intelligence
* all participants were given fake feedback
* self-complexity measured by traits (each group describes an aspect of life; can have as mean aspects and groups as you like)
* high self-complexity individuals will have many groups and aspects as well as not much overlap
* experimental manipulation: participants given fake success or failure feedback from the fake “intelligence tasks”
* the experimenters were assessing current mood and self-esteem
\
RESULTS:
Low self-complexity showed largest change in mood and self- esteem following failure/success feedback (Evidence of spillover and affective extremity)
* participants told they were doing an analytic task that measures intelligence
* all participants were given fake feedback
* self-complexity measured by traits (each group describes an aspect of life; can have as mean aspects and groups as you like)
* high self-complexity individuals will have many groups and aspects as well as not much overlap
* experimental manipulation: participants given fake success or failure feedback from the fake “intelligence tasks”
* the experimenters were assessing current mood and self-esteem
\
RESULTS:
Low self-complexity showed largest change in mood and self- esteem following failure/success feedback (Evidence of spillover and affective extremity)
38
New cards
self-complexity Study 2: Linville
Is low self-complexity also associated with more variation in mood over time?
* Method: Field study to look at swings in emotions over 2 weeks
* Self-complexity measured using trait sort (same like study 1)
* Participants completed daily emotion diary for 14 days
\
RESULTS: Low self-complexity associated with greater variation in emotion ratings over time (more fluctuation in mood over time → high high’s and low low’s)
Whereas, high S-C would have more stable emotions over time
* Method: Field study to look at swings in emotions over 2 weeks
* Self-complexity measured using trait sort (same like study 1)
* Participants completed daily emotion diary for 14 days
\
RESULTS: Low self-complexity associated with greater variation in emotion ratings over time (more fluctuation in mood over time → high high’s and low low’s)
Whereas, high S-C would have more stable emotions over time
39
New cards
can self-complexity be a stress buffer?
High in self-complexity may serve as a buffer against negative consequences of stressful life events. This may explain why some people are more resilient in the face of stress.
40
New cards
self-complexity study 3 (Linville): stress buffering
Does high self-complexity protect against the negative health effects of stress?
* Method: Measured the following at baseline and again 2 weeks later
* Self-complexity using trait sort (same like study 1&2)
* Stressful events experienced by student
* Indicators of negative health consequences: (Depression, Perceived stress, Illness symptoms)
\
Results:
* Following stressful events, people high in self-complexity(vs.low in self- complexity) showed less depression, less perceived stress, and Fewer physical symptoms of illness (including flu!).
* No difference in # of stressful events experienced between low and high self- complexity people however, those in high self-complexity have a buffer against negative effects of stress which provides with resilience and less vulnerability to stress-related depression and illness.
* Method: Measured the following at baseline and again 2 weeks later
* Self-complexity using trait sort (same like study 1&2)
* Stressful events experienced by student
* Indicators of negative health consequences: (Depression, Perceived stress, Illness symptoms)
\
Results:
* Following stressful events, people high in self-complexity(vs.low in self- complexity) showed less depression, less perceived stress, and Fewer physical symptoms of illness (including flu!).
* No difference in # of stressful events experienced between low and high self- complexity people however, those in high self-complexity have a buffer against negative effects of stress which provides with resilience and less vulnerability to stress-related depression and illness.
41
New cards
What 3 aspects does self-complexity have important consequences on?
1. mood
2. self-esteem
3. vulnerability to stress-induced health outcomes
42
New cards
Is there mixed evidence for self-complexity as a stress buffer? (Rafaeli-Mor & Steinberg, 2002)
Yes, review of 24 studies examining buffering effects of self-complexity. 7 studies support stress-buffering hypothesis, 4 found reverse impact and 13 didn’t show any effect.
43
New cards
Why mixed evidence of stress buffering?
1. Differences in well-being measure (dependent variable)→Positive effect of self-complexity on mood and emotional stability but more mixed results when measuring self-esteem or depression.
