Accessory Organs of the Eye Study Guide
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to the accessory organs of the eye, particularly focusing on the tear film, lacrimal apparatus, and eyelid functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the Two-phase tear film model composed of?
Lipid Layer and Mucoaqueous Layer.
What glands secrete the lipid layer of the tear film?
Meibomian glands and Zeis glands.
What glands secrete the aqueous and mucin component of the tear film?
Aqueous component: main lacrimal gland and accessory glands (Krause & Wolfring)
Mucin component: conjunctival goblet cells
What is the main function of the mucoaqueous layer?
Provides oxygen to the avascular cornea
Maintains electrolyte composition
Antibacterial and antiviral defense
Keeps the corneal surface smooth
Hydrates and lubricates the ocular surface
Converts the corneal epithelium from hydrophobic to hydrophilic (stabilizes tear film)
Name one function of the tear film.
Lubricates the cornea and conjunctiva.
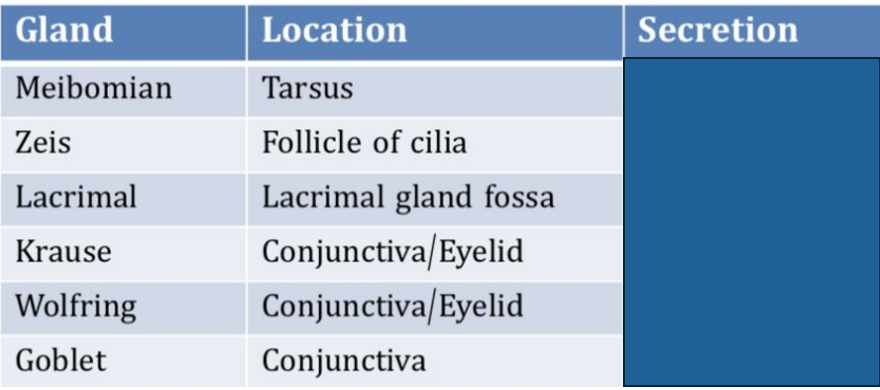
Fill in the blank for the component secreted
Meibomian: Oily
Zeis: Oily
Lacrimal: Aqueous
Krause: Aqueous
Wolfring: Aqueous
Goblet: Mucin
What is the role of the main lacrimal gland?
To provide the aqueous component of tears.
What is epiphora?
Excessive tearing due to blocked drainage.
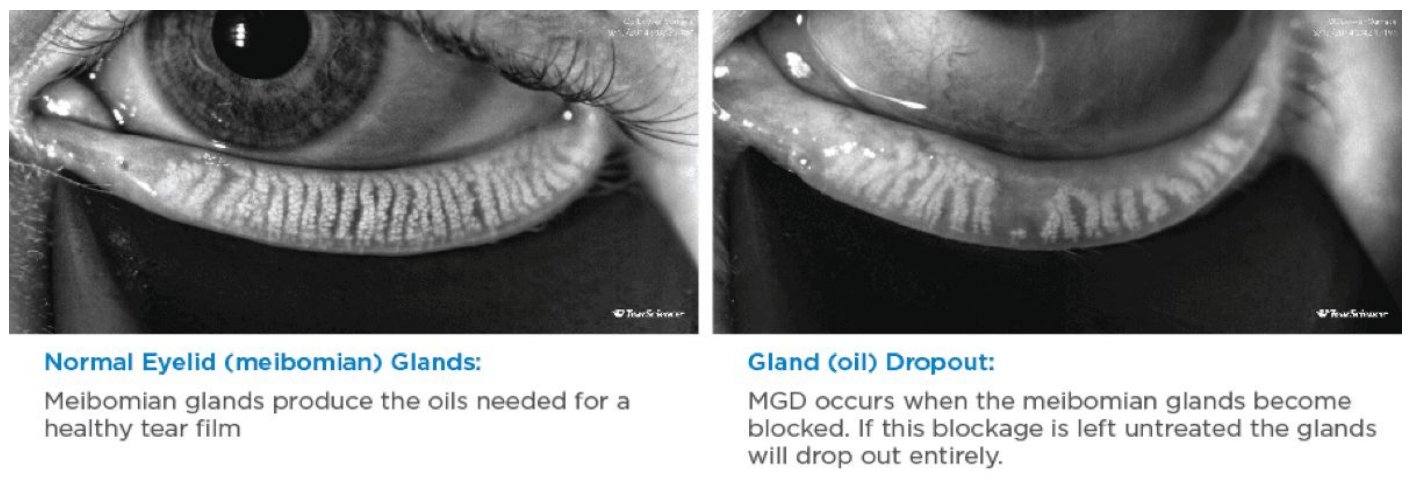
Name this clinical condition
Meibomian gland disease
What does the nasolacrimal duct do?