2. One part of definition of self-complexity is more important than the other (independent variable)
* # of self-aspects → + effect on well-being
* Degree of distinction between self-aspects → no effect on well-being
3. Integration of self-aspects also matters
* Having high self-complexity (many self-aspects) may only be helpful if self-aspects are well-integrated into a clear and coherent sense of self
* If someone has many self-aspects BUT has an unclear, incoherent sense of self, then high self-complexity may lead to confusion about self
44
New cards
Does having a clear sense of self matter?
Having a clear sense of who you are as a person really does matter → high S-C can be problematic if you’re not sure how to integrate these different elements of yourself.
45
New cards
Self-concept Clarity (SCC)
The extent to which the contents of the self-concept are clearly defined, consistent, and stable. → Reflects the extent to which you feel like you know who you are
\
*****having a clear idea of who you are*********
\
*****having a clear idea of who you are*********
46
New cards
Was Remi (detail-oriented, hard-working, responsible) high or low in SCC?
All characteristics fit together → therefore, High SCC
47
New cards
Was Pablo (creative, spontaneous, expressive OR unmotivated, needy, uninspired) high or low in SCC?
Not sure who he is as a person; sees himself different w/ different people and situations → therefore Low SCC.
48
New cards
Self-complexity vs. SCC
* SCC is unrelated to self-complexity
* A person could be high in self-complexity but low in SCC (many different aspects but lacking in clarity/consistency and coherence btw aspects)
OR…..
* low in self-complexity but high in SCC (few aspects but high degree of clarity/consistency and coherence btw aspects)
* A person could be high in self-complexity but low in SCC (many different aspects but lacking in clarity/consistency and coherence btw aspects)
OR…..
* low in self-complexity but high in SCC (few aspects but high degree of clarity/consistency and coherence btw aspects)
49
New cards
SCC and Well-being
High SCC is important for well-being associated with:
* Less neuroticism (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Less rumination about the self (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Less loneliness (Light & Visser, 2013)
* Lower feelings of depression and perceived stress (Treadgold,1999)
* Higher self-esteem (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Higher perception of meaning in life (Bigler et al., 2001)
* Higher general life-satisfaction (Ritchie et al., 2011)
* Less neuroticism (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Less rumination about the self (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Less loneliness (Light & Visser, 2013)
* Lower feelings of depression and perceived stress (Treadgold,1999)
* Higher self-esteem (Campbell et al., 1996)
* Higher perception of meaning in life (Bigler et al., 2001)
* Higher general life-satisfaction (Ritchie et al., 2011)
50
New cards
SCC and COVID-19 (Alessandri et al., 2021)
Is SCC a protective factor that promotes more adaptive responses during times of uncertainty?
* Method: Longitudinal daily diary study during COVID-19 outbreak in Italy in March 2020 (participants were already being followed with daily diaries pre-covid)
* Experimenters monitored negative emotions and measured SCC
\
RESULTS:
On average, high SCC people experienced fewer negative emotions compared to low SCC people → no matter what day post lockdown.
* Method: Longitudinal daily diary study during COVID-19 outbreak in Italy in March 2020 (participants were already being followed with daily diaries pre-covid)
* Experimenters monitored negative emotions and measured SCC
\
RESULTS:
On average, high SCC people experienced fewer negative emotions compared to low SCC people → no matter what day post lockdown.
51
New cards
Is SCC important for well-being? How about in times of intense stress?
Yes SCC is important for well-being and it also appears to facilitate more adaptive responses during times of intense uncertainty/stress
52
New cards
What fosters or lowers SCC?
changes with age/time throughout life (unstable personality trait)
* Such as changes in social roles (jobs, relationships, hobbies) → role changes cause uncertainty (periods we are less sure about ourselves)
* Such as changes in social roles (jobs, relationships, hobbies) → role changes cause uncertainty (periods we are less sure about ourselves)
53
New cards
SCC and role transitions (Slotter & Walsh, 2016)
Do role changes lead to lower SCC?
* Methods: Collected writing samples from an online forum for new parents
Research assistants analyzed and rated writing for:
* Amount of self-concept change: “To what extent has the transition to parenthood changed the participants’ perceptions of who he/she is as a person – the content of his/her self-concept?”
* Positivity of self-change: “How positive would you rate the participant’s feelings about his/her experienced role transition?”
* Degree of self-concept confusion (more self-concept confusion = lower SCC): “To what extent is the participant confused or uncertain about who they are as a person/ about their identity?”
* Methods: Collected writing samples from an online forum for new parents
Research assistants analyzed and rated writing for:
* Amount of self-concept change: “To what extent has the transition to parenthood changed the participants’ perceptions of who he/she is as a person – the content of his/her self-concept?”
* Positivity of self-change: “How positive would you rate the participant’s feelings about his/her experienced role transition?”
* Degree of self-concept confusion (more self-concept confusion = lower SCC): “To what extent is the participant confused or uncertain about who they are as a person/ about their identity?”
54
New cards
Self change x Positivity (Slotter & Walsh, 2016)
* SCC depends on amount of self-change AND how positive the person feels about the change
* For those who felt positively about the role transition, no relationship between amount of self-change and SCC
* For those who felt less positive about the role transition, more self- change associated with less SCC (more self-concept confusion)
\
**only plays huge role if you feel negative about the change*\*
**same results across different life changes*\*
* For those who felt positively about the role transition, no relationship between amount of self-change and SCC
* For those who felt less positive about the role transition, more self- change associated with less SCC (more self-concept confusion)
\
**only plays huge role if you feel negative about the change*\*
**same results across different life changes*\*
55
New cards
What are the implications of the relationship between SCC and role transitions?
Role transitions may alter the organization of self-concept (ex: SCC).
* Role entries AND exits predict lower SCC if the person doesn’t feel particularly positive about the way the new role has changed them → how they feel about the change is very important.
* Role entries AND exits predict lower SCC if the person doesn’t feel particularly positive about the way the new role has changed them → how they feel about the change is very important.
56
New cards
Does culture impact the self?
Yes, the way we think about ourselves is going to be heavily influenced by the context we find ourselves in (culture is a very powerful context that shapes our sense of self behaviour).
57
New cards
What is culture?
Culture is a loosely integrated system of ideas, practices, and social institutions that enable coordination of behaviour in a population. (nationality, ethnicity)
58
New cards
Is canada/USA an individualistic or collectivistic culture?
Individualistic
59
New cards
Is china/korea/japan an individualistic or collectivistic culture?
collectivistic
60
New cards
What are social orientations of individualistic cultures?
* Common in Western countries
* Attending to self, self-assertion, uniqueness
* Distinguishing self from others
* “the squeaky wheel gets the grease”
* Personal identity (traits, states, behaviors)
* Self-interest, personal happiness
* “My way”
* Attending to self, self-assertion, uniqueness
* Distinguishing self from others
* “the squeaky wheel gets the grease”
* Personal identity (traits, states, behaviors)
* Self-interest, personal happiness
* “My way”
61
New cards
What are social orientations of collectivistic cultures?
* Common in East Asian countries
* Attending to group, group harmony, fitting in
* Fitting self with others
* “the nail that stands out gets pounded down”
* Collective identity (social roles and relationships)
* Social happiness, suspension of self-interest
* “The right way”
* Attending to group, group harmony, fitting in
* Fitting self with others
* “the nail that stands out gets pounded down”
* Collective identity (social roles and relationships)
* Social happiness, suspension of self-interest
* “The right way”
62
New cards
What kind of self-concept does an individualistic culture promote?