Drains tears into the inferior nasal meatus.
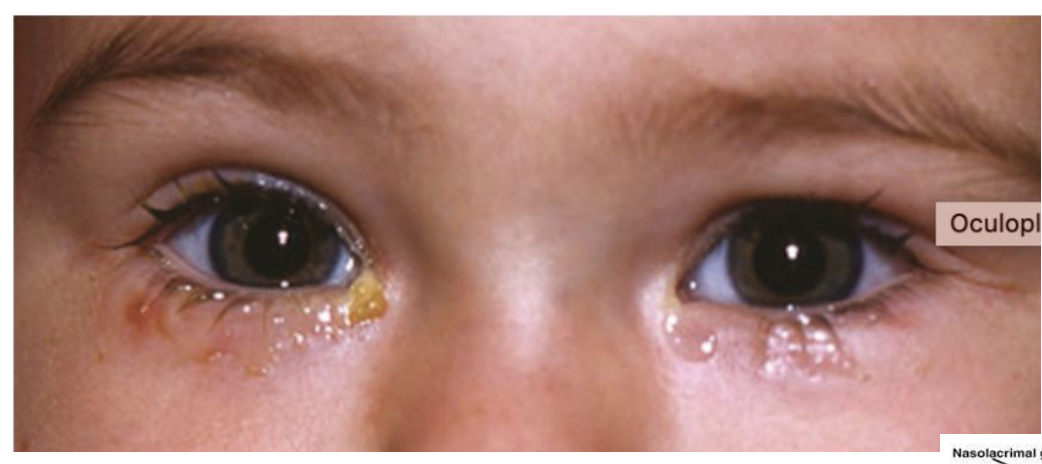
What is this clinical condition
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
What condition does nasolacrimal duct obstruction lead to?
Epiphora
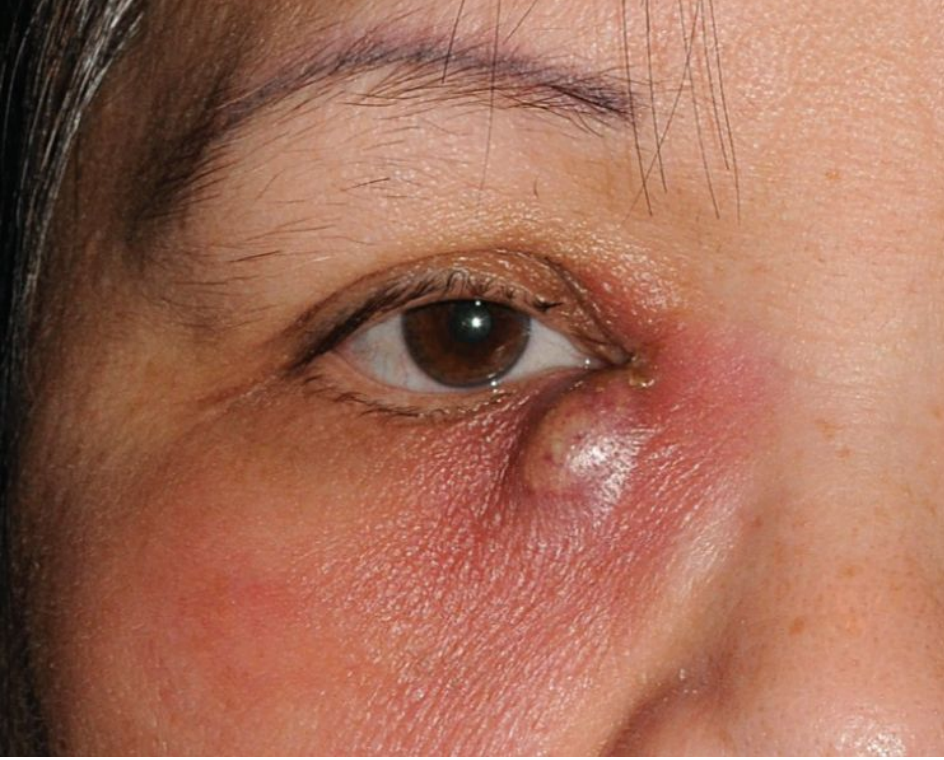
What is the clinical term for inflammation of the lacrimal sac?