Independent self-concept
63
New cards
What kind of self-concept does a collectivistic culture promote?
interdependent self-concept
64
New cards
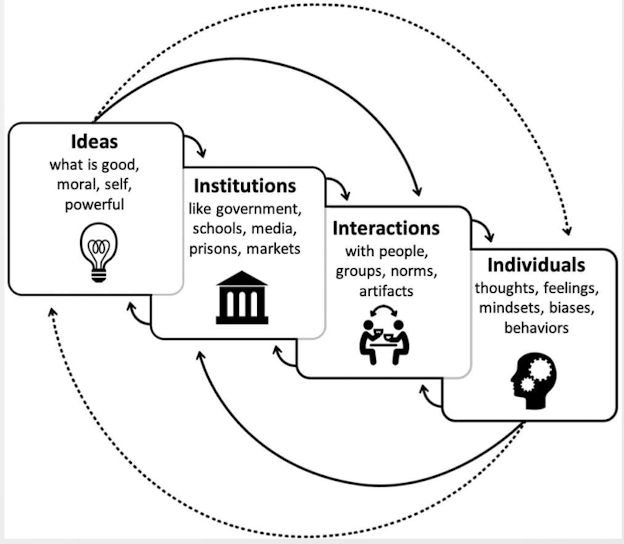
How Do Cultural Differences Shape the Individual?
Important function of culture is to provide guidance for what is normal and how to be a person.
* Individualistic cultures: prioritize tasks that focus on personal preferences, emotions, and goals
* Collectivistic cultures: prioritize tasks that focus on fitting in and being subordinate to others
We internalize this guidance and in doing so, this shapes our self- concept
* Individualistic cultures: prioritize tasks that focus on personal preferences, emotions, and goals
* Collectivistic cultures: prioritize tasks that focus on fitting in and being subordinate to others
We internalize this guidance and in doing so, this shapes our self- concept
65
New cards
Parenting across individualistic cultures
* Infants spend lots of time with mothers, and not with other adults or children
* Mothers teach infants early on to spend time on their own and not depend on others
* Toys play an important role of distraction
* Babies are expected to start sleeping alone without parents, possibly in own room, starting at 3 months
* Parents talk to infant about what a person did during a day or how they feel
* Emotional self-expression is encouraged
* Babies are encouraged to smile and to make positive vocalizations
* Mothers teach infants early on to spend time on their own and not depend on others
* Toys play an important role of distraction
* Babies are expected to start sleeping alone without parents, possibly in own room, starting at 3 months
* Parents talk to infant about what a person did during a day or how they feel
* Emotional self-expression is encouraged
* Babies are encouraged to smile and to make positive vocalizations
66
New cards
parenting across collectivistic cultures
* Infants spend lots of time with multiple caregivers and other children
* Mothers teach infants early on that obedience and respect are important
* Co-sleeping for the first couple years of life
* Conversations with children are directive and instructional
* Parenting is often anticipatory, rather than waiting for infant to express a need
* Emotional self-expression is criticized and obedience is praised
* Mothers teach infants early on that obedience and respect are important
* Co-sleeping for the first couple years of life
* Conversations with children are directive and instructional
* Parenting is often anticipatory, rather than waiting for infant to express a need
* Emotional self-expression is criticized and obedience is praised
67
New cards
Subsistence theory
the way people in a culture historically made a living influences culture
68
New cards
origin differences between interdependent and independent
Farming cultures (interdependent/eastern cultures):
* Many people have to work on one field
* People have to share the harvest of farming for the rest of the year
Herding and fishing/hunting cultures (independent/western cultures):
* Food is more consistent so have to negotiate with others less
* Herders rely on working with others less
* Can move if conflict arises
* Many people have to work on one field
* People have to share the harvest of farming for the rest of the year
Herding and fishing/hunting cultures (independent/western cultures):
* Food is more consistent so have to negotiate with others less
* Herders rely on working with others less
* Can move if conflict arises
69
New cards
Cultural Differences in Cognition
Collectivistic Cultures = Holistic thinking:
* Focus on context as a whole and associations
* Attend to relationships among objects and relationships among objects and context
* Relationships are used to explain behavior and make predictions
Individualistic Cultures = Analytic thinking:
* Focus on objects
* Objects exist independent of context
* Attributes
* Rules and categories used to explain behavior and make predictions
* Focus on context as a whole and associations
* Attend to relationships among objects and relationships among objects and context
* Relationships are used to explain behavior and make predictions
Individualistic Cultures = Analytic thinking:
* Focus on objects
* Objects exist independent of context
* Attributes
* Rules and categories used to explain behavior and make predictions
70
New cards
American vs. Chinese children “which two go together”?