Dacryocystitis
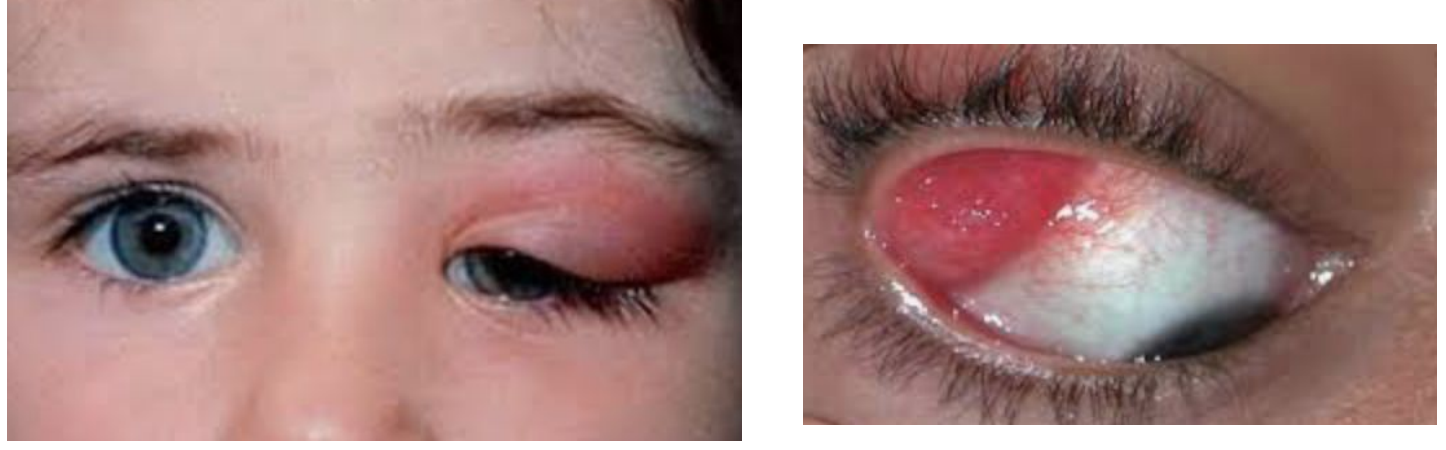
What is the clinical term for inflammation of the lacrimal gland?
Dacryoadenitis
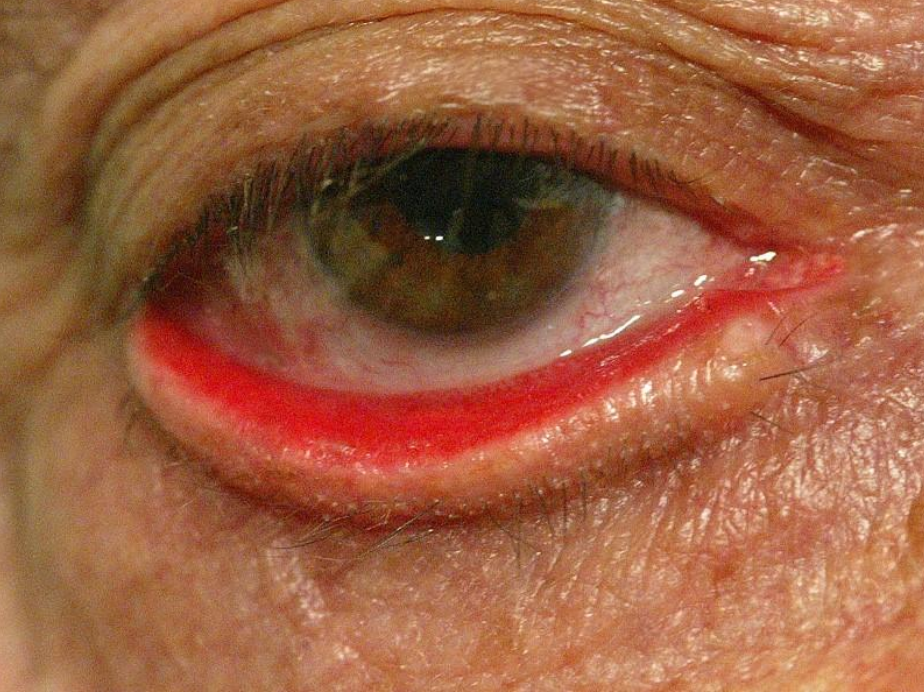
Name this condition
Ectropion
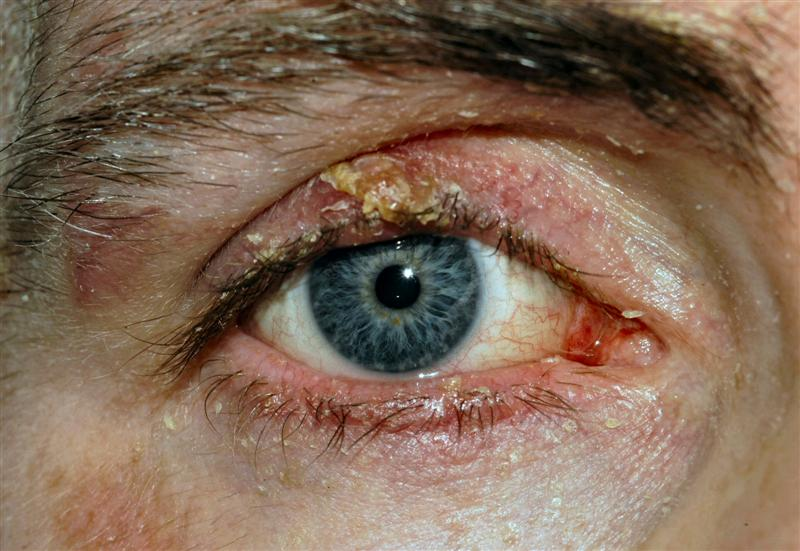
What is the clinical condition for inflammation of eyelid margins?
Blepharitis
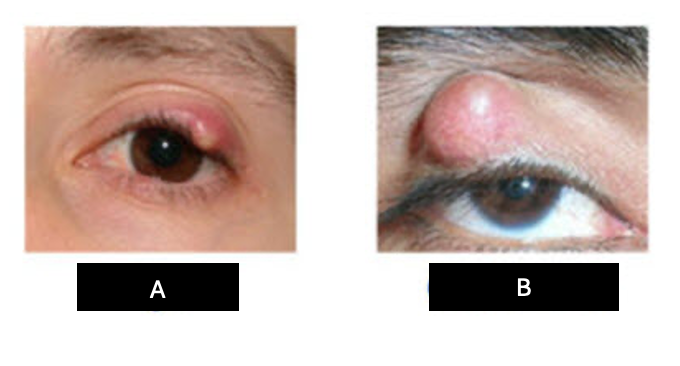
In the image presented, which is chalazion and hordeolum
A: hordeolum
B: chalazion
What triggers reflex closure of the eyelids?
Auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli.
What distinguishes a chalazion from a hordeolum?
Chalazion is chronic and non-painful, while hordeolum is acute and painful.
How does blinking aid in tear distribution?
Moves tears from lateral to medial eyelid margin.
What is the approximate frequency of spontaneous blinking?
~15 times per minute.
What is the role of conjunctival goblet cells?
Secrete mucin component of tear film.
What is the primary purpose of the eyelids?
Protect the eye from light and debris.
What is the gray line in the eyelid anatomy?
Muscle of Riolan.
What is the primary function of the tarsus in the eyelid?
Contains Meibomian glands and dense connective tissue
How does airflow relate to the tear film's stability?
Air–tear interface must be reduced for stability.
What happens during eyelid opening?
Creates negative pressure, pulling tears into the lacrimal sac.
What are the segments of the eyelid?
Skin
Subcutaneous connective tissue
Lid margin
Tarsus
Orbicularis oculi muscle
Orbital septum
Levator palpebrae superioris
Conjunctiva.