* American children put the chicken and cow together (both are animals)
* Chinese children put the cow and grass together (the cow eats grass) → the cow need the grass; its about the relationship
* Chinese children put the cow and grass together (the cow eats grass) → the cow need the grass; its about the relationship
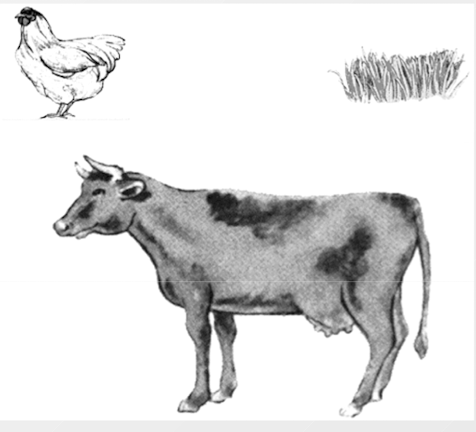
71
New cards
Field Dependence/ Independence (Ji et al., 2000)
The degree to which a person’s perception is affected by the context or surrounding environment (“field”) → tested through rod and frame test
* Field dependent: More affected by context/environment → distracted by the frame
* Field independent: Less affected by context/environment → less distracted by the frame so able to give more accurate answers
* East Asians are more field-dependent (cultural views influence how people see the world; including detail-oriented things that have nothing to do with social norms
* Field dependent: More affected by context/environment → distracted by the frame
* Field independent: Less affected by context/environment → less distracted by the frame so able to give more accurate answers
* East Asians are more field-dependent (cultural views influence how people see the world; including detail-oriented things that have nothing to do with social norms
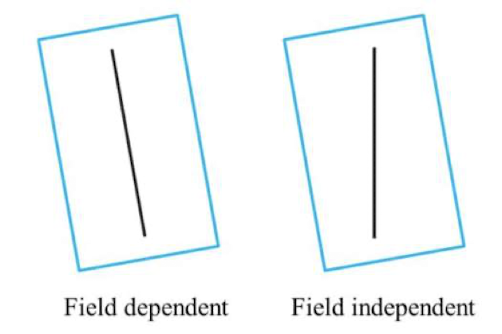
72
New cards
Cultural differences in causal attribution (Menon et al., 1999)
Hypothesis: North Americans and East Asians should attribute responsibility differently
Study: Attribution of responsibility in newspapers
* Analyzed articles about “rogue trader” scandals reported in American vs. Japanese newspapers
* Counted # references to individual (disposition) vs. organization (situation) as responsible for scandal
RESULTS:
* American newspapers more likely to attribute responsibility to individuals (disposition)
* Japanese newspapers more likely to attribute responsibility to organizations (situation)
Study: Attribution of responsibility in newspapers
* Analyzed articles about “rogue trader” scandals reported in American vs. Japanese newspapers
* Counted # references to individual (disposition) vs. organization (situation) as responsible for scandal
RESULTS:
* American newspapers more likely to attribute responsibility to individuals (disposition)
* Japanese newspapers more likely to attribute responsibility to organizations (situation)
73
New cards
Which cultures (Western or Asian) are more emotionally expressive?
Western
74
New cards
Which cultures (Western or Asian) are more emotionally restrained?
East Asian
75
New cards
Cultural differences in emotion (Soto et al., 2011)
The value of expressing emotions should depend on the culture
* Western cultures: Suppressing emotions is distressing and can lead to negative mental and physical health outcomes
* Personalexpressionisvalued
* East Asian cultures: Suppressing emotions may not lead to negative mental and physical health outcomes
* Emotional restraint is valued
RESULT: Emotional suppression related to poor psychological functioning only for European Americans, but not for Hong Kong Chinese
* Western cultures: Suppressing emotions is distressing and can lead to negative mental and physical health outcomes
* Personalexpressionisvalued
* East Asian cultures: Suppressing emotions may not lead to negative mental and physical health outcomes
* Emotional restraint is valued
RESULT: Emotional suppression related to poor psychological functioning only for European Americans, but not for Hong Kong Chinese
76
New cards
what population of the world does psychology studies focus on?
WEIRD (15% of world)
* wester
* educated
* industrialized
* rich
* democratic
* wester
* educated
* industrialized
* rich
* democratic
77
New cards
What are two examples of interdependence looking different in different cultures?
1. Expressive interdependence in Latin culture
2. Assertive interdependence in Arab culture
78
New cards
Study by Salvador et al (2020): investigated this idea by comparing European Americans, Colombians, and Japanese students on cognition, attributions, and emotional experience
\
This study is evidence of?
\
This study is evidence of?
Expressive Interdependence in Latinx Culture
79
New cards
Cognition in Latinx Culture (Salvador et al., 2020)
Finding: Columbians in between Americans and Japanese on field dependence vs. independence
80
New cards
Attribution in Latinx Culture (Salvador et al., 2020)
FINDING: Columbians in between Americans and Japanese in making situational vs. dispositional attributions
81
New cards
Emotions in Latinx Culture (Salvador et al., 2020)
FINDINGS: Columbians more emotionally expressive than Japanese, and similar to Americans
BUT, express more socially engaging (vs. disengaging) emotions than Americans, similar to Japanese
BUT, express more socially engaging (vs. disengaging) emotions than Americans, similar to Japanese
82
New cards
Assertive Interdependence in Arabs (San Martin et al., 2018)
investigated this idea by comparing European Americans, Saudis, Lebanese, and Japanese students on cognition and self-assertion
RESULTS:
* Arabs showed holistic cognition similar to Japanese
* Arabs shows self-assertion similar to Americans
RESULTS:
* Arabs showed holistic cognition similar to Japanese
* Arabs shows self-assertion similar to Americans
83
New cards
Emotional Experience in USA vs. Germany (Koopmann-Holm et al., 2014)
Germany is an independent culture but emotional experience is different from USA
Study: European Americans (vs. Germans) report greater desire to avoid negative emotions
RESULTS:
* Leads to differences in how sympathy is expressed
* European Americans more likely to send sympathy card that focuses on the positive
* Germans more likely to send sympathy card that focuses on negative
Study: European Americans (vs. Germans) report greater desire to avoid negative emotions
RESULTS:
* Leads to differences in how sympathy is expressed
* European Americans more likely to send sympathy card that focuses on the positive
* Germans more likely to send sympathy card that focuses on negative
84
New cards
Multicultural identity
Sense of belonging to 2 or more cultural groups
85
New cards
Acculturation
Process of learning and incorporating the values, beliefs, language, customs and mannerisms of the new country (mainstream culture) that immigrants and their families are living in
86
New cards
What is acculturation on a psychological level called?
emotional acculturation
87
New cards
Individual Emotional Acculturation (Consedine et al., 2014)
Study of 915 immigrant women from Eastern Europe and Caribbean living in USA compared to USA-born non-immigrant women.
\
Results: Longer amount of time they had spent in USA, the more they fit mainstream American emotional norms ( r = 0.11)
\
Results: Longer amount of time they had spent in USA, the more they fit mainstream American emotional norms ( r = 0.11)
88
New cards
Generational Emotional Acculturation (de Leersnyder et al., 2020)
How well does each immigrant generations’ emotional experience fit with characteristic majority culture pattern?
Study: Compared emotional fit between Turks and Belgians
* Turks(“Turkish majority”)
* 1st generation Turkish immigrants in Belgium
* 2nd generation Turkish immigrants in Belgium
* Belgians(“Belgian majority”)
Assessed “emotional fit” by:
* Self-report answers to emotional experiences questionnaire
* Average emotional experiences for each group
* Compare Turkish majority and immigrants’ scores to Belgian majority
\
Results: More contact a generation has with Belgian culture, more emotional acculturation
* Turkish majority least like Belgians emotionally
* 2nd generation Turkish immigrants indistinguishable from Belgians
* Evidence of emotional acculturation at a generational level
Study: Compared emotional fit between Turks and Belgians
* Turks(“Turkish majority”)
* 1st generation Turkish immigrants in Belgium
* 2nd generation Turkish immigrants in Belgium
* Belgians(“Belgian majority”)
Assessed “emotional fit” by:
* Self-report answers to emotional experiences questionnaire
* Average emotional experiences for each group
* Compare Turkish majority and immigrants’ scores to Belgian majority
\
Results: More contact a generation has with Belgian culture, more emotional acculturation
* Turkish majority least like Belgians emotionally
* 2nd generation Turkish immigrants indistinguishable from Belgians
* Evidence of emotional acculturation at a generational level
89
New cards
What are the implications of acculturation?
Minority individuals become psychologically more similar to majority individuals
90
New cards
Cultural Frame Switching
Multicultural individuals’ cognitive, emotional, and behavioural reactions are context specific
91
New cards
Cultural frame switching in emotion (de Leersnyder et al., 2020)
Study: Examined 2nd generation Turkish immigrants’ emotional experience in Belgium
Results:
* Work/school: emotions more consistent with characteristic Belgian pattern
* Home: emotions fit characteristic Belgian and Turkish patterns equally well
* Suggests that multicultural individuals flexibly shift behaviour to fit culture that’s most salient in a situation
Results:
* Work/school: emotions more consistent with characteristic Belgian pattern
* Home: emotions fit characteristic Belgian and Turkish patterns equally well
* Suggests that multicultural individuals flexibly shift behaviour to fit culture that’s most salient in a situation
92
New cards
Cultural frame switching in self-concept (Ross et al., 2016)
Do multicultural individuals engage in cultural frame-switching in their self-descriptions?
Method: Recruited European-Canadian and Chinese born students at a Canadian university
* Wrote open-ended self description:“Describe what you’re like as a person”
* Coded writing for references to others and collective self-statement
* Questionnaire assessing agreement with Chinese cultural views
Experimental manipulation for Chinese students:
* Study done in Chinese or study done in English
* European Canadians all did study in English
\
RESULTS: Chinese participants’ self-descriptions are more characteristically Chinese when answering in Chinese than in English
Method: Recruited European-Canadian and Chinese born students at a Canadian university
* Wrote open-ended self description:“Describe what you’re like as a person”
* Coded writing for references to others and collective self-statement
* Questionnaire assessing agreement with Chinese cultural views
Experimental manipulation for Chinese students:
* Study done in Chinese or study done in English
* European Canadians all did study in English
\
RESULTS: Chinese participants’ self-descriptions are more characteristically Chinese when answering in Chinese than in English
93
New cards
Is integration a type of acculturation?
yes
94
New cards
What is Integration? (multicultural identity)
Participate in mainstream culture and hold onto heritage identity
95
New cards
What is assimilation? (multicultural identity)
Participate in mainstream culture, give up heritage identity
96
New cards
What is separation? (multicultural identity)
Hold onto heritage identity, avoid mainstream culture
97
New cards
What is marginalization? (multicultural identity)
Little interest in participating in mainstream or heritage culture
98
New cards
What is the opposite of Integration?
Marginalization
99
New cards
What is the opposite of assimilation?
separation
100
New cards
Navigating Multicultural Identity (Berry et al., 2006)
Method: Study of immigrant youth from 26 different cultural backgrounds and living in 13 different countries
* Assessed multicultural identity strategy
Psychological adaptation: life satisfaction, self-esteem, and psychological problems
Sociocultural adaptation: school and behaviour problems (e.g., dropping out of school, substance use)
* Assessed multicultural identity strategy
Psychological adaptation: life satisfaction, self-esteem, and psychological problems
Sociocultural adaptation: school and behaviour problems (e.g., dropping out of school, substance use)